Etymology
Derived from the Latin words centrum (center) and lobulus (small lobe), centrilobular emphysema refers to the predominant involvement of the central portion of the secondary pulmonary lobule.
AKA
Centrilobular emphysema; Centriacinar emphysema
What is it?
Centrilobular emphysema is a subtype of emphysema characterized by the destruction of the respiratory bronchioles and the central portions of the secondary pulmonary lobule, with relative sparing of the peripheral alveoli. It is the most common form of emphysema and is strongly associated with smoking.
Caused by:
- Most common cause: Cigarette smoking
- Other causes include:
- Biomass smoke inhalation (e.g., wood-burning stoves)
- Occupational exposures to inhaled dust and chemicals
- Chronic inflammation from air pollutants
Resulting in:
- Progressive destruction of central alveolar walls, coalescence of airspaces, and airflow obstruction.
- Reduced elastic recoil and impaired gas exchange, leading to hypoxemia and hypercapnia in advanced stages.
Structural changes:
- Enlargement of airspaces in the central portion of the secondary pulmonary lobule.
- Relative sparing of the peripheral alveoli and interlobular septa in early stages.
Pathophysiology:
- Chronic exposure to cigarette smoke or other toxins triggers inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Protease-antiprotease imbalance (e.g., increased elastase activity) leads to the destruction of elastin and alveolar walls.
- Mechanical stress and reduced perfusion in the upper lobes predispose to localized damage.
Pathology:
- Gross: Hyperinflation, especially in the upper lobes, with focal areas of destruction.
- Microscopic: Loss of alveolar septa, centrilobular capillaries, and structural integrity in the respiratory bronchioles.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical:
- Symptoms:
- Gradual onset of exertional dyspnea.
- Chronic cough with or without sputum production (often part of COPD).
- Risk factors:
- Cigarette smoking or significant exposure to biomass fuels.
- Symptoms:
- Radiology:
- CXR: May show hyperinflation with flattened diaphragms, increased retrosternal airspace, and upper-lobe lucencies (suggestive but nonspecific).
- CT: Low-attenuation areas (representing destroyed lung tissue) predominantly in the upper lobes and centrally located in the secondary pulmonary lobules.
- Labs:
- Arterial blood gas (ABG): May show hypoxemia and hypercapnia in advanced stages.
- Serum alpha-1 antitrypsin levels: Recommended in early-onset or atypical cases to rule out alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Management:
- Smoking Cessation:
- Most critical intervention to prevent disease progression.
- Pharmacological Therapy:
- Bronchodilators: Long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) to relieve airflow obstruction.
- Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS): For patients with frequent exacerbations.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
- Exercise training and education to improve quality of life and functional capacity.
- Oxygen Therapy:
- Prescribed for patients with chronic hypoxemia (PaO₂ ≤55 mmHg or SpO₂ ≤88%).
- Surgical Interventions:
- Bullectomy: For symptomatic bullae compressing functional lung tissue.
- Lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS): For upper-lobe predominant emphysema in carefully selected patients.
Radiology Detail:
- CXR:
- Findings:
- Hyperlucency with reduced vascular markings in the upper lobes.
- Flattened diaphragms and increased retrosternal airspace.
- Associated Findings:
- Signs of coexisting chronic bronchitis or pulmonary hypertension in advanced disease.
- Findings:
- CT:
- Parts:
- Destruction primarily affects the respiratory bronchioles and central portions of the secondary pulmonary lobules.
- Size:
- Low-attenuation areas <1 cm in early stages; may enlarge with progression.
- Shape:
- Irregular or round low-attenuation areas surrounded by relatively preserved lung tissue.
- Position:
- Predominantly upper-lobe and central distribution, sparing the subpleural regions.
- Character:
- Heterogeneous distribution of low-attenuation areas with scattered preservation of lung parenchyma.
- Time:
- Progresses over years with ongoing exposure to risk factors.
- Associated Findings:
- Bullae, secondary pneumothorax, or superimposed infections in advanced stages.
- Parts:
- Other Relevant Imaging Modalities:
- MRI: Rarely used for diagnosis; may help evaluate functional lung volumes.
- PET-CT: Utilized to evaluate for coexisting malignancy in high-risk patients.
- Nuclear Medicine (Ventilation-Perfusion Scan): May reveal ventilation-perfusion mismatch in advanced emphysema.
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs):
- Obstructive pattern with:
- Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio.
- Increased residual volume (RV) and total lung capacity (TLC).
- Decreased diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) in advanced disease.
- Obstructive pattern with:
Recommendations:
- Smoking cessation is essential to halt progression.
- Regular follow-ups with spirometry and imaging to monitor disease status.
- Vaccinations (e.g., influenza and pneumococcal) to reduce risk of respiratory infections.
Key Points and Pearls:
- Centrilobular emphysema is the most common form of emphysema and strongly associated with smoking.
- CT is the gold standard for diagnosis, showing low-attenuation areas in the central regions of secondary pulmonary lobules.
- Smoking cessation and pulmonary rehabilitation significantly improve outcomes.
- Upper-lobe predominance on imaging reflects the effects of mechanical stress and reduced perfusion.
- “Pink puffers” maintain oxygenation through hyperventilation, while “blue bloaters” experience chronic hypoxemia and are more prone to pulmonary hypertension.
-
Feature Pink Puffer (Emphysema) Blue Bloater (Chronic Bronchitis) Primary Disease Emphysema Chronic bronchitis Mechanism of Oxygenation Hyperventilation compensates for reduced gas exchange Hypoventilation leads to chronic hypoxemia Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) Normal to mild hypoxemia, hypocapnia early; hypoxemia and hypercapnia later Significant hypoxemia and hypercapnia Key Symptoms Dyspnea, minimal cough Chronic productive cough, wheezing Lung Function Reduced elastic recoil; airflow limitation due to loss of alveolar walls Airway obstruction due to mucus hypersecretion and inflammation Structural Changes Destruction of alveoli, hyperinflation, loss of capillary-alveolar surface area Thickened bronchial walls, mucus gland hypertrophy, goblet cell hyperplasia Predisposition to Pulmonary Hypertension Less prone in early stages; occurs in advanced disease due to capillary loss More prone due to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction Complications Respiratory failure, pneumothorax Pulmonary hypertension, cor pulmonale (right heart failure) Body Appearance Thin, cachectic (‘pink’ due to preserved oxygenation) Stocky, cyanotic (‘blue’ due to chronic hypoxemia) Risk of Pulmonary Hypertension Less common in early stages; occurs in advanced disease due to capillary loss More common due to chronic hypoxemia and hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
Association with COPD
- CLE as a subtype of emphysema: Centrilobular emphysema is one of the pathological subtypes of emphysema, which is a core component of COPD. It contributes to the disease by causing irreversible damage to the lungs.
- Alveolar destruction: In CLE, the primary damage occurs in the respiratory bronchioles, leading to the enlargement of air spaces and destruction of alveolar walls. This results in loss of elastic recoil, which impairs the ability of the lungs to expel air efficiently, contributing to air trapping and hyperinflation.
- Airway obstruction: The destruction of alveolar attachments around small airways leads to their collapse during exhalation, which is a hallmark of the airflow limitation seen in COPD.
- Upper lobe predominance: CLE typically affects the upper lobes, which are more vulnerable to the damaging effects of smoking—the primary risk factor for both CLE and COPD. The upper lobe involvement is consistent with the ventilation-perfusion mismatch seen in COPD.
- Impaired gas exchange: The destruction of alveolar walls reduces the surface area for gas exchange, leading to decreased oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide elimination. This contributes to the hypoxemia and hypercapnia observed in advanced COPD.
- Clinical overlap with chronic bronchitis: While CLE affects the parenchyma, chronic bronchitis (another component of COPD) affects the airways. Patients with COPD often have overlapping features of emphysema (including CLE) and chronic bronchitis, with varying contributions to symptoms like dyspnea, cough, and sputum production.
- Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) findings: In COPD patients with CLE:
- Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio: Indicates obstructive airway disease.
- Increased residual volume (RV): Reflects air trapping.
- Decreased diffusion capacity (DLCO): Due to alveolar destruction.
- Imaging findings in COPD:
- CT scans of patients with COPD often reveal CLE as focal areas of low attenuation predominantly in the upper lobes, distinguishing it from other forms of emphysema like panlobular emphysema.
- Impact on disease progression: CLE exacerbates the airflow limitation and hyperinflation that define COPD, leading to progressive dyspnea, exercise intolerance, and increased risk of complications like pneumothorax.
By incorporating CLE’s pathophysiology into the framework of COPD, it is evident that CLE plays a significant role in the structural and functional abnormalities that characterize this chronic disease.
- Buzz Words
- Alveolar destruction
- Loss of elasticity
- starting in the respiratory bronchiole and progressing toward the proximal and central portion of the secondary lobule
Normal (above) And Centrilobular Emphysema Starting at the Respiratory Bronchiole

