Vessels
Arteriole, Bronchiole Venule Lymphatics
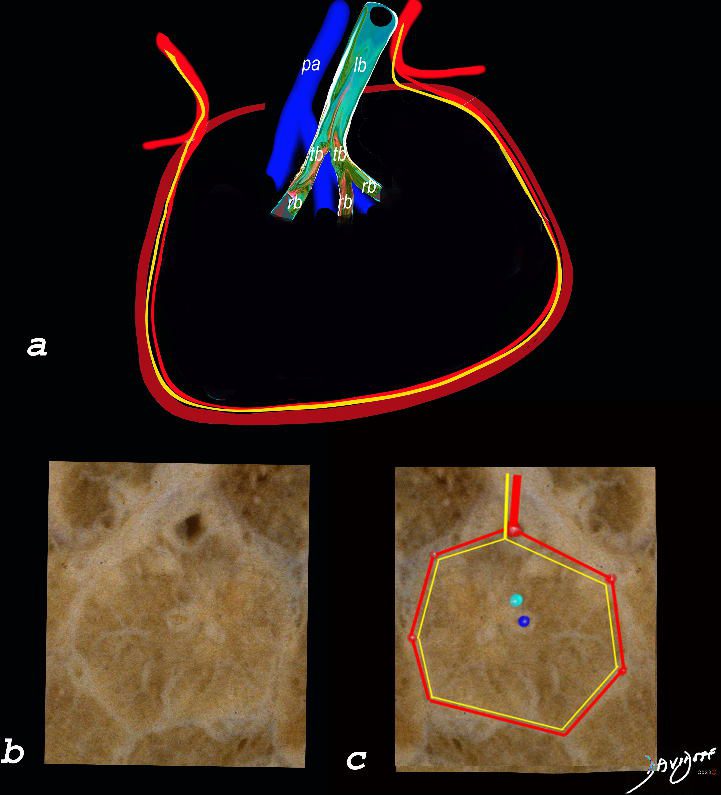
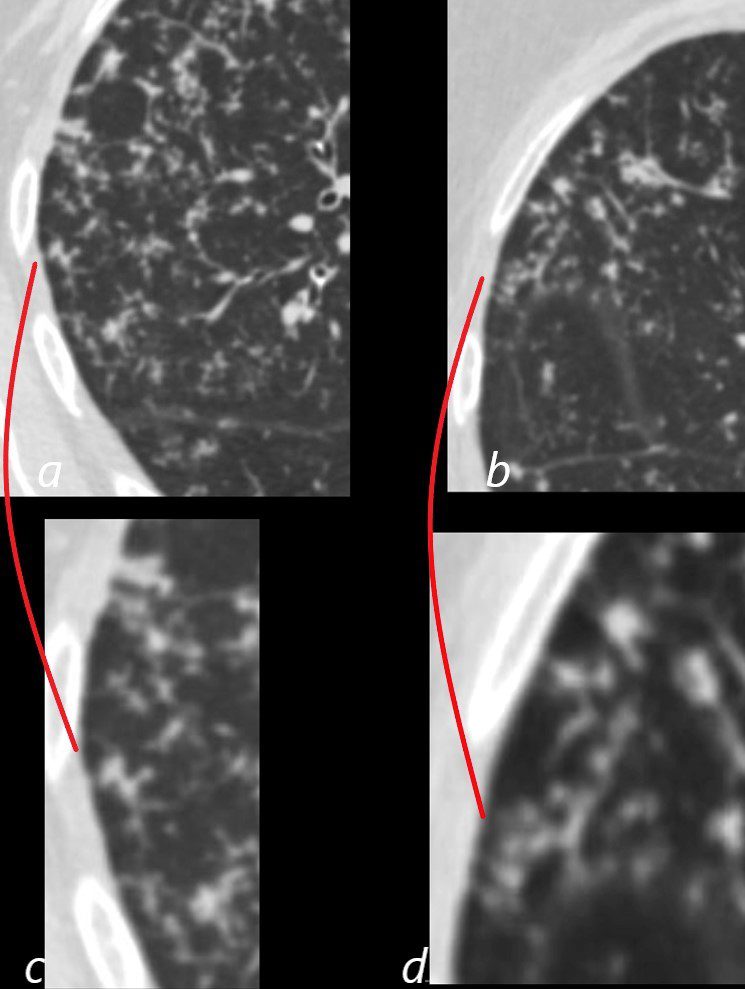
The top image (a) shows an anatomic drawing of a secondary lobule of the lung subtended by a lobular bronchiole (lb) and arteriole (pa). The interlobular septum contains the venule (red) lymphatic (yellow) and septum (maroon)
The anatomical specimen of the lung (b) shows normal intralobular parenchyma while image c shows the centrilobular arteriole (navy blue) and centrilobular bronchiole (teal) and interlobular venule (red) and lymphatics (yellow) The interlobular septum is slightly thickened
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Airways
Lobular Bronchiole (secondary lobule)
Terminal Bronchiole
Respiratory Bronchiole (acinus)
Alveolar Duct and Alveoli Sacs Alveoli
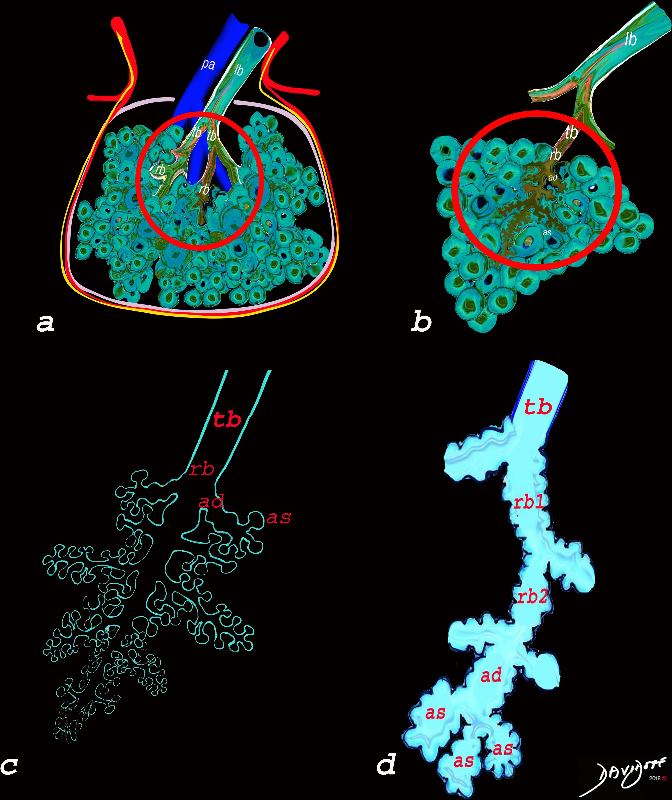
The diagram allows us to understand the the components and the position of the small airways starting in (a) which is a secondary lobule that is fed by a lobular bronchiole(lb) which enters into the secondary lobule and divides into terminal bronchioles (tb) which is the distal part of the conducting airways, and at