Clarifying Consolidation vs. Ground-Glass Opacity (GGO) and Atelectasis
1. Ground-Glass Opacities (GGOs) and Consolidation
- Key distinction
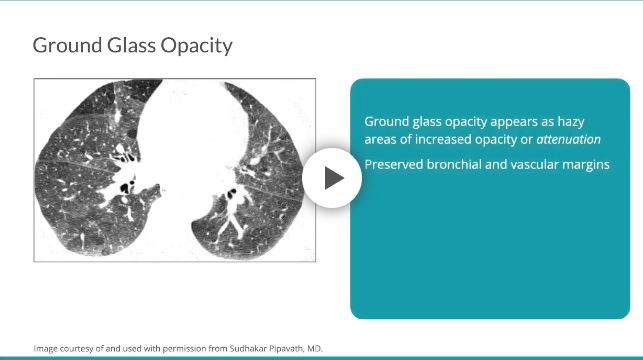
Ground-glass opacities (GGOs) and consolidations are related but distinct imaging findings:- Consolidation: Complete filling of alveoli with material such as fluid, pus, blood, or cells, leading to loss of normal aeration. It results in a homogeneous increase in lung attenuation on CT, where the underlying lung architecture is obscured, and air bronchograms are typically visible.
- GGO: A partial filling of alveoli with fluid, inflammatory exudate, or interstitial thickening. On CT, GGOs appear as hazy areas of increased attenuation, where the underlying lung architecture remains visible.
- Air bronchograms in GGOs
GGOs can exhibit air bronchograms, especially when partial alveolar filling occurs, but this does not make GGOs synonymous with consolidation. The persistence of visible pulmonary vessels and interstitial structures within GGOs distinguishes them from true consolidation. - Key takeaway
GGOs are not considered consolidations because they represent incomplete alveolar filling and preserved underlying architecture, whereas consolidation represents complete alveolar filling with loss of architectural visibility.
2. Atelectasis and Consolidation
- Key distinction
Atelectasis and consolidation are also distinct processes, although they may share overlapping features such as air bronchograms:- Atelectasis: Collapse or loss of lung volume due to airway obstruction, compression, or decreased surfactant. Atelectasis results in increased lung density but is accompanied by volume loss, evidenced by displacement of fissures, crowding of vessels and bronchi, and mediastinal shift (if extensive).
- Consolidation: Involves alveolar filling without volume loss, usually caused by pathological substances rather than mechanical collapse.
- Air bronchograms in atelectasis
Air bronchograms may occur in atelectasis if the airways remain patent while the surrounding alveoli collapse. However, the presence of volume loss (e.g., retracted fissures) and other indicators distinguishes atelectasis from consolidation. - Key takeaway
Atelectasis is not considered consolidation. While both can show air bronchograms, consolidation is characterized by alveolar filling without volume loss, whereas atelectasis involves volume loss due to lung collapse.
Summary of Differences
- Ground-glass opacity: Partial alveolar filling; underlying architecture visible; not consolidation.
- Atelectasis: Volume loss due to lung collapse; not consolidation despite potential air bronchograms.
- Consolidation: Complete alveolar filling; increased attenuation with obscured architecture.
Key Points and Pearls
- Air bronchograms are not specific to consolidation and can appear in GGOs or atelectasis if airways remain patent.
- Differentiation between these entities relies on evaluating secondary features like lung architecture (visible in GGOs), volume changes (present in atelectasis), and extent of alveolar filling (complete in consolidation).

Courtesy Ashley Davidoff
Ashley Davidoff thecommonvein.net notes scale music-0019-low resb

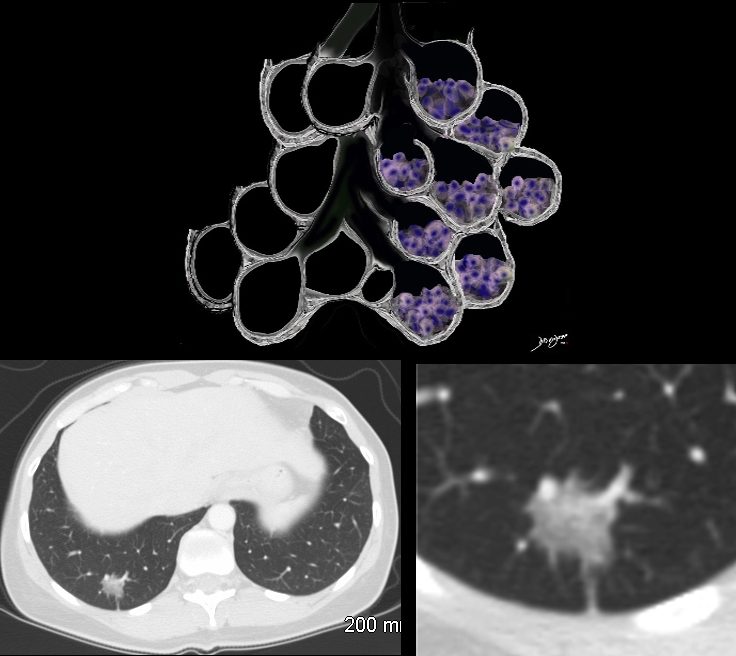
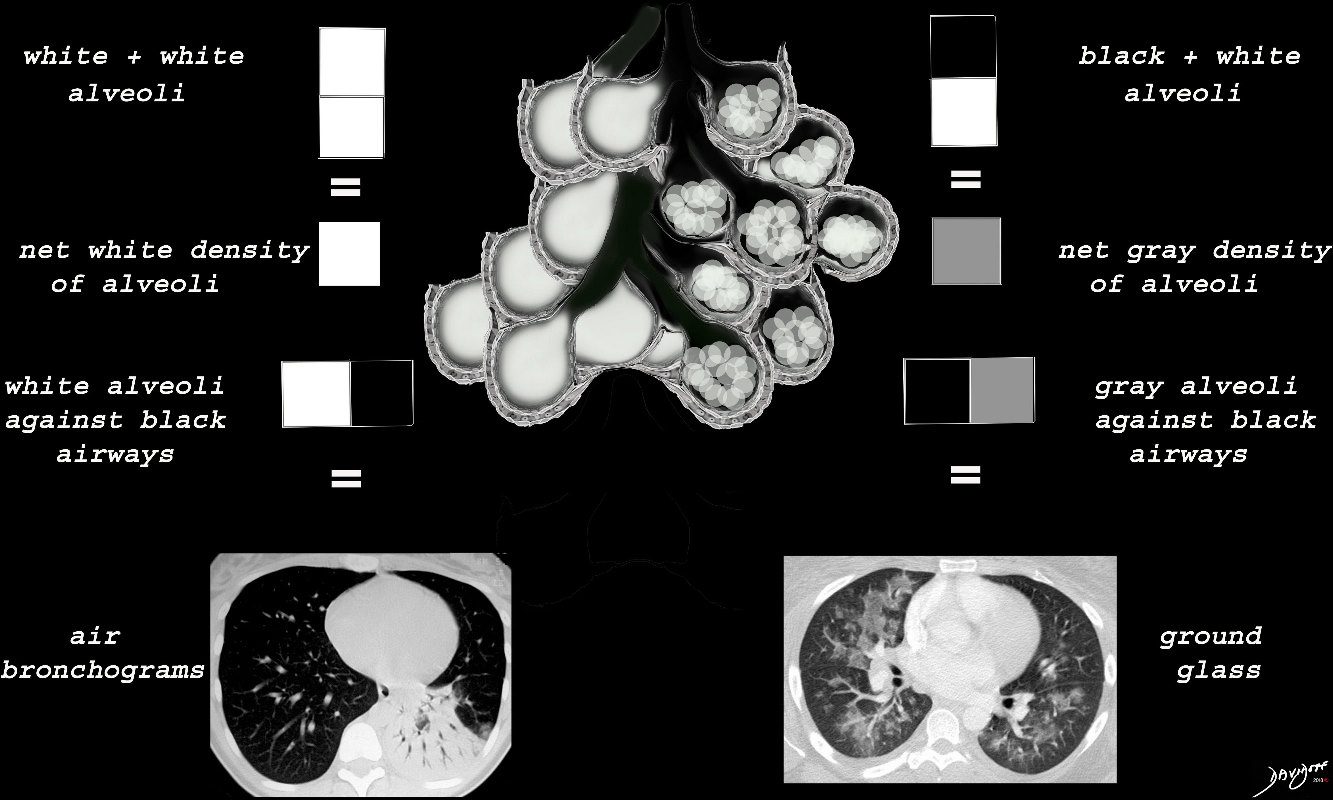
When the alveoli are fully filled with fluid, tumor, or pus for example, the overall net density will be white, and when adjacent to air filled airways, air bronchograms are visible (left side of image)
When the alveoli are only partially filled, the density of the fluid added to the density of the air results in an overall gray density, and when positioned next to air filled bronchi, there is insufficient contrast to create an air bronchogram and sufficient to enable visualization of the blood vessels. This is called ground glass opacification
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00681
Chest radiologists adopted it in the 1980s, with a first appearance in the Fleischner Society Glossary of Terms for Thoracic Radiology in 1984




When the alveoli are fully filled with fluid, tumor, or pus for example, the overall net density will be white, and when adjacent to air filled airways, air bronchograms are visible (left side of image)
When the alveoli are only partially filled, the density of the fluid added to the density of the air results in an overall gray density, and when positioned next to air filled bronchi, there is insufficient contrast to create an air bronchogram and sufficient to enable visualization of the blood vessels. This is called ground glass opacification
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
- Gray areas of increase density arising from
- Disease in the
- airways
- alveoli
- inter-alveoalar septa
- interstitium
- Disease in the


TheCommonVein.net


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0733


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0702d- lo res


The Ground Glass Opacity (GGO) in this case is caused by partial filling of the alveolus with malignant cells Ground glass opacification may be caused by partial filling of the alveolus with cellular material resulting in partial replacement of air with solid material. The net density is gray rather than white in the situation where the alveolus is fully replaced with cells or fluid. There is blending of the black of the subtending airways and the white of the vessels with the gray density of the cellular infiltrate and hence the normal vessels are not visualized in ground glass opacities.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 134375b01

Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
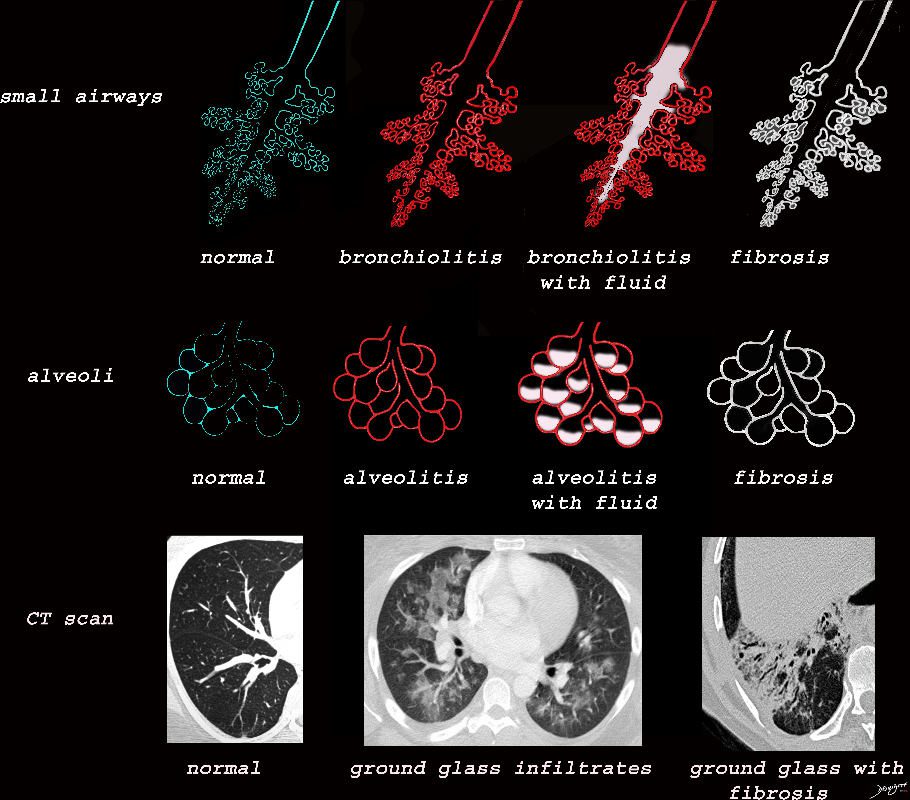
Normal Structure
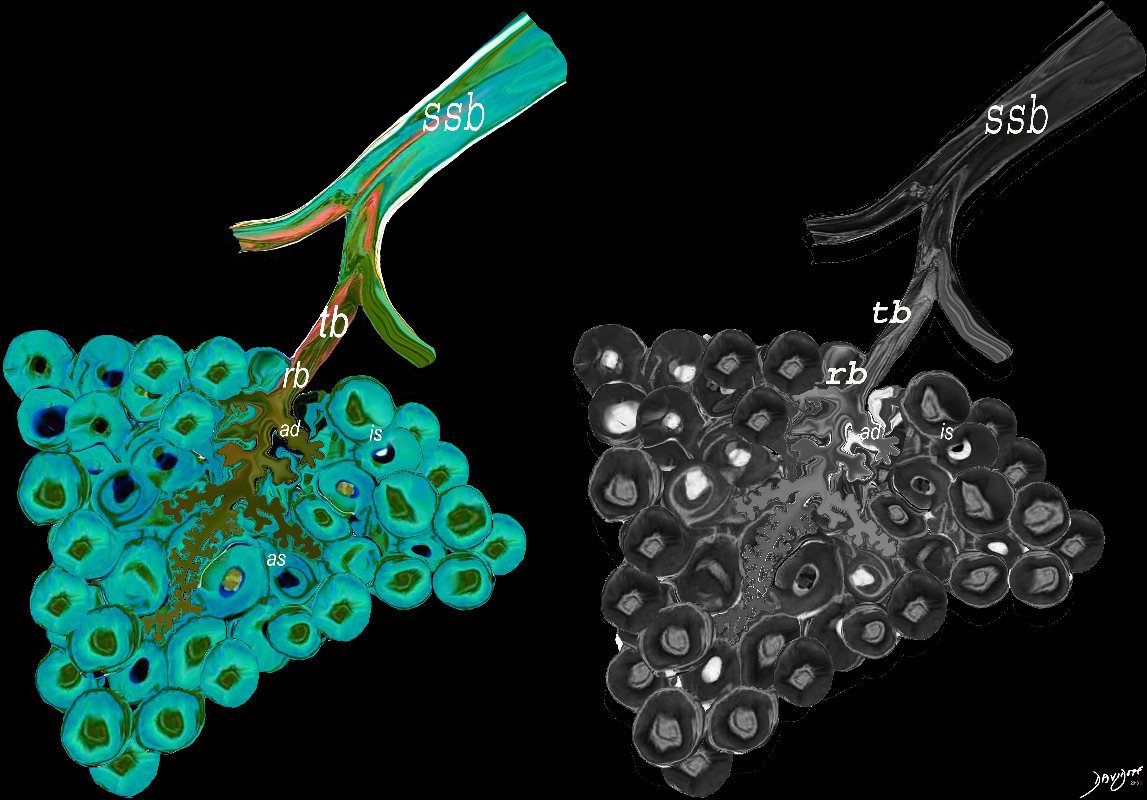

The subsegmental medium sized airways give rise to the terminal bronchiole (tb) which gives rise to the membranous airways. These include in order, the respiratory bronchiole (rb), alveolar duct (ad) and alveolar sac (as)
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net
- Ground Glass Changes May result from Disease in the
- Small Airways
- Alveoli
- Interalveolar Septa
- Interstitium



Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0733
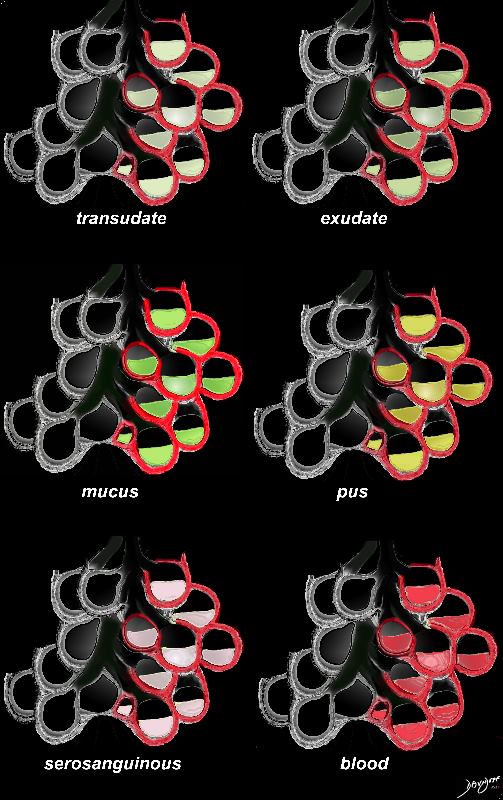
Origin in the Alveoli
Types of Fluids that Can Partially Fill in the Alveoli



Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0702d- lo res
Application to Radiology
Concept of the Fully Filled Alveolus with Net “White Density”
vs.
Half Filled Fluid Alveolus with a Net of “Gray” Density




When the alveoli are fully filled with fluid, tumor, or pus for example, the overall net density will be white, and when adjacent to air filled airways, air bronchograms are visible (left side of image)
When the alveoli are only partially filled, the density of the fluid added to the density of the air results in an overall gray density, and when positioned next to air filled bronchi, there is insufficient contrast to create an air bronchogram and sufficient to enable visualization of the blood vessels. This is called ground glass opacification
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Acute Ground Glass Infiltrates Caused by partial Filling of the Alveoli with Fluid
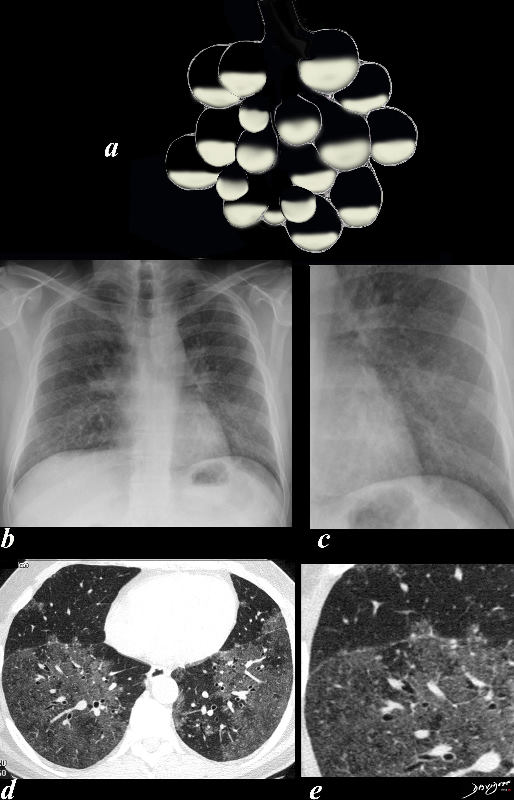

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
lungs-0708d- lo res
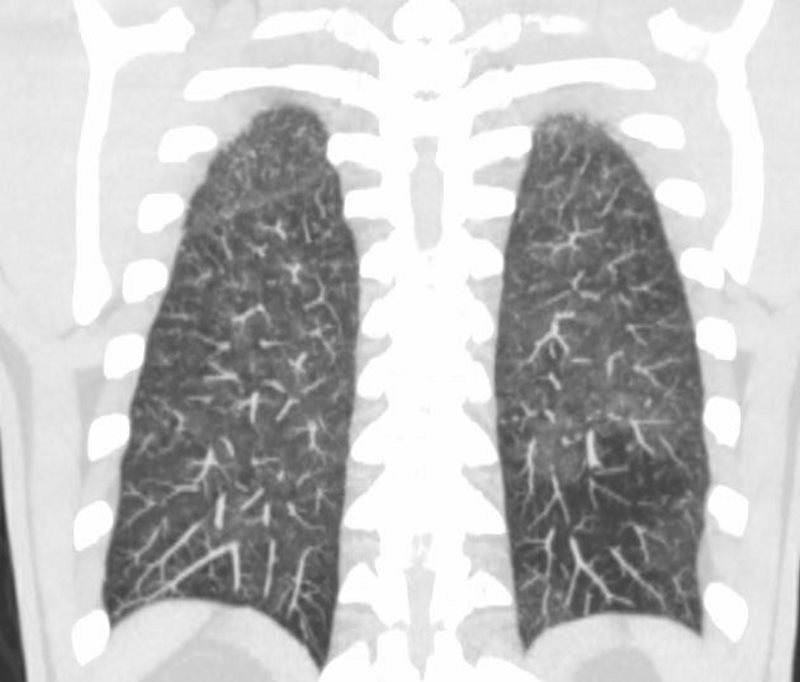
CHF


50 year old female with diabetes, chronic renal failure with congestive heart failure. CT in the coronal plane shows diffuse ground glass changes, Kerley B lines at the right base,
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-003-CT


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-004-CT


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-010-CT
Types of Cells that Can Partially Fill in the Alveoli
Examples include Langerhans Cells, Macrophages, Eosinophils and Malignant Cells
-

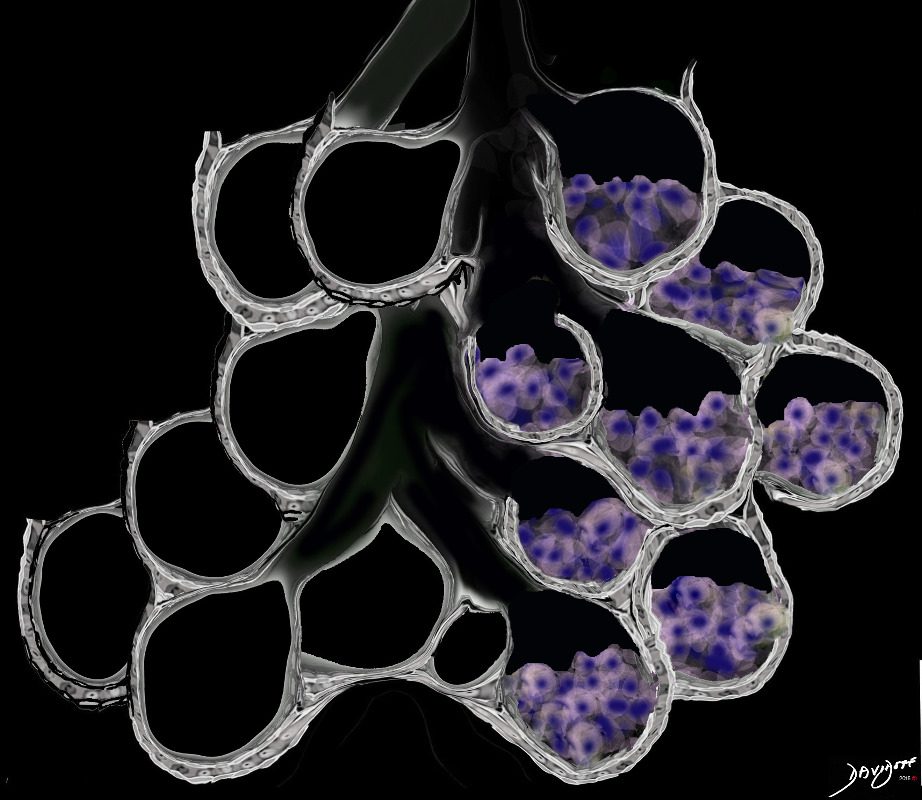
Half Filled Cellular Accumulation in the Alveolus Type of Cells include Langerhans Cells Macrophages and Malignant Cells
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0707a
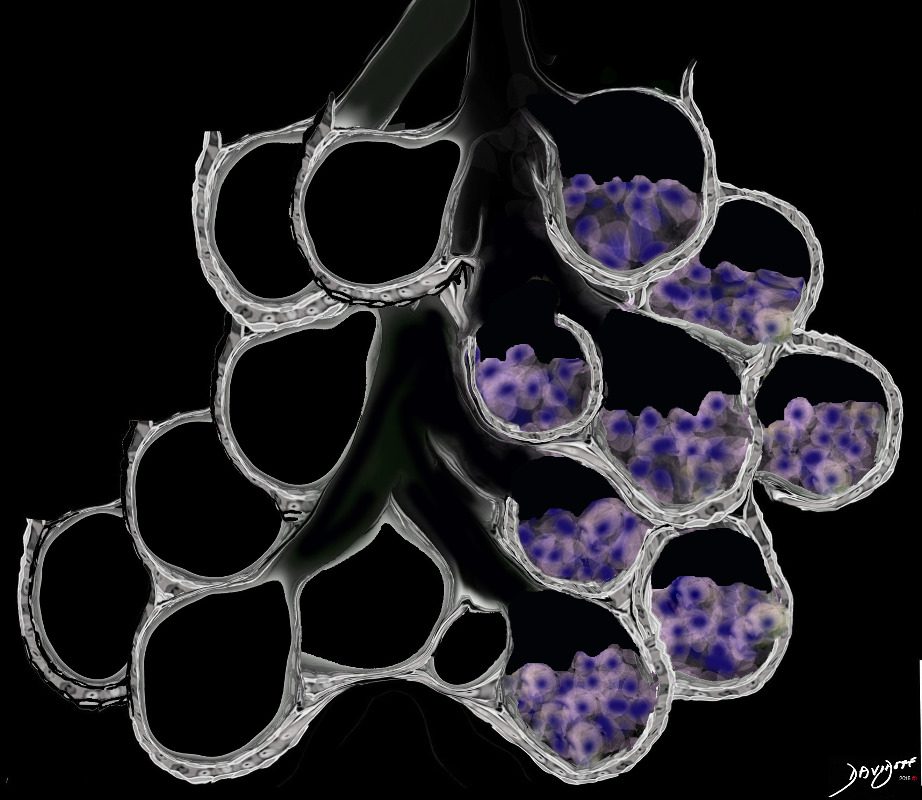
Ground Glass Opacity (GGO) Caused by Cellular Accumulation with Partial Filling of the Alveolus Type of Cells include Langerhans Cells Macrophages and Malignant Cells
Ground glass opacification may be caused by partial filling of the alveolus with cellular material with partial replacement of air with solid material with the net density being gray rather than white if the alveolus were fully filled. The black of the airway nor the white of the vessels may blend with the gray density and hence they are not visualised in ground glass opacities. ore is usually lood vessels and airway walls The replacement may be due to cellular infiltration including inflammatory ,benign or malignant cells without or with fluid.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0707adEosinophils in Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia


Infiltration of eosinophils and exudation into the alveoli and interalveolar septa and interstitium
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
lungs-0756b01Application to Radiology
Concept of the Fully Filled Alveolus with Net “White Density”
vs.
Half Filled Fluid Alveolus with a Net of “Gray” Density

When there are extensive cellular accumulations in the alveoli, such as adenocarcinoma with lepidic growth, Langerhans cells or other macrophages, the overall net density of the region of involvement will be gray, and when adjacent to the black air filled airways, a ground glass appearance will be apparent
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
ssb = subsegmental bronchiole
tb = terminal bronchiole
rb = respiratory bronchiole
as = alveolar duct
as = alveolar sac
is = interalveolar septum
lungs-00682-lo res
- Difference Between Consolidation and Ground Glass
GGO -(Nodule) in Adenocarcinoma with Lepidic Growth



The Ground Glass Opacity (GGO) in this case is caused by partial filling of the alveolus with malignant cells Ground glass opacification may be caused by partial filling of the alveolus with cellular material resulting in partial replacement of air with solid material. The net density is gray rather than white in the situation where the alveolus is fully replaced with cells or fluid. There is blending of the black of the subtending airways and the white of the vessels with the gray density of the cellular infiltrate and hence the normal vessels are not visualized in ground glass opacities.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 134375b01
GGO with Origins in the Interstitium
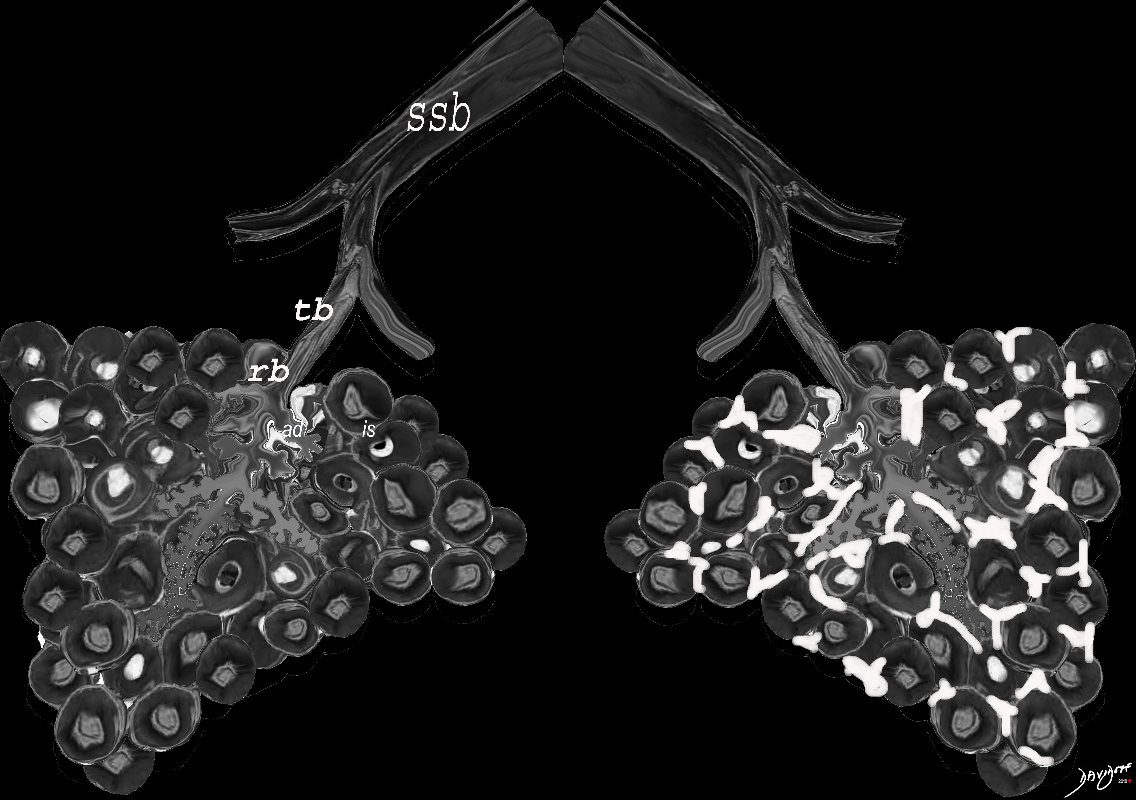

When there are extensive interstitial fibrotic changes in the interstitial compartments of the lung which include the and the interalveolar septa, and the supporting interstitium of the lung between the acini and small airways, the overall net density of the region of involvement will be gray, and when adjacent to the black air filled airways, a ground glass appearance will be apparent
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
ssb = subsegmental bronchiole
tb = terminal bronchiole
rb = respiratory bronchiole
as = alveolar duct
as = alvelar sac
is = anteralveolar septum
lungs-00682-lo res
Ground Glass from Interlobular Septal Fibrosis
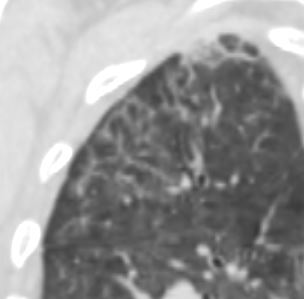

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
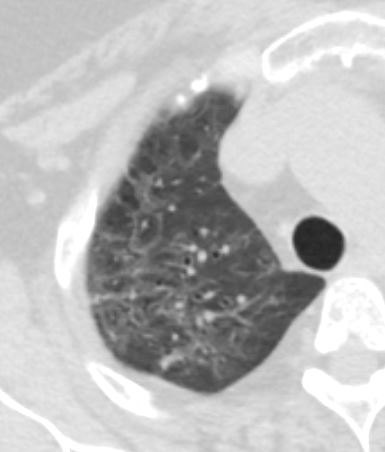

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
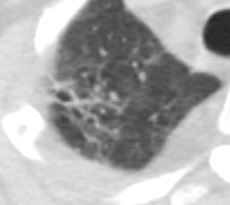

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
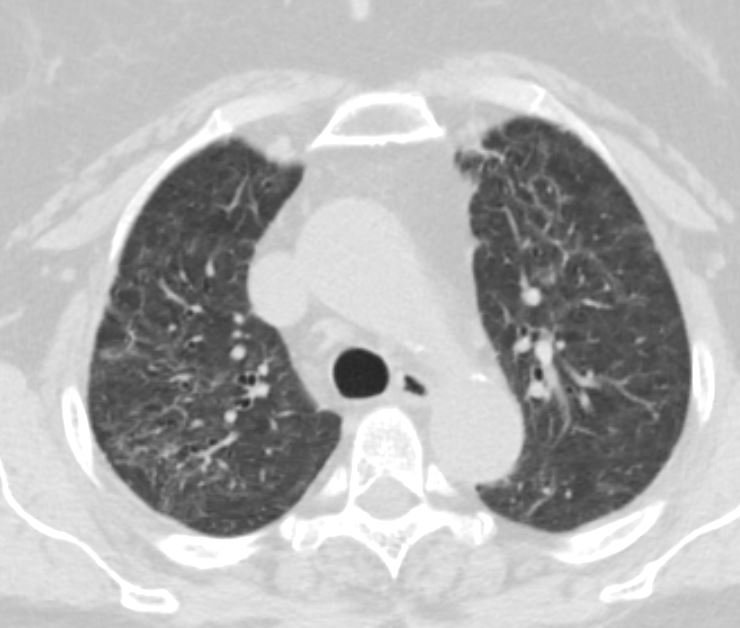

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
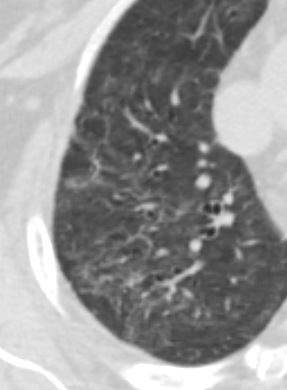

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
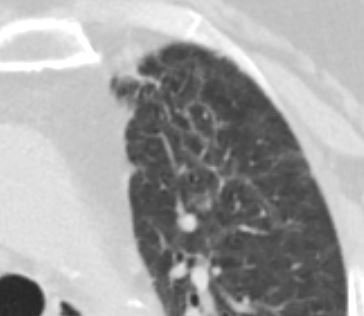

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
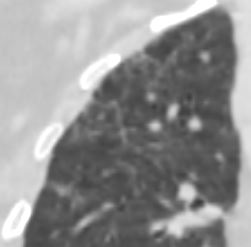

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
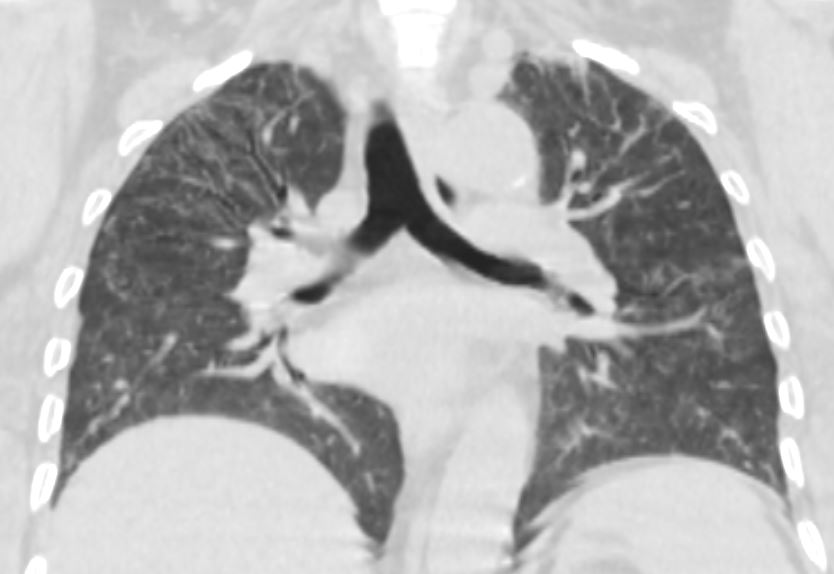

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Combination of Elements resulting in ground Glass Changes
In Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia Changes include;
Alveolar, and Interalveolar Interstitial Infiltration with Eosinophils and Inflammatory Exudate
The ground glass changes are a combination of the cellular and exudative inflammatory response in the small airways, alveoli, interalveolar septa and interstitium, and thickened alveolar septum
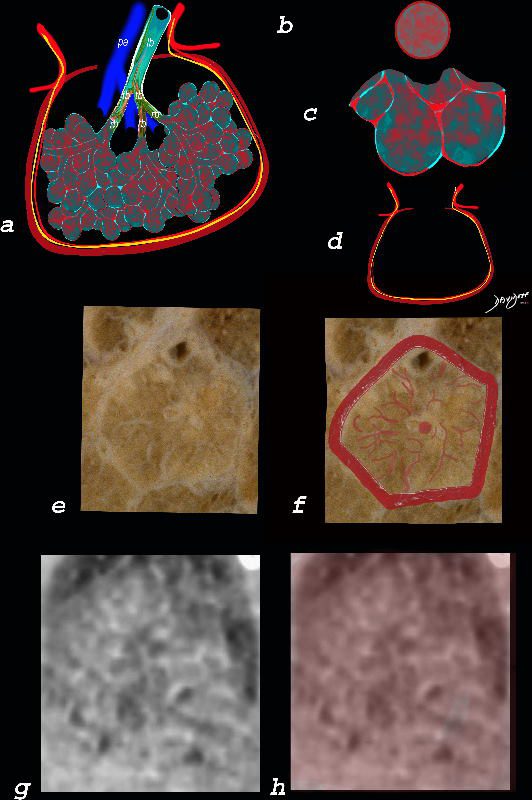

