Right Sided Pleural Effusion In CHF
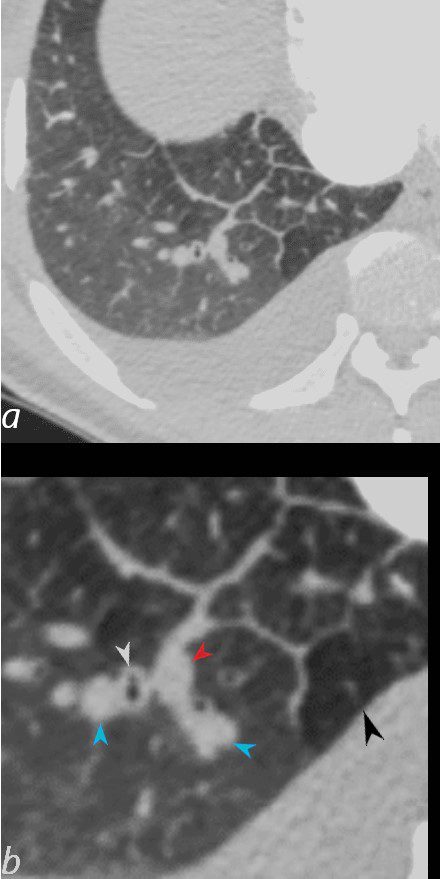
50-year-old female with diabetes, chronic renal failure and congestive heart failure. CT in the axial plane through the right posterior recess, shows thickened interlobular septa at the right base, congested arterioles (light blue arrowheads, b), alongside the bronchioles, peribronchial cuffing (white arrowheads, b), a congested pulmonary venule in the interlobular septum (red arrowhead arrowheads, b), ground glass changes and a secondary lobule demonstrating mosaic attenuation (black arrowhead arrowheads, b). The IVC is dilated and a small complex effusion is present.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135783cL 193Lu

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-010-CT
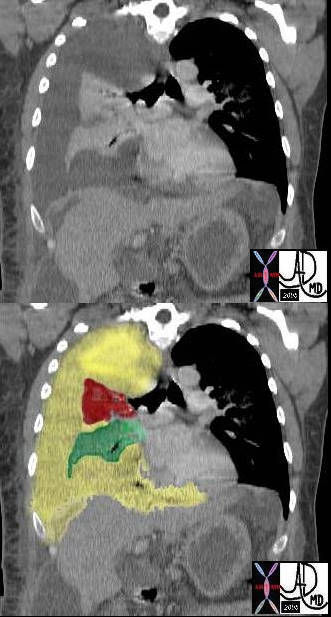