a diameter of 2mm or less . It divides into the respiratory bronchiole (rb) a transitional airway which then advances into the alveolar ducts(ad) and alveolar sacs (as) Diseases isolated to the small airways do not affect the alveoli and hence there is peripheral sparing Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0749
The diagram allows us to understand the the components and the position of the small airways starting in (a) which is a secondary lobule that is fed by a lobular bronchiole(lb) which enters into the secondary lobule and divides into terminal bronchioles (tb) which is the distal part of the conducting airways, and at a diameter of Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0744
Small Airway Disease
Infection
TB Tree in Bud
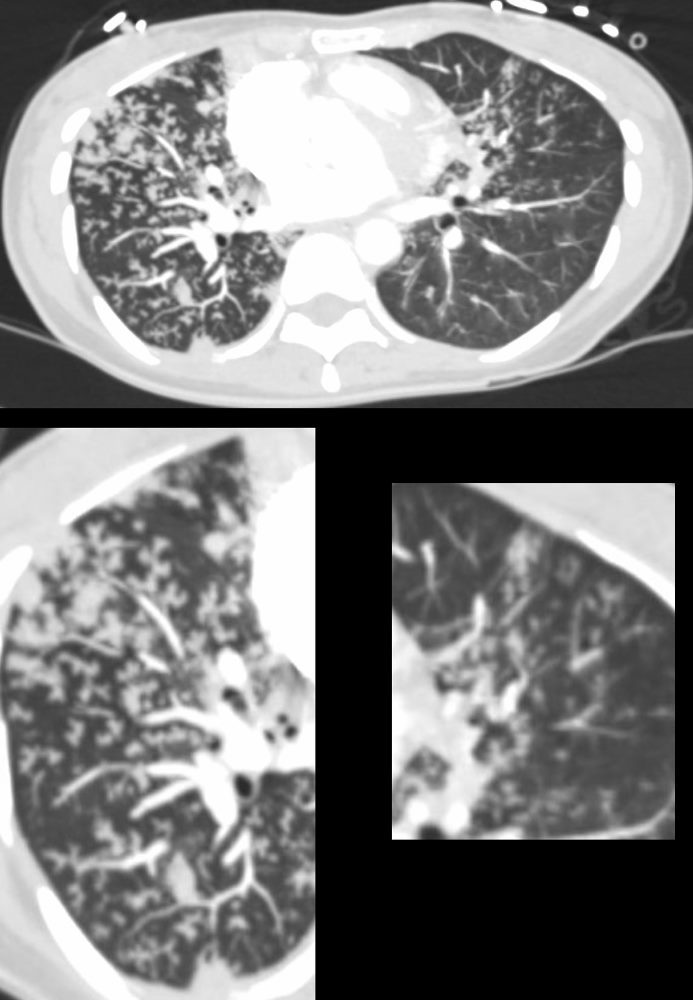
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats fever and cough. CT in the axial plane through the mid chest shows innumerable micronodules resulting from transbronchial spread with resultant tree in bud pattern scattered through the right lung (magnified in the right lower image). There are minimal similar changes in the lingula (magnified left lower image)..
