- Amyloidosis is a
- characterized by the deposition of
- abnormal protein aggregates called amyloid
Structural Involvement
- Trachea and Bronchi
- Pulmonary Vasculature
- Lung Parenchyma
- Pleura
- Lymph Nodes
- Mediastinum
Findings
| Imaging Finding | Description |
|---|---|
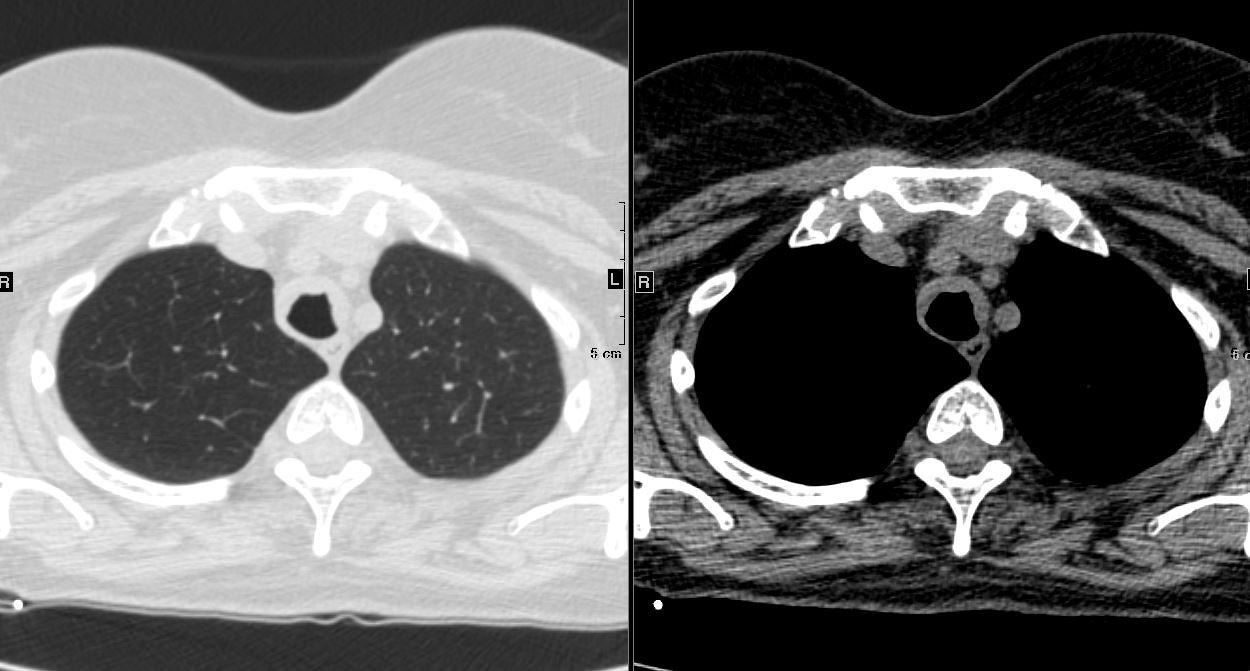
| Tracheobronchial Involvement: | Amyloid deposits in the trachea and bronchi, leading to wall thickening and luminal narrowing. |
| Submucosal Deposits: | Amyloid deposits beneath the mucosa of the trachea and bronchi, contributing to airway compromise. |
| Nodular or Mass-like Lesions: | Formation of nodules or mass-like lesions in the lung parenchyma due to amyloid deposits. |
| Pulmonary Parenchymal Involvement: | Amyloid deposition in the lung parenchyma, leading to diffuse or focal interstitial infiltrates. |
| Ground-Glass Opacities (GGOs): | Areas of ground-glass opacities on imaging studies, reflecting parenchymal involvement. |
| Septal Thickening | |
| Pleural Involvement: | Amyloid deposition in the pleura, leading to pleural thickening or effusion in some cases. |
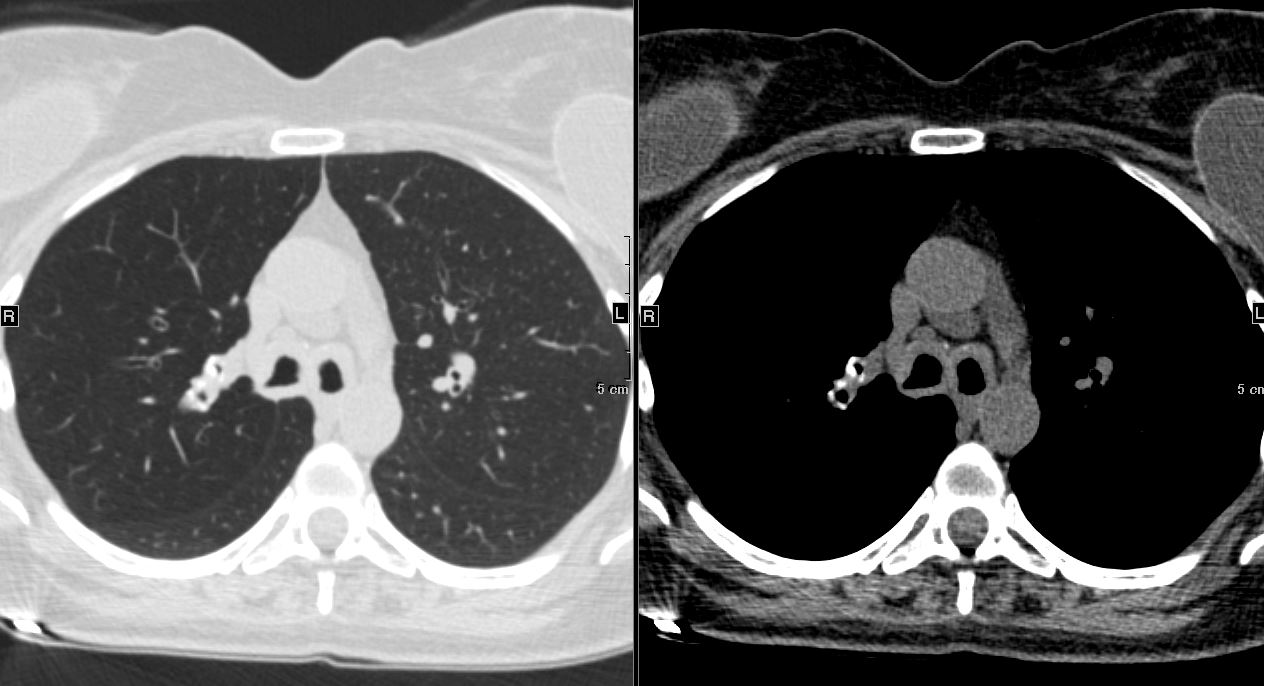
| Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy: | Enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum, due to amyloid deposits can calcify. |