Image on the left shows normal size and appearance of terminal bronchioles and alveoli. On the right the image shows the effects on the respiratory bronchioles and when severe, on the alveoli as well
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Definition
- Emphysema is an inflammatory disease of the lung
- characterized
- alveolar and small vessels destruction with
- Loss of elasticity
- starting in the respiratory bronchiole and progressing toward the proximal and central portion of the secondary lobule
- clinically characterised by
- shortness of breath, and other respiratory problems.
- characterized
- Caused by
- smoking
- Results
- Structurally
- alveolar wall destruction
- progressive expansion of the acinus without fibrosis,
- decreased lung elasticity,
- architectural distortion of the capillary bed.\ loss of functioning surface are
- alveolar wall destruction
- Clinically
- presents in middle age and older,
- as a barrel chested
- “pink-puffer,
- breathing often with pursed lips, with
- insidious and unrelenting dyspnea.
- Diagnosis
- CXR shows
- hyperinflated lungs, with
- propensity for the upper lobes,
- flattened diaphragms and a
- s carinatum)”barrel chest”
- CT
- Swiss Cheese appearance
- areas of low attenuation correspond to the regions where the alveoli and bronchioles are enlarged due to destruction
- resemble the appearance of holes or gaps, similar to the holes in Swiss cheese.
- Swiss Cheese appearance
- Lug Function tests
- reduction in the maximal expiratory flow during forced exhalation. (decreased FEV1)
- Treatment
- bronchodilators,
- diuretics,
- corticosteroids,
- antibiotics
- low-flow oxygen,
- pulmonary rehabilitation.
- CXR shows
- Structurally
Centrilobular Emphysema Dilated Air Spaces Localized around a Bronchovascular Bundle.

This drawing shows a secondary lobule with centrally located dilated airspaces starting with the respiratory bronchiole and extending to the proximal structures including the alveolar ducts, sacs and alveoli
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Alveolar Wall Destruction Localized around a Bronchovascular Bundle.
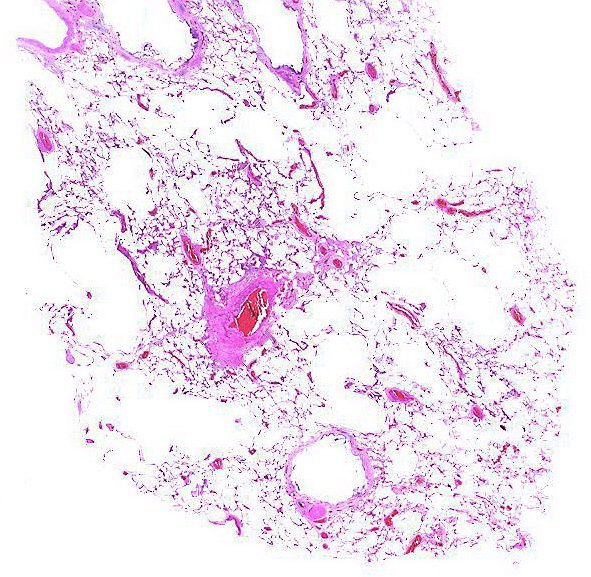

Alveolar wall destruction is localized around a bronchovascular bundle.
Courtesy Yale Rosen MD
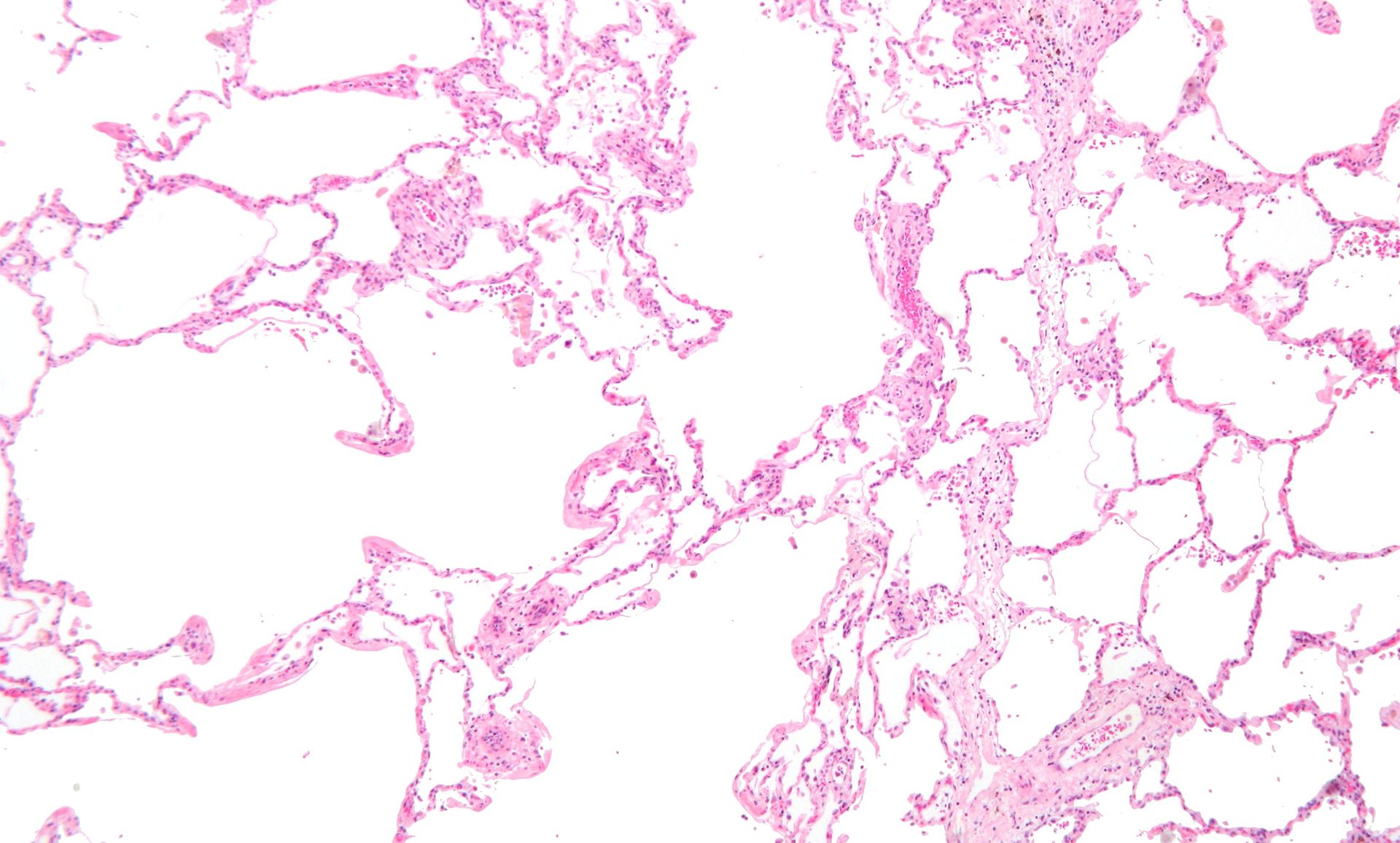

