- Sequestration
- nonfunctional and dysplastic lung tissue that is
- lacking a normal connection to the tracheobronchial tree
- and the pulmonary arteries
- and possessing an aberrant arterial blood supply,
- Read More: https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.05.0155?mobileUi=0
- Intralobar sequestrations (ILS) are
- located within a normal lobe
- lack their own visceral pleura.
- occur in the lower lobes,
- about60 percent are located in the posterior basal segment of the left lower lobe
- can occur anywhere within the thorax
- rare instances of bilateral ILS (
- or ILS with contralateral extralobar sequestration have been reported [23]. T
- no bronchial connection to the proximal airway.
- pores of Kohn may cause recurrent infection,
- connections to the gastrointestinal tract +/-10 percent,
-

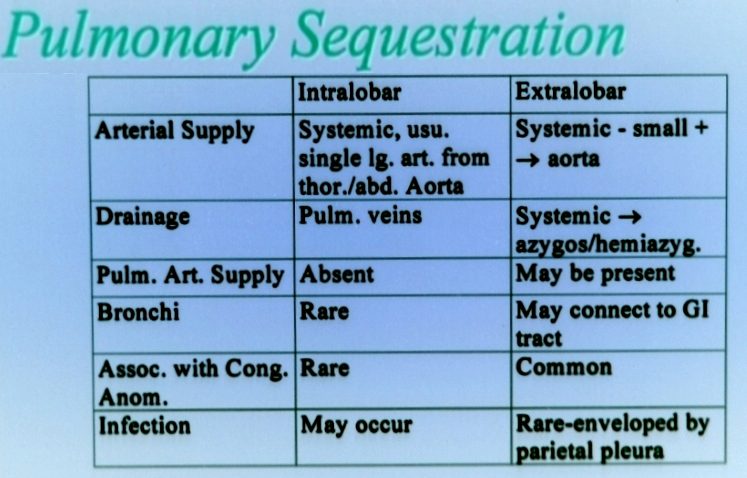
Difference Intralobar and Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration -

SEQUESTRATION
