75- Year-Old Male presents with Hemoptysis following Trauma
He is S/P AVR and is on anticoagulants and is afebrile and has no elevation in his white count
CXR
Extensive Ground Glass Changes and Consolidation
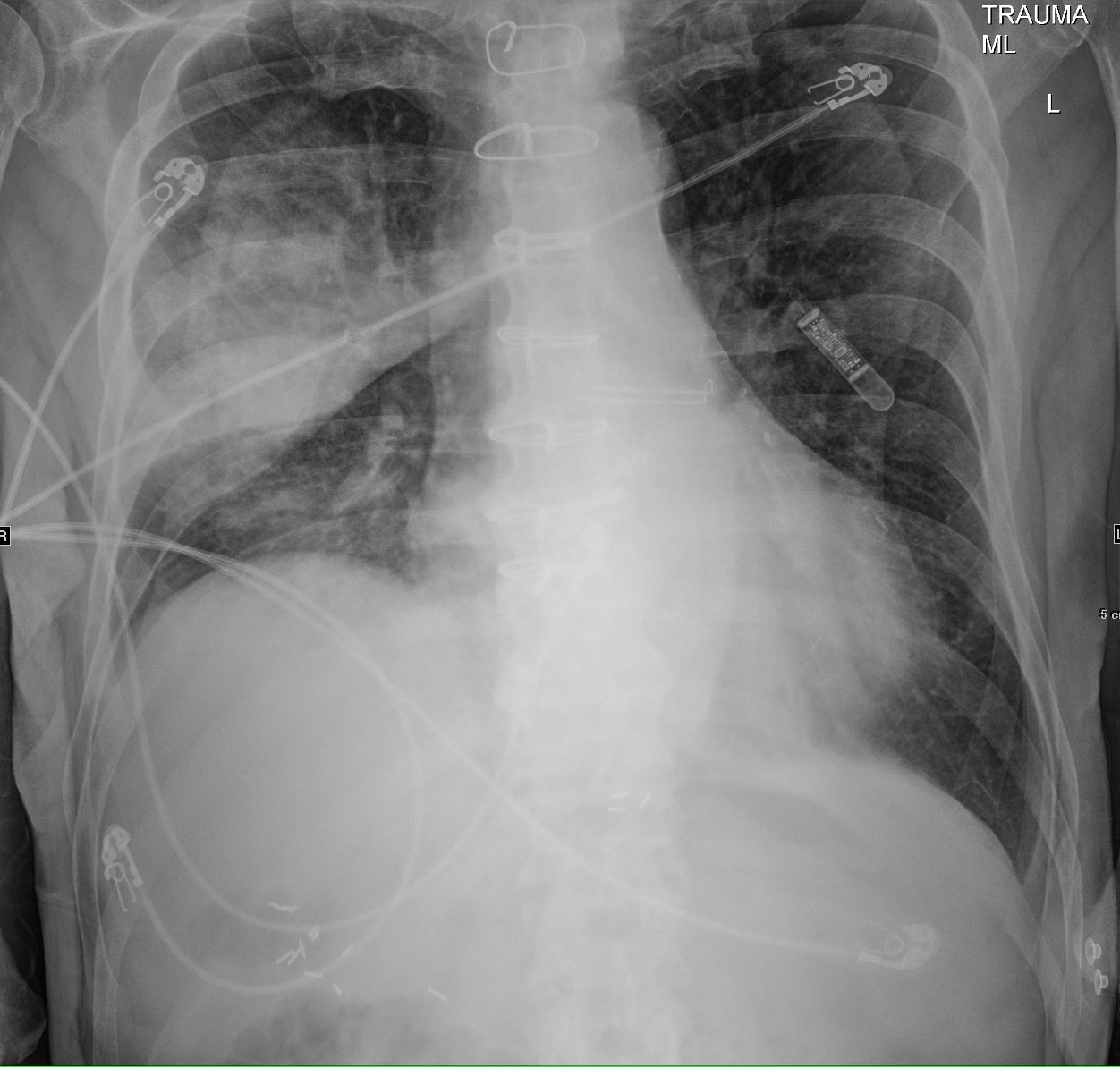
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
CXR shows an elevated right hemidiaphragm and inferior displacement of the major fissure with a dense right upper lobe consolidation. The mass effect on the major fissure likely results from a hematoma, and the hemorrhage results in air bronchograms and groundglass changes.
Skin folds manifest as bilateral pseudo-pneumothoraces. A loop recorder is noted overlying the left upper chest.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135849
Scout CT shows an elevated right hemidiaphragm and inferior displacement of the major fissure with a dense right upper lobe consolidation.