In this case there a large right sided pleural effusion (yellow) with secondary atelectasis of the right lung. (red and green) This coronal CT of the chest at the level of the left ventricle shows a large right pleural effusion which lies between the visceral and parietal pleura. Once the effusion is large enough to weaken the capillary forces that hold the parietal and visceral pleura together, it fail, and the lung collapses which is what is noted on this image – ie total lung collapse because of loss of cohesive adhesive forces.
Courtesy of: Ashley Davidoff, M.D. TheCommonvein.net 42558c
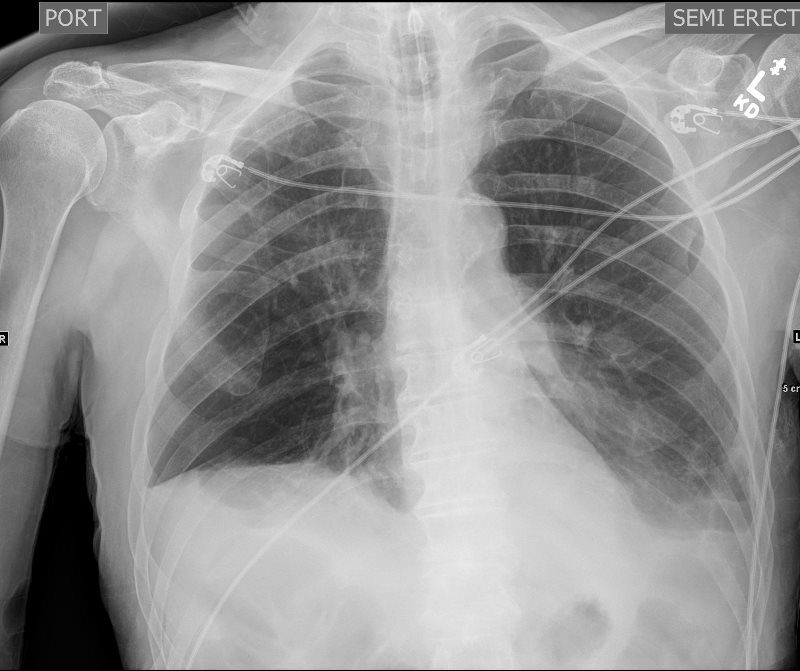
CXR and Pleural Effusion – Blunting of the Costophrenic Angle
Ashley Davidoff MD
thecommonvein.net
Not Obvious when the Effusion is Small

