- ARDS is characterized by an
- acute and diffuse inflammatory damage
- into the alveolar-capillary barrier
- increased vascular permeability increase and
- Caused by
- direct (pulmonary ARDS) or
- indirect (nonpulmonary ARDS),
- Most Common
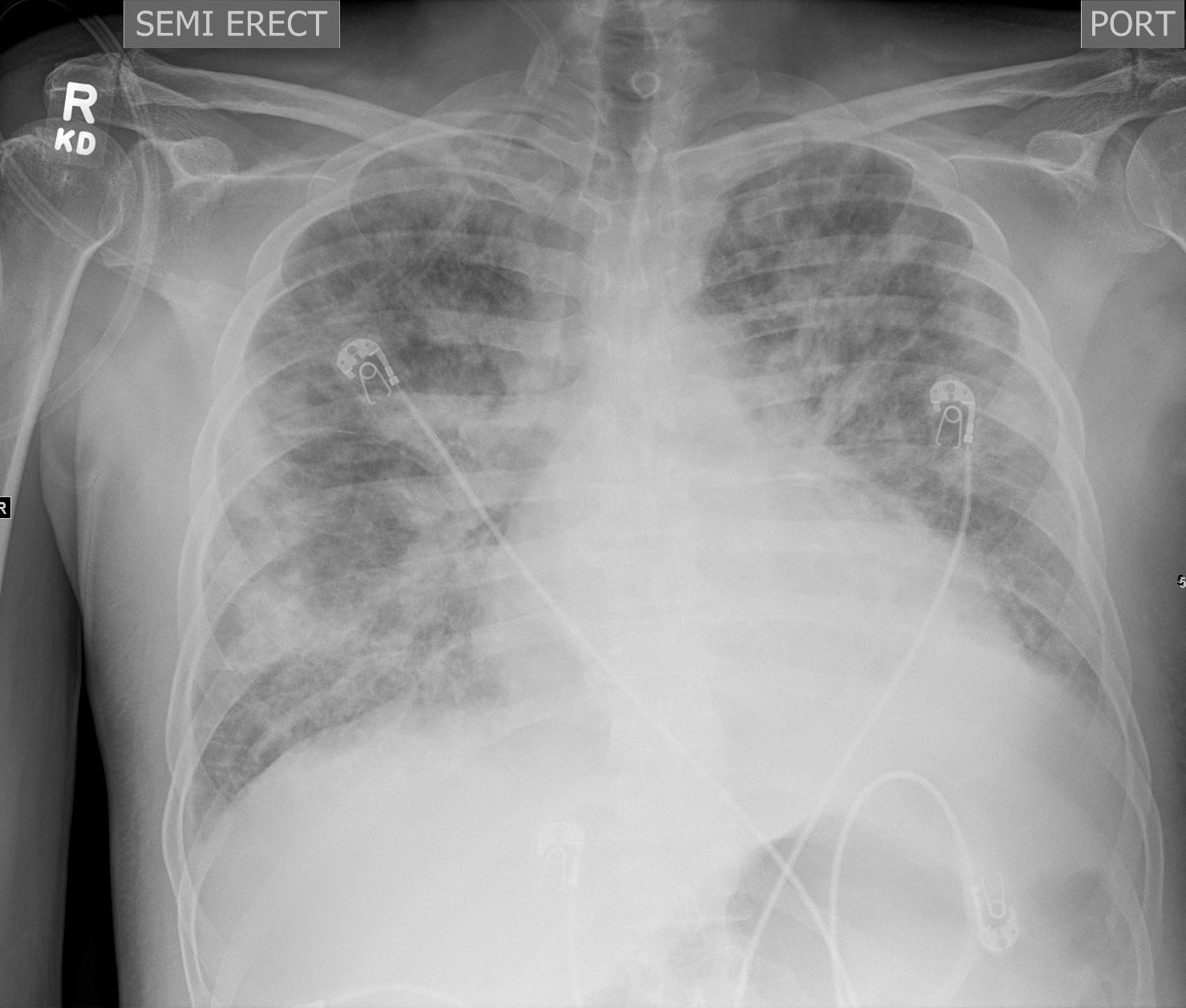
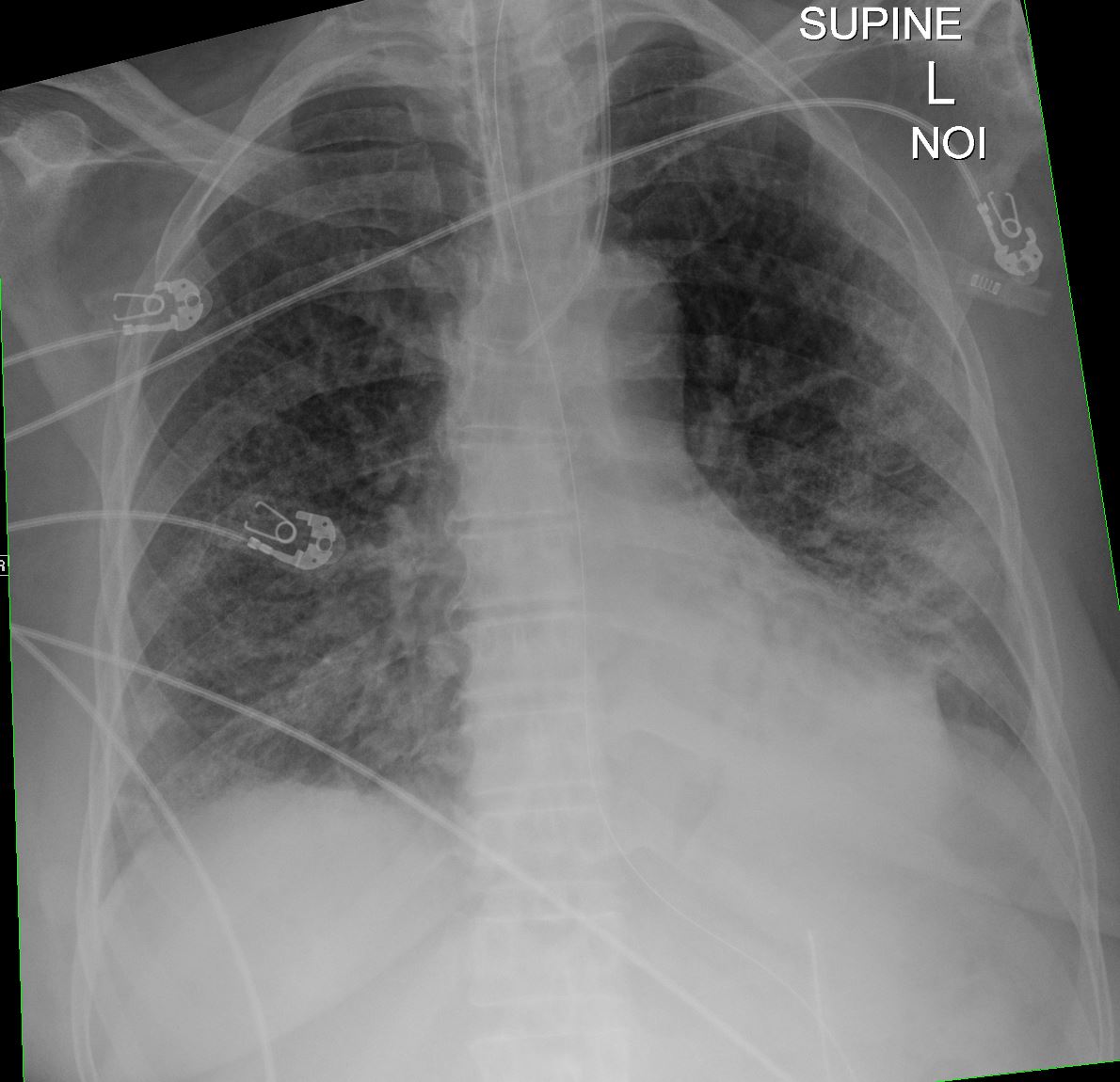
CXR shows diffuse ground glass and multifocal subsegmental infiltrates consistent with ARDS
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net
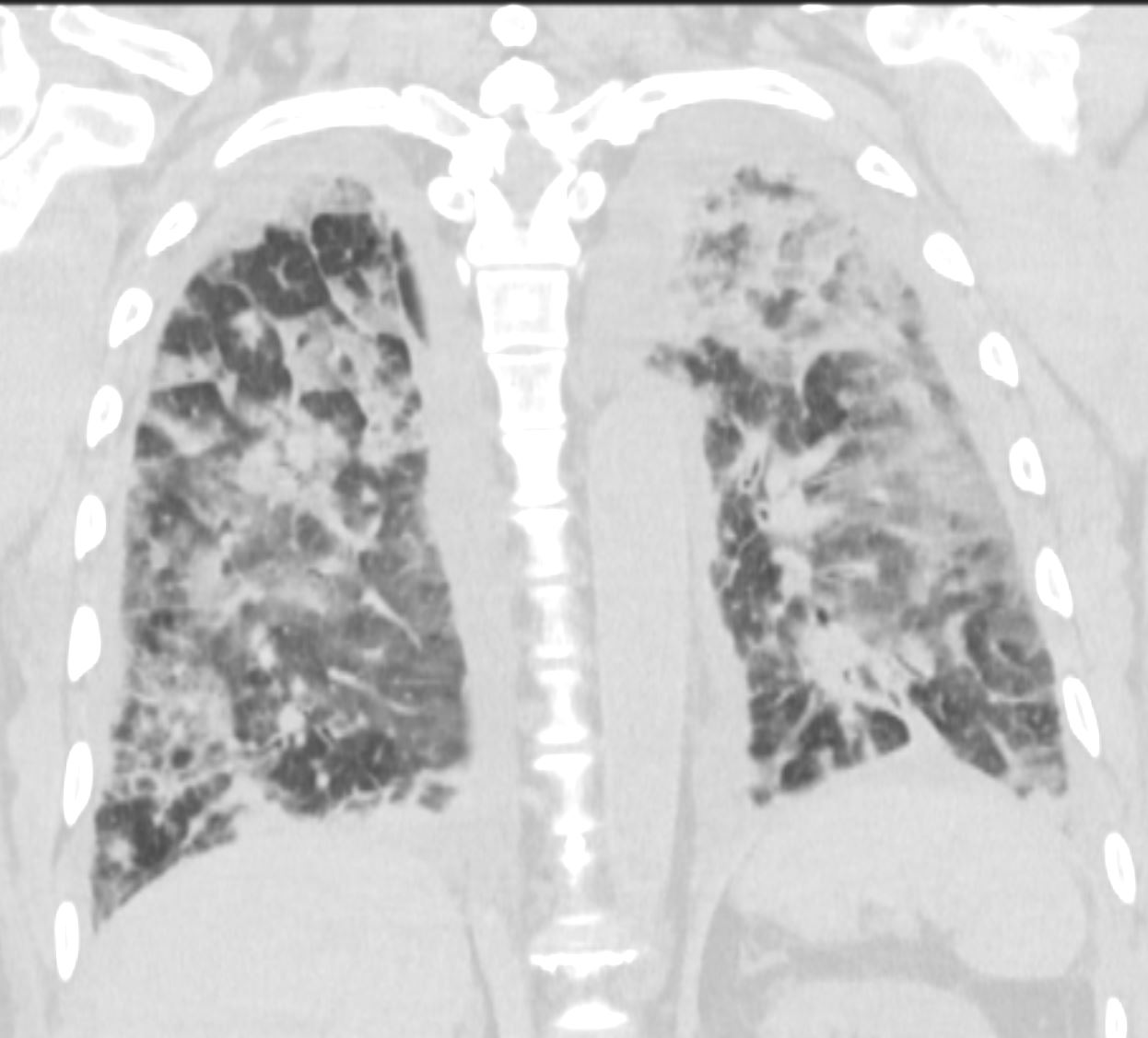
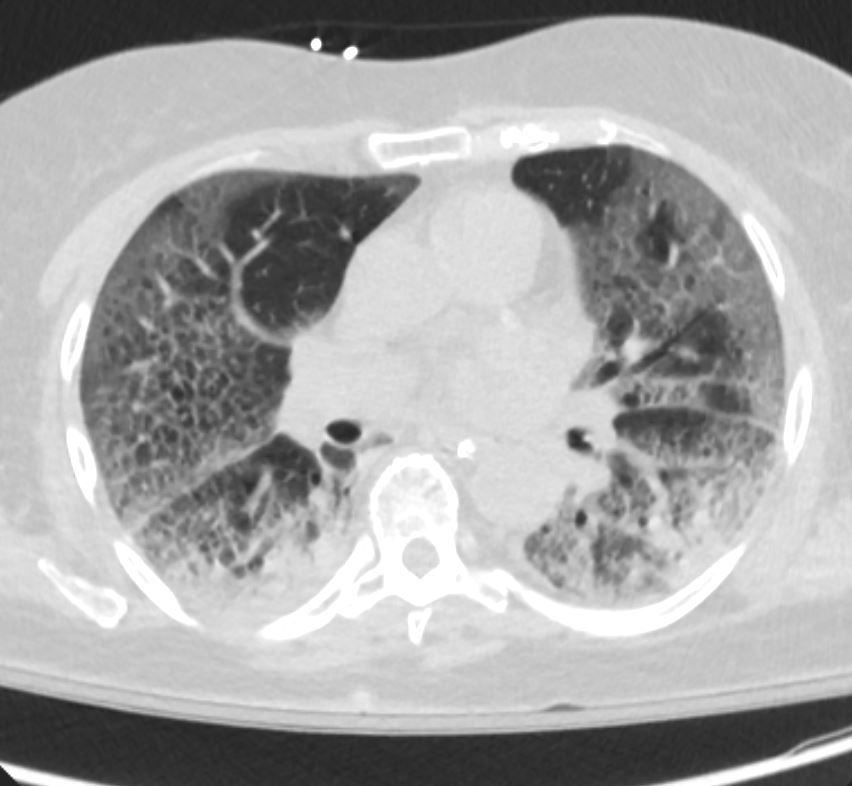
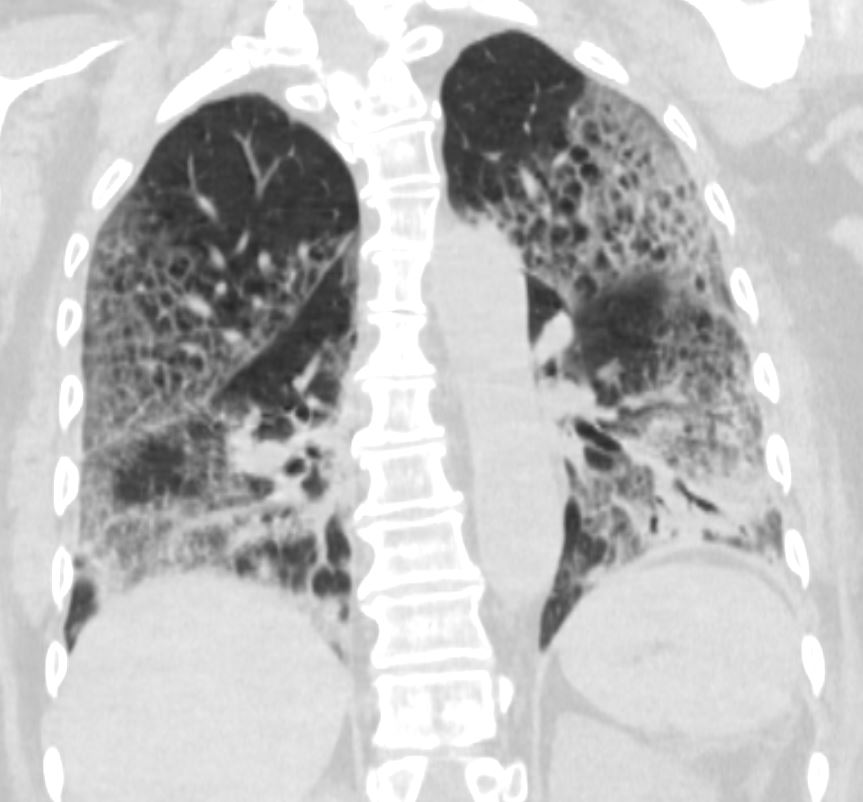
CTscan shows diffuse ground glass and multifocal subsegmental infiltrates consistent with ARDS
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net
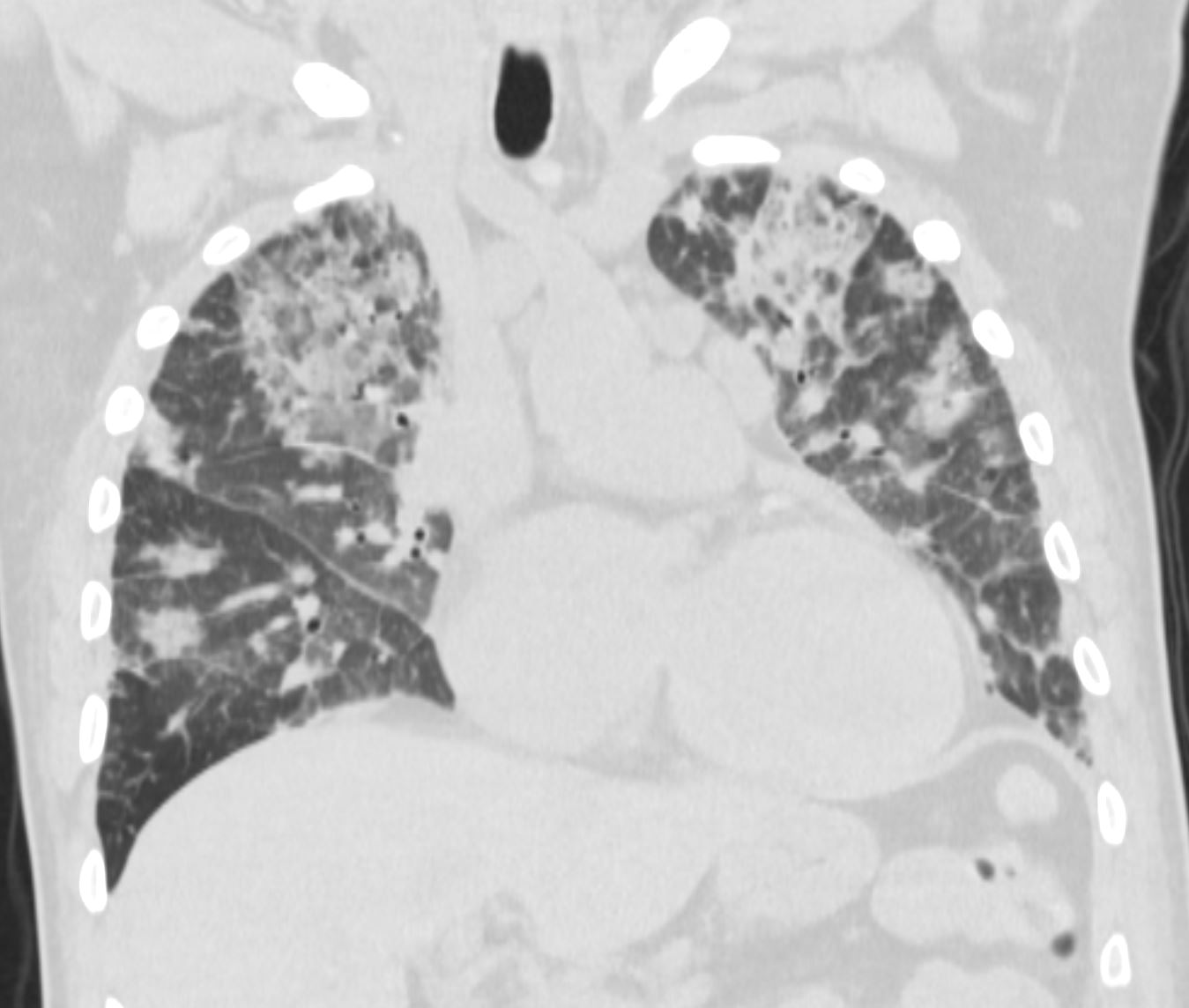
CTscan shows diffuse ground glass and multifocal subsegmental infiltrates consistent with ARDS
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net
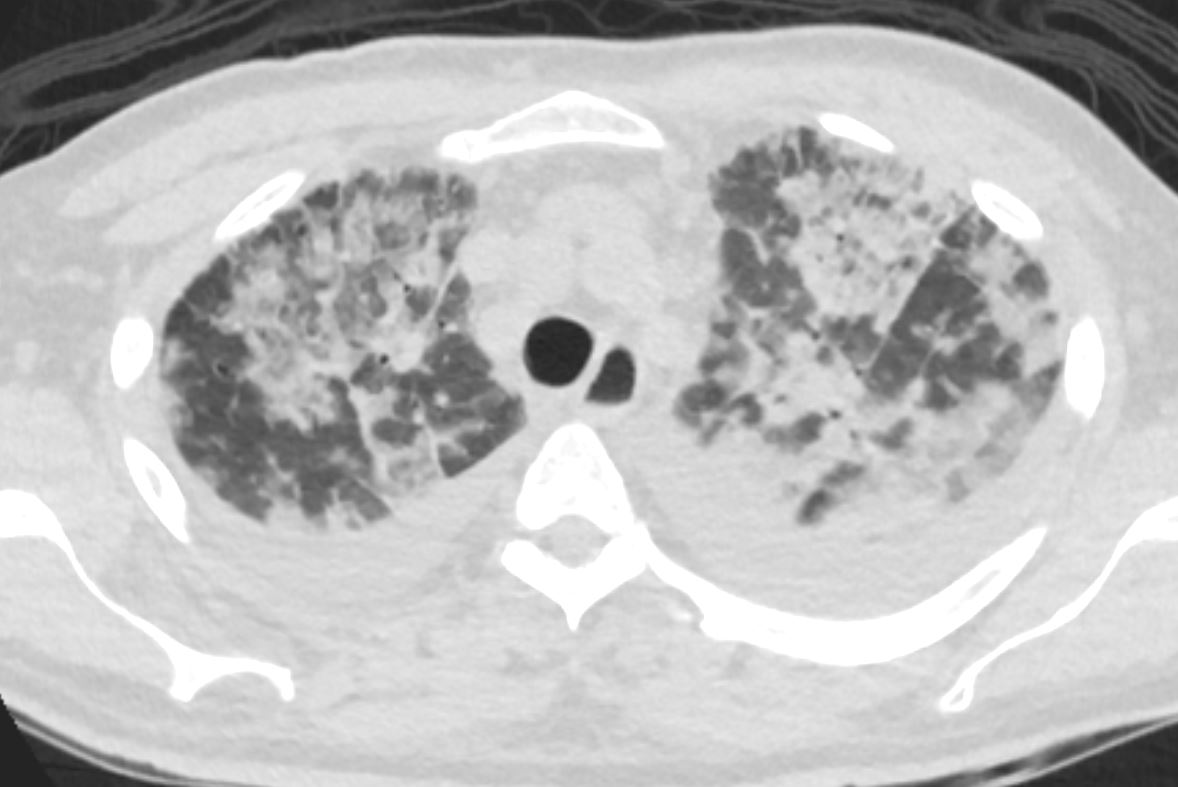
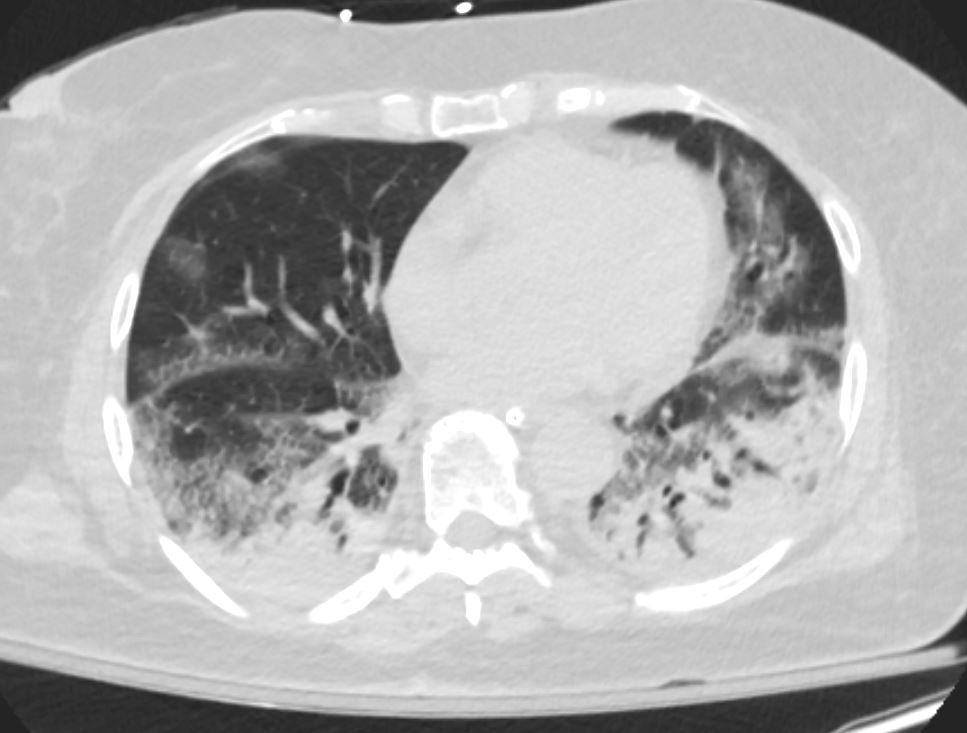
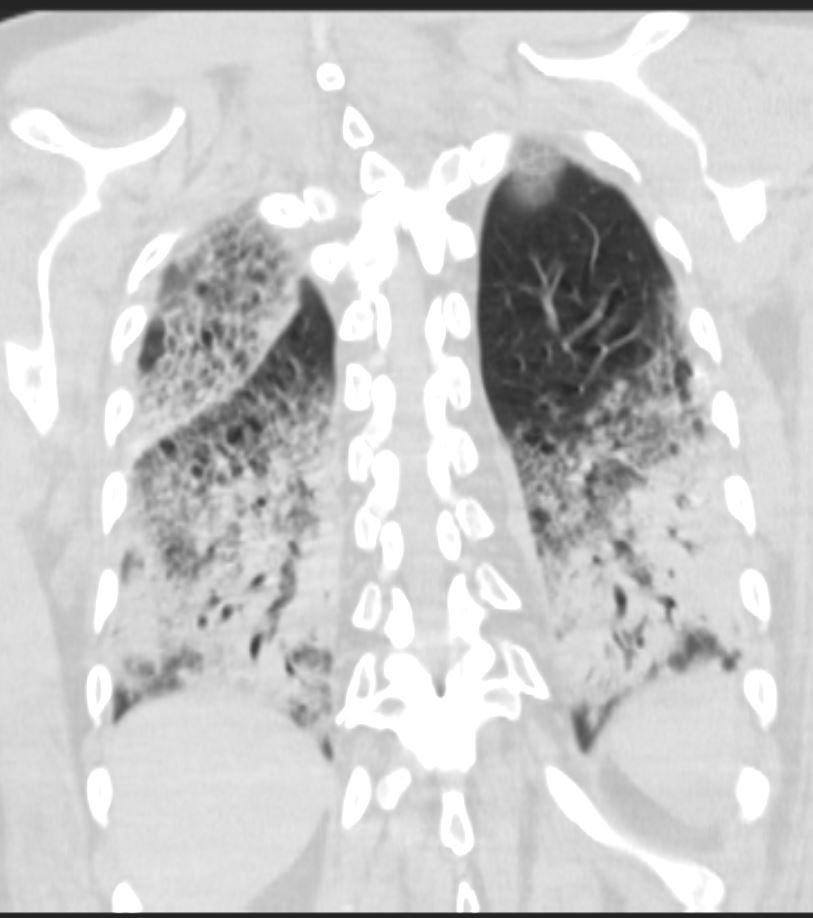
CTscan shows diffuse ground glass and multifocal subsegmental infiltrates consistent with ARDS. Noted also are moderate bilateral effusions
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net
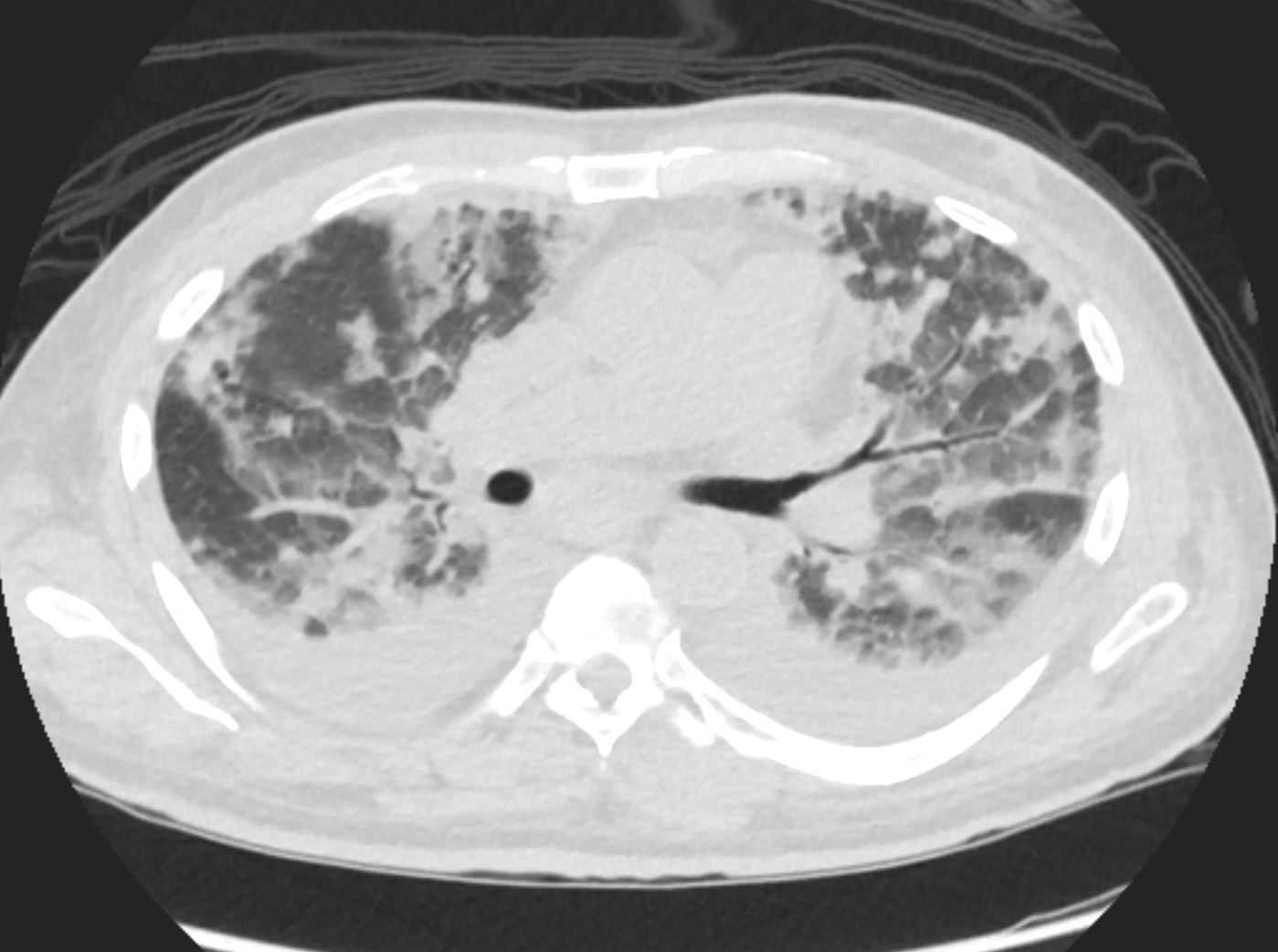
CTscan shows diffuse ground glass and multifocal subsegmental infiltrates consistent with ARDS. Noted also are moderate bilateral effusions
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net
- DAD
- Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is manifested by
- injury to alveolar lining and