The ground glass changes are a combination of the cellular and exudative inflammatory response in the small airways, alveoli, interalveolar septa and interstitium, and thickened alveolar septum
The diagram shows the abnormal secondary lobule (a) The involved components include the small airways(b) alveoli and interalveolar interstitium (c) and the thickened interlobular septum (d) surrounding the secondary lobule due to an inflammatory process, cellular infiltrate and congestion of the venules and lymphatics in the septum. An anatomic specimen of a secondary lobule from a patient with thickened interlobular septa and interstitial thickening is shown in image e, and is overlaid in red (f) . A magnified view of an axial CT of the lungs in a patient with acute eosinophillic pneumonia shows thickened interlobular septa and centrilobular nodules (g) The inflammatory changes in the aforementioned structures result in an overall increase in density of the lung manifesting as ground glass changes (g) and overlaid in red (h)
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0762



Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
lungs-0756b01
- Diseases Associated with GGO
-
Types of GGO
There are several types of GGO. These include:
-
- Nodules
- Focal
- Diffuse
-
- Subsegmental
- Segmental
- Lobar
- Patchy
- Central
-
- Halo
- Reversed Halo
- Head Cheese
Focal
- Nodules and Nodular: This type can indicate both benign and malignant conditions. GGO that persists over several scans may indicate either premalignant or malignant growths.
- Centrilobular: This type appears within one or several lobules of the lung. Lobules are the hexagonal divisions of the lung. The connective tissue between the lobules is unaffected.
-

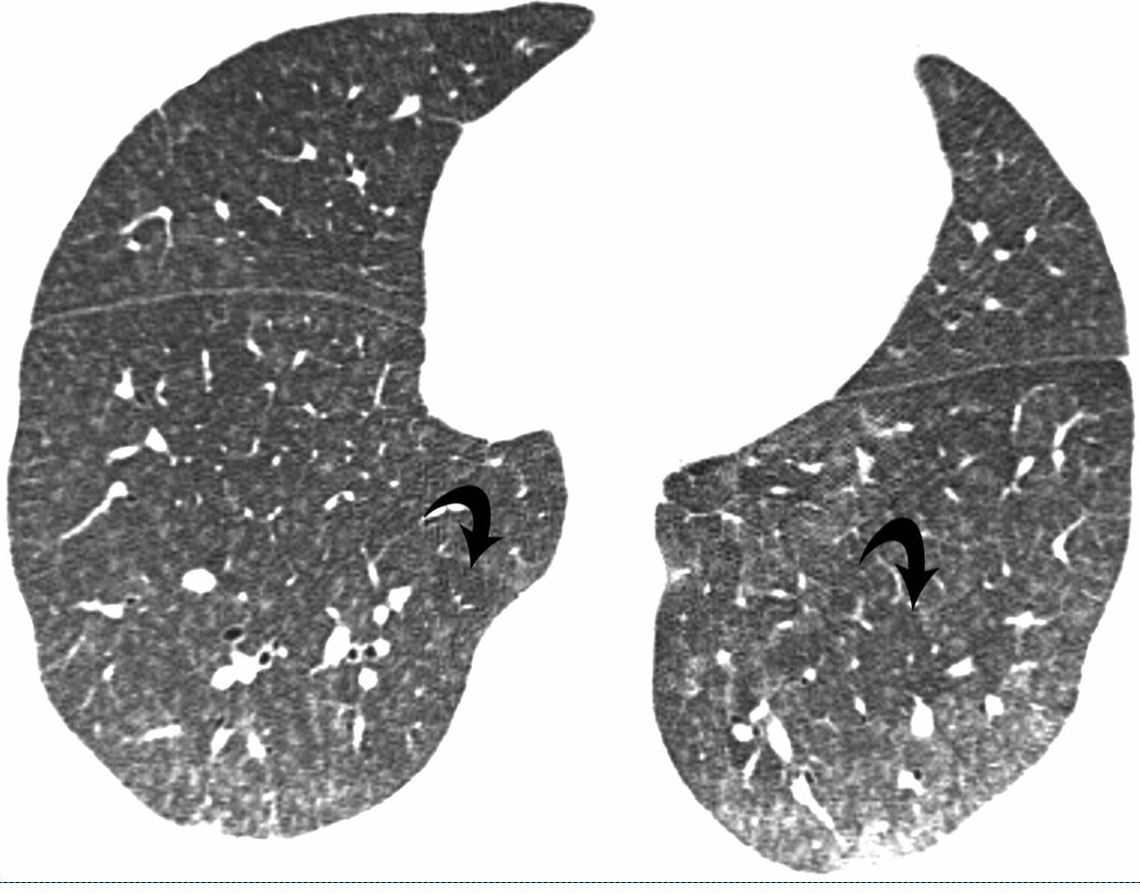
41-year-old man with subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis. High-resolution CT image shows bilateral poorly defined centrilobular nodules and ground-glass opacities. Also evident are lobular areas (arrows) of decreased attenuation. Intralobular
-

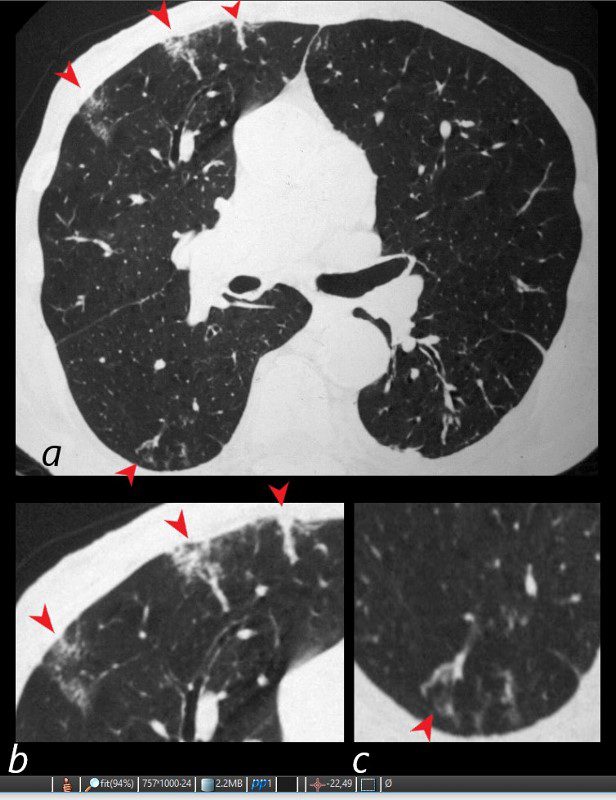
WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS, GPA,VASCULITIS AND MICROINFARCTION
81-year-old male with weight loss, renal failure, and hemoptysis
CT axial view (a) shows multiple peripheral wedge shaped ground glass densities subtended by distended feeding vessels (a,b,c, red arrowheads) reflecting areas of microinfarction due to vasculitis that affects both the arterioles and venules.
Priscilla Slanetz MPH MD
TheCommonVein.net-

26 male SOB s/p RFA ablation for atrial fibrillation lung pulmonary let upper lobe pulmonary vein thrombosed secondary lobule interlobular septa are thickened secondary lobule due to congestion and hemorrhage dx pulmonary vein thrombosis secondary to radiofrequency ablation therapy iatrogenic CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Scott Tsai MD ground glass changes pulmonary infarction venous infarction
TheCommonVein.net
-
- Diffuse:
- Diffuse opacities show up in multiple lobes of one or both lungs. This pattern occurs when the air in the lungs is replaced with fluid, inflammation, or damaged tissue.
- Segmental
- Subsegmental
- Lobar
- Diffuse opacities show up in multiple lobes of one or both lungs. This pattern occurs when the air in the lungs is replaced with fluid, inflammation, or damaged tissue.
- Subsegmental
-
-

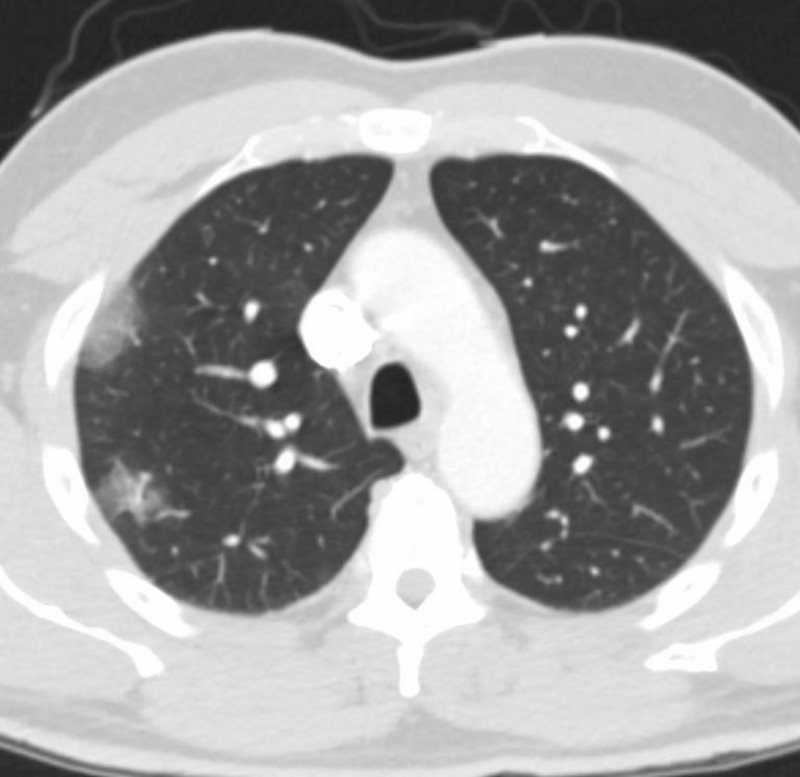
COVID 19
55-year-old male presents with a fever and a cough.
CXR findings reveal vague peripheral, bibasilar, “ground glass” changes in the lower lung zones.
The CT scan confirms the presence of bilateral, predominantly basilar, nodular, and peripheral mixes ground glass and consolidative opacifications consistent with the diagnosis of COVID 19. Differential diagnosis however includes other viral pneumonias, allergic alveolitis and other multifocal and organizing pneumonias.
Courtesy Kevin Chang MD
TheCommonVein.net
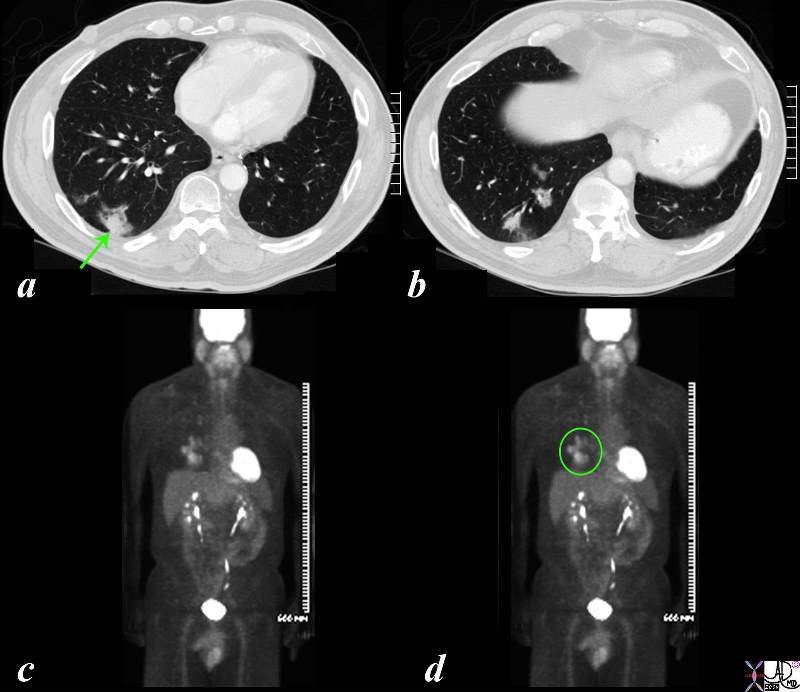
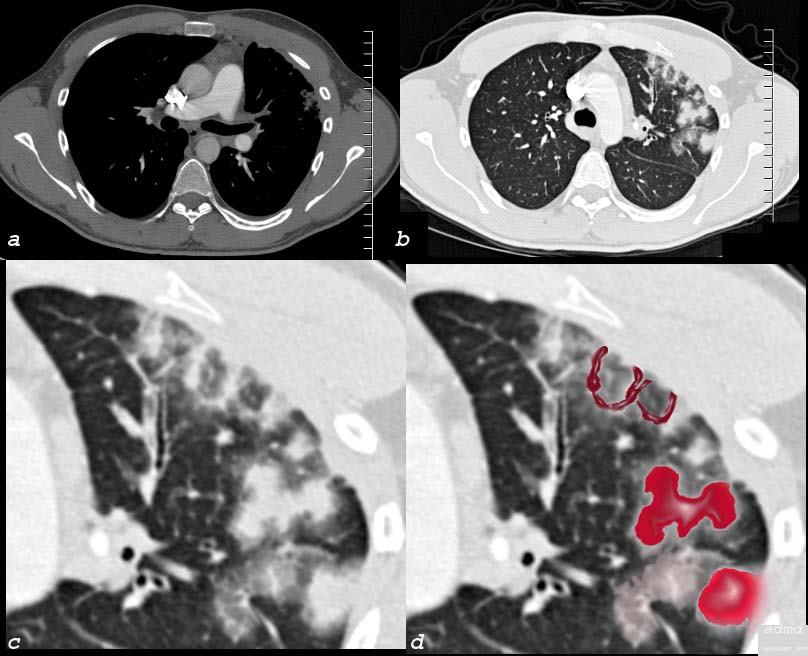
PET Positive Adenocarcinoma in a Background of Multicentric Adenocarcinoma with Lepidic Growth
The CT is from a 51 year old male who is a smoker who shows a ground glass opacity (GGO) mixed with a solid mass (arrow in a) and multicentric BAC in a lower cut (b) characterised by three areas in the right lower lobe of partial alveolar opacification. Ground glass appearance is the result of partial opacification of the alveoli. Two of the GGOs measure close to 2cms each and the third more anterior measures about 8mms. In this instance a PET scan was positive in the area (green ring in d) It is likely that the solid component in image a represents the transformation of BAC – (really a carcinoma in situ) into adenocarcinoma.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
87769c02b.8s
-
-
- Subsegmental
-