- Involvement of the mediastinum, including lymph nodes, may occur in some cases of amyloidosis.
- Extracellular deposition
- insoluble proteins
- Lung
-
Perivascular and peribronchiolar infiltration of amorphous acellular infiltration of pink amyloid in a mouse model
NIH National Toxicology Program
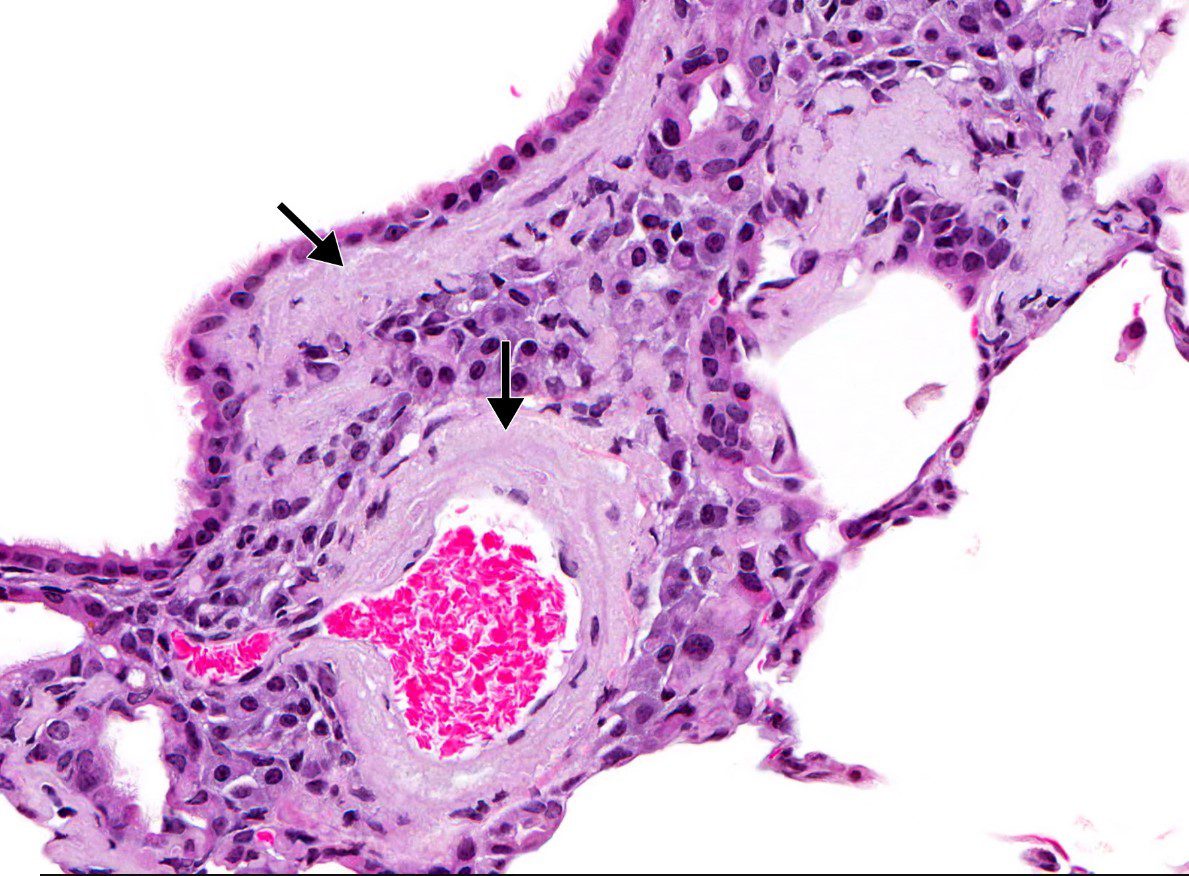
The diagram shows infiltration of dark pink, amorphous, acellular amyloid deposition In the wall of the arteriole
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
A normal bronchiole usually 1mm or less in diameter. The wall consists of ciliated cuboidal epithelium and a layer of smooth muscle. Bronchioles divide into even smaller bronchioles, called terminal bronchioles, which are 0.5 mm or less in diameter and are primarily lined by club cells, and accompanied by a small number of ciliated cuboidal cells.. Respiratory bronchioles are the final division of the bronchioles within the lung and they are .5mm or less in diameter and contain a simple non ciliated cuboidal epithelium and a thin layer of smooth muscle
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0721
The diagram shows infiltration of dark pink, amorphous, acellular amyloid deposition In the wall of the bronchiole
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net- Tracheobronchial
- Parenchyma
- Mass Like that may
- calcify,
- cavitate, and
- slowly enlarge.
