Etymology
- Derived from the Latin word folliculus, meaning “little sac,” and the Greek words bronchion, meaning “small airway,” and -itis, meaning “inflammation.” The term refers to inflammation of the bronchioles characterized by lymphoid follicle formation.
AKA
- Lymphoid follicular bronchiolitis
What is it?
- Follicular bronchiolitis is a rare inflammatory condition of the small airways characterized by the presence of hyperplastic lymphoid follicles within and around the bronchioles. It is often associated with underlying autoimmune or connective tissue diseases.
Caused by:
- Most common causes:
- Connective tissue diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome)
- Immune deficiency disorders (e.g., common variable immunodeficiency)
- Less common causes:
- Infection:
- Chronic or recurrent respiratory infections
- Inflammation:
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Immune:
- Autoimmune disorders (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Inherited and Congenital:
- Genetic conditions predisposing to immune dysregulation
- Other:
- Idiopathic follicular bronchiolitis
- Infection:
Resulting in:
- Narrowing and obstruction of small airways
- Chronic inflammation and mucus stasis
- Impaired gas exchange
Structural Changes:
- Hyperplastic lymphoid follicles around bronchioles
- Bronchiolar wall thickening
- Peribronchiolar inflammation and fibrosis in chronic cases
Pathophysiology:
- Follicular bronchiolitis arises from chronic immune activation, often triggered by infection, autoimmunity, or immune deficiency. Lymphoid follicles proliferate in response to antigenic stimulation, causing bronchiolar narrowing and airflow obstruction. Persistent inflammation can lead to secondary fibrosis and remodeling of small airways.
Pathology:
- Enlarged lymphoid follicles with germinal centers around bronchioles
- Chronic inflammatory infiltrates in the bronchiolar walls
- Associated fibrosis in advanced stages
Diagnosis
Clinical:
- Symptoms include:
- Chronic cough
- Progressive dyspnea
- Wheezing in some cases
- Recurrent respiratory infections
- History of underlying autoimmune or immune deficiency disorder
Radiology:
- CXR:
- Non-specific findings such as reticulonodular opacities
- Peribronchial thickening in some cases
- CT of the Chest:
- Centrilobular nodules
- Ground-glass opacities
- Mosaic attenuation indicating air trapping
- Bronchiolar wall thickening
Labs:
- Autoimmune panel to detect associated connective tissue diseases
- Serum immunoglobulin levels for immune deficiencies
- Microbiological cultures to rule out infections
Management:
- Treatment of underlying conditions:
- Immunosuppressive therapy (e.g., corticosteroids, disease-modifying agents) for autoimmune diseases
- Immunoglobulin replacement for immune deficiencies
- Supportive care:
- Bronchodilators for symptomatic relief
- Management of superimposed infections
Radiology Detail
CXR
Findings:
- Reticulonodular or peribronchial opacities
Associated Findings:
- Hyperinflation in cases with air trapping
CT of the Chest
Parts:
- Terminal and respiratory bronchioles
Size:
- Centrilobular nodules typically 2-3 mm in diameter
Shape:
- Small, rounded nodules or irregular thickening
Position:
- Centrilobular distribution in the lung parenchyma
Character:
- Nodular opacities with ground-glass attenuation
Time:
- Chronic process, often progressive
Associated Findings:
- Air trapping on expiratory imaging
- Peribronchial thickening
Other relevant Imaging Modalities
MRI/PET CT/NM/US/Angio:
- PET-CT: May demonstrate metabolic activity in areas of inflammation or lymphoid hyperplasia
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs):
- Restrictive or obstructive patterns depending on the stage of the disease
- Reduced diffusion capacity in advanced cases
Recommendations:
- High-resolution CT for detailed assessment of small airway involvement
- Biopsy for definitive diagnosis if imaging and clinical correlation are inconclusive
- Early identification and management of underlying autoimmune or immune deficiency disorders
Key Points and Pearls:
- Follicular bronchiolitis is a rare condition associated with autoimmune diseases and immune deficiencies.
- High-resolution CT findings include centrilobular nodules and air trapping.
- Management focuses on treating underlying conditions and providing supportive care.
- Biopsy may be required for a definitive diagnosis in uncertain cases.
