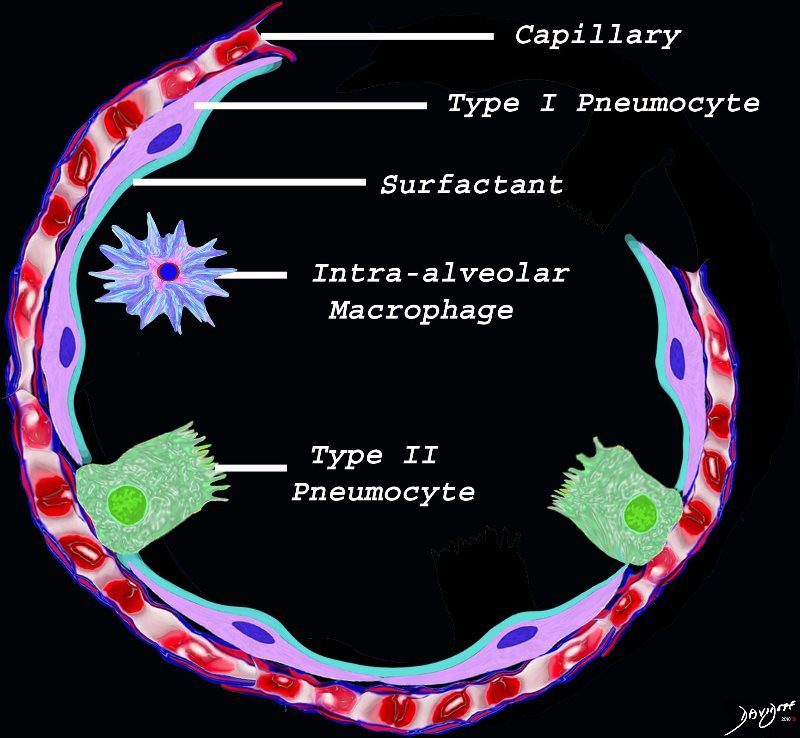
The diagram shows the lining of the normal alveolus composed of type 1 pneumocyte squamous in nature and the cuboidal cell (type pneumocyte) which rest on a lamina propria, and basement membrane (not shown) shared with the inner endothelial layer of the capillary. Intra-alveolar macrophage lies within the alveolar lumen
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
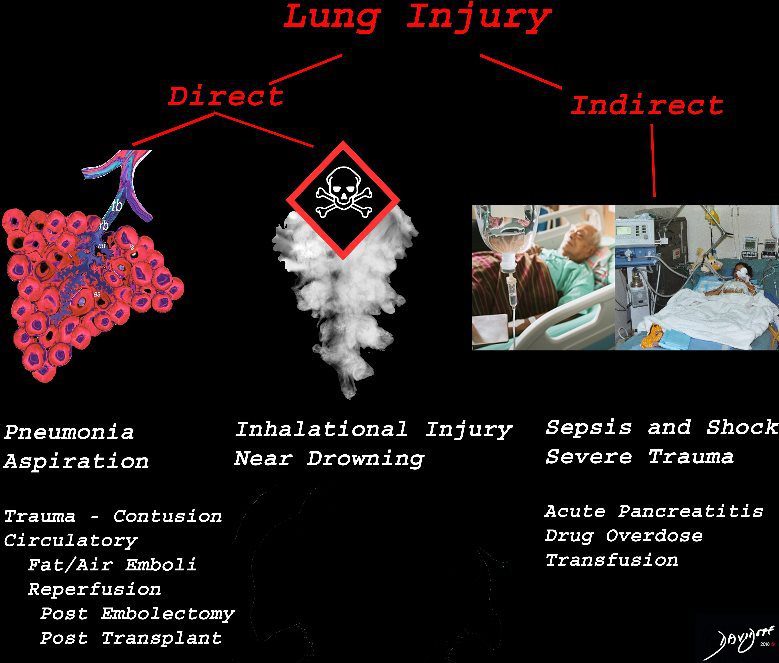
The lung is injured either by direst causes most commonly pneumonia, aspiration or from inhalation of toxic substances. Severe systemic illnesses, most commonly sepsis with shock, and severe trauma are considered indirect causes.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
