Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0751
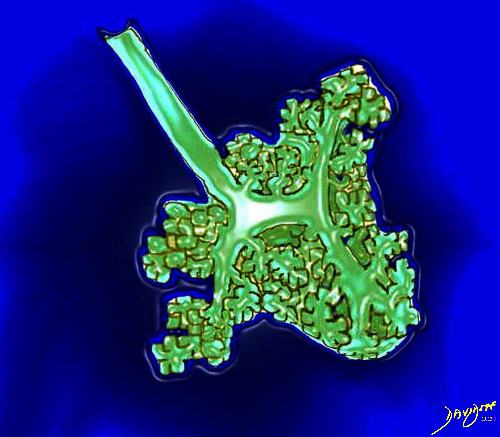
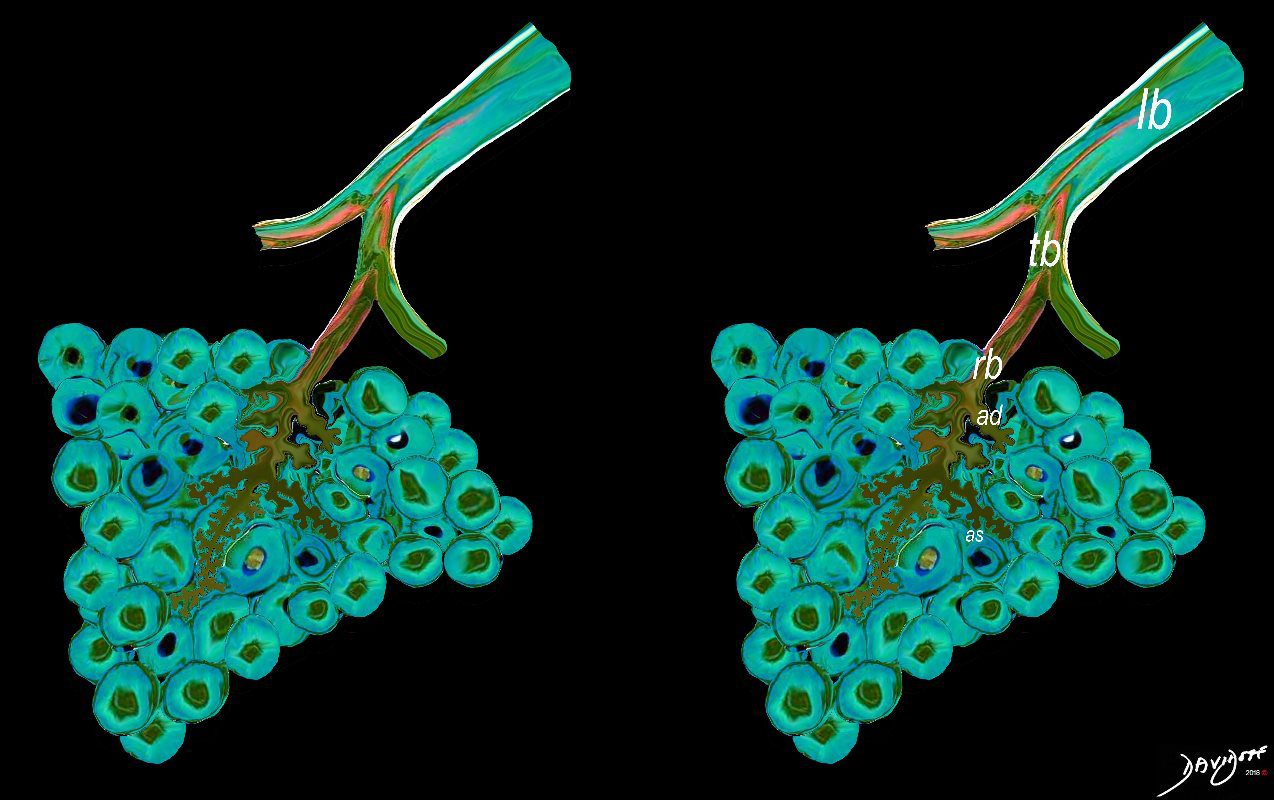
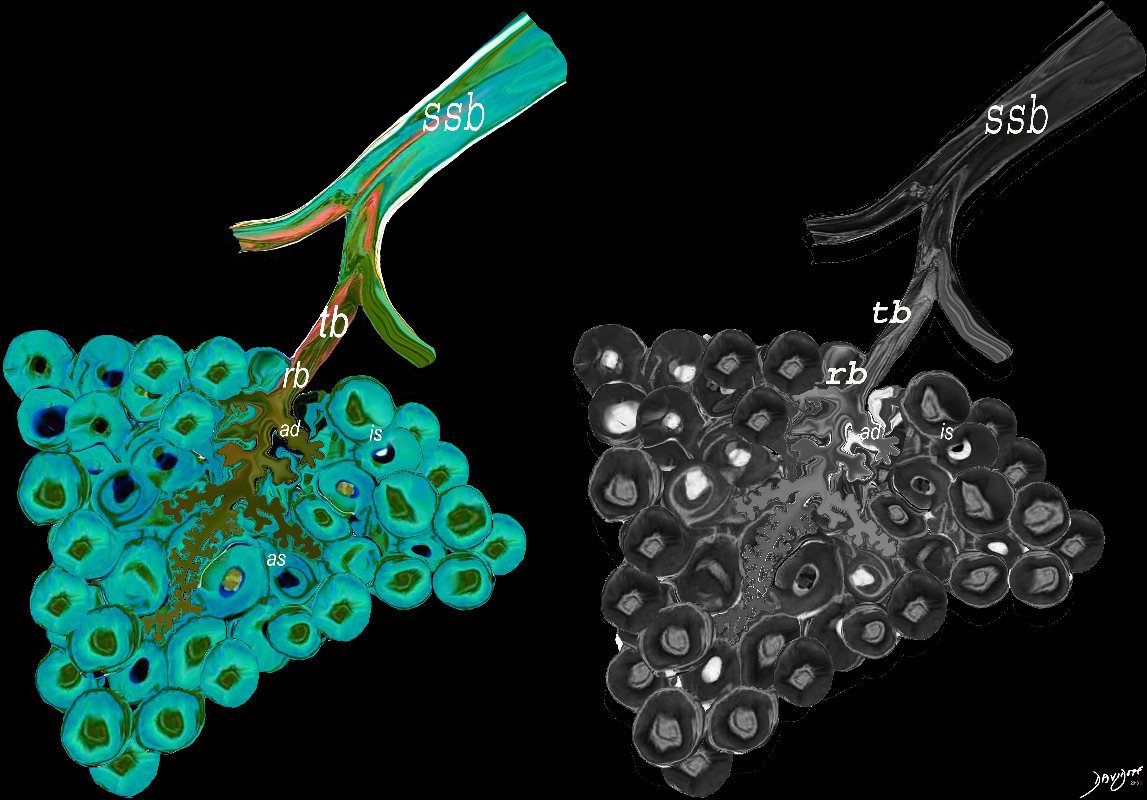
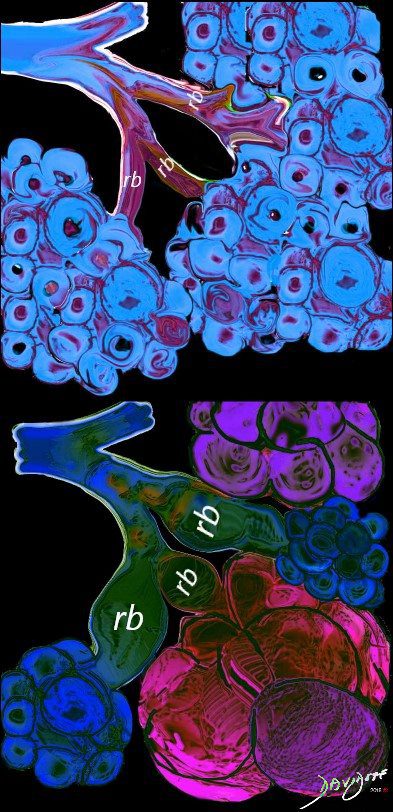
The lobular (most distal of the subsegmental airways give rise to the terminal bronchiole which give rise to the membranous airways. These include in order, the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-0007