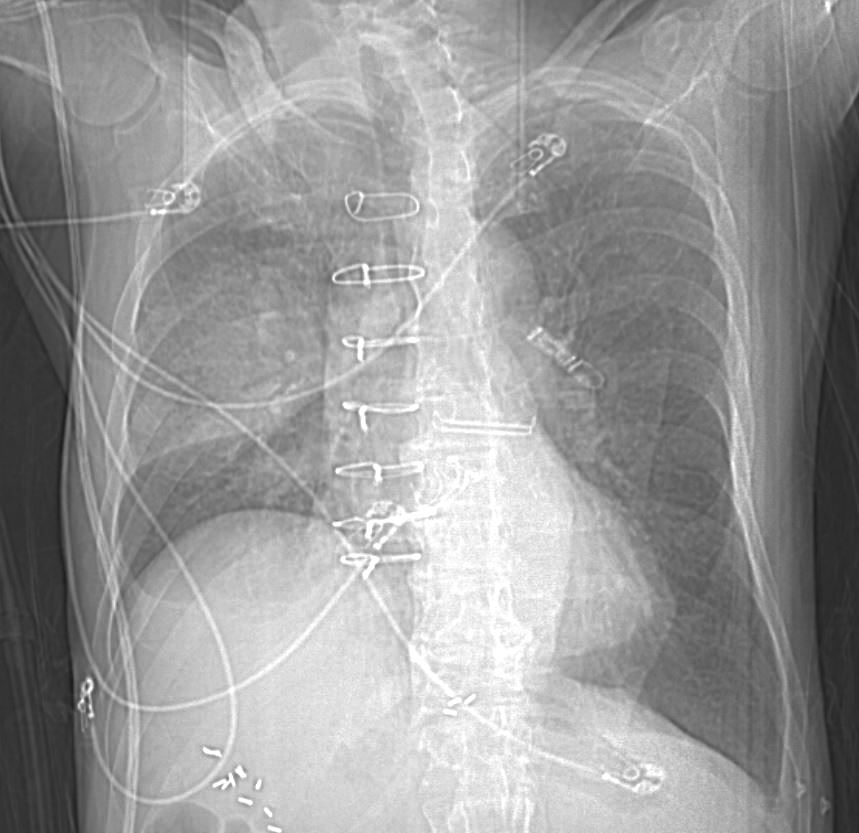
Skin folds on the left results in a pseudo-pneumothorax. A loop recorder is noted overlying the left upper chest.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135850
Pulmonary Hemorrhage Ground Glass Changes and Consolidation Axial CT
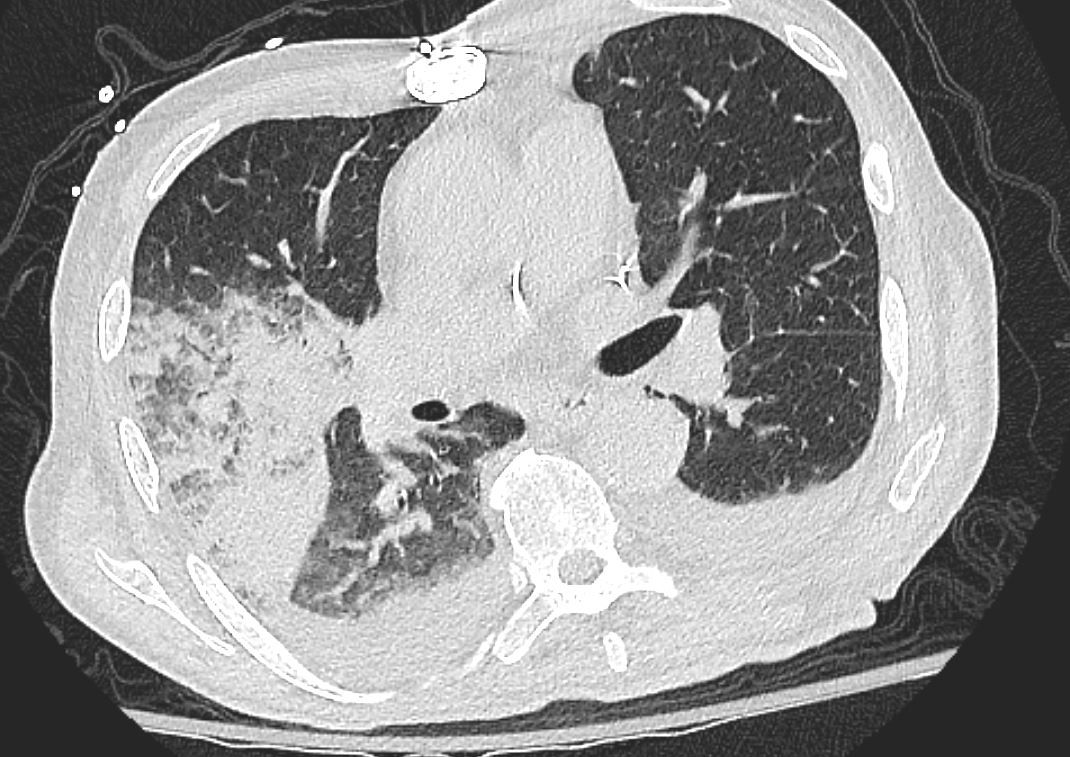
Axial CT at the level below the carina shows medial displacement of the major fissure by a dense right upper lobe consolidation. The mass effect on the major fissure likely results from a hematoma. Anterior to the consolidation there is a combination of ground glass opacity with thickened interlobular septa, and minor region of subsegmental consolidation with air bronchograms, likely resulting from hemorrhage.