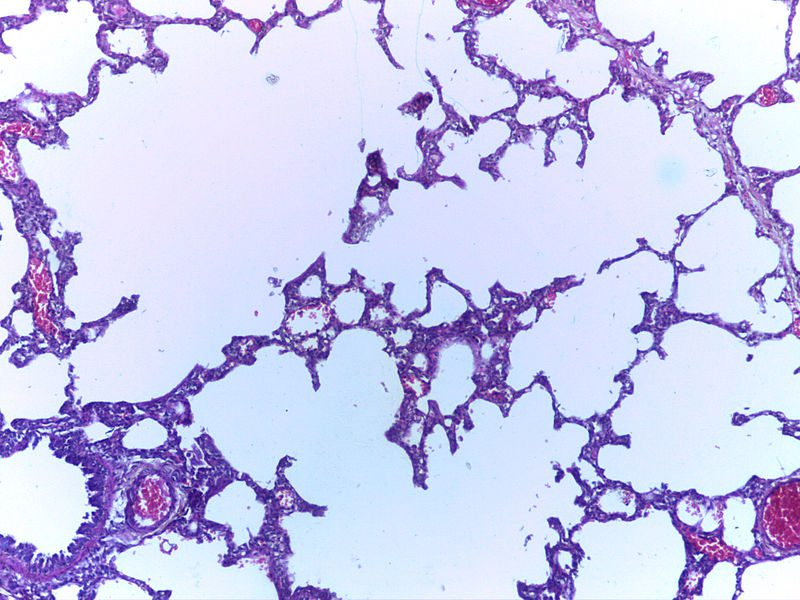
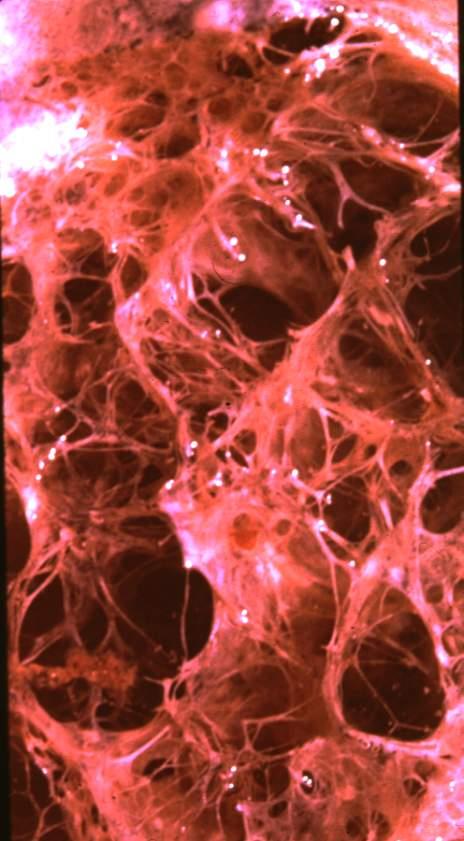
Low magnification micrograph of emphysema. H&E stain. The left of image shows severe emphysema (large empty spaces). The lung tissue on the right of the image has relative preservation of the alveoli. The top of the image is very near the pleural surface.
Courtesy Nephron

Micrograph of empysema lung showing dialated, large alveoli separated by thin septa. Some septae are ruptured and appear to be floating in the alveloar spaces. Grossly emphysematous lung appears pale and voluminous.
Source DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, CALICUT MEDICAL COLLEGE
Gross Anatomy of Upper Lobe and Apical Centrilobular Emphysematous Changes and Normal Lung Below
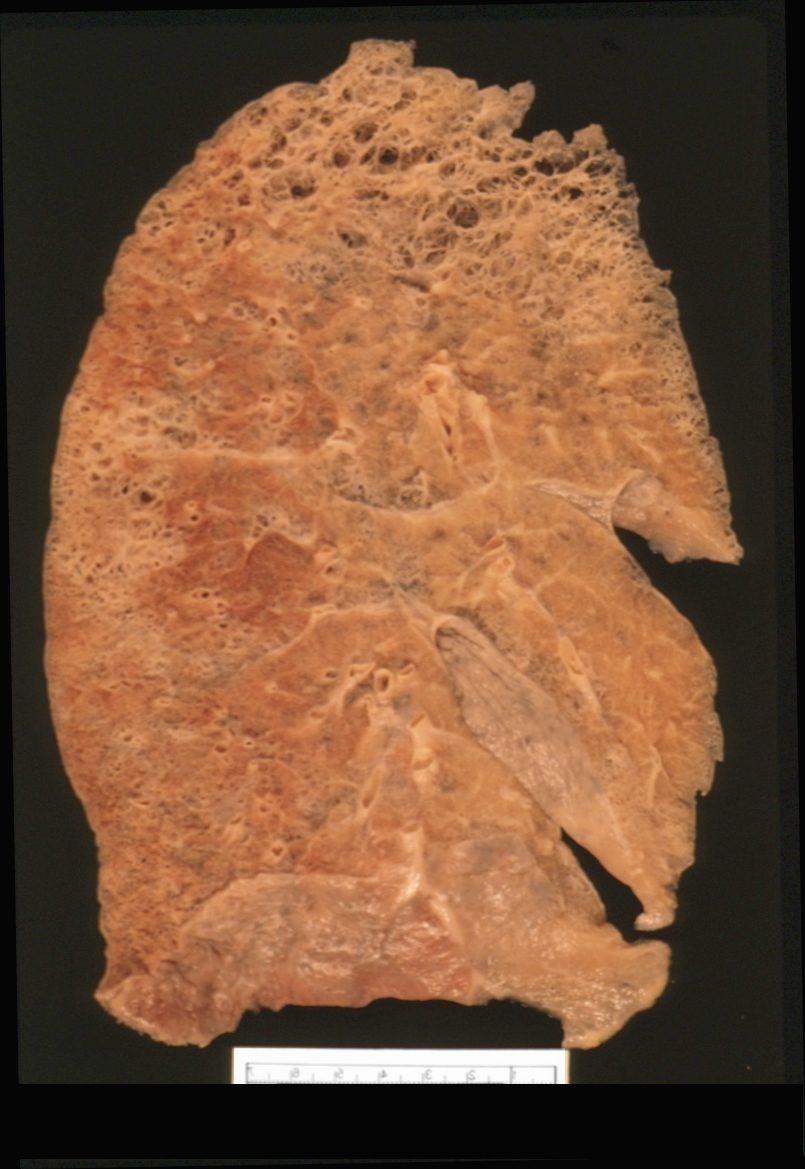

