Aspergillus Infection
Types
invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA),
angioinvasive aspergillosis:
chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA), and
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA).
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) and angioinvasive aspergillosis are related terms, and they are often used interchangeably to describe a severe form of Aspergillus infection involving the lungs. However, there is a subtle distinction between the two terms:
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis (IPA): a broader term that encompasses Aspergillus infections that invade the lung tissue, causing tissue destruction and inflammation. It includes a spectrum of manifestations ranging from localized invasion to more disseminated and severe forms.
formation of nodules, infiltrates, and, in some cases, cavities within the lung tissue.
-
- Angioinvasive Aspergillosis: is a specific subset of IPA characterized by the invasion of blood vessels by Aspergillus hyphae leading to vascular thrombosis and tissue infarction.
Structures Involved
- Bronchi and Bronchioles
- Blood Vessels
- Alveoli
- Pleura
Structural Changes
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis (IPA):
- Nodules
- Infiltrates:
- Cavities
- Angioinvasive aspergillosis:
- Angioinvasion:
- invade and grow within blood vessels, including arteries and veins.
- Vascular Thrombosis:
- tissue ischemia.
- Tissue Infarction:
- Dissemination:
- systemic infection.
- Clinical Consequences:
- may include
- respiratory distress,
- organ failure, and a
- high mortality,
- (especially in immunocompromised individuals).
- may include
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA):
- Bronchiectasis:
- Chronic Inflammation:
- fibrosis, scarring, and
- Cavities:
- cavitation may occur, leading to
- cystic spaces
- Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA):
- Bronchiectasis:
- Fungal Plugs: Mucus plugs containing Aspergillus hyphae may obstruct the airways, contributing to bronchial changes.
- Parenchymal Infiltrates:
It’s important to note that the structural changes in the lung can vary among individuals, and the severity of the changes depends on factors such as the type of Aspergillus infection, duration of infection, and the individual’s immune response. Imaging studies, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, play a crucial role in visualizing these structural changes and guiding the diagnosis and management of Aspergillus infections.

Artistically rendered by Ashley Davidoff from original CDC image
TheCommonVein.net
- Aspergilloma
-
- Fungus ball in the lungs
- Does not spread
- Can be asymptomatic
-
- Allergic Bronchopulmonary Pulmonary Aspergillosis
-
- allergic response in patients with
- asthma
- cystic fibrosis
- bronchiectasis
- allergic response in patients with
-
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)
-
- colonize
- cavities in the lungs,
- aspergillomas may also be present in the lungs.
- colonize
-
- Invasive Aspergillosis including Angioinvasive Aspergillosis:
-
- serious infection,
- may be systemic
- immunocompromised
-
- Aspergillosis is a
- fungal infection of usually the lungs,
- caused by the
- genus Aspergillus,
- a common mould that is
- breathed in
- does not usually affect most people.
- most commonly
- Aspergillus fumigatus and
- Aspergillus flavus,
- genus Aspergillus,
- Predisposing factors
- lung diseases such as
- asthma,
- cystic fibrosis
- tuberculosis,
- immunocompromised
- stem cell or organ transplant,
- steroids
- chemotherapy
- lung diseases such as
- Pathogenesis
- acute forms
- immunocompromised
- chronic form
- asthma
- copd
- cystic fibrosis,
- tuberculosis
- sarcoidosis
- chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA),
- aspergilloma, or
- allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA).
- or a combination
- eg ABPA and CPA
- or aspergilloma can progress to CPA.
- acute forms
- Clinical
- Signs and symptoms
- Aspergilloma – fungus ball in the lungs
- chest pain
- hemoptysis
- cause no symptoms
- incidental discovery on a chest X-ray, or it may cause repeated coughing up of blood, chest pain, and occasionally severe, even fatal, bleeding.[2] A rapidly invasive Aspergillus infection in the lungs often causes cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
- Aspergilloma – fungus ball in the lungs
- Signs and symptoms
Poorly controlled aspergillosis can disseminate through the blood to cause widespread organ damage.[2] Symptoms include fever, chills, shock, delirium, seizures, and blood clots. The person may develop kidney failure, liver failure (causing jaundice), and breathing difficulties.[2] Death can occur quickly.