There are bilateral effusions
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135851
CT Pulmonary Hemorrhage – Heterogeneity of the Secondary Lobule
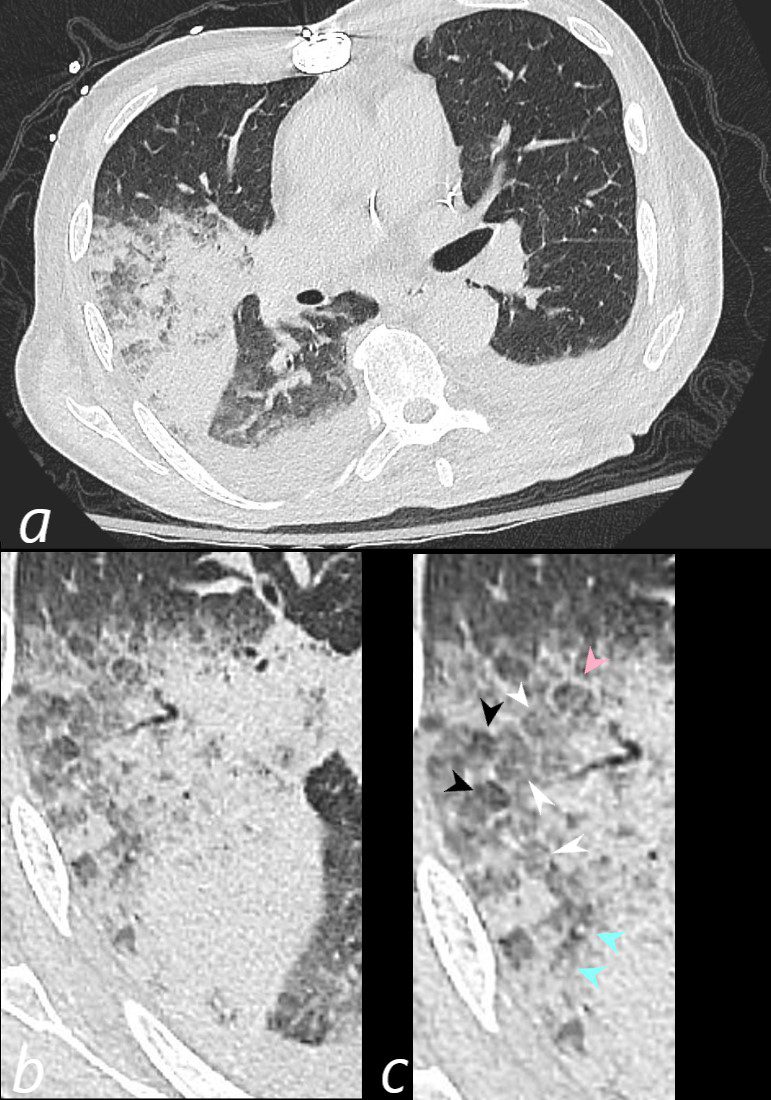
Axial CT at the level below the carina shows medial displacement of the major fissure by a dense right upper lobe consolidation. The mass effect on the major fissure likely results from a hematoma. Anterior to the consolidation there is a combination of ground glass opacity with thickened interlobular septa, and minor region of subsegmental consolidation with air bronchograms, likely resulting from hemorrhage.
The lower panels magnify the regions of the heterogeneity of the secondary lobule with most showing ground glass changes, some normal or with mosaic attenuation (black arrowheads, c), some showing thickened smooth interlobular septa (pink arrowhead, c) and others revealing centrilobular nodules (teal arrowheads, c).
There are bilateral effusions
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135851cL
Heterogeneous Changes in the Secondary Lobules
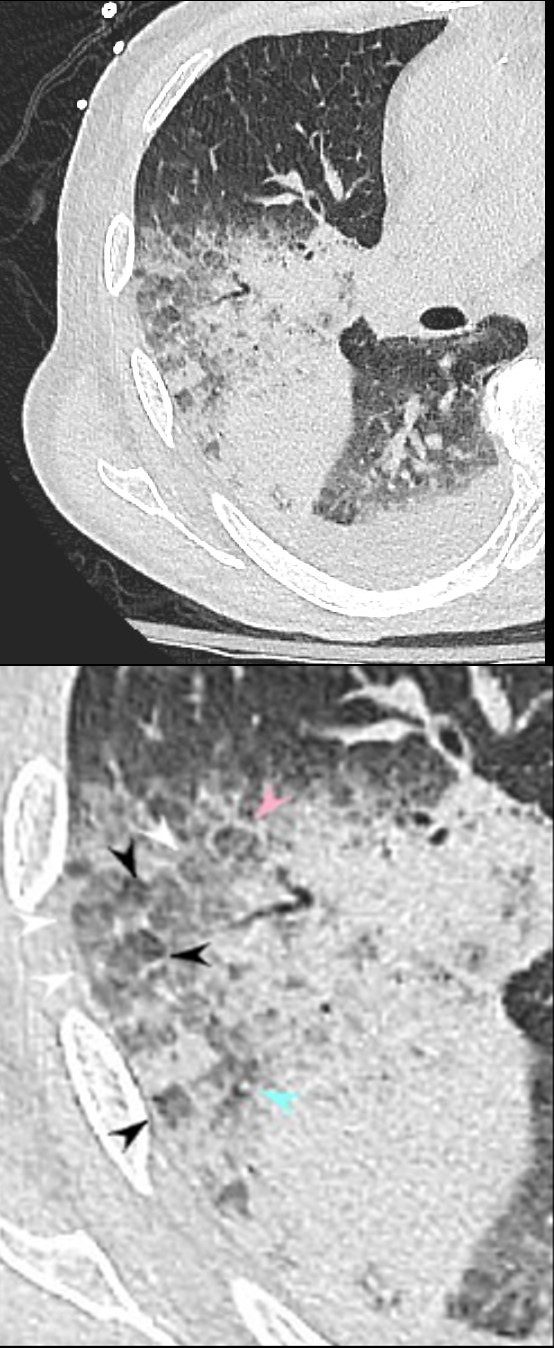
Axial CT at the level below the carina shows medial displacement of the major fissure by a dense right upper lobe consolidation. The mass effect on the major fissure likely results from a hematoma. Anterior to the consolidation there is a combination of ground glass opacity with thickened interlobular septa, and minor region of subsegmental consolidation with air bronchograms, likely resulting from hemorrhage.