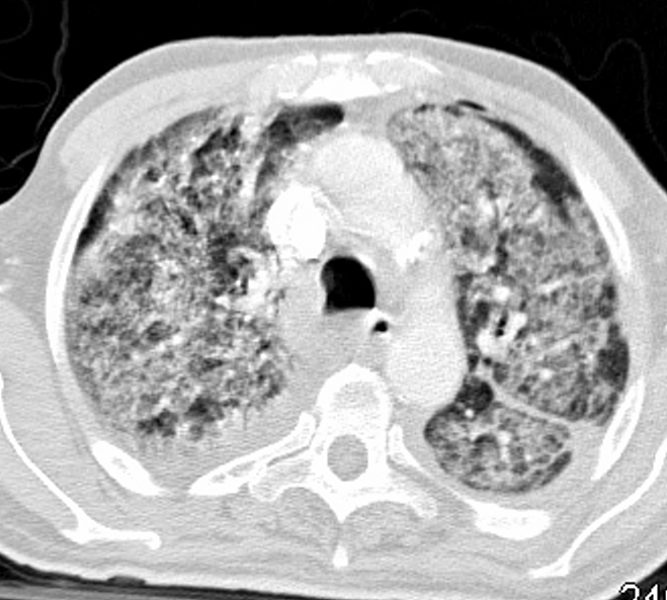
79M
Patchy Diffuse Ground Glass Pattern
Dominant – Central Location
Relative Lower Lobes and Subpleural Sparing
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
134294
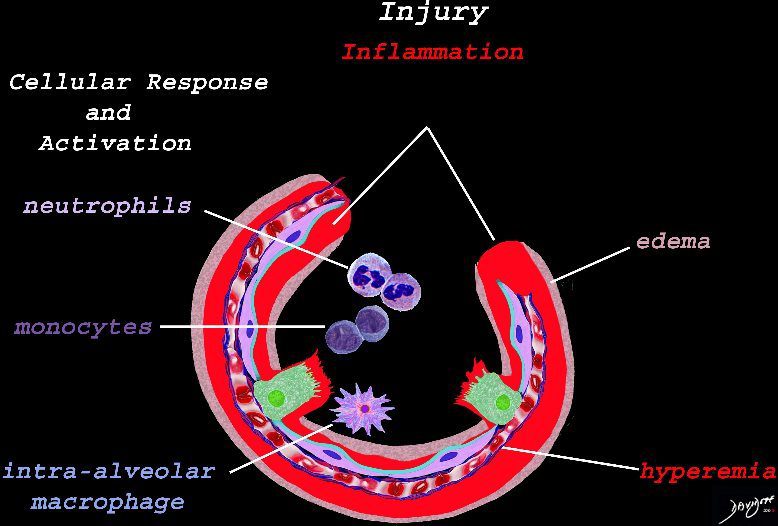
The initial injury results in an acute severe inflammatory response consisting hyperemia , edema with migration initially of neutrophils in the first 6-24 hours followed by monocytes (24-48hours). The intra -alveolar macrophages are activated.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
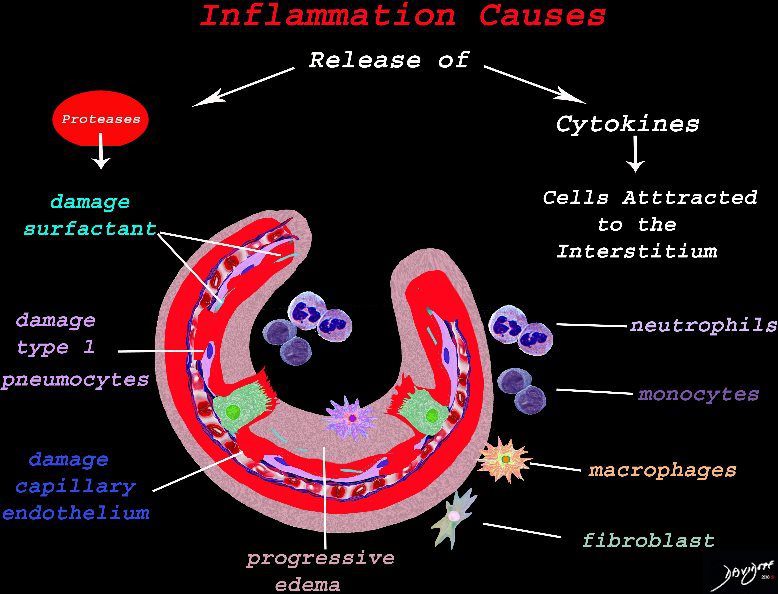
The cells of the immune system release cytokines, chemotactic agents and proteases. Immune cells , macrophages and fibroblasts are attracted to the interstitium. Some