In addition to the symptoms, an X-ray or computerised tomography (CT) scan of the infected area provides clues for making the diagnosis. Whenever possible, a doctor sends a sample of infected material to a laboratory to confirm identification of the fungus.[citation needed]
Cause[edit]
Aspergillus 235 mags 3X3 copy
Aspergillosis is caused by Aspergillus, a common mold, which tends to affect people who already have a lung disease such as cystic fibrosis or asthma, or who cannot fight infection themselves.[3] The most common causative species is Aspergillus fumigatus.[18]
Risk factors[edit]
-
- usually Aspergillus fumigatus
- aspergilloma (saprophytic/noninvasive aspergillosis
- allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
- invasive aspergillosis
- subacute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
- Chronic Aspergillosis
- airway invasive aspergillosis
- (or bronchopneumonic aspergillosis)
- angioinvasive aspergillosis
- obstructive bronchopulmonary aspergillosisOther described groupings include 6:
Aspergilloma
- usually Aspergillus fumigatus

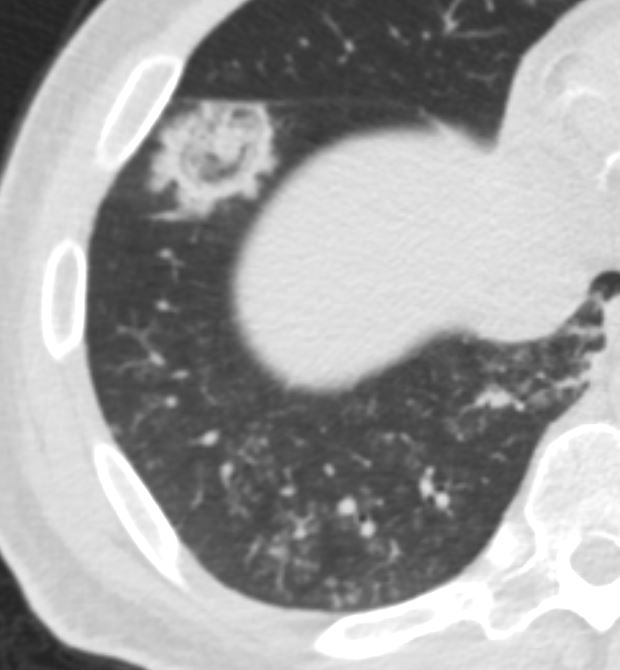
Ashley Davidoff MD

Source
Signs in Thoracic Imaging
Journal of Thoracic Imaging21(1):76-90, March 2006
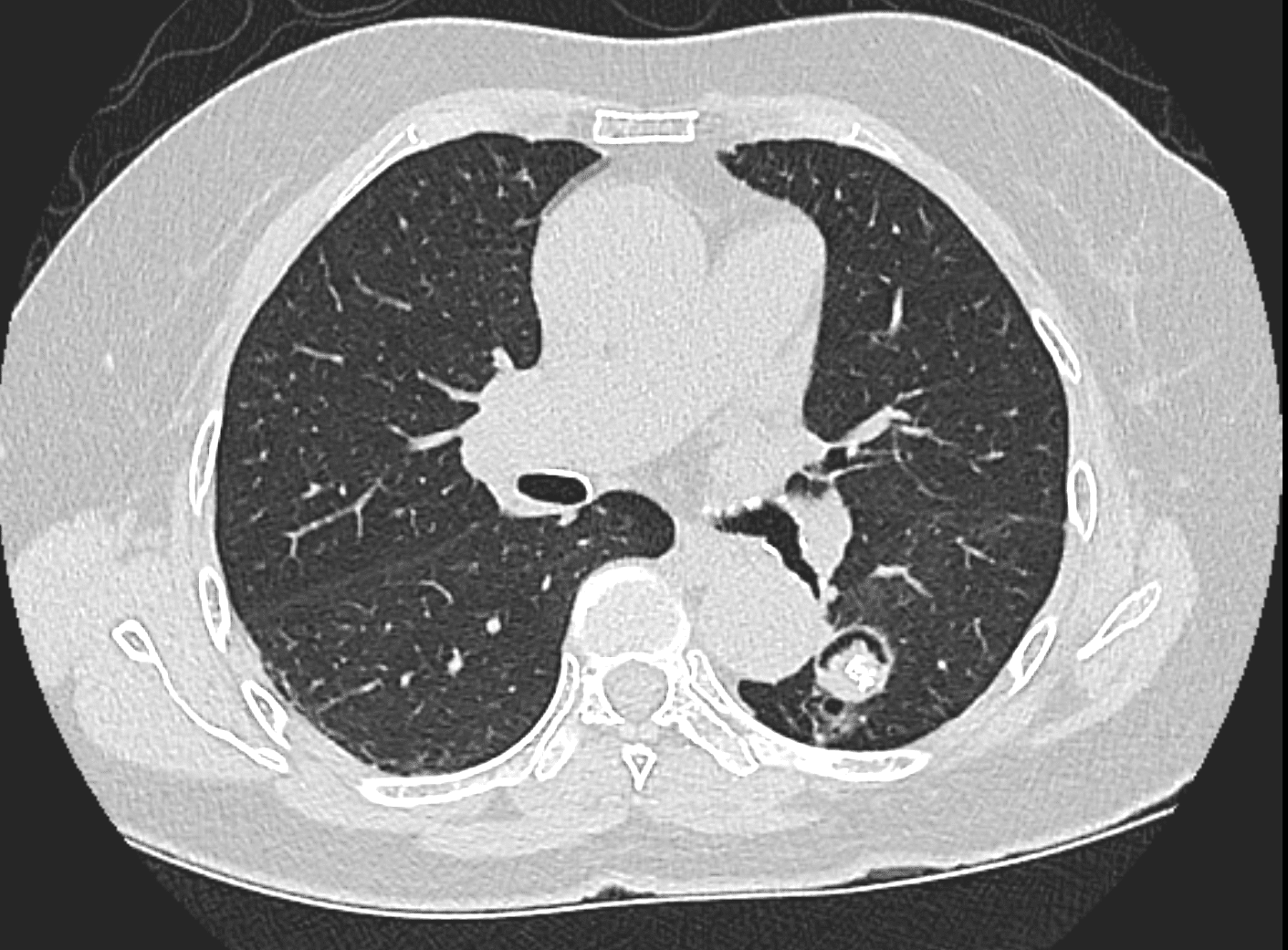
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
ABPA Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
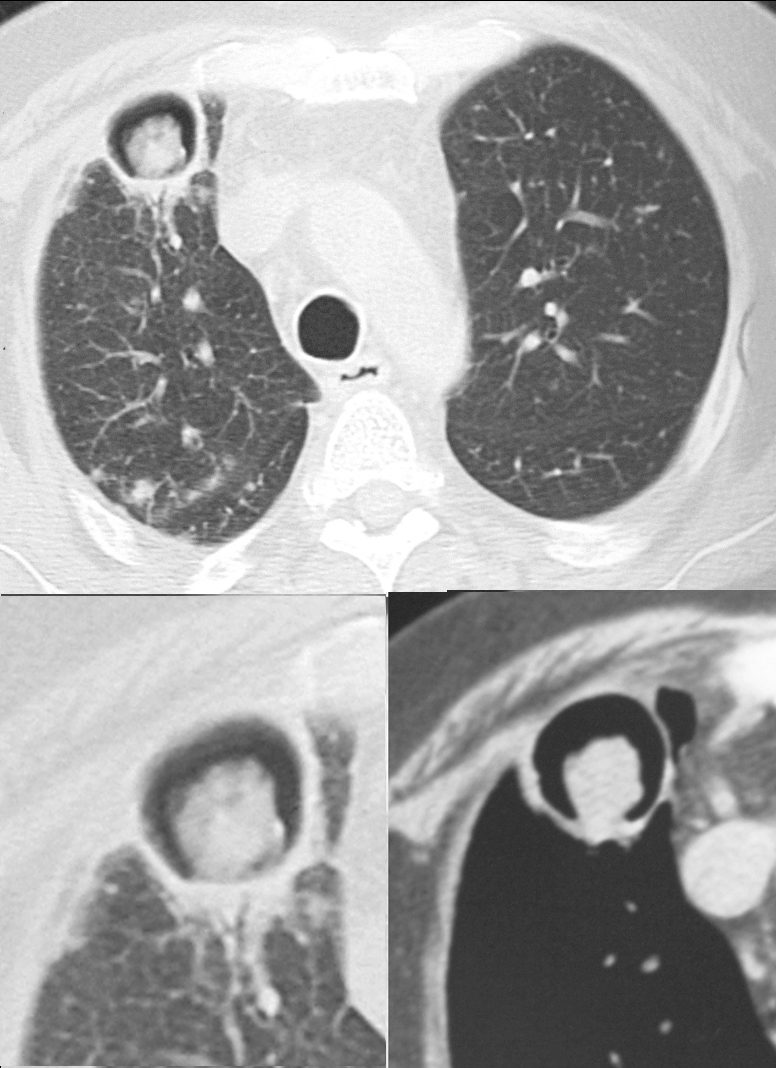