The lower panel magnifies the regions of the heterogeneity of the secondary lobule with most showing ground glass changes (white arrowheads), some normal or with mosaic attenuation (black arrowheads), some showing thickened smooth interlobular septa (pink arrowhead), and others revealing centrilobular nodules (teal arrowhead).
There are bilateral effusions
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135852cL
Heterogeneous Changes in the Secondary Lobules
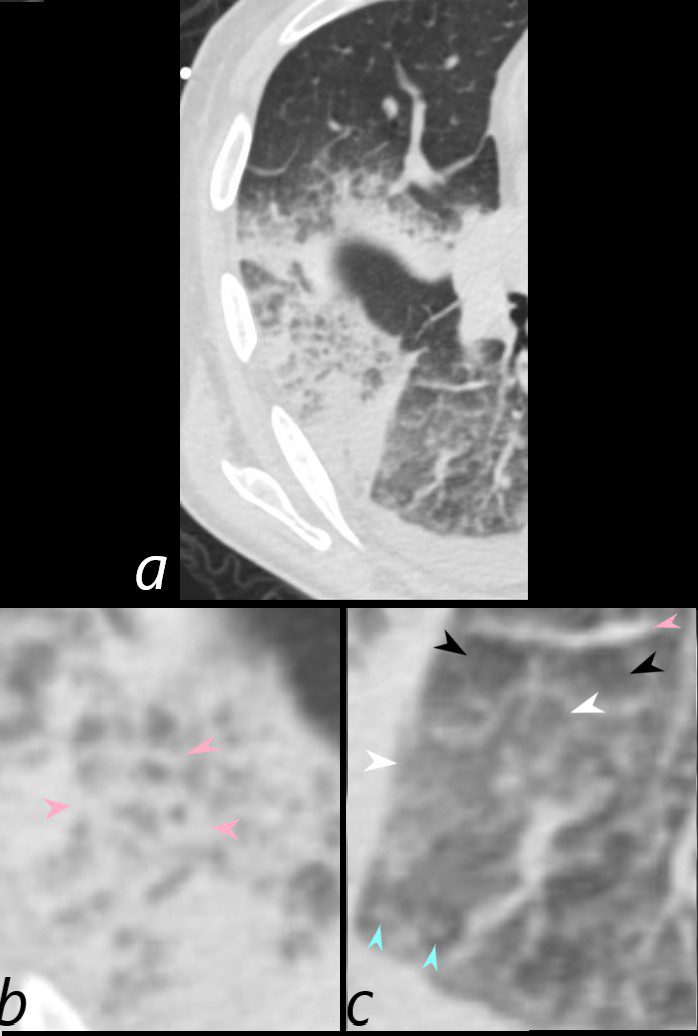
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Axial CT at the level below the carina at the inferior aspect of the hematoma shows heterogenous changes of the secondary lobules. The changes in the post segment of the right upper lobe (b) show significantly thickened interlobular septa (pink arrowheads) and relatively small secondary lobules caused by the compression of the hematoma. The changes in the apical segment of the lower lobe (c) show a combination of secondary lobules with ground glass changes (white arrowheads) some normal or with mosaic attenuation (black arrowheads), some showing mildly thickened smooth interlobular septa (pink arrowheads), and others revealing centrilobular nodules (teal arrowheads).