Ashley Davidoff MD
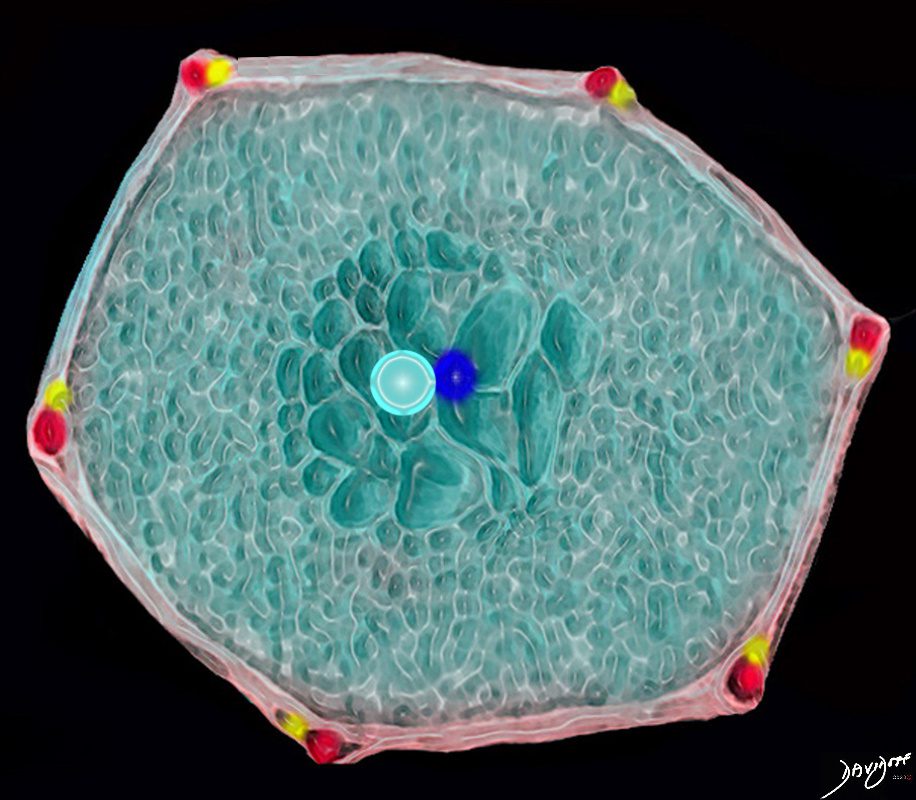
Normal Secondary Lobule
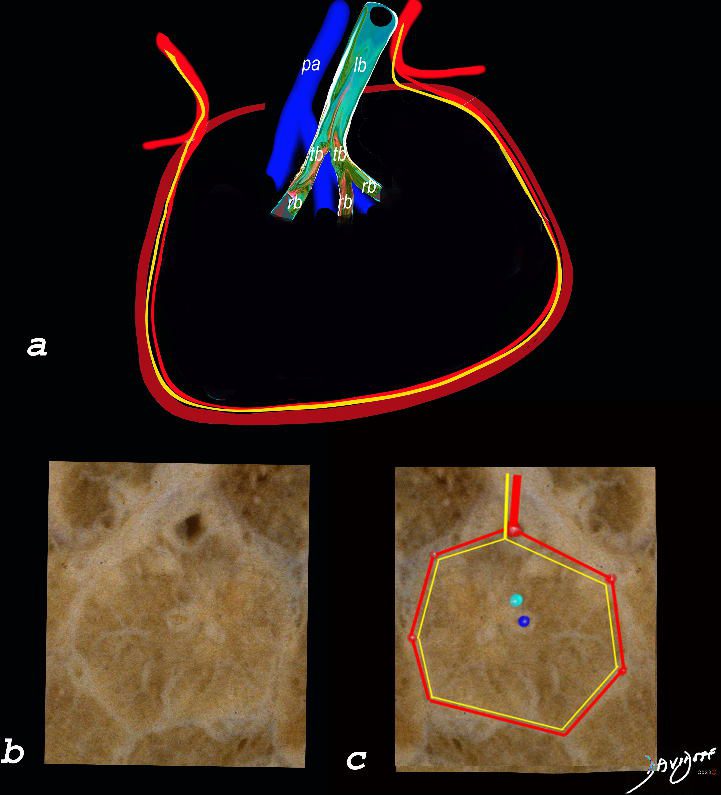

The top image (a) shows an anatomic drawing of a secondary lobule of the lung subtended by a lobular bronchiole (lb) and arteriole (pa). The interlobular septum contains the venule (red) lymphatic (yellow) and septum (maroon)
The anatomical specimen of the lung (b) shows normal intralobular parenchyma while image c shows the centrilobular arteriole (navy blue) and centrilobular bronchiole (teal) and interlobular venule (red) and lymphatics (yellow) The interlobular septum is slightly thickened
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Normal CT
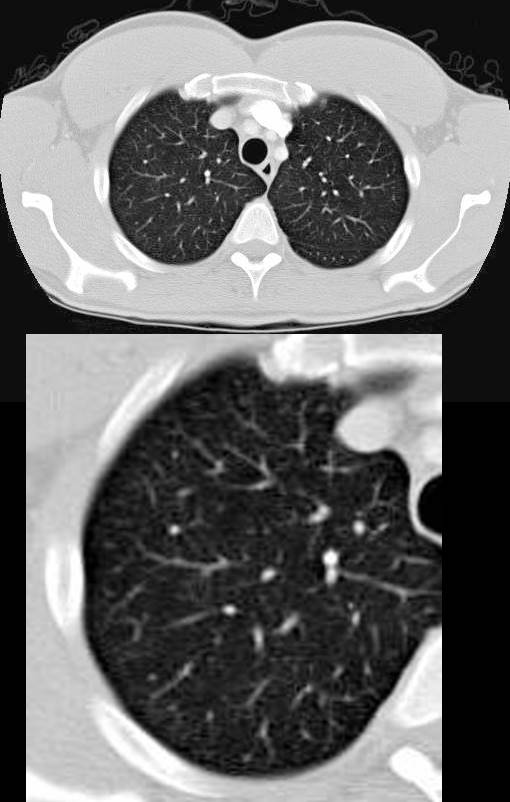

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Centrilobular Emphysema Gross Pathology
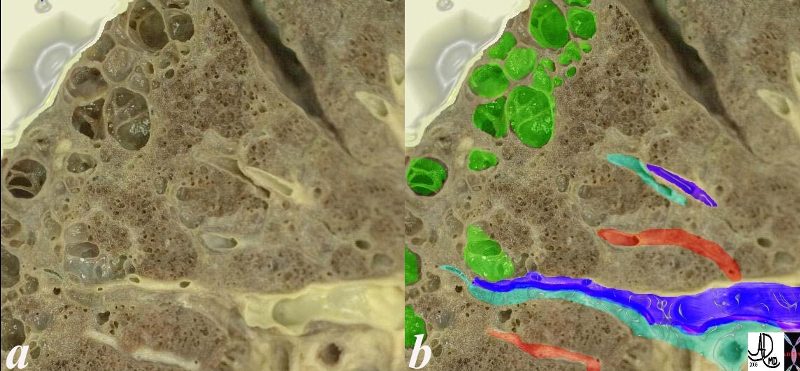

This is an image of an emphysematous lung. Note the larger air spaces where the septae between the alveoli, alveolar sac alveolar ducts and respiratory bronchioles have been broken down (green).
The bronchovascular bundle consisting of the arteriole (navy blue) and bronchiole (teal) subtends the secondary lobule. The pulmonary venule (red) originates from interlobular septa where it is intimately related to the lymphatics. 19932e

Ashley Davidoff MD 19.jpg
Electron Microscopy
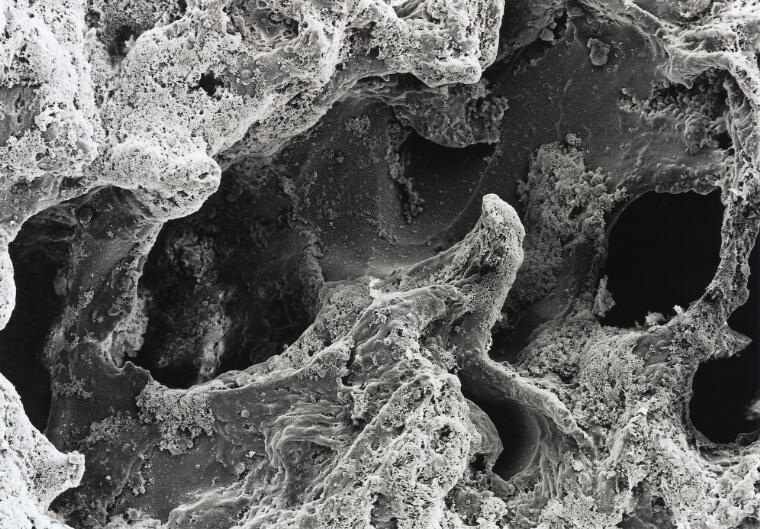


