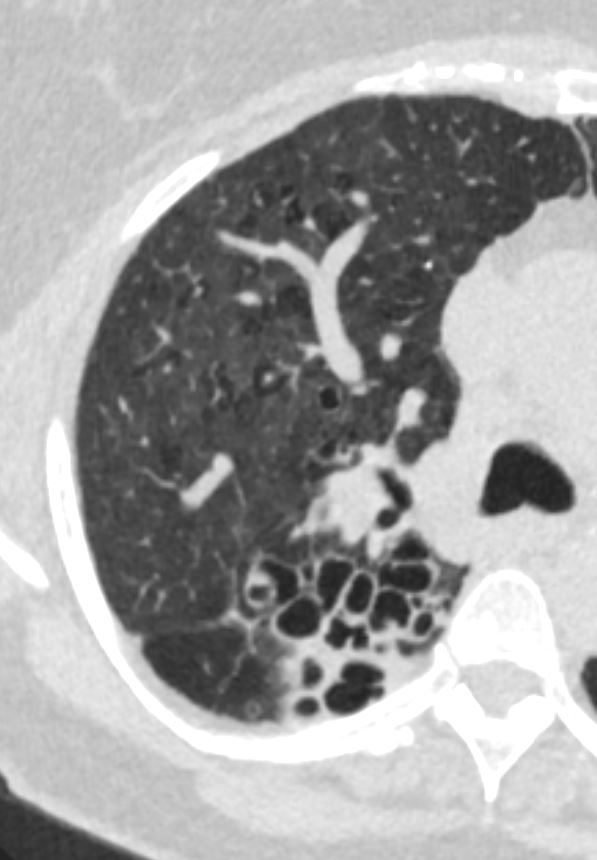
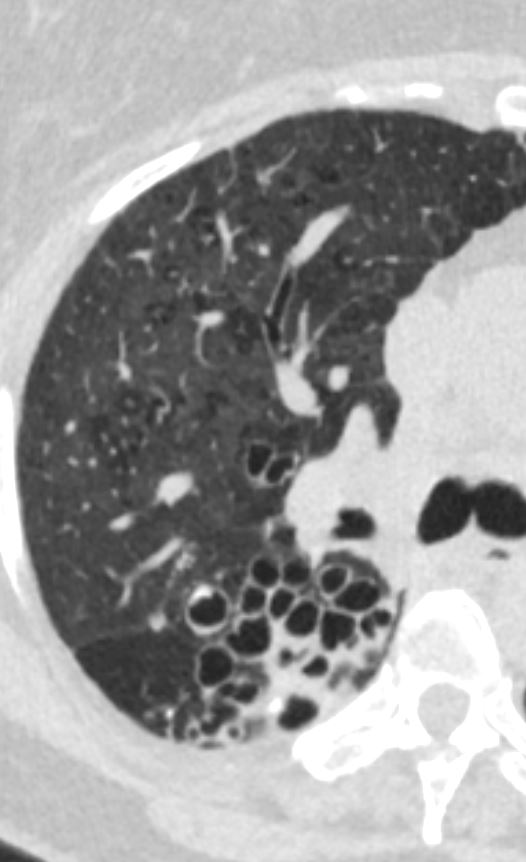
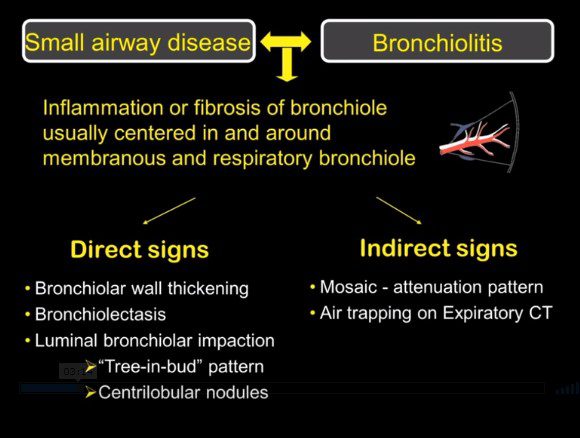
- Small Airways
- internal diameter
- less than 2 mm (1-2mm).
- terminal bronchioles
- 3-5 terminal bronchioles in a secondary lobule
- respiratory bronchioles
- alveolar ducts
- alveolar sacs

-


Small Airways
The diagram allows us to understand the the components and the position of the small airways starting in (a) which is a secondary lobule that is fed by a lobular bronchiole(lb) which enters into the secondary lobule and divides into terminal bronchioles (tb) which is the distal part of the conducting airways, and at a diameter of 2mm or less . It divides into the respiratory bronchiole (rb) a transitional airway which then advances into the alveolar ducts(ad) and alveolar sacs (as) Diseases isolated to the small airways do not affect the alveoli and hence there is peripheral sparing Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0749

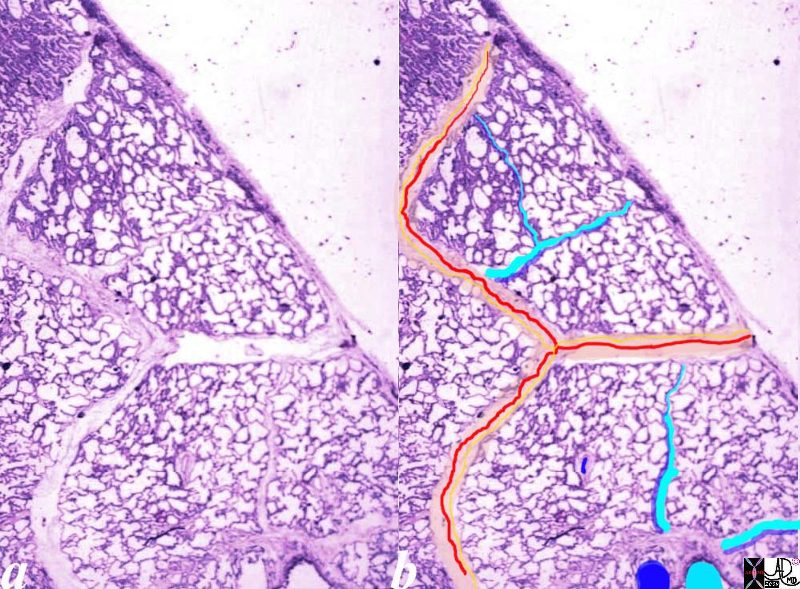
This image is a panoramic view of the lung showing in this case almost rectangular secondary lobules surrounded by interlobular septa (cream borders)
Courtesy of: Armando Fraire, M.D. Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net - In a Nutshell
-


Small Airways Definition
Society of Thoracic Radiology Santiago Rossi - Size
- Bronchiolectasis
-


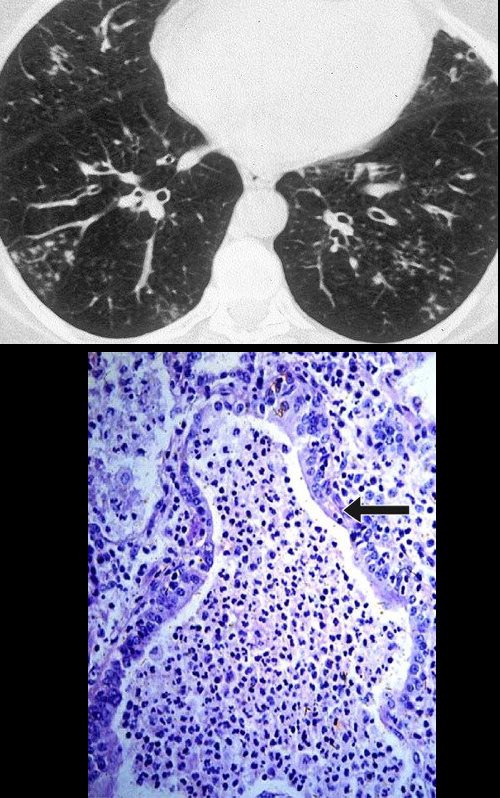
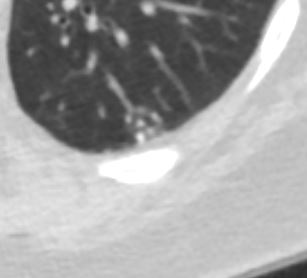
Magnified CT of an abnormal small airway in a patient with sarcoidosis with thickened walls centrilobular nodules and ground glass opacity
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 29289


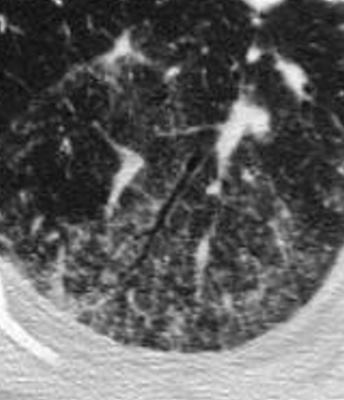
Magnified CT of an abnormal small airway in a patient with sarcoidosis with thickened walls centrilobular nodules and ground glass opacity
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 29288mThickened Walls


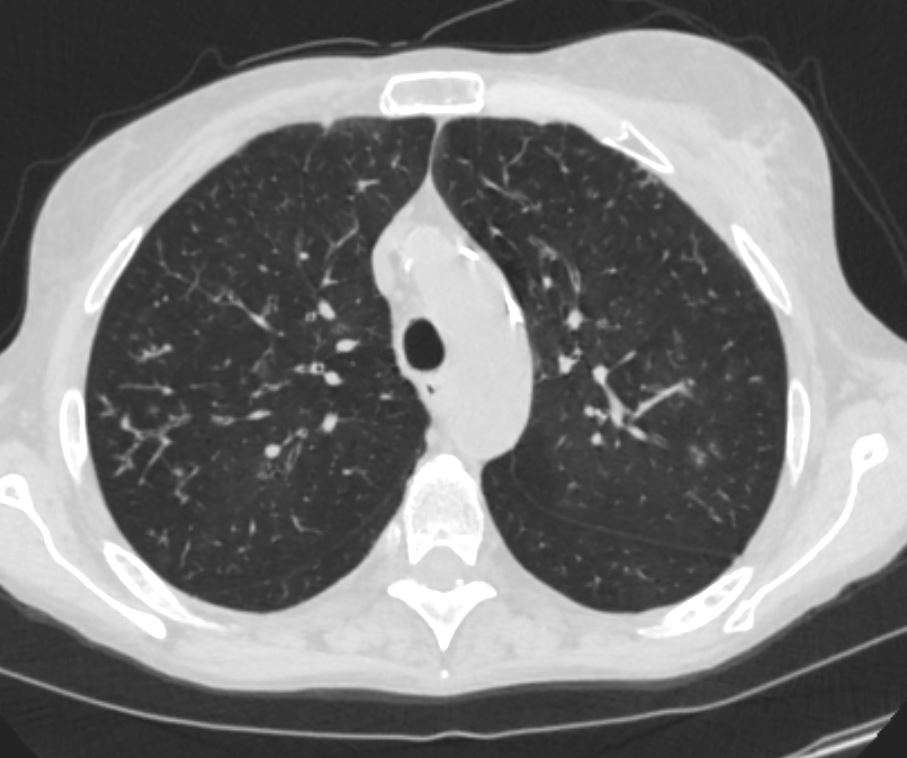
In this patient there is thickening of all the visualized segmental, subsegmental and small airways. In the lateral basal segment of the right lower lobe there is thickening of the small airways as well as suggestion of tree in bud nodularity due to mucoid impaction
Keywords lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 54f-001
-
- Shape
- Tree in Bud
-


