- Etymology
“Ground-glass” refers to the hazy, frosted-glass appearance seen on imaging, originating from glasswork terminology. A “nodule” is a small, rounded opacity in the lung. - AKA and abbreviation
Ground-glass nodule (GGN). - What is it?
A ground-glass nodule (GGN) is a specific subtype of ground-glass opacity (GGO), defined as a focal, hazy area of increased lung attenuation on CT imaging. GGNs are circumscribed, smaller than 3 cm, and do not obscure underlying bronchial or vascular structures. Unlike GGNs, GGOs are a broader category that includes diffuse, non-nodular hazy opacities. - Characterized by
- Hazy opacity on imaging, typically identified on high-resolution CT (HRCT).
- Subdivided into:
- Pure GGNs: No solid component.
- Part-solid GGNs: A combination of ground-glass and solid components.
- Size: Typically up to 3 cm in diameter; larger lesions may indicate malignancy.
- Caused by
- Most Common Cause(s): Benign causes such as transient inflammation (e.g., atypical pneumonia, viral infections) are more frequent overall. Persistent GGNs are more commonly associated with atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) or early adenocarcinoma.
- Other Causes Include:
- Infection: Atypical pneumonia, fungal infections.
- Inflammation/Immune: Organizing pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia.
- Neoplasm: Invasive adenocarcinoma, metastatic disease.
- Congenital: Rarely, congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM).
- Resulting in:
- Potential for malignant transformation if persistent or part-solid.
- Misinterpretation if transient, leading to unnecessary interventions.
- Structural changes:
- Alveolar or interstitial involvement without significant collapse or consolidation.
- Pathophysiology:
GGNs arise due to partial filling of airspaces, interstitial thickening, or increased cellularity, which scatters x-rays and reduces air content. Persistent GGNs often represent early neoplastic processes, while transient GGNs are typically inflammatory or infectious. - Pathology:
- Pure GGNs: Often associated with atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) or early adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS).
- Part-solid GGNs: More likely to indicate invasive adenocarcinoma.
- Inflammatory GGNs: Alveolar exudates or interstitial infiltration.
- Diagnosis:
- Clinical context: Symptoms (if any), patient history (e.g., smoking, exposure, immune status).
- Imaging: HRCT for detection and characterization.
- Follow-up: Serial imaging for persistent nodules.
- Biopsy: Indicated for nodules with high suspicion of malignancy or growth over time.
- Clinical:
Symptoms are usually absent but may include cough, hemoptysis, or constitutional symptoms if associated with malignancy or infection. - Radiology Detail:
- CXR
- Findings: Rarely visible on CXR due to subtle density.
- Associated Findings: Not specific unless part of a larger process (e.g., consolidation).
- CT
- Parts: Solitary or multiple.
- Size: Usually <3 cm for nodules; larger lesions suggest higher suspicion.
- Shape: Round or irregular.
- Position: Can occur anywhere within the lung parenchyma.
- Character: Pure ground-glass or part-solid.
- Time: Stable, transient, or progressive (growth or increasing solid component).
- Associated Findings: Pleural retraction, air bronchograms, satellite nodules.
- Other relevant Imaging Modalities
- PET-CT: Typically recommended for solid nodules ≥7 mm in size; GGNs may show lower metabolic activity due to paucicellularity. PET is more reliable for nodules with part-solid components or if the GGN exceeds 10 mm.
- MRI: Rarely used but may provide soft-tissue contrast.
- CXR
- Pulmonary function tests (PFTs):
Usually normal unless associated with underlying lung disease. - Recommendations
- Fleischner Guidelines for GGNs:
- Pure GGNs ≤6 mm: No routine follow-up is needed unless specific clinical risks are present.
- Pure GGNs >6 mm: CT at 6-12 months, then every 2 years for up to 5 years if stable.
- Part-solid GGNs >6 mm: CT at 3-6 months to confirm persistence; additional imaging based on growth or development of new solid components.
- Follow-up should focus on growth and evolution, especially the development of solid components, which is concerning for adenocarcinoma with lepidic growth and may necessitate PET scanning or biopsy.
- GGNs typically grow more slowly than solid nodules. While a solid nodule that remains stable for 2 years may not require further follow-up, GGNs often necessitate prolonged surveillance beyond 2 years to monitor for late malignant transformation.
- Persistent GGNs, especially part-solid, warrant close monitoring to detect malignancy early.