- Mass Like that may

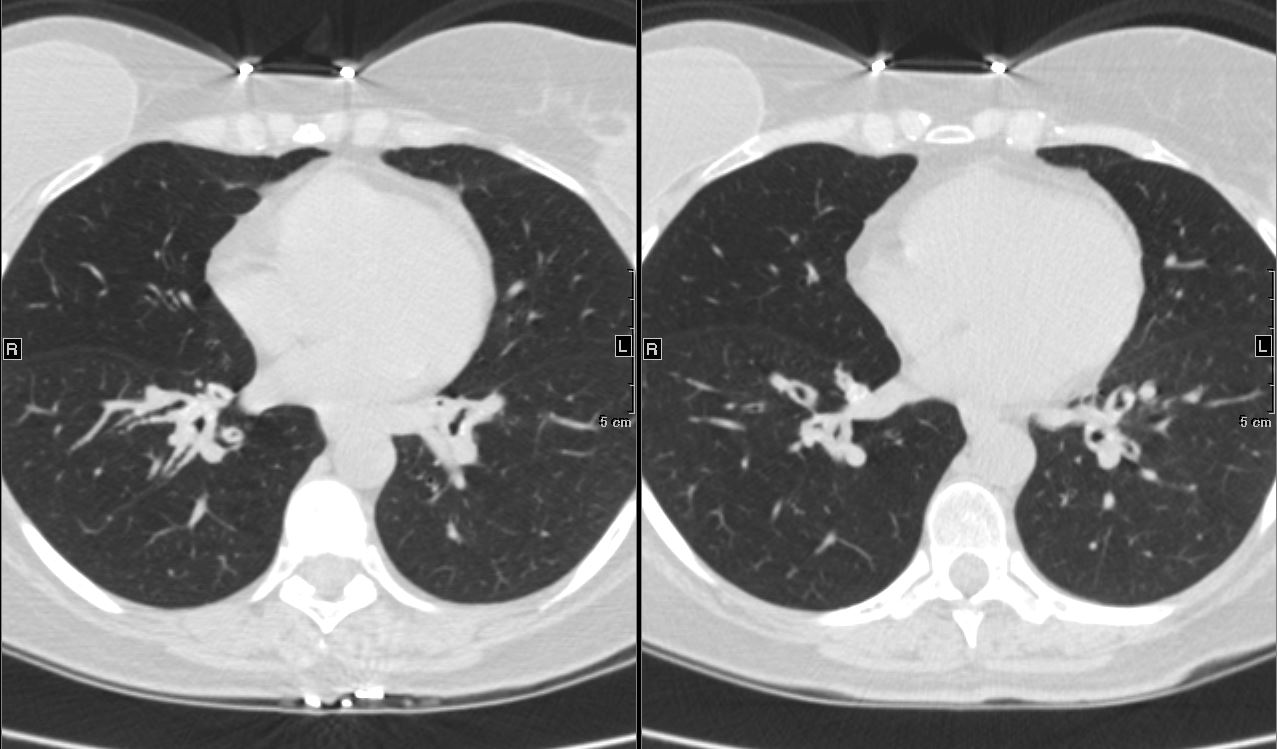
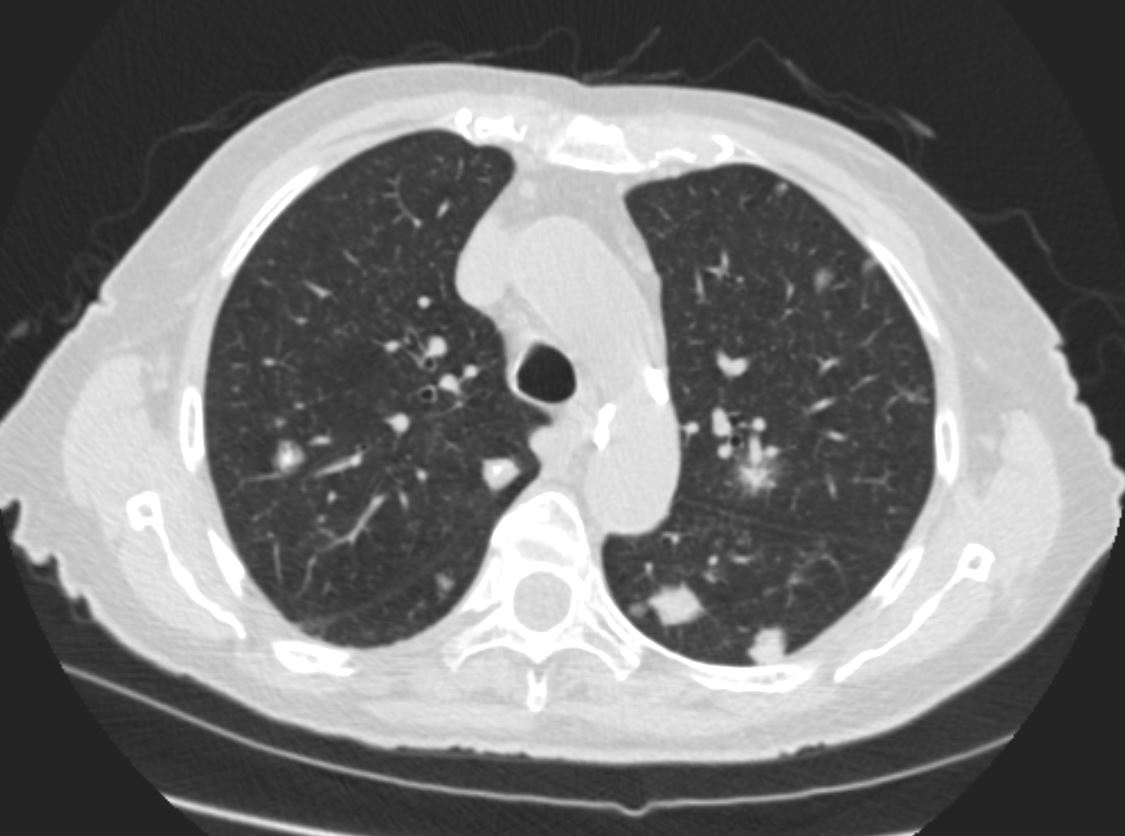
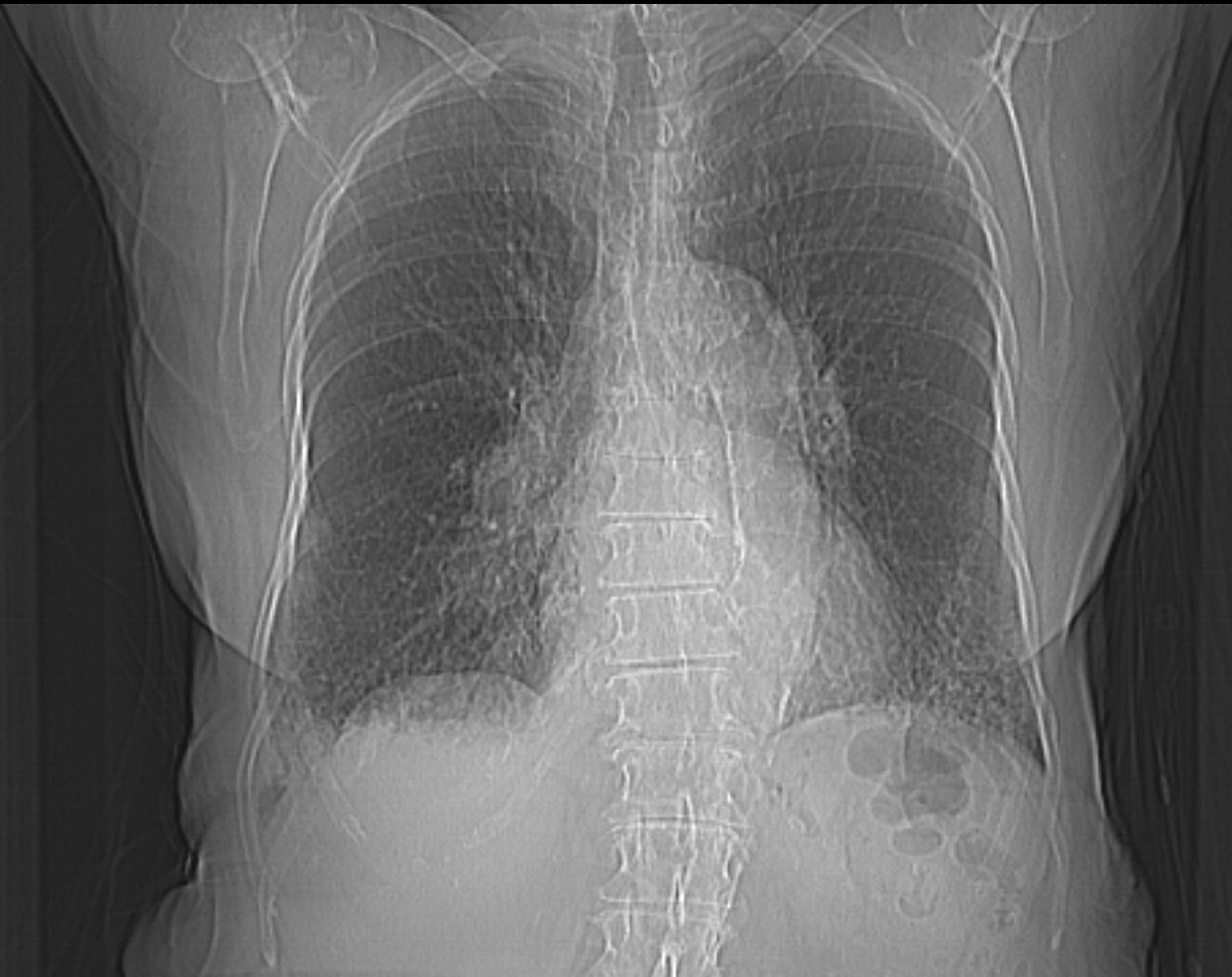
83 y.o. male with biopsy proven nodular lung AL amyloidosis diagnosed by lung biopsy 5 years ago . His underlying