42651c
keywords lung chest

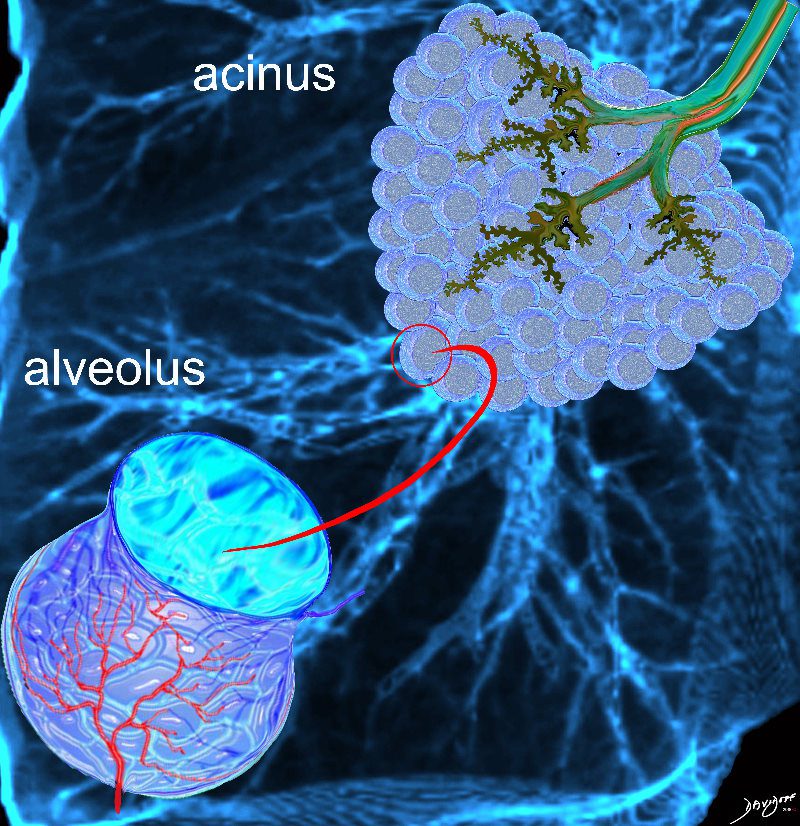
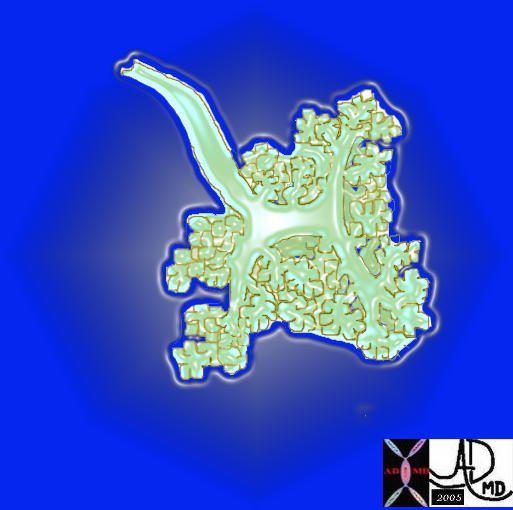
This artistic rendition of the small parts of the lung shows the beginning of the peripheral system just before it enters the acinus. This duct is called the terminal duct and it is the last part of the ductal system that has no ability for gas exchange. After its first division, the bronchioles become the respiratory bronchioles, and they are the first in the system to have an ability to both transport the gases as well as enable gas exchange.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
lungs- lo res 0002
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0059
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net lungs-0056