92-year-old female presents with a dyspnea. CXR shows a moderate sized right effusion. CT scan shows bilateral pleural effusions. On the right there is a moderate effusion with compressive atelectasis and on the left, there is a small effusion with a minor degree of atelectasis with atelectasis of the left lung.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
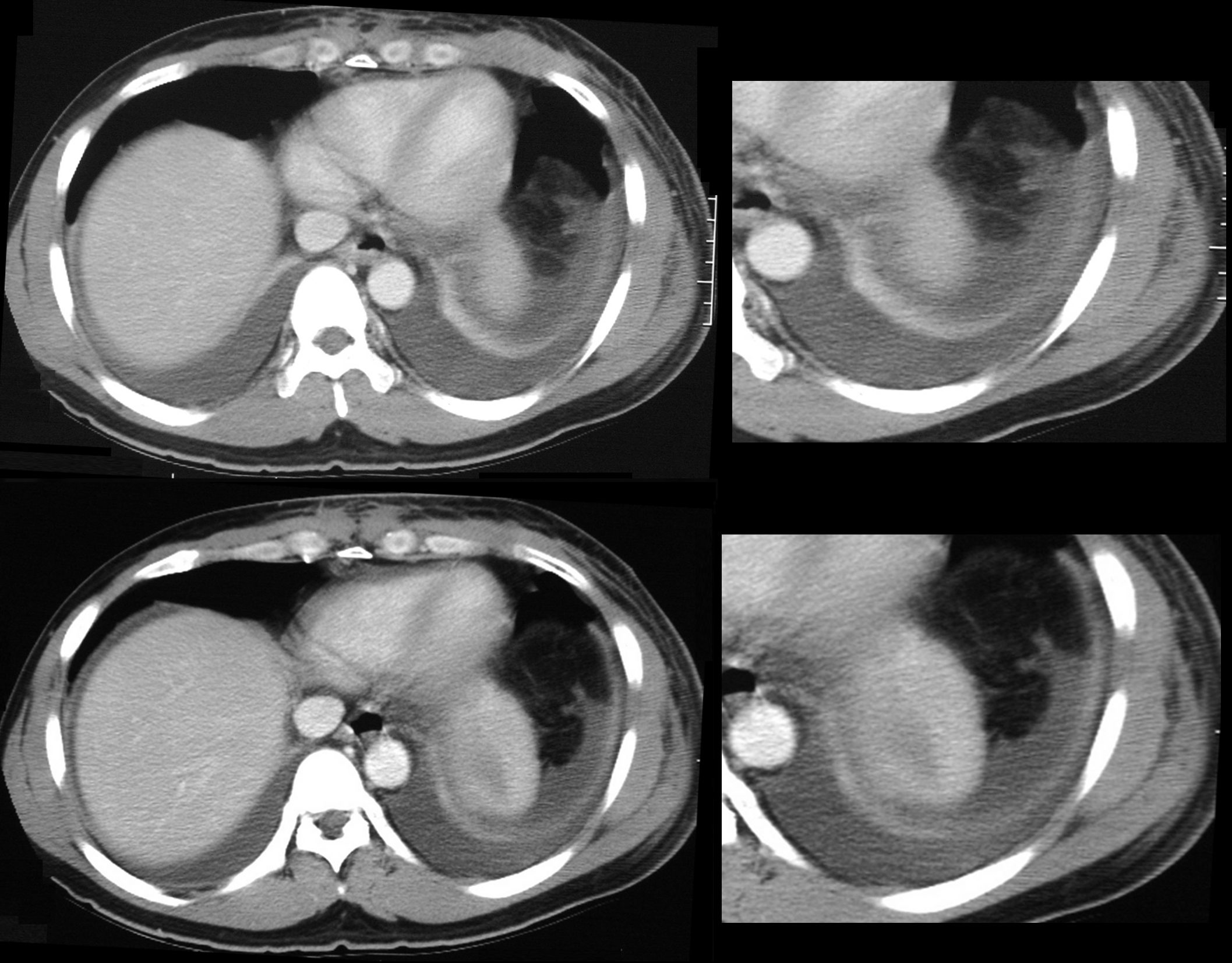
58year old male presents with dyspnea. CT scan shows bilateral pleural effusions with crescentic region of compressive atelectasis in the left lower lobe
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
79 year-old female with bilateral simple pleural effusions and compressive atelectasis with a variation in the shape of the atelectasis in the right lower lobe.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
66 year-old female with bilateral simple pleural effusions and compressive atelectasis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net