Follicular Bronchiolitis Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
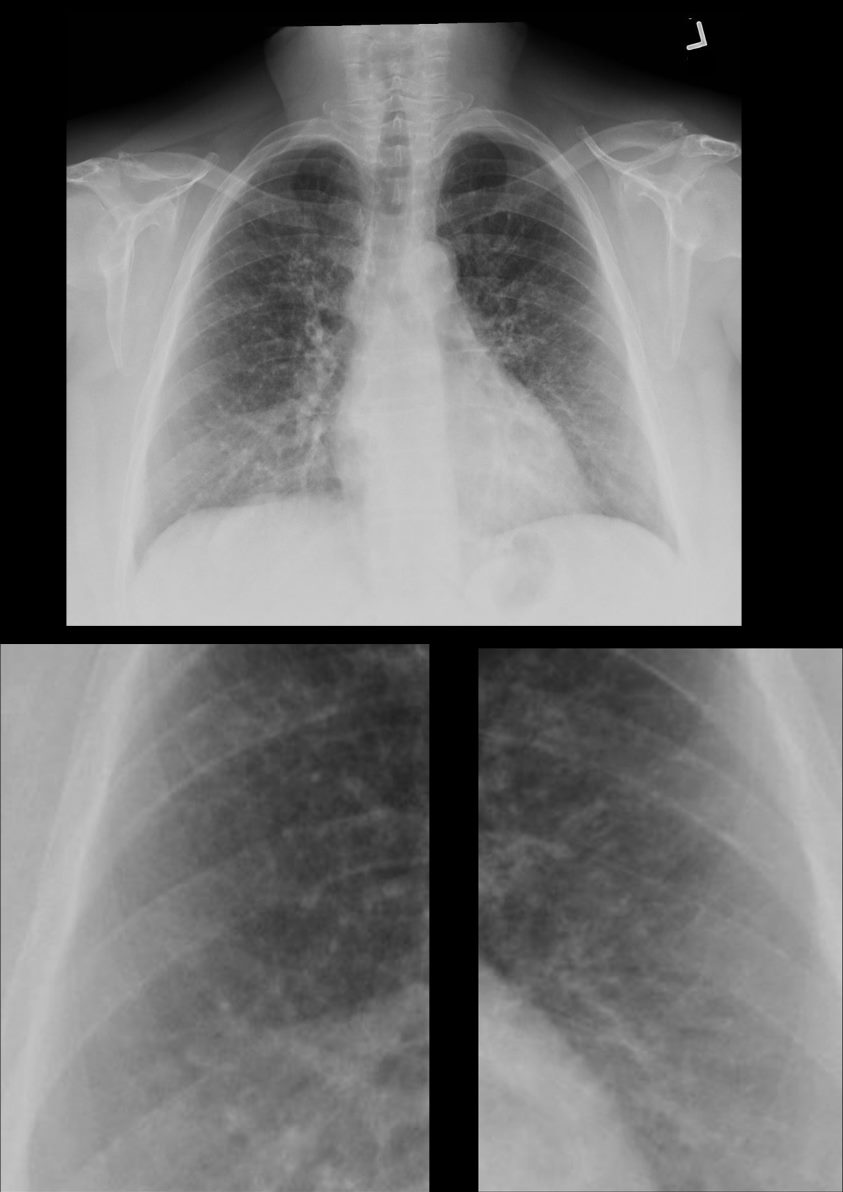
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea. Frontal view of the chest reveals a coarsened nodular interstitial pattern with magnified views showing the micronodularity in the lower panels.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136650c01
Follicular Bronchiolitis,, Centrilobular Nodules, Air Trapping, Ground Glass Opacities (GGO) in Upper Lobes
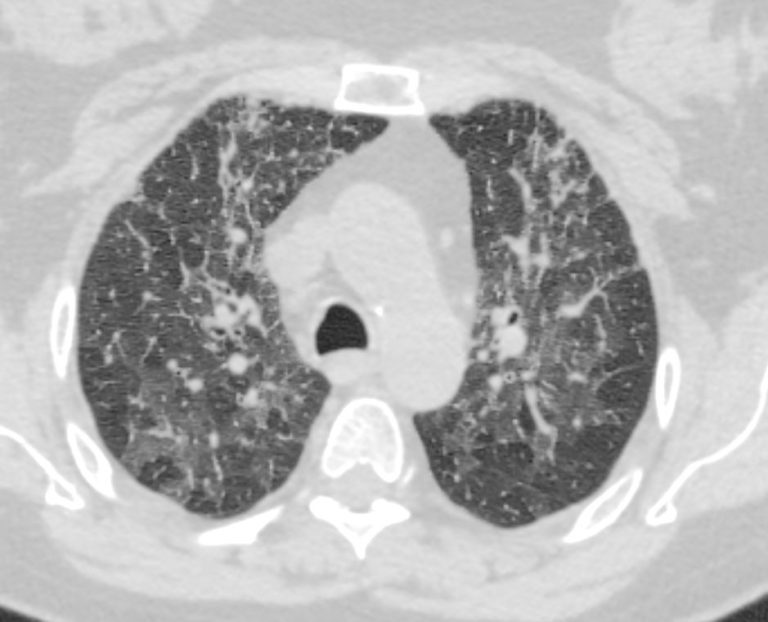
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the aortic arch reveals centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context) and bronchial wall thickening. In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136652
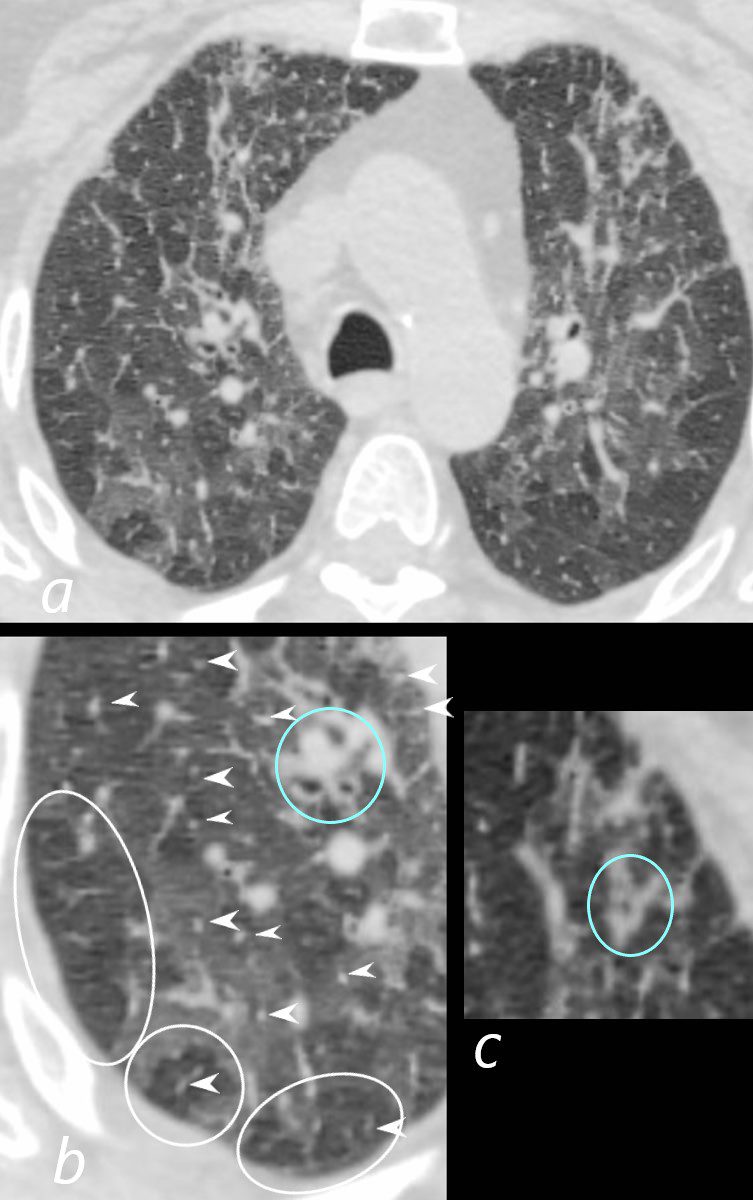