CT scan through the chest shows medium sized bronchi, bronchioles and small airways impacted with fluid. This collage is presented to reveal tree in bud changes resulting from impaction in the smaller terminal bronchioles and respiratory units. The tree-in-bud pattern also results in small centrilobular nodules connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber from a single stalk. Originally it was felt to result from endobronchial spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but is is now recognized in diverse entities including peripheral airway diseases caused by infection (bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic), congenital disorders, idiopathic disorders (obliterative bronchiolitis, pan bronchiolitis), aspiration or inhalation of foreign substances, immunologic disorders, connective tissue disorders and peripheral pulmonary vascular diseases such as neoplastic pulmonary emboli.
In this case there are also dilated medium sized airways, impacted with soft tissue characteristic of the finger in glove sign and most likely due to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
Ashley Davidoff MD Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
47113c01
Atelectasis and Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosus (ABPA)
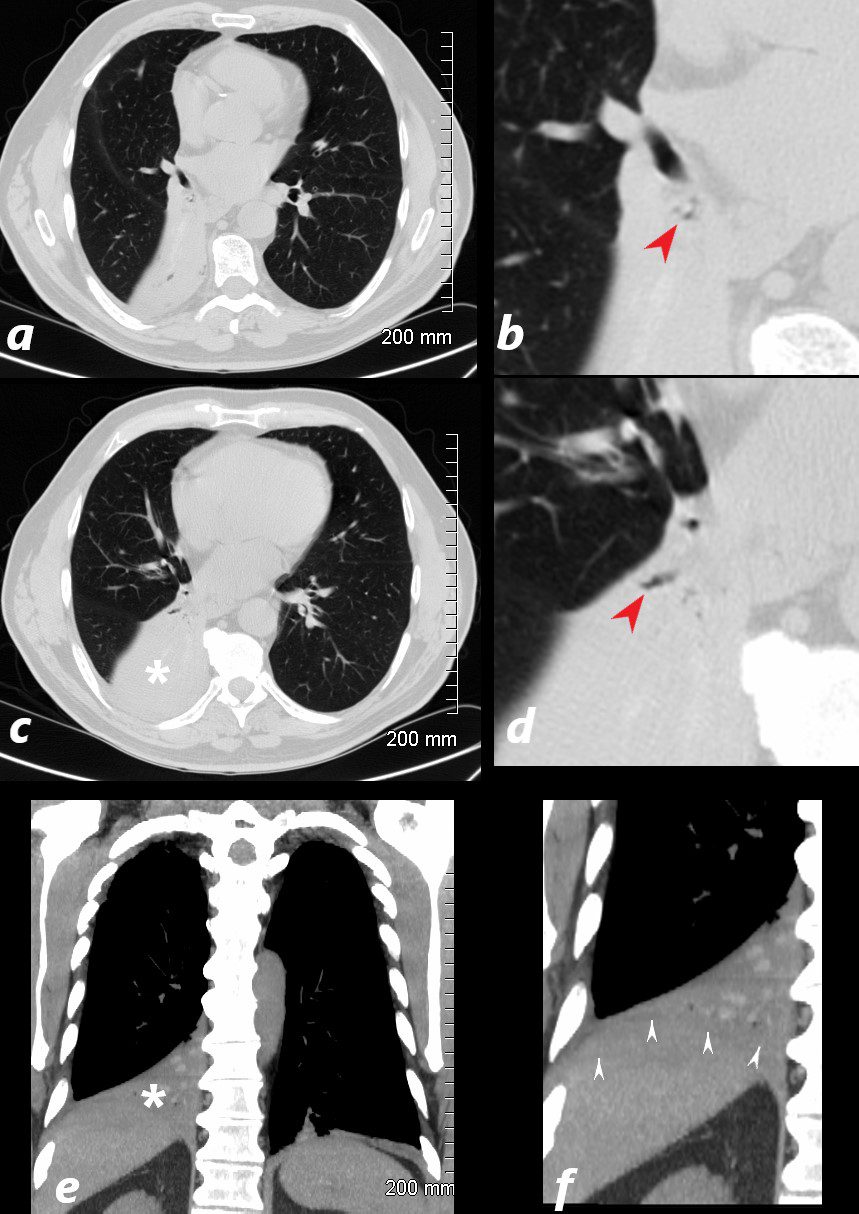

77 year old male prents chest discomfort