HEAD CHEESE SIGN, GROUND GLASS, MOSAIC PATTERN
SARCOIDOSIS, STAGE IV, PTX, ENCASEMENT
Ashley Davidoff MD
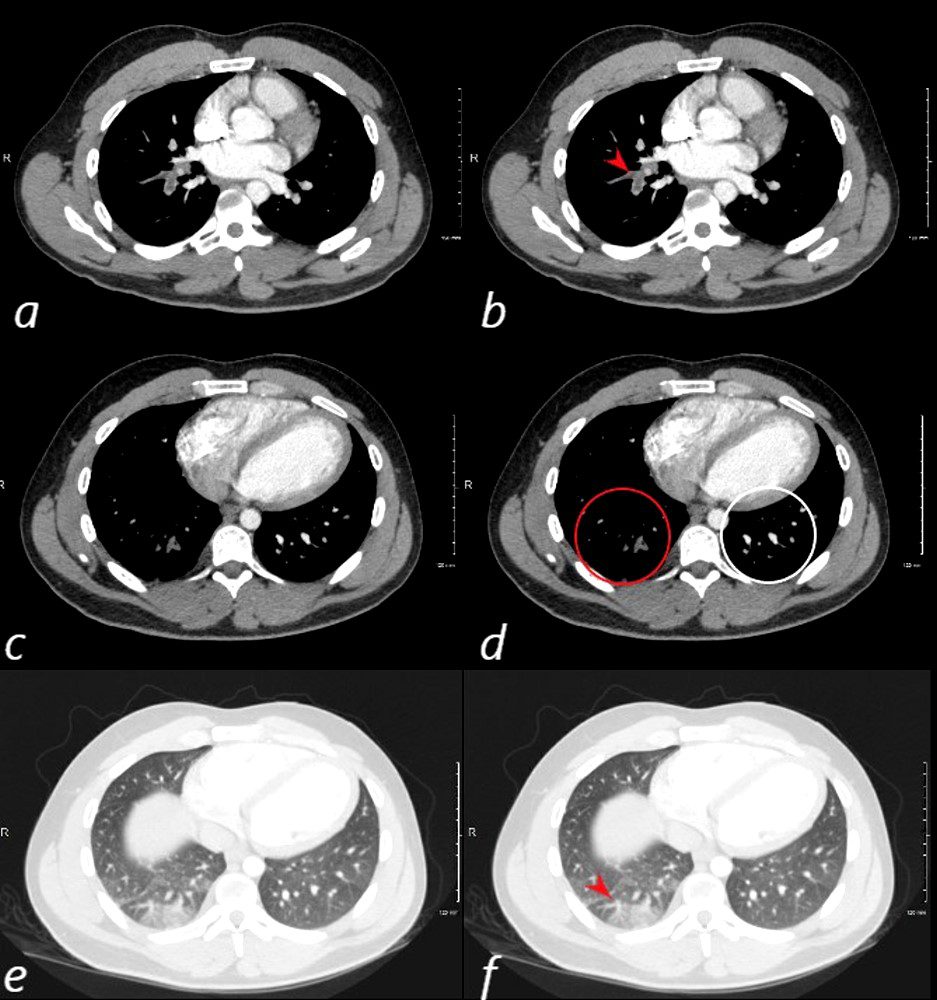
SLE AND PE
24 year old male with SLE presented with chest pain and dyspnea and initial CT showed occlusive pulmonary emboli to the right lower lobe (a,b, red arrowhead) with total occlusion of the right lobe artery extending into posterior basal segmental vessels (red ring d compared with normal vessels surrounded by white rin (d). An associated wedge shaped ground glass region is noted (e,f red arrowhead) representing either hemorrhage or early infarction
Ashley Davidoff MD
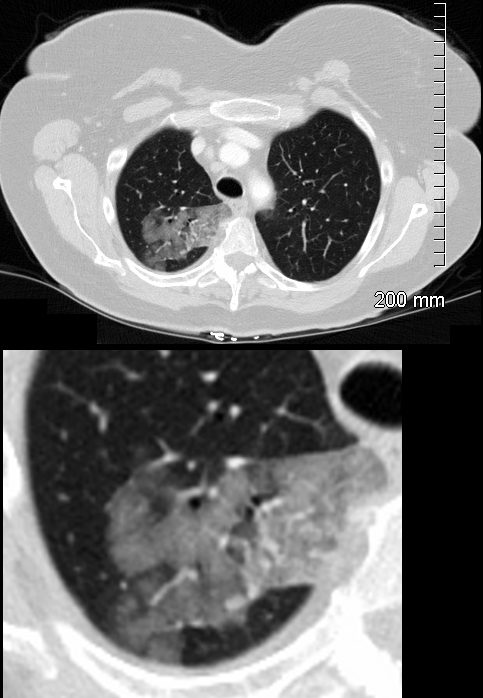
Ground Glass Nodules with ? Lymphangitic Spread
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
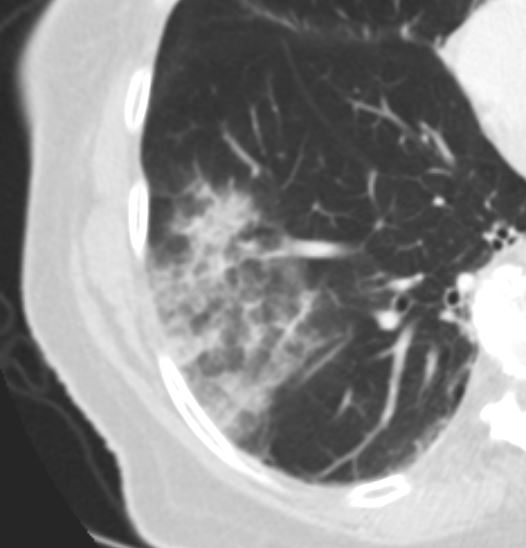
60 year old female who presents with hemoptysis. Ct scan shows a focal region of ground glass change in the superior segment of the left lower lobe, abutting the fissure, likely reflecting hemorrhage
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.netSegmental
-

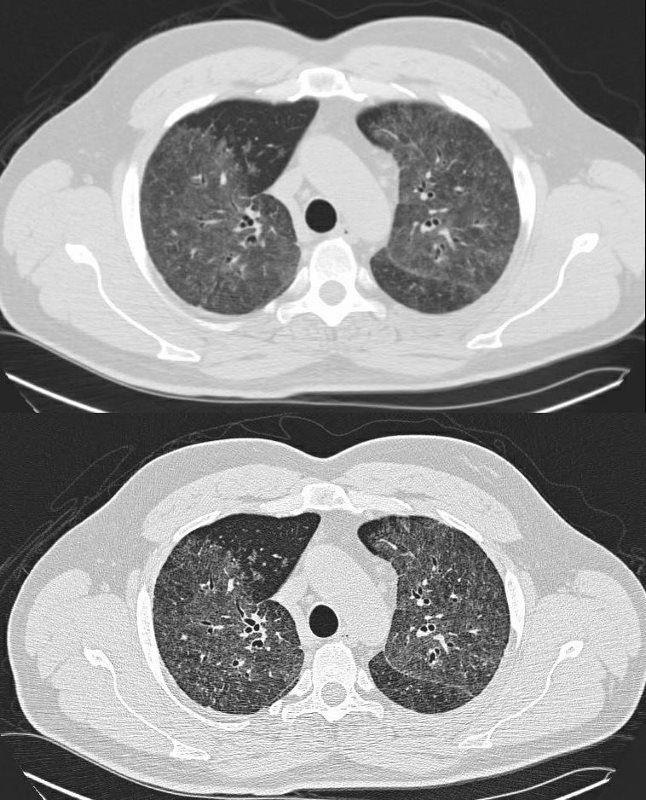
LEFT PTX (green arrow) , ENCASEMENT OF AIRWAYS (red arrows) and GROUND GLASS (blue arrows)
SARCOIDOSIS, STAGE IV, PTX, ENCASEMENT
Ashley Davidoff MD
-
-
-
-
Lobar or Almost Lobar
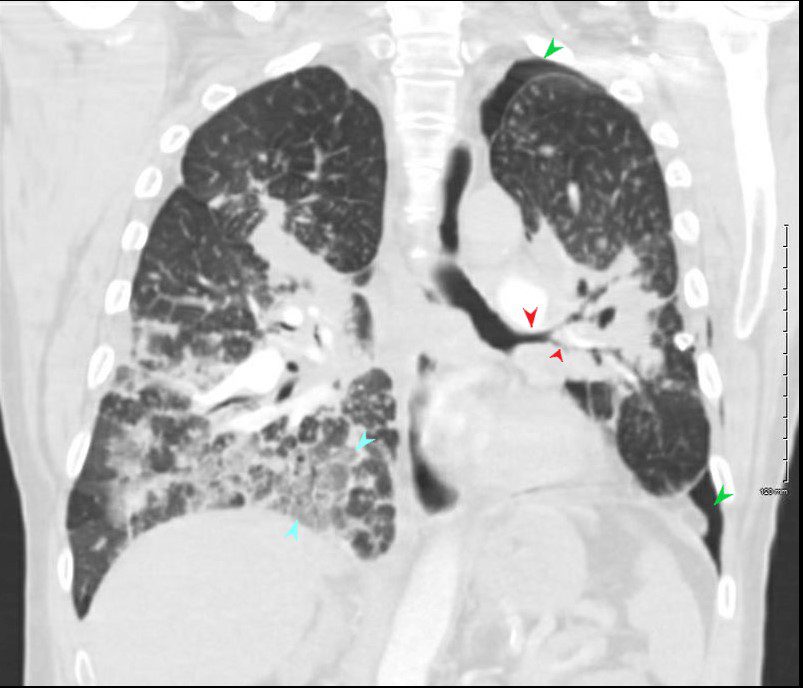
- 44-year-old male presents with history of sarcoidosis manifesting as diffuse ground glass involving the upper lobes and lower lobes sparing the middle lobe and lingula to some extent.
-
-
-