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135789c 006Lu
Small Airway Disease and Tree in Bud Changes -Right Upper Lobe Active TB
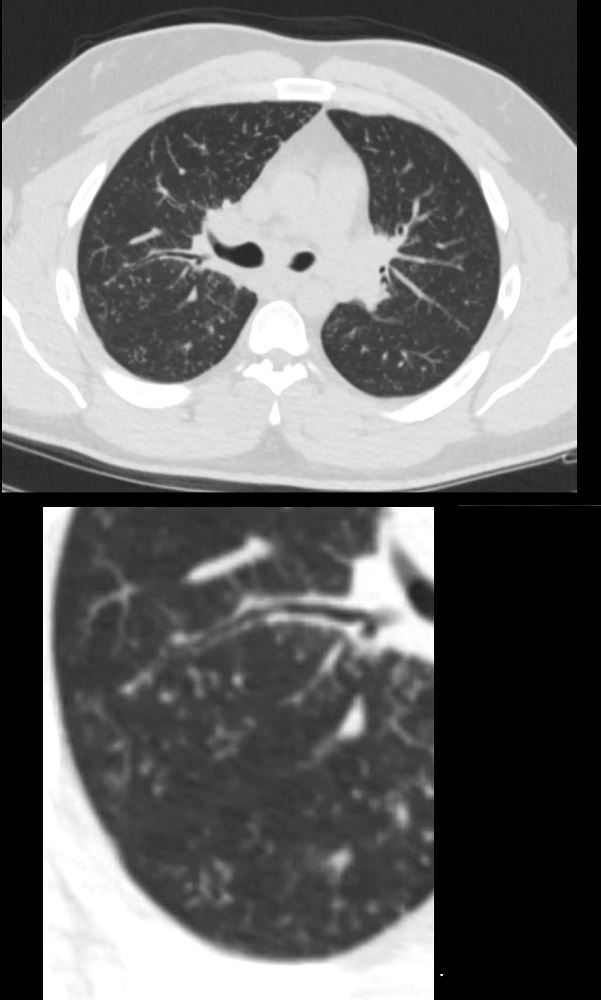
CT in the axial plane shows extensive small airway disease dominant in the right upper lobe characterized by innumerable, ground glass micronodules, and tree in bud changes. (a magnified in c and b magnified in d)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135827aL 192Lu
TB
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
Micronodules Tree in Bud
29-year-old male presents with night sweats
CT at the level of the carina shows extensive accumulation of ground glass micronodules and noted regions of tree in bud morphology. Wedge biopsy and culture revealed a diagnosis of MAC (mycobacterium avium complex)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135813c 247Lu
Centrilobular Nodules and Micronodules and Possible Perivenous Lymphatic Involvement-
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
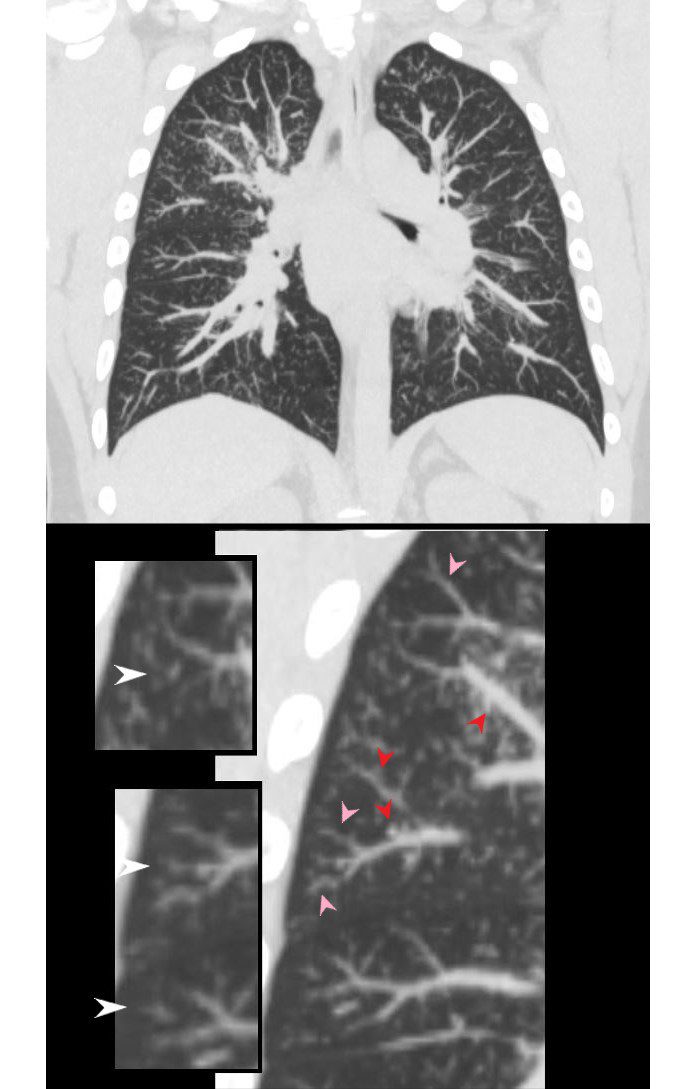

29-year-old male presents with night sweats