86 year-old female presents with a dyspnea. US shows a left effusion with compressive atelectasis. CT scan shows bilateral pleural effusions with atelectasis of the left lung.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
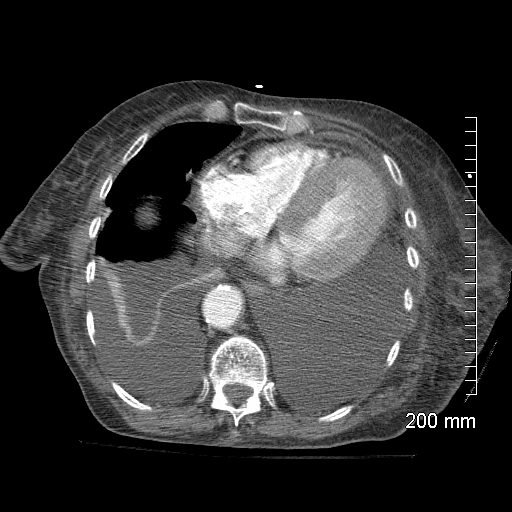
48 year-old male presents with a dyspnea. CXR shows a total white out of the left chest with pulmonary congestion. CT scan shows a large left pleural effusion with total atelectasis of the left lung. Incidental note is made of premature calcific coronary artery disease.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
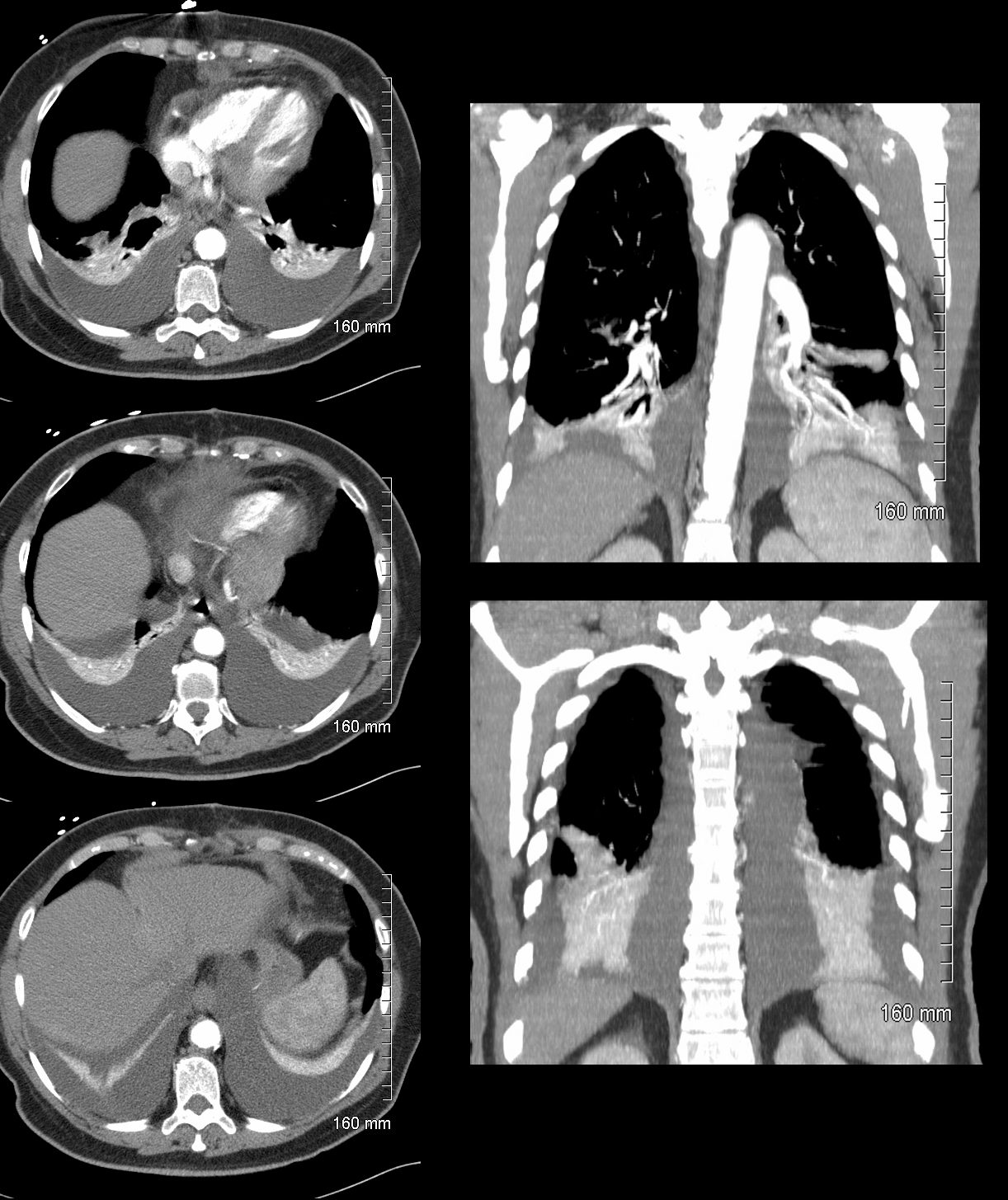
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
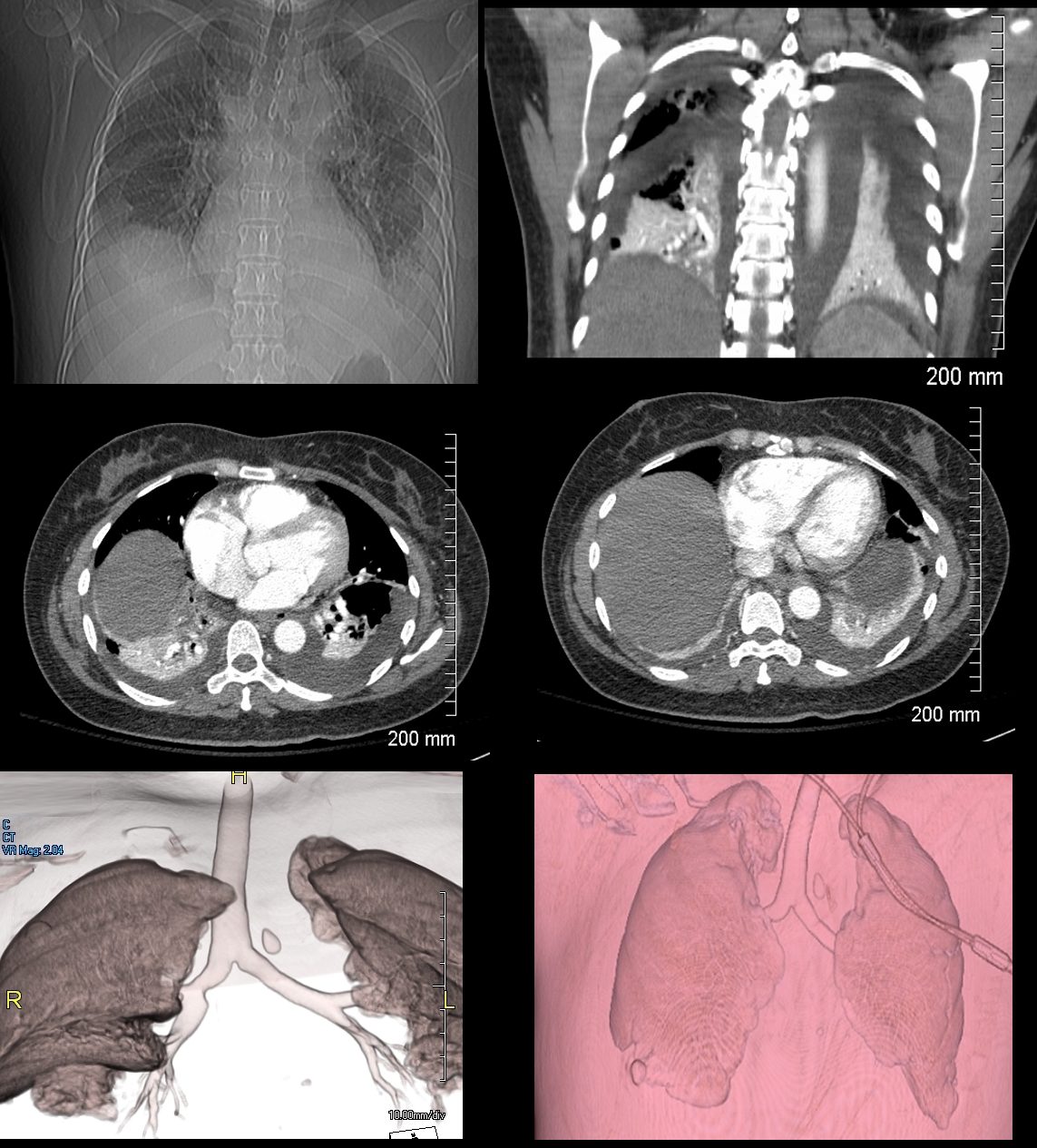