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0059

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0058
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0034
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0030-low res
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-00680
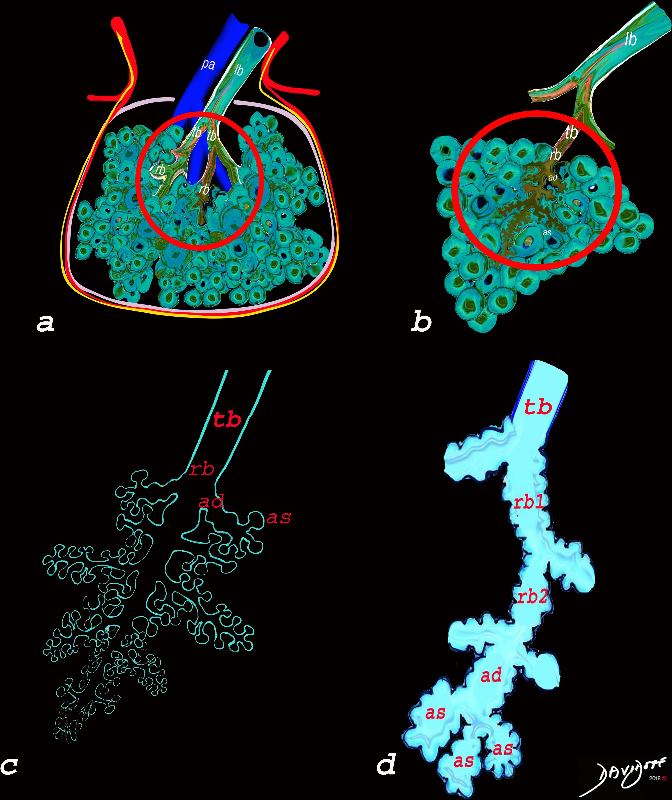
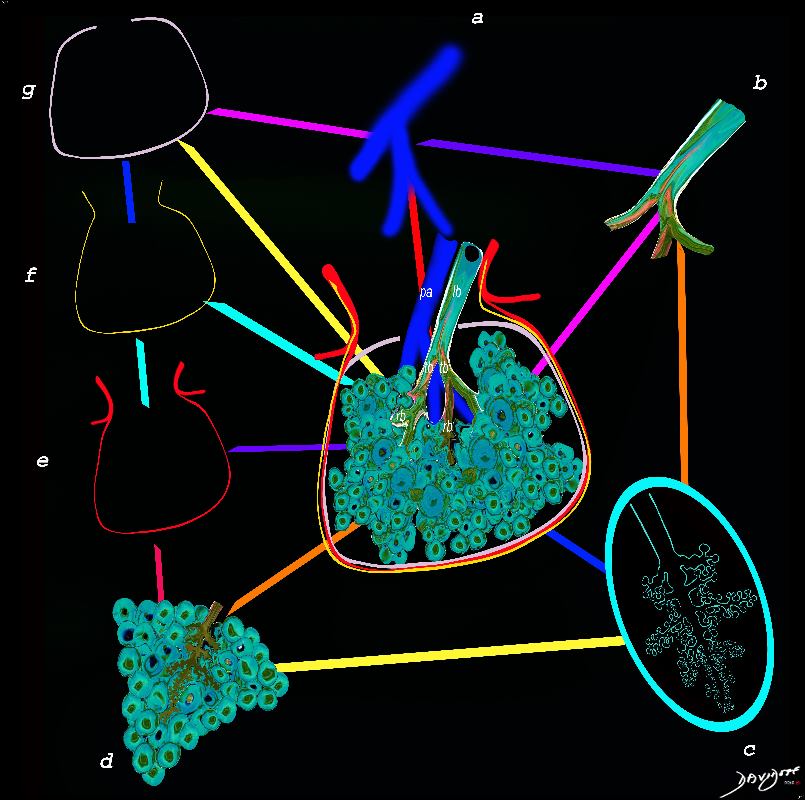
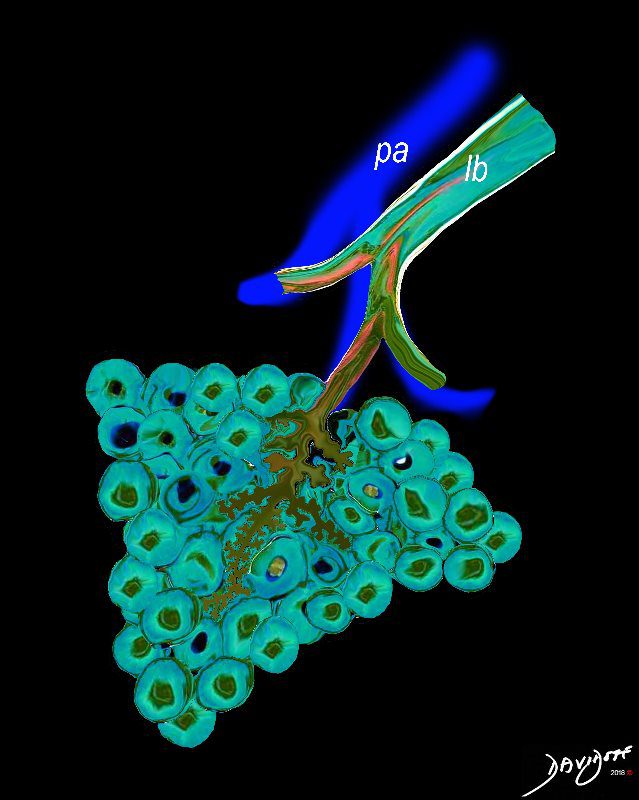