- endothelial cells,
- pulmonary edema,
- hyaline membrane formation and
- later by proliferative changes involving
- alveolar and
- bronchiolar lining cells and
- interstitial cells
- later by proliferative changes involving
- Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is manifested by
- DAD is the stereotypical morphology of ARDS,
- Clinical syndrome of ARDS is not synonymous with the pathologic diagnosis of DAD
- DAD pattern is often characterized by hyaline membranes in acute phase but shows a wide variety of findings that makes the diagnosis challenging
- Buzz in a Nutshell
- Acute
- Diffuse
- Extensive
- bilateral
- without upper or lower lobe predominance
- Can be regional,
- depending on the degree and cause of the inflammation
- Alveoli
- Causes either
- pulmonary or
- severe systemic disease
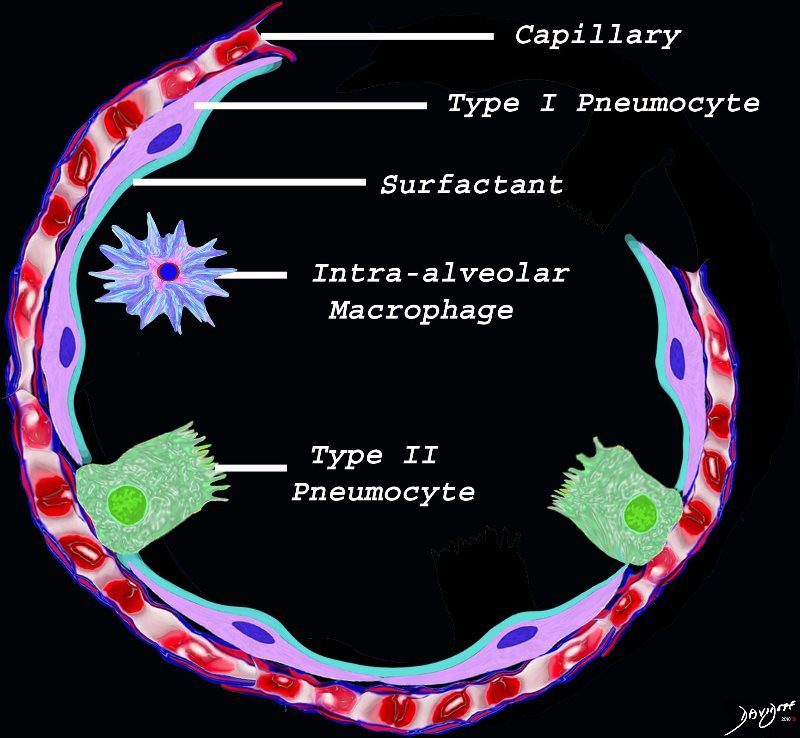
The diagram shows the lining of the normal alveolus composed of type 1 pneumocyte squamous in nature and the cuboidal cell (type pneumocyte) which rest on a lamina propria, and basement membrane (not shown) shared with the inner endothelial layer of the capillary. Intra-alveolar macrophage lies within the alveolar lumen
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
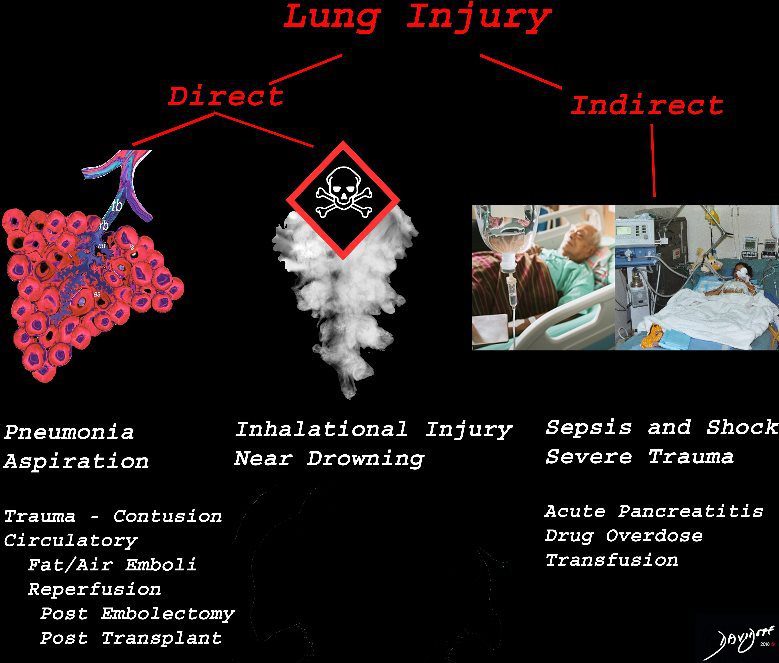
The lung is injured either by direst causes most commonly pneumonia, aspiration or from inhalation of toxic substances. Severe systemic illnesses, most commonly sepsis with shock, and severe trauma are considered indirect causes.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
-
- Exudative (acute) phase: 1 – 7 days
-