CT scan without contrast shows atelectasis of the right lower lobe )asterisk c and r) and also seen axial projection (a) magnified in (b) and in (c) magnified in {d) Red arrowheads in b and d show airways filled with material. Aspergillus was isolated at bronchoscopy. Coronal imaging (e magnifird in f) show silhouetting of the righ hemmidiaphragm by the atelectatic lung (white arrowheads
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
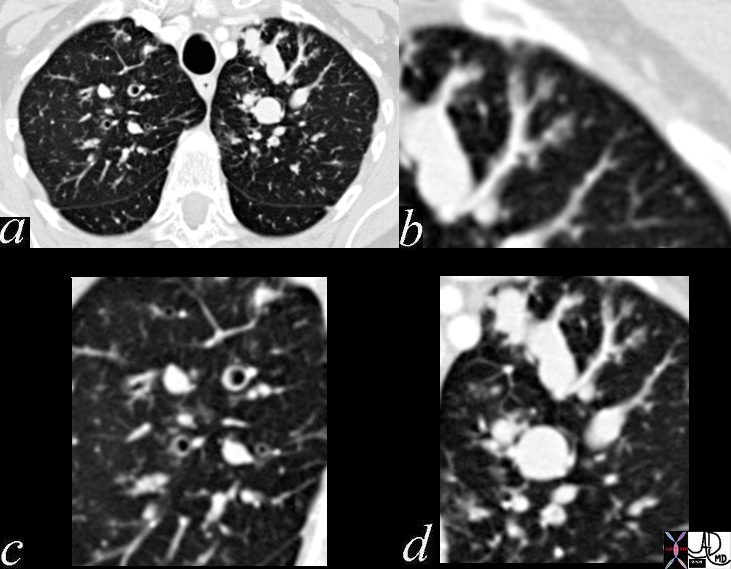
Broncho pneumonic Form of Aspergillosis

Note a subsegmental consolidation in the anterior segment of the left upper lobe in a 43 year old man with known aspergillus infection. Note the thickening of the walls of the segmental subsegmental and small airways with bronchiectasis and bronchiolectasis. There are centrilobular nodules indicating the small airway disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 117811c
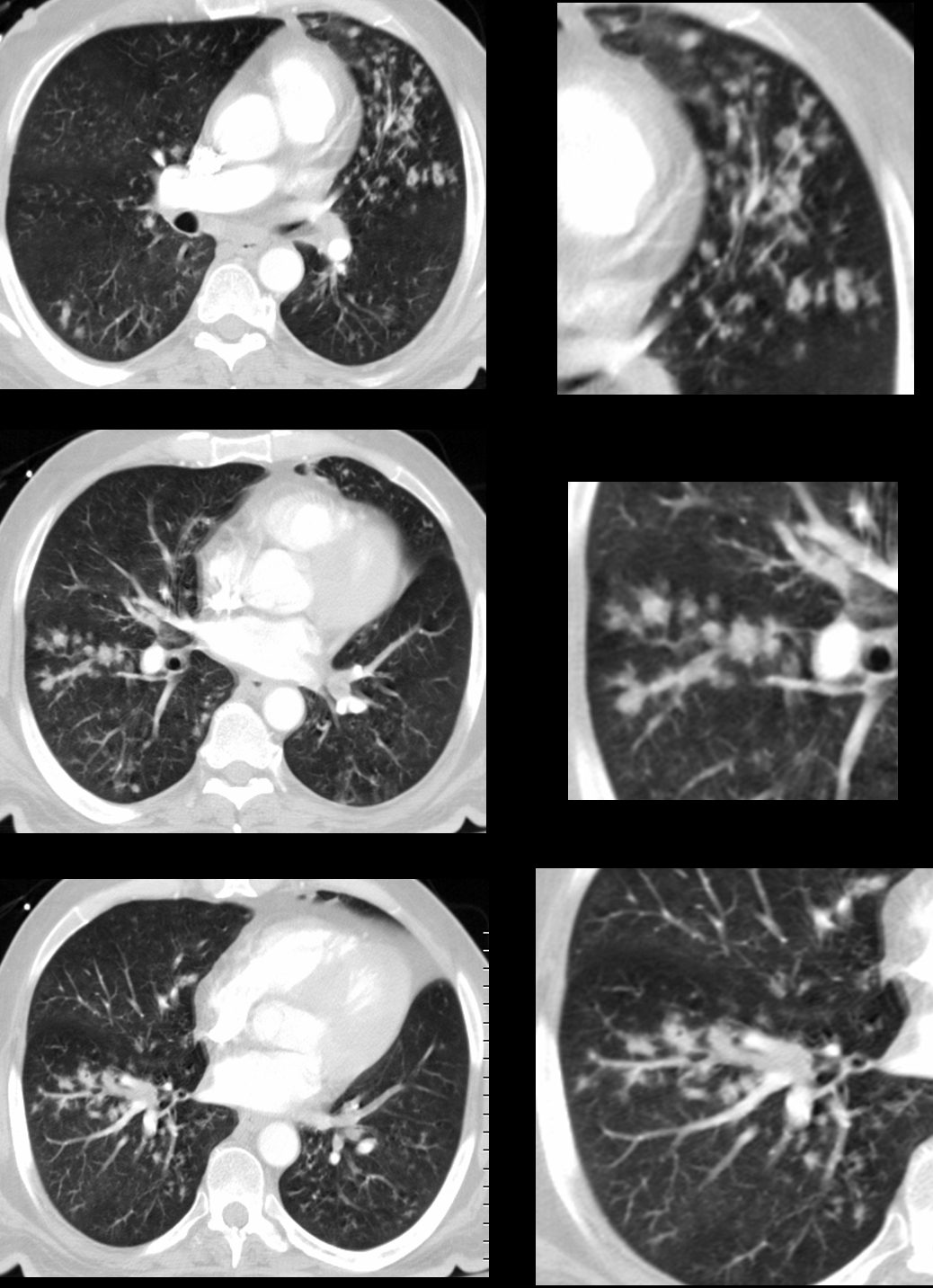

43 year old man with known aspergillus infection. Note the thickening of the walls of the segmental subsegmental and small airways with extensive tree in bud changes and bronchial wall thickening. There are centrilobular nodules indicating the small airway disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
117816c

Source
Signs in Thoracic Imaging
Journal of Thoracic Imaging 21(1):76-90, March 2006.