There is a right sided effusion
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135853cL
Heterogeneous Changes in the Secondary Lobules
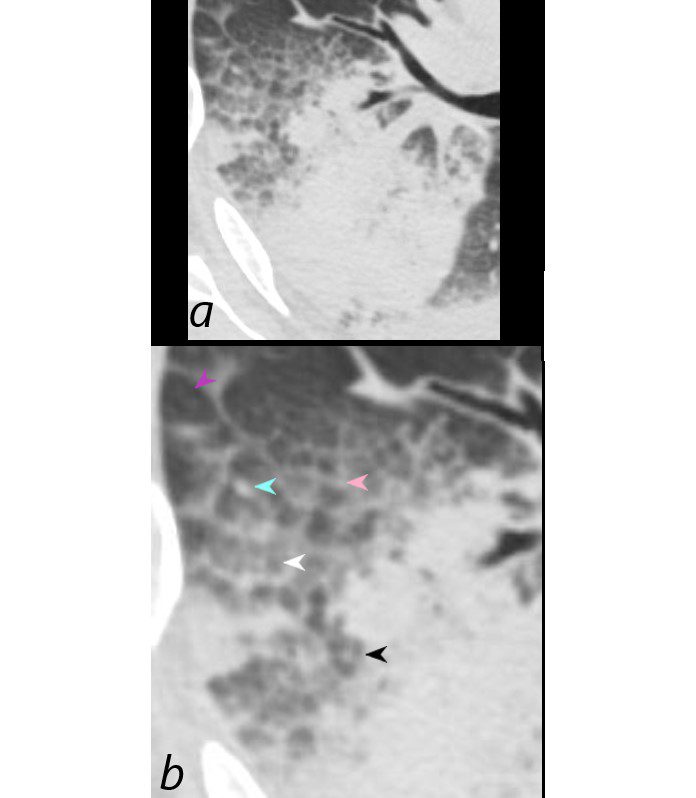
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Axial CT at the level below the carina shows heterogenous changes of the secondary lobules. The changes in the post segment of the right upper lobe (a, and magnified in b) show thickened interlobular septa (pink arrowhead) and mostly relatively small secondary lobules caused by the compression of the hematoma, but also by virtue of their more centrally located position. Compare their size to the larger more peripherally located secondary lobule (purple arrowhead). There is also a combination of secondary lobules with ground glass changes (white arrowhead) some normal or with mosaic attenuation (black arrowheads), some showing mildly thickened smooth interlobular septa (pink arrowhead), and others revealing centrilobular nodules (teal arrowhead).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135854cL
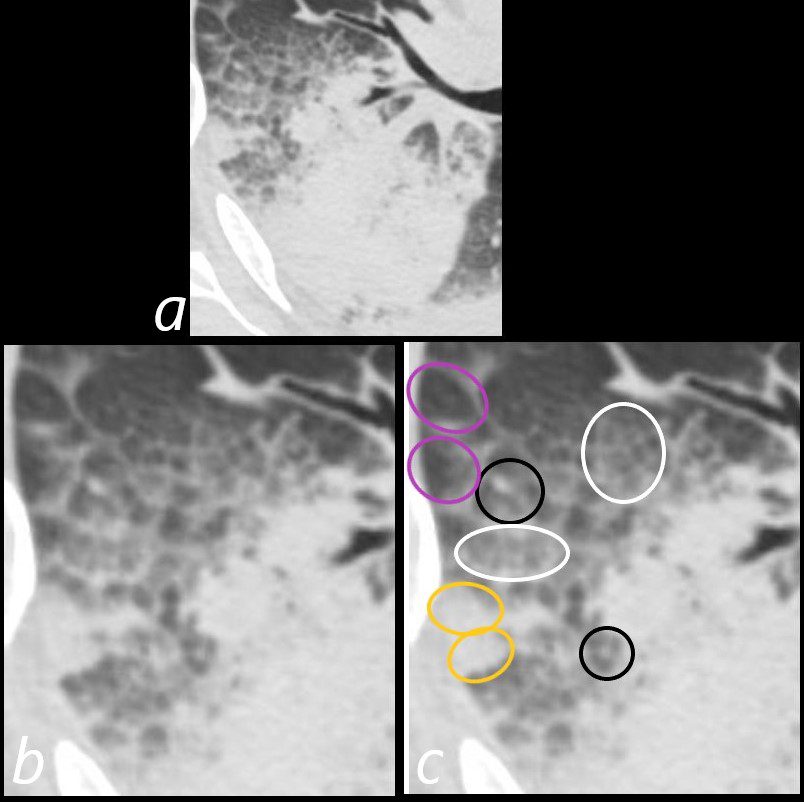
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Axial CT at the level below the carina shows heterogenous changes of the secondary lobules. The changes in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe (a magnified below in b and c ) and show secondary lobules with ground glass changes (white rings) It is difficult to distinguish