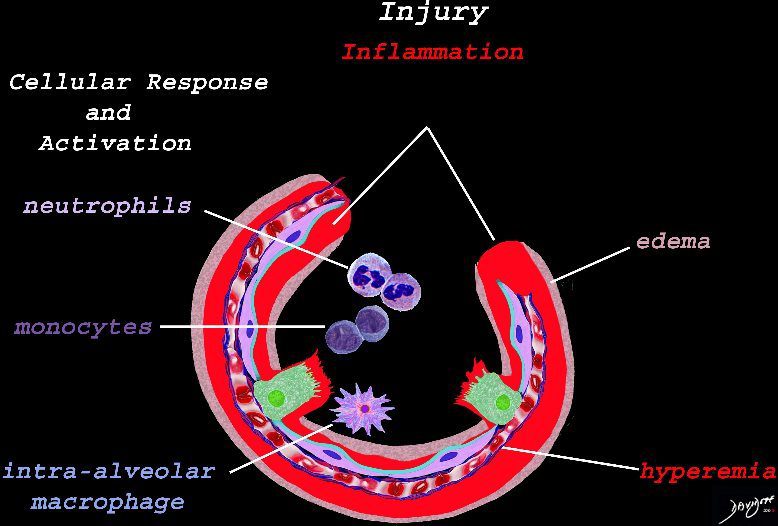
Early Events in the Pathophysiology of the ARDS
The initial injury results in an acute severe inflammatory response consisting hyperemia , edema with migration initially of neutrophils in the first 6-24 hours followed by monocytes (24-48hours). The intra -alveolar macrophages are activated.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
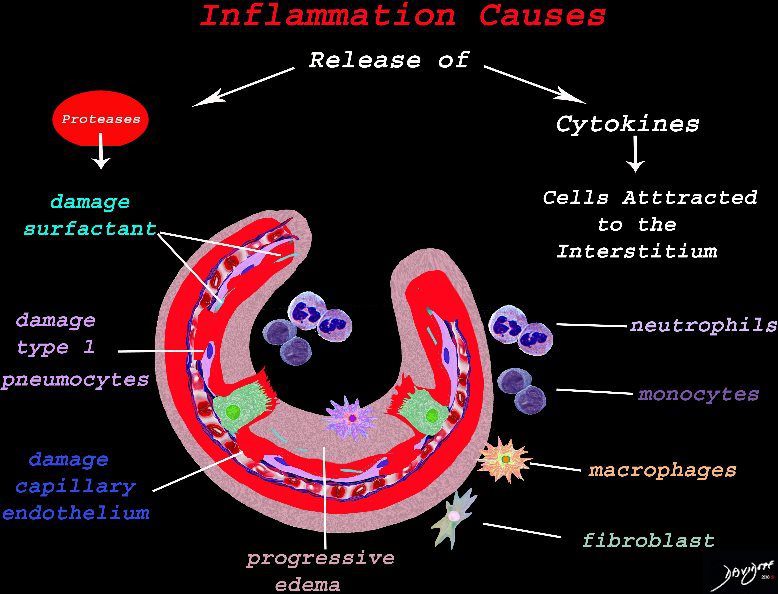
Result of Cellular Response
The cells of the immune system release cytokines, chemotactic agents and proteases. Immune cells , macrophages and fibroblasts are attracted to the interstitium. Some of proinflammatory agents are toxic to the cell lining causing damage to the surfactant, type 1 pneumocytes and the capillary endothelium. There is progressive edema.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
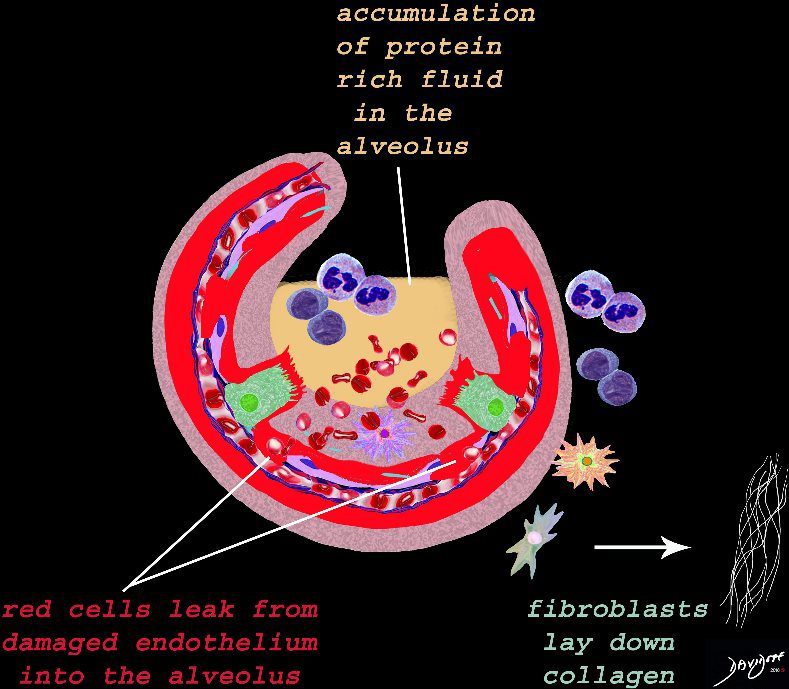
Result of Cellular Response and Associated Tissue Injury
The damage to the endothelium of the capillary results in bleeding into the alveoli. The severe tissue damage and fluid exudation results in protein rich intra-alveolar fluid . The fibroblasts start to lay down collagen as part of the early repair process
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Hyaline Membrane
A hyaline membrane evolves covering the damaged surface of the alveolus. This impedes gas exchange
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
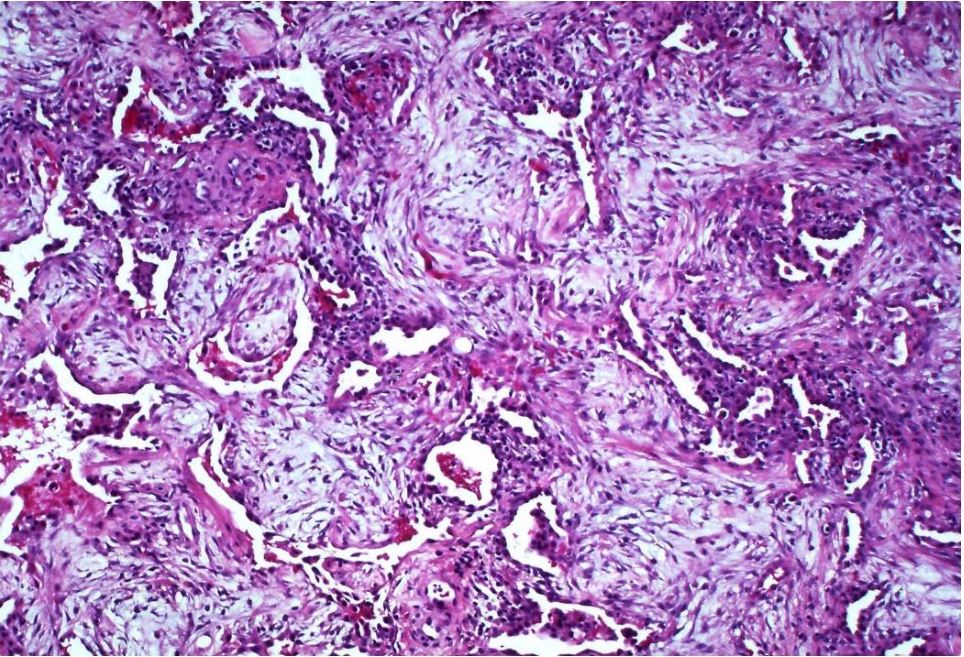
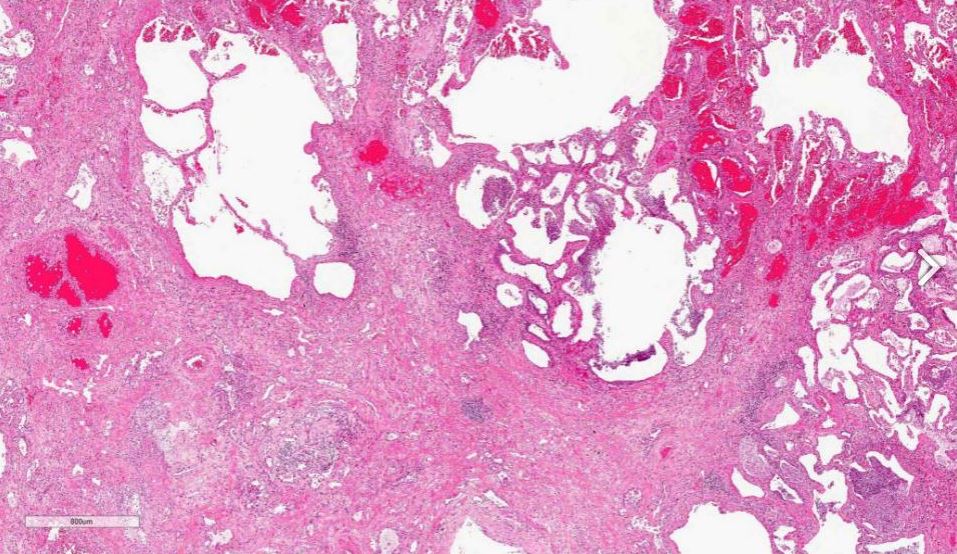
Acute exudative phase of diffuse alveolar damage with prominent hyaline membranes (DAD)
Courtesy Dr Yale Rosen