CT shows innumerable ground glass nodules most prominent in the right upper lobe but also apparent in the right lower lobe and left apex. The inserts in the lower panel, highlight the centrilobular nodules (white arrowheads), thickening and irregularity of the interlobular septa likely with lymphatic involvement (pink arrowheads) and suggestion of nodules along the pulmonary venules (red arrowheads). Wedge biopsy and culture revealed a diagnosis of MAC (mycobacterium avium complex)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135816c02L 247Lu



29-year-old male presents with night sweats
CT at the level of the carina shows extensive accumulation of ground glass micronodules and noted regions of tree in bud morphology. Wedge biopsy and culture revealed a diagnosis of MAC (mycobacterium avium complex)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135813c 247Lu
Histoplasmosis
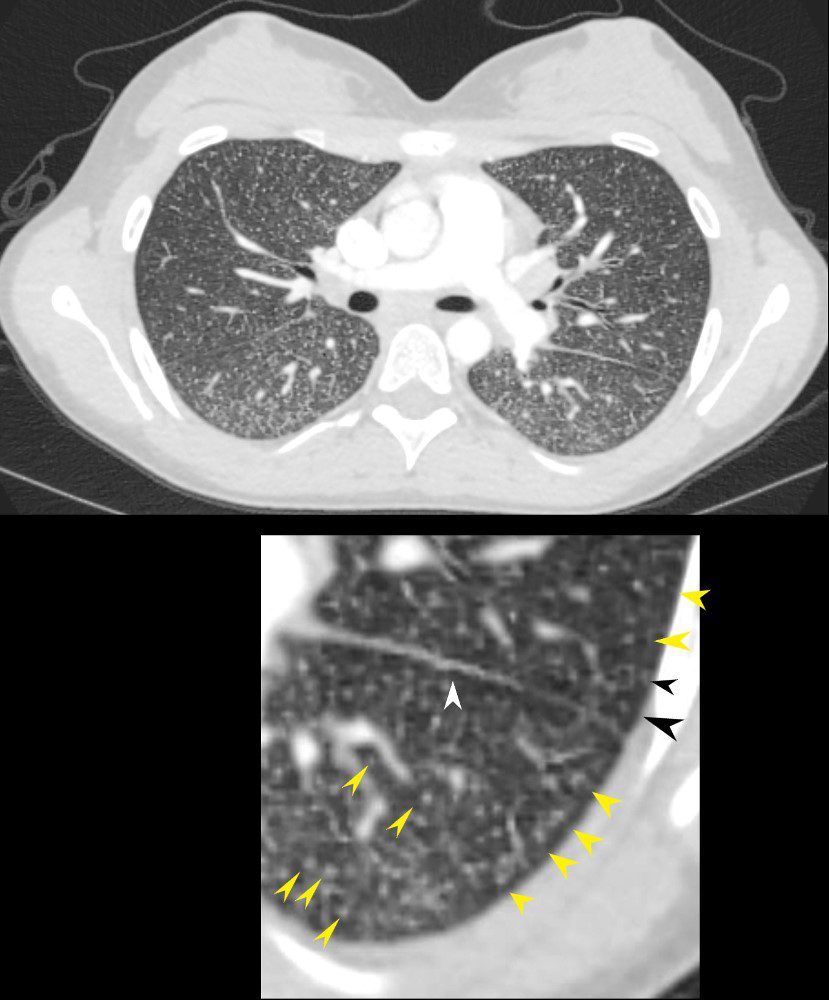

22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms
CT of the chest at the level of the main pulmonary artery shows extensive diffuse miliary disease. Some of the nodules are centrilobular (yellow arrowheads). Some of the secondary lobules suggest mosaic attenuation (black arrowhead). The nodular and irregular appearance on the fissure (white arrowhead) indicates peri-lymphatic distribution.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 131708cL
Cystic Fibrosis
Note Centrilobular Nodules