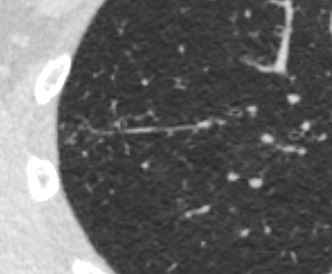
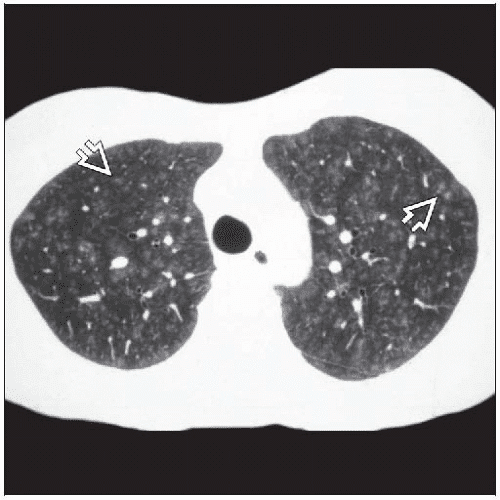
Tree in Bud from approximately the Terminal Bronchiole to the Alveolar Sacs
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net bronchiole to periphery 57MMultiple Ill Defined Ground Glass Nodules Characteristic of Small Airway Disease

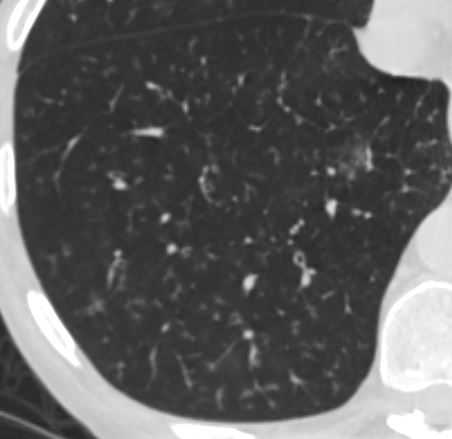
bronchiolitis with Ill Defined ground Glass Nodules
Keywords
lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.netCharacter Small Airways Filled with Fluid or Cells Results in Increased Density eg Eosinophilic Pneumonia

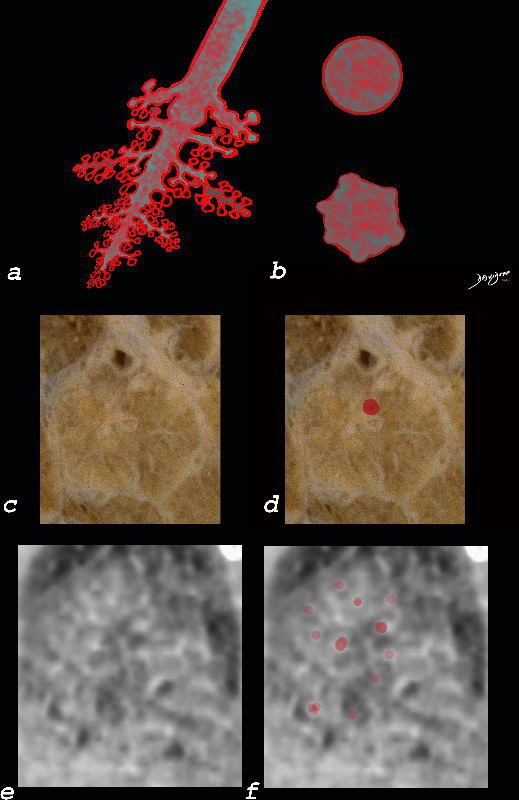
Acute Eosinophillic Pneumonia
Small Airways Infiltration with Eosinophils and Inflammatory Exudate – Centrilobular Nodules
The diagram shows the small airways of the lung including the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs in coronal (a) and in cross section (b) and correlated with an anatomic specimen of a secondary lobule that contains a thickened interlobular septum . The respiratory bronchiole is overlaid in maroon (d), next to the arteriole. Images e and f are magnified views of a CT of the lungs in a patient with acute eosinophillic pneumonia and the centrilobular nodules reflecting small airway disease are highlighted in f.
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0760b

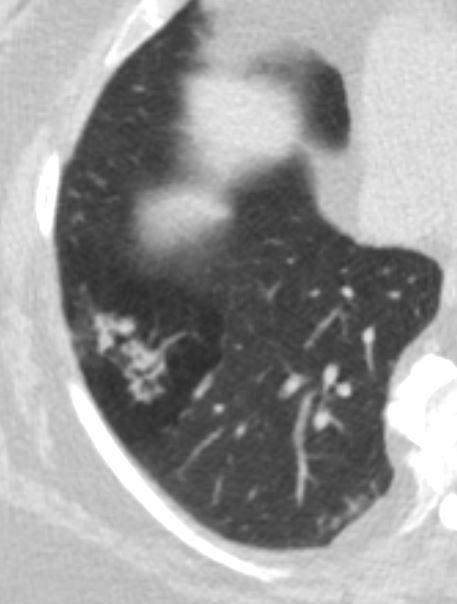
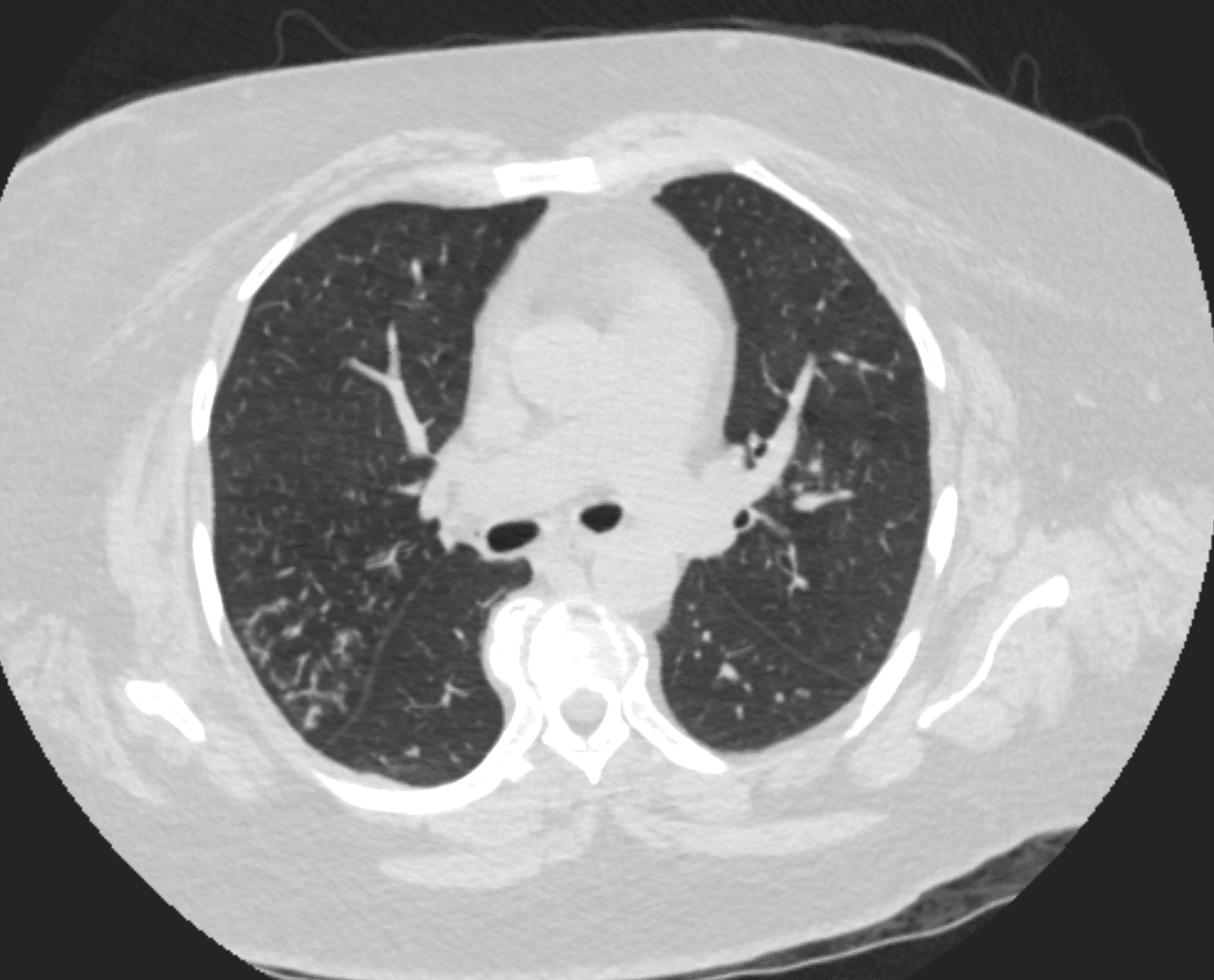
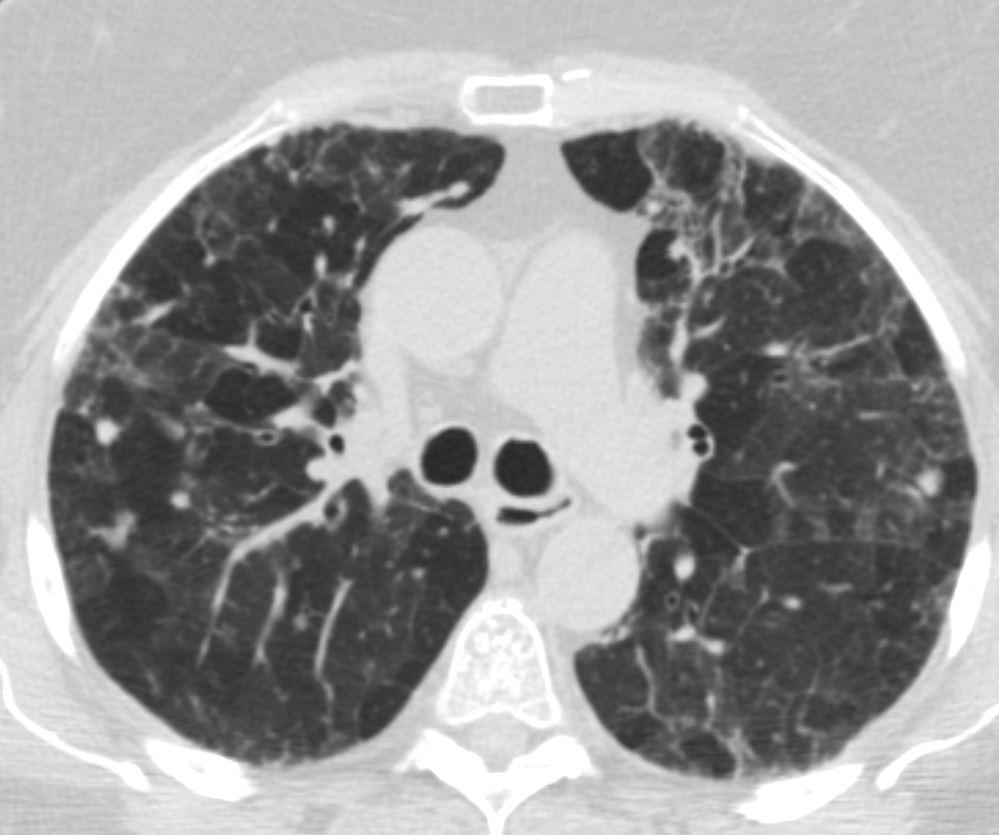
Mosaic attenuation with thickening of the walls of the small airways in the right lower lobe
Small Airways are filled with mucus in a patient with COPD – Note centrilobular impaction of mucus Small Airways are obstructed and air is trapped
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net bronchioles 001Mosaic Attenuation Caused by Small Airway Disease or Small Blood Vessel Disease
- Persistent Mosaic Attenuation During Expiration = Small Airway Disease Dx Sarcoidosis