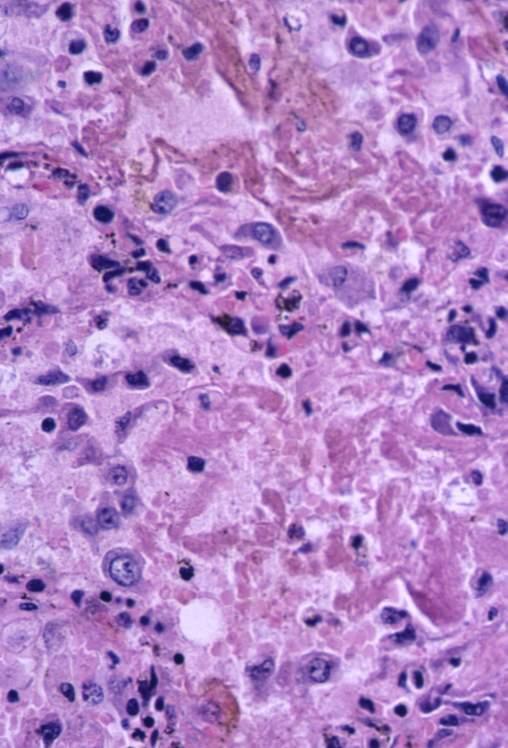
ARDS
Acute Exudative Phase
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
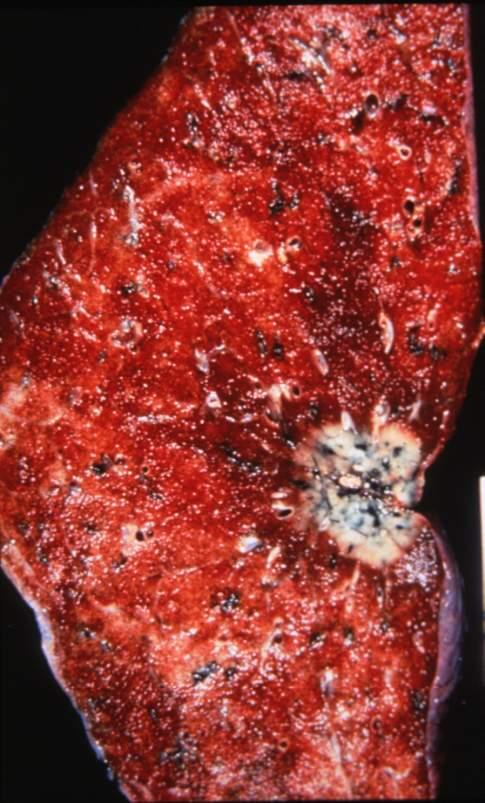
ARDS
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net - Neutrophil mediated inflammation
- neutrophils predominate in the first 6 to 24 hours
- (monocytes predominate in 24-48 hours)
- Neutrophils destroys the alveolar capillary barrier (alveolar epithelium and endothelium),
- increases its permeability
- results in intra-alveolar hemorrhage and
- edema
- interacts with alveolar surfactants,
- resulting in decreased pulmonary compliance
- hyaline membranes develop in the alveolar wall
- neutrophils predominate in the first 6 to 24 hours
-
- Proliferative / organizing (subacute) phase: 8-14 days
- restoration of type II pneumocytes a
- differentiation into type I pneumocytes
- proliferation of myofibroblasts
- Exudative (acute) phase: 1 – 7 days
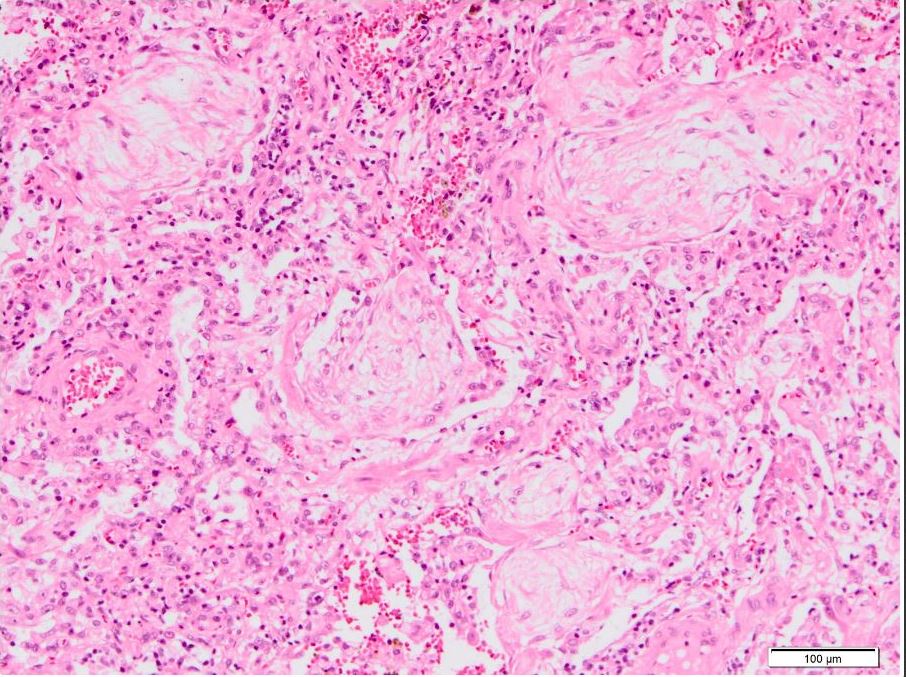