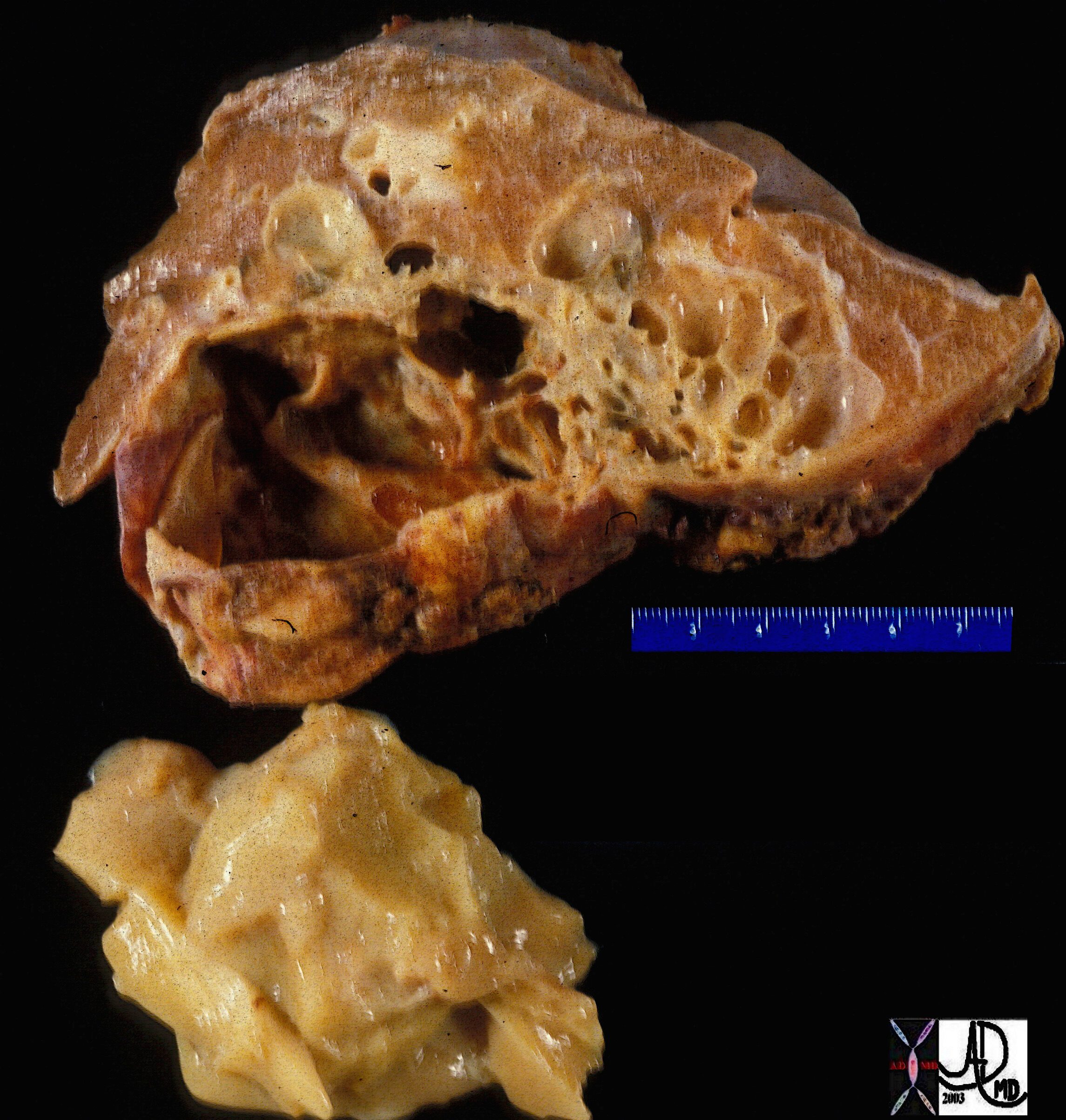
Gross pathology specimen of a resected sequestration of the lung. and Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32302
Keywords:
lungs pulmonary congenital growth sequestration gross pathology
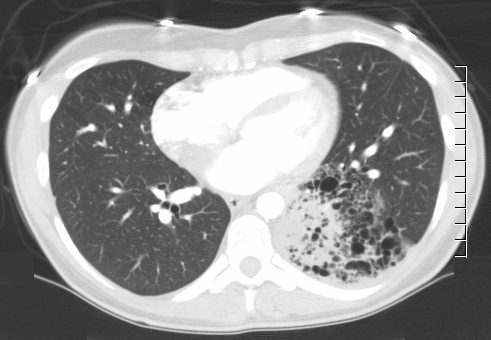
(A) An axial CT scan of a 26-year-old man with an intralobar sequestration shows a heterogeneous subsegmental soft tissue density in the left lower lobe . An artery arising from the descending aorta supplies the sequestration.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Pulmonary Sequestration 
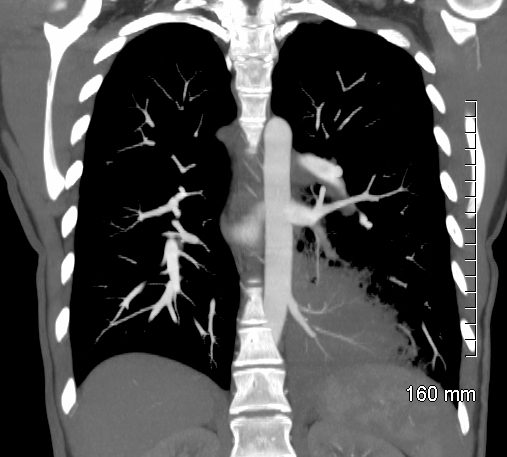
An axial CT scan (top) of a 31-year-old woman with an intralobar sequestration shows a left lower pneumonia (arrowhead) with a surrounding region of emphysema . A reformatted coronal image (bottom) shows a systemic artery arising from the descending aorta (arrow) that supplies the sequestration. Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net -
-