- Fleischner Guidelines for GGNs:
- Key Points and Pearls
- Persistent GGNs, especially those with part-solid components, require close follow-up due to higher malignancy risk.
- Transient GGNs are often inflammatory or infectious and may resolve spontaneously.
- GGNs are a subset of GGOs, which can include diffuse or patchy opacities. GGNs are circumscribed and focal.
- A structured approach using Fleischner guidelines is essential for consistent management.
- Evolution of solid components within GGNs is a critical marker for potential malignant transformation, highlighting the importance of serial imaging and timely intervention.
- GGNs grow more slowly than solid nodules, necessitating a longer follow-up interval to detect changes indicative of malignancy.
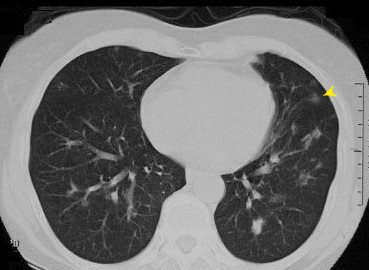 This CT shows a ground glass nodule in the lung which is characterized by a small round hazy opacity that are usually less than 3cm in size (yellow arrows)Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net29787L B.A
This CT shows a ground glass nodule in the lung which is characterized by a small round hazy opacity that are usually less than 3cm in size (yellow arrows)Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net29787L B.A
- Etymology
“Ground-glass” refers to the hazy, frosted-glass appearance seen on imaging, originating from glasswork terminology. A “nodule” is a small, rounded opacity in the lung. - AKA and abbreviation
Ground-glass nodule (GGN). - What is it?
A ground-glass nodule (GGN) is a specific subtype of ground-glass opacity (GGO), which is defined as a focal, hazy area of increased lung attenuation on CT imaging. GGNs are circumscribed, smaller than 3 cm, and do not obscure underlying bronchial or vascular structures. Unlike GGNs, GGOs are a broader category that includes diffuse, non-nodular hazy opacities. - Characterized by
- Hazy opacity on imaging, typically identified on high-resolution CT (HRCT).
- Subdivided into:
- Pure GGNs: No solid component.
- Part-solid GGNs: A combination of ground-glass and solid components.
- Size: Typically up to 3 cm in diameter; larger lesions may indicate malignancy.
- Caused by
- Most Common Cause(s): Benign causes such as transient inflammation (e.g., atypical pneumonia, viral infections) are more frequent overall. Persistent GGNs are more commonly associated with atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) or early adenocarcinoma.
- Other Causes Include:
- Infection: Atypical pneumonia, fungal infections.
- Inflammation/Immune: Organizing pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia.
- Neoplasm: Invasive adenocarcinoma, metastatic disease.
- Congenital: Rarely, congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM).
- Resulting in:
- Potential for malignant transformation if persistent or part-solid.
- Misinterpretation if transient, leading to unnecessary interventions.
- Structural changes:
- Alveolar or interstitial involvement without significant collapse or consolidation.
- Pathophysiology:
GGNs arise due to partial filling of airspaces, interstitial thickening, or increased cellularity, which scatters x-rays and reduces air content. Persistent GGNs often represent early neoplastic processes, while transient GGNs are typically inflammatory or infectious. - Pathology:
- Pure GGNs: Often associated with atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) or early adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS).
- Part-solid GGNs: More likely to indicate invasive adenocarcinoma.
- Inflammatory GGNs: Alveolar exudates or interstitial infiltration.
- Diagnosis:
- Clinical context: Symptoms (if any), patient history (e.g., smoking, exposure, immune status).
- Imaging: HRCT for detection and characterization.
- Follow-up: Serial imaging for persistent nodules.
- Biopsy: Indicated for nodules with high suspicion of malignancy or growth over time.
- Clinical:
Symptoms are usually absent but may include cough, hemoptysis, or constitutional symptoms if associated with malignancy or infection. - Radiology Detail:
- CXR
- Findings: Rarely visible on CXR due to subtle density.
- Associated Findings: Not specific unless part of a larger process (e.g., consolidation).
- CT
- Parts: Solitary or multiple.
- Size: Usually <3 cm for nodules; larger lesions suggest higher suspicion.
- Shape: Round or irregular.
- Position: Can occur anywhere within the lung parenchyma.
- Character: Pure ground-glass or part-solid.
- Time: Stable, transient, or progressive (growth or increasing solid component).
- Associated Findings: Pleural retraction, air bronchograms, satellite nodules.