Courtesy Akira Yoshikawa
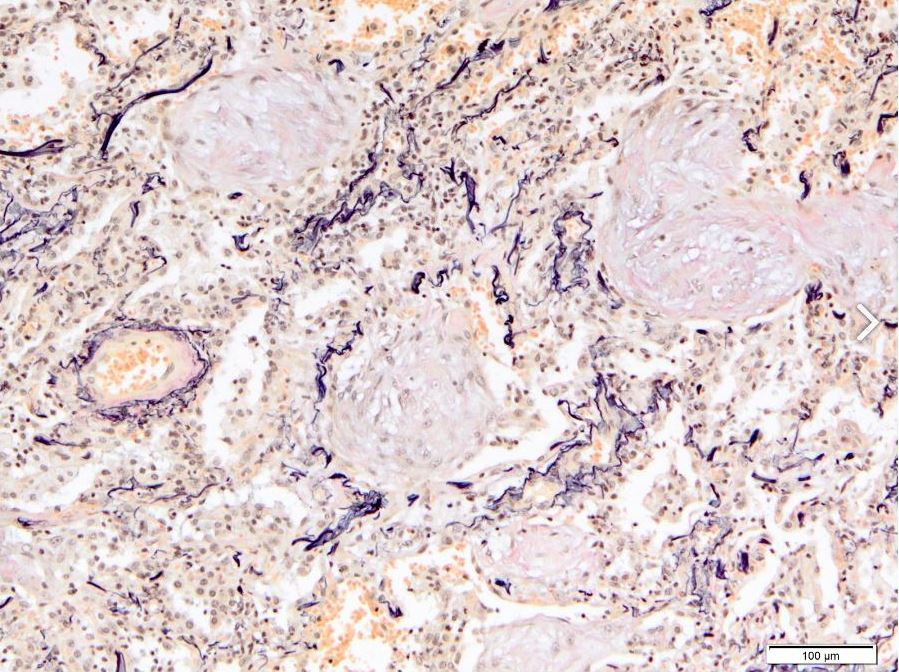

Courtesy Akira Yoshikawa
- CXR
- diffuse coarse reticular opacities
- does not imply irreversible fibrosis,
-
- opacities may resolve
- Fibrotic (chronic) phase: after 3 weeks
-
53 F ARDS
Diffuse Ground Glass with Basilar Infiltrates
Acute Exudative Phase
-



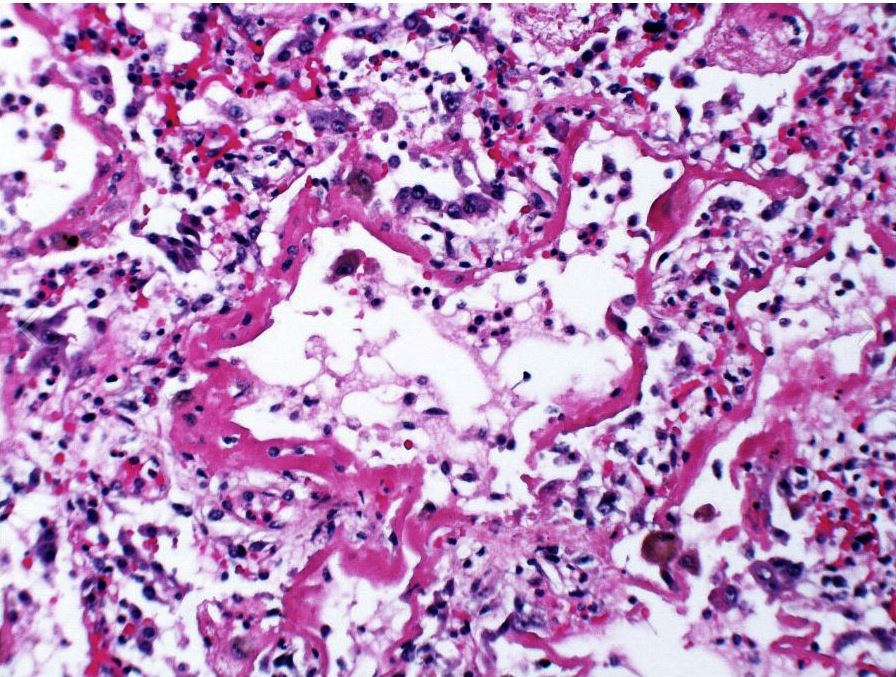
Acute exudative phase of diffuse alveolar damage with prominent hyaline membranes (DAD)
Courtesy Dr Yale Rosen


ARDS
Acute Exudative Phase
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

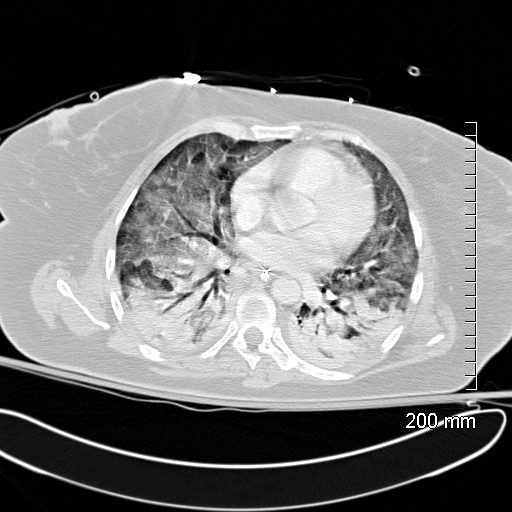
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Bibasilar Infiltrates in the dependent portions
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
8 Months Later
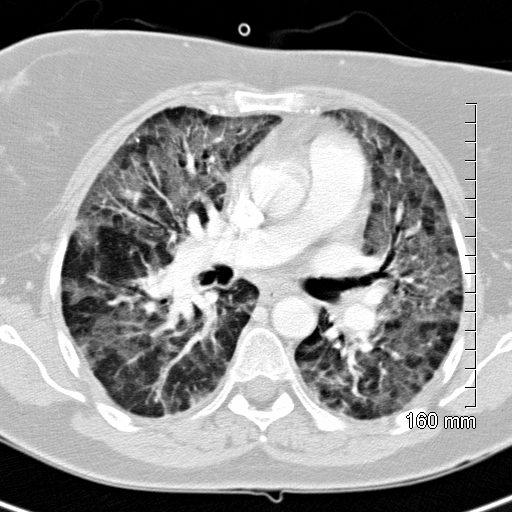

8months later
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Post MVA 58M
Acute Exudative Phase




Courtesy Dr Yale Rosen
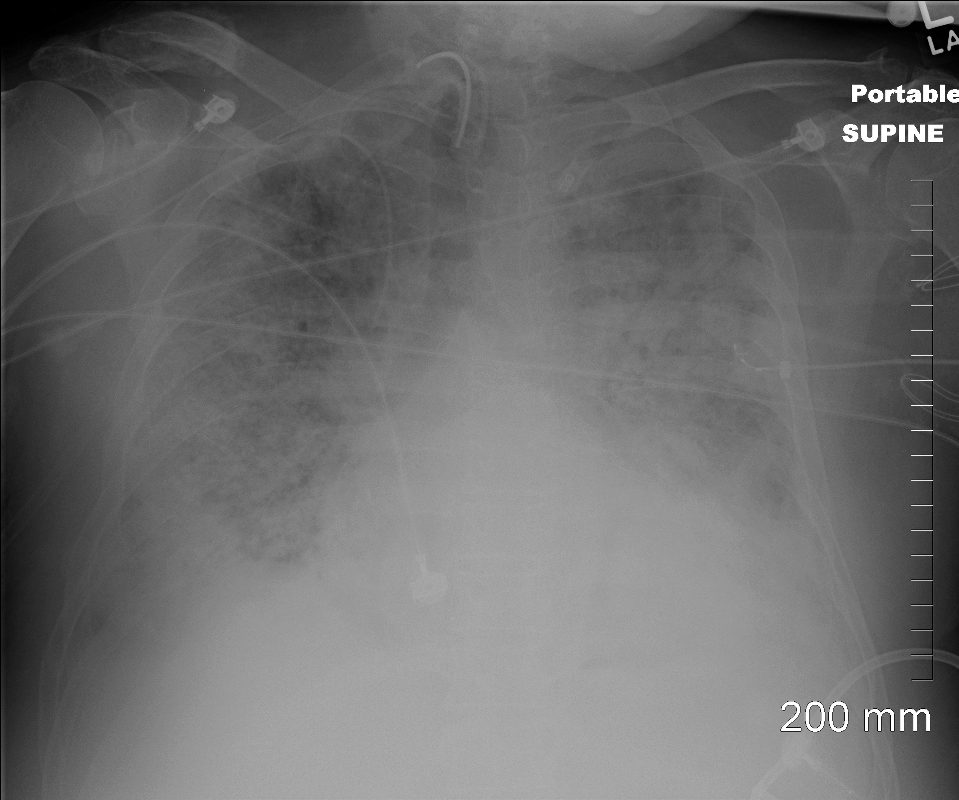

58M ARDS
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Post MVA
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
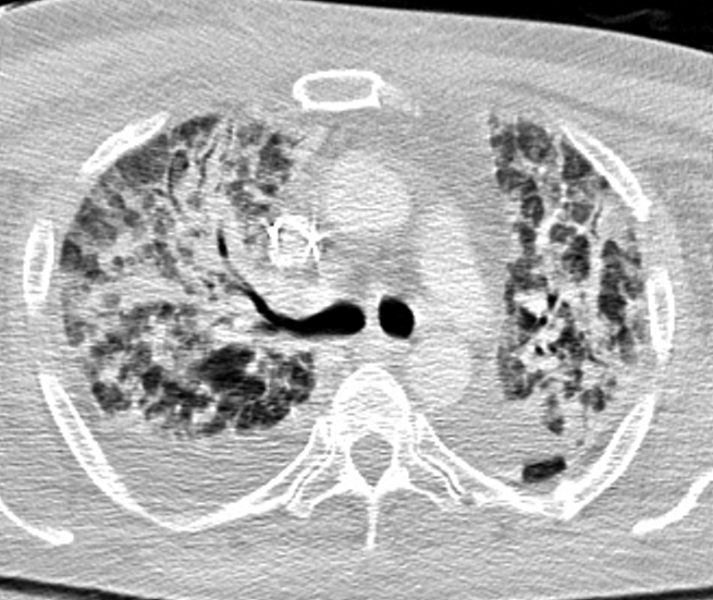

58M
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Peribronchovascular Infiltrates
Focal Consolidation and Effusion
Post MVA
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134273
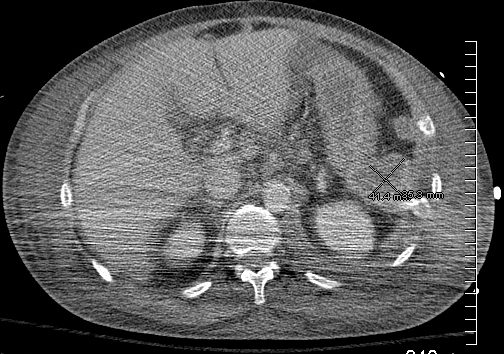

58M
Post MVA
3rd Spacing in the Subcutaneous Tissue
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134270
Post MVA 12 Days Later
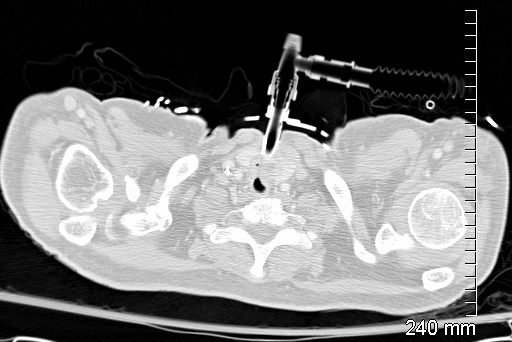

