-
Etymology: Derived from the Greek word mikros (small) and Latin word nodulus (small knot), describing their minute size and nodular appearance.
AKA: Pulmonary micronodules.
What is it? Micronodules are small, well-defined, round opacities in the lung parenchyma, typically measuring less than 3 mm in diameter. They represent various pathological processes, including infectious, inflammatory, small airway diseases, or neoplastic conditions.
Caused by:
- Most commonly caused by:
- Infection (e.g., tuberculosis, fungal infections, viral pneumonias)
- Inflammation (e.g., sarcoidosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis)
- Other Causes:
- Small airway diseases (e.g., bronchiolitis, bronchiolitis obliterans)
- Neoplasm (e.g., lymphangitic carcinomatosis, miliary metastases)
Resulting in:
- Increased lung opacity on imaging
- Variable distribution based on etiology (centrilobular, perilymphatic, random)
Structural changes:
- Small, round opacities with smooth or slightly irregular margins
- Ground-glass or solid attenuation
Pathophysiology: Micronodules result from:
- Cellular infiltration of the alveolar spaces (e.g., inflammatory or infectious processes)
- Tumor cell spread along lymphatics (e.g., lymphangitic carcinomatosis)
- Small airway involvement due to inflammation or fibrosis
Pathology:
- Granulomatous inflammation (e.g., TB, sarcoidosis)
- Malignant cells (e.g., miliary metastases)
- Small airway inflammation (e.g., bronchiolitis)
Diagnosis:
- Imaging-based identification (chest CT preferred)
- Confirmatory testing for specific etiologies: TST for TB, serologies for fungal infections, biopsy when needed
Clinical:
- Symptoms vary based on etiology: asymptomatic, dyspnea, cough, fever
- Exposure history and systemic signs guide diagnosis
Radiology: Chest CT (preferred):
- Parts: Discrete or clustered micronodules within the lung parenchyma
- Size: Less than 3 mm
- Shape: Round or slightly irregular
- Position: Centrilobular, perilymphatic, or random distribution
- Character: Solid or ground-glass attenuation
Chest X-ray:
- Rarely visible due to small size
- Subtle reticulonodular patterns if numerous
Labs:
- Tuberculin skin test (TST) or IGRA for TB
- Fungal serologies
- Autoimmune panels for inflammatory causes
Management:
- Treat underlying cause (e.g., antituberculous therapy, corticosteroids for inflammation)
- Surveillance imaging for unresolved micronodules
Radiology Detail:
- CXR: Rarely visible, subtle reticulonodular opacities
- CT:
- Parts: Lung parenchyma
- Size: <3 mm
- Shape: Round or oval
- Position: Centrilobular, perilymphatic, random
- Character: Solid or ground-glass
- Time: Acute or chronic depending on cause
- Associated Findings: Septal thickening, lymphadenopathy
- Other Imaging:
- PET-CT for metabolic activity in suspected malignancy
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs):
- May show restrictive or obstructive patterns depending on underlying disease
Recommendations:
- High-resolution CT for distribution assessment
- PET-CT for malignancy workup
- Biopsy in uncertain cases
Key Points and Pearls:
- The distribution of micronodules helps narrow the differential diagnosis.
- Centrilobular nodules sparing the pleura suggest small airway diseases.
- Perilymphatic nodules often indicate sarcoidosis or lymphatic malignancy.
- Random nodules suggest hematogenous spread (e.g., miliary TB, metastases).
- “Micronodules measuring <3 mm are commonly identified in granulomatous, infectious, or neoplastic processes depending on their distribution and imaging features.” Radiopaedia
- “Centrilobular micronodules sparing the pleura often indicate small airway disease like hypersensitivity pneumonitis.” Radiographics
- Most commonly caused by:
Random distribution
-
- random nodules in the vascular distribution and lymphatic
- lower lobes (that is where blood flow goes)
- solid
- well defined
- +/- feeding vessel sign
- +/- cavitation
- +/- lymphangitic appearance
- Causes
- Metastases
- renal
- melanoma
- thyroid
- testicular
- Miliary
- TB
- Fungal
-
- coccidiomycoses
- histoplasmosis
- pneumocytis
- Viral
-
- Metastases
TB
Transbronchial Spread of TB with Extensive Tree in Bud Changes Masquerading as Miliary TB
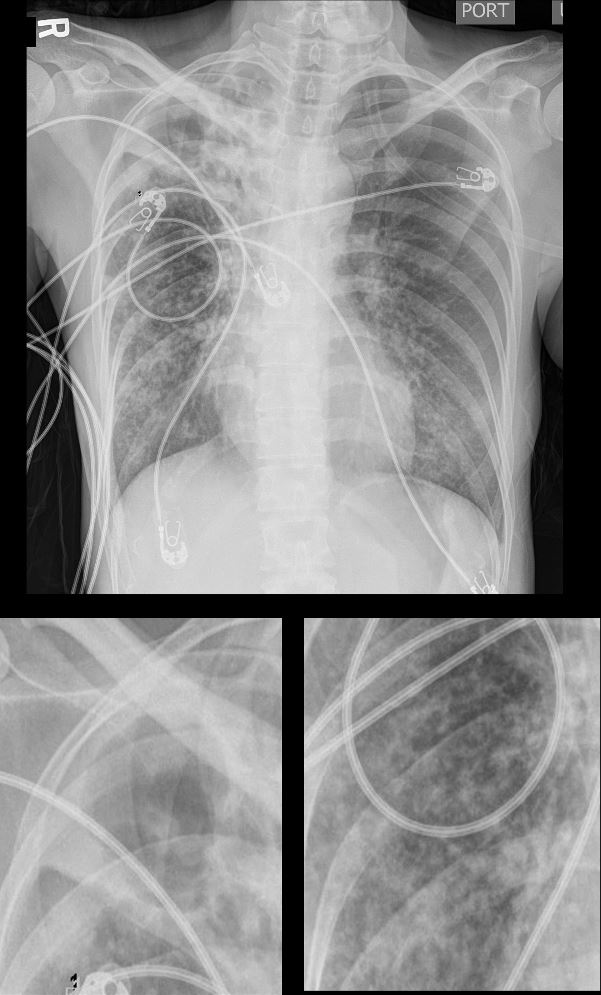
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats fever and cough
CXR shows a cavitating lesion in the apex of the right lung (magnified lower image, right) associated with an ipsilateral micronodular pattern (magnified lower image, left)
Although the right lung has the appearance of a “miliary” pattern, this term is usually referred to the hematogenous spread of the disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 131708cL
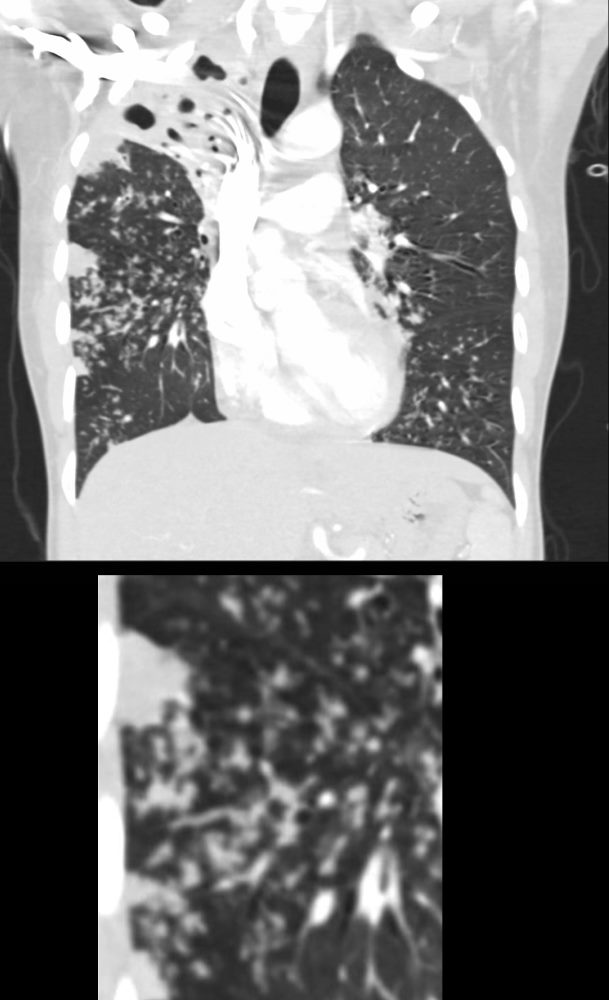
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats, fever, and cough. CT in the coronal plane of the chest shows a large cavitating lesion in the right upper lobe, with innumerable micronodules dominantly in the right midlung field, and to lesser extent in the right upper lung field. Some micronodules are probably present in the left lower lobe as well. Close to the largest subsegmental consolidation there is a bronchus which shows thickening of its wall.
Although it has the appearance has a “miliary” pattern, this term is usually referred to the hematogenous spread of the disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135786c
006Lu
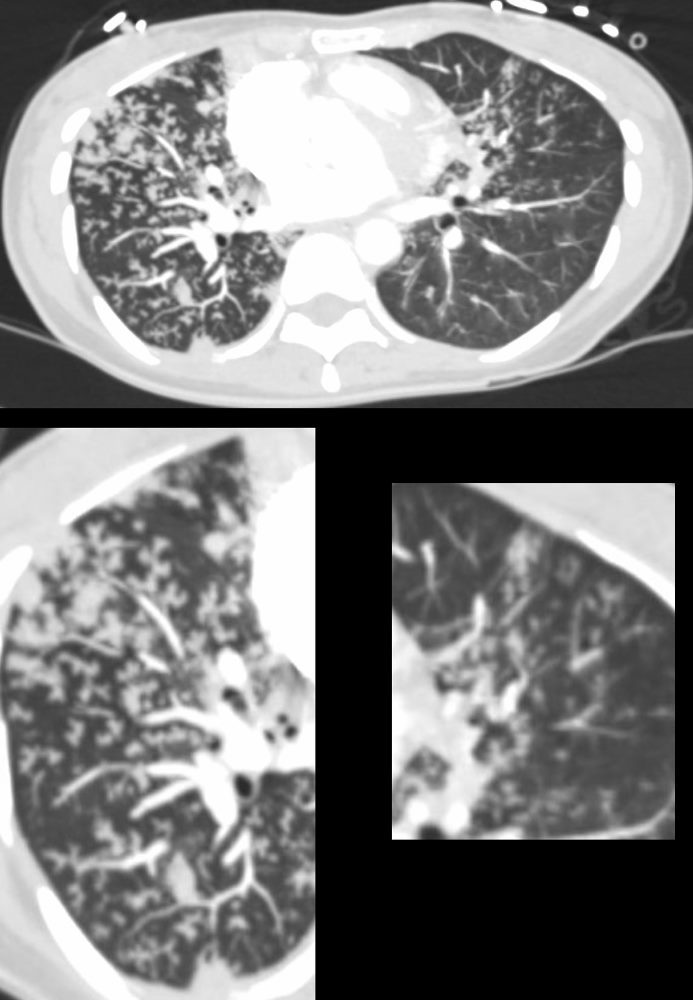
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats fever and cough. CT in the axial plane through the mid chest shows innumerable micronodules resulting from transbronchial spread with resultant tree in bud pattern scattered through the right lung (magnified in the right lower image). There are minimal similar changes in the lingula (magnified left lower image)..
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135789c 006Lu
Acute Miliary Histoplasmosis
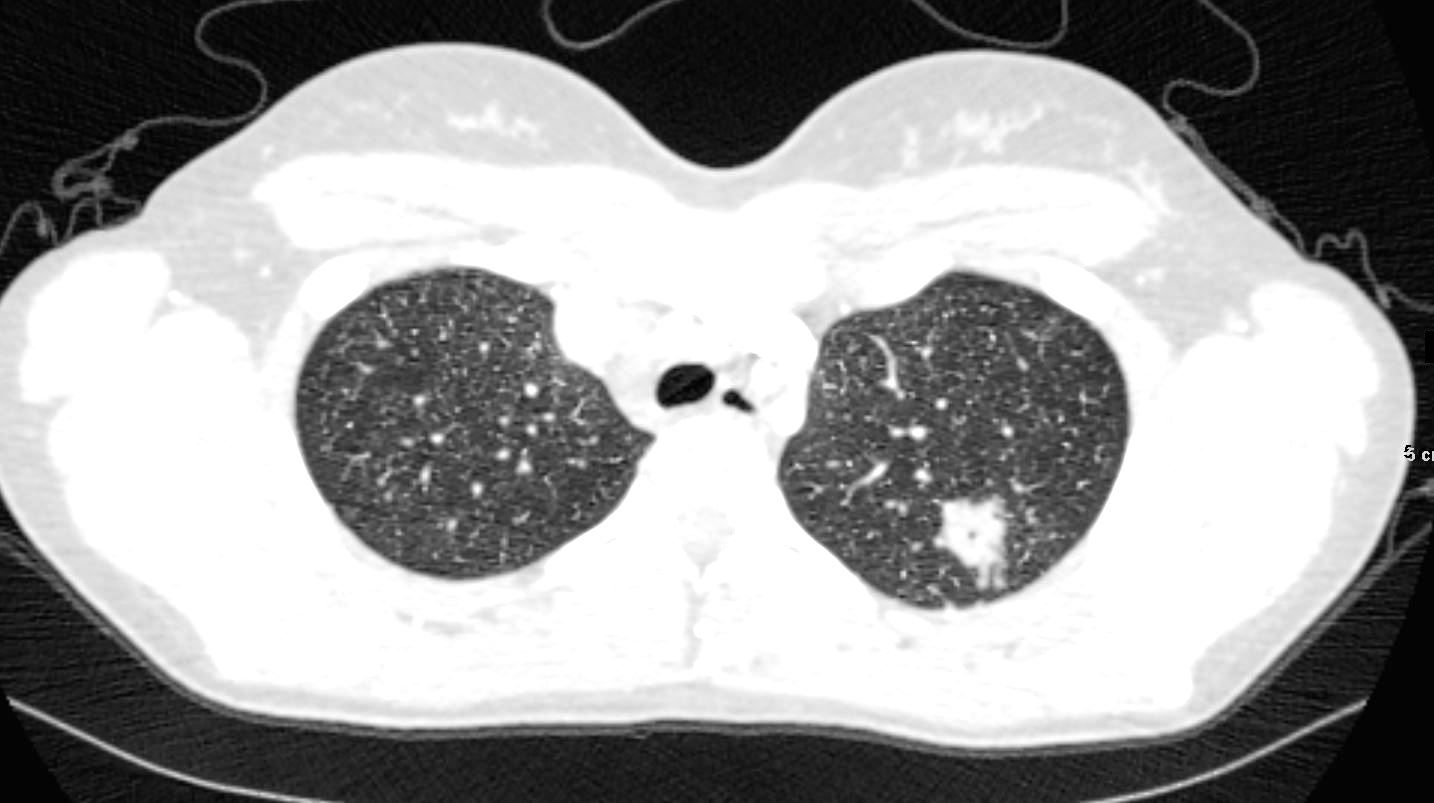
22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms. 3 weeks later a chest CT shows a cavitating nodule in the left upper lobe, and extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular miliary disease.
Ashley Davidoff MD Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131706
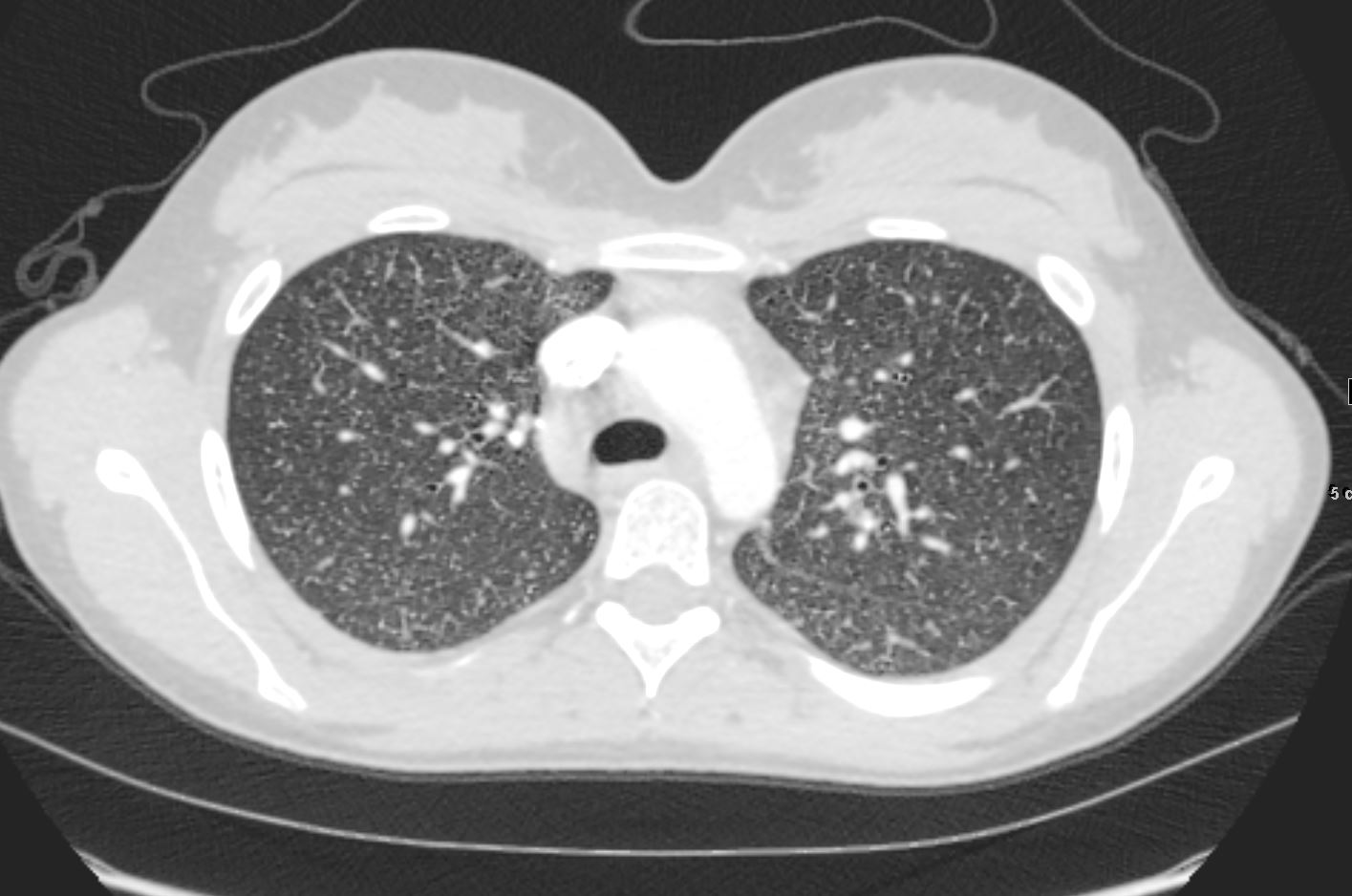

