-
Cellular NSIP
- NSIP can be divided into two subtypes based on the predominant histological pattern seen on lung biopsy: cellular NSIP and fibrotic NSIP.
- In Cellular NSIP, the lung tissue is
- relatively little fibrosis.
- CT
- patchy or diffuse ground-glass opacities
- may be associated with a reticular pattern and
- traction bronchiectasis
- more pronounced in the
- peripheral regions of the lungs, and may be
- subpleural or
- peribronchovascular
- may also be consolidation in some areas of the lung.
- CT
Predominant Ground Glass Pattern
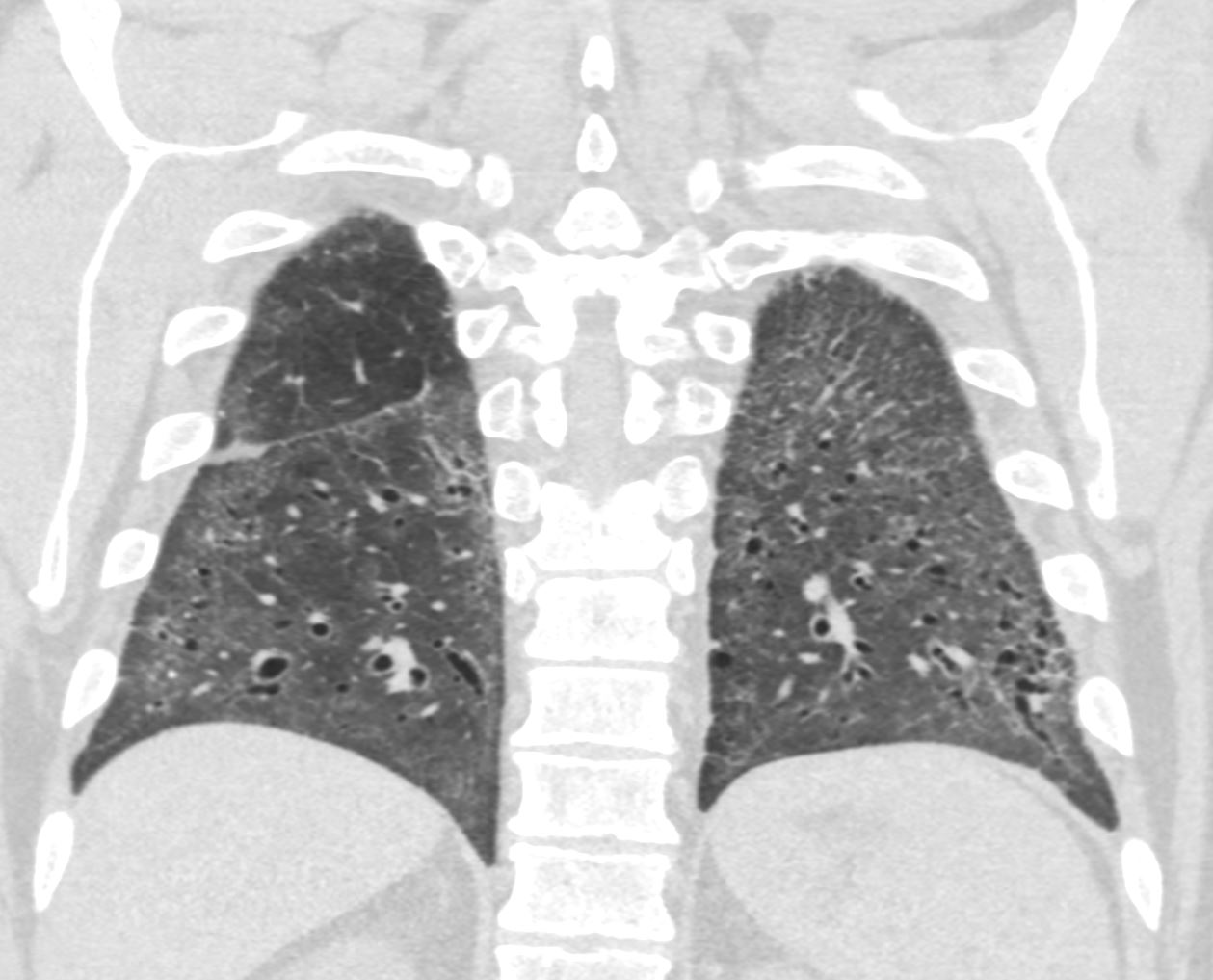
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net scleroderma NSIP 009

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net scleroderma NSIP 005

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net scleroderma NSIP 006
-
- In Fibrotic NSIP
- presence of fibrosis or
- scarring within the lung tissue.
- worse prognosis c
- more severe respiratory symptoms,
- lower lung function, and a
- greater likelihood of developing pulmonary hypertension.
- CT
- shows more pronounced and
- diffuse reticular opacities and
- traction bronchiectasis, with
- less ground-glass opacities
- fibrotic changes may be
- more extensive and involve
- larger areas of the lung tissue.
- may also be
- honeycombing in advanced cases.
- CT
- In Fibrotic NSIP
References and Links