This artistic rendition of the small parts of the lung shows the beginning of the peripheral system just before it enters the acinus. This duct is called the terminal duct and it is the last part of the ductal system that has no ability for gas exchange. After its first division, the bronchioles become the respiratory bronchioles, and they are the first in the system to have an ability to both transport the gases as well as enable gas exchange.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
32645b04b05.8s
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
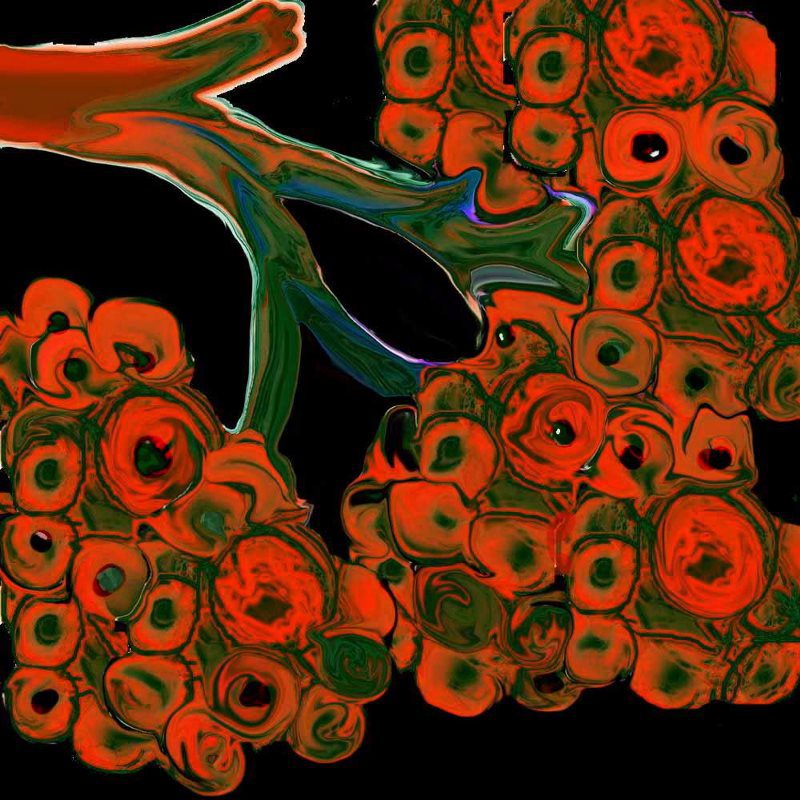
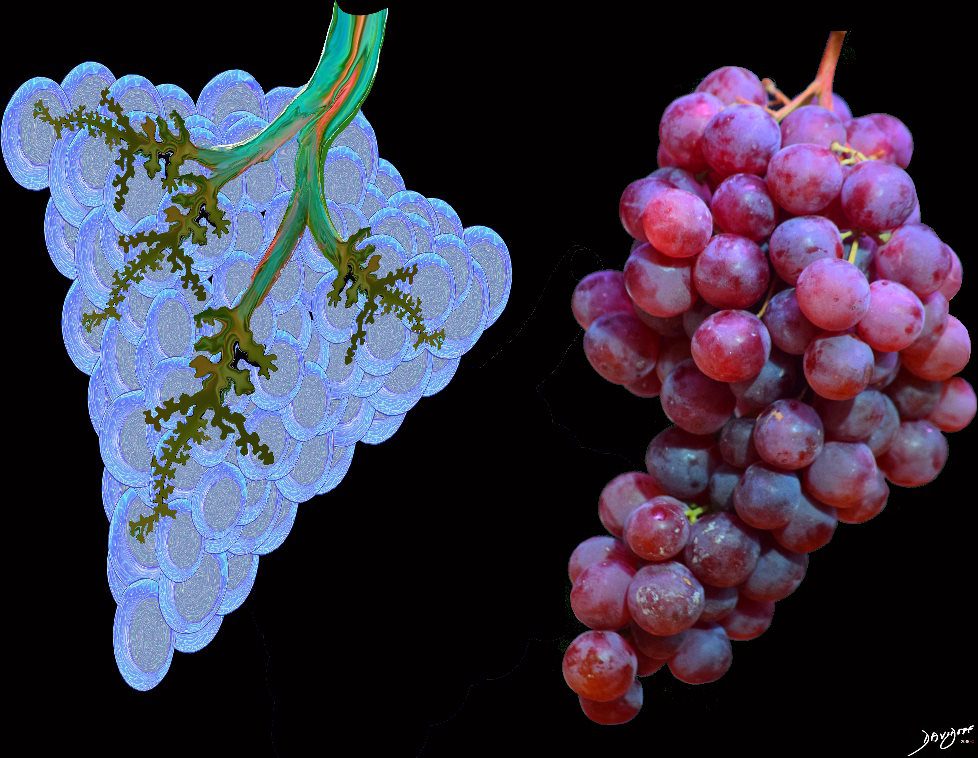
The acinus with its arborizations is shaped more like a bunch of grapes.