CT scan through the chest shows medium sized bronchi, bronchioles and small airways impacted with fluid. This collage is presented to reveal tree in bud changes resulting from impaction in the smaller terminal bronchioles and respiratory units. The tree-in-bud pattern also results in small centrilobular nodules connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber from a single stalk. Originally it was felt to result from endobronchial spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but is is now recognized in diverse entities including peripheral airway diseases caused by infection (bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic), congenital disorders, idiopathic disorders (obliterative bronchiolitis, pan bronchiolitis), aspiration or inhalation of foreign substances, immunologic disorders, connective tissue disorders and peripheral pulmonary vascular diseases such as neoplastic pulmonary emboli.
In this case there are also dilated medium sized airways, impacted with soft tissue characteristic of the finger in glove sign and most likely due to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
Ashley Davidoff MD Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
47113c01
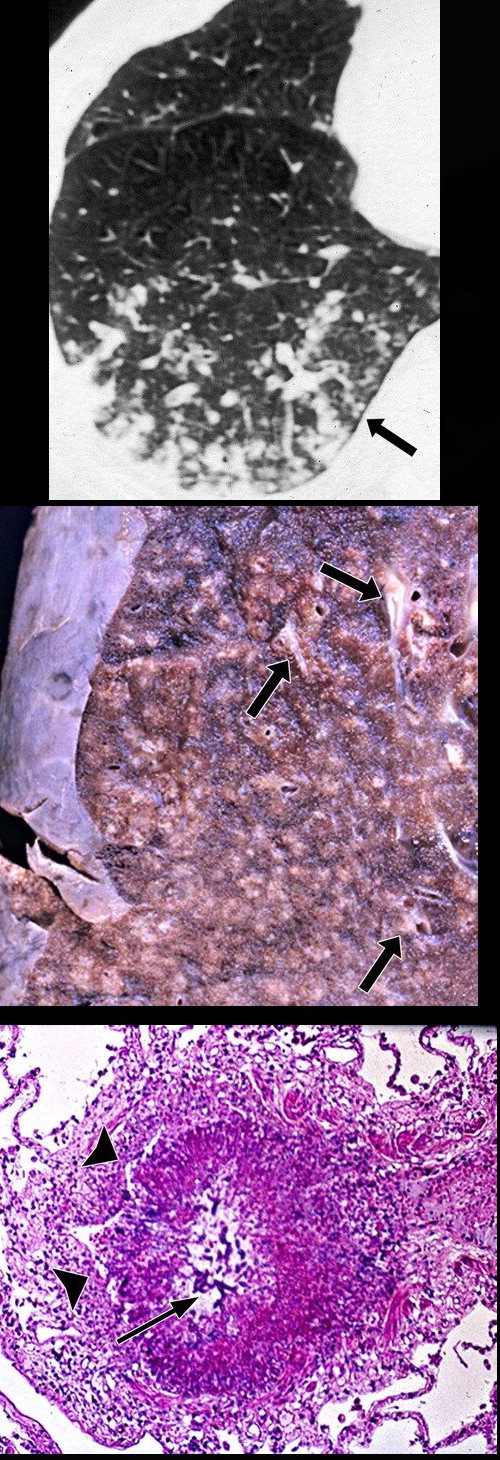

Rossi, SE et al Tree-in-Bud Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: Radiologic-Pathologic Overview RadioGraphics Vol. 25, No. 3 2005

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net

Source Signs in Thoracic Imaging Journal of Thoracic Imaging 21(1):76-90, March 2006.