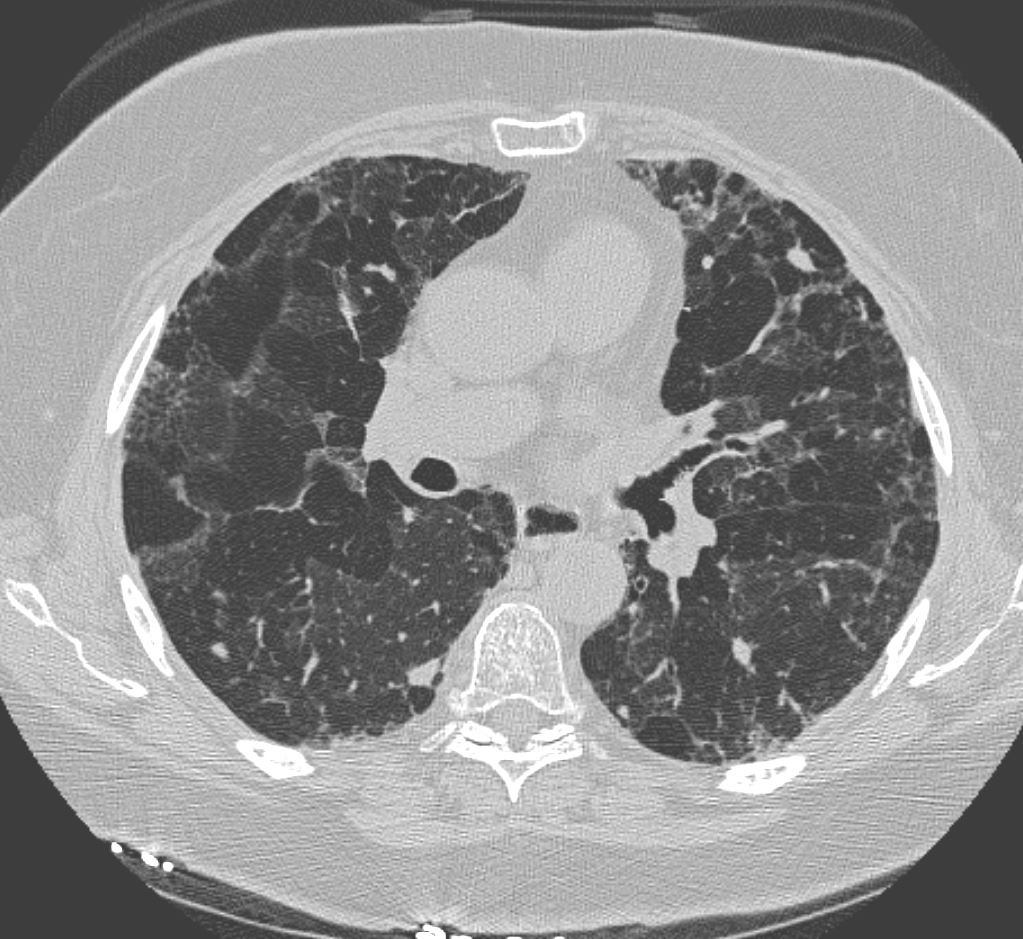
Mosaic Attenuation on Expiration Imaging Small Airway Disease
77F with long history of dyspnea and cough showing medium and small airway disease, centri-lobular nodules, para-septal nodules ground glass changes and mosaic attenuation Diagnosis includes Stage 3 sarcoidosis
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net - Do not usually see the small airways
-


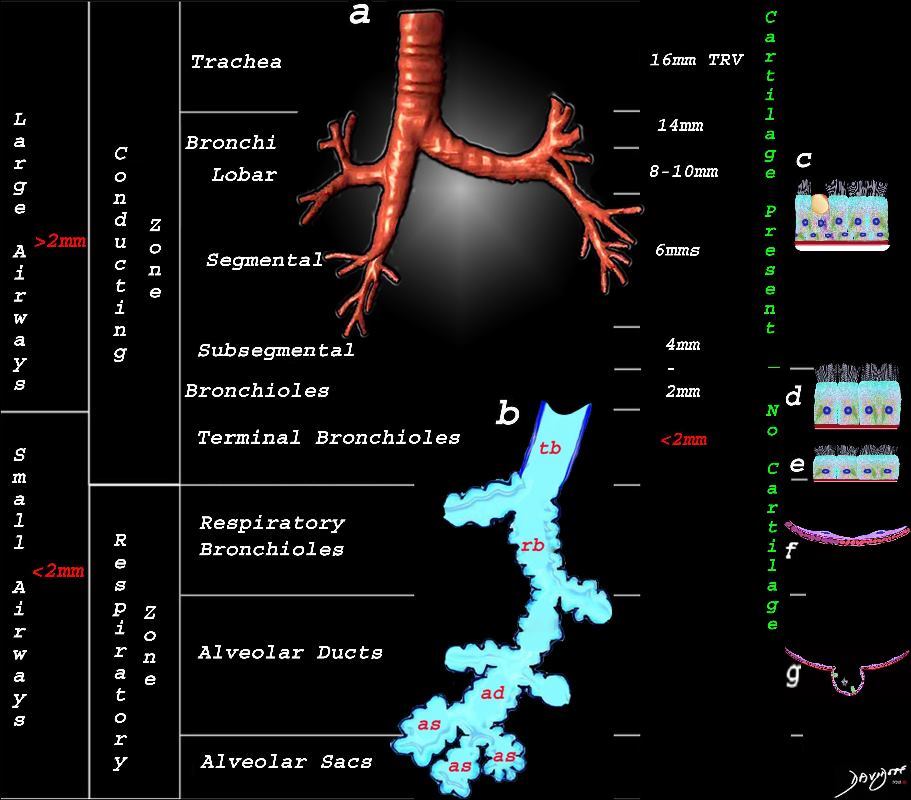
Overview of the Anatomy of the Lungs Large Airways and Small Airways
This image shows the division of the airways in the lungs classified as large airways and small airways.
A large airway is considered any airway larger than 2mm, and therefore includes all the airways involved with transport of air except for the terminal bronchiole. Included as seen in image a, are the trachea, mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi segmental and subsegmental airways and the 3 subsequent divisions of subsegmental bronchi and bronchioles till the last transporting airway – the respiratory bronchiole which is usually about 2mm and is considered a small airway Image (a) shows the airways starting in the trachea and continuing to the mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi, segmental bronchi, and subsegmental bronchi.
Image b shows the structures that make up the small airways starting with the terminal bronchiole (tb) followed by the respiratory bronchiole (rb) alveolar duct, (ad) and alveolar sacs (as)
Image (c) shows the histologic makeup of the large airways that include a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with mucus secreting goblet cells a muscular layer (red) and a prominent cartilage layer (white) In the larger bronchioles (d) the epithelium remains as a pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium with prominent muscular layer (red). The columnar epithelium transitions to a stratified ciliated cuboidal epithelium by the terminal bronchiole s (f) both still with a muscular layer. The respiratory epithelium transitions from a cuboidal epithelium to a squamous epithelium (f) with alveoli and type I and II pneumocytes starting to branch (g)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0740nL
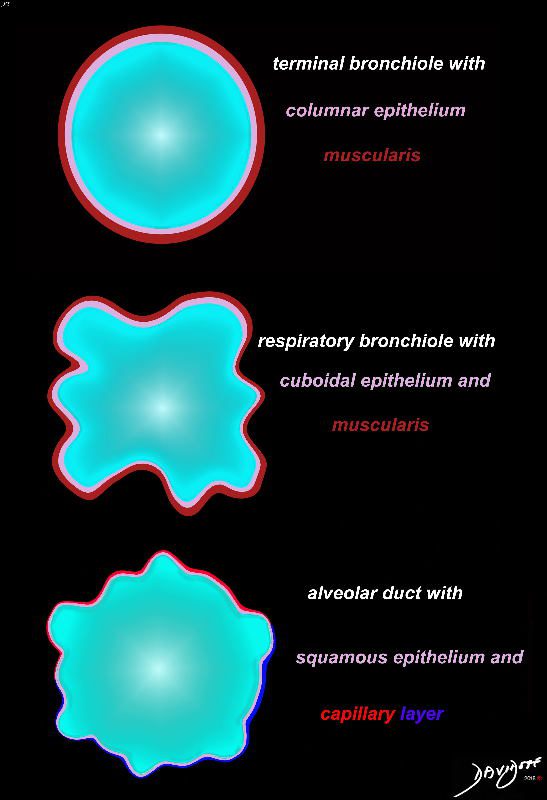
Small Airways Terminal Bronchiole and Alveolar Duct
Cross section diagrams of the small airways. The top diagram shows a normal terminal bronchiole with columnar epithelium (pink), and muscularis (maroon). The respiratory bronchiole starts to have features of evolving respiratory airways, and he mucosa becomes cuboidal with persistence of the muscularis.
The alveolar duct has a squamous epithelium (pink), and is surrounded by a capillary network (blue – arteriolar component, and red venular component)
Ashley Davidoff MD thecommonvein.net lungs-0776b
- terminal bronchioles
- less than 2 mm (1-2mm).
- internal diameter
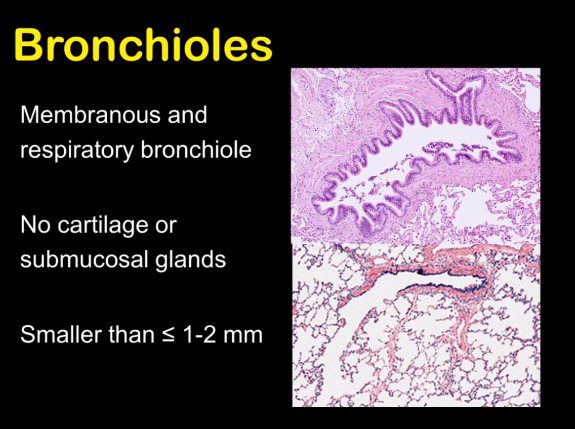
Bronchioles are fine airways which constitute the passages produced by the 11th to 17th divisions of the bronchi within the lung parenchyma.
- Types
- conducting bronchioles
- ciliated pseudostratified columnar cells
- goblet cells
- no cartilage
- smooth muscle appears
- terminal bronchiole
- 70,000 each lung
- diameters 1 mm or less
- Clara cells – surfactant
- still ciliated
- no glands
- smooth muscle
- respiratory bronchioles
- primary 150,000 each lung
- 3 divisions so that there are 500,00 in each lung
- .5mm or less
- Clara cells
- some ciliated
- have alveoli and alveolar ducts along their walls
- conducting bronchioles
-