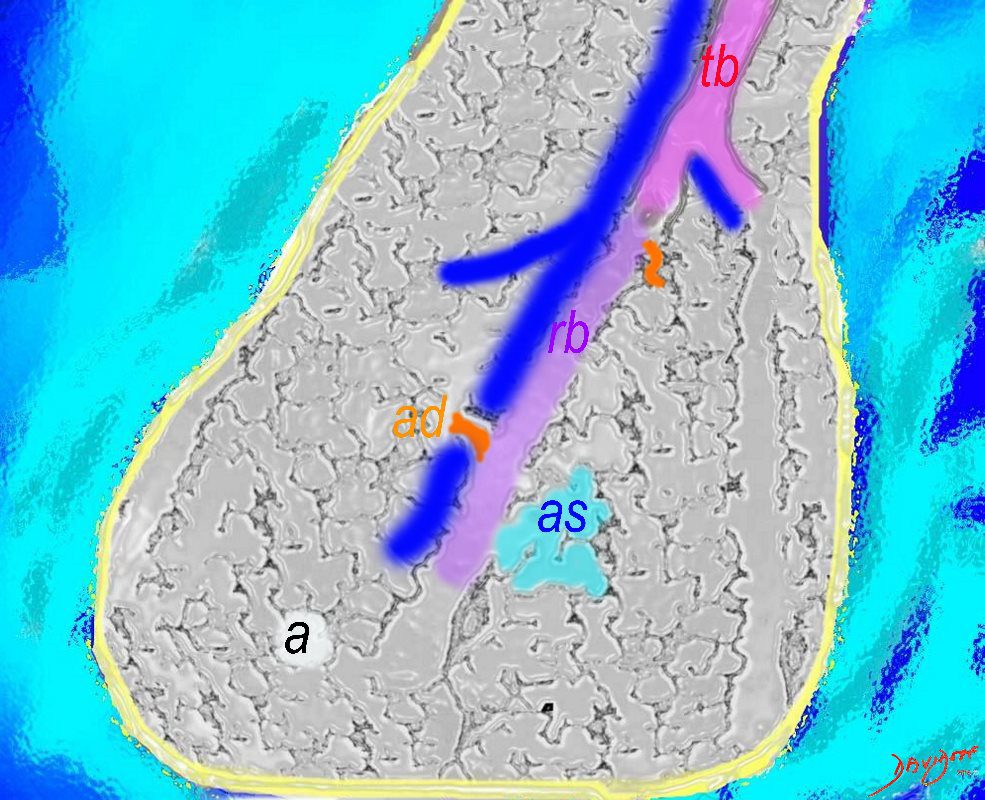
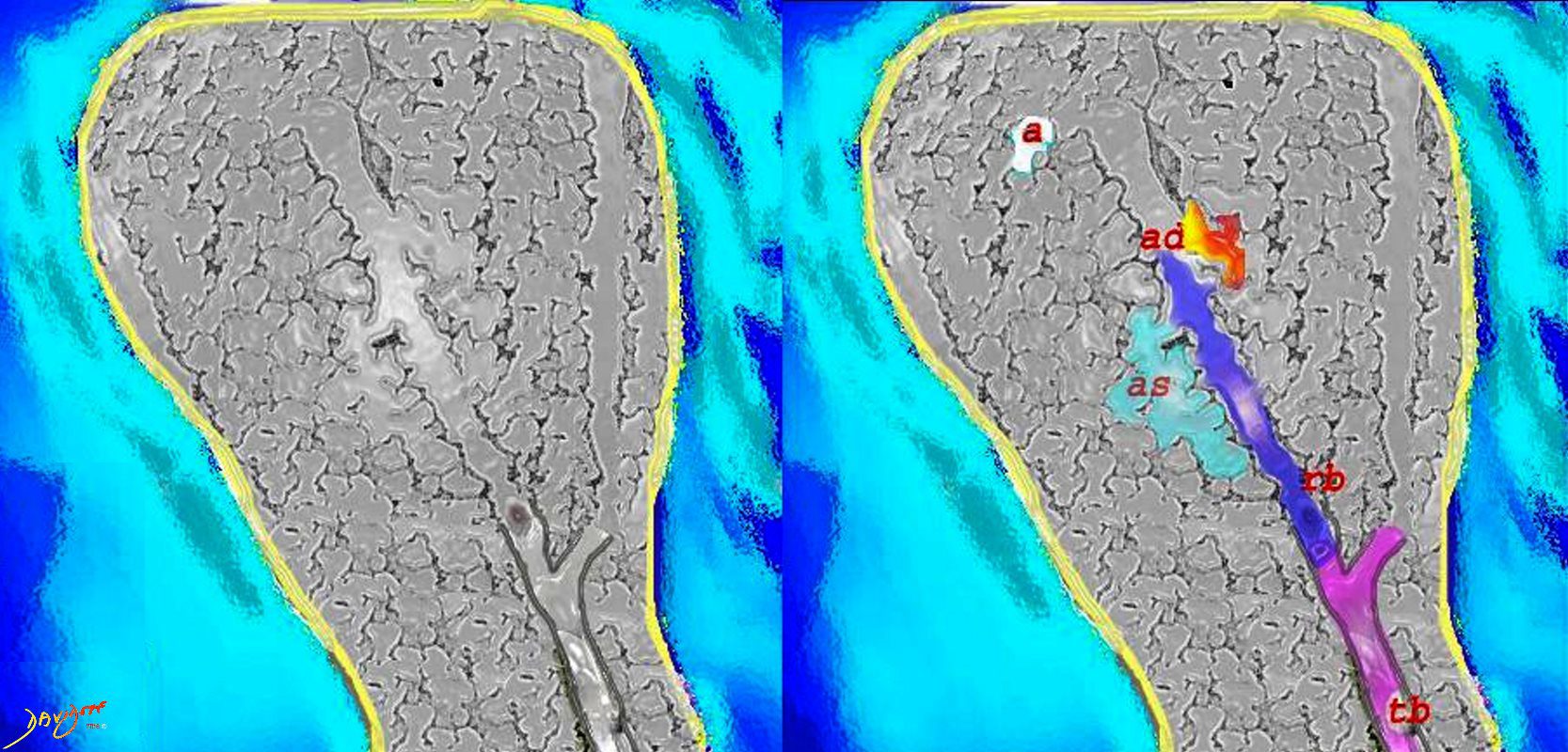
The diagram allows us to understand the the components and the position of the small airways starting in (a) which is a secondary lobule that is fed by a lobular bronchiole(lb) which enters into the secondary lobule and divides into terminal bronchioles (tb) which is the distal part of the conducting airways, and at a diameter of 2mm