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the aortic arch reveals centrilobular nodules (b, white arrowheads) , ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (b, white rings) likely due to air trapping in this context, and bronchial wall thickening (b, c teal rings). There is some irregular thickening of the interlobular septa. In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136652cL
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
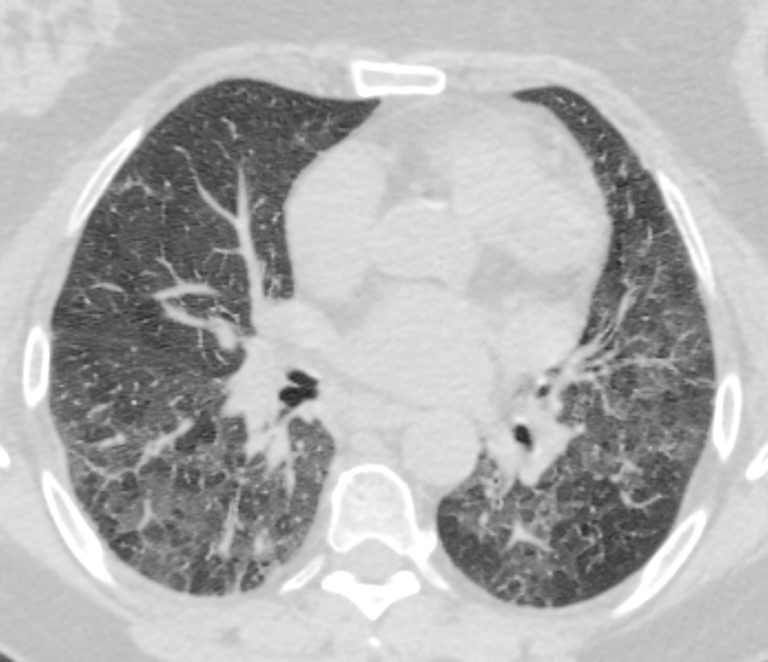
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the lower lung fields reveals centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context). In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136657
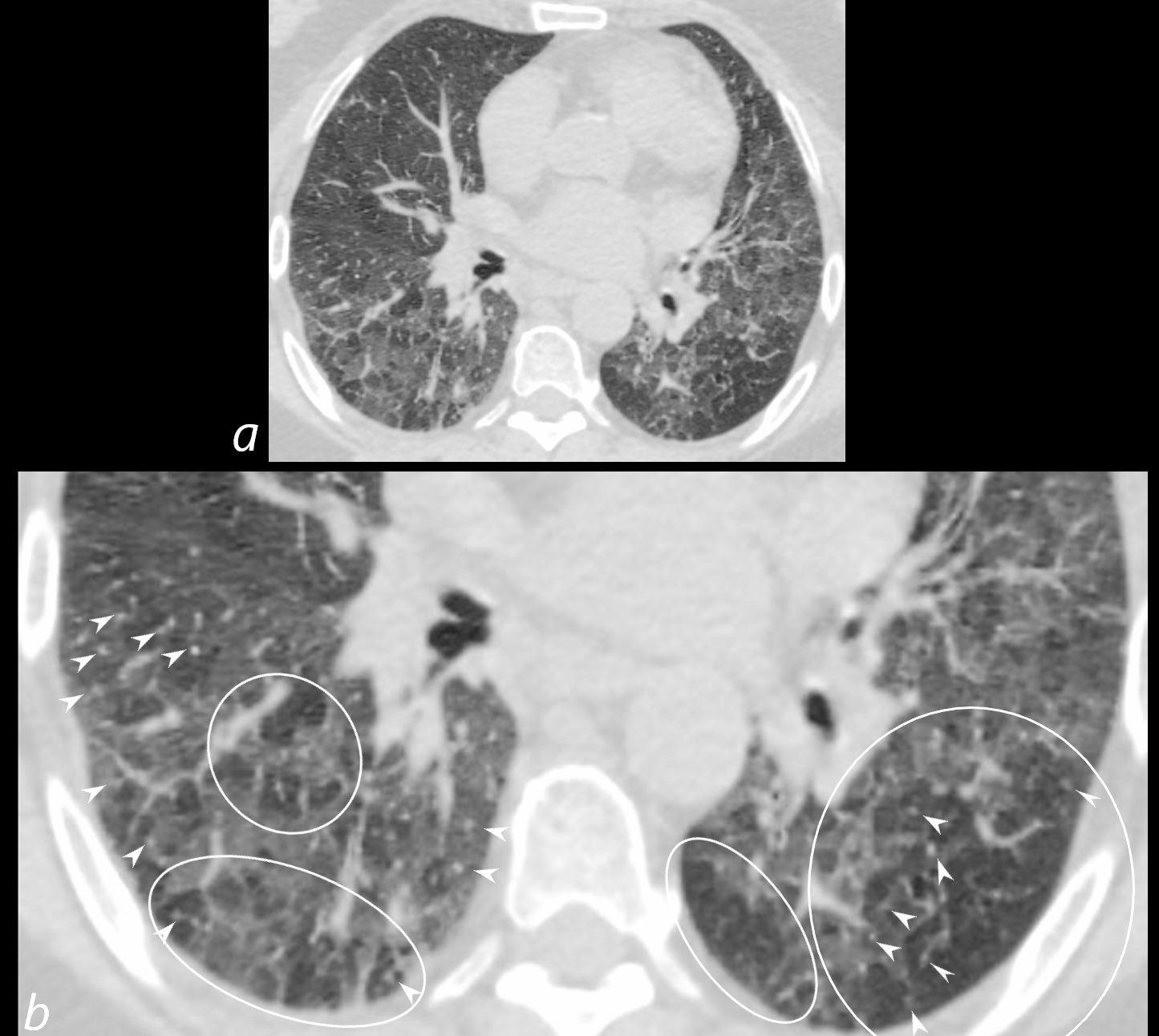
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the lower lung fields reveals centrilobular nodules (b white arrowheads), ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (b, white rings) likely due to air trapping in this context.