46-year-old female presents with a dyspnea and a cough. Imaging of the chest shows cardiomegaly with bilateral moderate sized pleural effusion with crescentic region of compressive atelectasis noted on the axial images at the bases and crowding of the bronchovascular bundles best evaluated on the coronal image. The 3D reconstructions show functionally “bare” lower lobe segmental airways.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
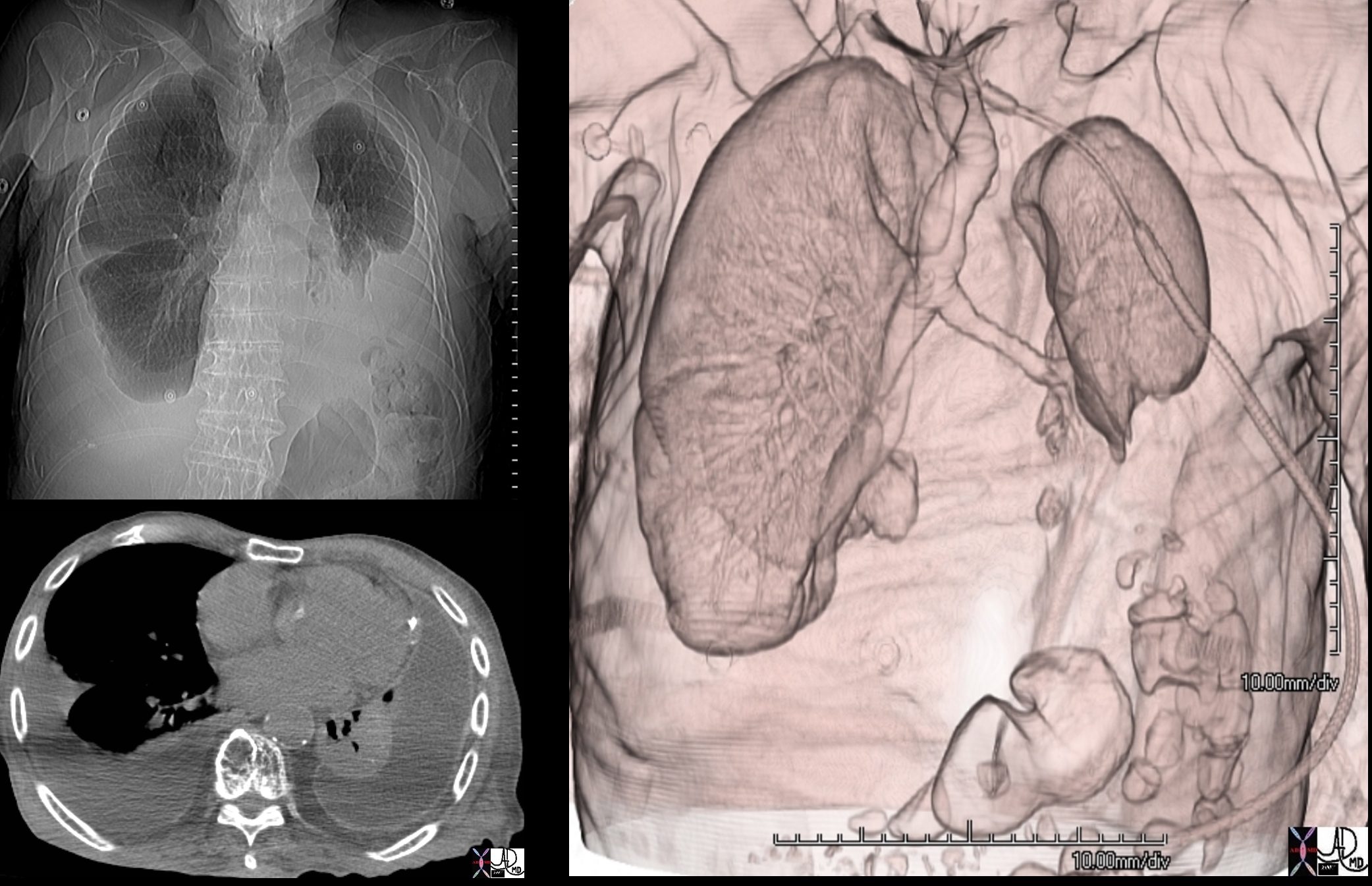
88 year old male with bilateral effusions shown on the CXR. Axial CT shows thickened pleura on the left with compressive atelectasis of the lower lobe and a smaller region of crescentic compressive atelectasis on the right. 3D reconstruction shows atelectasis of the left lower lobe and portion of the lingula
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff MD
Tension Hydrothorax
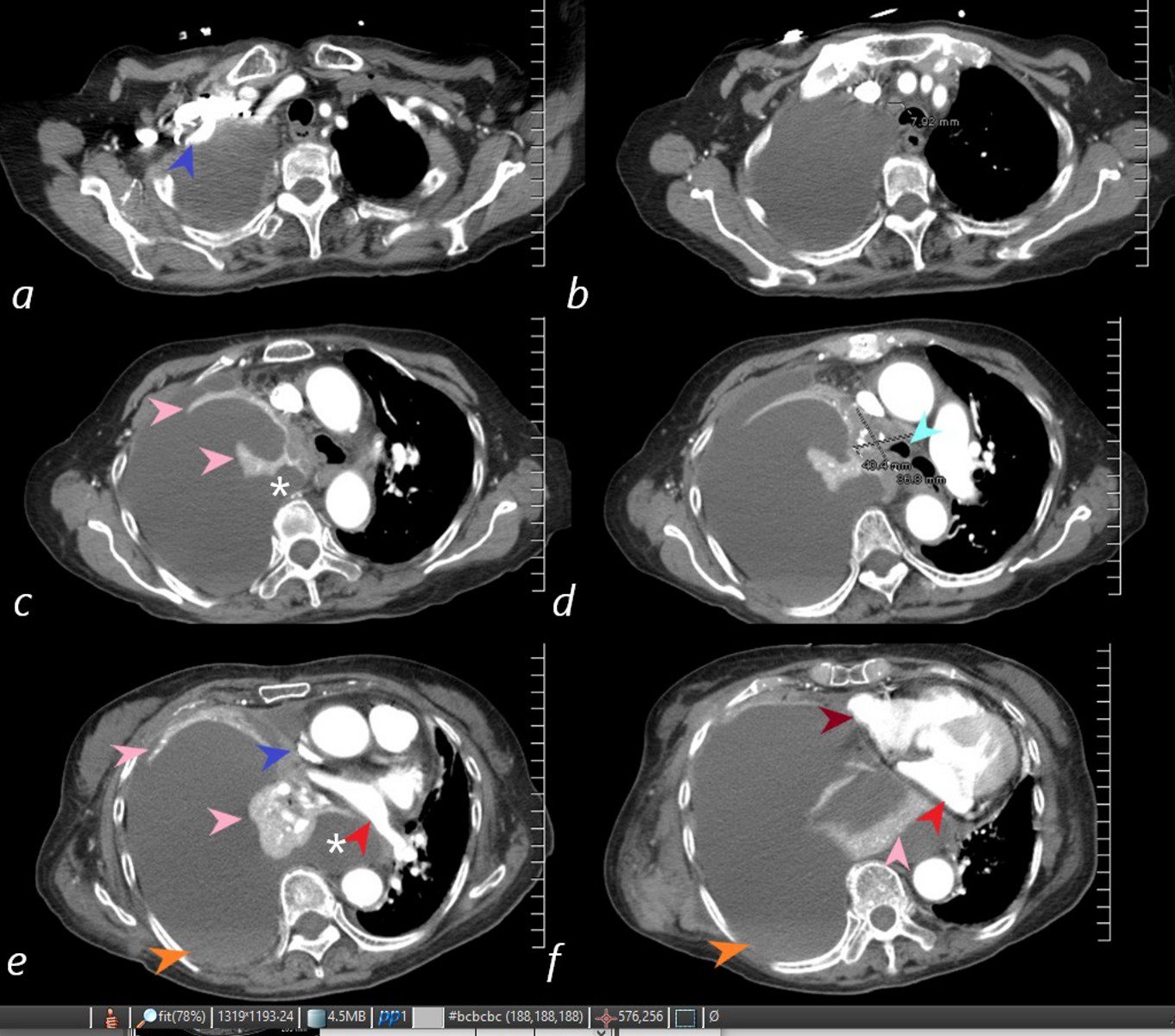