David Gregory & Debbie Marshall
Licence: Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
CXR Emphysema
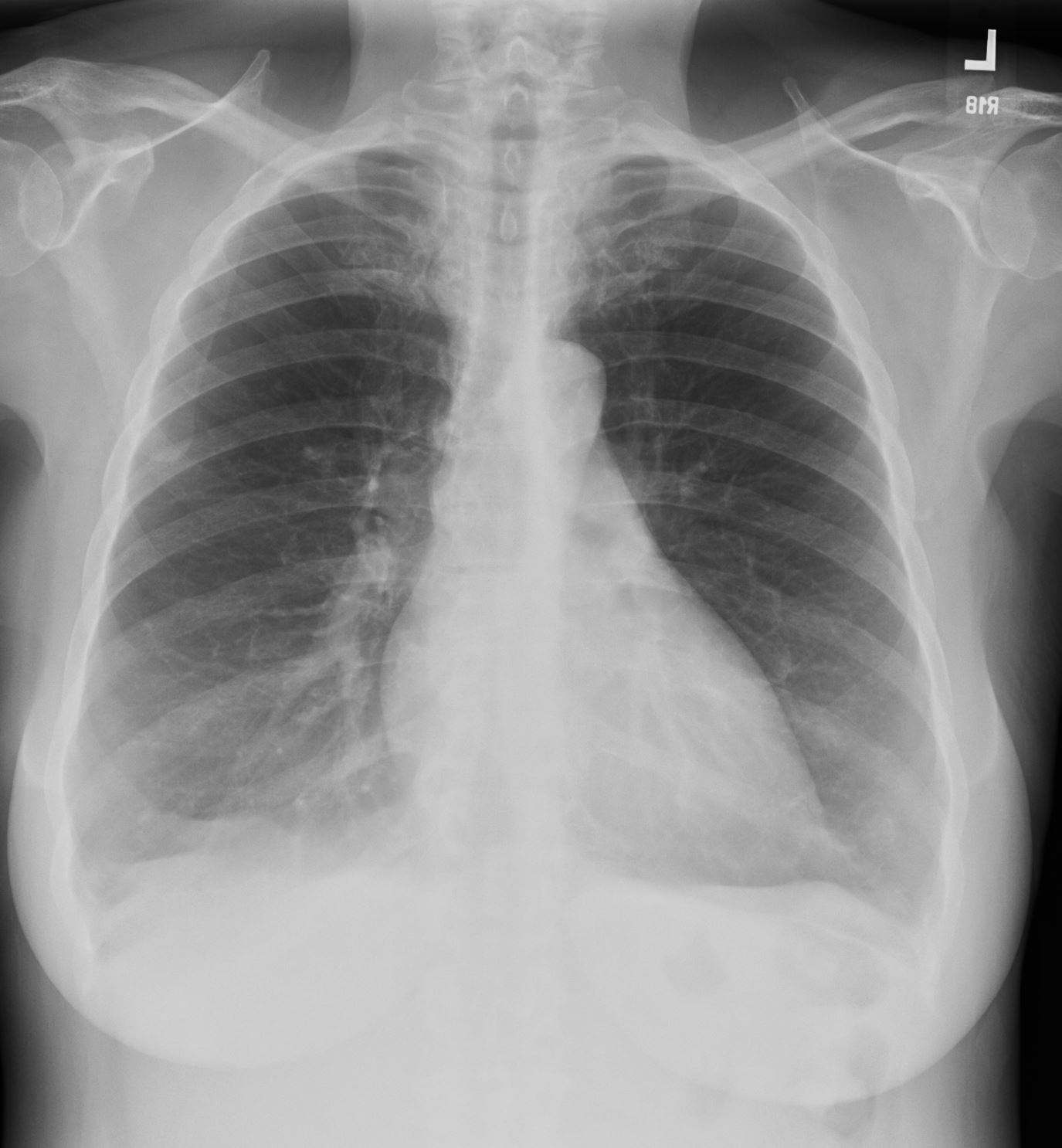

Flattened and Partially Inverted
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
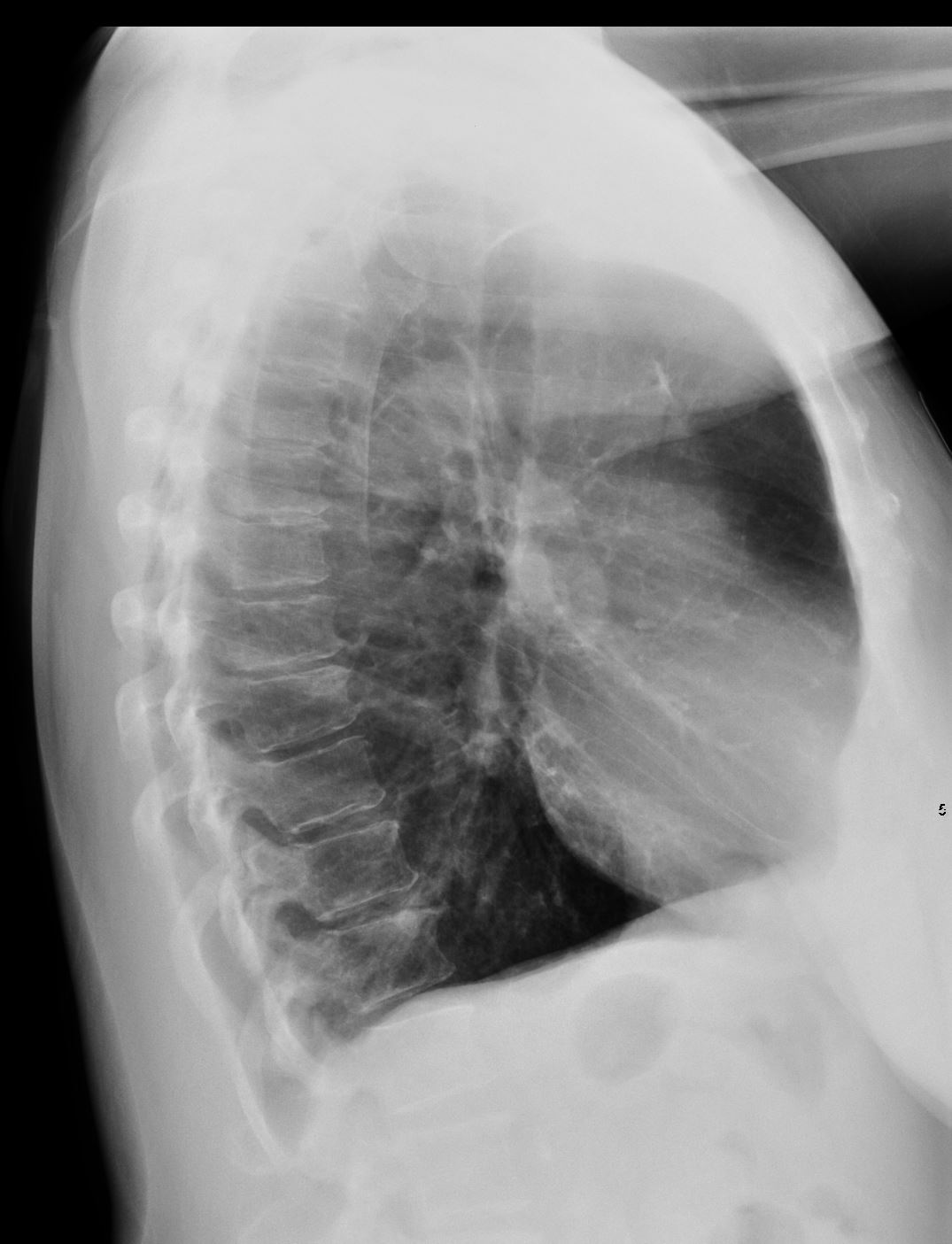

Flattened and Partially Inverted
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net