Respiratory Bronchiole
This diagram illustrates the acinus which consists of the respiratory bronchioles (rb 1, 2, 3) the alveolar duct (ad) the alveolar sac (as) and the alveoli. (a)
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 42446b12
TheCommonVein.net
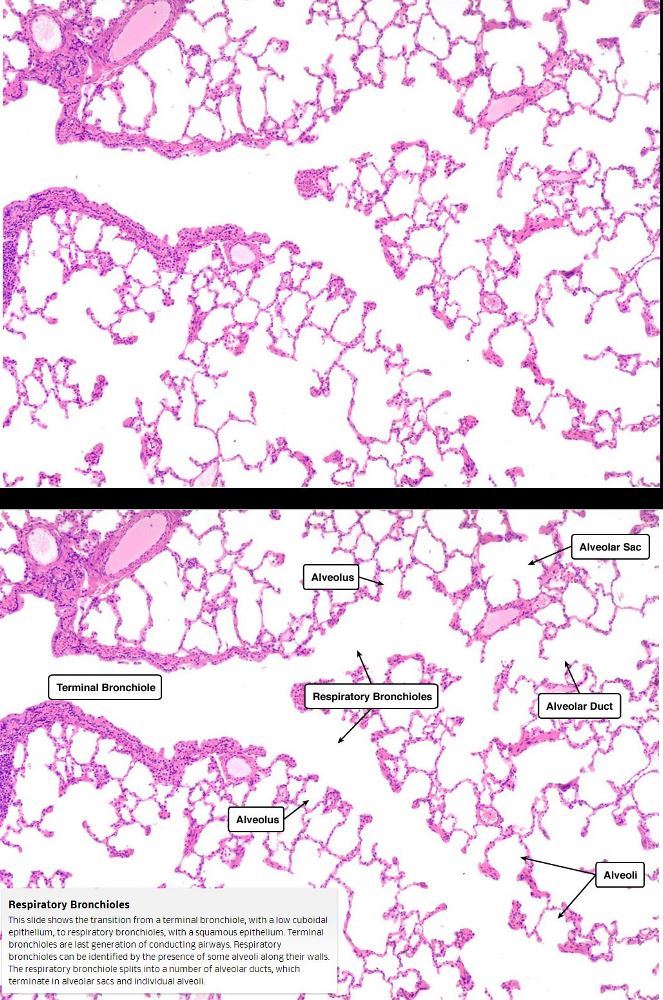
Respiratory Bronchioles
This slide shows the transition from a terminal bronchiole, with a low cuboidal epithelium, to respiratory bronchioles, with a squamous epithelium. Terminal bronchioles are last generation of conducting airways.
Respiratory bronchioles can be identified by the presence of some alveoli along their walls. The respiratory bronchiole splits into a number of alveolar ducts, which terminate in alveolar sacs and individual alveoli
Courtesy medcell.med.Yale.edu - within their walls:
- no hyaline cartilage
- no submucosal glands
- prominent outer wall layer with
- smooth muscle cells responsive to neural control including
- parasympathetic (vagal) inputs;
- sympathetic fibers
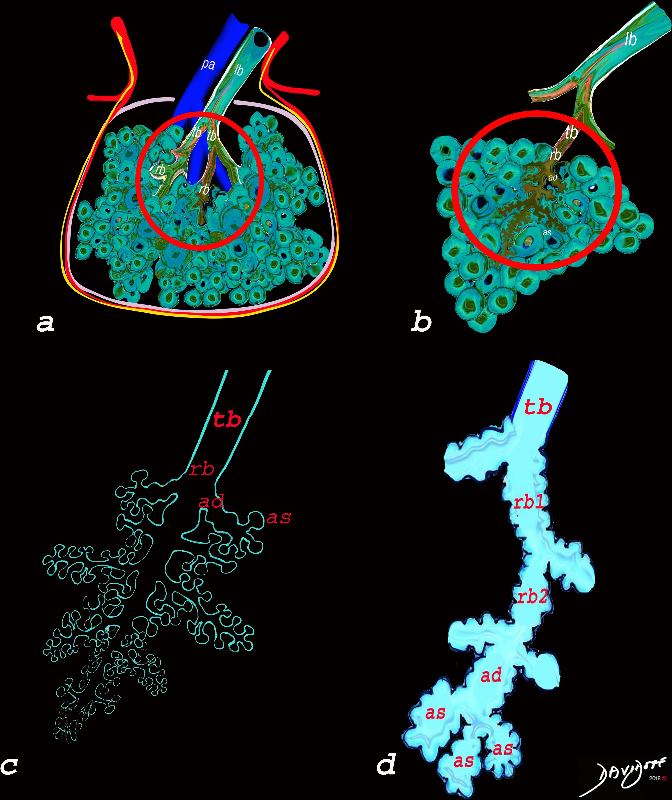
The Secondary Lobule Fed by a Lobular Bronchiole and Small Airways Start in the Secondary Lobule
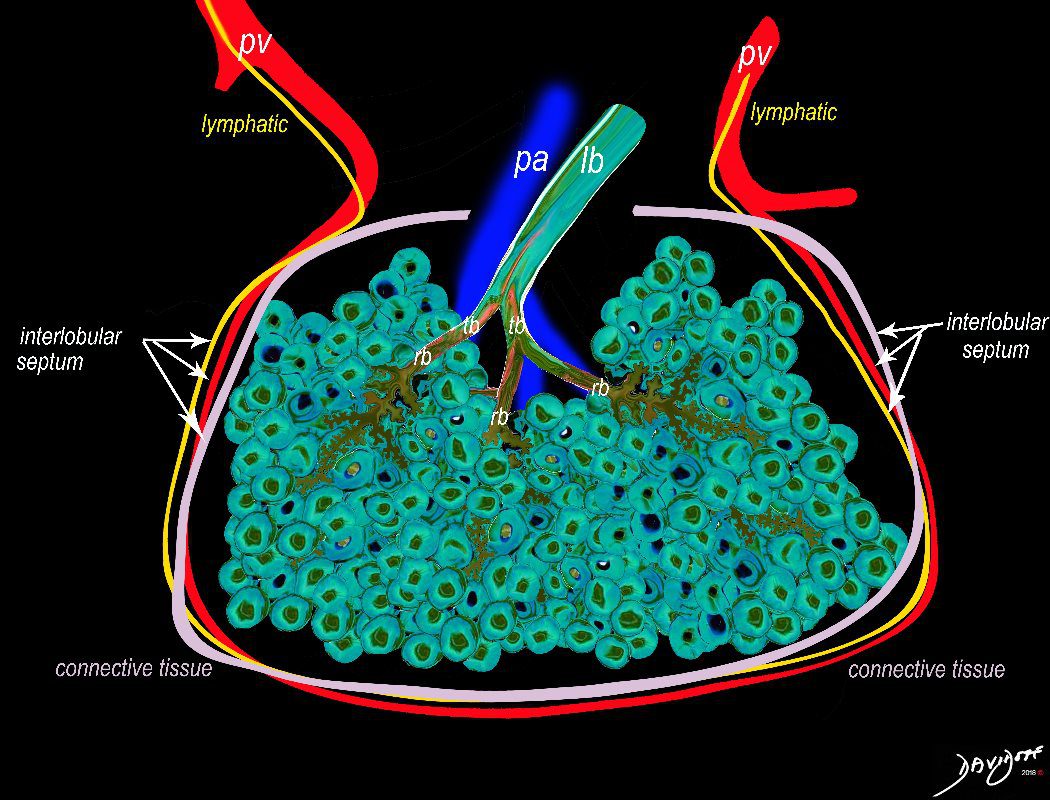