of proinflammatory agents are toxic to the cell lining causing damage to the surfactant, type 1 pneumocytes and the capillary endothelium. There is progressive edema.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
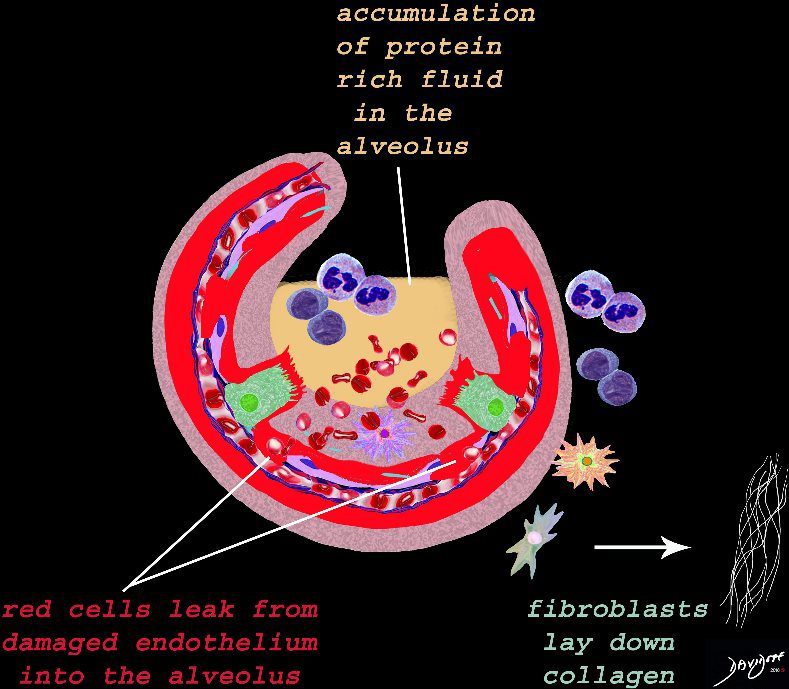
The damage to the endothelium of the capillary results in bleeding into the alveoli. The severe tissue damage and fluid exudation results in protein rich intra-alveolar fluid . The fibroblasts start to lay down collagen as part of the early repair process
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

A hyaline membrane evolves covering the damaged surface of the alveolus. This impedes gas exchange
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
