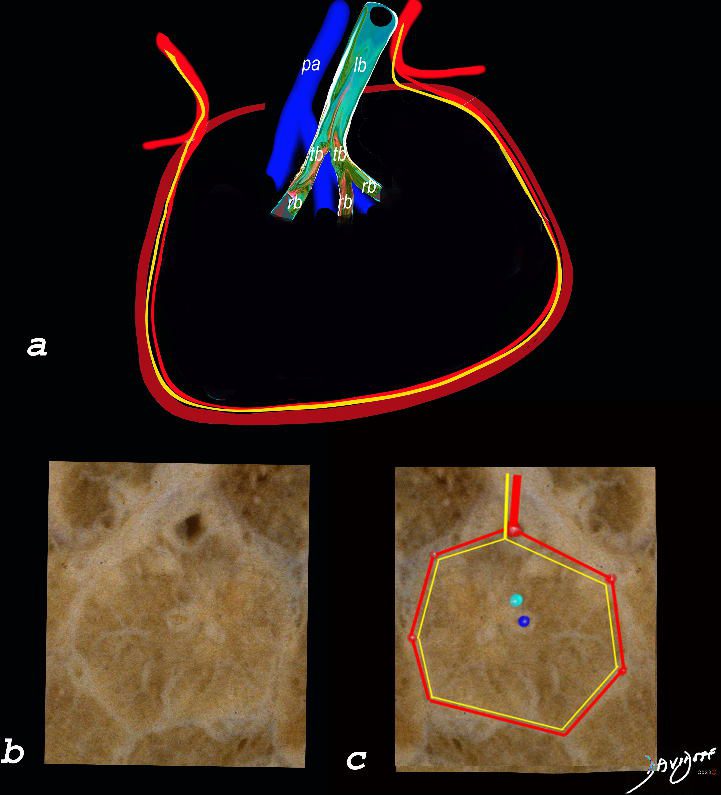
The top image (a) shows an anatomic drawing of a secondary lobule of the lung subtended by a lobular bronchiole (lb) and arteriole (pa). The interlobular septum contains the venule (red) lymphatic (yellow) and septum (maroon)
The anatomical specimen of the lung (b) shows normal intralobular parenchyma while image c shows the centrilobular arteriole (navy blue) and centrilobular bronchiole (teal) and interlobular venule (red) and lymphatics (yellow) The interlobular septum is slightly thickened
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
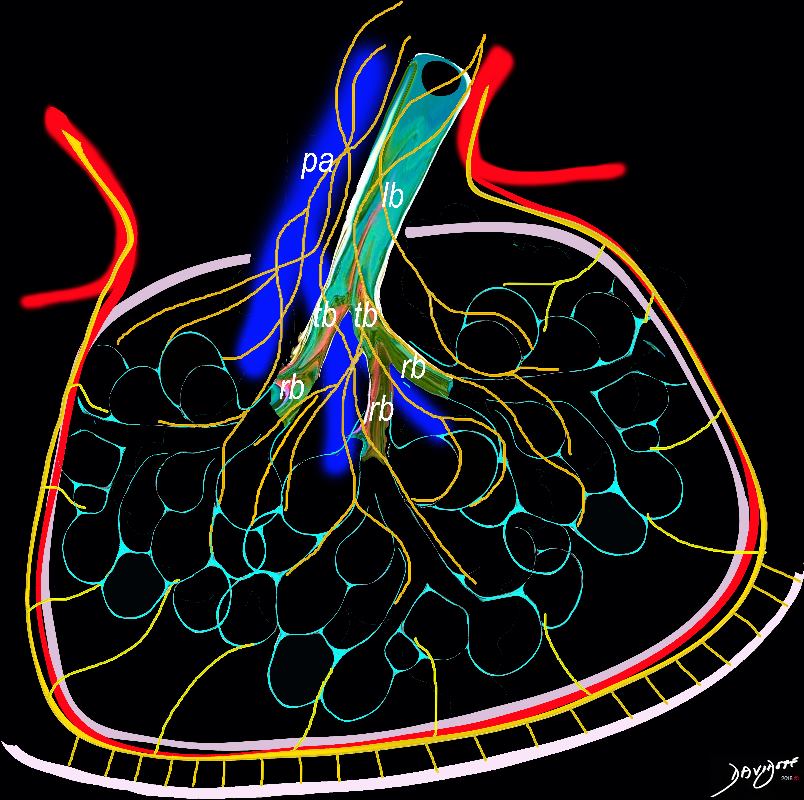
The diagram shows the 2 systems of lymphatic drainage at the level of the secondary lobule. The superficial system drains some of the interstitium of the secondary lobule, runs in the interlobular septa and drains all the pleura. Thee pathway to the lymph