A 36-year-old male with a known diagnosis of asthma, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA).
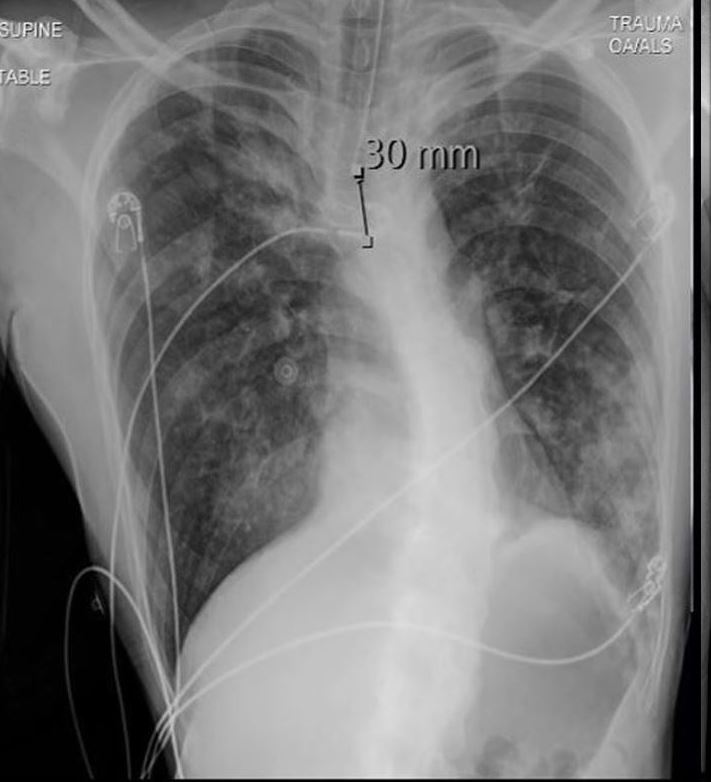
A 36-year-old male with a known diagnosis of asthma, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA). Frontal CXR shows a finger-in-glove appearance in the right apex (a) indicative of bronchial mucoid impaction. Additionally, there are diffuse nodular opacities scattered throughout both lungs. These nodular opacities most likely represent mucus plugging and peribronchial inflammation due to the allergic response associated with ABPA. The differential diagnosis includes endobronchial spread of infection and aspiration pneumonia, though the constellation of findings, including the allergic history, suggests ABPA as the most likely cause.
Comment:
The finger-in-glove sign in the right apex is characteristic of ABPA, reflecting bronchiectasis with mucoid impaction and endobronchial fungal infection due to Aspergillus species. The nodular opacities are consistent with mucus plugging and allergic peribronchial inflammation, which are hallmarks of ABPA.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net (b12311-00).(309Lu)