- Other relevant Imaging Modalities
- PET-CT: Typically recommended for solid nodules ≥7 mm in size; GGNs may show lower metabolic activity due to paucicellularity. PET is more reliable for nodules with part-solid components or if the GGN exceeds 10 mm.
- MRI: Rarely used but may provide soft-tissue contrast.
- CXR
- Pulmonary function tests (PFTs):
Usually normal unless associated with underlying lung disease. - Recommendations
- Fleischner Guidelines for GGNs:
- Pure GGNs ≤6 mm: No routine follow-up is needed unless specific clinical risks are present.
- Pure GGNs >6 mm: CT at 6-12 months, then every 2 years for up to 5 years if stable.
- Part-solid GGNs >6 mm: CT at 3-6 months to confirm persistence; additional imaging based on growth or development of new solid components.
- Follow-up should focus on growth and evolution, especially the development of solid components, which is concerning for adenocarcinoma with lepidic growth and may necessitate PET scanning or biopsy.
- GGNs typically grow more slowly than solid nodules, and follow-up intervals reflect this difference.
- Persistent GGNs, especially part-solid, warrant close monitoring to detect malignancy early.
- Fleischner Guidelines for GGNs:
- Key Points and Pearls
- Persistent GGNs, especially those with part-solid components, require close follow-up due to higher malignancy risk.
- Transient GGNs are often inflammatory or infectious and may resolve spontaneously.
- GGNs are a subset of GGOs, which can include diffuse or patchy opacities. GGNs are circumscribed and focal.
- A structured approach using Fleischner guidelines is essential for consistent management.
- Evolution of solid components within GGNs is a critical marker for potential malignant transformation, highlighting the importance of serial imaging and timely intervention.
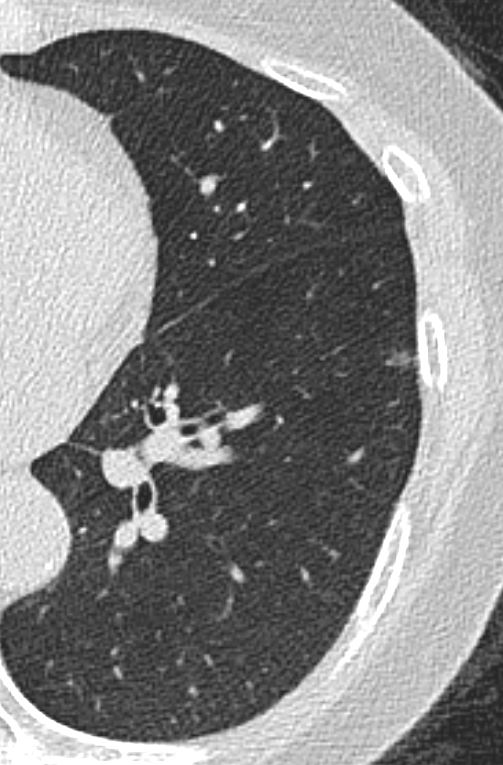
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
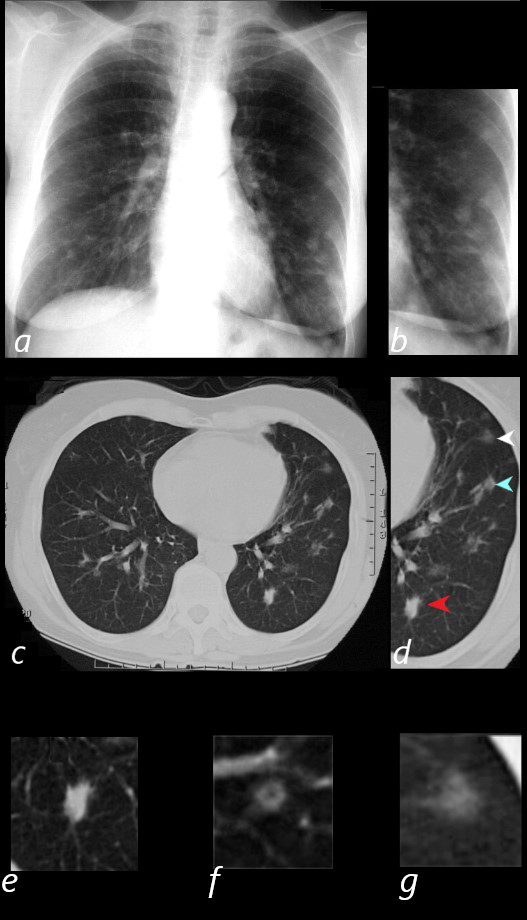
65 year old female presents with epistaxis and with nodular changes on CXR (a) magnified in b.