12 Days later
Still Intubated
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134282
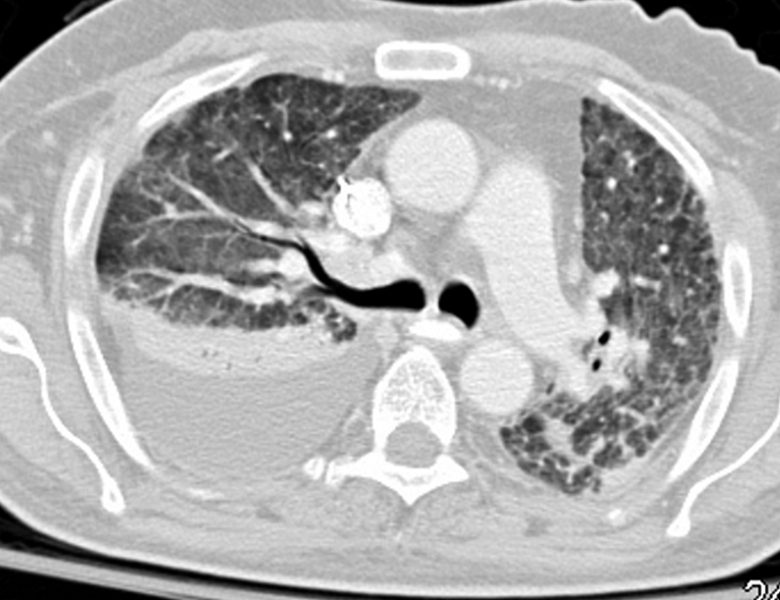

12 Days later
Improved Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134284
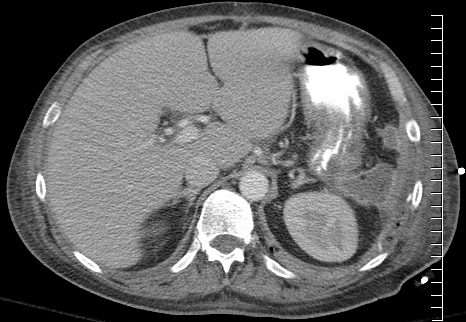

12 Days later
Improved Diffuse
Improved subcutaneous 3rd spacing of fluids
Organized collection in the LUQ
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134281
ARDS – Dominant Central Distribution with Relative Lower Lobe Subpleural Sparing
2 Weeks Earlier

79M
2 weeks earlier
Cardiomegaly CHFwith interstitial edemaand complex left effusion
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134304a
2 Weeks Later
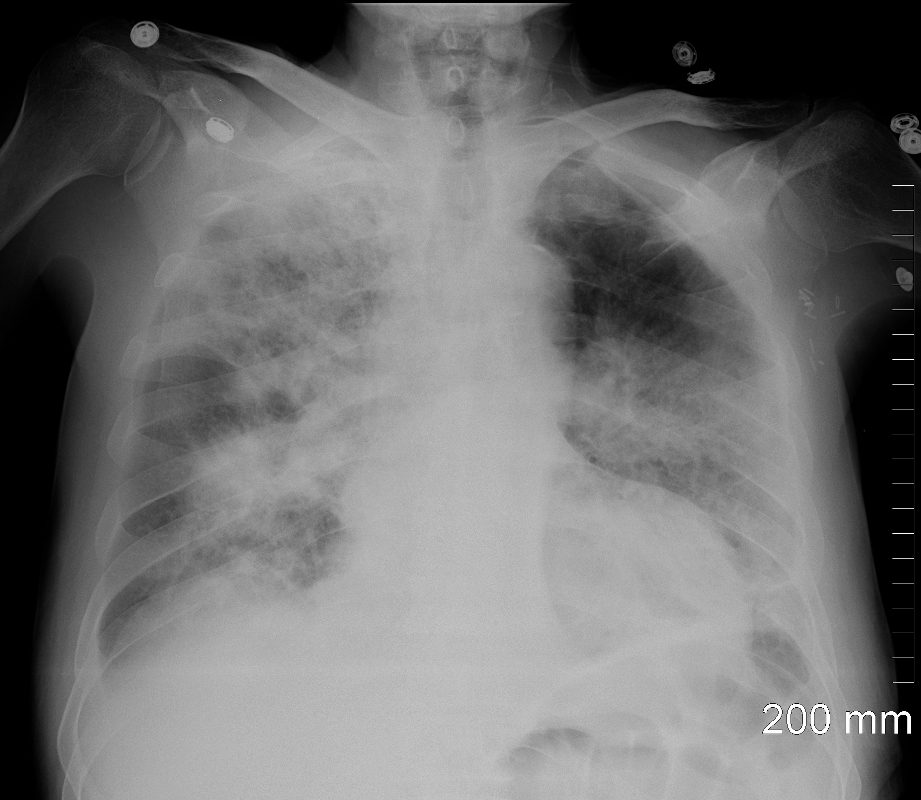

79M
Patchy Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Dominant – Central Location
Relative Lower Lobes and Subpleural Sparing
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134304
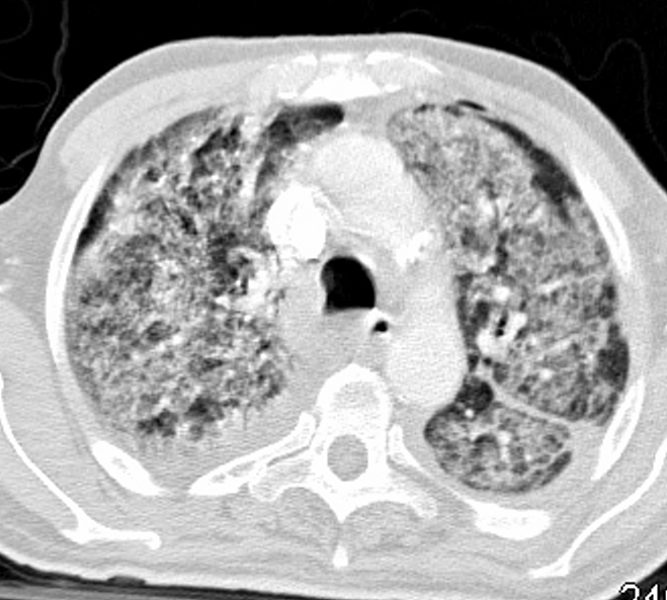

79M
Patchy Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Dominant – Central Location
Relative Lower Lobes and Subpleural Sparing
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134294
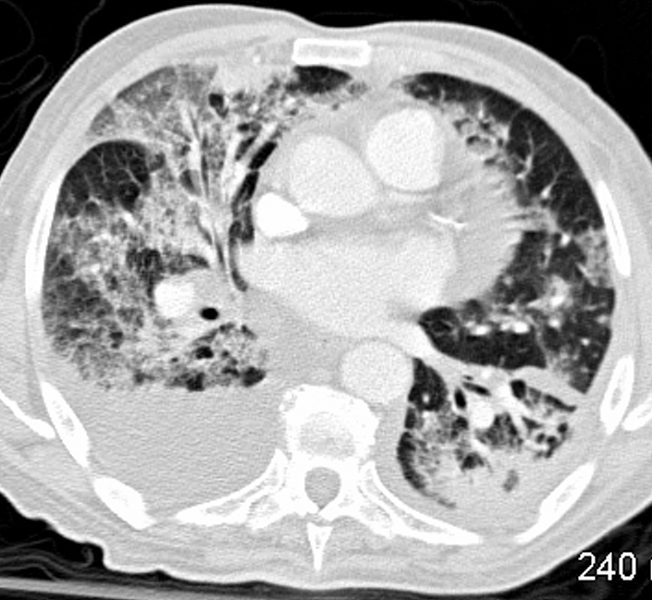

79M
Patchy Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Dominant – Central Location
Relative Lower Lobes and Subpleural Sparing
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134300
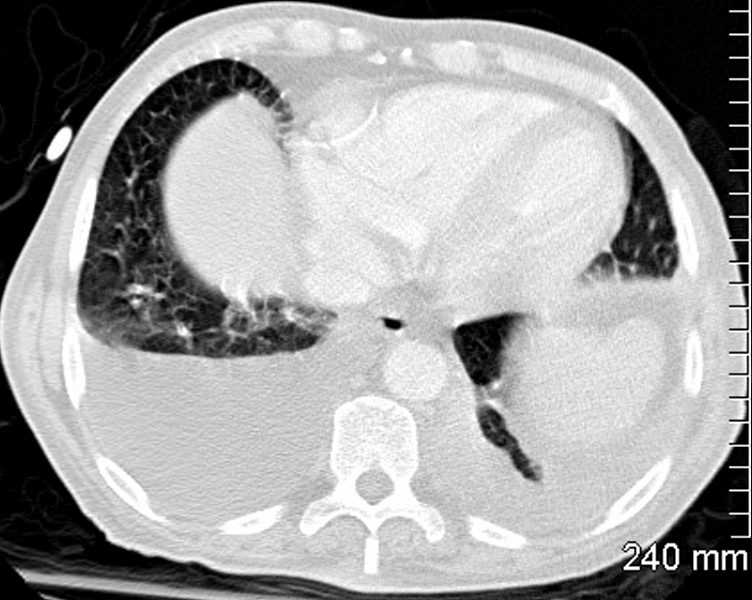

79M
Patchy Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Dominant – Central Location
Relative Lower Lobes and Subpleural Sparing
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134301

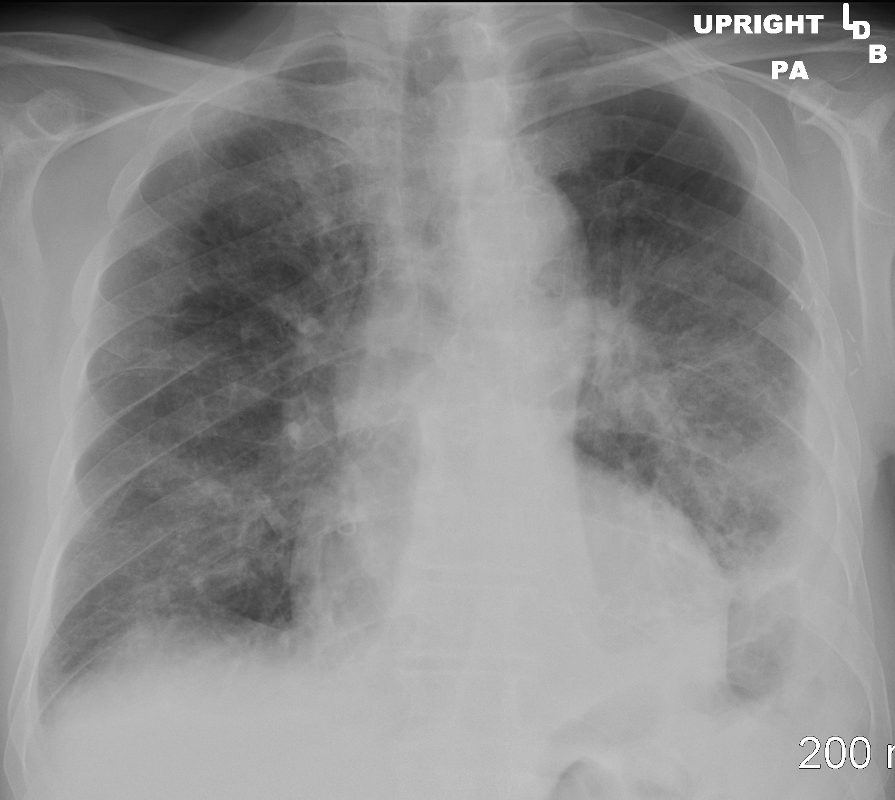
54 year old female with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Ground Glass Pattern with Patchy Infiltrates
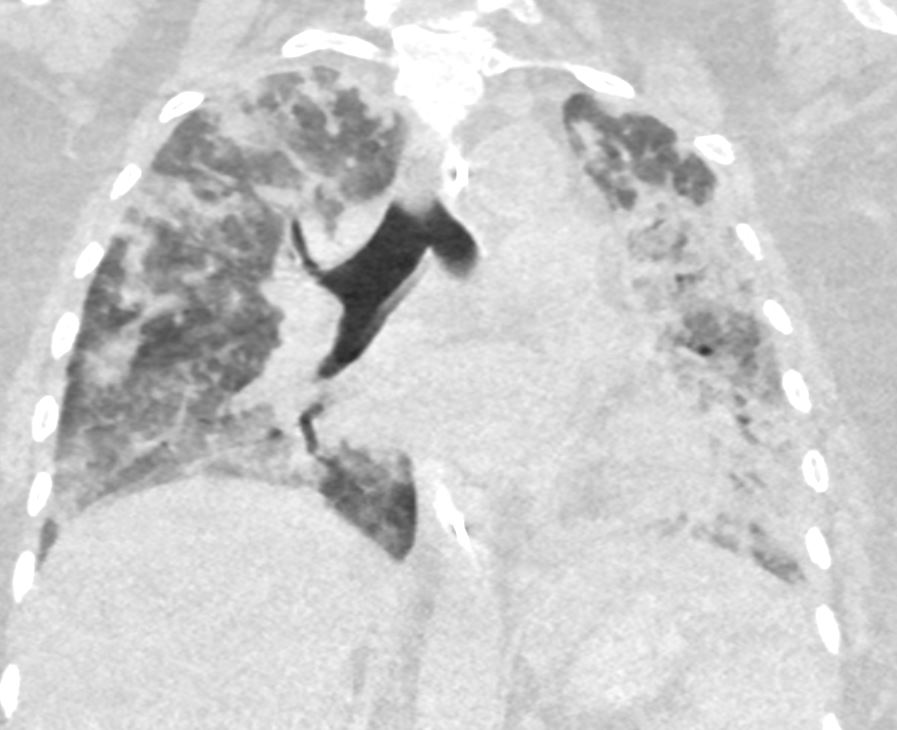