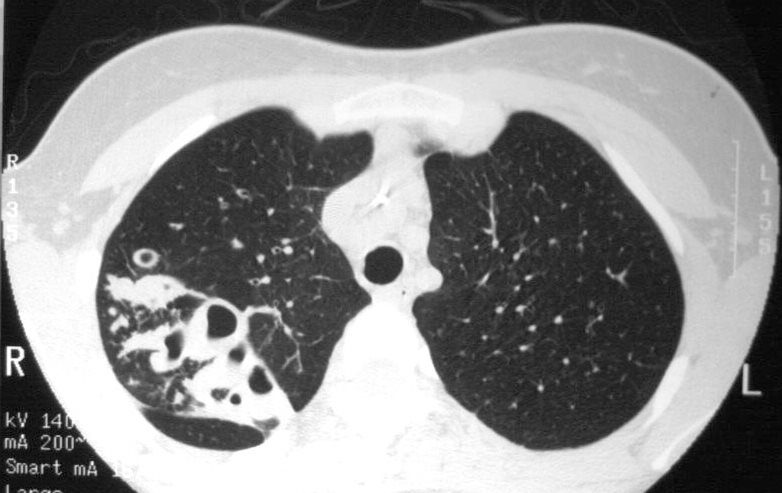

19 year old female with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis
CT scan through the upper lung fields shows multiple thickened and mucin filled subsegmental bronchi of the posterior segment of the right upper lobe
Courtesy Priscilla Slanetz MD MPH TheCommonVein.net
Inflammation
Disease Infection Inflammation
Aspiration
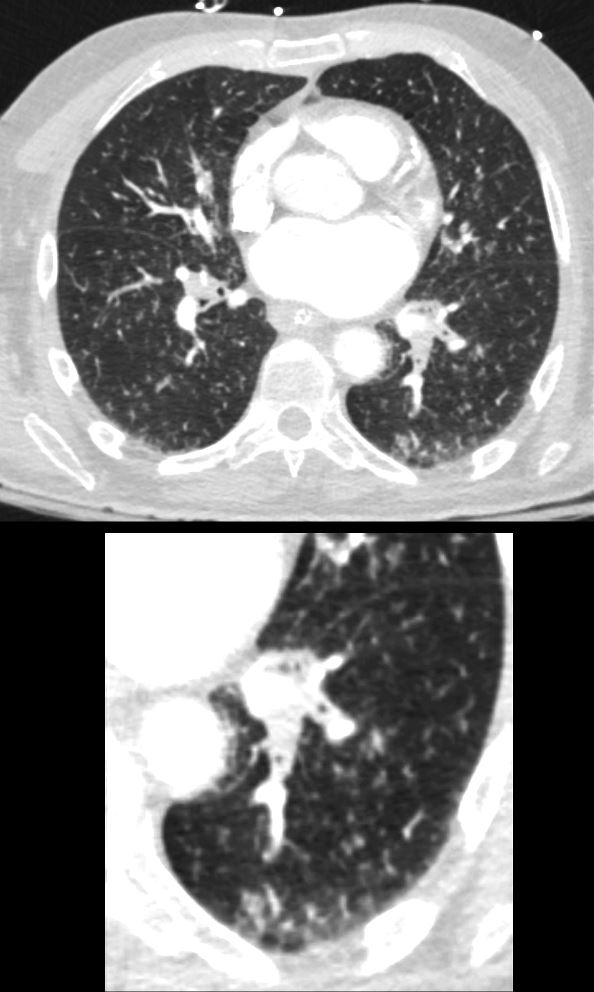

73-year-old man presents with respiratory difficulty following trauma and difficult placement of a nasogastric tube. CT scan through the chest at the level of the left atrium shows aspirated material in the left lower segmental airways and inferior lingula airways. There is thickening of the right sided segmental airways as well. Extensive ill-defined micronodules are noted throughout the lung fields. Centrilobular nodules are noted in the periphery of the left lower lobe. In the clinical context of technical difficulty with a recently placed NG tube acute, aspiration of fluid gastric content with small airway involvement is a diagnostic consideration despite the lack of alveolar changes
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135763c 244Lu
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) Bronchitis and Bronchiectasis