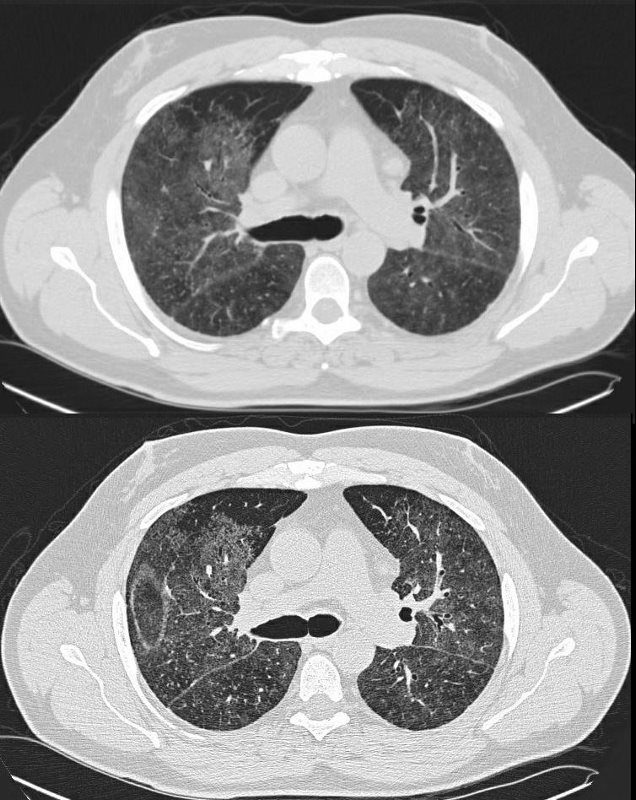

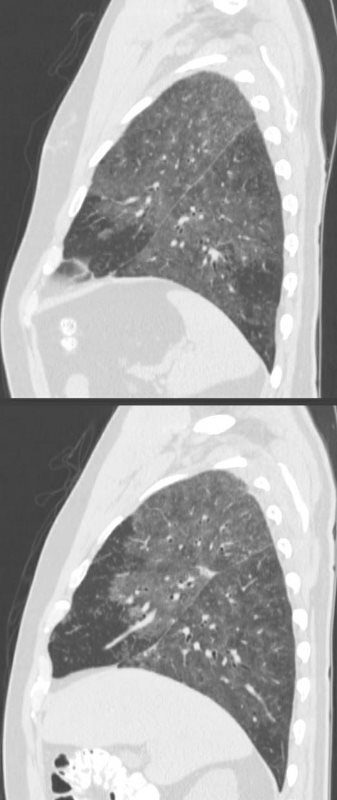
SARCOIDOSIS, STABLE DIFFUSE GROUND GLASS AND ADENOPATHY OVER 9 YEARS
Ashley Davidoff MD
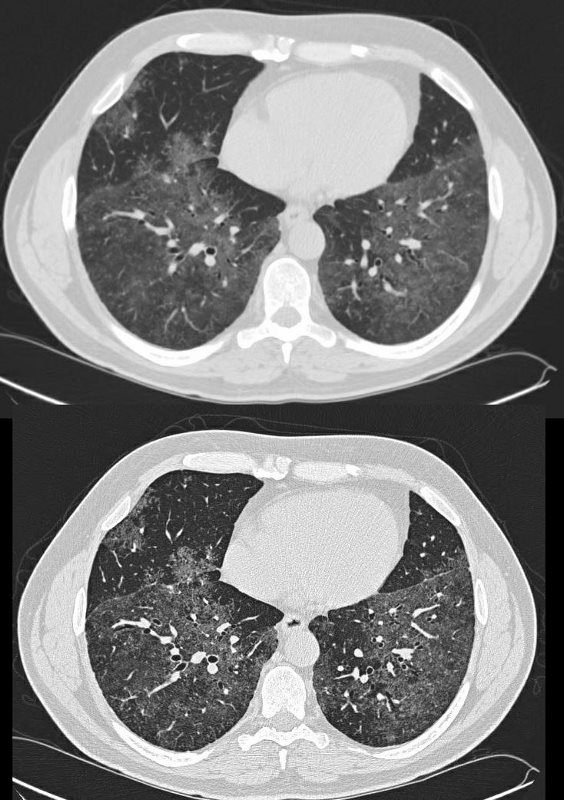
SARCOIDOSIS, STABLE DIFFUSE GROUND GLASS AND ADENOPATHY OVER 9 YEARS
Ashley Davidoff MD-
Multilobar
-
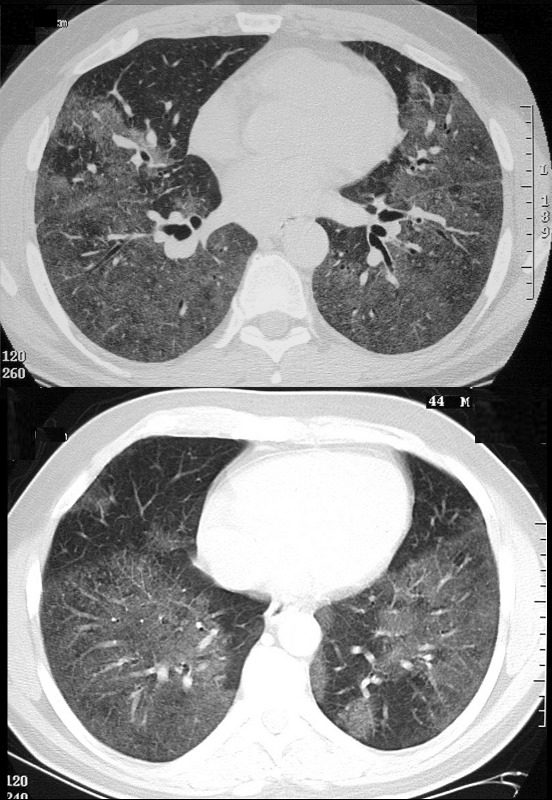

Axial CT through the base of the lungs show diffuse ground glass density, with some segmental sparing in the middle lobe and lingula characterized by increased density without obscuring the airways and vessels
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
-
- CHF
-

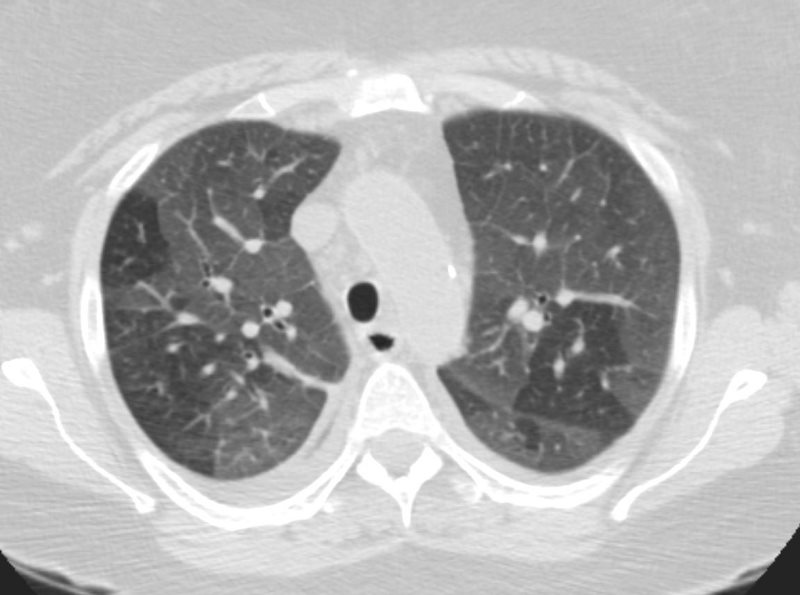
DIFFUSE GROUND DISEASE WITH REGIONS OF NORMAL LUNG
CHF, INTERSTITIAL EDEMA KERLEY A and B
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net- Diffuse Multilobar with Mosaic Attenuation : This pattern develops when small arteries or airways within the lung are blocked. The opaque areas vary in intensity.
-

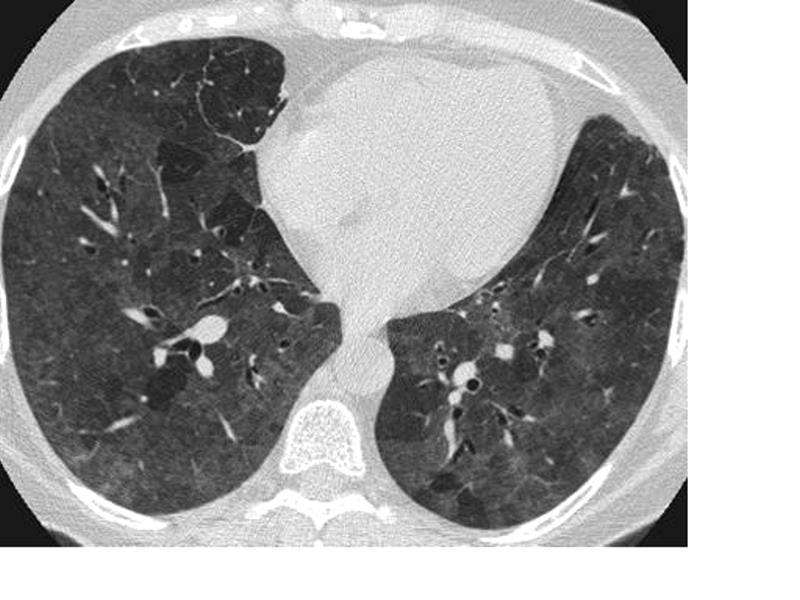
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
High-resolution CT: increase in density in areas of ground glass and air trapping in lower lobes in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Courtesy Mluisamtz11
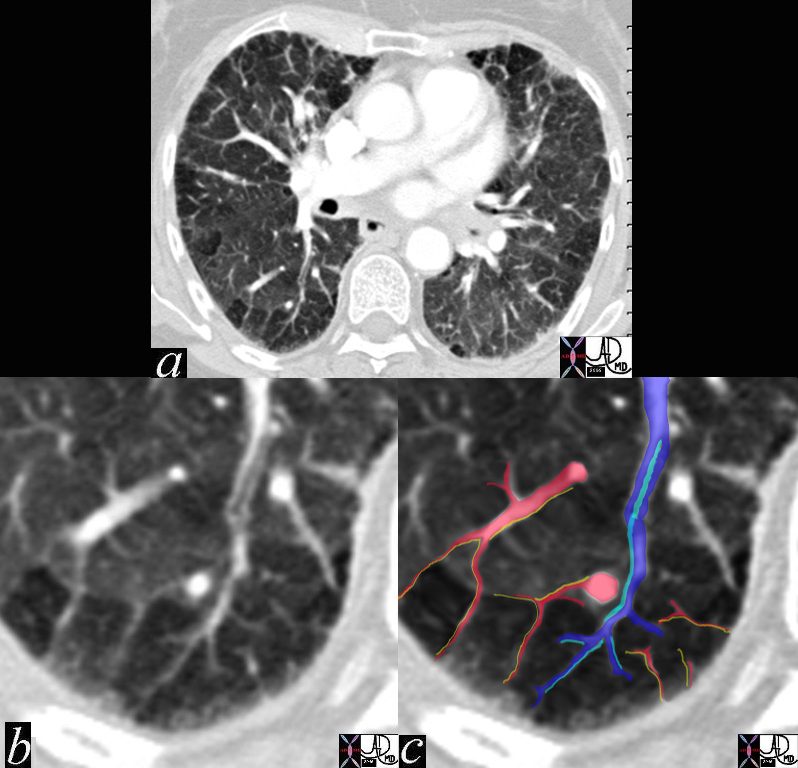
SECONDARY PULMONARY LOBULE
lung pulmonary lobule secondary lobule arteriole venule interlobular septa bronchovascular bundle mosaic pattern air trapping fx ground glass XCTscan
Davidoff MD - Diffuse Multilobar with Crazy paving: Crazy paving shows up as a linear pattern. It can occur when the spaces between the lobules widen.

