Panlobular Ground Glass Opacities of the
Secondary Lobule in CHF
Panlobular Ground Glass Opacities of the
Secondary Lobule in CHF with
Crazy Paving and
Air Bronchiolograms
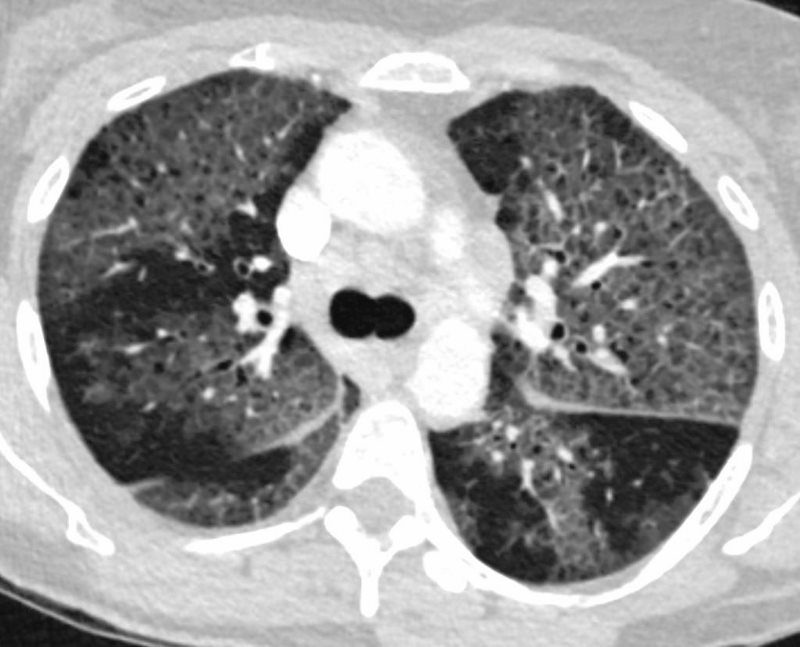
57-year-old female with progressive dyspnea.
CT shows diffuse ground glass change with crazy paving morphology characterized by bilateral diffuse ground-glass opacities (GGO) with interlobular and intralobular septal thickening. There is a pan-lobular distribution .
Differential diagnosis ARDS PCP pneumonia ,CHF, Alveolar Hemorrhage, UIP, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, XRT pneumonitis, COP Chronic Eosinophilic Lymphangitis Veno-Occlusive Disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132247.8
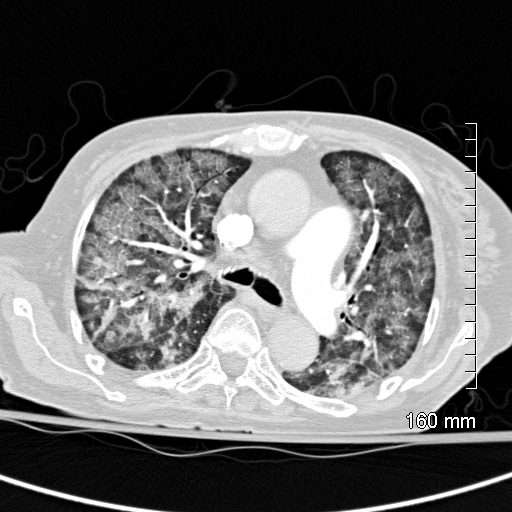
CT scan shows Diffuse ground glass pattern with thickening of the interlobular septa and manifesting as crazy paving pattern
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131742
Amyloidosis
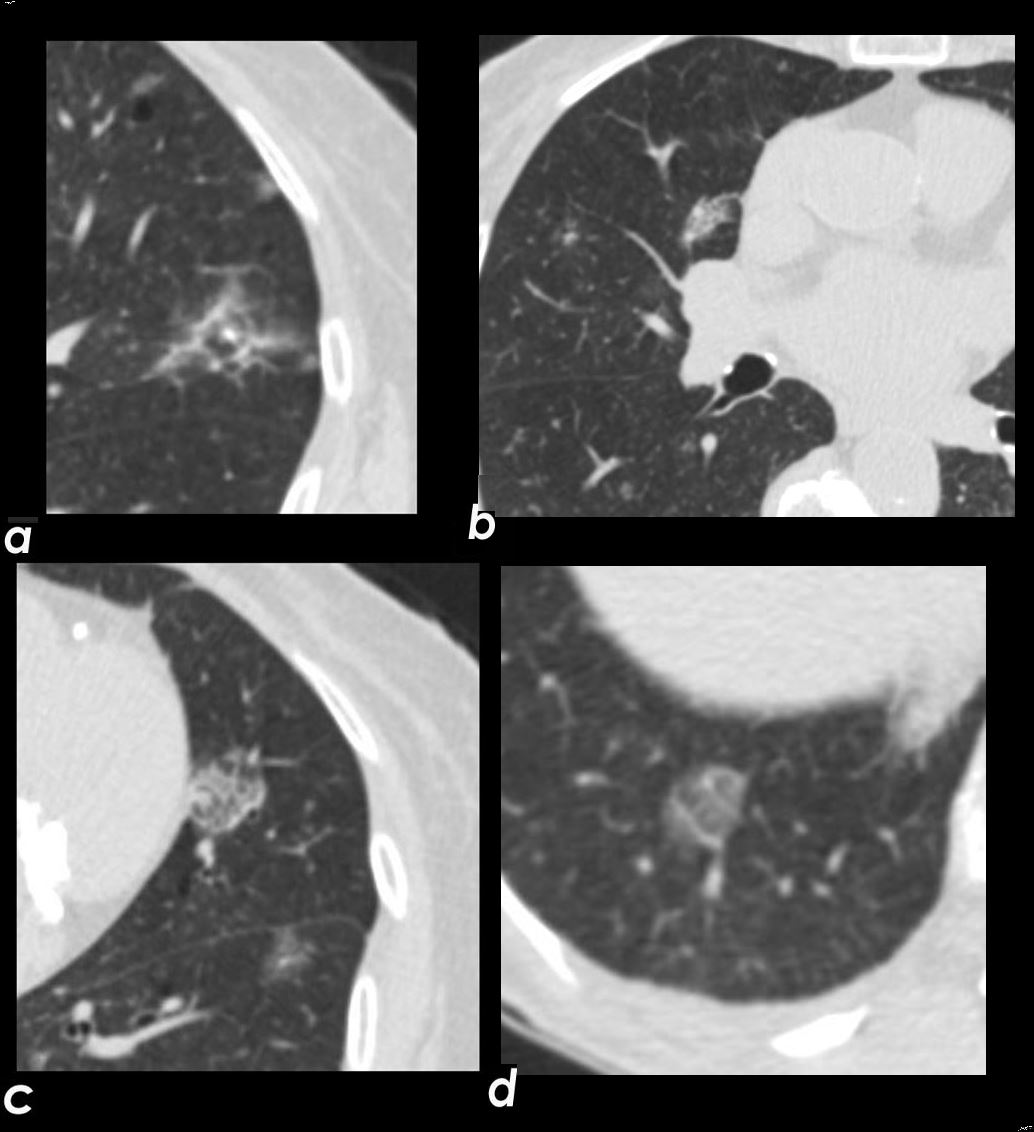
Axial CT images through the chest exemplifies the diffuse alveolar-septal amyloidosis at its mildest and earliest form
Image a, shows a secondary lobule with thickened interlobular septa with a centrilobular nodule either reflecting peribronchial or periarteriole involvement. Image b shows a mixed nodule likely reflecting intralobular alveolar involvement. Images c and d show thickened interlobular septa and a reticular intralobular ground glass abnormality pattern each with a centrilobular nodule