those with normal lung parenchyma and those with mosaic attenuation. It is hypothesized that those with prominent centrilobular nodules (black rings c) more than likely represent mosaic attenuation due to small airway disease. The lower density secondary lobules which do not have a prominent centrilobular nodule (c, purple rings), may either reflect normal parenchyma or mosaic attenuation. The orange rings likely reflect consolidation in side-by-side secondary lobules.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135854cL01
Pulmonary Hemorrhage RLL Bronchovascular Consolidation
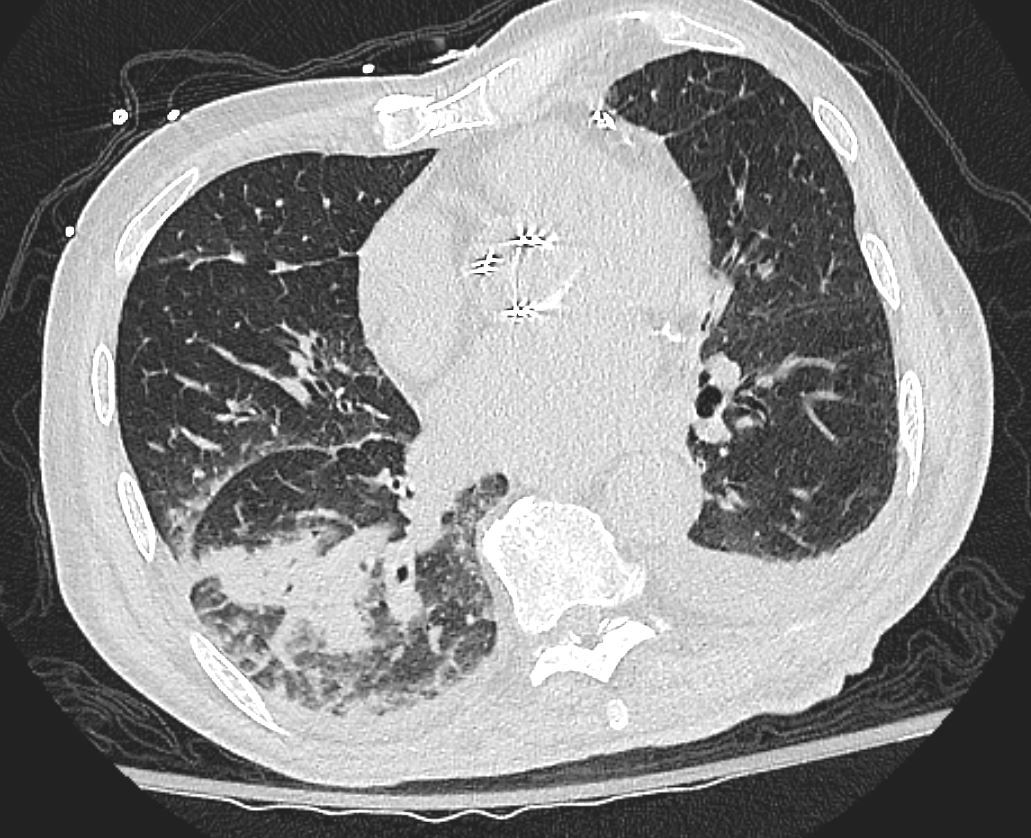
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Axial images through the apical segment of the right lower lobe shows a bronchovascular consolidation and some interstitial thickening. Examination of the heart shows left atrial enlargement aortic valve replacement and CABG clips along the LAD. There are bilateral effusions left greater than right.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135855
Pulmonary Hemorrhage Consolidation and Hematoma
RUL and RLL
Displacement of the Major Fissure
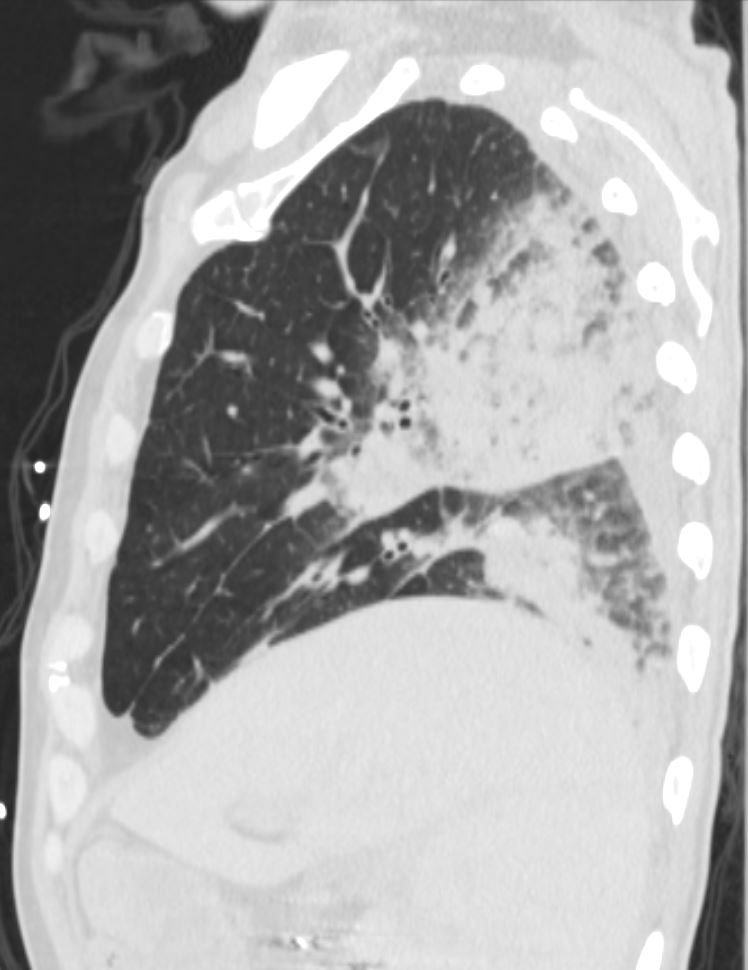
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Sagittal images of the right side show inferior displacement of the major fissure causes by mass effect of the hematoma and consolidation in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe.