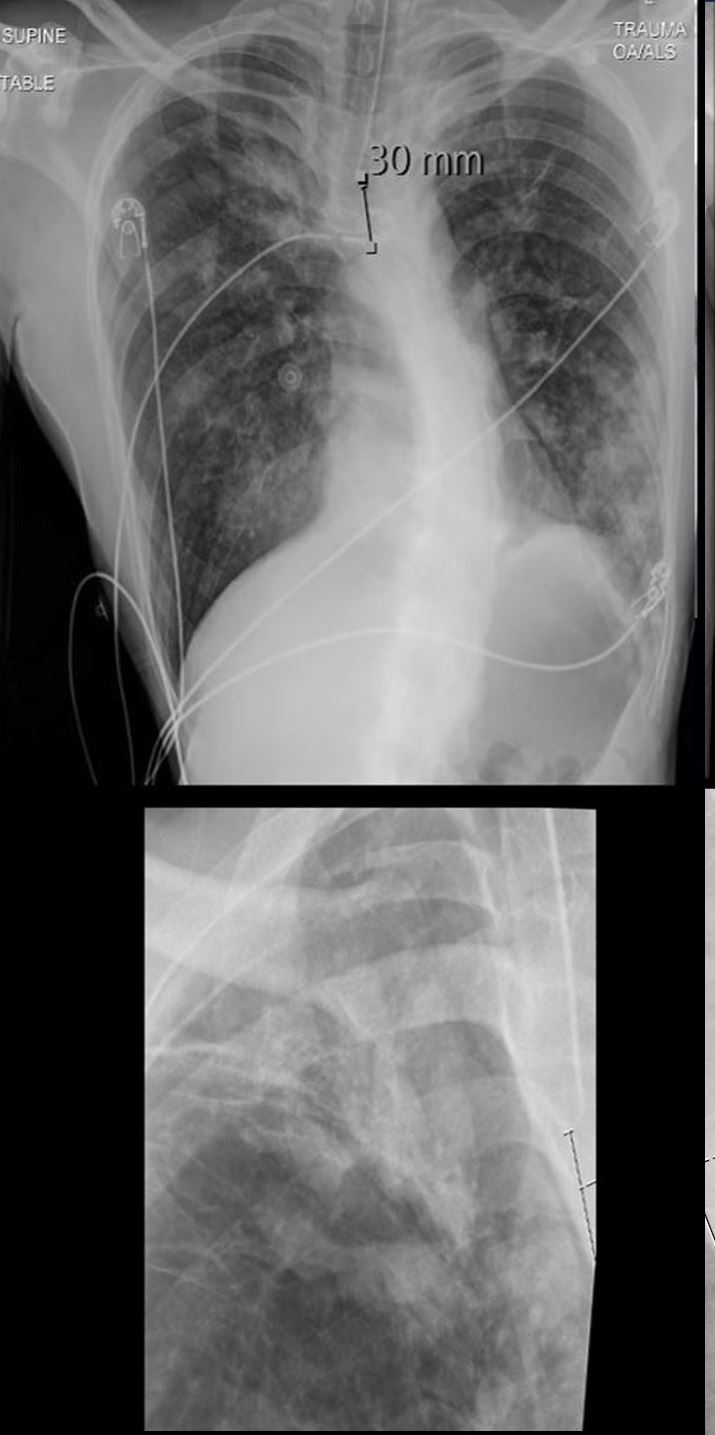
A 36-year-old male with a known diagnosis of asthma, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), and aspergillosis. CXR of the lungs in a frontal projection shows a finger-in-glove appearance in the right apex (a, magnified in b), indicative of bronchial mucoid impaction. Additionally, there are diffuse nodular opacities scattered throughout both lungs. These nodular opacities most likely represent mucus plugging and peribronchial inflammation due to the allergic response associated with ABPA. The differential diagnosis includes endobronchial spread of infection and aspiration pneumonia, though the constellation of findings, including the allergic history, suggests ABPA as the most likely cause.
Comment:
The finger-in-glove sign in the right apex is characteristic of ABPA, reflecting bronchiectasis with mucoid impaction and endobronchial fungal infection due to Aspergillus species. The nodular opacities are consistent with mucus plugging and allergic peribronchial inflammation, which are hallmarks of ABPA.