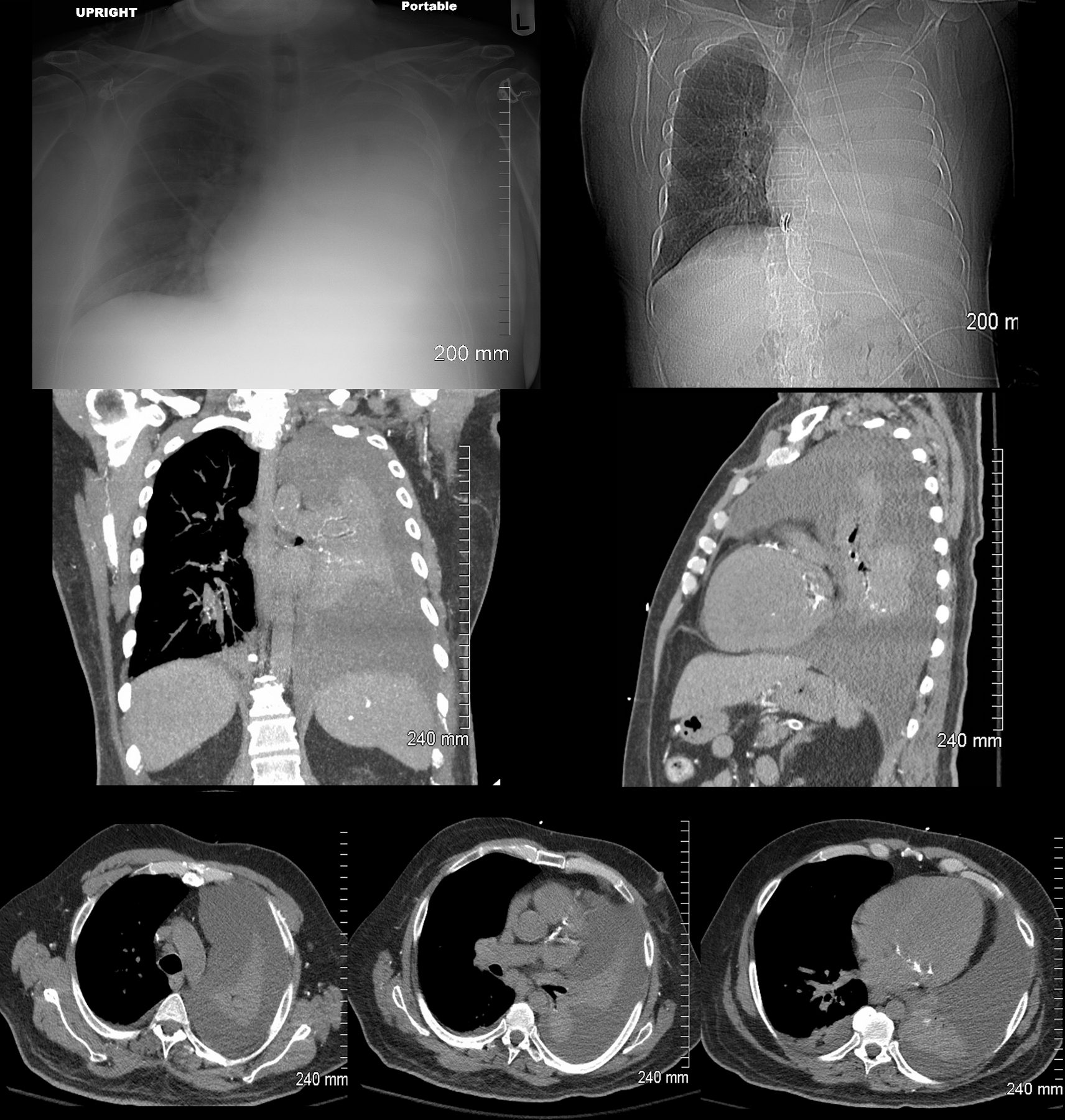
85-year-old female with a history of lung cancer, presents with a dyspnea and hypotension. CT scan shows a large right pleural effusion under pressure, suggestion of blood in the pleural cavity (orange arrowheads e, f) and mediastinal shift to the right. In addition, there is compression of the heart with back up of venous return due the pressure effect on the heart and vascular structures. Among the structures showing compressive effects are the SVC (blue arrowhead, c) with venous distension on right sided upper limb veins (blue arrowhead a). There is also pressure effect on the trachea with narrowing (light blue arrow d) The effusion in the right pleural cavity with atelectatic lung herniates into the left hemithorax, (white asterisk c, e). There is a dense sediment in the pleural fluid (orange arrowheads, e