#signs in medicine
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
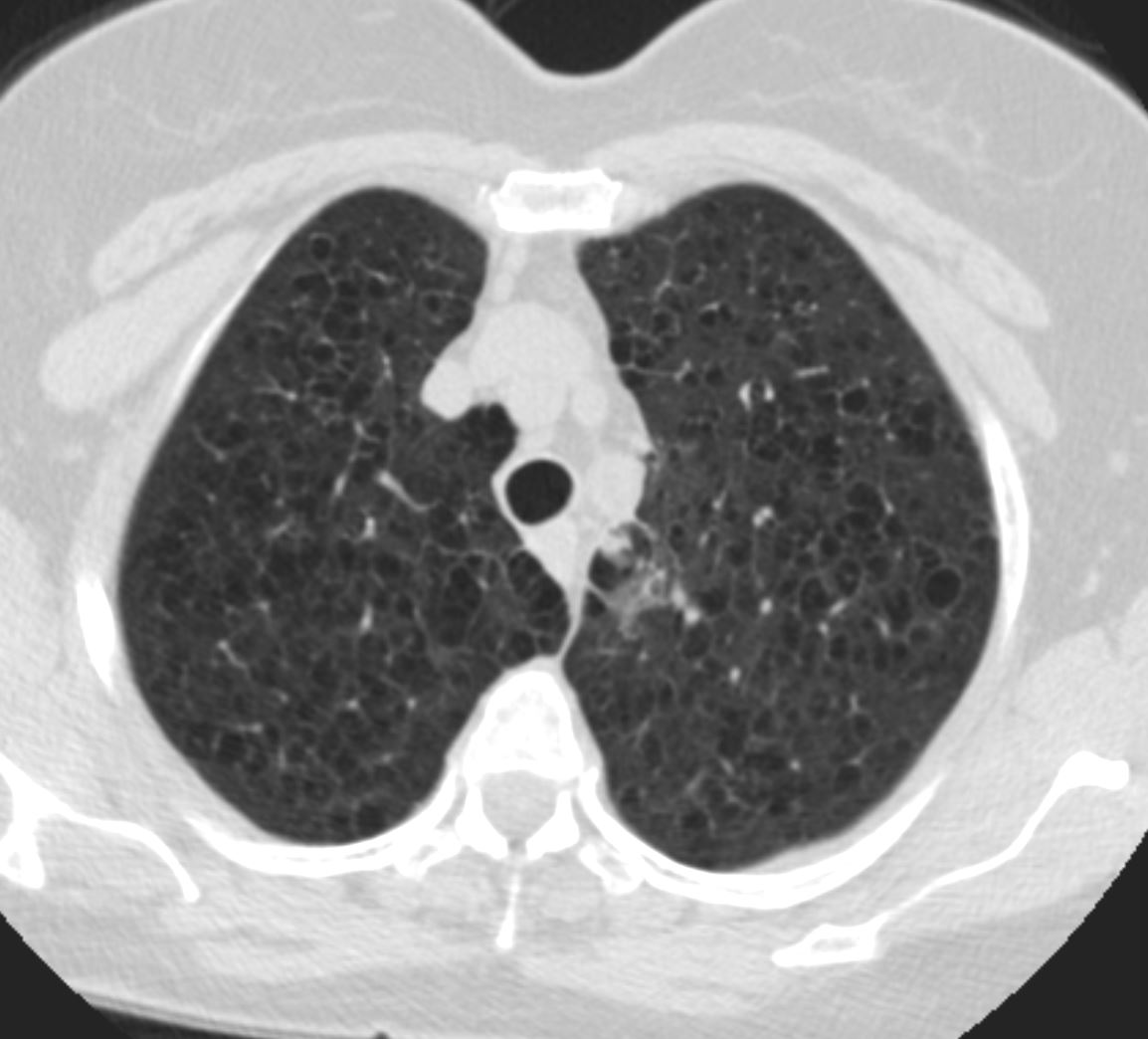
CT Scan of Centrilobular Emphysema Swiss Cheese
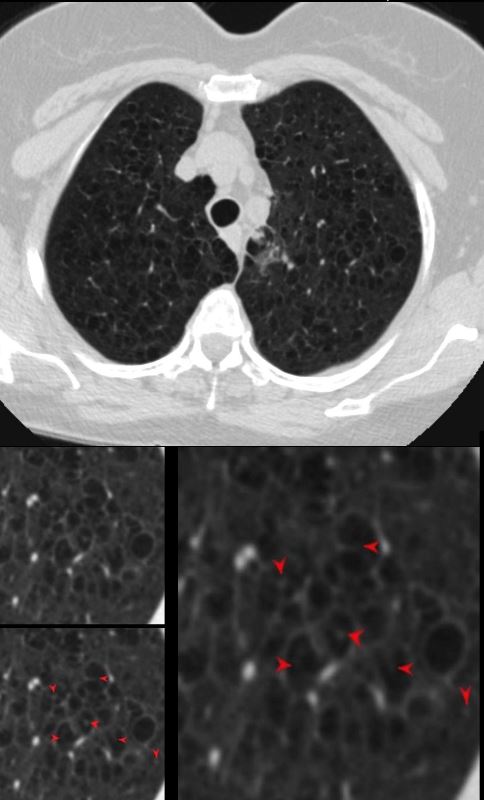

The axial CT of a 66 year old female with moderately severe centrilobular emphysema of the upper lobes. The magnified views show the focal central punctate density of the pulmonary artery indicating the presence of the central bronchovascular bundle (red arrow)
Ashley Davidoff MD The Common Vein.net
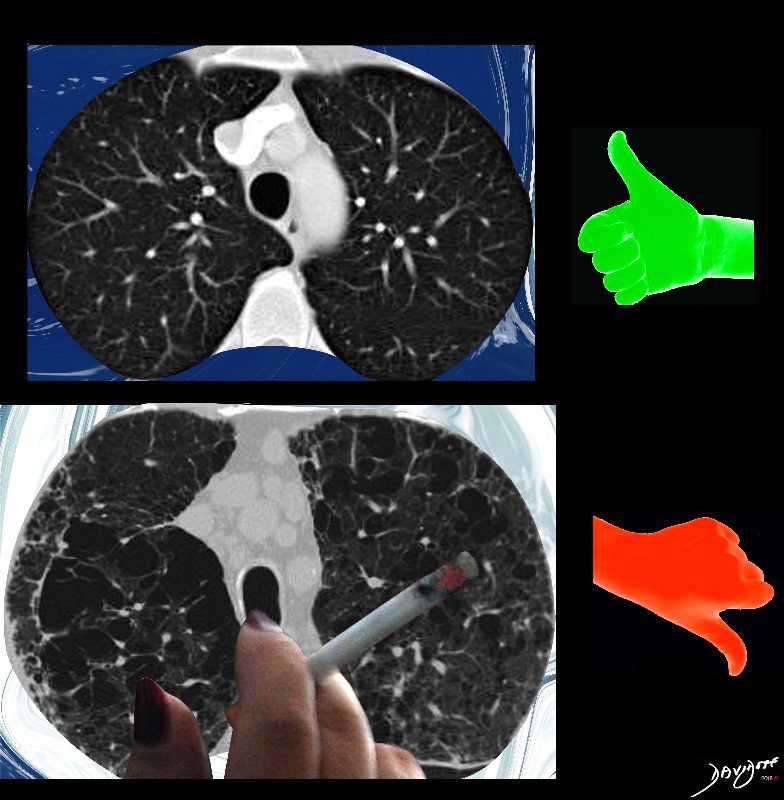
Side by Side Normal and Centrilobular Emphysema
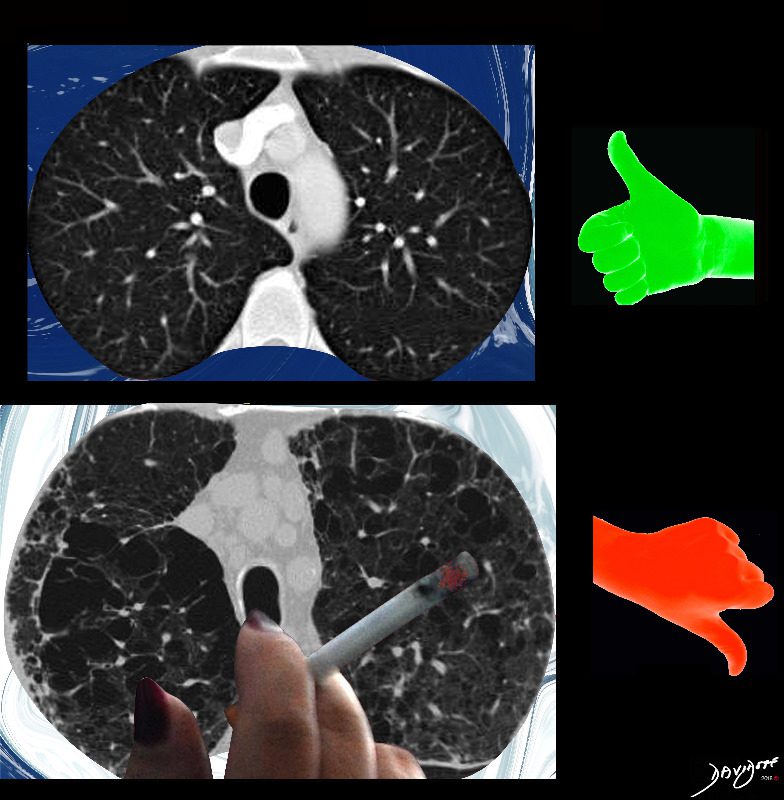