Credit:
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net (b12311-01).(309Lu)
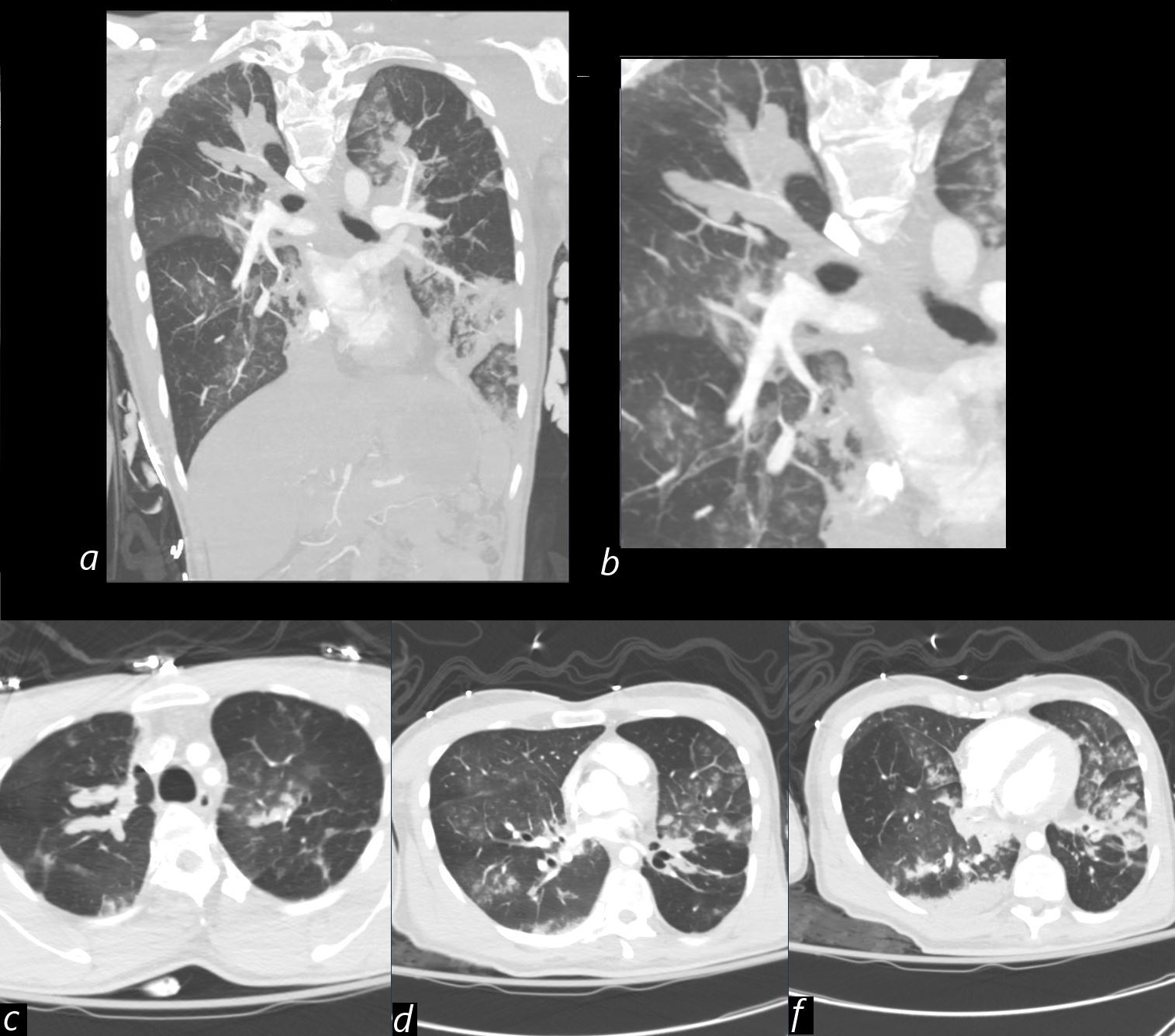
CT of the lungs in the coronal projection (a magnified in b) show impacted and distended right upper lobe airways with “finger in glove ” morphology. There is a consolidation in the left lower lobe.
Axial images in, at the level apices (a) , shows the finger-in-glove appearance, and also shownin image e, in the posterior segment of the left upper lobe. consistent with mucoid impaction and bronchiectasis typical of ABPA. Images d and e, show scattered tree-in-bud patterns and ground glass opacities, . These findings are characteristic of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA),
Comment
The finger-in-glove sign and tree-in-bud opacities seen in ABPA reflect central bronchiectasis with mucoid impaction, often associated with allergic reactions to Aspergillus species
Differential diagnosis includes endobronchial spread of infection and aspiration pneumonia.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net (b12311-02 )(309Lu)