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136657cL
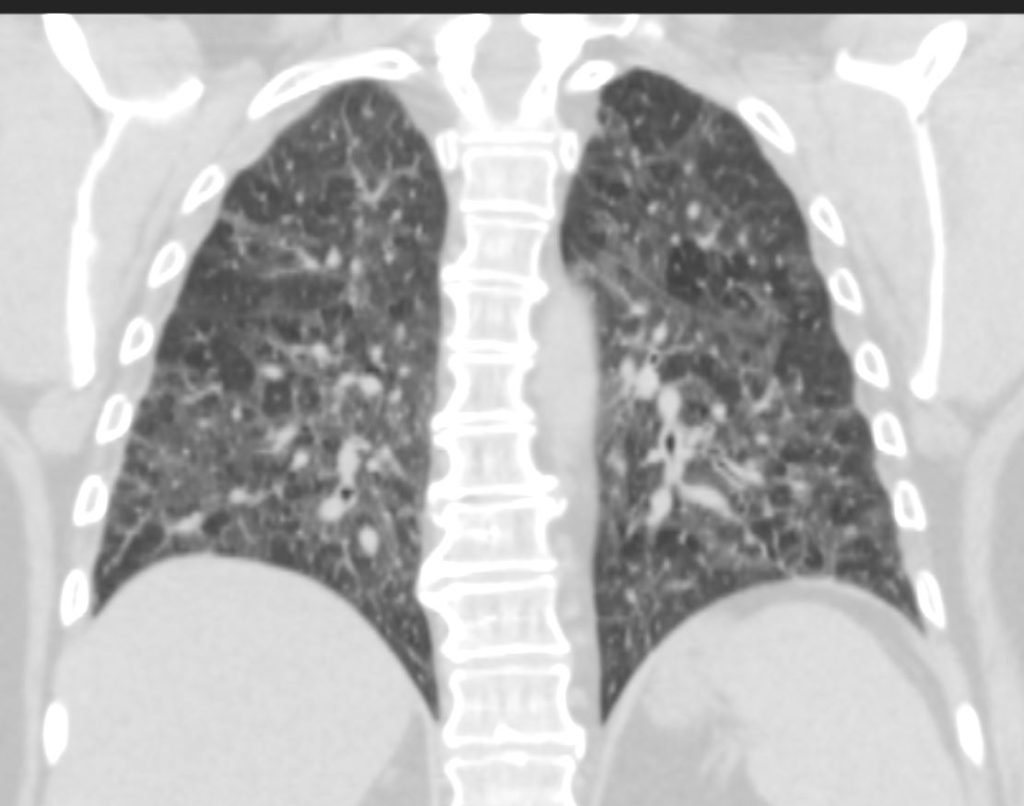
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
CT in the coronal plane of the chest at the level of the spine reveals bilateral diffuse changes in the lungs characterized by centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context) and irregular thickening of the interlobular septa.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136663
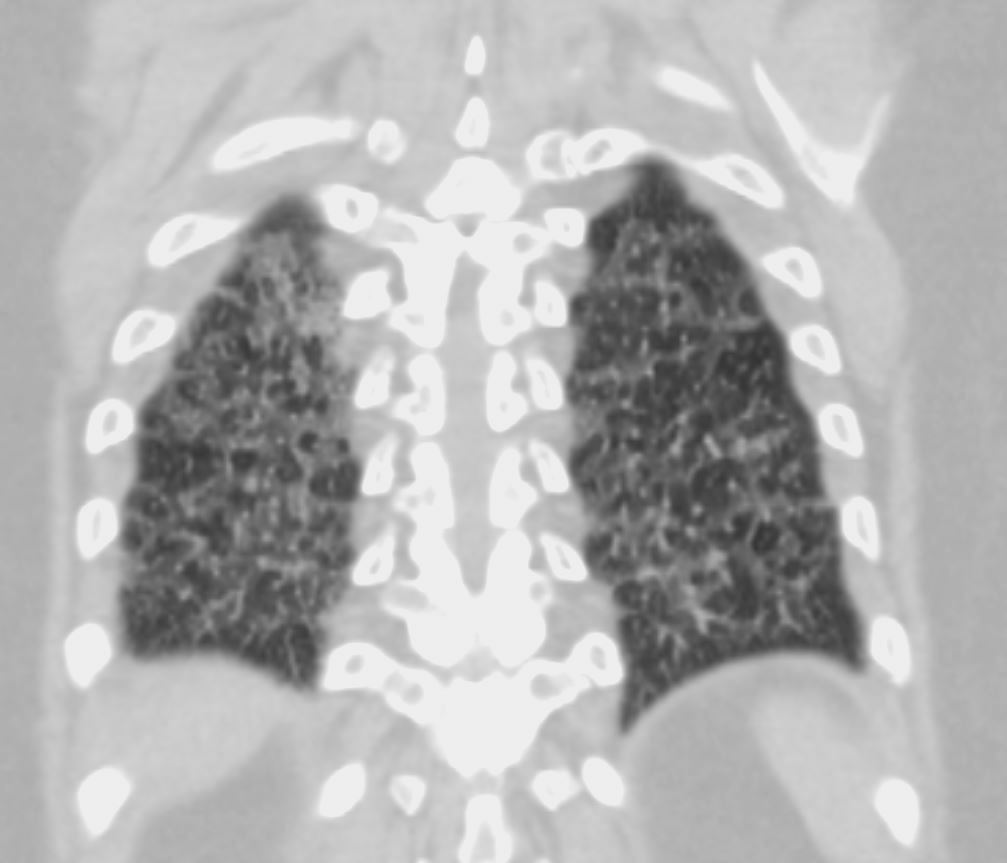
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
CT in the coronal plane of the chest at the level of the spine reveals bilateral diffuse changes in the lungs characterized by centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context) and irregular thickening of the interlobular septa.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136664