22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms. CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular miliary disease.
Ashley Davidoff MD Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131707
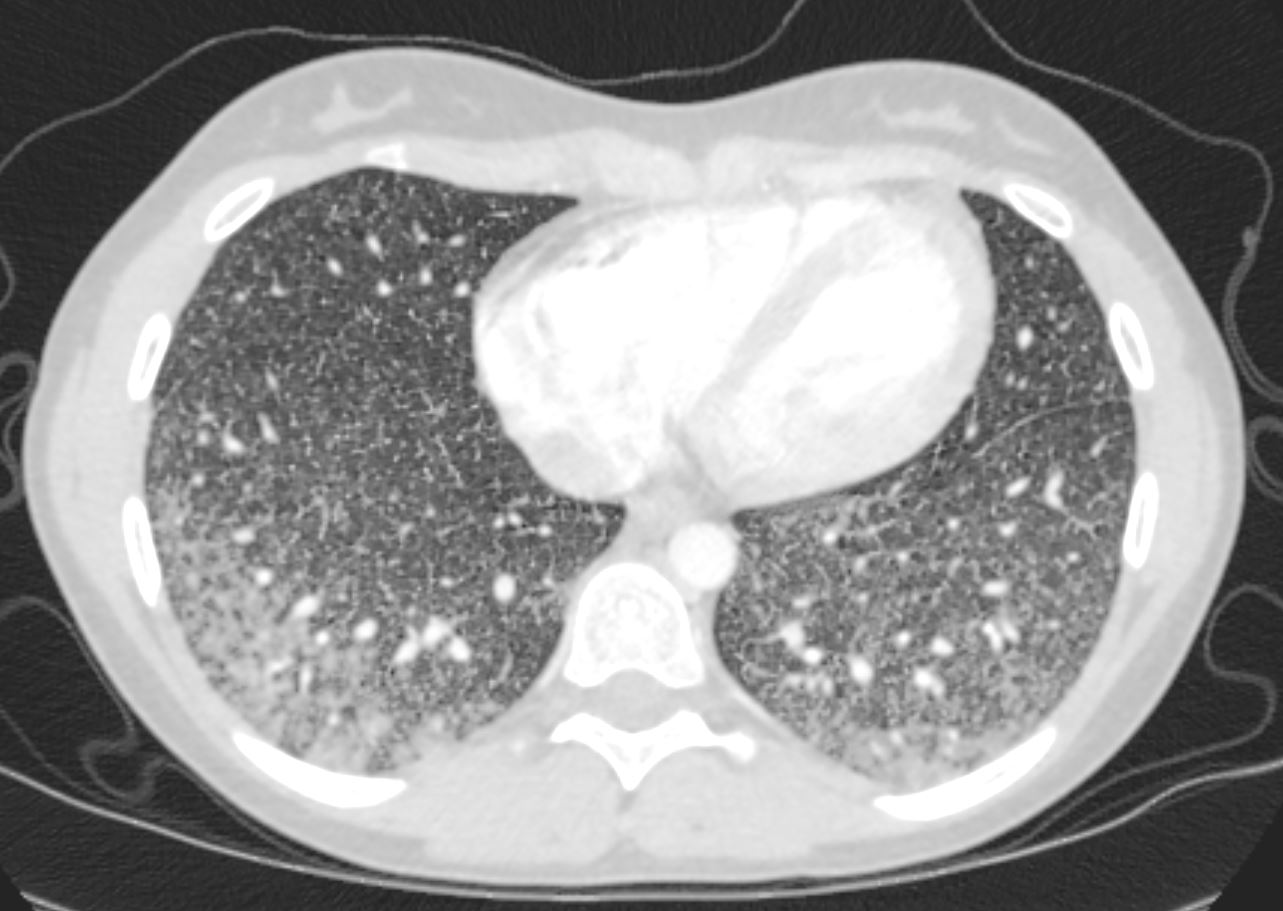