The secondary lobule is housed in a connective tissue framework in which run the lymphatic and venular tributaries . Together these 3 structures form the interlobular septum.
The lobular arteriole enters the framework, accompanied by the lobular bronchiole, and they all run together and form the interlobular septa. This structure measures between .5cms and 2cms and is visible on CT scan.
It is important in clinical radiology since many of the structures can be identified in health, and more particularly in disease, enabling the identification and characterization of many pathological processes.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0036-low res
Secondary Lobule Acinus and Small Airways



The diagram allows us to understand the the components and the position of the small airways starting in (a) which is a secondary lobule that is fed by a lobular bronchiole(lb) which enters into the secondary lobule and divides into terminal bronchioles (tb) which is the distal part of the conducting airways, and at a diameter of 2mm or less . It divides into the respiratory bronchiole (rb) a transitional airway which then advances into the alveolar ducts(ad) and alveolar sacs (as) Diseases isolated to the small airways do not affect the alveoli and hence there is peripheral sparing Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
-
- diameter less than 2 mm
- wall thickness of less than 0.5 mm
- include
- terminal bronchi (have cartilage)
- bronchioles
- no cartilage
- supported instead
- smooth muscle and
- surrounding connective tissue
- terminal bronchioles <1mm
- respiratory bronchioles
- narrowest airways in the lungs
- major site of pathology in many lung diseases
-

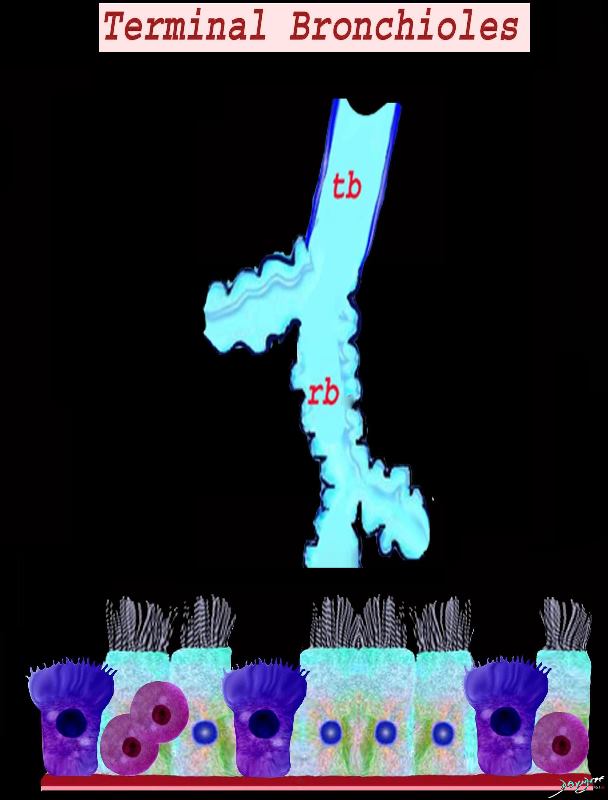
Histology of the terminal bronchiole showing the cellular components of the mucosa including the ciliated columnar cells, Clara cell and the neuroendocrine cells
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0746
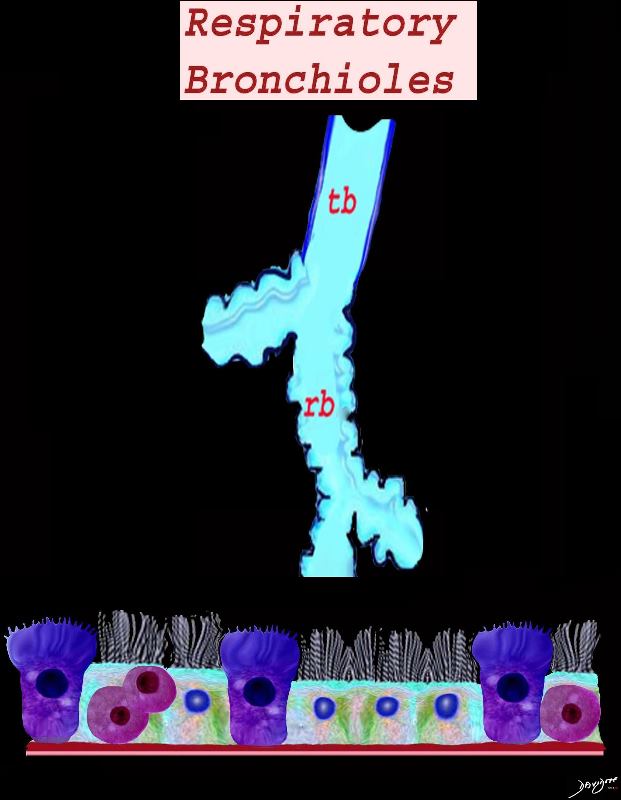
Histology of the respiratory bronchiole showing the cellular components of the mucosa including the ciliated cuboidal cells, cells, Clara cell and the neuroendocrine cells
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0747
Thickened Walls



Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 29289




Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 29288m
Tree in Bud



Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net bronchiole to periphery 57M
Terminal bronchioles have a diameter of <2 mm. They do not contain cartilage in their walls like bronchi. The epithelium is comprised of simple columnar ciliated cells
Membranous bronchioles include terminal bronchioles are lined by columnar epithelial cells with cilia. The more distal respiratory bronchioles are lined by transitioning columnar to cuboidal epithelium and lead into alveolar ducts and alveolar spaces with flattened epithelium
- Tubes of the Body – Principles
- FUNCTION
- Physiology
-
- In health, they contribute minimally to airflow resistance.
- FEV1/FVC ratios are abnormal,
- In health, they contribute minimally to airflow resistance.
-
- DISEASES
- Small Airway Diseases (SAD)
- results from
- remodeling,
- obstruction by mucus, and
- disappearance of
- terminal and
- transitional bronchioles,
- Changes
- characterised by
- bronchiolar goblet cell hyperplasia.
- at the expense of Clara cells
- which, together with the serous cells of the
- of the bronchial glands,
- secrete an airway-specific low-molecular-weight protease inhibitor (antileukoprotease),
- characterised by
- Inflammatory Diseases
- Acute Infection
- Acute Inflammation
- Chronic Inflammation
- Smoking
- COPD
- Asthma
- Bronchioles
- TDisease is as a result of disorder in the
- lumen
- fluids
- cells
- wall
- mucosa
- submucosa
- muscularis
- adventitia
- lumen
- results from
Cellular Bronchiolitis,
Granulomatous (Sarcoid)Bronchiolitis
Follicular Bronchiolitis (external lymphoid tissue)
Bronchiolitis Obliterans
Obliterative (Constrictive) Bronchiolitis
Mucus Plugging
- results in
- air trapping
- dynamic hyperinflation