and f) suggesting blood in the pleural cavity. The left atrium is compressed (red arrowhead, e, f), and the right atrium is compressed (maroon arrow f).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 106Lu 118450cL

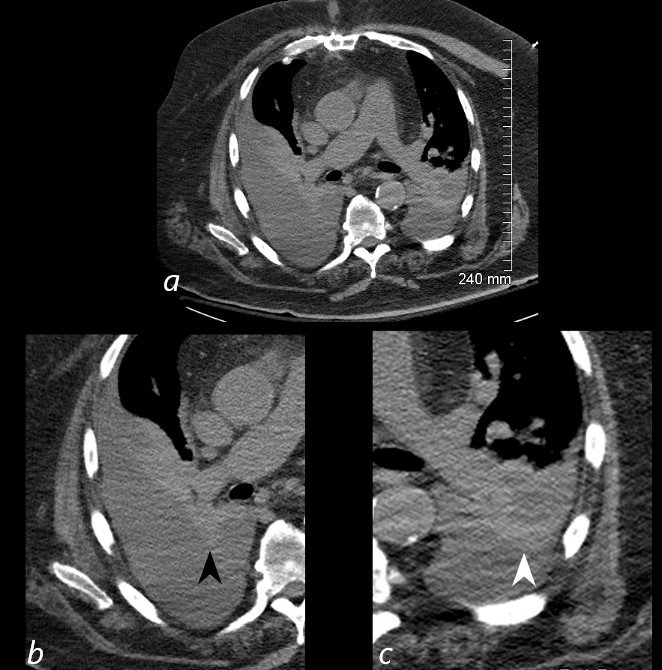
85-year-old female with a history of lung cancer, presents with a dyspnea and hypotension. Reconstruction of the CT scan in the coronal plane, shows a large right pleural effusion under pressure with herniation into the left chest (white asterisk e,and f) , with mediastinal shift to the left (yellow arrowhead b, c, d). In addition, there is compression of the heart with back up of venous return due the pressure effect on the heart and vascular structures. Among the structures showing venous distension are the SVC (blue arrowhead, c) right sided upper limb veins (blue