amylogenic protein was typed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry as kappa.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
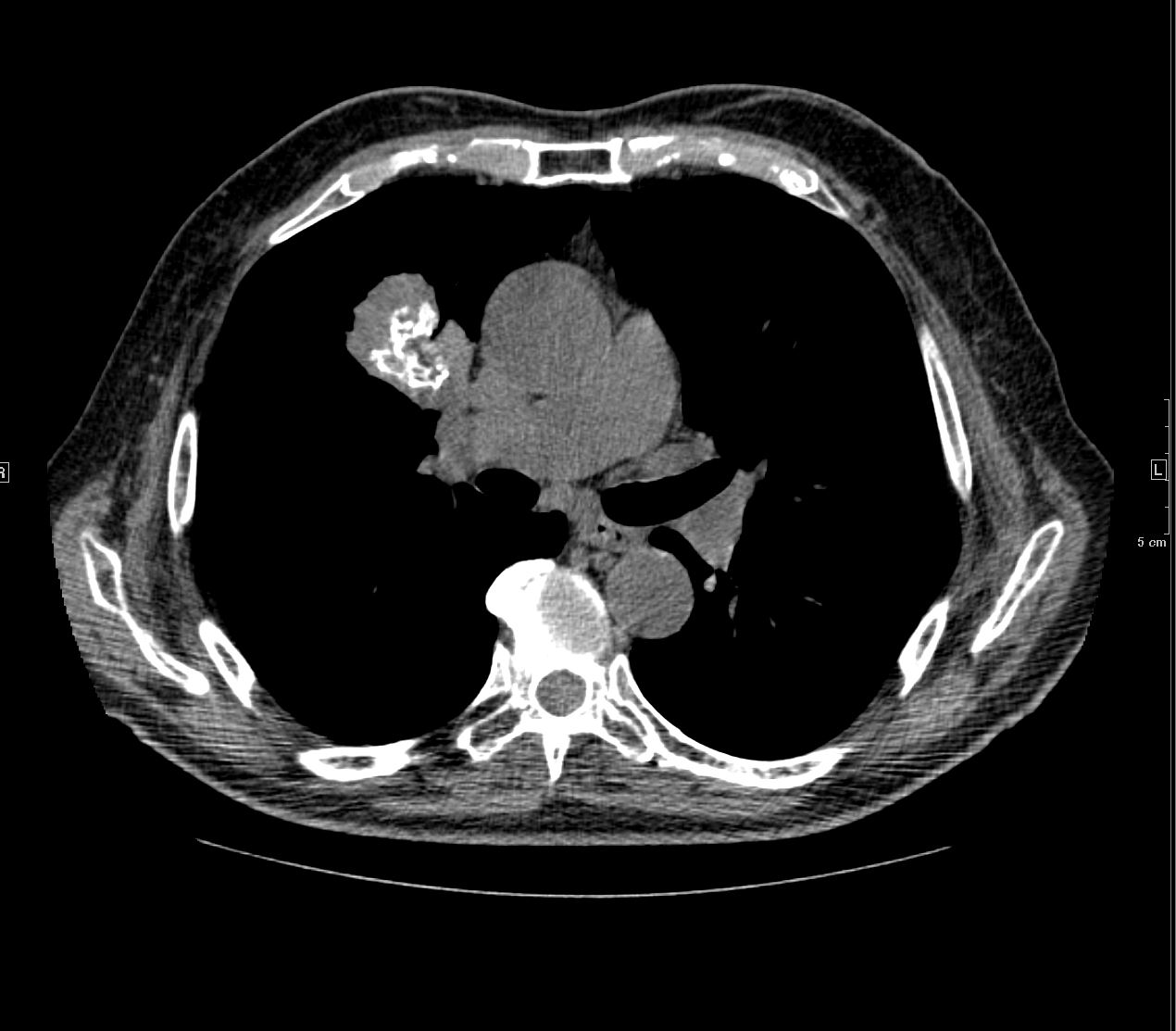
83 y.o. male with biopsy proven nodular lung AL amyloidosis diagnosed by lung biopsy 5 years ago . His underlying amylogenic protein was typed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry as kappa.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
- Nodular Form that may
-
- calcify,
- cavitate, and
- slowly enlarge.