The imaging difference between healthy lungs (thumbs up) and emphysematous lungs (thumbs down)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVeein.net lungs-0071
key words emphysema, CTscan cigarettes smoking
Pathophysiology of Cigarette Smoking on Medium Sized Airways, Small Airways and Alveoli
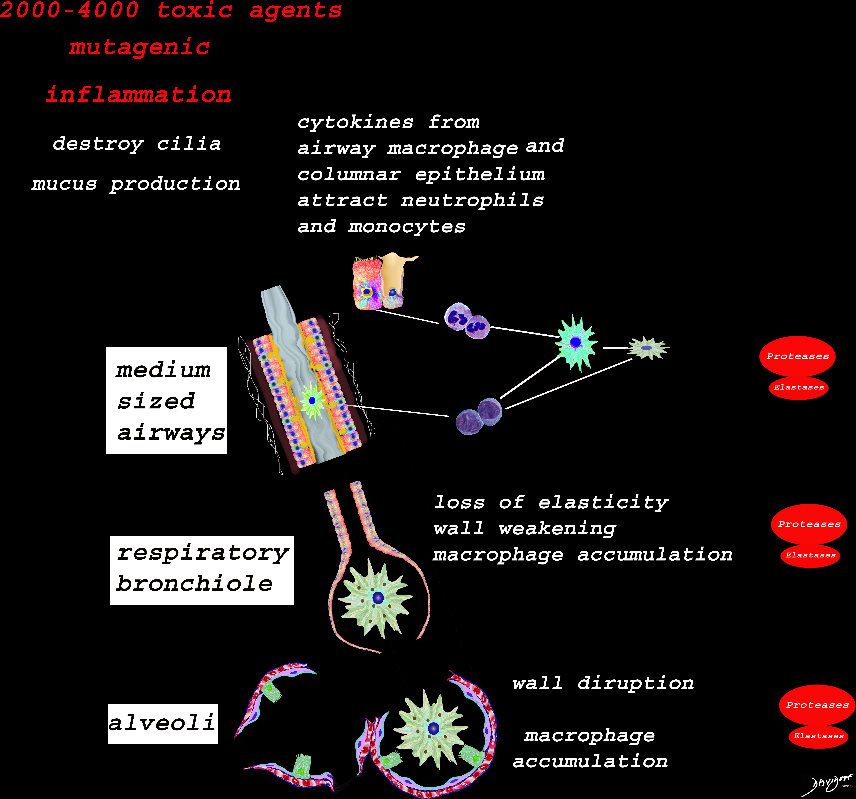

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00683
Structural Effects of Smoking on the Respiratory Bronchiole , Alveolar Ducts and Alveolar Sacs
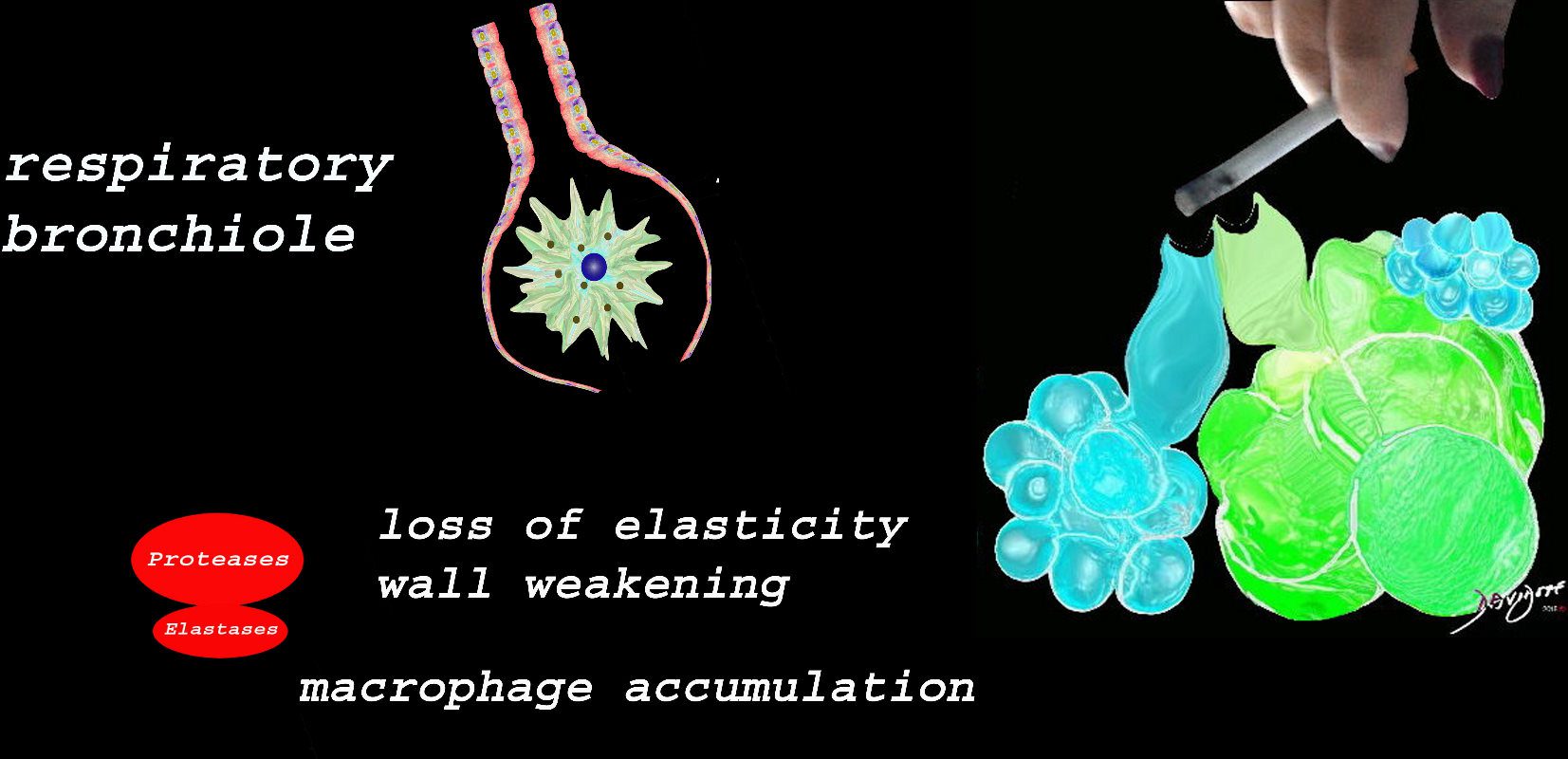