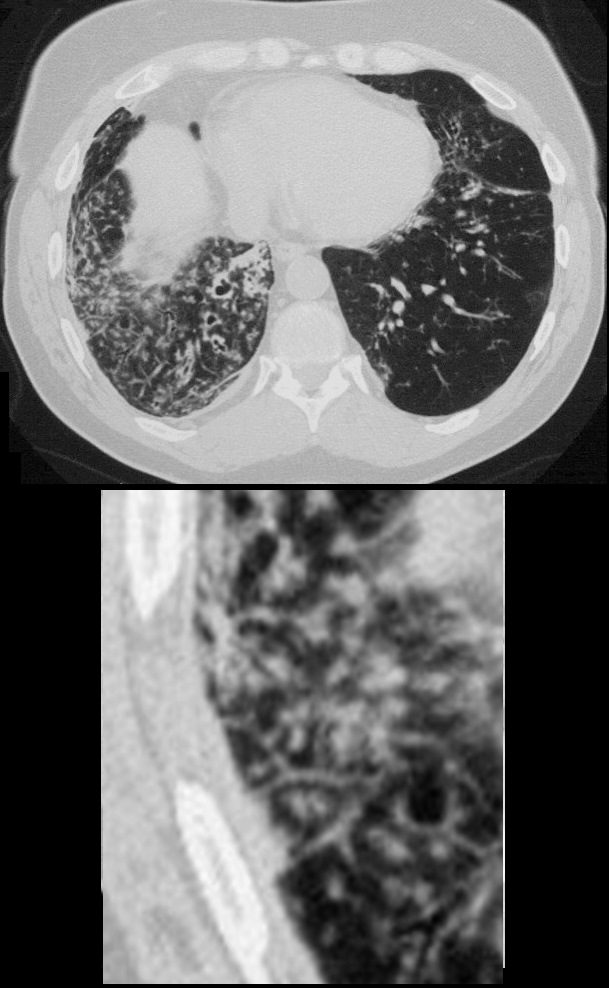

54 year old female with history of asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, ABPA
Current CT scan shows extensive small airway disease in the right lower lobe, magnified in lower image with centrilobular nodules and thickened interlobular septa characterized by ground glass micronodules.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) Bronchitis and Bronchiectasis
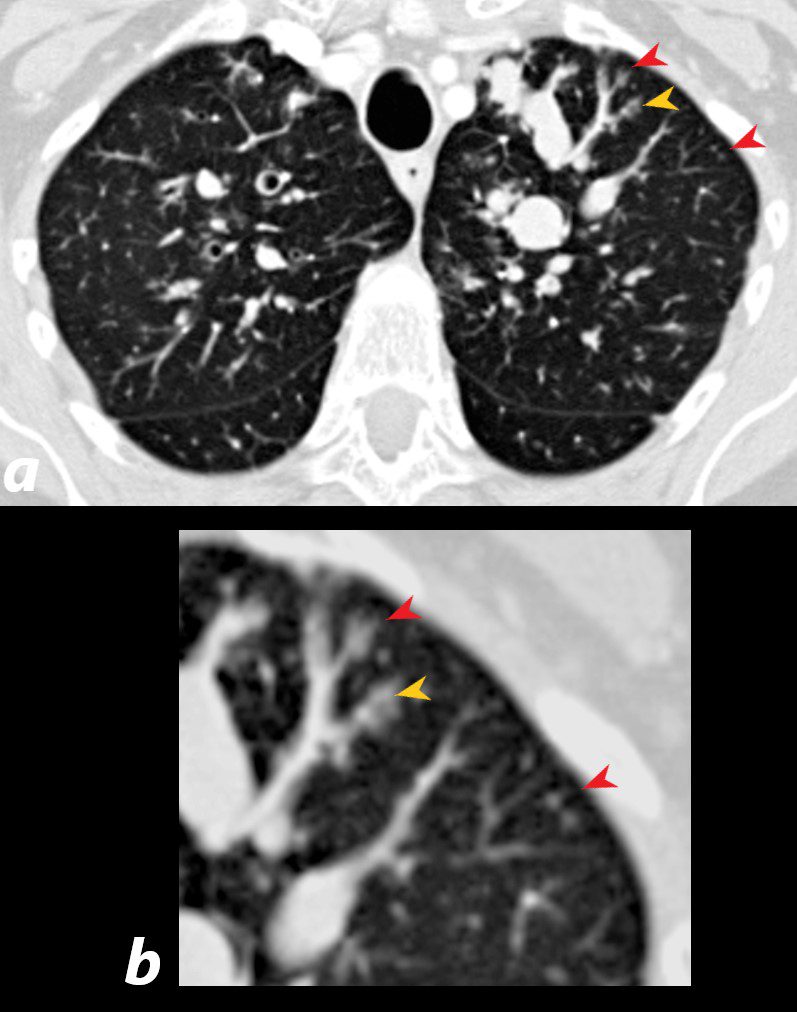

60 year old male with history of asthma, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
CT scan shows left upper lobe bronchiectasis and soft tissue/fluid impaction in the anterior segmental and subsegmental airways associated with tree in bud appearance (yellow arrowhead) and centrilobular nodules (red arrowhead) reminiscent of associated small airway disease
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia (CEP)

Alveolar and Interalveolar Interstitial Infiltration with Eosinophils and Inflammatory Exudate – Ground Glass Changes
The ground glass changes are a combination of the cellular and exudative inflammatory response in the small airways, alveoli, interalveolar septa and interstitium, and thickened alveolar septum
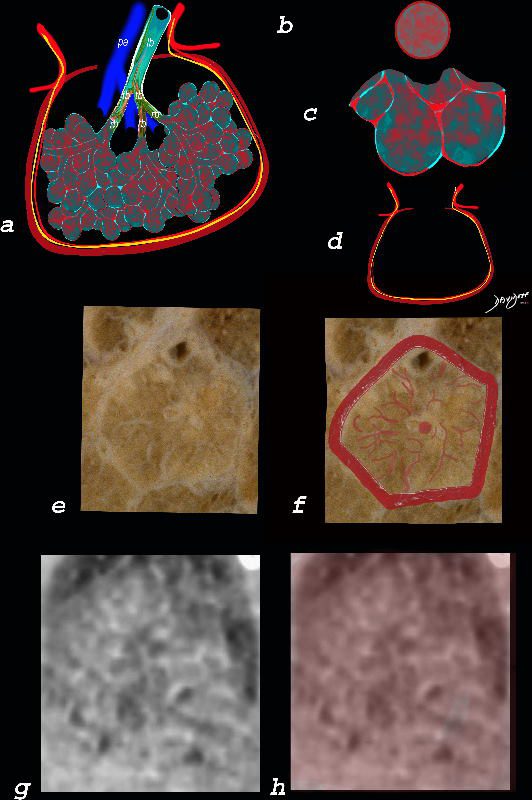