The right lobe also shows a region of consolidation and peripherally shows secondary lobules with ground glass changes, thickened interlobular septa and prominent secondary nodules
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135857
Pulmonary Hemorrhage
Consolidation Hematoma and Ground Glass
Changes in the Secondary Lobules
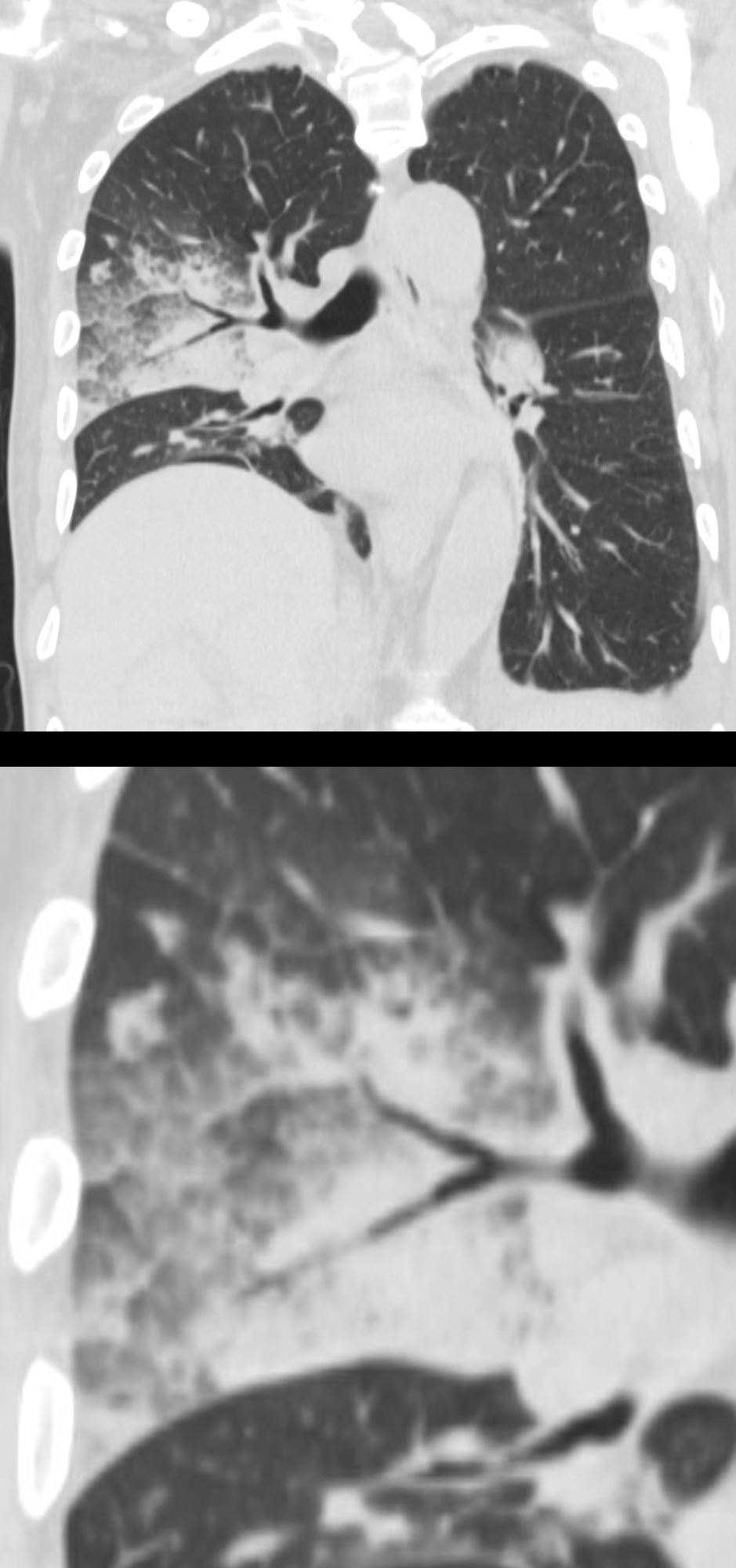
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Coronal images focused on the right side and magnified in the lower panel show heterogenous changes of the secondary lobules including thickened interlobular septa with ground glass changes, and some normal or with mosaic attenuation. The consolidation in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe manifests as an air bronchogram
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135859c
Pulmonary Hemorrhage Hematoma
Fissural Displacement Ground Glass Changes
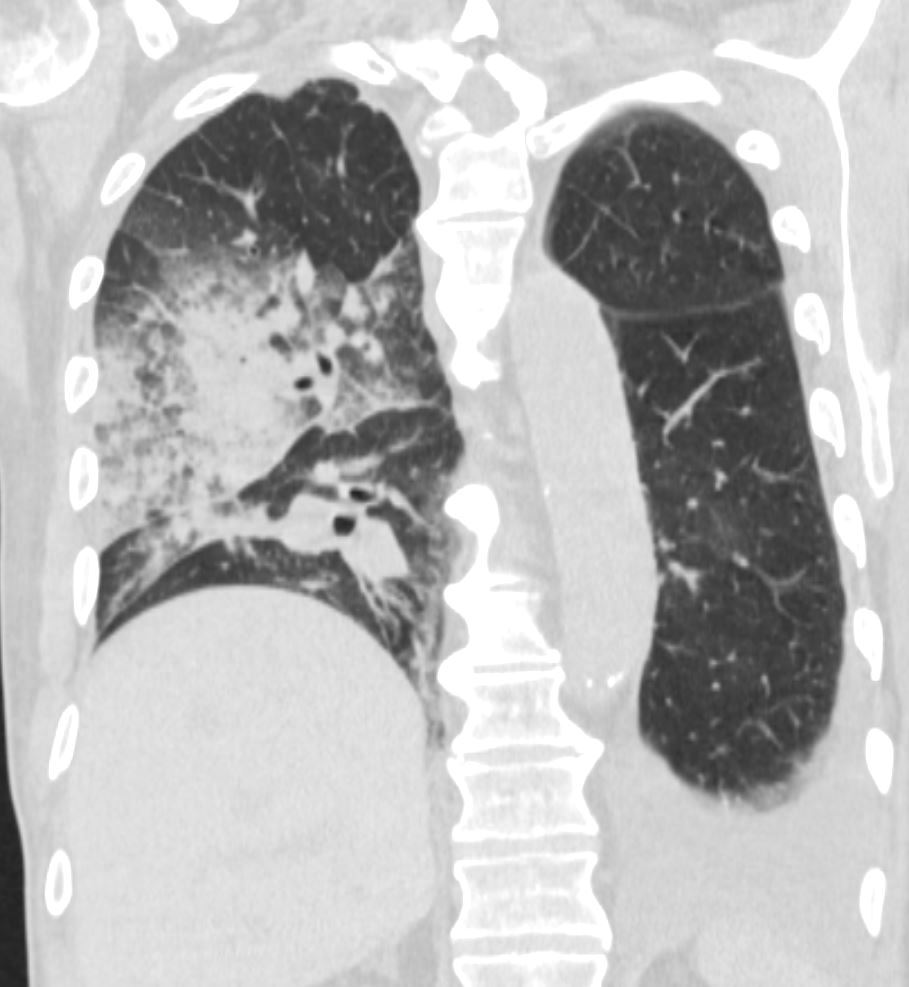
Coronal CT of the posterior lung fields shows inferior displacement of the major fissure by a dense right upper lobe consolidation. The mass effect on the major fissure likely results from a hematoma. Lateral to the consolidation there is a combination of ground glass opacity. There is elevation of the right hemidiaphragm. Left sided pleural effusion is present