-

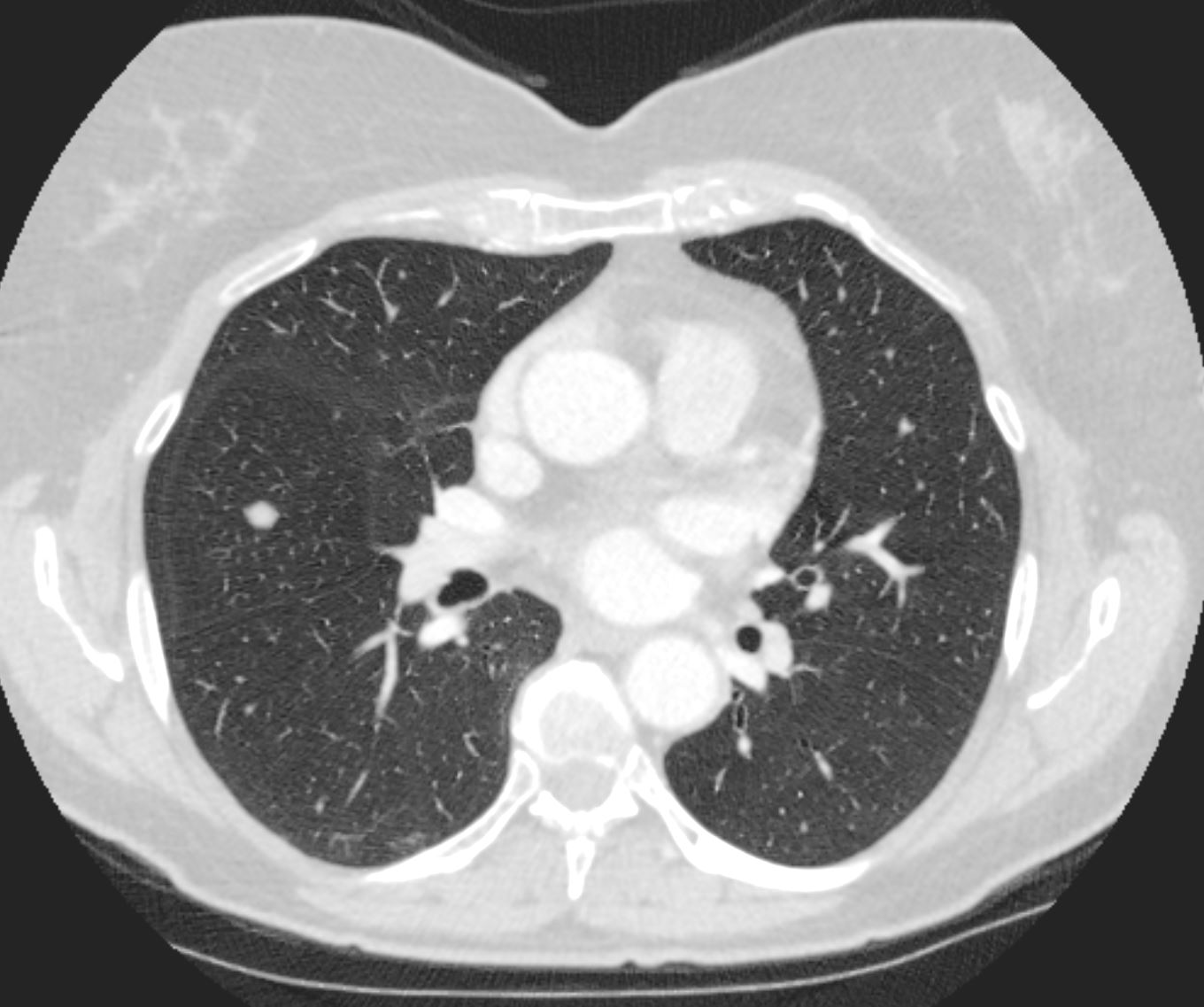
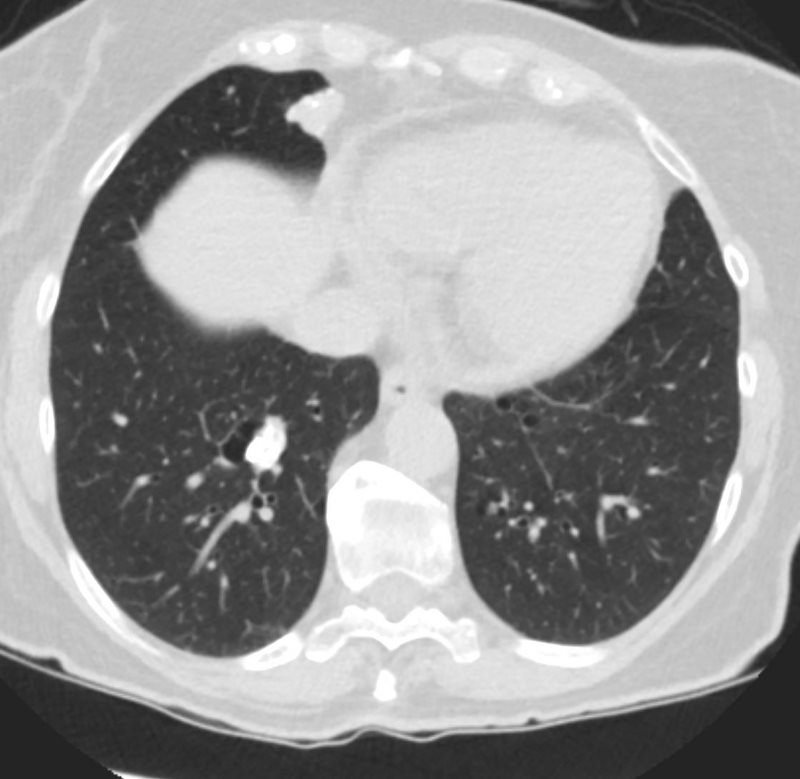
Small non descript nodule in a 65 year old female with path proven lung amyloid
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Small non descript nodule in a 65 year old female with path proven lung amyloid
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
- Multiple parenchymal nodules that may
- Alveolar septal pulmonary amyloidosis
- Diffuse reticulonodular interstitial thickening,
- Alveolar septal pulmonary amyloidosis is
- less common
- clinically more important than the nodular parenchymal form.
- more commonly symptomatic
- more likely to progress to pulmonary hypertension and respiratory failure
