Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0736a01
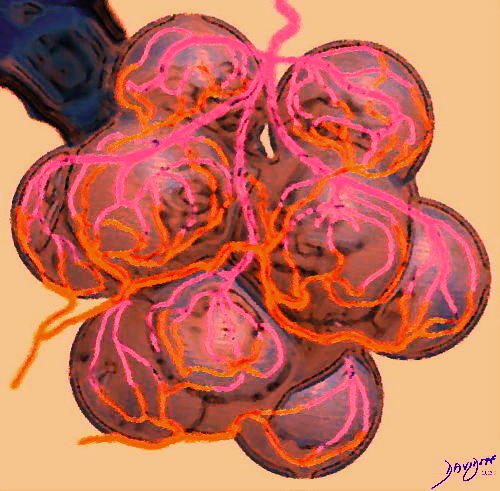

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
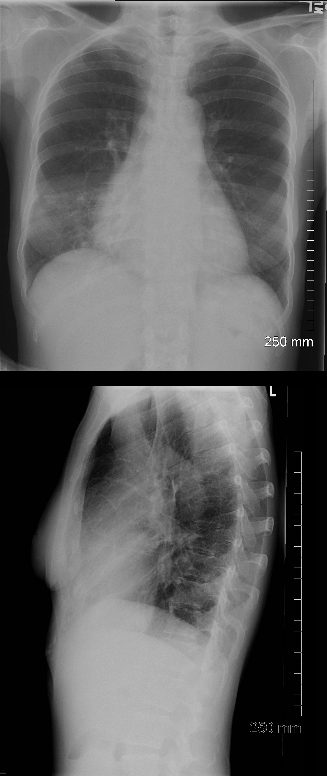
PA and lateral chest X-ray of a 54 year old female with SLE shows bibasilar ground glass infiltrates.
The heart is slightly enlarged and the region of the IVC on the lateral examination is also enlarged
Ashley Davidoff MD
key word
acute pneumonitis
SLE
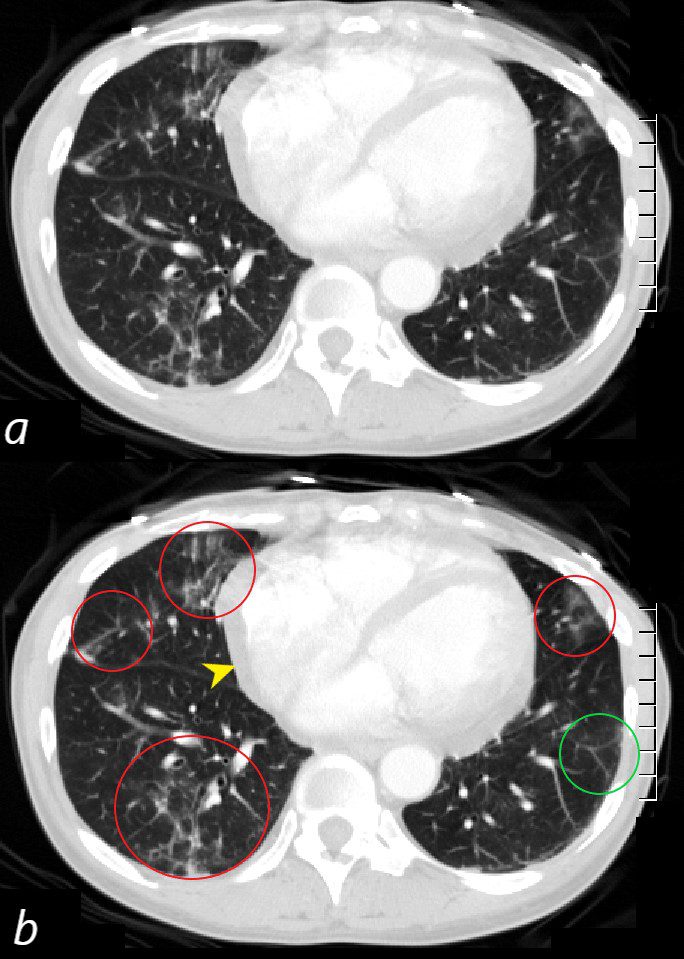
CT scan through the 4 chambers of the heart using lung windows is from a a 54 year old female with SLE. Recent CXR showed bibasilar ground glass infiltrates.
The scan shows basilar multicentric infiltrates with elements of ground glass change and small airway wall thickening (red circles in the right lower lobe middle lobe and lingula, as well as interlobular septal thickening (green circle) in the lateral basal segment of the left lower lobe. A small pericardial effusion is present (yellow arrowhead)
Ashley Davidoff MD
key words
SLE
acute pneumonitis
pericardial effusion
Acute alveolar pneumonitis, also known as acute interstitial pneumonitis, is a type of lung inflammation that affects the small air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. It is a severe form of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) that can cause rapid breathing, low blood oxygen levels, and respiratory failure.
The condition can be caused by various factors, including viral infections, bacterial infections, and exposure to toxins or other irritants. Symptoms of acute alveolar pneumonitis include shortness of breath, cough, fever, fatigue, and chest pain.
Diagnosis is typically made through imaging tests, such as a chest X-ray or CT scan, and a physical examination. Treatment may include oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and medications such as corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Acute alveolar pneumonitis can be a life-threatening condition and requires immediate medical attention.