The diagram shows the abnormal secondary lobule (a) The involved components include the small airways(b) alveoli and interalveolar interstitium (c) and the thickened interlobular septum (d) surrounding the secondary lobule due to an inflammatory process, cellular infiltrate and congestion of the venules and lymphatics in the septum. An anatomic specimen of a secondary lobule from a patient with thickened interlobular septa and interstitial thickening is shown in image e, and is overlaid in red (f) . A magnified view of an axial CT of the lungs in a patient with acute eosinophillic pneumonia shows thickened interlobular septa and centrilobular nodules (g) The inflammatory changes in the aforementioned structures result in an overall increase in density of the lung manifesting as ground glass changes (g) and overlaid in red (h)
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0762
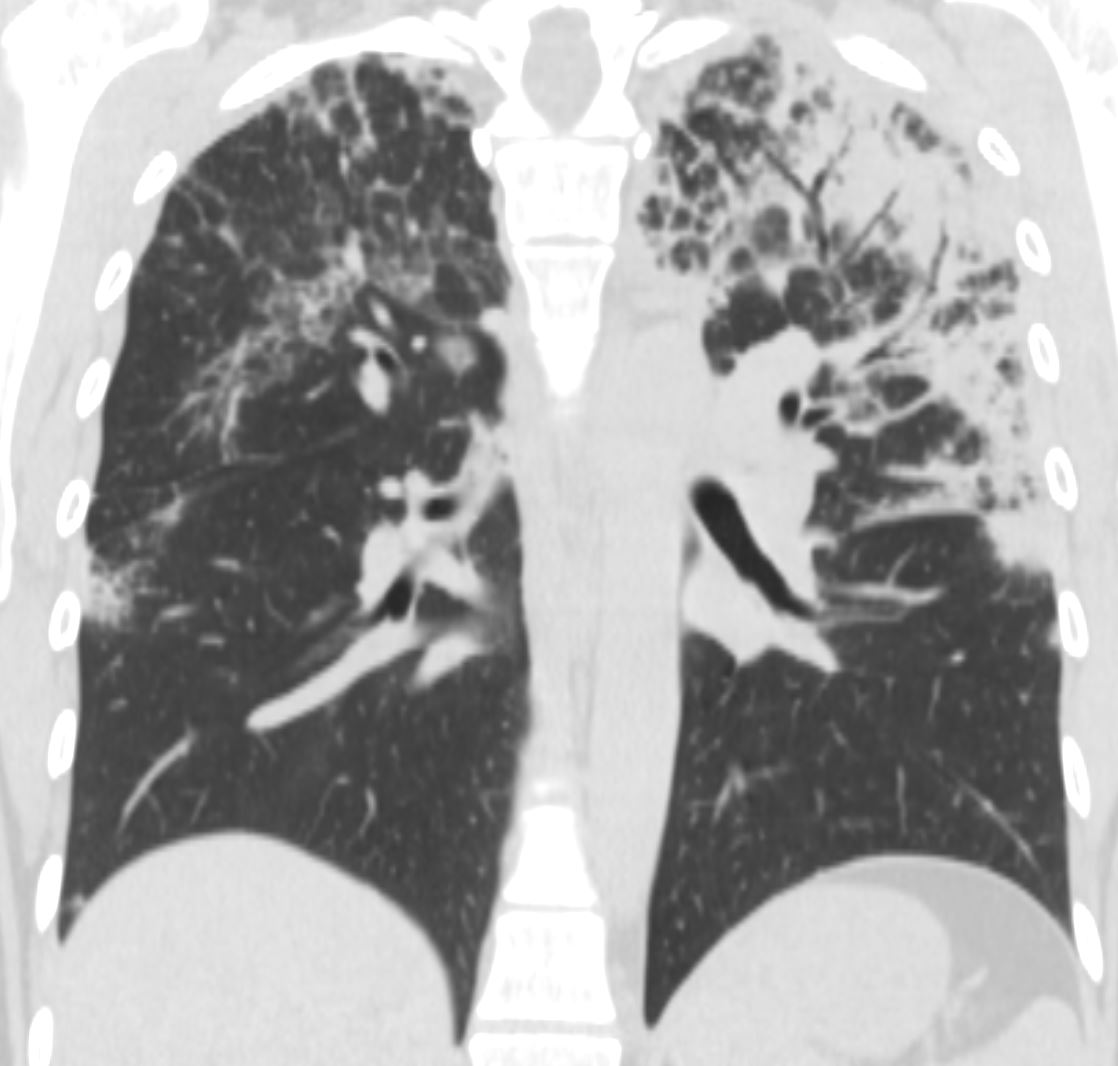

CT scan in the coronal performed 6 months ago at the time of clinical presentation shows upper lobe predominant peripheral infiltrates more prominent in the left upper lobe. Subsequent diagnosis by BAL of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) was made
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
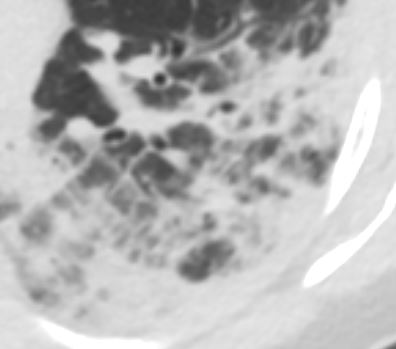