- systemic involvement,
- an independent predictor of poor survival,
- more common in this subtype.
-
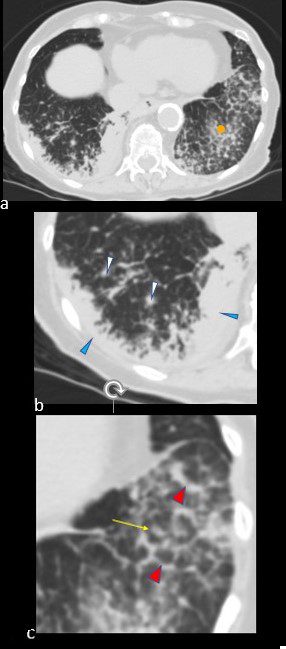
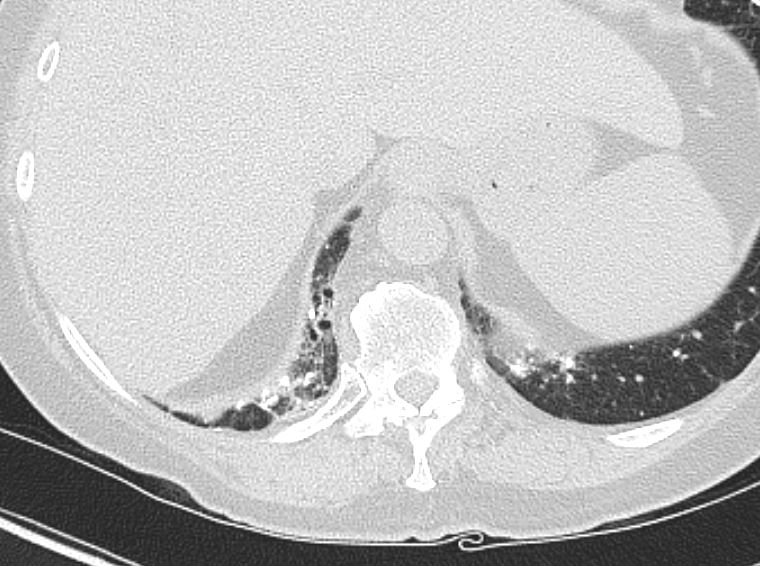
CT scan in the axial projection at the base of the lungs show many features of amyloidosis including lung nodules (white arrowheads) and infiltrates (b), and diffuse deposition within the alveolar septa (red arrowheads, c) and centrilobular nodules(yellow arrow c)
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
-
-
-


- consolidations, or
- Nodular form
- solitary or
- solitary or
- Pleural involvement most commonly manifests as
- pleural effusions.