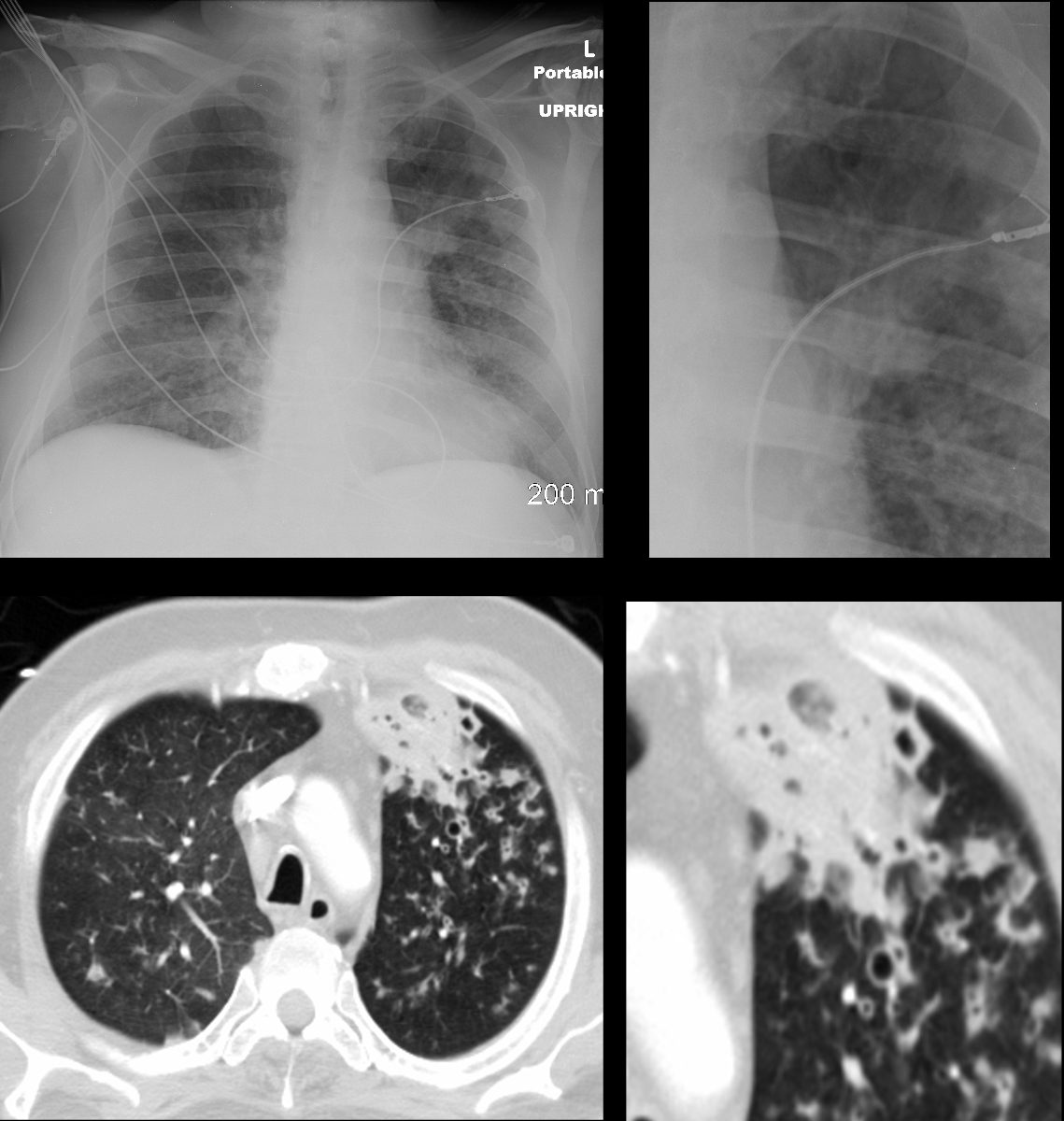
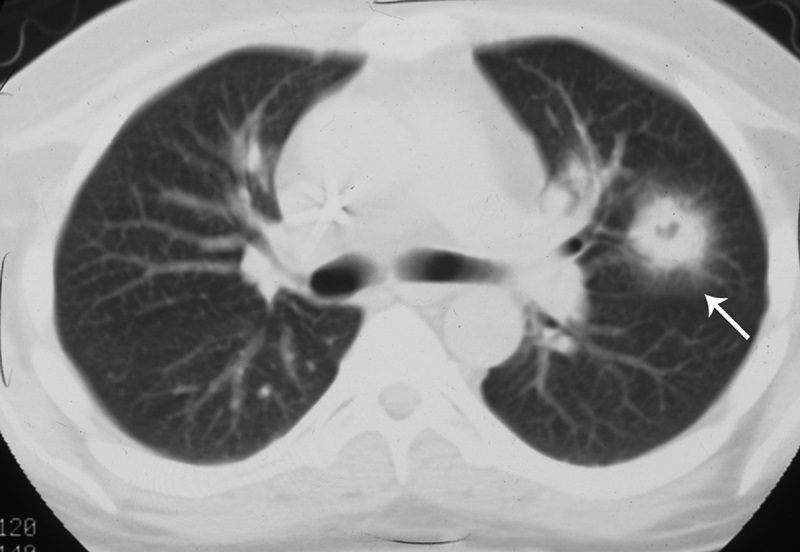
Reversed Halo Sign – Atoll Sign

The Frontal CXR shows a rapidly progressive interstitial infiltrate in the left upper lobe with a focal subsegmental infiltrate in the right lower lobe Diagnosis Aspergillus Infection
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
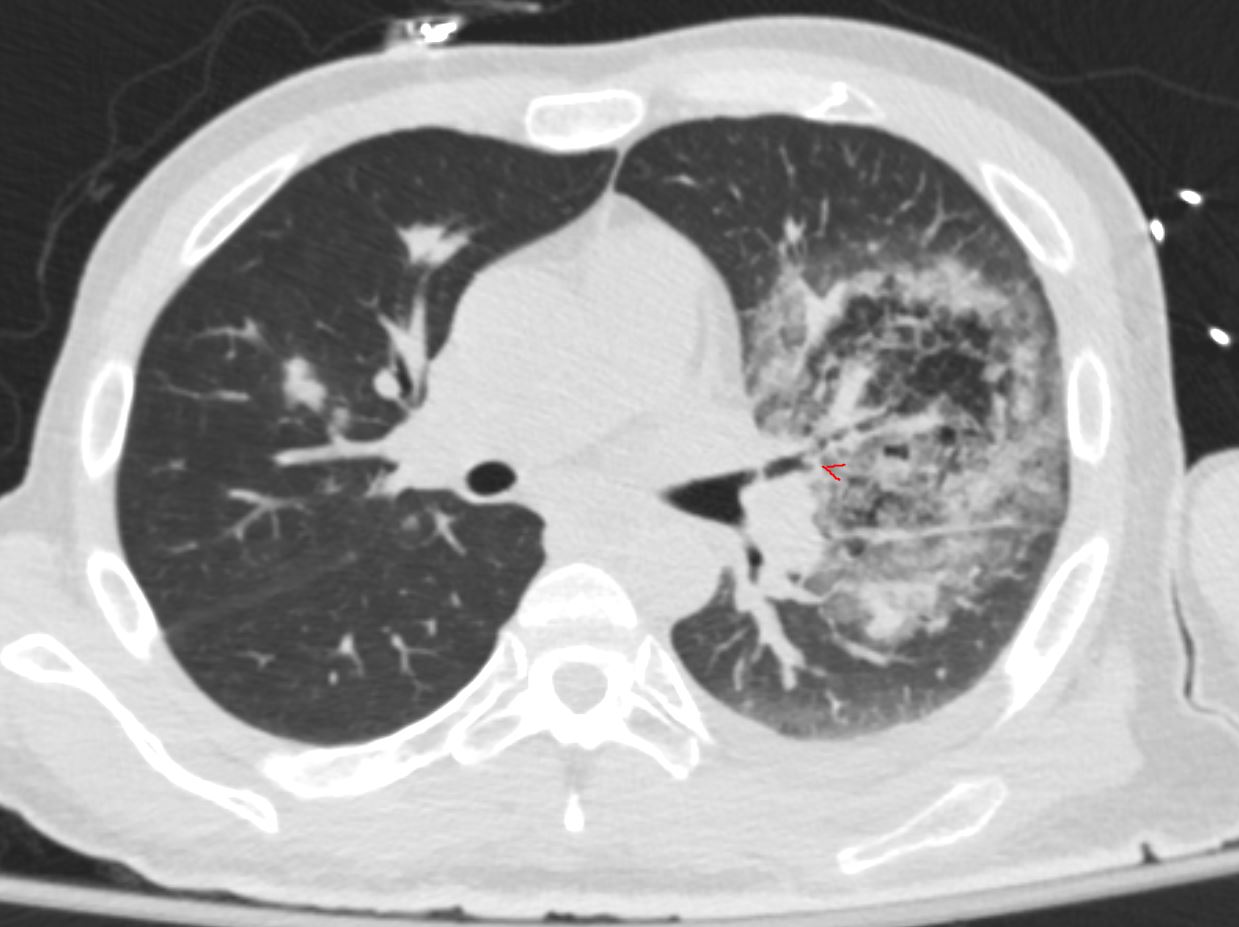

The coronal CT scan shows a rapidly progressive interstitial infiltrate in the left upper and lower lobes