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135860
Pulmonary Hemorrhage Hematoma Consolidation
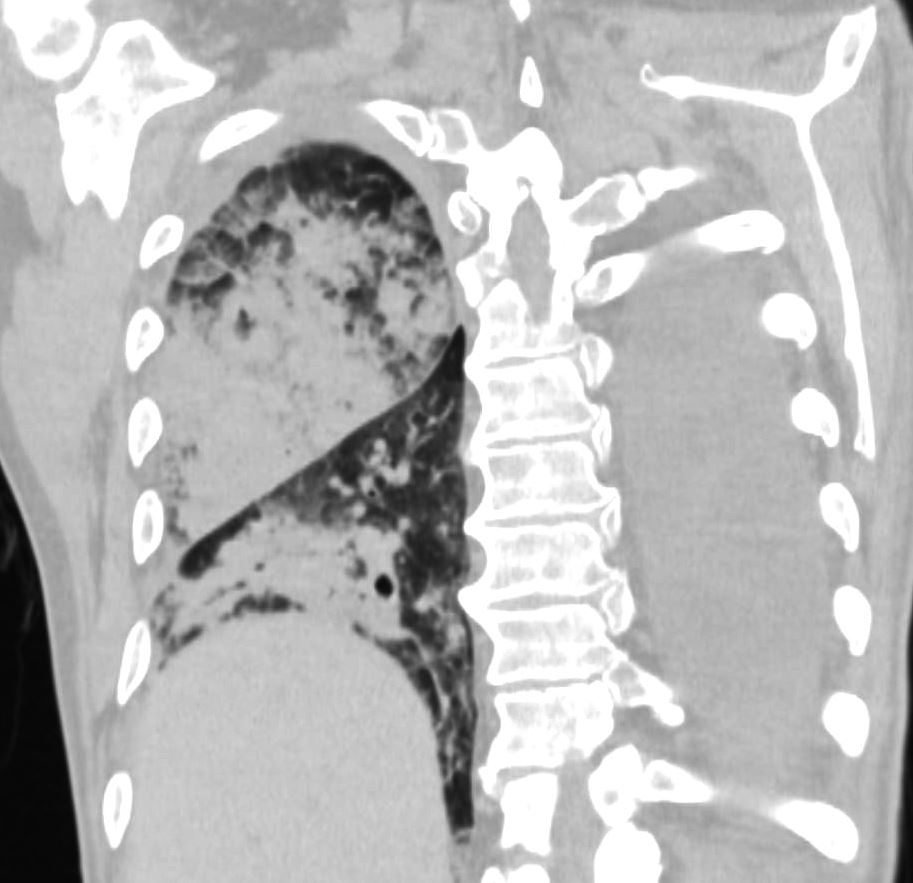
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Coronal CT of the posterior lung fields shows a dense right upper lobe consolidation with minor ground glass changes. There is also a region of consolidation in the right lower lobe with consolidation Elevation of the right hemidiaphragm is noted. Left sided pleural effusion is present
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135861
Despite the lack of fever and WCC he was empirically started on antibxs for suspected PNA c/b hemoptysis in setting of anticoagulation. He underwent bronchoscopy with BAL showing blood tinged sputum w/no foreign body
Completed a 5 day course of antibxs for suspected bacterial pneumonia.
One of two BAL cxs obtained with bronch grew 1+ normal upper resp tract flora and 1+ candida. No acid fast bacilli observed on BAL cx.
lungs 165Lu Lung Hemorrhage on Anticoagulation following Trauma
