Broncho vascular distribution associated with increased reticular changes, more prominent traction bronchiectasis, decreased lung volumes , and decreased lung volumes, dominantly in the lower lobes but to some extent in the middle lobe and upper lobes. Pulmonary hypertension becomes more common.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net lungs-0771d
- In Fibrotic NSIP
- presence of fibrosis or
- scarring within the lung tissue.
- worse prognosis
- more severe respiratory symptoms,
- lower lung function, and a
- greater likelihood of developing pulmonary hypertension.
- CT
- shows more pronounced and
- diffuse reticular opacities and
- traction bronchiectasis, with
- less ground-glass opacities
- fibrotic changes may be
- more extensive and involve
- larger areas of the lung tissue.
- may also be
- honeycombing in advanced cases
- CT
- Volume Loss
- due to the presence of
- extensive fibrosis results in
- distortion and stiffening of the lung parenchyma,
- leading to a
- reduction in lung compliance
- decrease in
- total lung capacity (TLC), and
- functional residual capacity (FRC),
- decrease in
- reduction in lung compliance
.
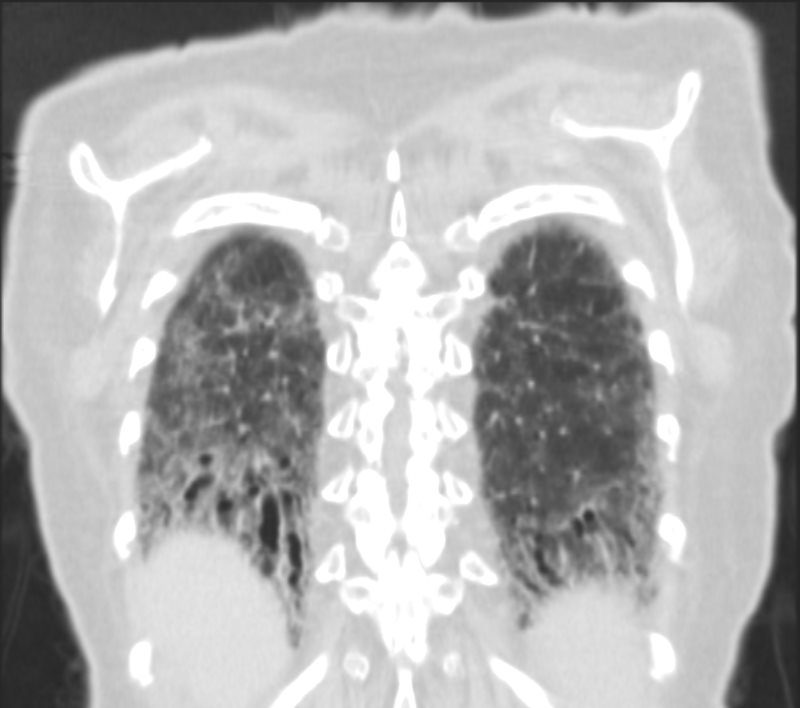
The degree of volume loss reticular change dominant over the ground glass changes suggest the fibrotic form of NSIP
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131500.8
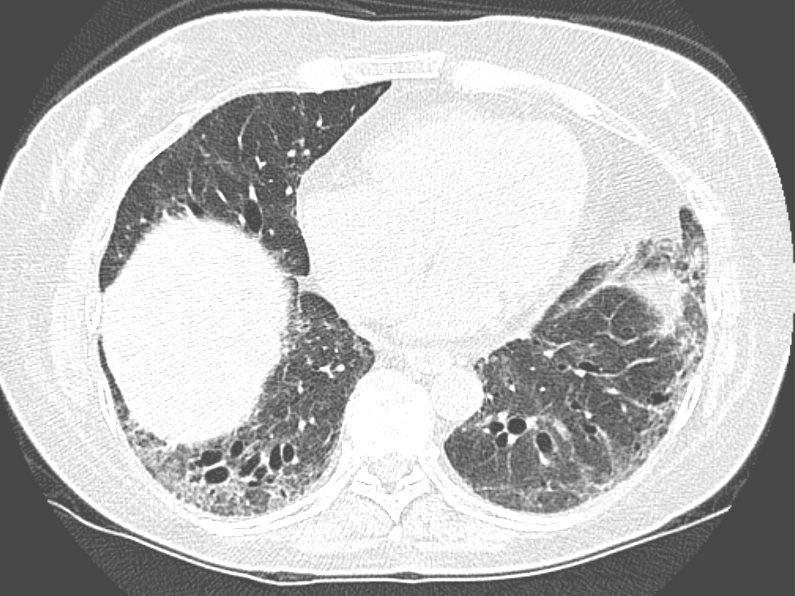
The degree of volume loss reticular change dominant over the ground glass changes suggest the fibrotic form of NSIP
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131503.8
- Links and References