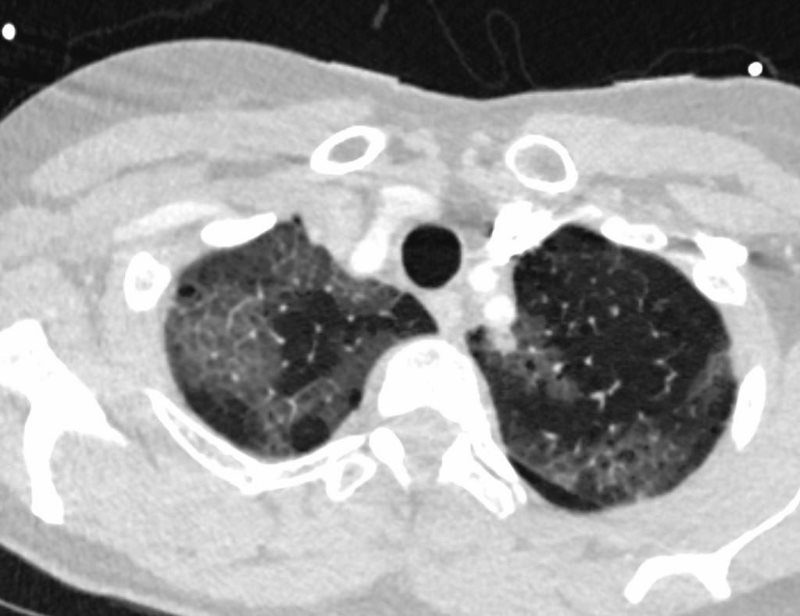

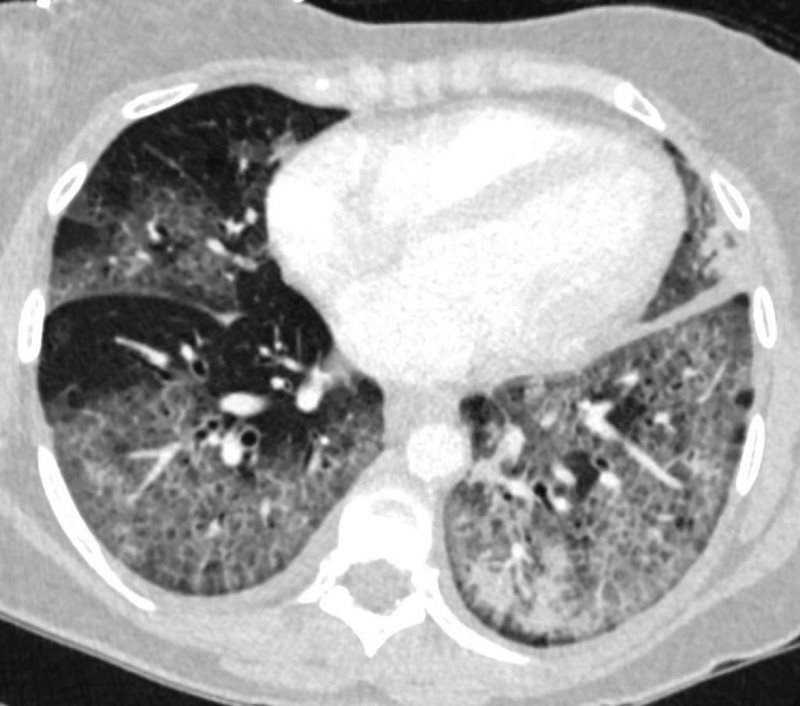
CRAZY PAVING
57-year-old female with progressive dyspnea.
CXR shows bilateral, diffuse alveolar opacities having a perihilar and basal distribution with sparing of the apices
CT shows diffuse ground glass change with crazy paving morphology characterized by bilateral diffuse ground-glass opacities (GGO) with interlobular and intralobular septal thickening. There is a geographical distribution .
Differential diagnosis
ARDS
PCP pneumonia
CHF
Alveolar Hemorrhage
UIP
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
XRT pneumonitis
COP
Chronic Eosinophilic
Lymphangitis
Veno-Occlusive Disease
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net-

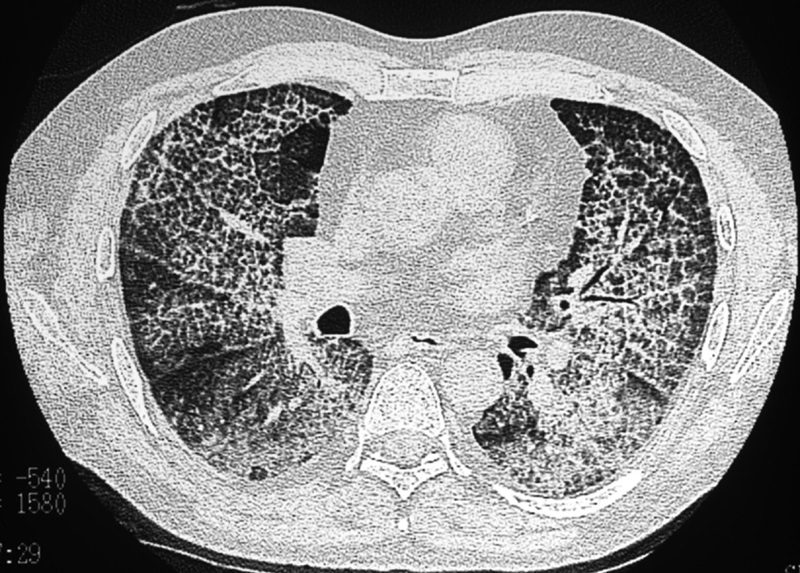
Crazy-paving sign. Axial CT of the chest shows thickening of the intralobular and interlobular septa with a superimposed background of ground-glass opacity in a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
Source
Signs in Thoracic Imaging
Journal of Thoracic Imaging 21(1):76-90, March 2006.Congestion of the Venules in the Interlobular Septa
Halo Sign in Angioinvasive Aspergillosis
-
-
-
Halo
-
Reversed Halo
-
Head Cheese
-



HEAD CHEESE SIGN, GROUND GLASS, MOSAIC PATTERN
SARCOIDOSIS, STAGE IV, PTX, ENCASEMENT
Ashley Davidoff MD
-
Focal Wedge Shaped
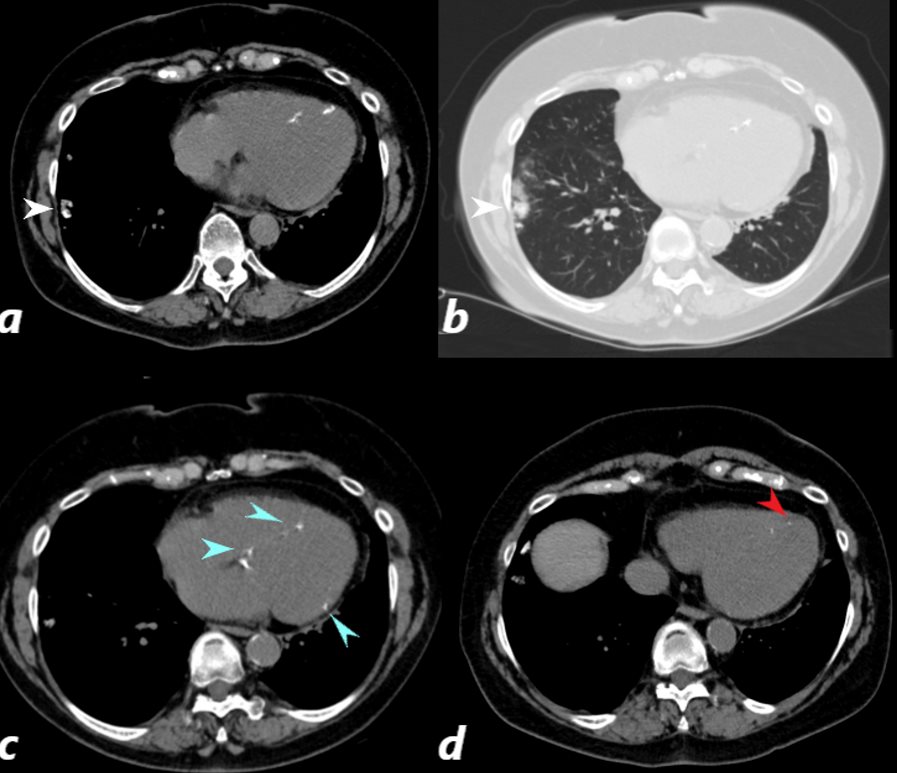

ANCA VASCULITIS WITH PULMONARY INFARCTION AND MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION CT scan of a 67 year old female with anca vasculitis shows regions of dystrophic calcification in the lateral aspect of the right lower lobe (white arrow, a and b) )with focal nodular parenchymal consolidation, that likely reflects a site of prior small vessel infarct. Dystrophic calcification in the LV myocardium (blue arrows c) and a suggestion of fatty dysplasia in the left ventricular apex red arrow d) suggest changes from small vessel infarct. Ashley Davidoff MD
Multicentric Mixed
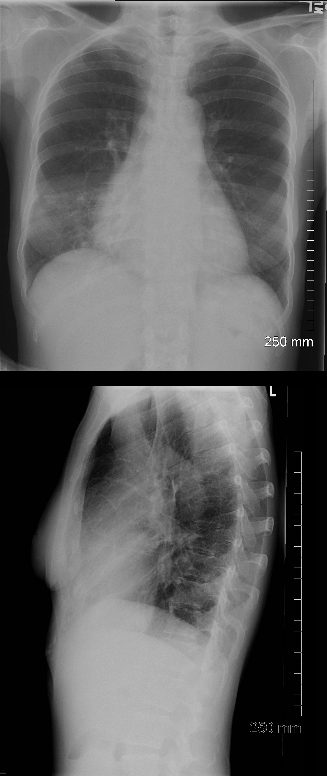

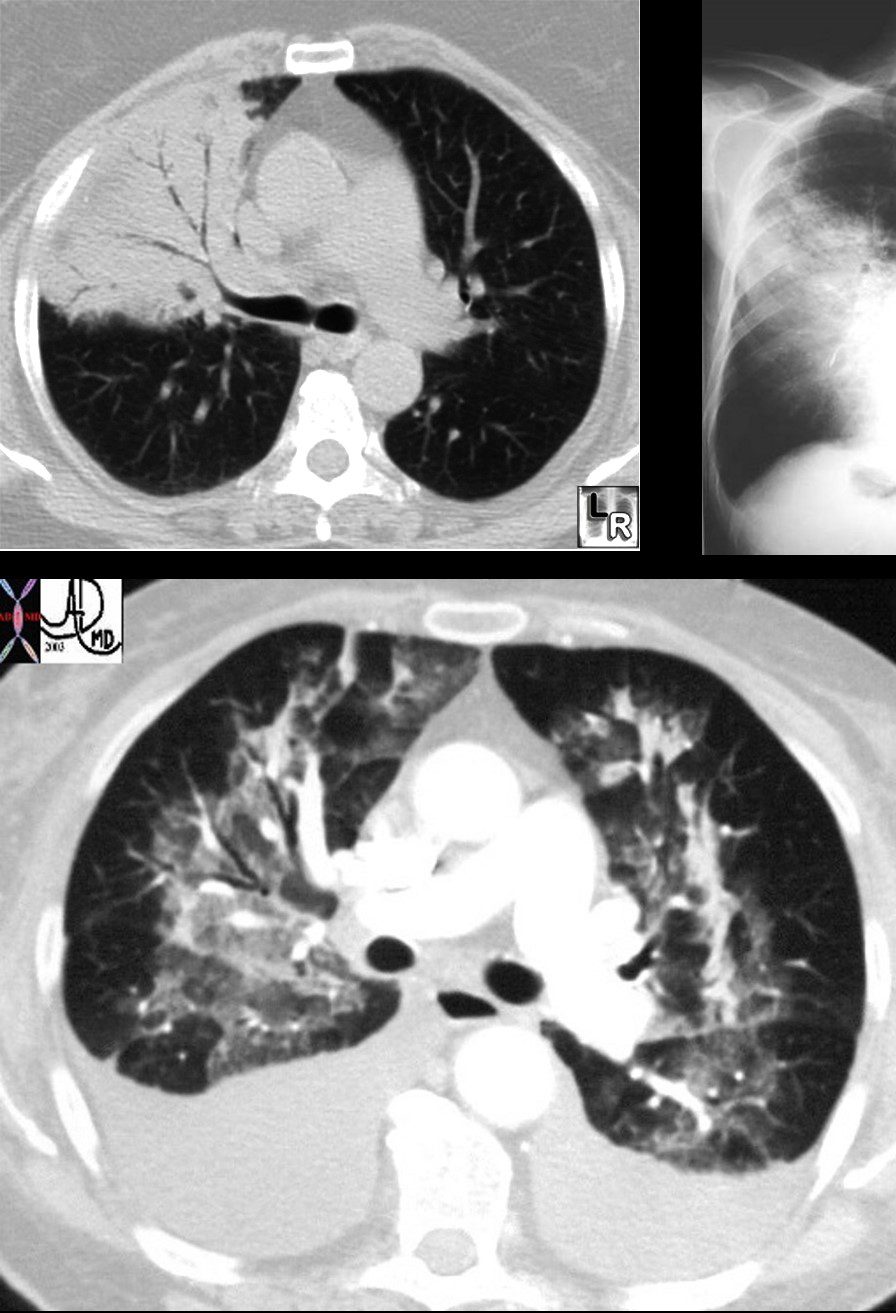
PA and lateral chest X-ray of a 54 year old female with SLE shows bibasilar ground glass infiltrates.
The heart is slightly enlarged and the region of the IVC on the lateral examination is also enlarged
Ashley Davidoff MD
key word
acute pneumonitis
SLE
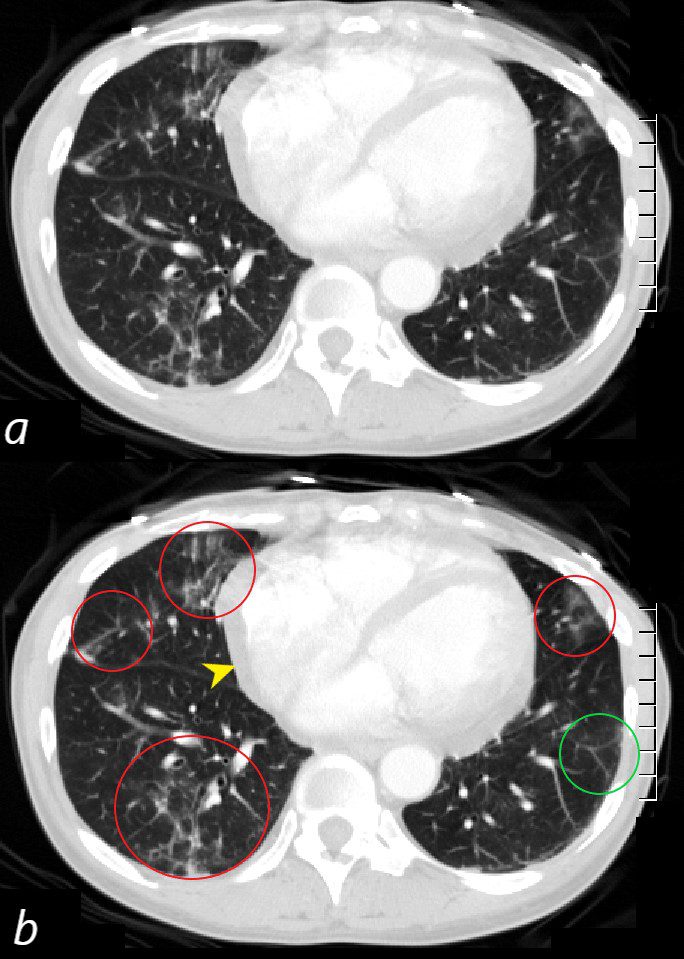

CT scan through the 4 chambers of the heart using lung windows is from a a 54 year old female with SLE. Recent CXR showed bibasilar ground glass infiltrates.
The scan shows basilar multicentric infiltrates with elements of ground glass change and small airway wall thickening (red circles in the right lower lobe middle lobe and lingula, as well as interlobular septal thickening (green circle) in the lateral basal segment of the left lower lobe. A small pericardial effusion is present (yellow arrowhead)
Ashley Davidoff MD
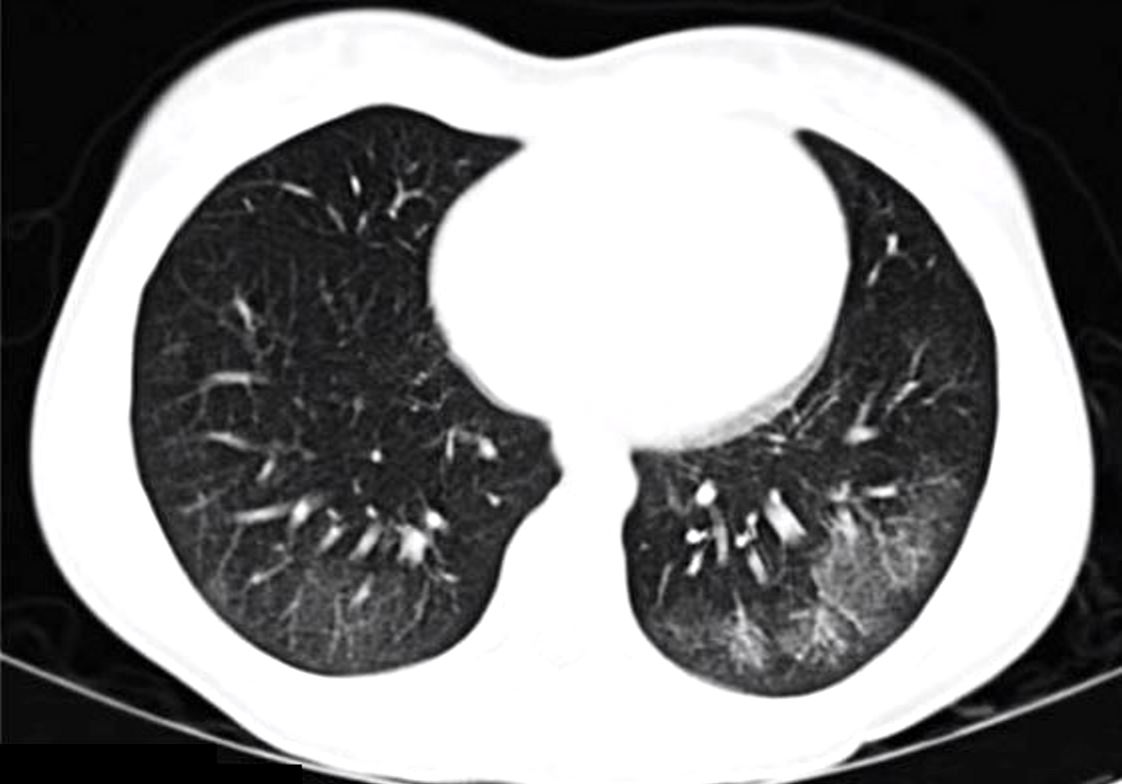

Ground glass infiltrates are one of the features of the interstitial disease with increased density without obscuring the airways and vessels
-
- Focal Associated with Other Diseases
- Halo sign:
- This type of opacity fills the area around the nodules.
-

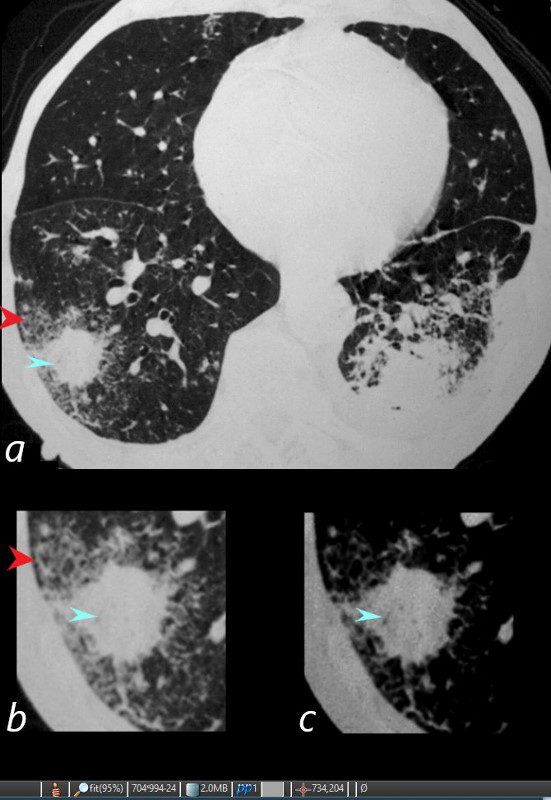
WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS, GPA, HALO SIGN AND AIR BRONCHOGRAMS
81-year-old male with weight loss, renal failure, and hemoptysis
CT axial view (a) shows a 2 cm solid nodule in the RUL surrounded by A HALO SIGN OF GROUND GLASS CHANGES AND RETICULAR CHANGES (a,b, red arrowheads), indicating surrounding hemorrhage, and subtle air bronchograms (a,b,c, teal arrowheads) best appreciated in c with narrowed windows.
Priscilla Slanetz MPH MD -

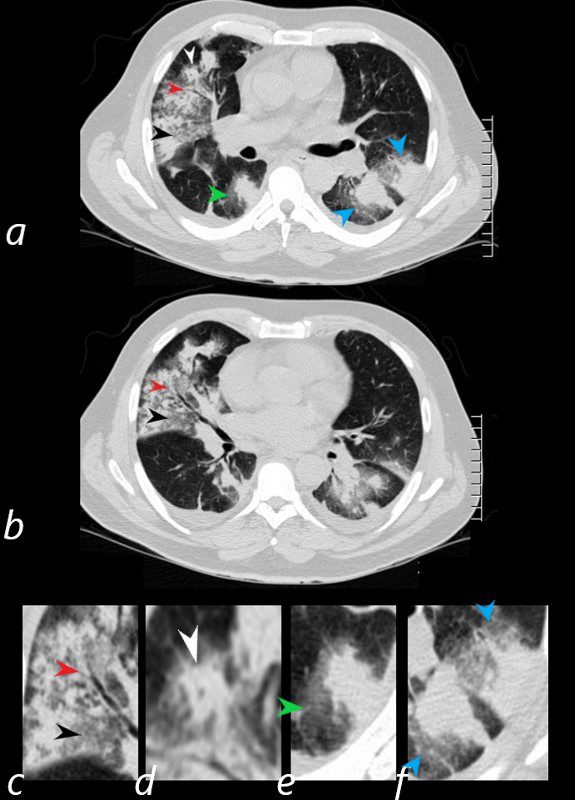
HEMORRHAGE, GROUND GLASS, HALO SIGN, AIR BRONCHOGRAM AND CHEERIO SIGN, WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS, GPA.
57 year old male presents with a history of hemoptysis and dyspnea.
Axial CT scans show multicentric nodular consolidations with air bronchograms (red arrowheads a ,b, c), ground glass infiltrate (black arrowheads, a,b,c) halo sound around nodules and masses in the RLL (a,e, green arrowheads) and in the LLL 9a,f, blue arrowheads). Lastly there is a cheerio sign (a,d, white arrowheads) either representing granulomatous mass surrounding an airway, or central cavitation of a nodule.
Ashley Davidoff MD.
57 year old male presents with a history of hemoptysis and dyspnea.
Axial CT scans show multicentric nodular consolidations with air bronchograms (red arrowheads a ,b, c), ground glass infiltrate (black arrowheads, a,b,c) halo sound around nodules and masses in the RLL (a,e, green arrowheads) and in the LLL 9a,f, blue arrowheads). Lastly there is a cheerio sign (a,d, white arrowheads) either representing granulomatous mass surrounding an airway, or central cavitation of a nodule.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net - Reversed halo sign: A reversed halo sign is an area that is almost totally surrounded by liquid-filled tissue.
Hemorrhage

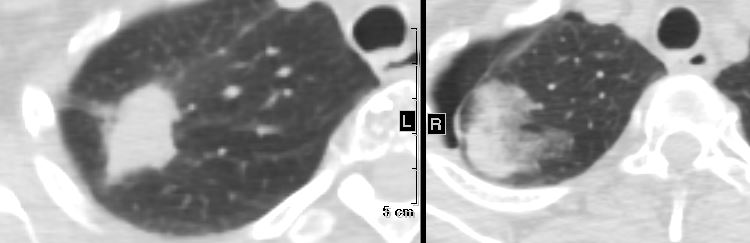
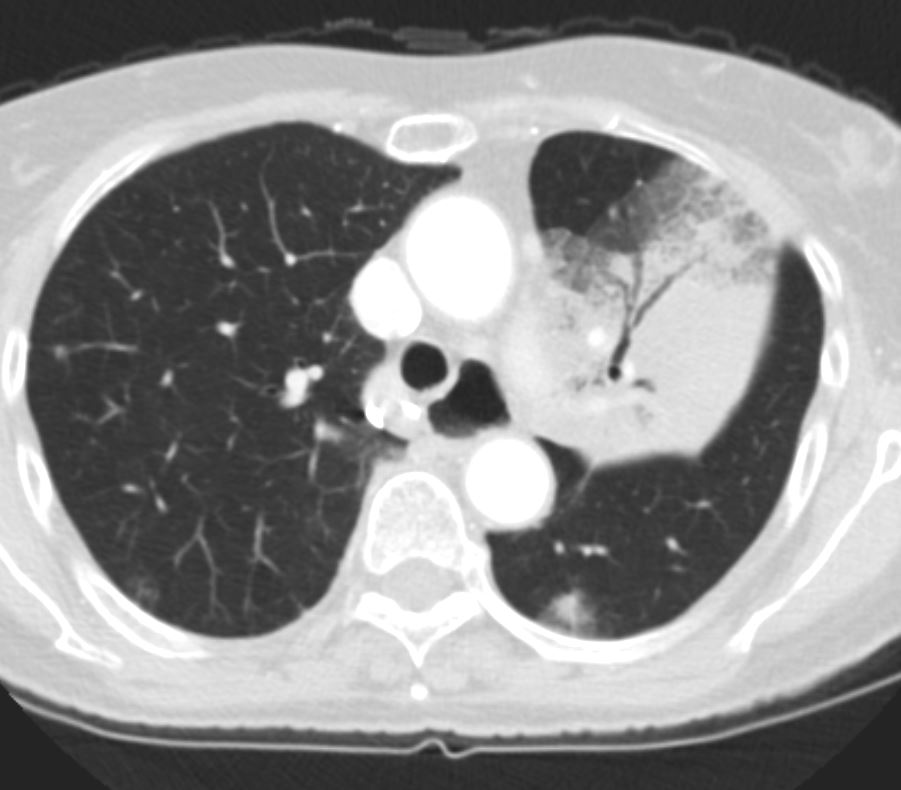
Pre and Post Biopsy – Hemorrhage and Pneumothorax Post Biopsy of an Adenocarcinoma
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
70m – adenocarcinoma- - Diffuse Disease
CAUSES
-
- normal expiration
- partial filling of air spaces
- partial collapse of alveoli
- interstitial thickening
- inflammation
- edema
- fibrosis
- lepidic proliferation of neoplasm