54 year old female with acute respiratory distress syndrome
MVA ARDS Bibasilar Infiltrates
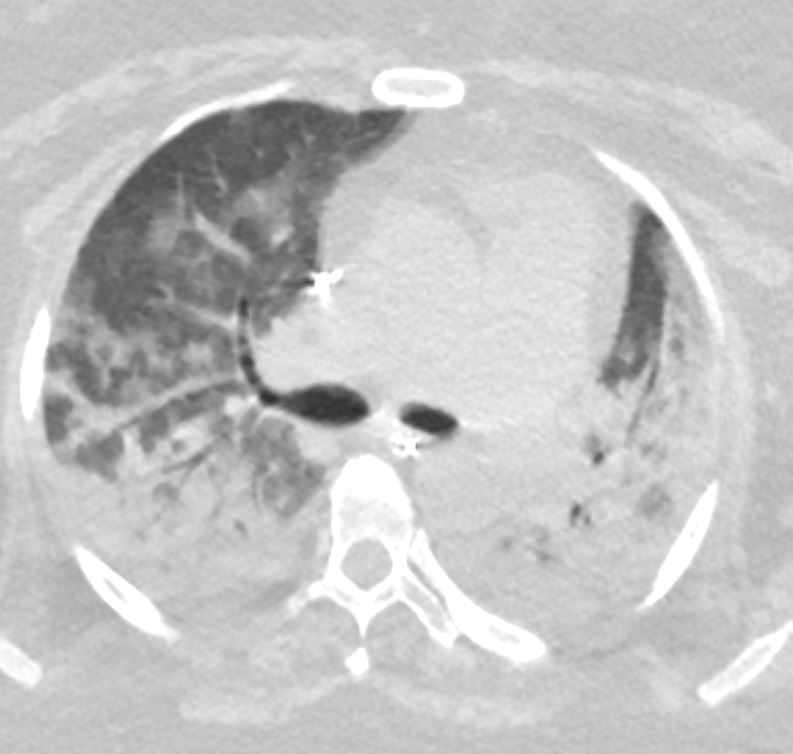

54 year old female with acute respiratory distress syndrome
AIP ARDS Immunotherapy Toxicity
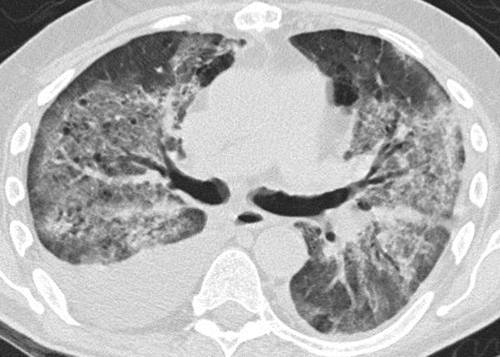

Pneumonitis in a 65-year-old man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after three cycles of rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride, vincristine sulfate, and prednisone (R-CHOP) therapy who presented with new shortness of breath. Axial CT image shows bilateral diffuse GGOs and areas of consolidation in both lungs, with traction bronchiectasis and loss of lung volumes. The findings reflect an AIP/ARDS pattern of pneumonitis related to rituximab. Bilateral pleural effusions were also present. The patient’s condition significantly deteriorated, and he died 1 month after presentation. Autopsy results showed diffuse alveolar damage in the lungs.
Nishino, M et al Thoracic Complications of Precision Cancer Therapies: A Practical Guide for Radiologists in the New Era of Cancer Care Radio Graphics Vol. 37, No. 5
Diffuse Ground Glass ARDS vs Atypical Pneumonia
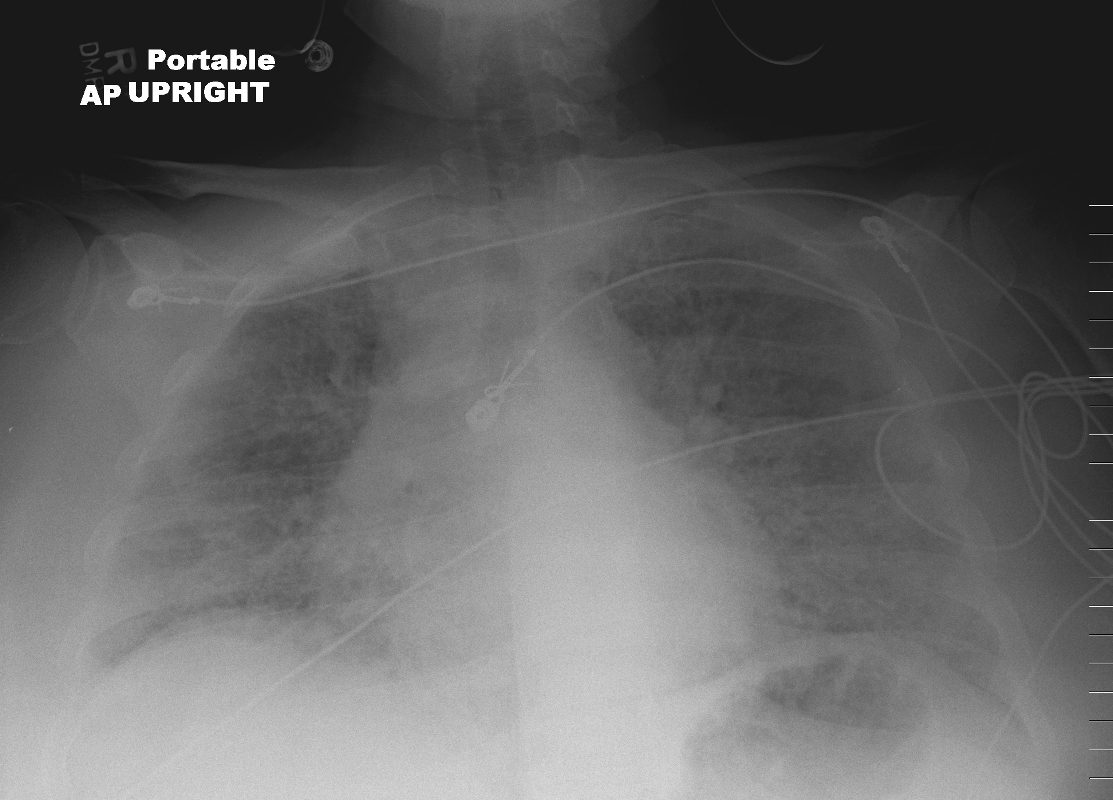

43F
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
117653
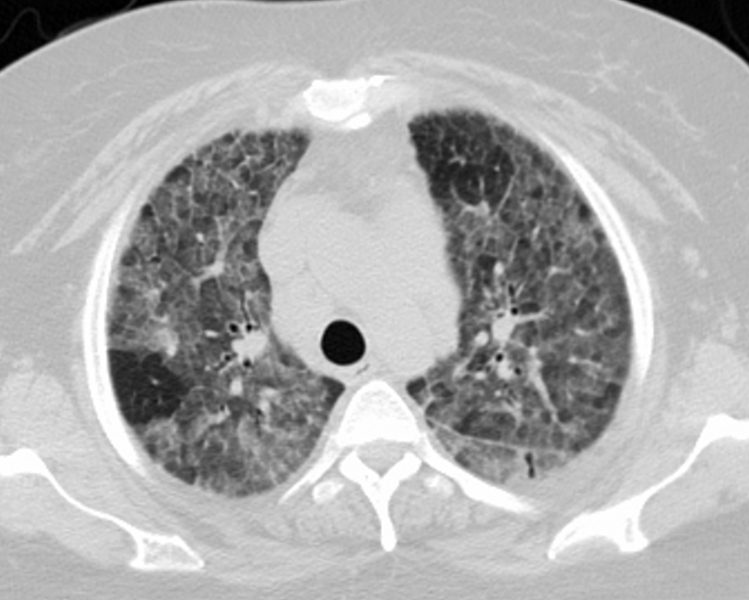

43F
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Mosaic Attenuation
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
117662
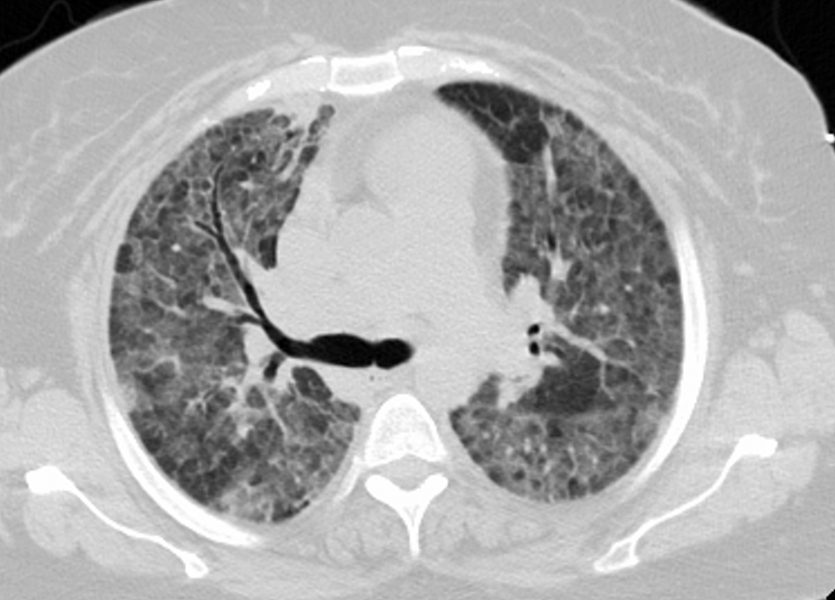

43F
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Mosaic Attenuation
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
117668
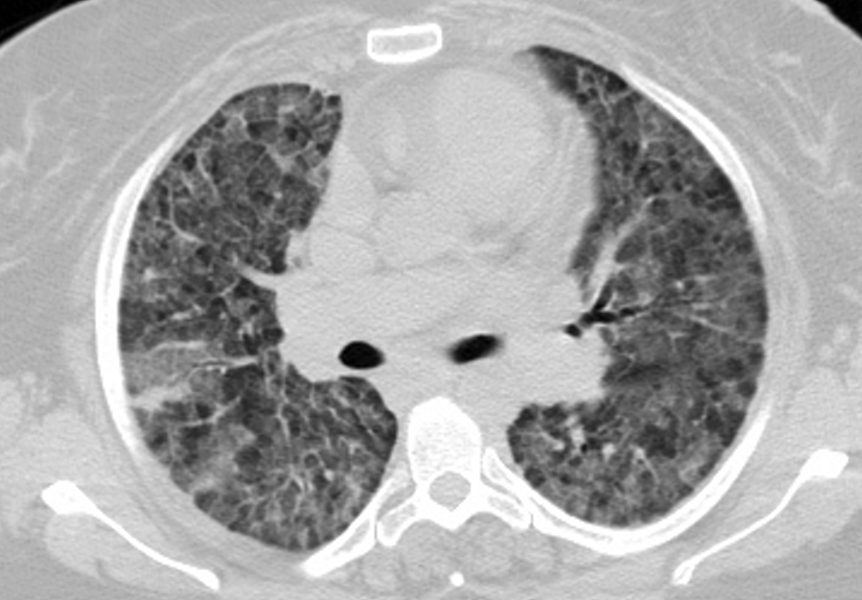