22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms. CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular miliary disease with ground glass changes at the bases with suggestion of thickening of the interlobular septa.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131710
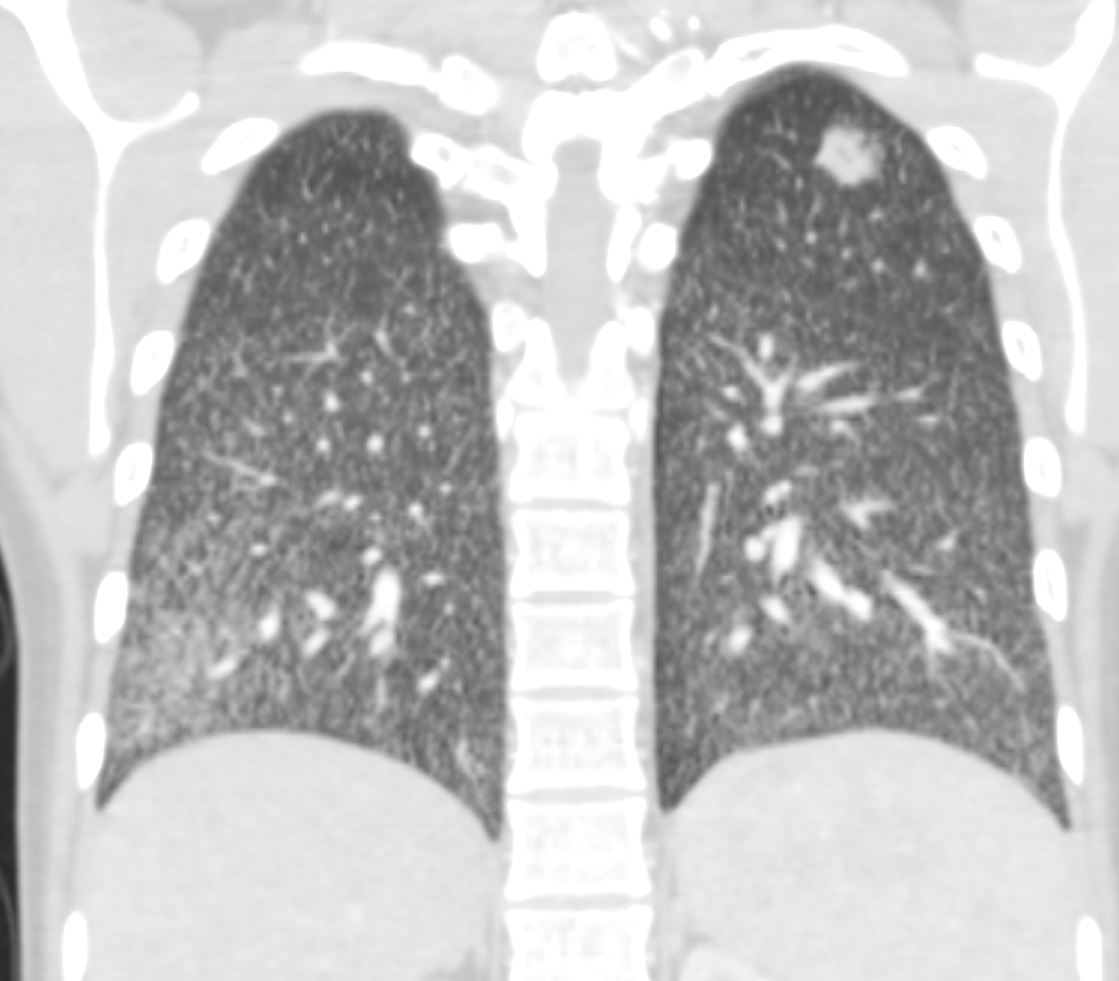


