Right Lung Parts: Basic Anatomy
The right lung has three lobes: upper, middle, and lower. The lobes are subdivided into segments that are determined by the branching of the main bronchi. The right lung usually has 10 segments subtended by 10 segmental bronchi. The right upper lobe has three segments called the apical, posterior and anterior segments. The right middle lobe has two segments named the lateral and the medial segments. The right lower lobe has five segments also named according to position; superior, anterior basal, lateral basal, posterior basal, and medial basal segments. The superior segmental bronchus is the first branch of the RLL system and it is directed posteriorly. The superior segment is vulnerable in the supine patient who aspirates because of its posterior position.
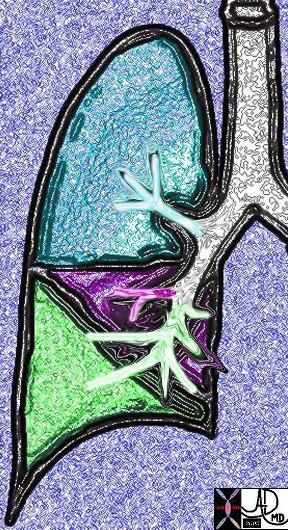
This diagram shows the segmental branches of the right bronchial system. The RUL has three branches, the apical, posterior and anterior segments. (teal overlay) The middle lobe has two segmental branches called lateral and medial segments. (pink) The right lower lobe has five: the superior, anterior basal, lateral basal, posterior basal and medial basal segments. Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 32686b03
The superior segment occupies the entire upper portion of the lower lobe. It sits atop the remaining four segments of the right lung: the anterior basal, lateral basal, posterior basal and medial basal segments. These basal segments form the base of the almost pyramidal shaped lower lobe as well as the base of the lung it and them rest upon the diaphragm.
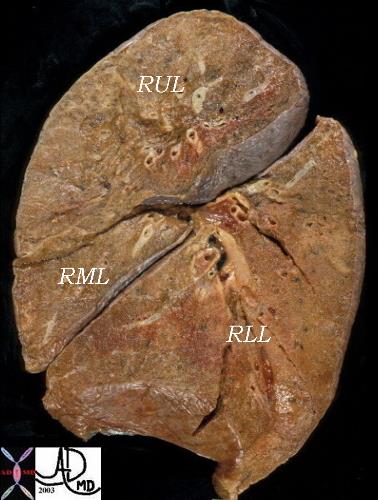
This pathologic specimen of the lung is viewed in the sagittal plane with the anterior aspect to your left. The RML is the triangular lobe in this projection and is the smallest of all the lobes. The RUL is above and the RLL which is inferior and posterior to the RML is the largest lobe of the right lung.
Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 32159B03b
Right Lung Parts: Applied
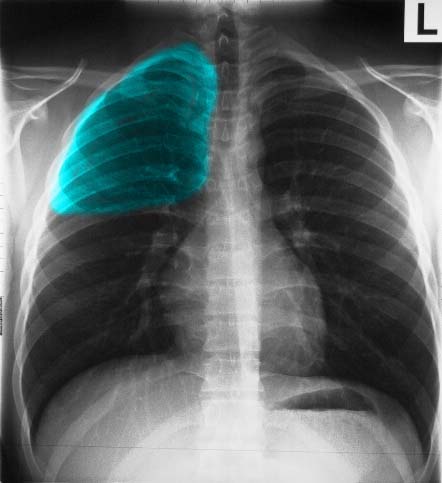
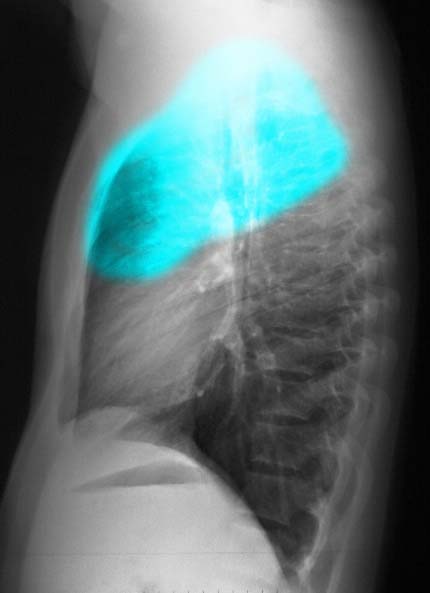
It is essential to know and understand the distribution of the lobes for accurate assessment of the CXR. For example, a disease process in the upper lung field on the right does not necessarily mean that the disease is in the RUL. Since the RLL is so large and extends almost the entire thoracic distance (see image 3a), it is difficult to localize on the P-A exam of the chest. However, if one reviews the lateral exam, the distinction between right upper and right lower lobe is much easier, since the lower lobe is mostly posterior and below the fissure, and the upper lobe mostly anterior and above the fissure.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 30397b01
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 30398b01
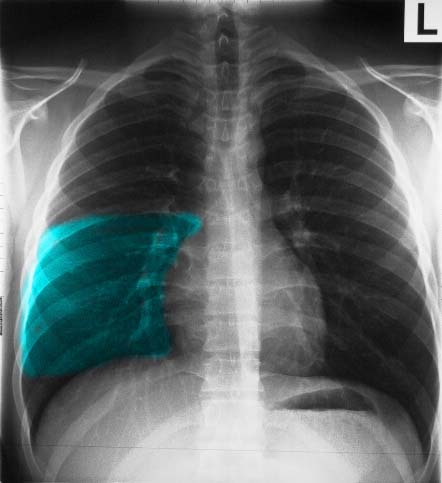
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 30397b03
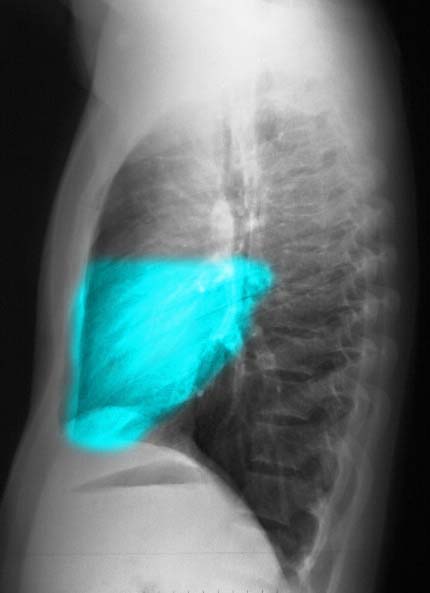
Ashley Davidoff MD The Common Vein.net 30398b03
The following images in P-A and lateral projection reveal the large posteriorly positioned right lower lobe (RLL). Note how much larger the RLL is compared to the RML and the RUL.
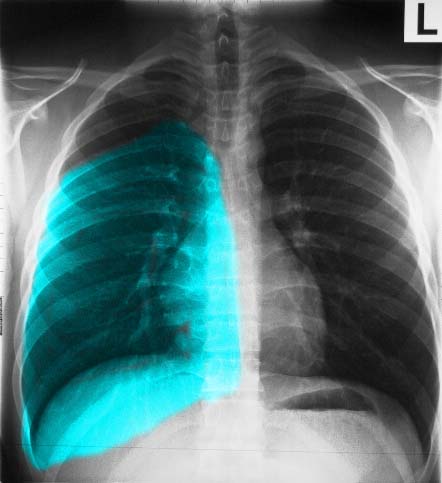
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
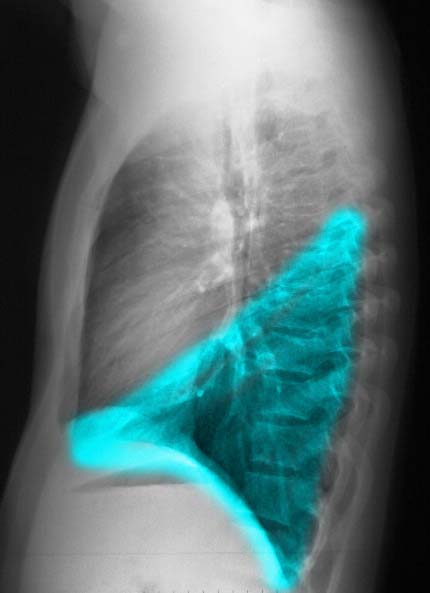
Ashley Davidoff MD
The major fissure is the dividing line between the RLL on the one hand and the RUL and RML on the other. The minor fissure, also known as the transverse fissure, divides the RUL from the RML and is easily perceived on the lateral examination.