or less . It divides into the respiratory bronchiole (rb) a transitional airway which then advances into the alveolar ducts(ad) and alveolar sacs (as) Diseases isolated to the small airways do not affect the alveoli and hence there is peripheral sparing Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0749
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-0033
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
lungs-0028-low res
The lobular (most distal of the subsegmental airways give rise to the terminal bronchiole which give rise to the membranous airways. These include in order, the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-0004

Ashley Davidoff The CommonVein.net lungs-0002
Diseases
COVID
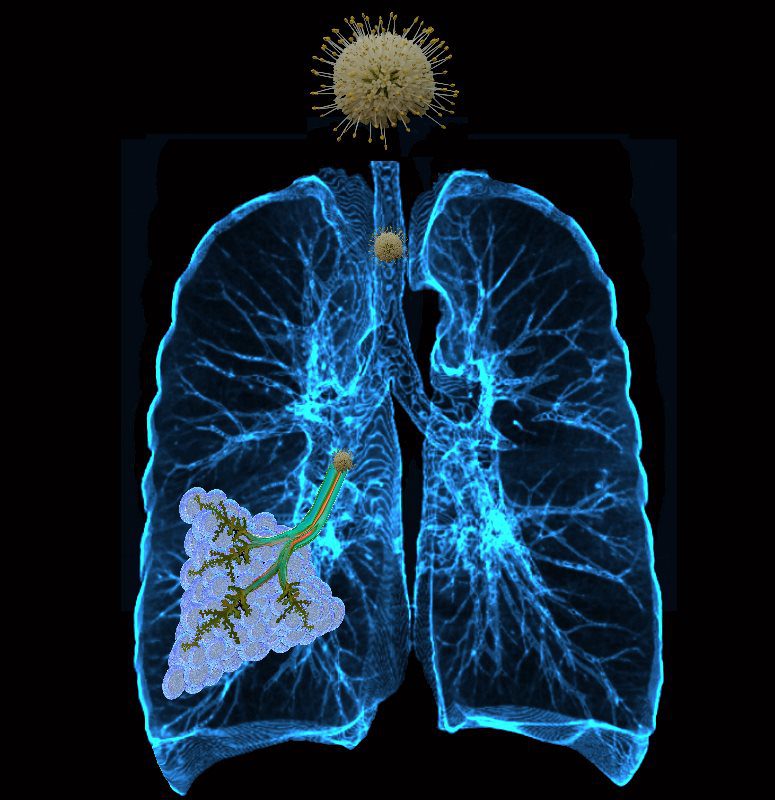
The virus enters the lungs and travels to the smallest parts of the lungs, tiny lung sacs called the alveoli where oxygen exchange takes place