Santiago Rossi ATS



Keywords:
lung pulmonary alveoli alveolus secondary lobule interlobular septa vein lymphatic histology interstitium interstitial normal copyright 2009 all rights reserved
The segments form the secondary lobules.
Normal lung histology. This image of the lung periphery shows secondary lobules and interlobular septa. Within the interlobular septae, one sees small venules and lymphatics. The matrix of the lobule contains alveoli.
Courtesy of: Armando Fraire, M.D. Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
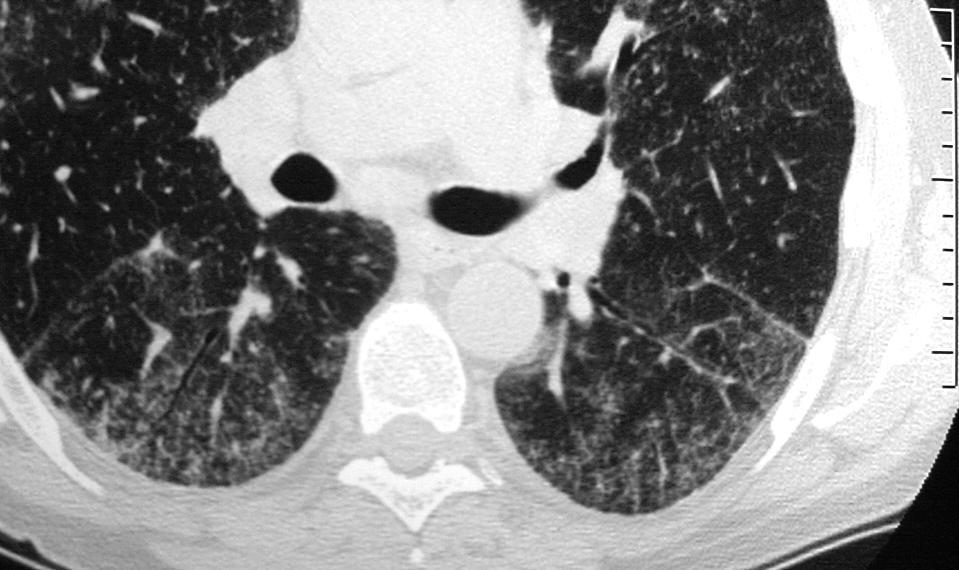
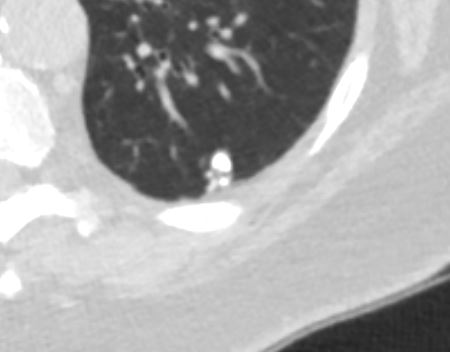
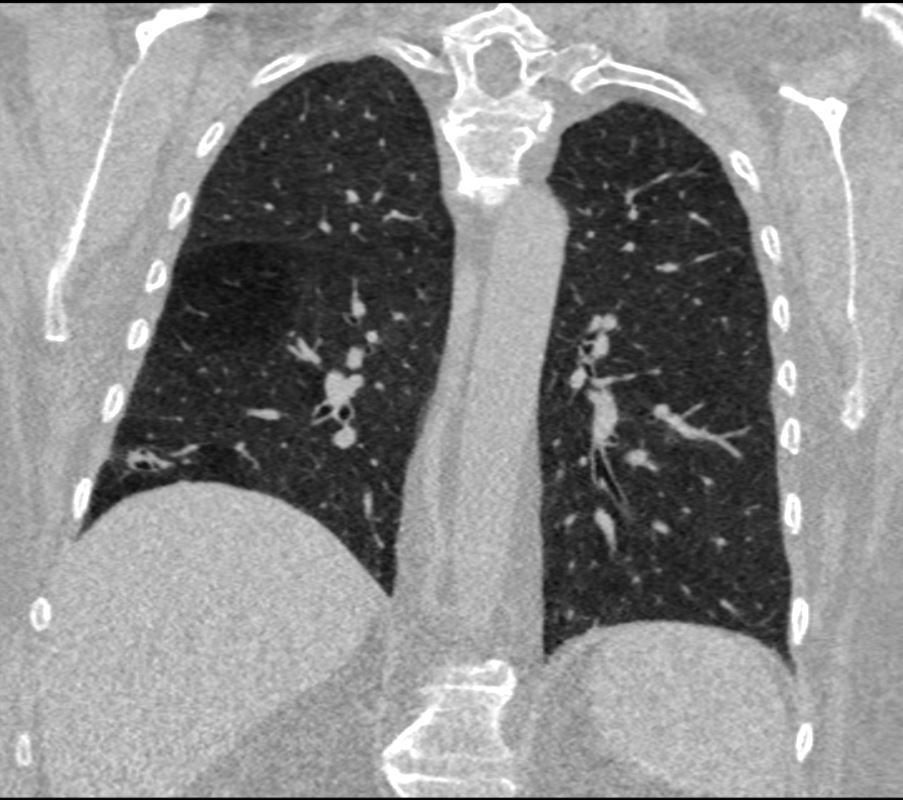
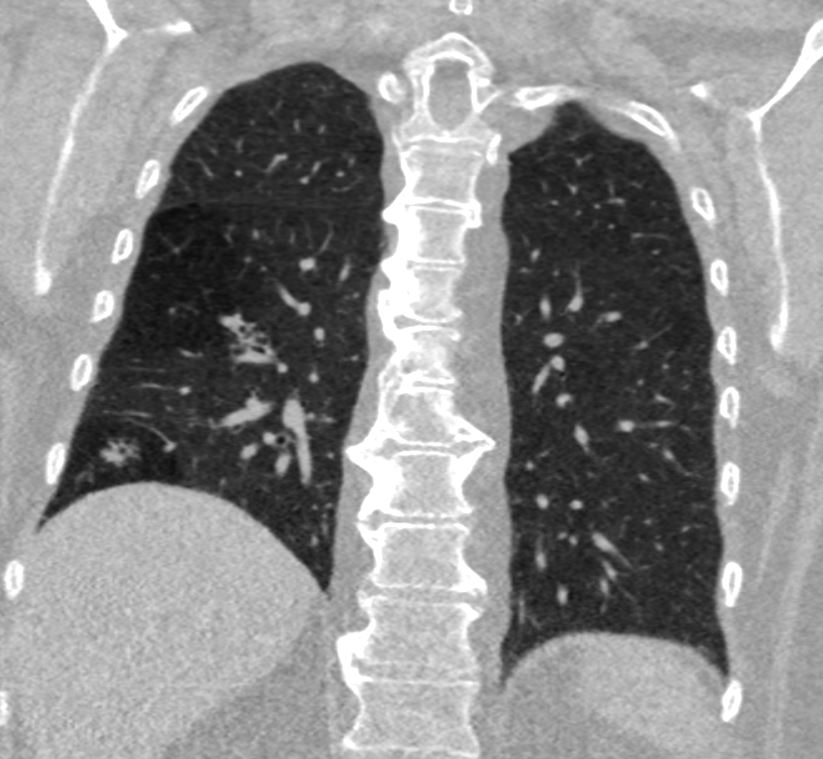
Imaging – The Normal Distal Small Airways
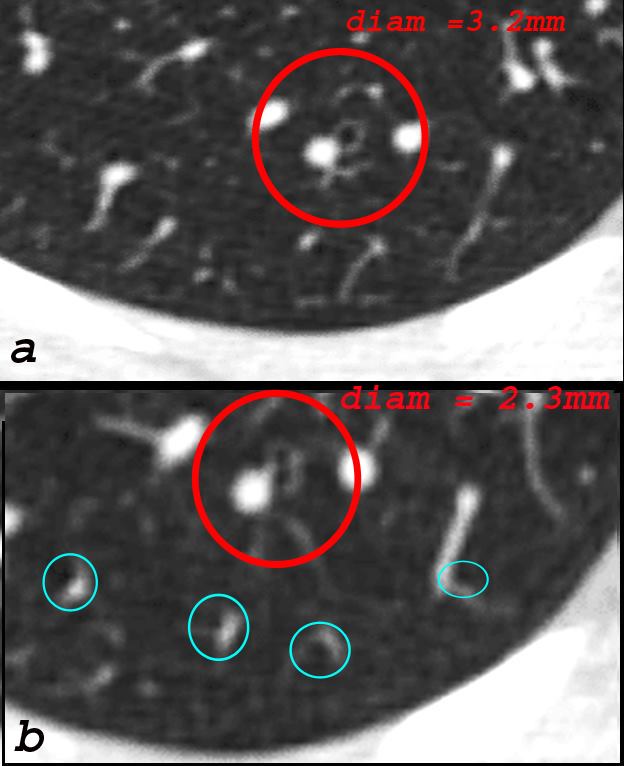

The bronchiole subtending the posterior segment of the right lower lobe (a) measured 3.2mm (red) just before its division. Image b, shows the next division and these bronchioles, measured 2.3mms( b – red). Thereafter the airways, likely terminal bronchioles, are barely seen alongside their arteriole (teal rings) likely measuring in the 2mms range and are within 1cms of the lung margin.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net



Society of Thoracic Radiology Santiago Rossi
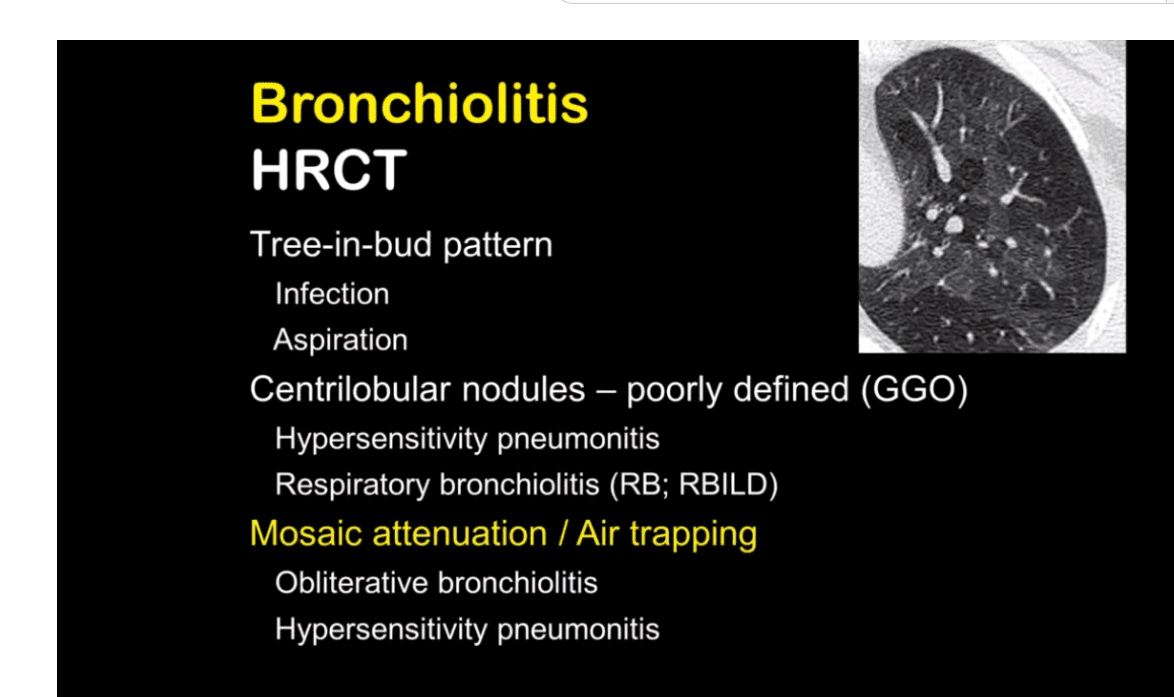


Pierre-Régis Burgel, P.R et al , Small airways diseases, excluding asthma and COPD: an overview European Respiratory Review 2013 22: 131-147; figs only
web lungs 367
Bronchiolar Wall Thickening



Keywords lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 54f-001

Keywords lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 54f-002
Bronchiolar Wall Thickening and Bronchiolectasis
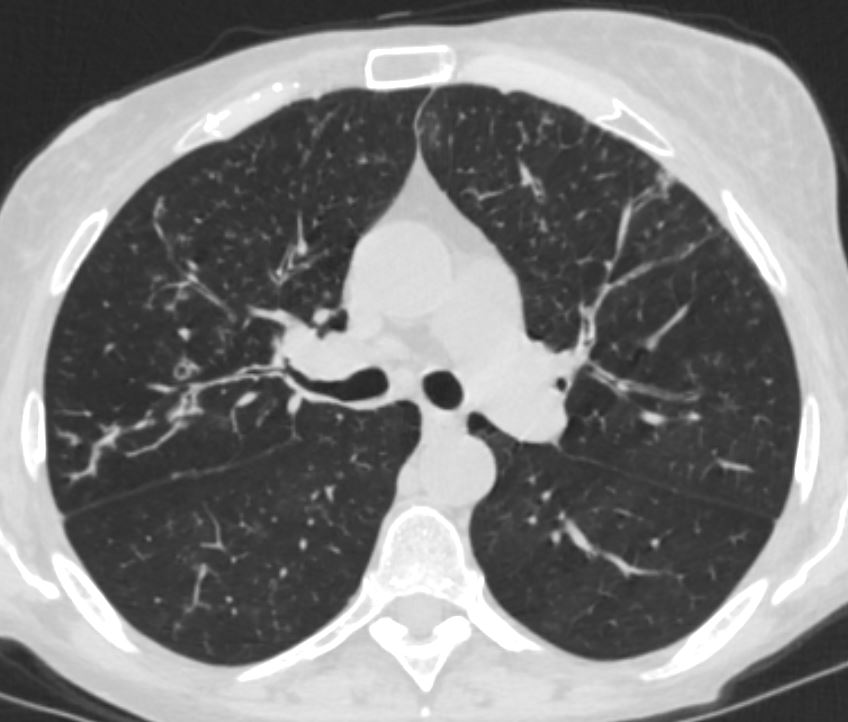