22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms. CT shows left apical cavitating nodule and extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular miliary disease.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131716
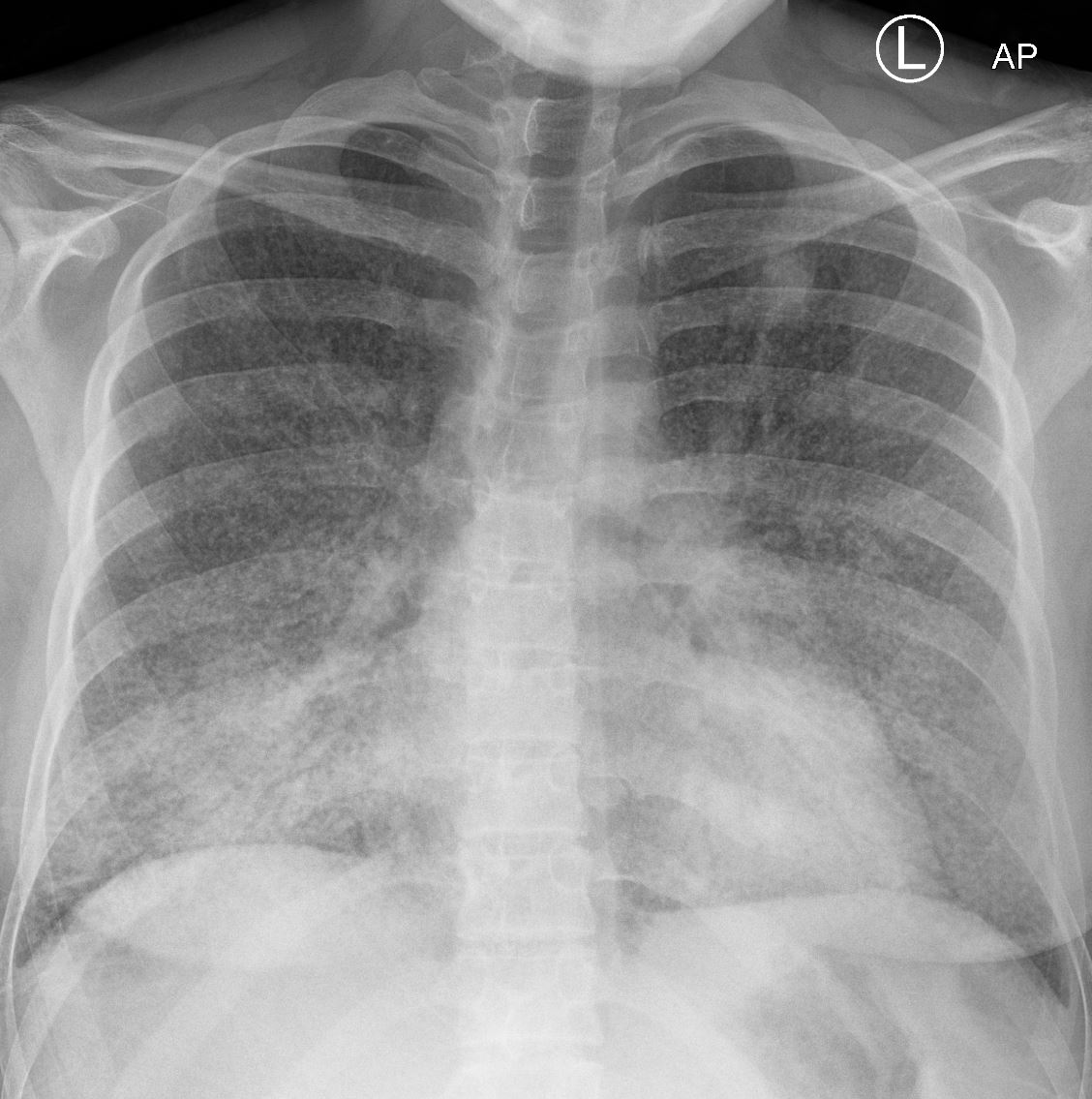


22-year-old female presented with flu like symptoms 1 week prior had a CT that showed extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
The current CXR 1 week later she required admission to the ICU and the CXR above shows confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes. Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 131721
Histoplasmosis



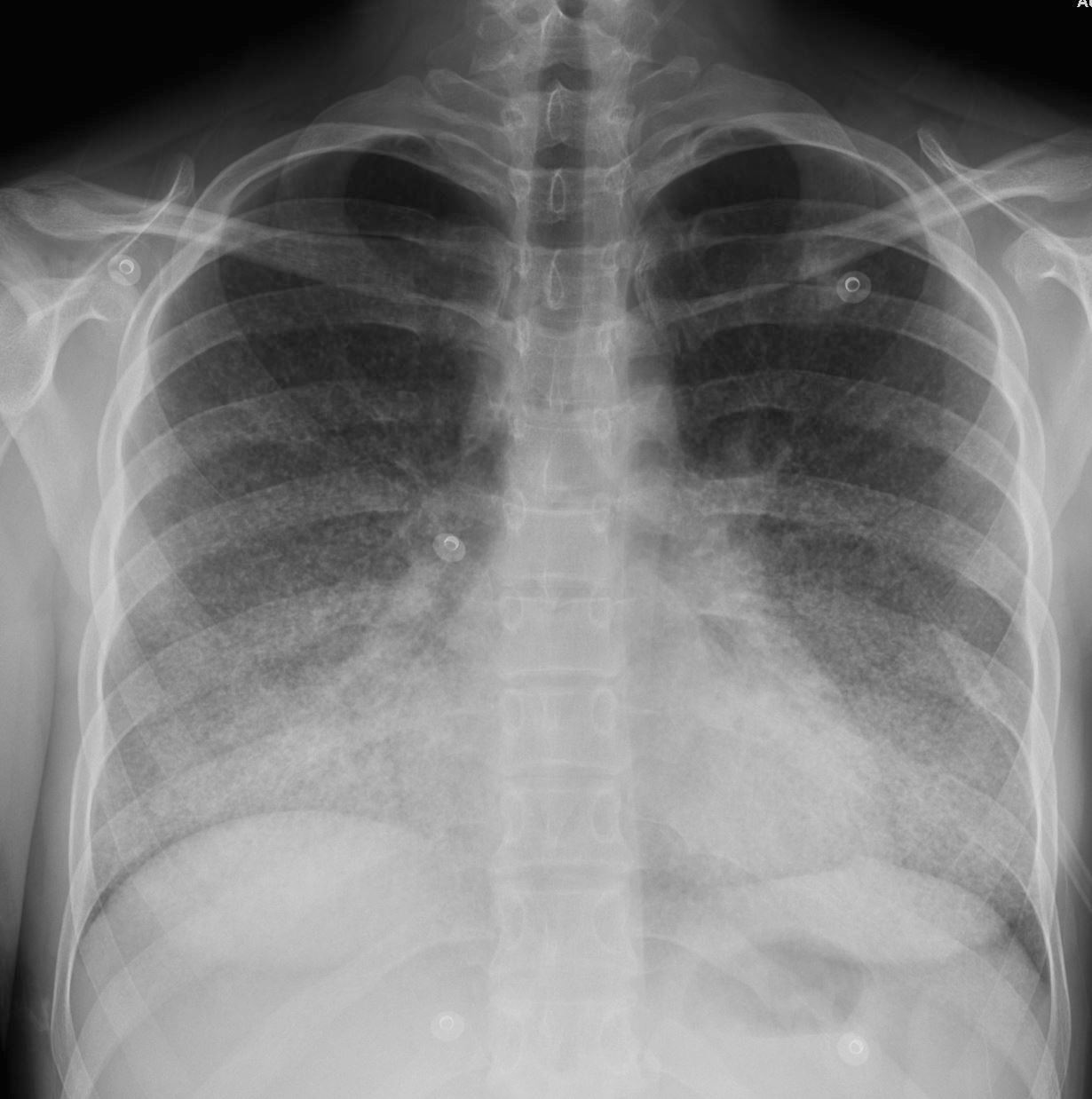
22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms and has a normal CXR
3 weeks later a chest CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
A week later she was admitted to the ICU with confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes.
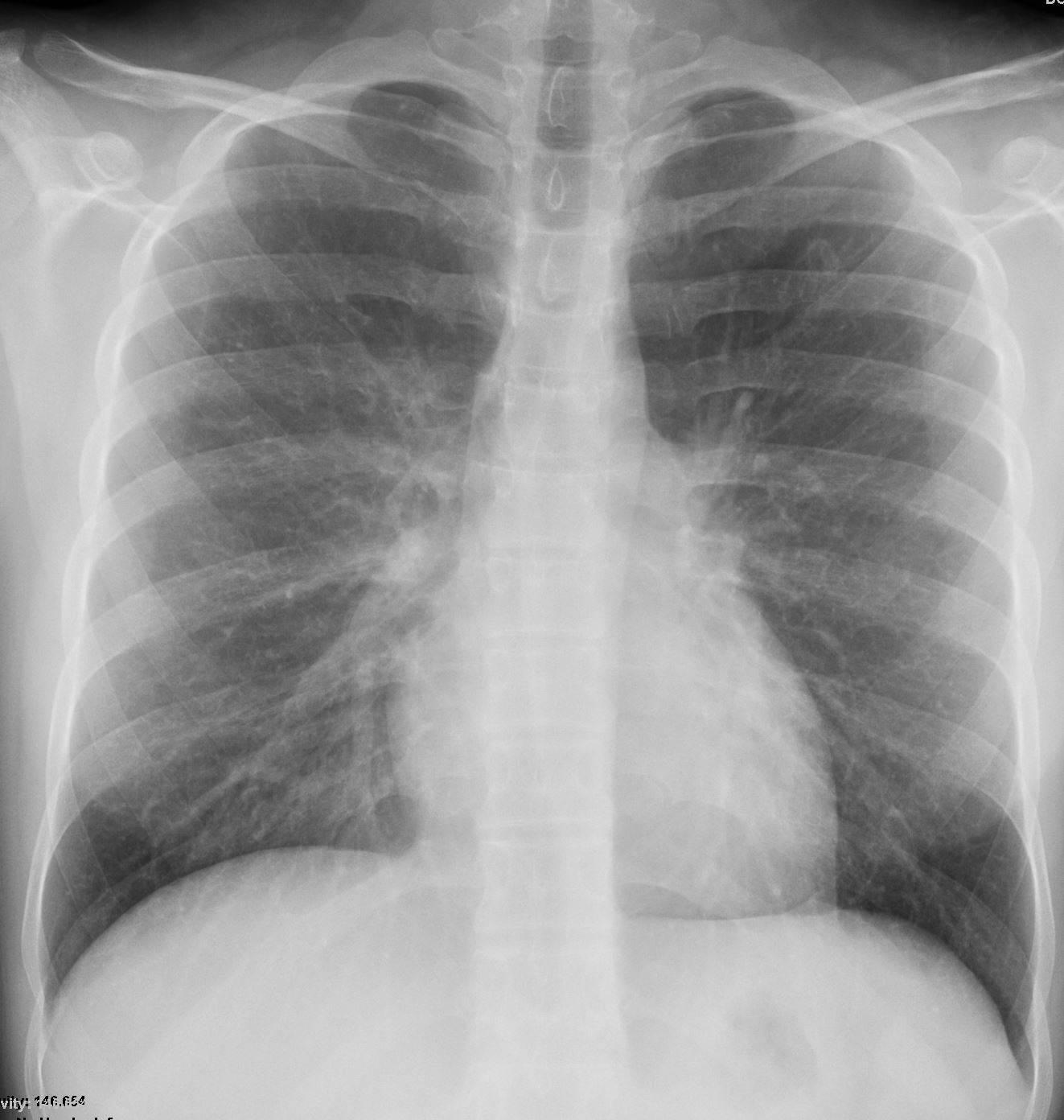
Later that month her CXR started to improve but still showed military disease.
A CXR 9 months later shows resolution.
Ashley Davidoff MD