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0039
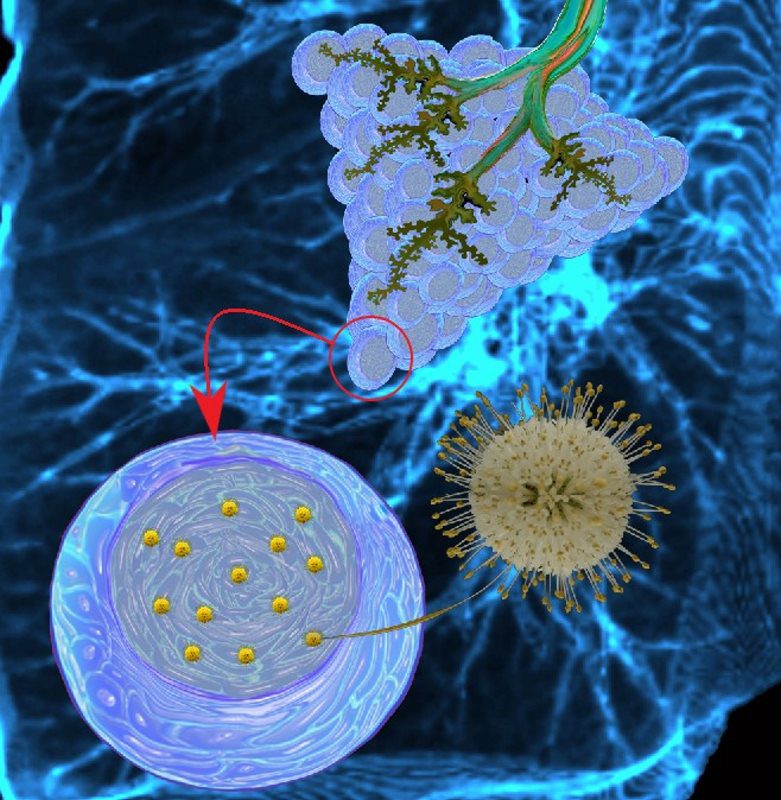
Corona virus invades the cells of the alveoli by using its spike glycoproteins. These spike proteins attach to the cell membrane and the virus can then enter the cell.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0042
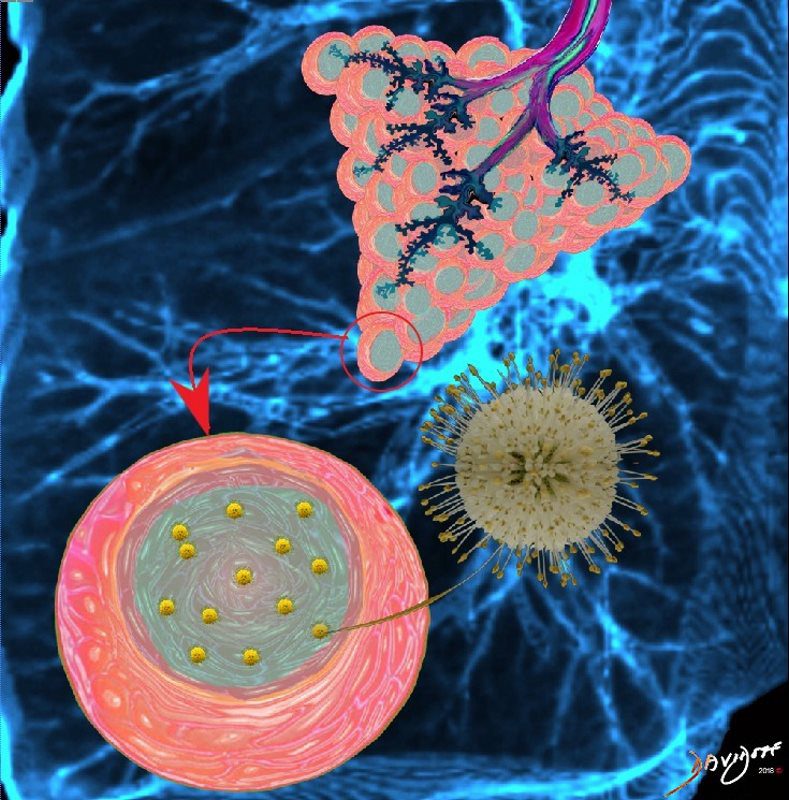