nodes in the mediastinum is via the pulmonary veins. The deeper system drains the interstitium in the interalveolar septa, and then they travel along the bronchovascular bundle accompanying the bronchi and pulmonary artery and into the lymph nodes of the hila and mediastinum
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0768
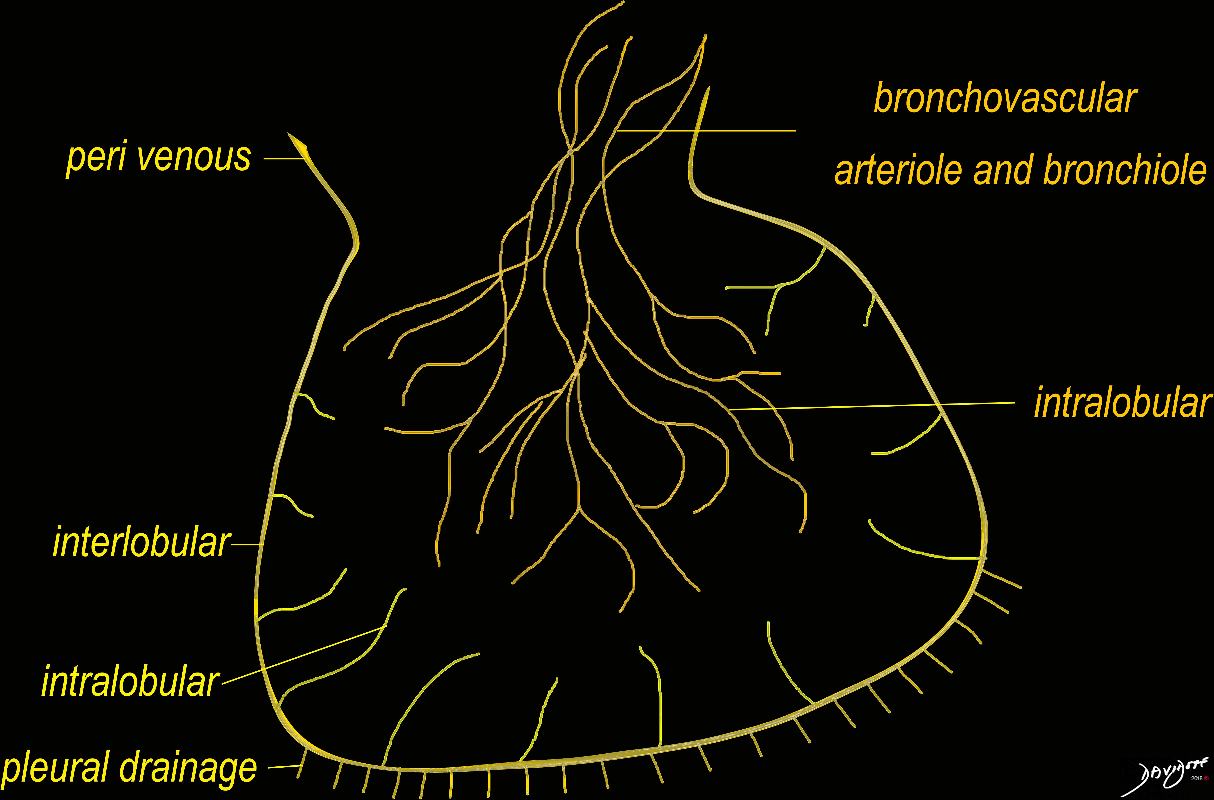
The diagram shows the 2 systems of lymphatic drainage at the level of the secondary lobule. The superficial system drains some of the interstitium of the secondary lobule, runs in the interlobular septa and drains all the pleura. Thee pathway to the lymph nodes in the mediastinum is via the pulmonary veins. The deeper system drains the interstitium in the interalveolar septa, and then they travel along the bronchovascular bundle accompanying the bronchi and pulmonary artery and into the lymph nodes of the hila and mediastinum
