Definition
- Atelectasis implies collapse of part of the lung.
- Caused by
- resulting in absence of air in the affected
- sub-segment
- segment,
- lobe
- lung
- When air does not fill the alveoli, the alveoli collapse.
- Diagnosed by
- stethoscope, percussion, x-ray, CT and bronchoscopy.
File source: commons.wikimedia.org/
Types
Post Obstructive (Resorbtive)
- Caused by
- complete obstruction
- neoplasm,
- mucus plugging
- foreign bodies
- complete obstruction
- Result
- air
- no new air can enter lung distal to the obstruction
- trapped air that is absorbed into the capillaries, l
- pleura
- cannot separate
- vacuum and
- traction of mediastinal structures and diaphragm
- mediastinal shift and elevated diaphragm
- air
- Compressive Atelectasis
- Caused by
- pleural effusion,
- pneumothorax and
- diaphragmatic abnormality
- Result
- air
- squeezed out of lung
- pleura
- separated
- potentially only minor or no vaccuum
- air
- Caused by
- Cicatrisation (Traction) Atelectasis
- Caused by
- graulomatous disease,
- necrotizing pneumonia and
- radiation fibrosis
- bronchietasis
- Result
- air
- lung cannot expand
- pleura
-
- cannot separate
- vacuum and
- traction on surrounding structures
-
- air
- Caused by
- Adhesive Atelectasis
- Caused by
- surfactant deficiency
- diffuse or
- localized
- Result
- surfactant deficiency
- Caused by
- Gravity Dependant Atelectasis (Dependent Atelectasis)
- Caused by
- weight of the lungs
- Result
- Crescentic shaped
- ground glass changes
- Crescentic shaped
- Caused by
- Osteophyte-Induced
- Caused by
- Result
- focal atelectasis
- fibrosis
- bronchiolectasis
Links and References
- TCV
- Discoid Atelectasis on CT

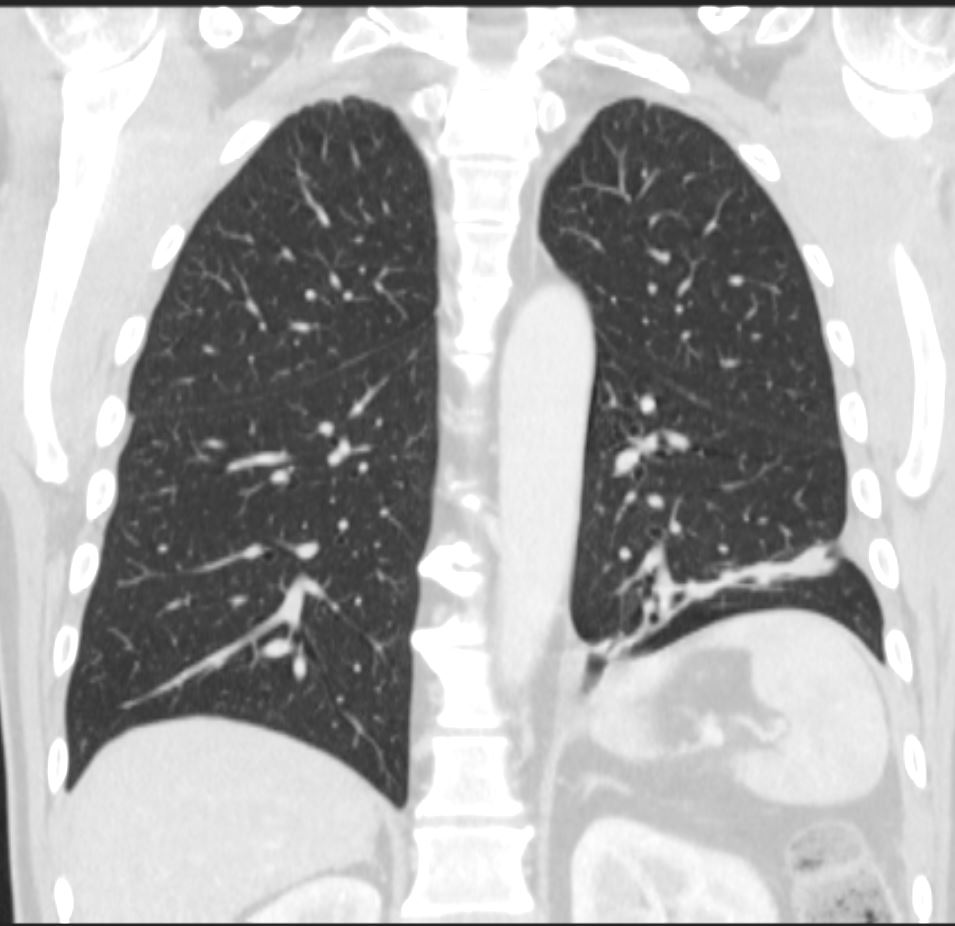
CT Linear Atelectasis 3 Months Later
CT scan in the coronal plane 3 months later shows significant improvement of the atelectasis involving a basal segment of the left lower lobe associated with persistent elevation of the left hemidiaphragm indicating volume loss. The atelectasis now has a discoid, linear, or plate-like appearance
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 276Lu 136238
aka discoid atelectasis aka plate-like atelectasis
Links and References
TCV