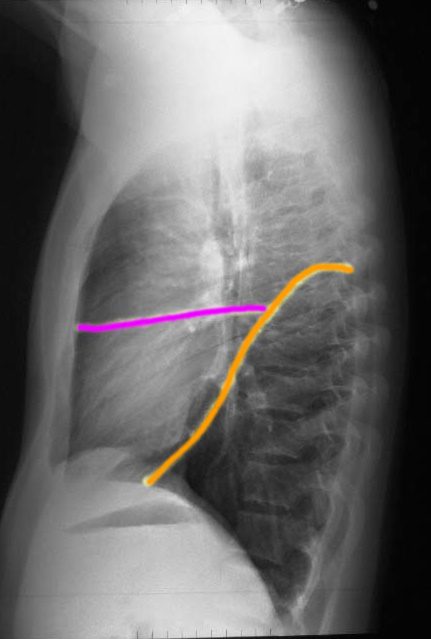
The right lung has a relatively small right upper lobe (RUL) separated from the middle lobe (RML) by the minor fissure (pink,lower image). Both the RUL and RML are anterior and are separated from the lower lobe by the major fissure (orange line)
Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 30398b06b
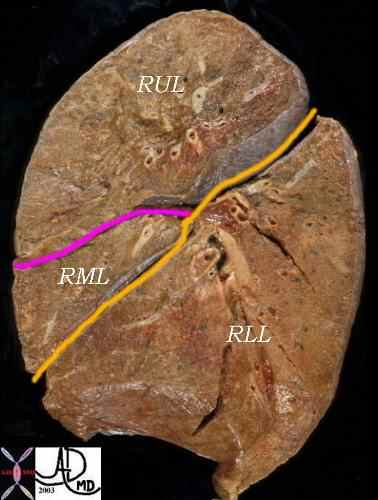
This lateral examination of the corresponding lung specimen in sagittal section demonstrates the major fissure in yellow/orange which divides the RLL from the RML and RUL. The minor fissure is in pink and it divides the RUL from the RML.
Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 32159B06
This coronal reformats through the tracheobronchial tree show the major fissures bilaterally. They are usually quite difficult to see and unless you know where to look you may miss them altogether. Usually there is a hint of hypovascularity along the fissure resulting in a relative lucency as can be appreciated in this examination. The fissures have been overlaid in orange in the next image. As the coronal cut proceeds posteriorly the lower lobe becomes more prominent and the upper lobes less so. If you review the lateral chest x-ray and project the cuts you would get a better sense of this concept of the dominance of the RLL and its posterior location .
Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 32682b
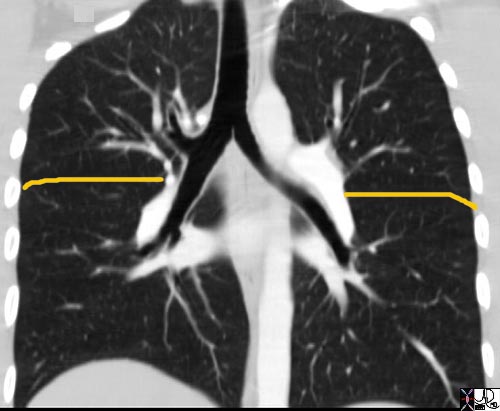
This coronal reformats through the tracheobronchial tree show the major fissures bilaterally. They are usually quite difficult to see and unless you know where to look you may miss them altogether. Usually there is a hint of hypovascularity along the fissure resulting in a relative lucency as can be appreciated in this examination. The fissures have been overlaid in orange. As the coronal cut proceeds posteriorly the lower lobe becomes more prominent and the upper lobes less so. If you review the lateral chest x-ray and project the cuts you would get a better sense of this concept of the dominance of the RLL and its posterior location .
Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 32682b01.jpg
Sometimes there is an extra lobe in the right upper lung field called the azygous lobe and the azygous vein runs in the accessory fissure. The azygous lobe is an accessory lobe in the apex of the right lung that is found in approximately 0.5% of routine chest x-rays. It is recognized by a fissure in the apex that has an inverted comma shape.
The following diagram demonstrates the cross sectional appearance of the right lung at the level where both the major and minor fissures are seen. It correlates the CTscan with the anatomical specimen.
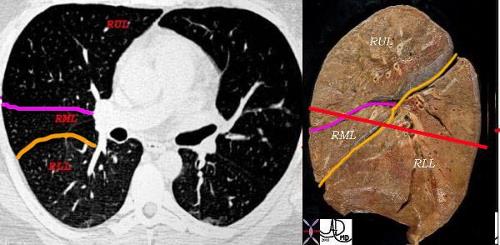
This combination shows the two fissures of the right lobe on the CT scan separating the RLL from the RML (major fissure in orange) and the RML from the RUL. (minor or transverse fissure in pink) The anatomic specimen is in the sagittal plane with the posterior aspect to your right. The red line drawn through the specimen represents the level of the X-sectional plane revealing in sequence from posterior to anterior, the RLL, major fissure, RML, minor fissure, RUL. On the left side there is the faint hint of hypovascularity along the major fissure.
Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 32160c2lb_6
key words medical students code chest CXR imaging lung plain film pneumonia radiology resolution
41819c02 Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net
31350 lung bronchus right middle lobe bronchus normal anatomy CTscan Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 31350