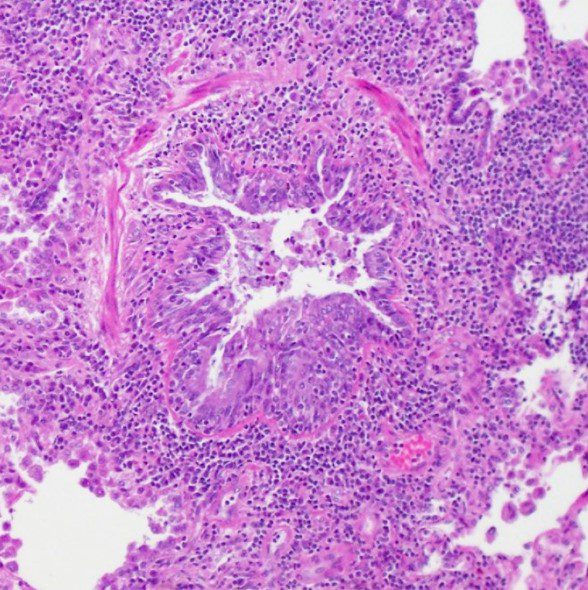
-

Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain from surgical lung biopsy showing airway narrowing with enlarged peribronchiolar lymphoid follicles, consistent with follicular bronchiolitis.
Assaad M, Aqeel A, Walsh J (February 13, 2022) Follicular Bronchiolitis Associated With Primary IgG2/IgG4 Deficiency in a Previously Healthy 40-Year-Old Woman. Cureus 14(2): e22183. doi:10.7759/cureus.22183- aka bronchiolar nodular lymphoid hyperplasia,
- aka hyperplasia of the bronchial associated lymphoid tissue (BALT),
- is a
- reactive pulmonary lymphoid disorders
- part of as group of
- lymphoproliferative pulmonary diseases (LPDs).
- characterized by the
- accumulation of lymphoid cells in the
- walls of small airways.
- caused by
- antigenic stimulation of BALT, followed by a
- polyclonal lymphoid hyperplasia. It is currently classified as one of the reactive pulmonary lymphoid disorders in a group known as the lymphoproliferative pulmonary diseases (LPDs).
- primary
- secondary
- Connective Tissue Disorders
- Sjogren’s syndrome,
- rheumatoid arthritis, and
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- Infection
- Pneumocystis jirovecii,
- Legionella pneumonia, and
- acute viral hepatitis
- ILD
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia,
- respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease,
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia,
- cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, and
- Immunodeficiencies
- CVID and AIDS
- Connective Tissue Disorders