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-005 c01
Pulmonary Hemorrhage and
Heterogeneous Changes in the Secondary Lobules
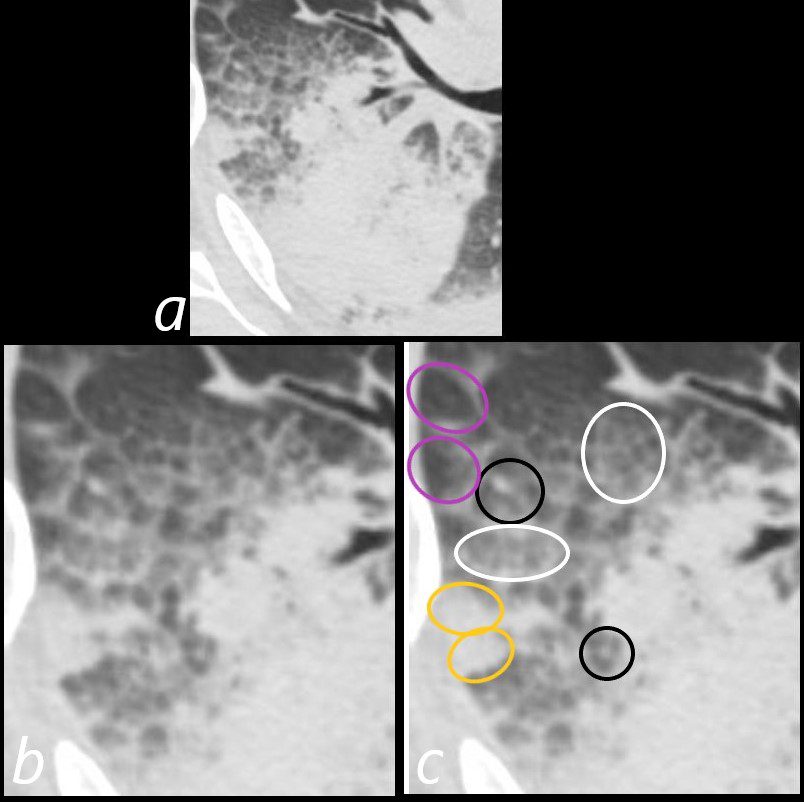
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Axial CT at the level below the carina shows heterogenous changes of the secondary lobules. The changes in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe (a magnified below in b and c ) and show secondary lobules with ground glass changes (white rings) It is difficult to distinguish those with normal lung parenchyma and those with mosaic attenuation. It is hypothesized that those with prominent centrilobular nodules (black rings c) more than likely represent mosaic attenuation due to small airway disease. The lower density secondary lobules which do not have a prominent centrilobular nodule (c, purple rings), may either reflect normal parenchyma or mosaic attenuation. The orange rings likely reflect consolidation in side-by-side secondary lobules.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135854cL01
- Panlobular Disease
- Lobular Consolidation
- Bronchopneumonia
- OP
- Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- BAC Adenocarcinoma with Lepidic growth
- Lobular GGO
- Bronchopneumonia
- Viral Infection
- Mycoplasma
- PCP
- pulmonary Edema
- HP
- Alveolar Proteinosis
- Lipoid Pneumonia
- Lobular Low Attenuation
- Mosaic Attenuation
- Head Cheese Sign
- HP
- DIP
- respiratory bronchiolitis ILD
- Sarcoidosis
- Atypical Infections
- Lobular Consolidation
Links and References
- TCV