At the level of the membranous airways the effect is predominantly related to the loss of elasticity, vessel destruction and aberrant accumulation of smoking related macrophages.
The weakening and destruction results in emphysema and the abnormal accumulation of smoking related macrophages relates to DIP
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00685
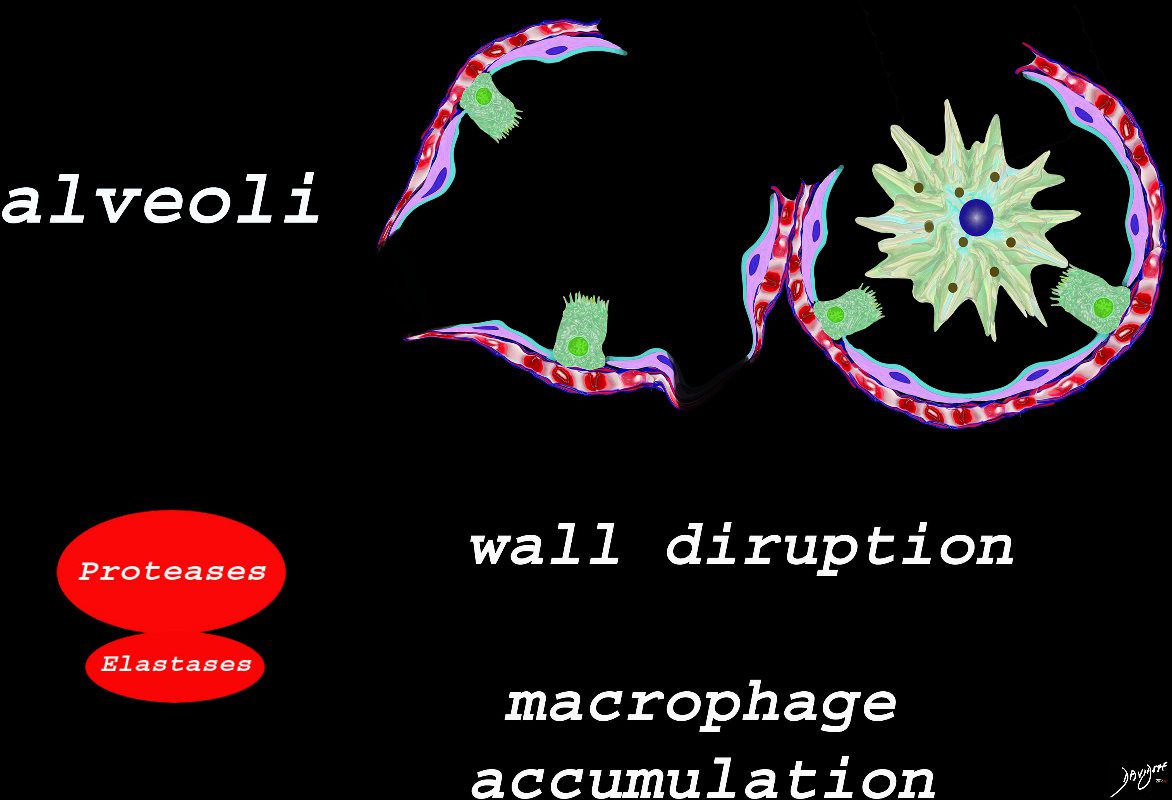

The effect of the proteases and and elastases cause destruction of the alveoli and loss of elasticity, and therefore overall function. The destruction leads to bullous disease
The accumulation of smokers macrophage, and in the case of Langerhans cell histiocytosis leads to space occupation of the alveoli also reducing function
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00687
It Starts at the Respiratory Bronchiole



Image on the left shows normal size and appearance of terminal bronchioles and alveoli. On the right the image shows the effects on the respiratory bronchioles and when severe, on the alveoli as well
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net

Ashley Davidoff Art TheCommonVein.net

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
Emphysema
- Centrilobular emphysema is an
- obstructive lung disease
- caused by
- obstructive bronchiolitis affecting the
- region of the proximal respiratory bronchiole
- allowing air into the secondary lobule but inhibiting
- exhalation with resultant
- air trapping and destruction of lung tissue
- obstructive bronchiolitis affecting the
- Destruction of small airways can lead to the formation of large bullae
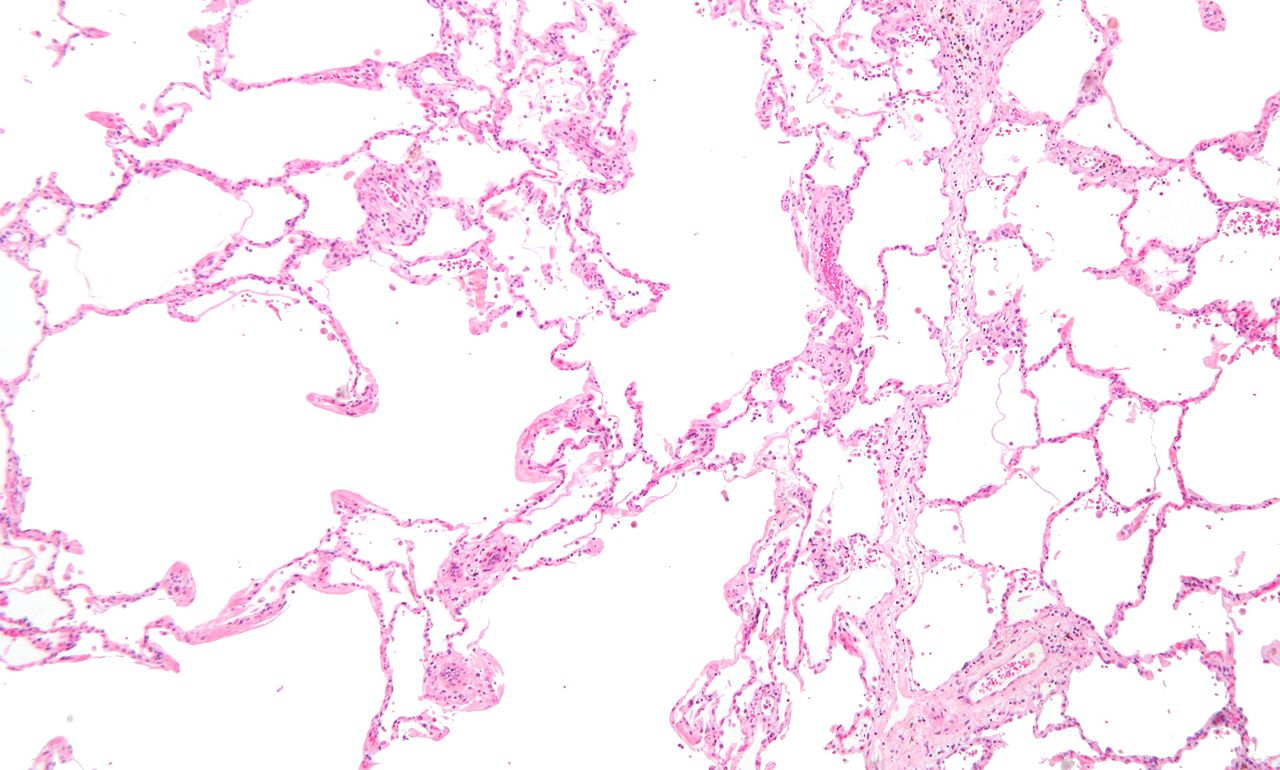

Micrograph showing emphysema (left – large empty spaces) and lung tissue with relative preservation of the alveoli (right)
Courtesy Nephron


Giovanni Battista Morgagni, who made one of the earliest recorded descriptions of emphysema in 1769
Public Domain
References and Links