Keywords lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 54f-004b
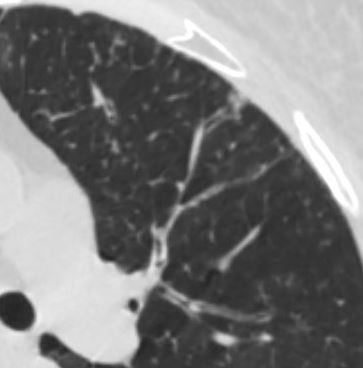

In the anterior segment of the left upper lobe there is thickening of the small airways as well as centrilobular nodules
Keywords lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 54f-004b01
Thickening of the Small Airways




Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 29288m
Centrilobular Nodules Likely from Bronchitis and Bronchiolitis Likely From Smoking
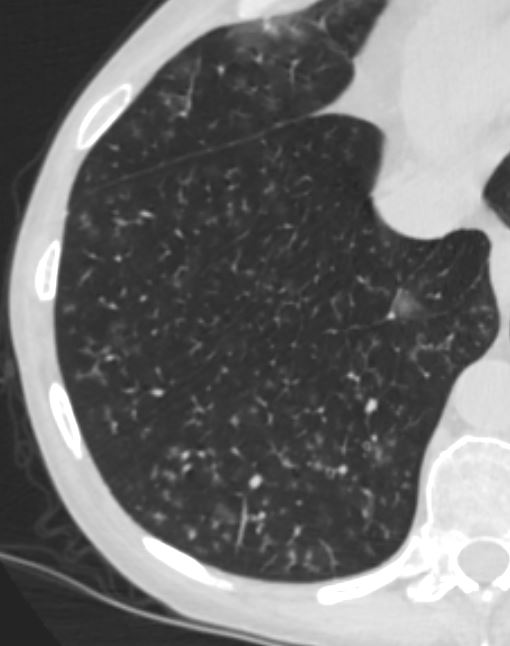

lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
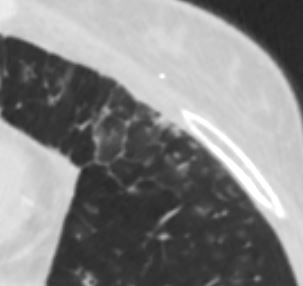

Extensive presence of centrilobular micronodules
Keywords lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 54f-006
Tree in Bud


Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Staph aureus bronchiolitis

Rossi, SE et al Tree-in-Bud Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: Radiologic-Pathologic Overview RadioGraphicsVol. 25, No. 3 2005

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
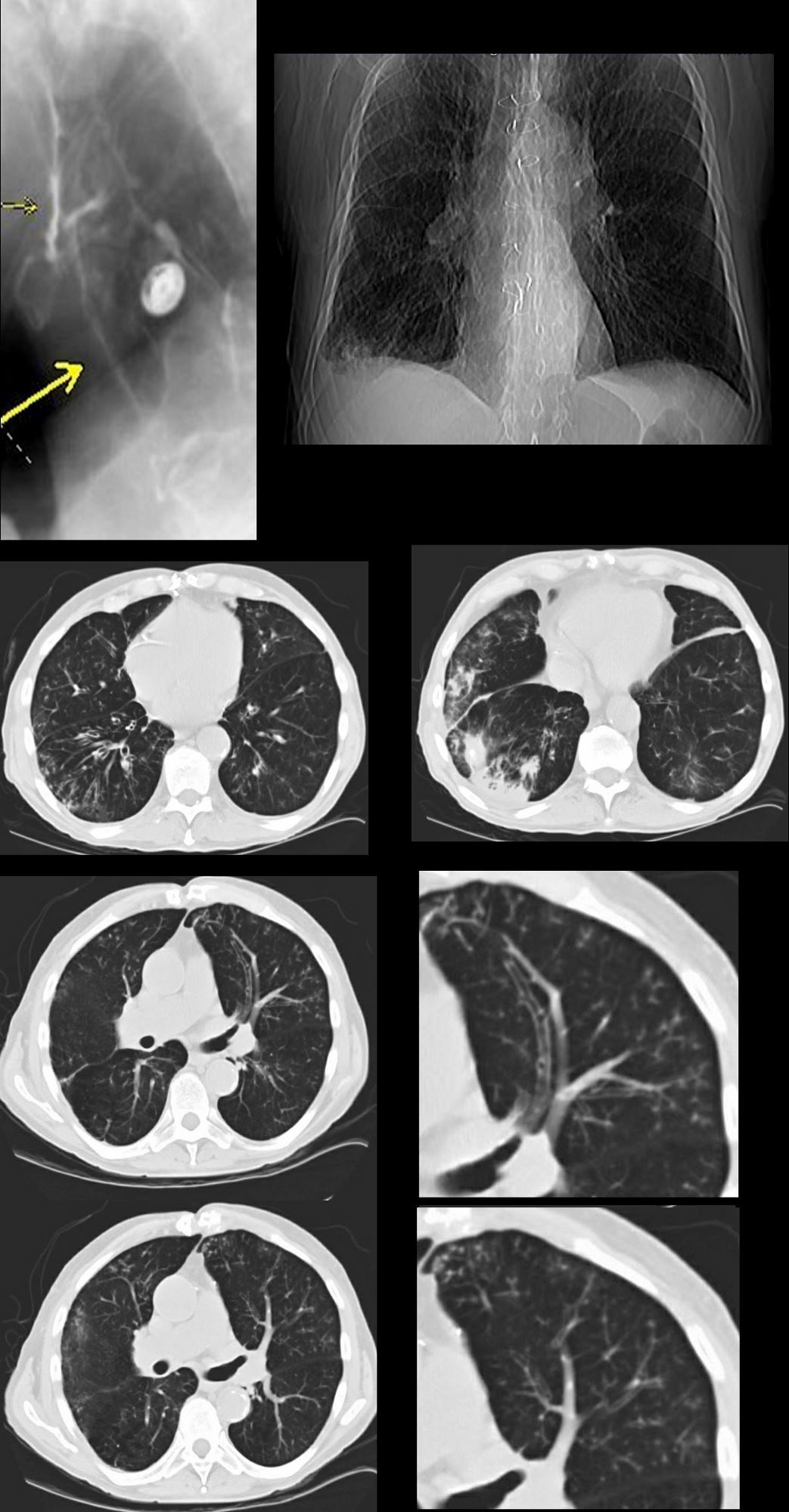

87 year old male with history of cough and suspicion of aspiration shows barium aspiration into the proximal trachea (upper right) The scout view ( upper right) shows an infiltrate at the right base, Thickened airways in the right lower lobe (2nd row left ) is associated with a pneumonic infiltrate in the right lower lobe (lower right) consistent with aspiration. There are thickened airways to the lingula (3rd and 4th row) with magnified view showing tree in bud changes (right sided images 3rd and 4th row)
All these finding likely relate to spiration though lingula involvement is not usual
Ashley Davidoff MD Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Small Airways and TB – Centrilobular Calcifications and – Tree in Bud

Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Ill defined Nodules

Courtesy Radiology Key
Well Defined Centrilobular Nodules
Mucus – Note Centrilobular Impaction of Mucus
Mosaic Attenuation Ground Glass Air Trapping
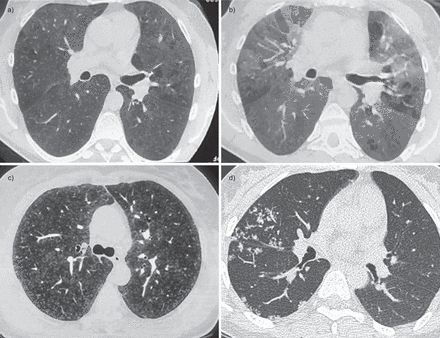

Representative images of computed tomography (CT) scans in patients with small airways disease. a) An inspiratory CT scan in a patient with hypersensitivity pneumonitis showing mosaic pattern of attenuation. b) Expiratory CT scan in the same patient showing air trapping that is characteristic of small airways disease. c) Ill-defined centrilobular nodules in a patient with farmer’s lung (personal communication; J.C. Dalphin). d) Localised micronodules branching with bronchovascular structures (tree-in-bud pattern) related to tuberculosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis receiving treatment with anti-tumour necrosis factor-α. Reproduced from [21] with permission from the publisher.
Burgel, P-R et al Small airways diseases, excluding asthma and COPD: an overview European Respiratory Review 2013 22: 131-147; web lungs 368
Mosaic Attenuation Head Cheese

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net head cheese sign 005

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net bronchioles 003

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net bronchioles 004

in a patient with COPD – Small Airways are obstructed and air is trapped
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net bronchioles 002