arrowhead d) and the left upper pulmonary veins (red arrowhead, d and f). The density of the systemic venous abd arterial systems is similar, but vascular structures as noted by the green arrowhead in a could represent venous collaterals.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.ne 106Lu 118467cL
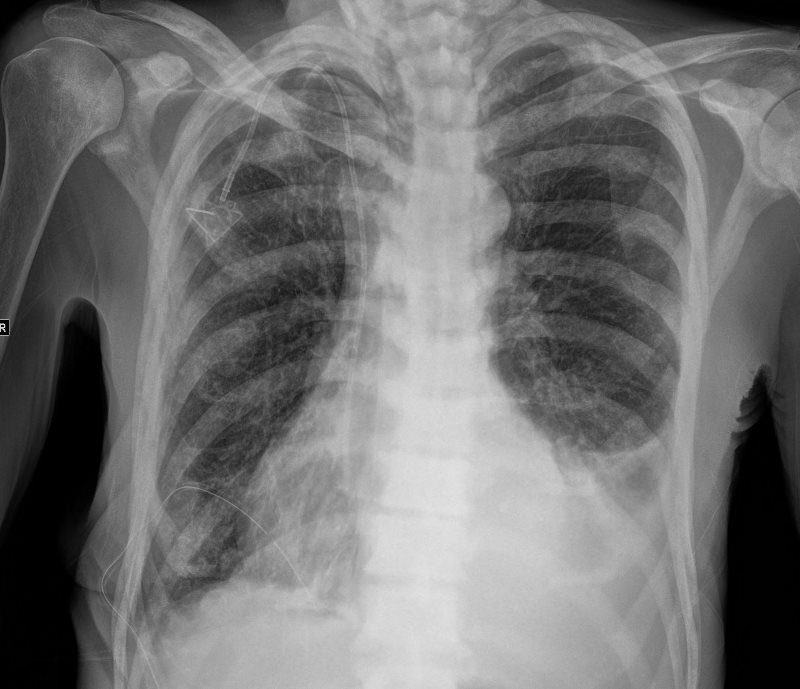
Ashley Davidoff MD
thecommonvein.net
Chylous Effusion
Cystic lung disease and an effusion
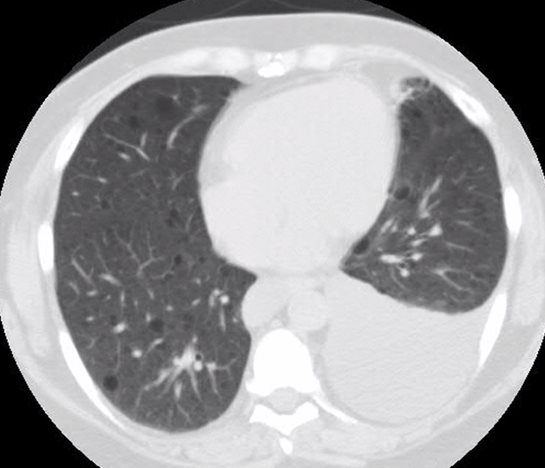
LAM Diffuse Cysts Chylous Effusion
Imaging of Cystic Lung Disease Thomas Hartman MD Mayo Clinic Video on Imaging Cystic Lung Disease Society of Thoracic Radiology
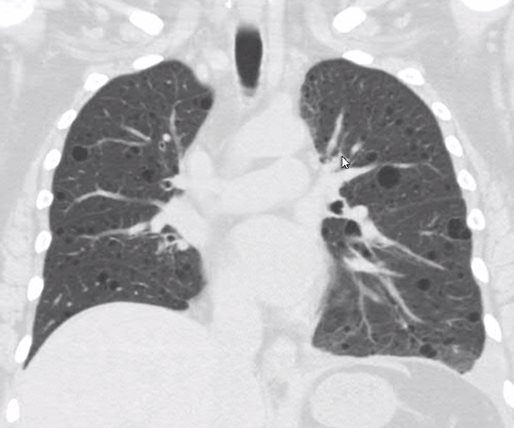
LAM Diffuse Cysts Chylous Effusion
Imaging of Cystic Lung Disease Thomas Hartman MD Mayo Clinic Video on Imaging Cystic Lung Disease Society of Thoracic Radiology