Courtesy of: Ashley Davidoff, M.D 42650
TheCommonVein.net
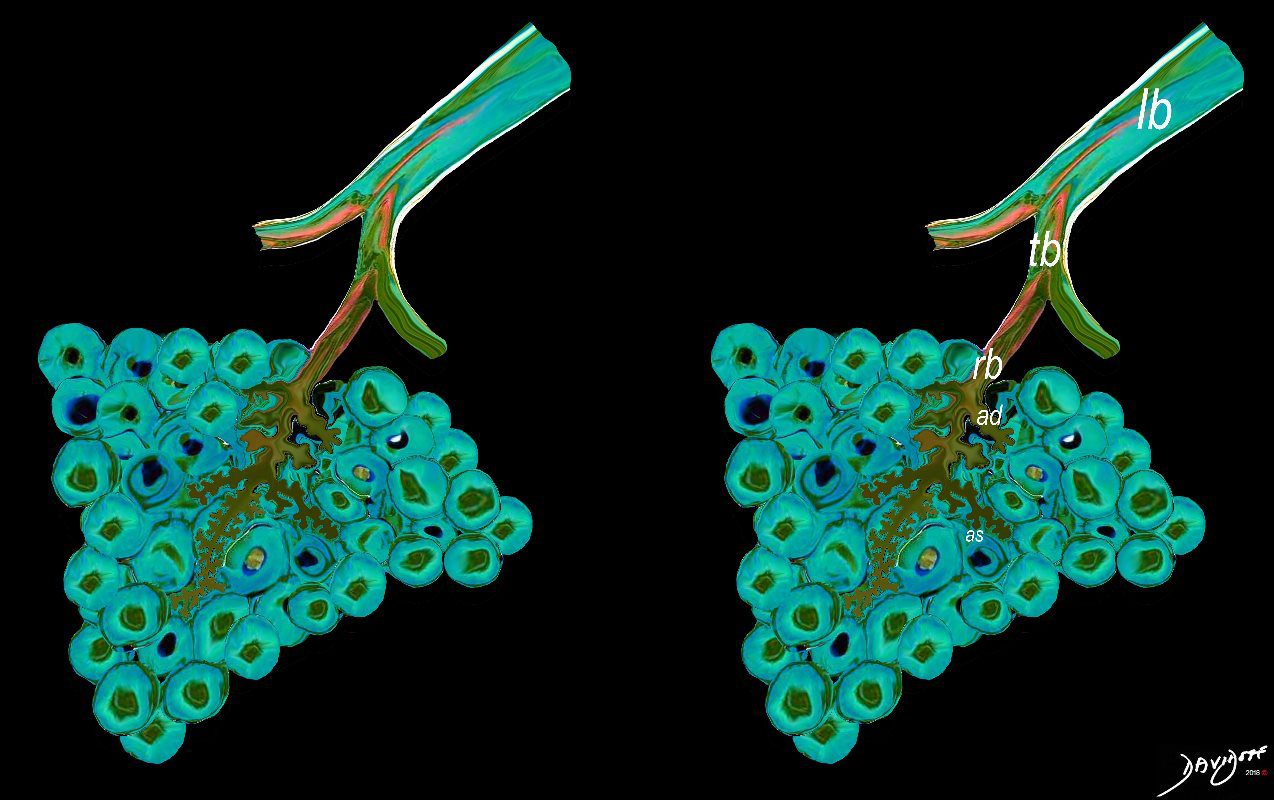
The acinus is defined as a unit of lung consisting of a single first order respiratory bronchiole that subtending a cluster of alveoli reminiscent of a bunch of grapes or berries (acinus in Latin means berry) . The lobular bronchiole (lb) branches into the terminal bronchiole (tb), which then branches into the first order respiratory bronchiole (rb). Subsequent branching after the respiratory bronchiole, includes in order, the alveolar duct (ad), alveolar sac (as), and then finally the berry like alveoli.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff 2019
lungs-0030-low res
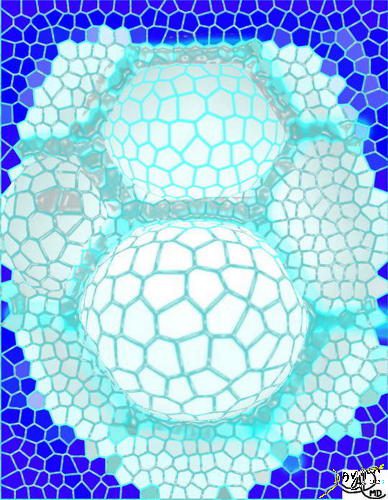
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0008

A drawing showing the normal acinus in teal and the abnormal emphysematous acinus in green characterised by destruction of the septal walls, enlargement of the alveoli, and loss of elasticity. The absence of involvement of the respiratory bronchiole makes the pathological diagnosis of centrilobular emphysema. Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net 32645