22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms and has a normal CXR
3 weeks later a chest CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
A week later she was admitted to the ICU with confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes.
Later that month her CXR started to improve but still showed military disease.
A CXR 9 months later shows resolution.
Ashley Davidoff MD
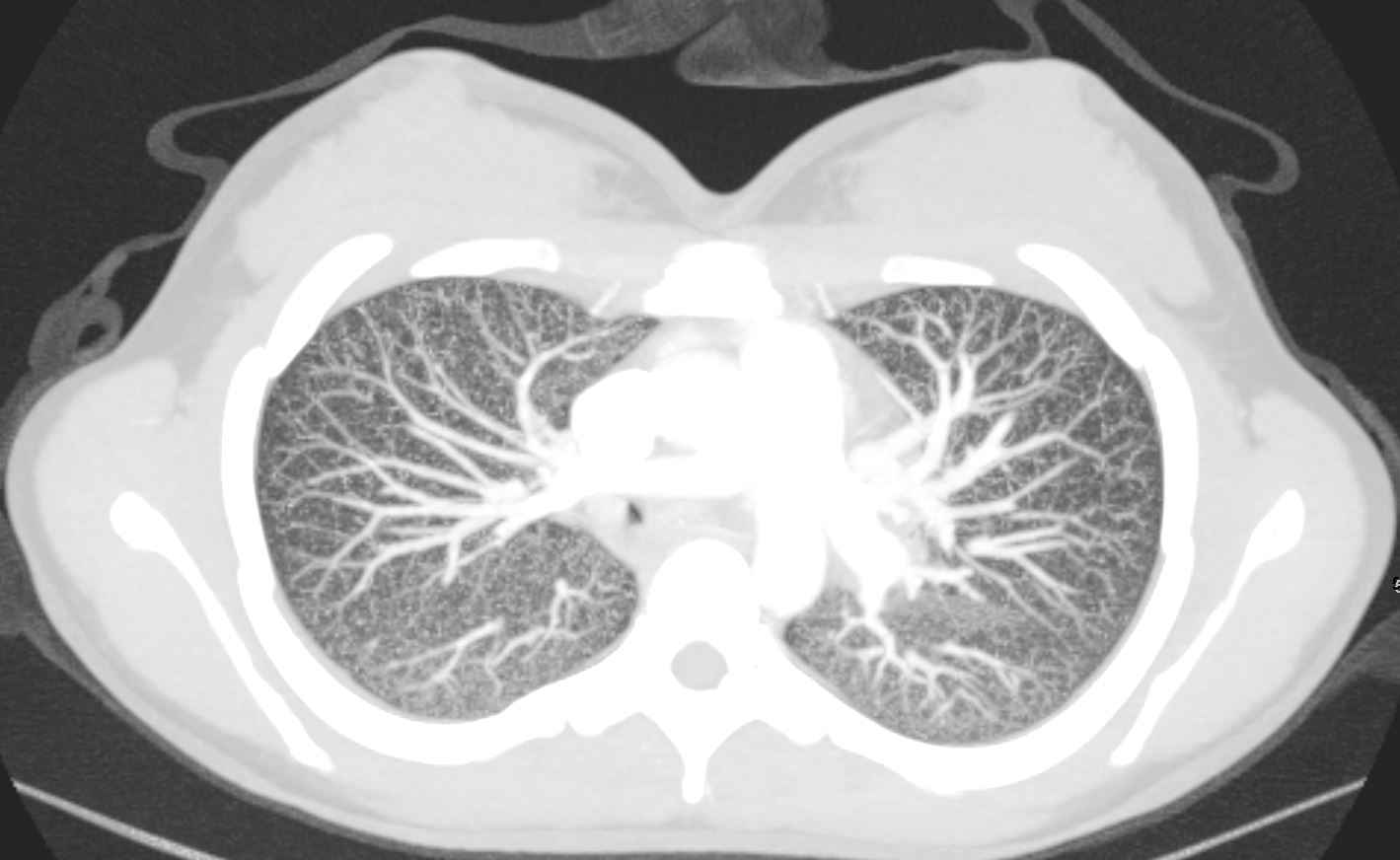

22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms and has a normal CXR
3 weeks later a chest CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
A week later she was admitted to the ICU with confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes.
Later that month her CXR started to improve but still showed military disease.
A CXR 9 months later shows resolution.
Ashley Davidoff MD



22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms and has a normal CXR
3 weeks later a chest CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
A week later she was admitted to the ICU with confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes.
Later that month her CXR started to improve but still showed military disease.
A CXR 9 months later shows resolution.
Ashley Davidoff MD

22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms and has a normal CXR
3 weeks later a chest CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
A week later she was admitted to the ICU with confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes.
Later that month her CXR started to improve but still showed military disease.
A CXR 9 months later shows resolution.
Ashley Davidoff MD

22-year-old female presents with flu like symptoms and has a normal CXR
3 weeks later a chest CT shows extensive diffuse bilateral micronodular military disease associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly.
A week later she was admitted to the ICU with confluent pneumonic infiltrates with air bronchograms in the lower lobes.
Later that month her CXR started to improve but still showed military disease.
A CXR 9 months later shows resolution.
Ashley Davidoff MD
MICRONODULES IN ILD
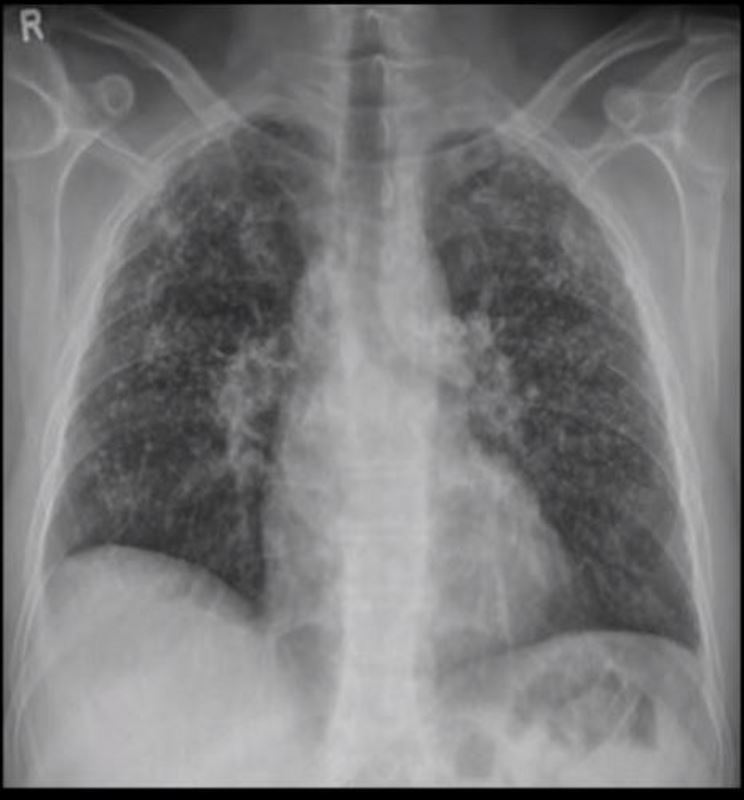