The virus replicates and invades more cells of the alveoli
As COVID-19 causes inflammation of the the lungs, infected fluid fills the lungs thus disrupting gas exchange.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0043
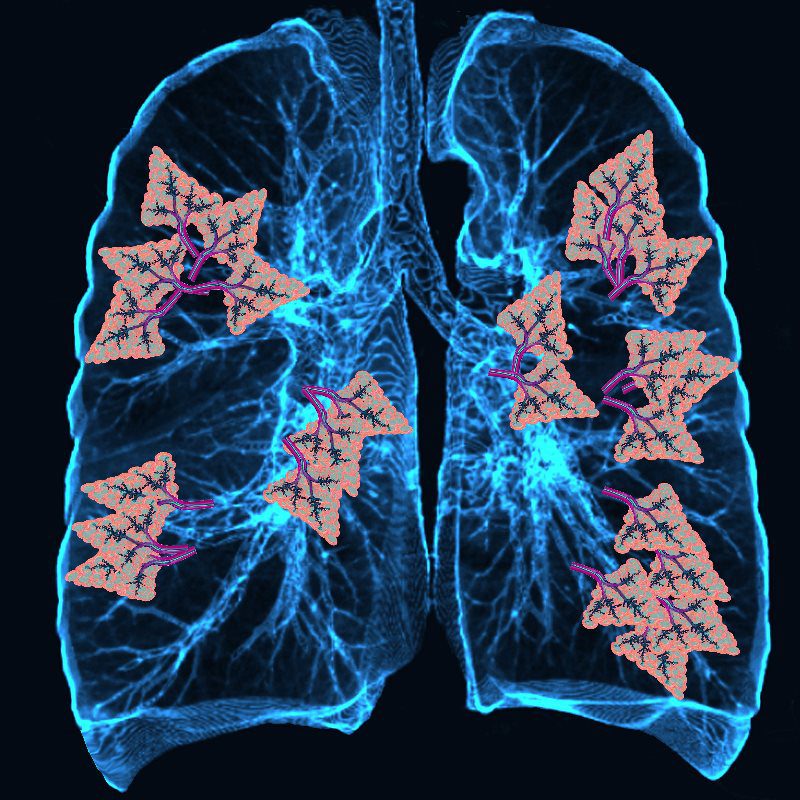
and progresses to involve more and more lung
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0047
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net lungs-0038