showing features of a reversed halo sign (Atoll sign) There is evidence of bronchial wall irregularity (arrowhead) Fungal Hyphae were identified at bronchoscopy
Diagnosis Aspergillus Infection
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
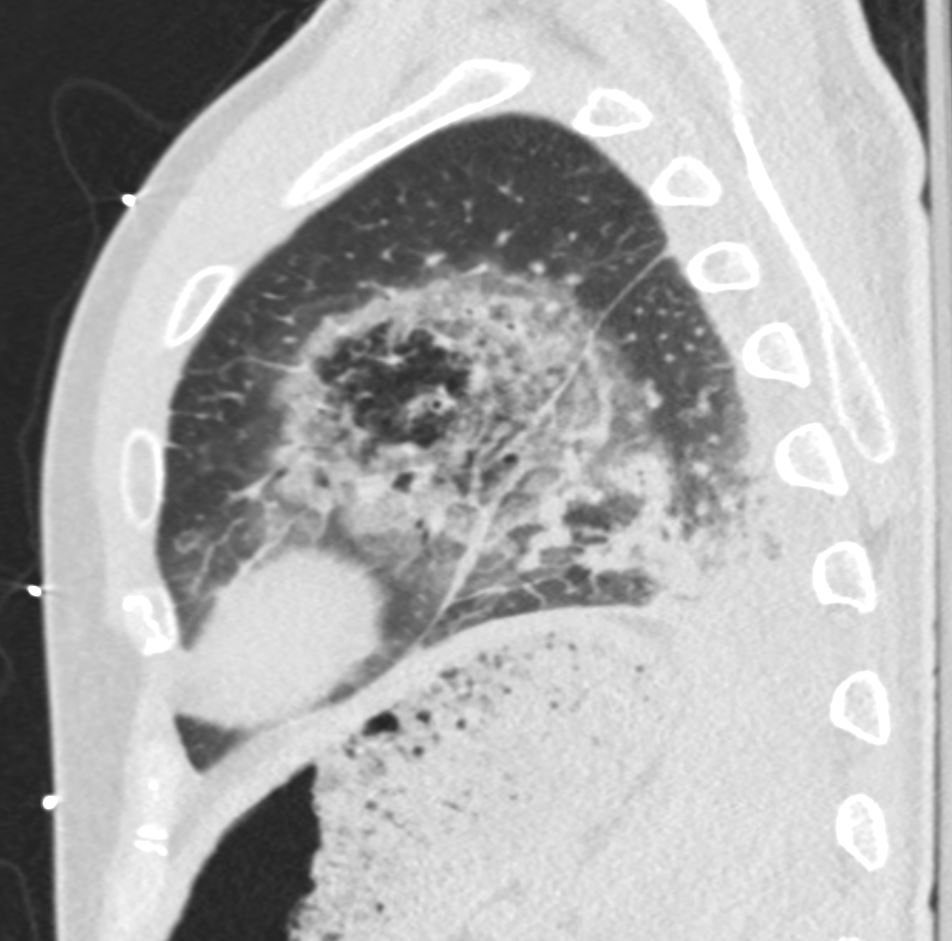

The coronal CT scan shows a rapidly progressive interstitial infiltrate in the left upper and lower lobes showing features of a reversed halo sign (Atoll sign) There is evidence of bronchial wall thickening.