Frontal view exemplifies a diffuse nodular pattern of ILD such as is seen in silicosis and sarcoidosis
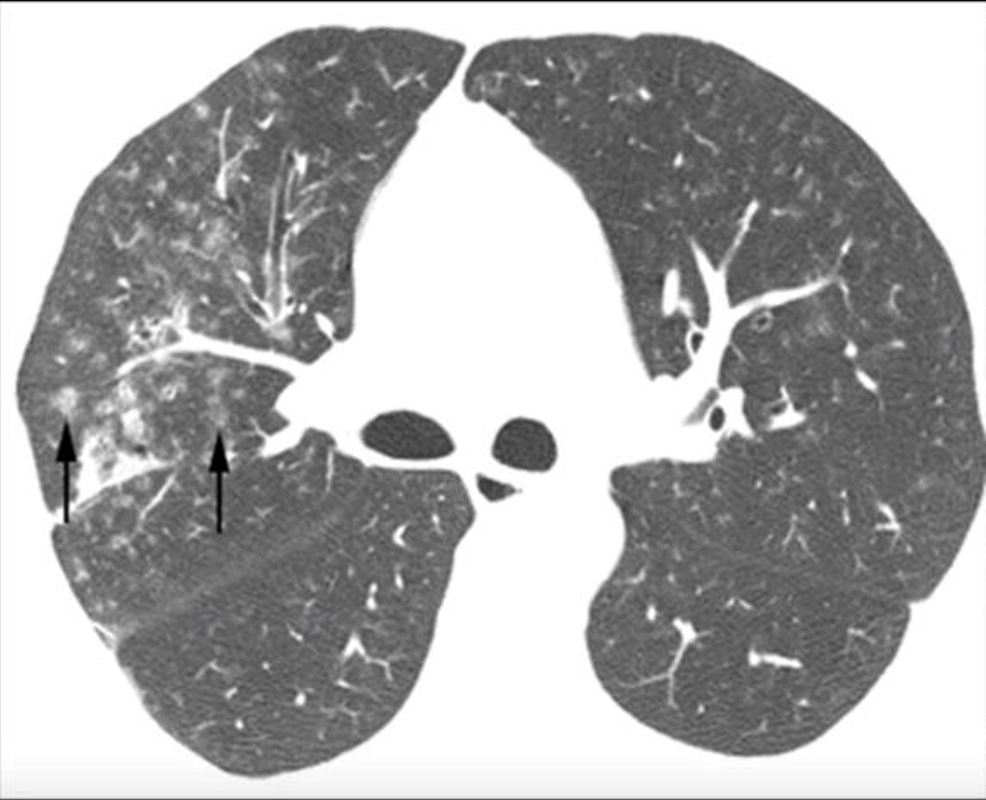


Micronodules in ILD is another feature of interstitial lung disease and is characterised by nodules of a variety of shapes and sizes and likely centrilobular in origin. Sometimes they are ill defined such as in this case.



Micronodules in ILD is another CT feature of interstitial lung disease and is characterised by nodules of a variety of shapes and sizes and likely centrilobular in origin. Sometimes they are ill defined such as in this case.
Silicosis
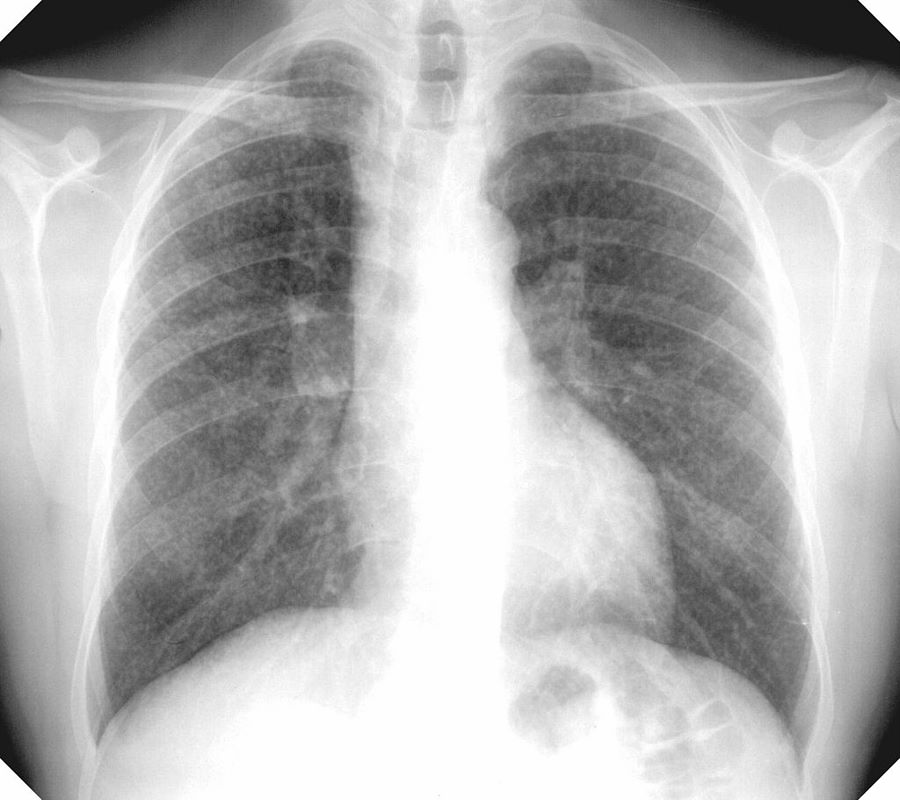

Chest X-ray showing uncomplicated silicosis
Courtesy Gumersindorego
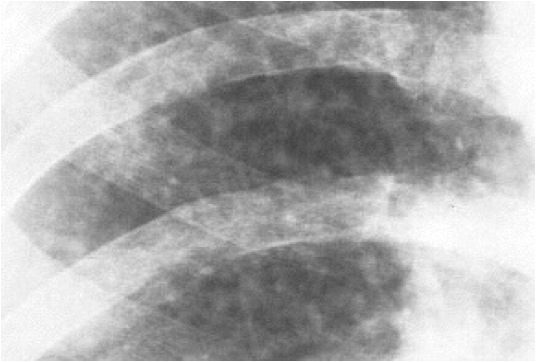

Courtesy DrSHaber
Silicosis vs Sarcoidosis
42-year-old cement worker presents with dyspnea .
A CXR performed 5 years prior was close to normal with possible right hilar prominence.
The CT scan, shows diffuse micronodular lung disease, predominantly in the upper lobes with mediastinal widening consistent with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, dominant in the right paratracheal region and in the subcarinal region.
Lung windows show the presence of extensive diffuse micronodular disease accumulating along lymphatics along fissures and pleural surfaces, and along the bronchovascular bundles. Although there is diffuse disease, the upper lobes are slightly more involved than the lower lobes. The extensive thickening along bronchovascular bundles and prominent adenopathy favors a diagnosis of sarcoidosis but with a work history of being a cement worker, silicosis still remains in the differential diagnosis as a less likely possibility.
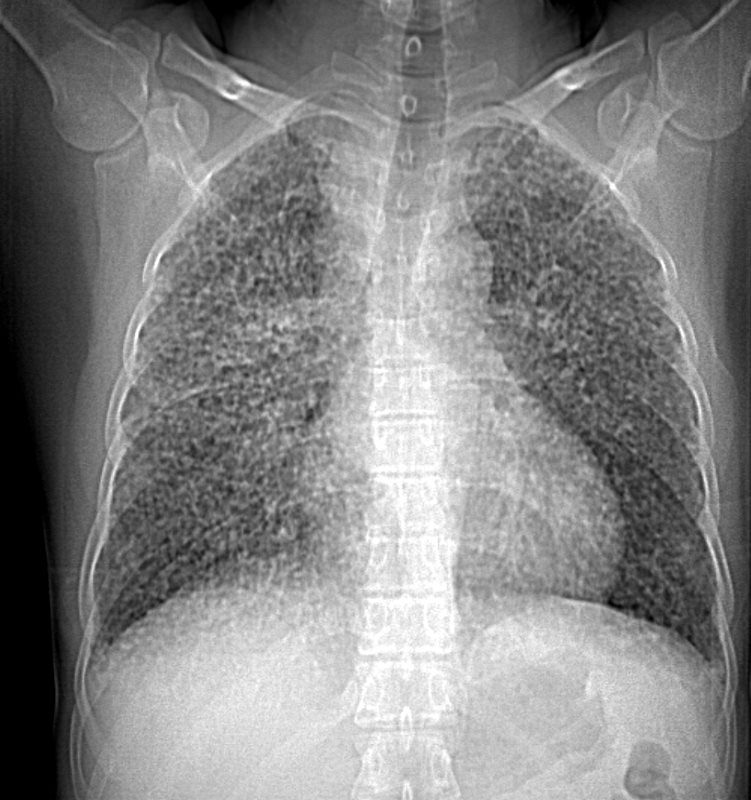

Ashley Davidoff MD
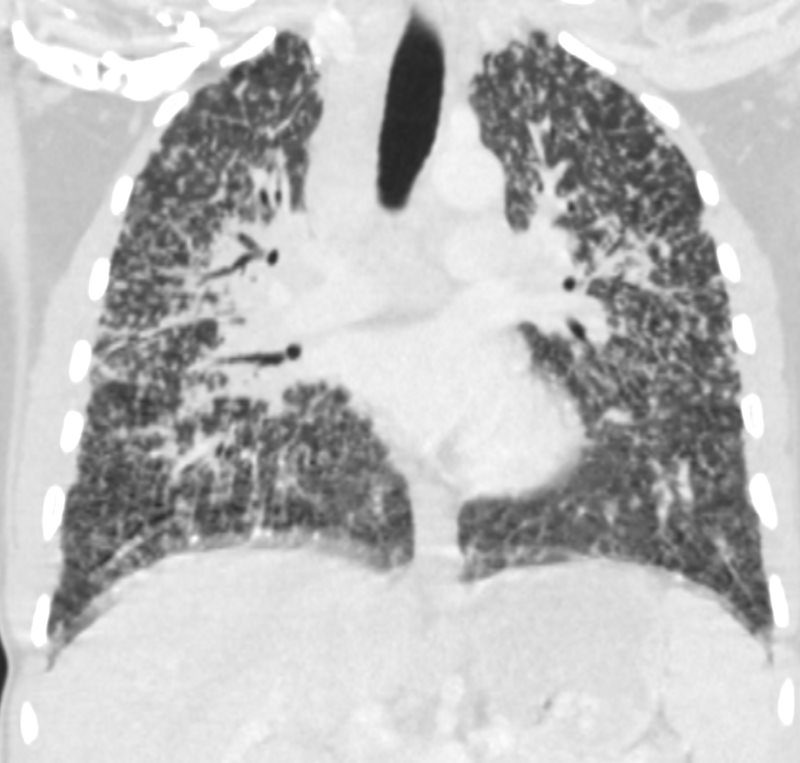

Ashley Davidoff MD
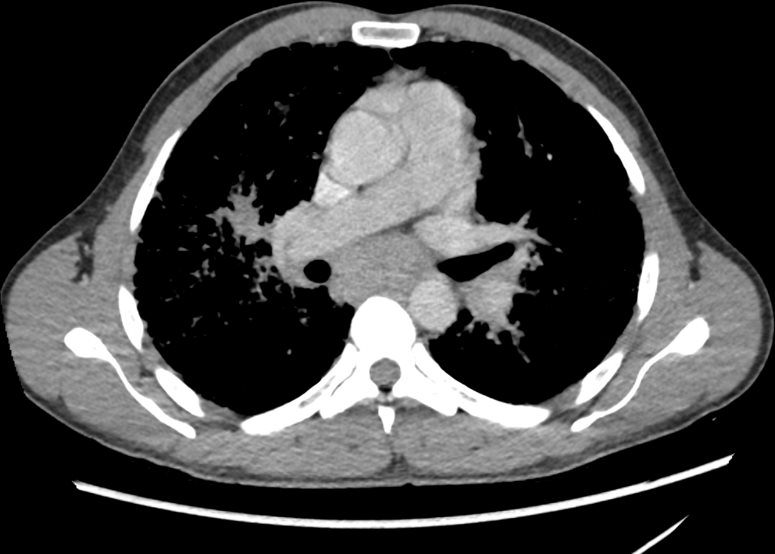

Ashley Davidoff MD
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
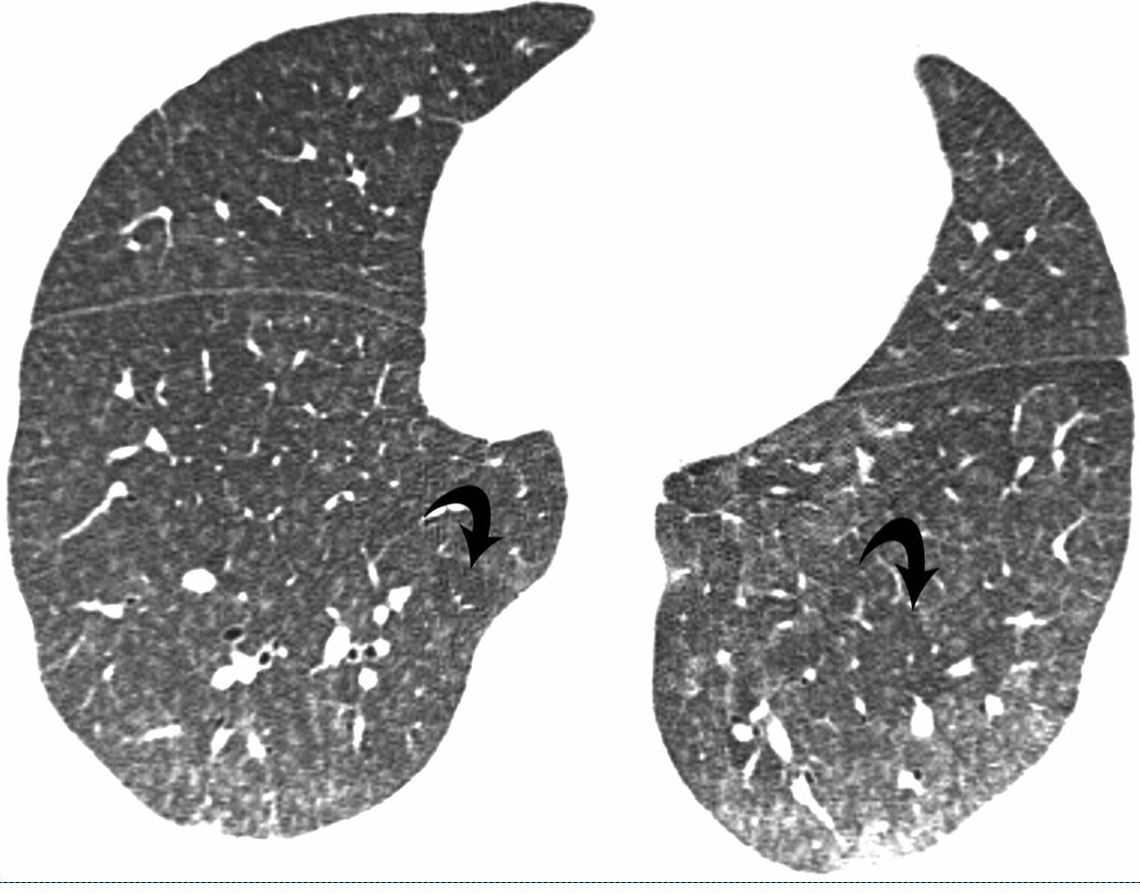