Small Airways are filled with mucus in a patient with COPD – Note centrilobular impaction of mucus Small Airways are obstructed and air is trapped
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net bronchioles 001
Emphysema
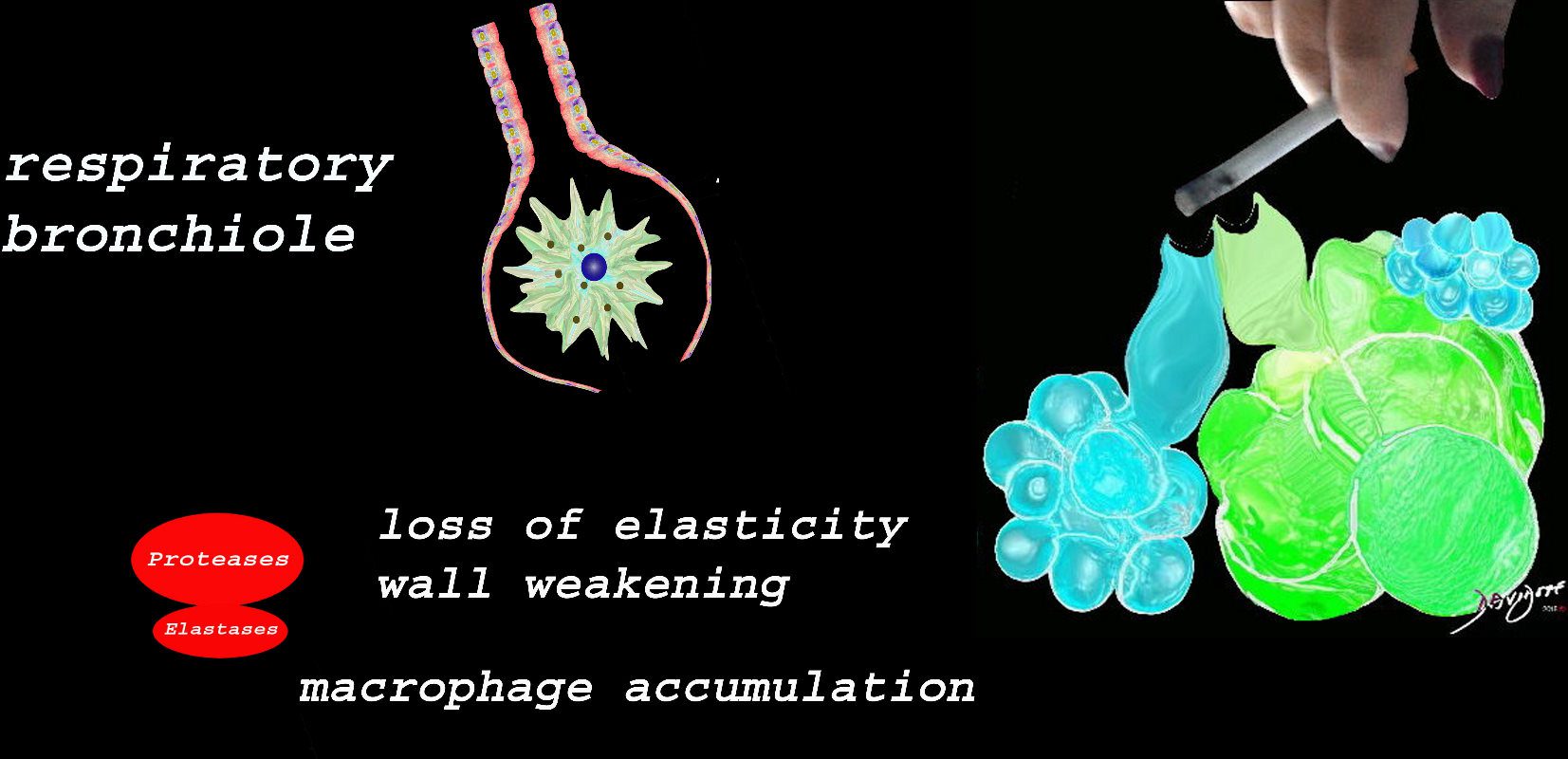

At the level of the membranous airways the effect is predominantly related to the loss of elasticity, and aberrant accumulation of smoking related macrophages.
The weakening and destruction results in emphysema and the abnormal accumulation of smoking related macrophages relates to DIP
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net


Image on the left shows normal size and appearance of terminal bronchioles and alveoli. On the right the image shows the effects on the respiratory bronchioles and when severe, on the alveoli as well
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
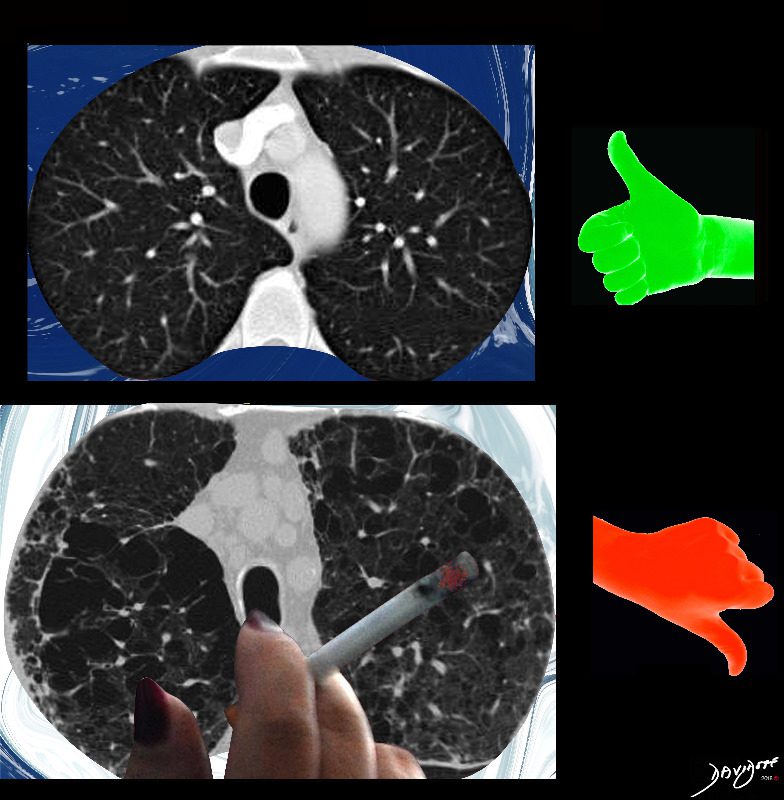

November is COPD Awareness Month
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVeein.net
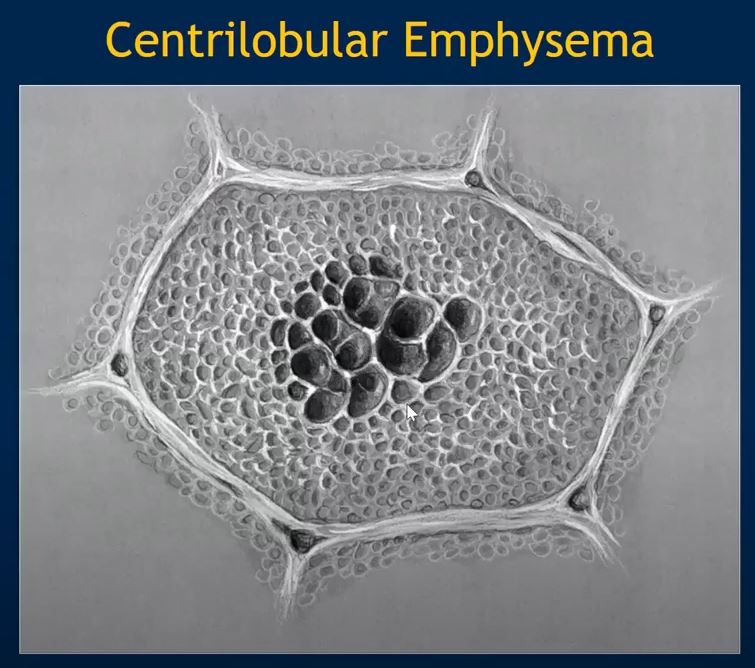


Alveolar wall destruction is localized around a bronchovascular bundle.
Courtesy Yale Rosen MD

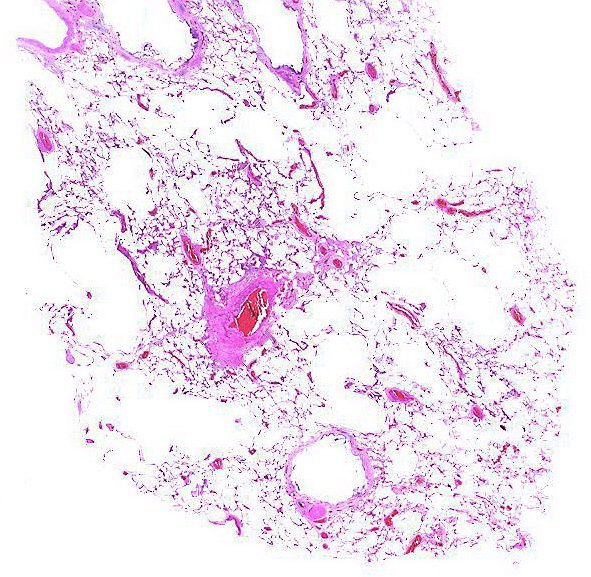
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia



The diagram shows the small airways of the lung including the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs in coronal (a) and in cross section (b) and correlated with an anatomic specimen of a secondary lobule that contains a thickened interlobular septum . The respiratory bronchiole is overlaid in maroon (d), next to the arteriole. Images e and f are magnified views of a CT of the lungs in a patient with acute eosinophillic pneumonia and the centrilobular nodules reflecting small airway disease are highlighted in f.
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0760b
- Bronchiolar Inflammation
- AEIOU
- A
- Asthma ABPA Asbestosis
- E
- Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- Infections
- Endobronchial
- TB
- Mycobacterium
- Non TB Mycobacteria and
- Other Granulomatous Infections
- ABPA
- TB
- viruses such as
- adenovirus,
- influenza, and
- respiratory syncytial virus (RSV),
- Endobronchial
- Inflammatory
-
- Sarcoidosis
- Inhalational
- Cigarette Smoke
- smokers bronchiolitis
- Langerhans Cell
- chemicals,
- fumes, or toxic gases
- occupational exposures,
- industrial chemicals
- diacetyl in the popcorn industry
- industrial chemicals
- Cigarette Smoke
-
- Immune
-
-
- HP
- RA
- Follicular Bronchiolitis (MALT Lymphoid Hyperplasia in collagen vasc and immune deficiency)
- Graft vs Host
-
-
- Inherited
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Idiopathic Bronchiolitis Obliterans
- A
- AEIOU
Links and References
Pierre-Régis Burgel, P.R et al , Small airways diseases, excluding asthma and COPD: an overview European Respiratory Review 2013 22: 131-147;
- Bronchiolitis Introduction
- 113Lu Bronchitis and Bronchiolitis
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans (aka Constrictive Bronchiolitis) Introduction