Diagnosis Aspergillus Infection
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
References and Links
https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiographics.21.4.g01jl03825
-
TCV
-
000 Aspergillus
- Aspergilloma
-
- Fungus ball in the lungs
- Does not spread
-
- Allergic Bronchopulmonary Pulmonary Aspergillosis
-
- allergic response in patients with
- asthma
- cystic fibrosis
- bronchiectasis
- allergic response in patients with
-
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)
-
- colonize
- cavities in the lungs,
- aspergillomas may also be present in the lungs.
- colonize
-
- Invasive Aspergillosis including Angioinvasive Aspergillosis:
-
- serious infection,
- may be systemic
- immunocompromised
-
- Aspergilloma
-
Aspergillus Cases
-
- 219Lu Acute Aspergillus Fungal Infection Atoll Sign
- 220Lu Asthma Bronchitis Bronchiectasis Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
- 220Lu Asthma Bronchitis Bronchiectasis Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
- 221Lu Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
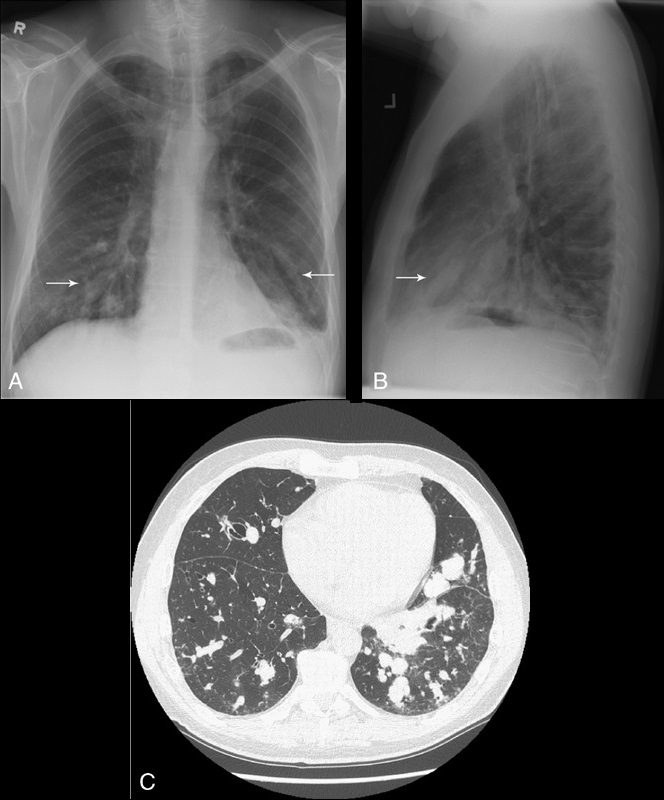
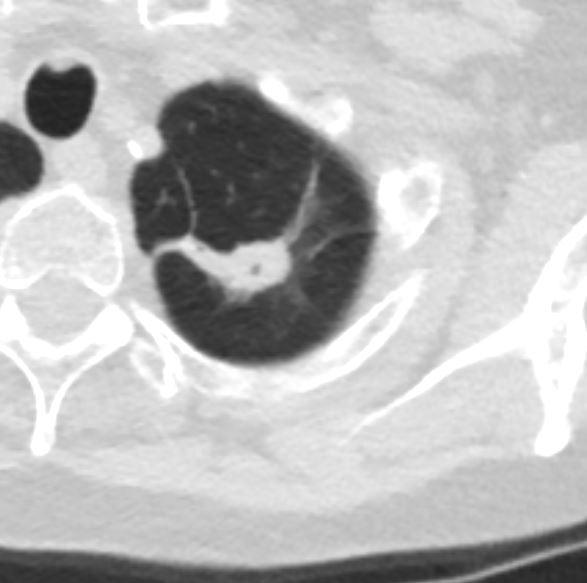
- 222Lu Aspergilloma Air Crescent Sign
-
-
Faces of Aspergillus on Imaging