Meticulous staging of lung cancer is necessary because treatment options and prognosis depend on accurate staging
Tumor (T) Status Descriptor
T0 No evidence of a primary tumor
TX Primary tumor cannot be assessed, or tumor proven by the presence of malignant cells in sputum or bronchial washings but not visualized by imaging or bronchoscopy
TIS Carcinoma in situ
T1 Tumor <3 cm in greatest dimension, surrounded by lung or visceral pleura, without bronchoscopic evidence of invasion more proximal than lobar bronchus (i.e., not in main bronchus)
T2 Tumor with any of following: >3 cm in greatest dimension; involves main bronchus, 2 cm distal to the carina; invades visceral pleura; associated with atelectasis or obstructive pneumonitis extending to hilum but does not involve entire lung
T3 Tumor of any size that directly invades any of the following: chest wall (including superior sulcus tumors), diaphragm, mediastinal pleura, parietal pericardium; or tumor in main bronchus <2 cm distal to carina but without involvement of carina; or associated atelectasis or obstructive pneumonitis of entire lung
T4 Tumor of any size that invades any of the following: mediastinum, heart, great vessels, trachea, esophagus, vertebral body, carina; or tumor with a malignant pleural or pericardial effusion, or with satellite tumor nodule(s) within the ipsilateral primary-tumor lobe of the lung.
Lymph Node (N) Involvement Descriptor
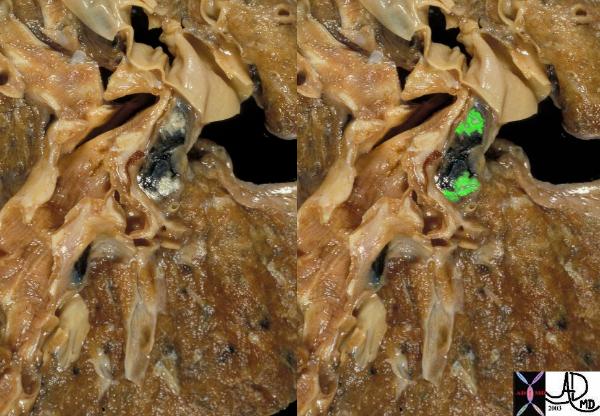
Metastases to Lymph Nodes
This is an autopsy specimen of a patient who had primary lung carcinoma. The malignant components in these hilar nodes are identified as white patches in the first image and are overlaid in green in the second.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
32192wc
NX Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0 No regional lymph node metastasis
N1 Metastasis to ipsilateral peribronchial and/or ipsilateral hilar lymph nodes, and intrapulmonary nodes involved by direct extension of the primary tumor
N2 Metastasis to ipsilateral mediastinal and/or subcarinal lymph nodes(s)
N3 Metastasis to contralateral mediastinal, contralateral hilar, ipsilateral or contralateral scalene, or supraclavicular lymph node(s)
Distant Metastasis (M) Descriptor
MX Presence of distant metastasis cannot be assessed
M0 No distant metastasis
M1 Distant metastasis present
Evaluation
ANATOMIC CLASSIFICATION – TNM
1997 – American Joint Committee on Cancer and the Union Internationale Contre le Cancer revised the stage groupings of the TNM subsets in the International System for Staging Lung Cancer. (Mountain)
This classification facilitated the evaluation of the extent of the disease based on the size of the primary tumor, extent of adenopathy and extent of the disease in the body.
T1:
A tumor less than or equal to 3 cm in greatest dimension, surrounded by lung or visceral pleura, without bronchoscopic evidence of invasion more proximal than the lobar bronchus (i.e., not in the main bronchus)
T2:
A tumor with any of the following features:
Larger than 3 cm in largest dimension
Involvement of the mainstem bronchus, but is greater than 2 cm from the carina
Invades the visceral pleura
Associated with atelectasis or post-obstructive pneumonitis that extends to the hilar region, but does not involve the entire lung
T3:
A tumor of any size that directly invades any of the following: the chest wall (including superior sulcus tumors), diaphragm, mediastinal pleura, parietal pericardium; tumor in the main bronchus less than 2 cm distal to the carina (but without involvement of the carina); tumor associated with atelectasis or obstructive pneumonitis of the entire lung.
T4:
A tumor of any size that invades any of the following: mediastinum, heart, great vessels, trachea, esophagus, vertebral body, carina; any tumor with a malignant pleural or pericardial effusion; or any tumor with satellite tumor nodules within the ipsilateral primary-tumor lobe of the lung.
TX:
The primary tumor cannot be assessed, or tumor proven by the presence of malignant cells in sputum or bronchial washings, but not visualized by imaging or bronchoscopy.
T0:
No evidence of a primary tumor
TIS:
Carcinoma in situ
Regional Lymph Node Metastasis
N0:
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1:
Ipsilateral peribronchial or hilar nodal metastases; or intrapulmonary nodes involved by direct extension of the primary tumor. All N1 nodes lie distal to the mediastinal pleural reflection.
N2:
Ipsilateral mediastinal and subcarinal lymph nodal metastases. Midline pre-vascular and retro-tracheal nodes are considered ipsilateral , while nodes to the contralateral side of midline are considered N3 Although subcarinal nodes may extend into the contralateral mediastinum, they are generally considered to be N2.
N3:
Contralateral mediastinal or contralateral hilar nodal metastases; also includes ipsilateral or contralateral scalene or supraclavicular nodes. Other cervical nodes are classified M1
NX:
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
31646c
Distant Metastasis (M)
M0:
No distant metastasis
M1:
Distant metastasis present; or separate tumor nodules in the ipsilateral no primary-tumor lobes of the lung. Separate tumor nodules in the contralateral lung are considered M1 if they are of the same histological cell type as the primary lesion. A contralateral lung tumor with a different cell type is considered a synchronous primary lesion and should be staged independently
MX:
Presence of distant metastasis cannot be assessed
Performance Status
Zubrod Performance Scale
0 Normal activity; asymptomatic
1 Symptomatic; fully ambulatory
2 Symptomatic; in bed <50% of time
3 Symptomatic; in bed 50% of time, not bedridden
4 100% bedridden
5 Dead
Therapy
Surgical resection for small cell carcinoma is so ineffective that the diagnosis essentially precludes surgery.
treatment of the non small cell group will be based on staging