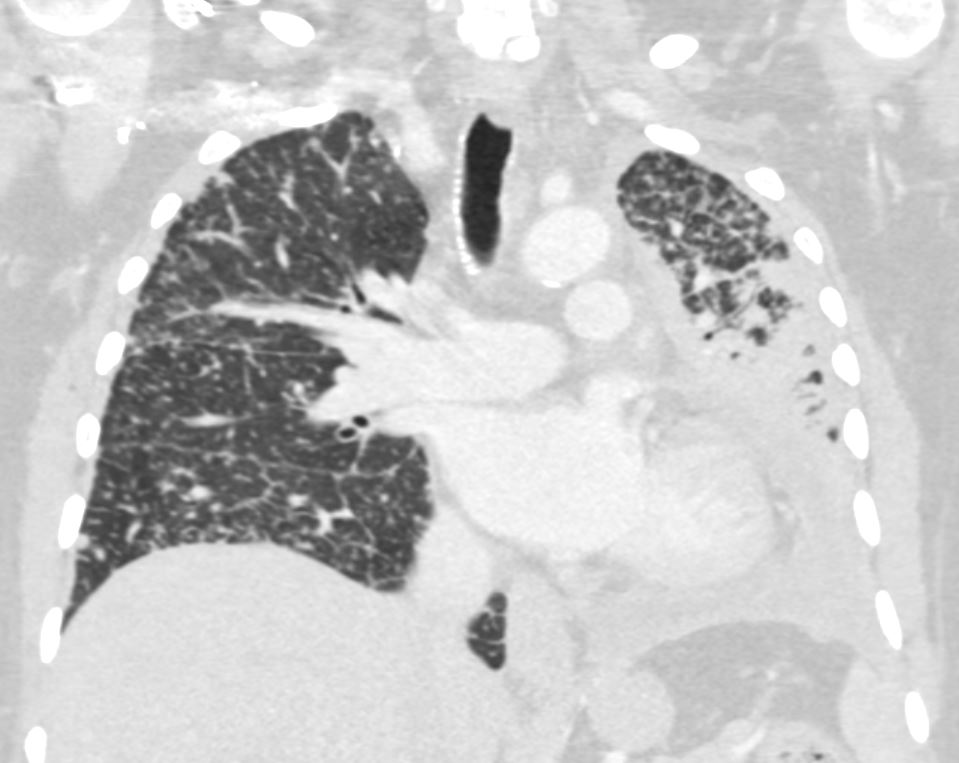
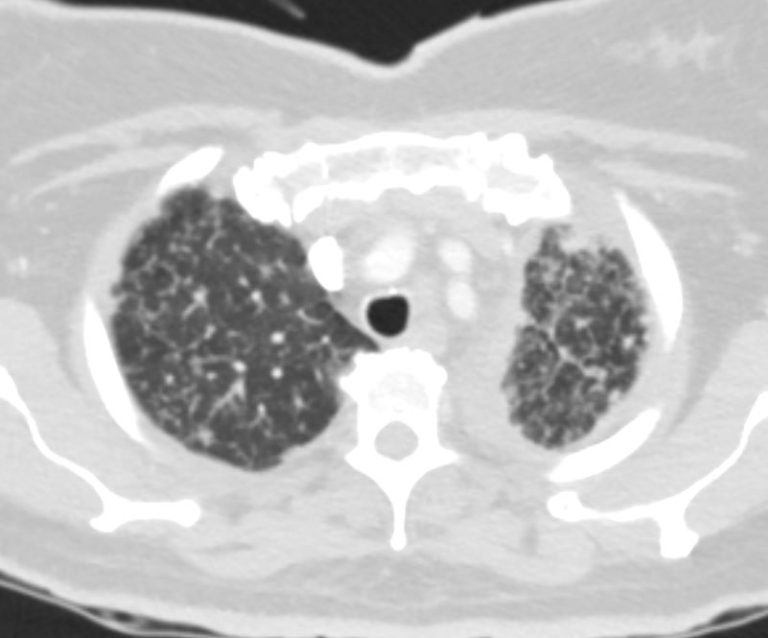
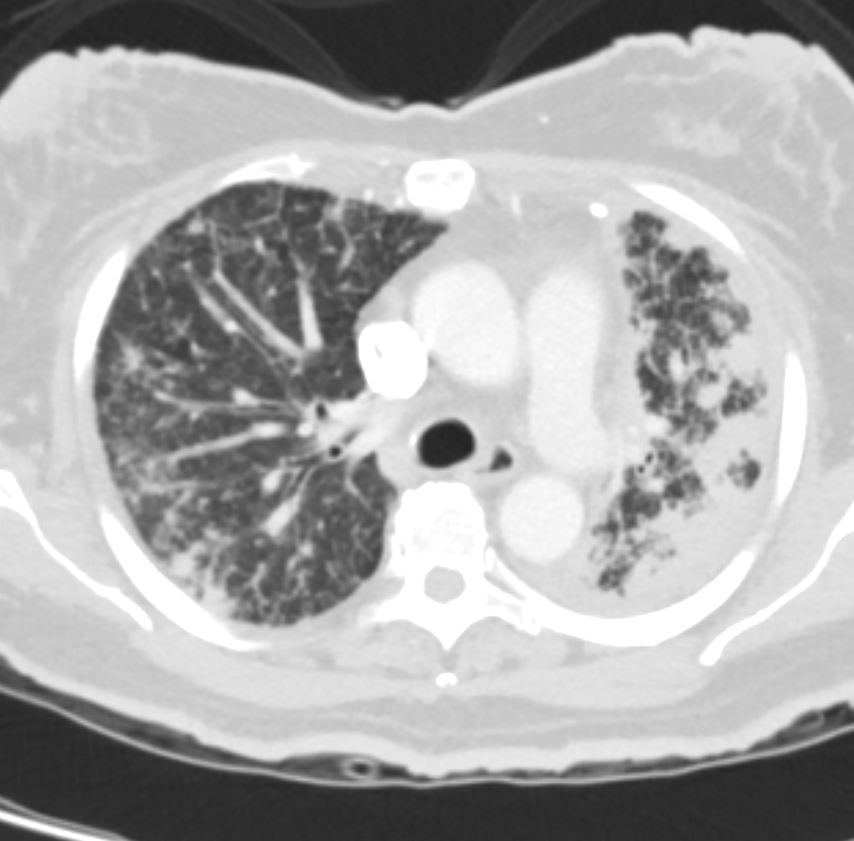
Bilateral Lymphangitis Carcinomatosis in a Patient with Adenocarcinoma


50 year old female with primary adenocarcinoma of the left lung with diffuse bilateral lymphangitic spread of disease characterized by lymphovascular distribution.
The nodularity on the fissures characterize the lymphatic distribution and the nodules are likely of a mixed nature, some being in the interlobular septa, and some in a centrilobular distribution .
Ashley Davidoff MD
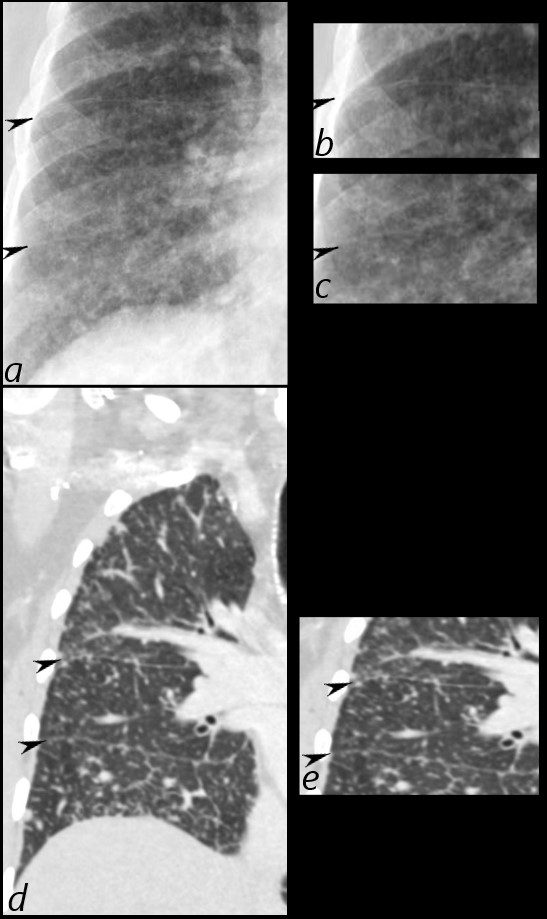

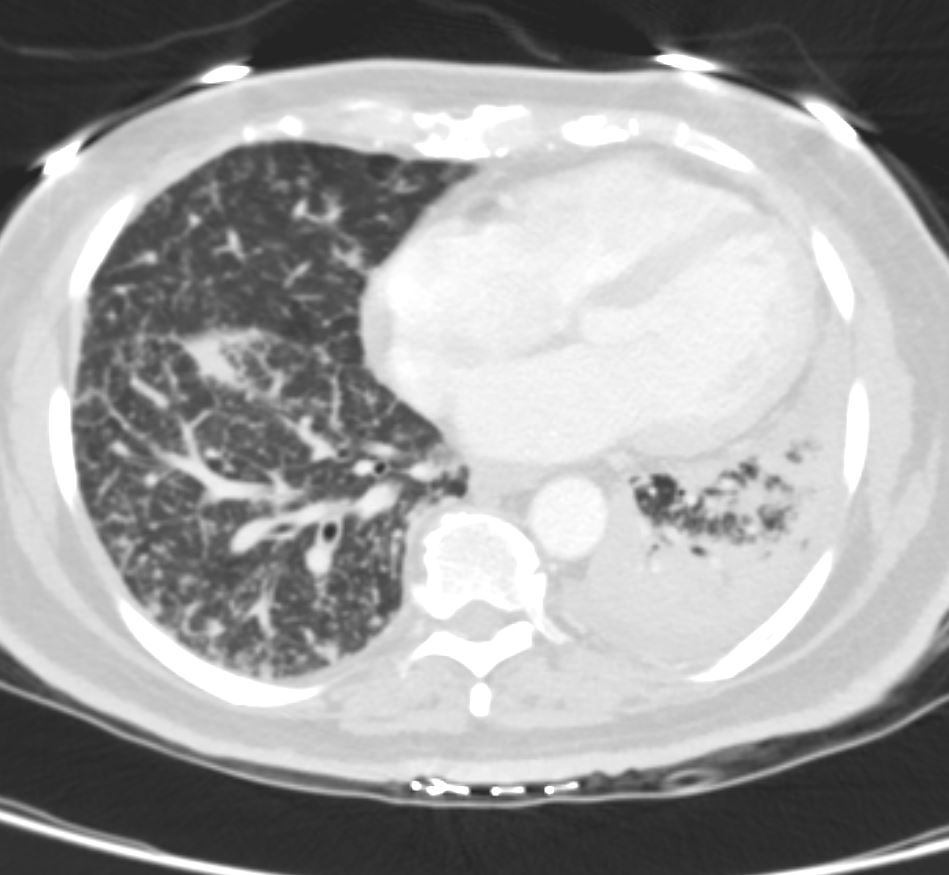
50 year old female with primary adenocarcinoma of the left lung with diffuse bilateral lymphangitic spread of disease characterized by lymphovascular distribution.
The nodularity on the fissures characterize the lymphatic distribution and the nodules are likely of a mixed nature, some being in the interlobular septa, and some in a centrilobular distribution .
Ashley Davidoff MD












References and Links
Videos
See around 25minutes