CT scan in axial projection (c) and magnified in d, reveals 3 types of nodules.
A spiculated solid nodule (red arrow head) is magnified in e, a bronchocentric nodule (teal arrowhead) is magnified in e. This may represent a cavitating nodule or hemorrhagic change around a bronchiole (cheerio sign) A ground glass nodule (white arrowhead) is magnified in g.
Ashley Davidoff MD
Sarcoidosis
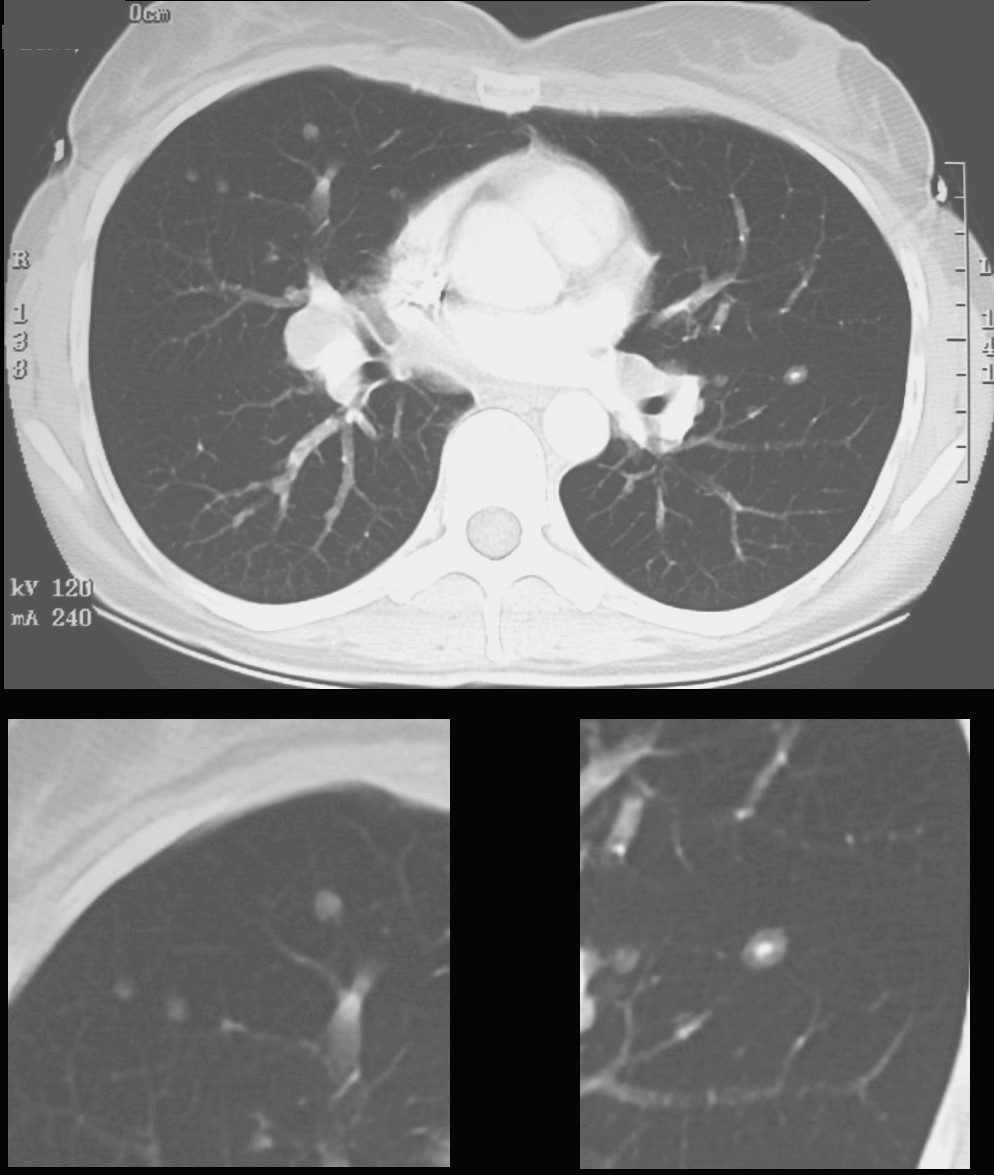
CT scan shows a 6mm nodule with central calcification in the ligula and ground glass nodules in the middle lobe
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
70060c
-
Links and References
- TCV
- TCV