43F
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Mosaic Attenuation
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net117672
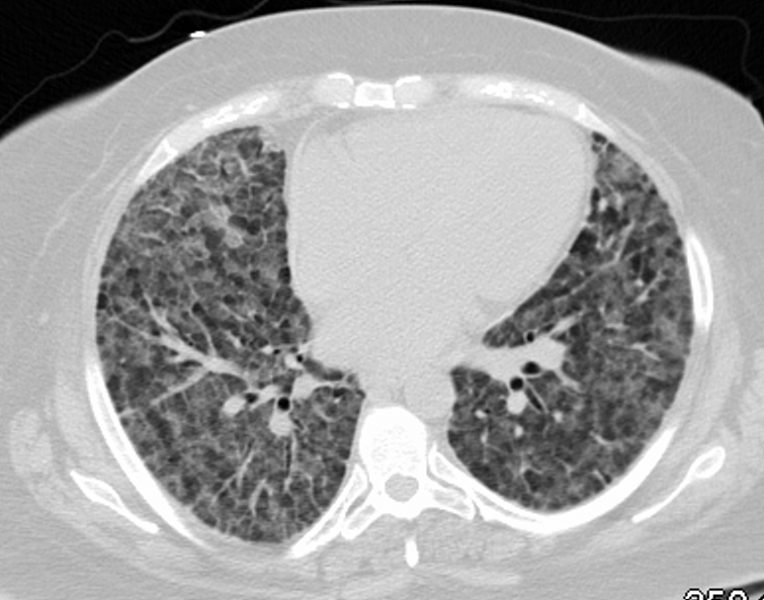

43F
Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
117687
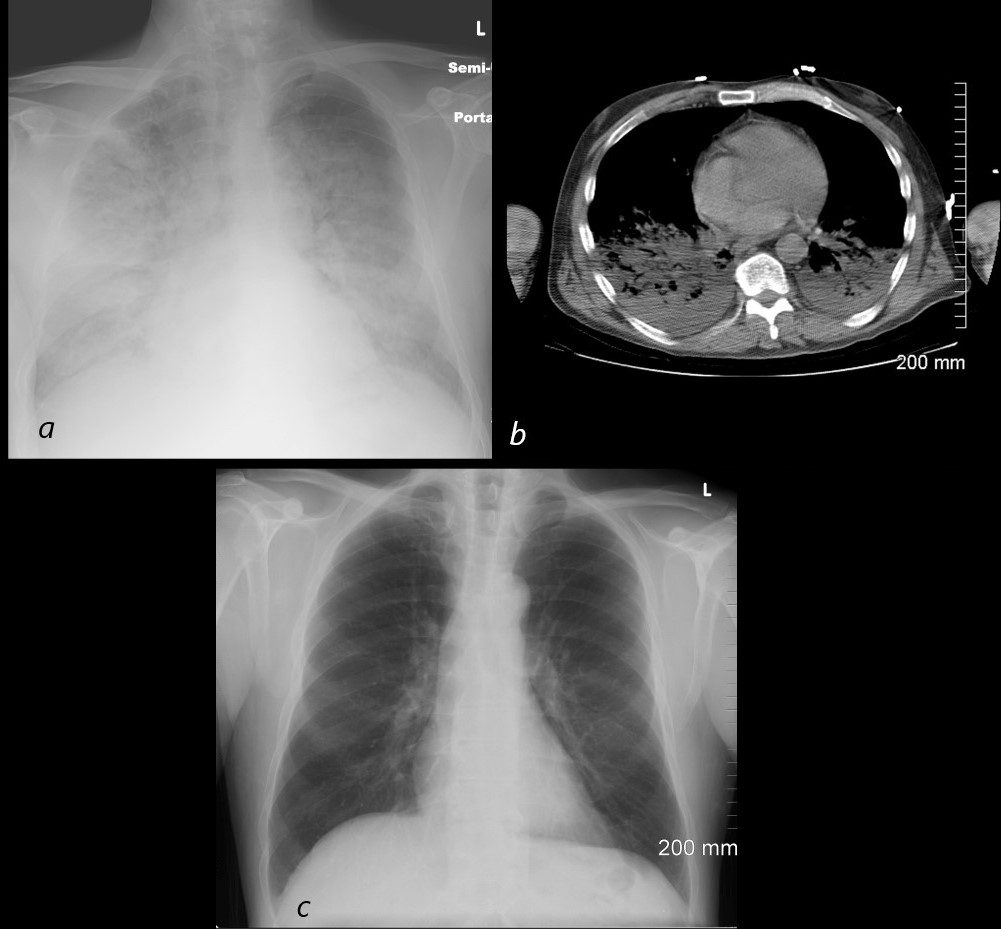

54 year old male alcoholic with seizures presents with diffuse alveolar disease consistent with pulmonary edema (a). CT scan (b) shows bibasilar infiltrates consistent with aspiration.
Follow up CXR 6 months later (c) shows resolution
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
70F Aspiration and Pneumonia with Crazy paving
62F-ARDS-post-abdominal-surgery-and-abdominal -abscess-shock
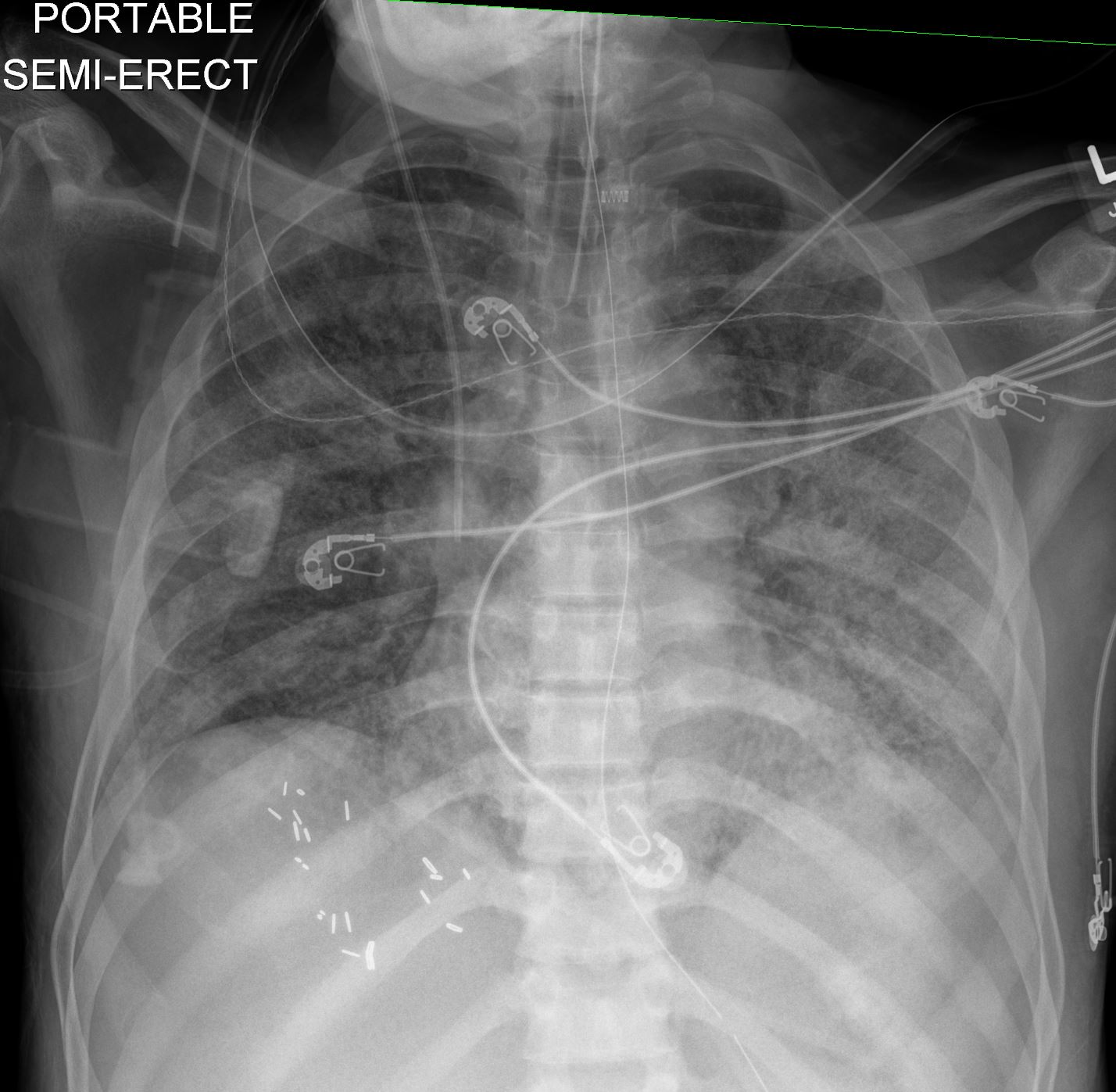

post-abdominal-surgery-and-abdominal -abscess-shock
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
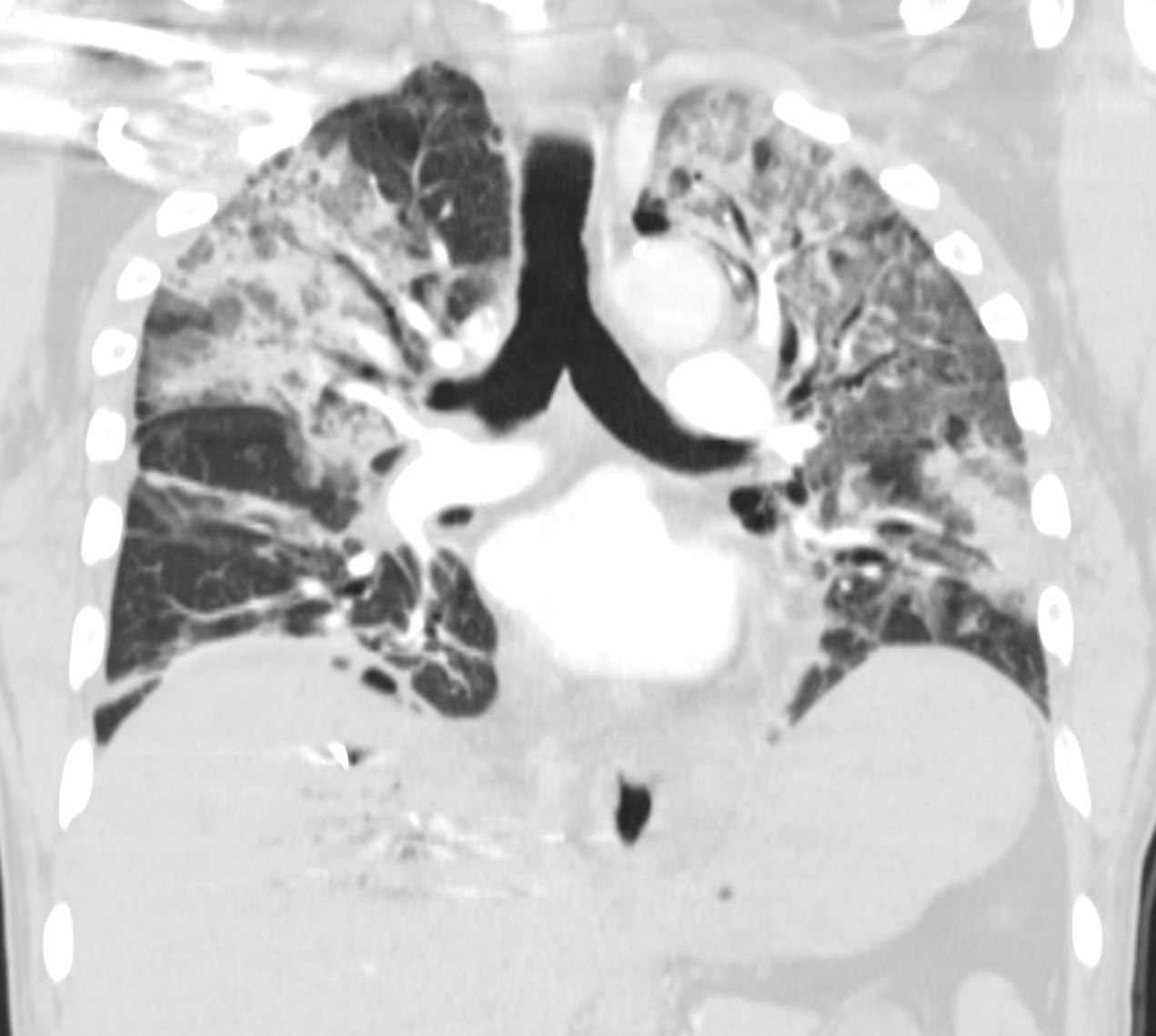

post-abdominal-surgery-and-abdominal -abscess-shock
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
References and Links
Radiopaedia
- Akira Yoshikawa, M.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. Pathology Outlines ARDS / DAD
- Sheard S et al Imaging of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome