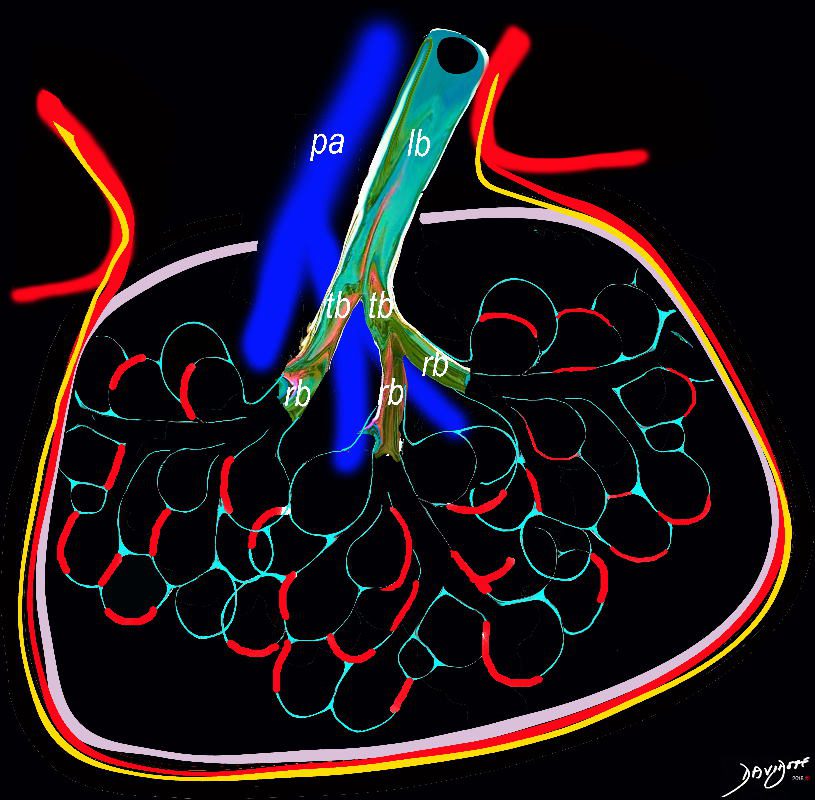
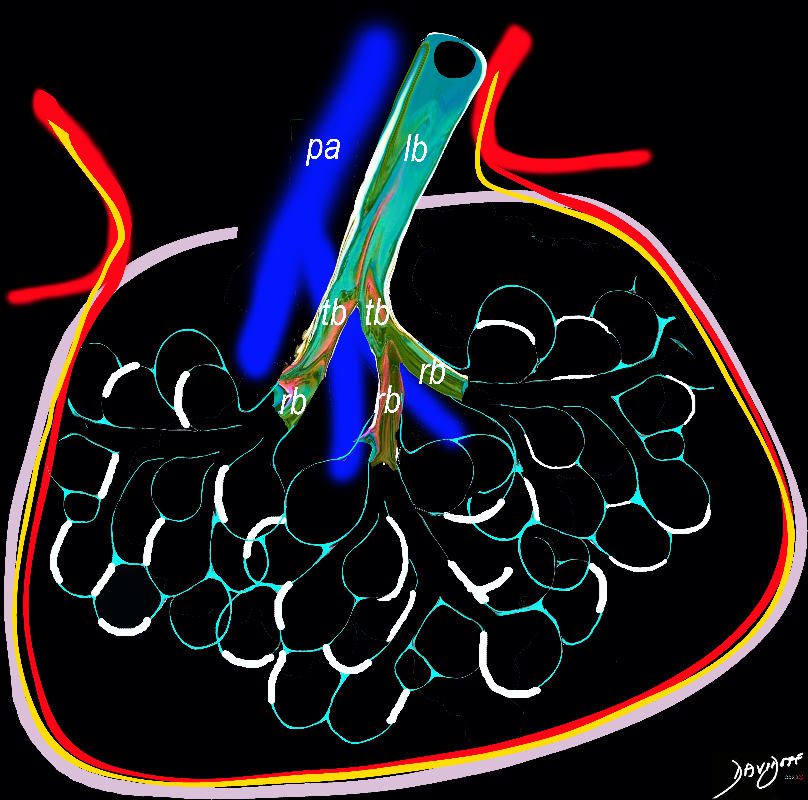
Interstitial Inflammation and Thickening Epicenter
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0736a01
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
lungs-0738b
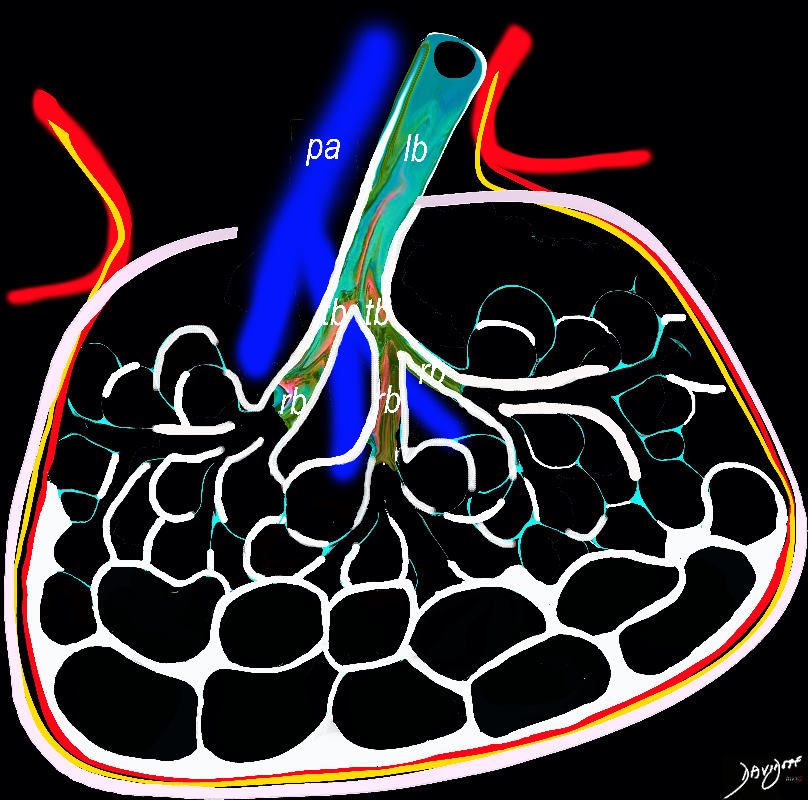
In patients with interstitial lung disease, the inflammatory process and interstitial fibrotic disease progresses and the walls between the alveoli are destroyed causing large subpleural, variably sized, subpleural, thick walled, stacked, cystic spaces . The appearance is reminiscent of a honeycomb and indicates end stage fibrosis
Ashley Davidoff MD thecommonvein.net lungs-0738bh
Inflammation
Follicular Bronchiolitis (Bronchiolitis Obliterans)
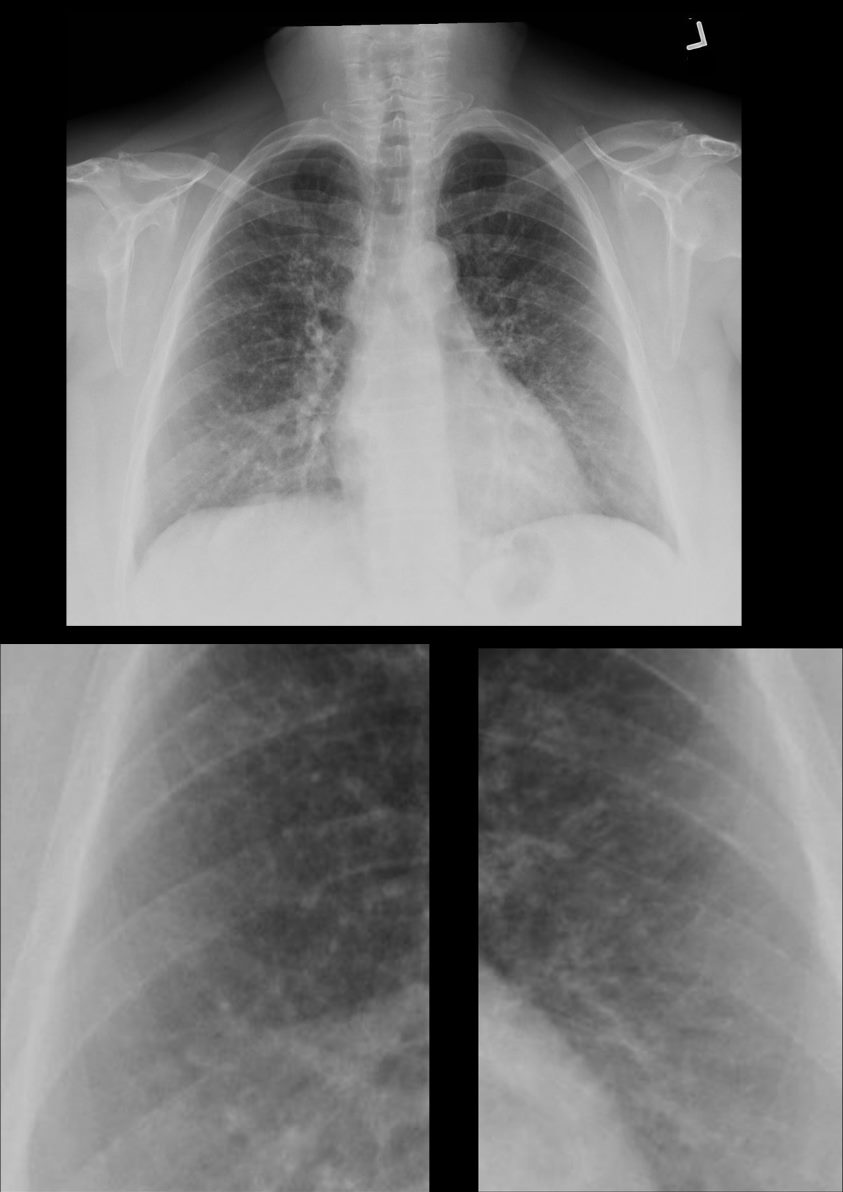
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea. Frontal view of the chest reveals a coarsened nodular interstitial pattern with magnified views showing the micronodularity in the lower panels.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136650c01
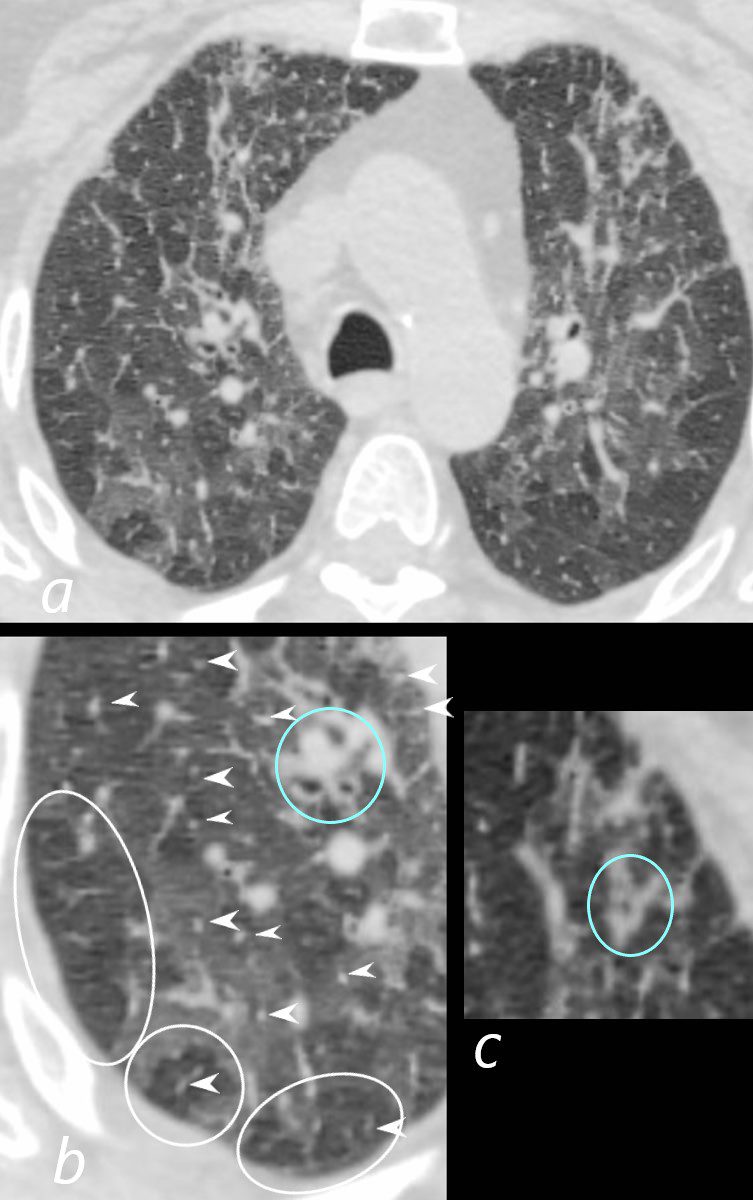
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the aortic arch reveals centrilobular nodules (b, white arrowheads) , ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (b, white rings) likely due to air trapping in this context, and bronchial wall thickening (b, c teal rings). There is some irregular thickening of the interlobular septa. In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136652cL
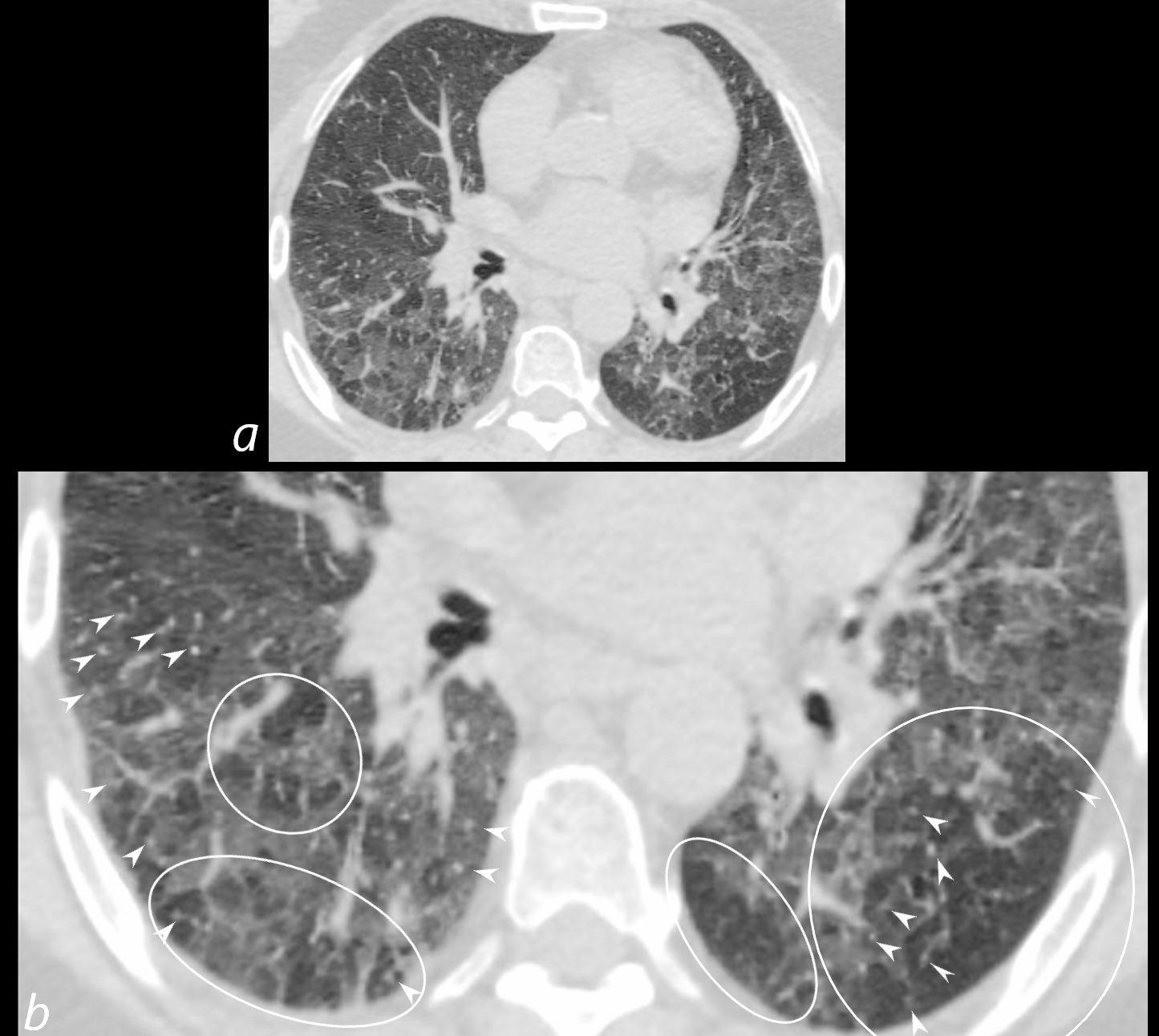
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the lower lung fields reveals centrilobular nodules (b white arrowheads), ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (b, white rings) likely due to air trapping in this context.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136657cL
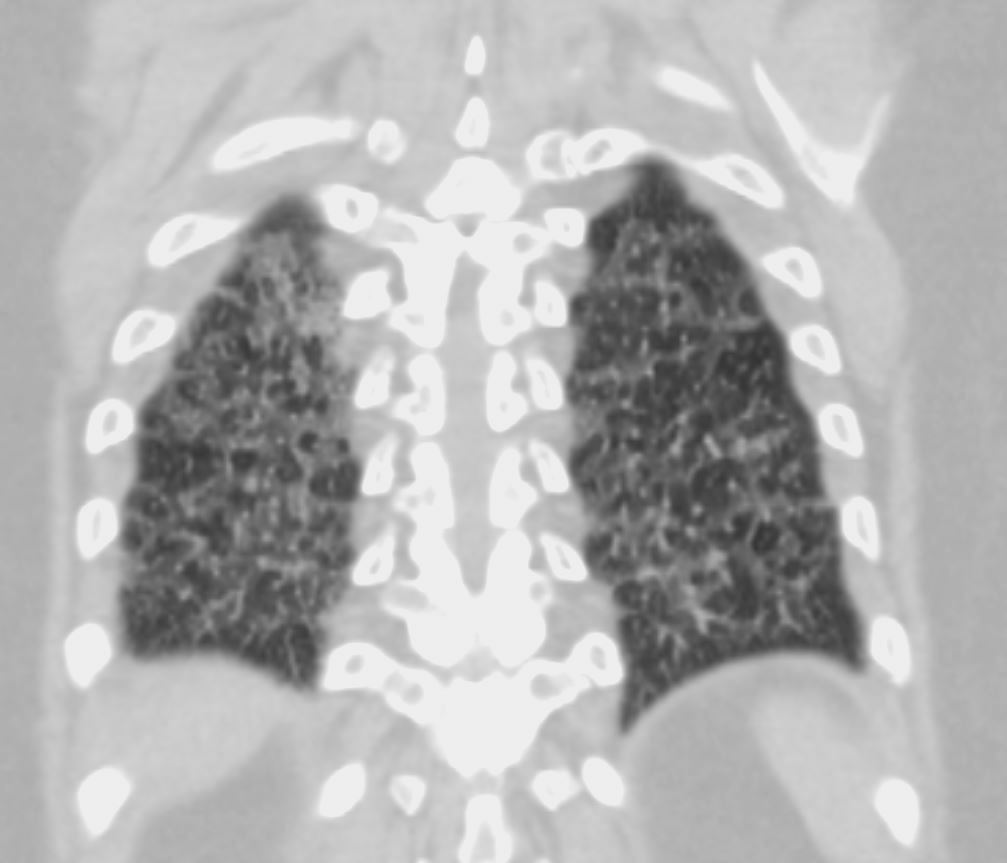
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
CT in the coronal plane of the chest at the level of the spine reveals bilateral diffuse changes in the lungs characterized by centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context) and irregular thickening of the interlobular septa.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136664
Bronchovascular Epicenter
Pneumonia and ILD
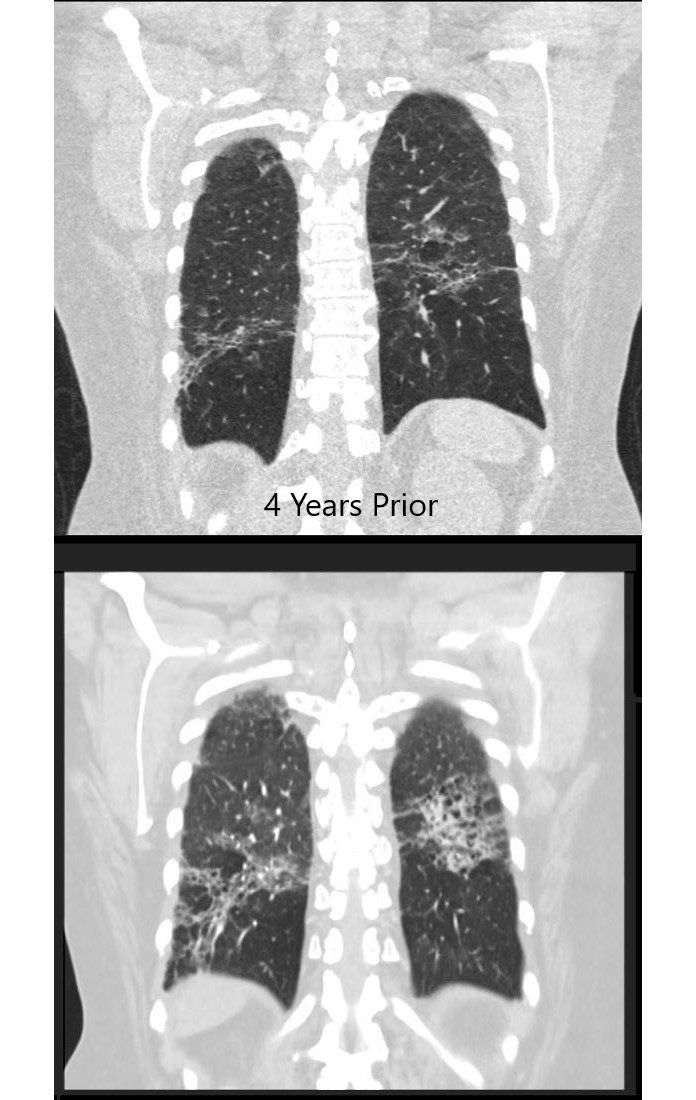
55-year-old female with shortness of breath. CT (above) is from 4 years prior and shows an interstitial process characterized by ground glass, reticular change, and bronchiectasis. The patient presents 4 years later with fever and white count and the CT (below) shows a pneumonic process in a background of ac chronic interstitial process with cystic air spaces ns bronchiectasis, and architectural distortion. Aspiration pneumonia was considered most likely
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135537
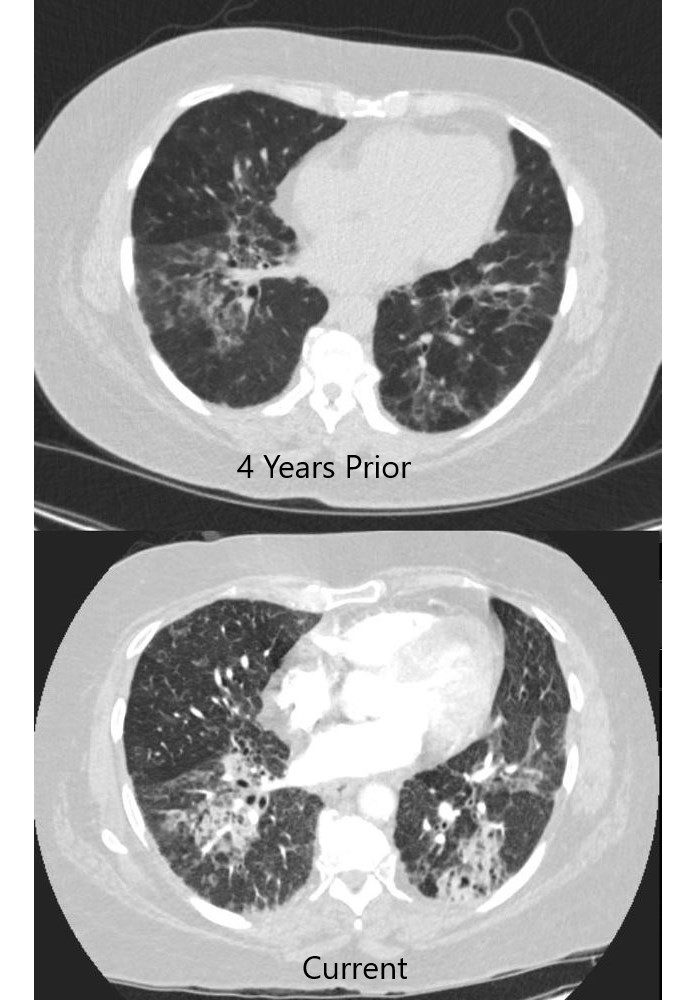
55-year-old female with shortness of breath. CT (above) is from 4 years prior and shows an interstitial process characterized by ground glass and reticular change. The patient presents 4 years later with fever and white count and the CT (below) shows a pneumonic process in a background of ac chronic interstitial process with cystic air spaces and architectural distortion. Aspiration pneumonia was considered most likely
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135536