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0767
Lymphangitis Associated with Necrotizing Pneumococcal Pneumonia
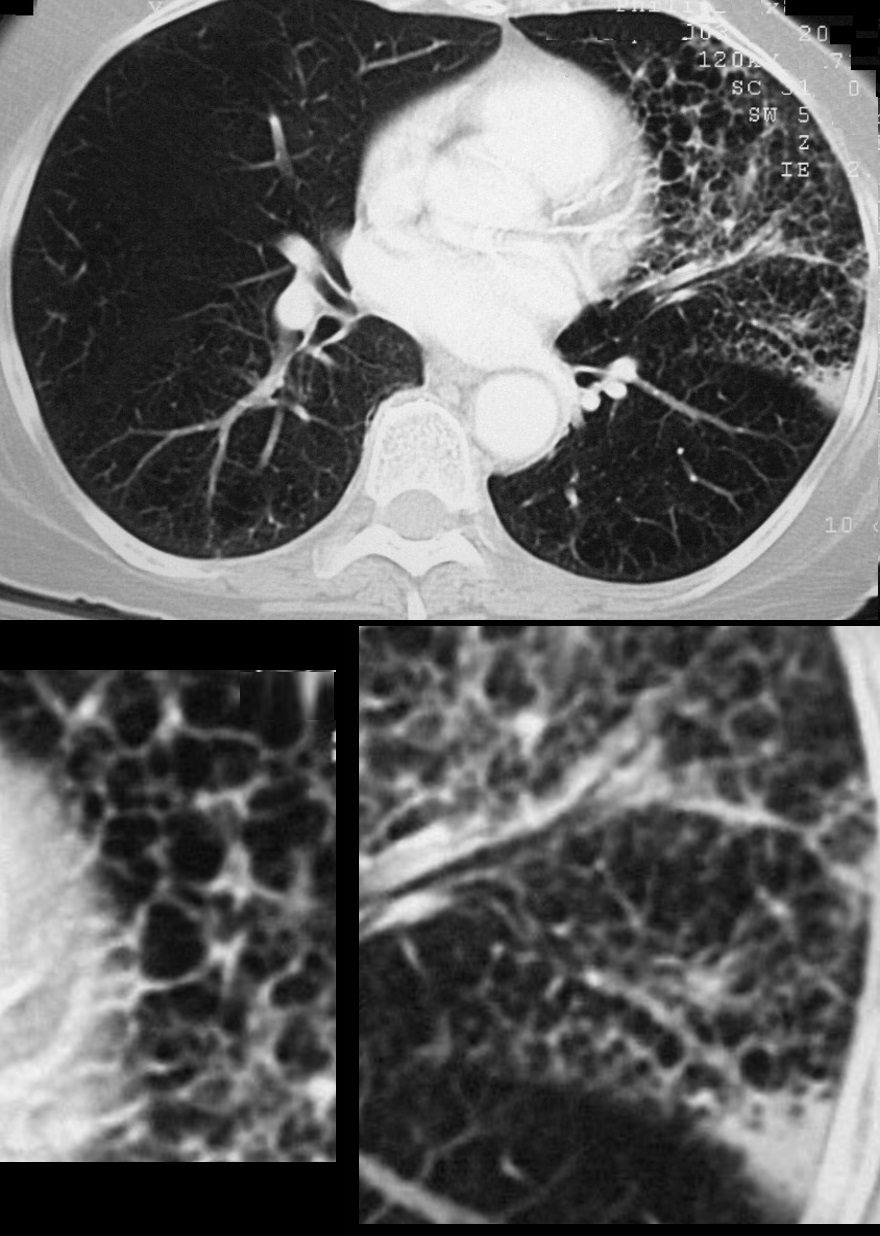
70-year-old female presents with a cough, fever and leukocytosis. CT in the axial plane shows extensive lymphangitis characterized by thickening of the interlobular septa in the inferior aspect of the upper lobe below the necrotizing pneumonia.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 260Lu 31631c
TB
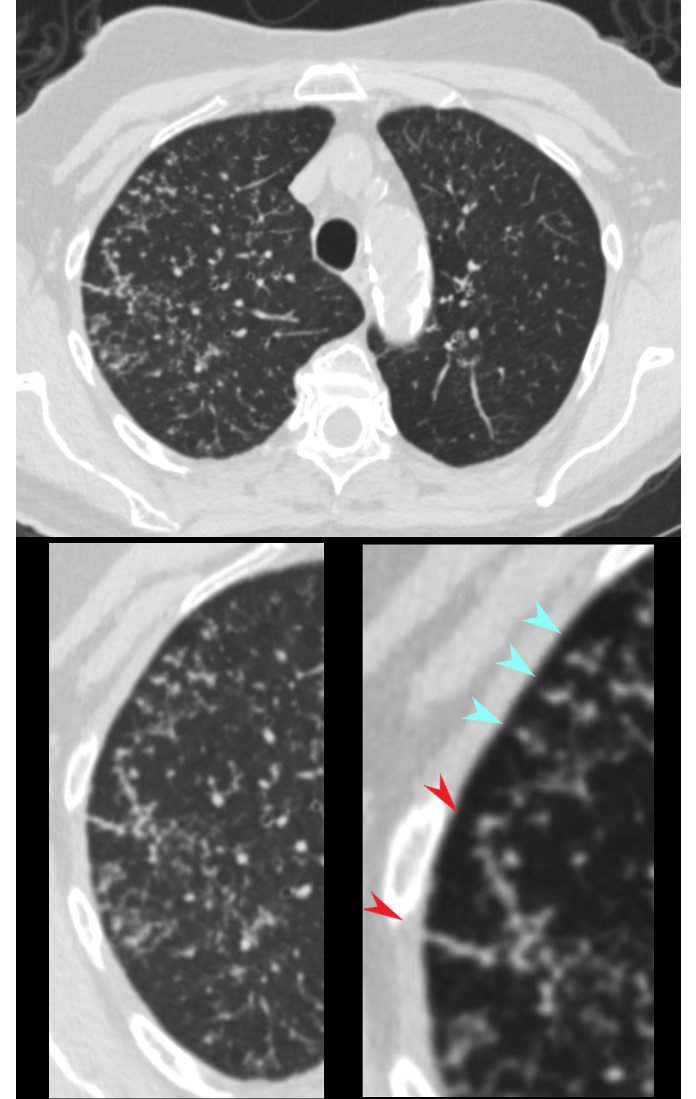
CT in the axial plane shows extensive small airway disease dominant in the right upper lobe characterized by innumerable, ground glass micronodules, centrilobular nodules (teal blue arrowheads) and nodular thickening of the interlobular septa likely reflecting lymphatic involvement (red arrowheads)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135825cL 192Lu
Sarcoidosis Septal and Intralobular Lymphatic Nodules
SARCOIDOSIS, ACTIVE – ALVEOLAR FORM
48-year-old previously well presented with dyspnea and initial CXR showed an infiltrate at the right base, and clinically resolved. He presented a year later with right chest pain and low grade ever and the CXR showed patchy opacities in the LUL and in the RLL
A subsequent CT showed LUL nodular opacities and subpleural rim of consolidation in the LUL and more prominently at both lung bases, associated with significant mediastinal adenopathy. Lymphovascular nodularity was noted in the bronchovascular bundles as well as in the interlobular septa, consistent with sarcoidosis
CXR and CT 4 years later showed almost complete resolution of the parenchymal findings and the CT findings except for minimal reticulation and scarring in the subpleural regions
Ashley Davidoff MD
Links and References
- TCV