ARDS -Anteroposterior Density Gradient
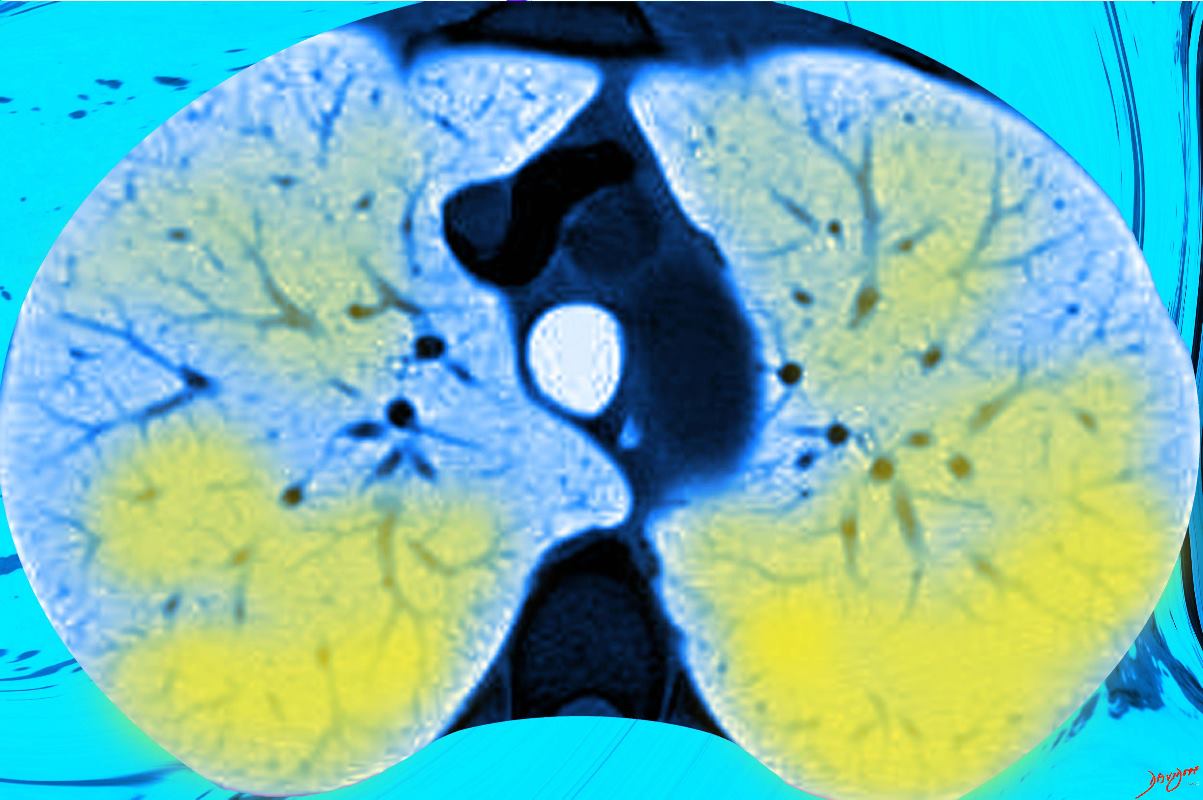
Since the patient is mostly in a supine position in the ICU setting the disease is distributed based on gravitational forces with the more dense consolidation in the most dependent regions posteriorly and less dense with ground glass changes anteriorly. Anteriorly more normal or even hyperexpanded lung is present.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0786
A Memory Image
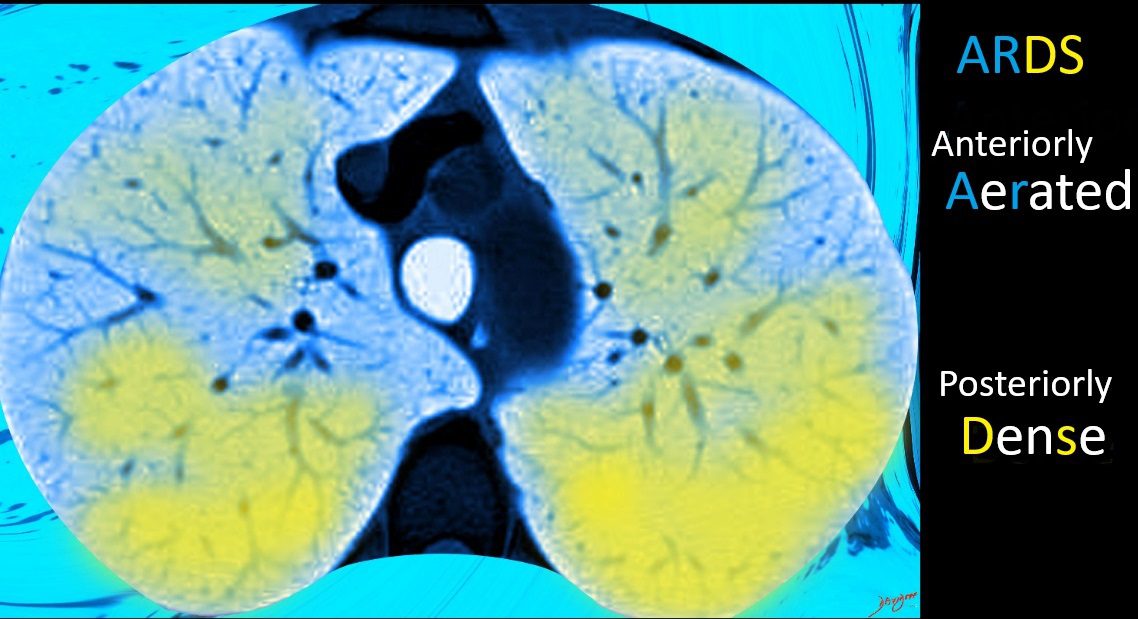
A Memory Image for ARDS
The anterior aspect of a CT in axial projection shows AeRation and the posterior aspect shows increase DenSity due to the gravitational effect of the fluid in the lungs
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0786-01L