CT scan in the axial plane performed 6 months ago at the time of clinical presentation, shows upper lobe interlobular septal thickening, and peripheral consolidations which are findings characteristic of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) in the appropriate clinical setting. Note of prominent centrilobular nodule likely reflects small airway involvement Subsequent diagnosis by BAL of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) was made
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
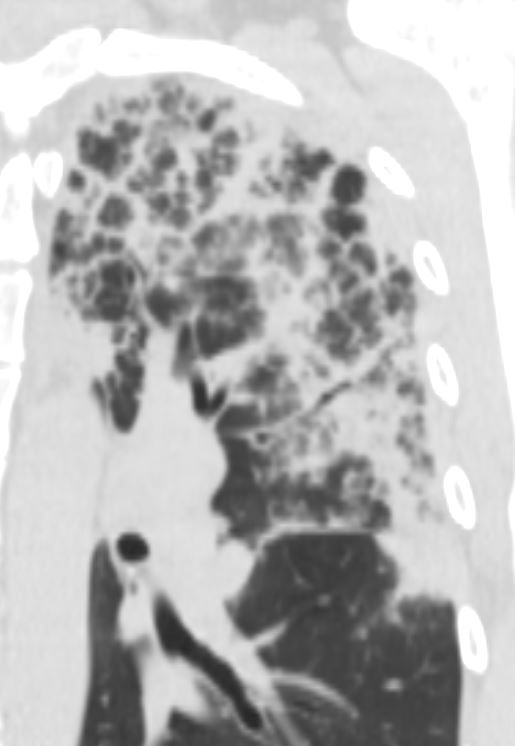

CT scan in the coronal performed 6 months ago at the time of clinical presentation shows upper lobe predominant peripheral infiltrates more prominent in the left upper lobe. Subsequent diagnosis by BAL of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) was made
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
- Bronchiole
-
- Endobronchial TB
- Non TB Mycobacteria and other Granulomatous Infections
- Infectious Bronchiolitis
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Bronchiolar Inflammation
- HP
- Asthma
- ABPA
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- OP and COP
- Smokers Bronchiolitis
- Asbestosis
- Follicular Bronchiolitis
-
Links and References
- TCV