- nodules



Pleural and Fissural based Nodules some with Calcification
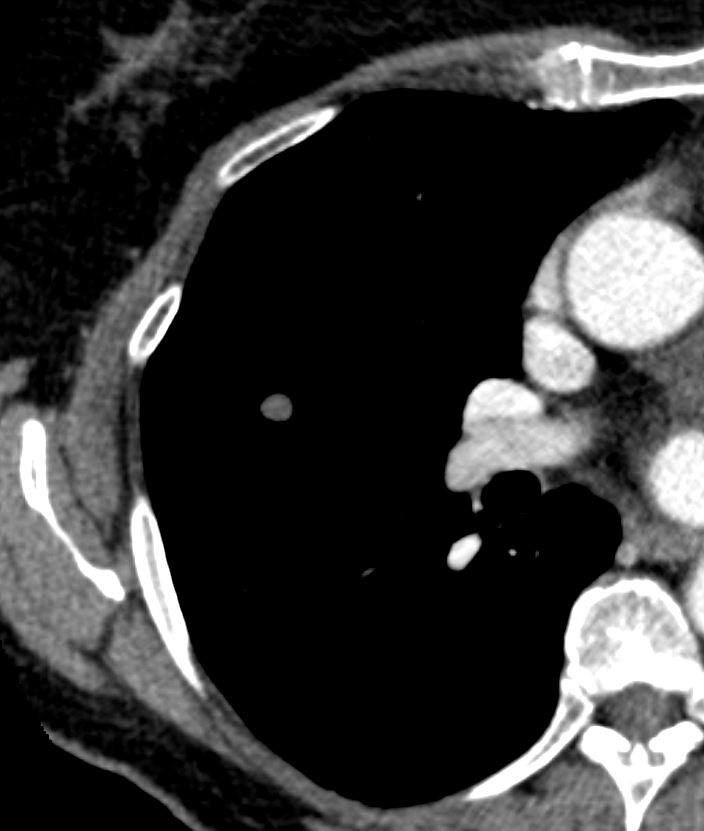
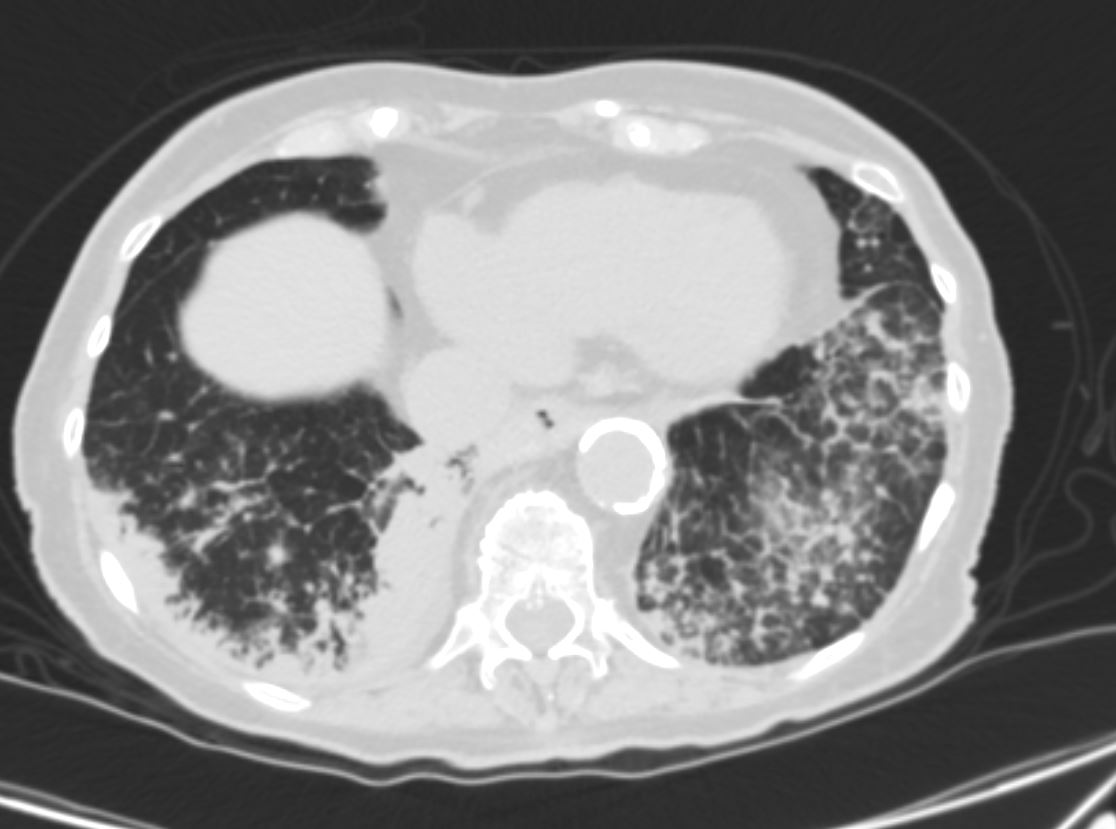
83 y.o. male with biopsy proven nodular lung AL amyloidosis diagnosed by lung biopsy 5 years ago . His underlying amylogenic protein was typed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry as kappa.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules on the pleural surfaces
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
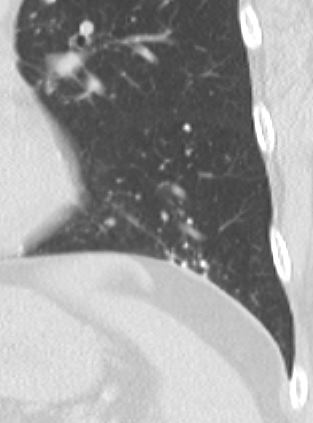
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
-
- Mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes may
-
-
- enlarge and
- frequently calcify.
-

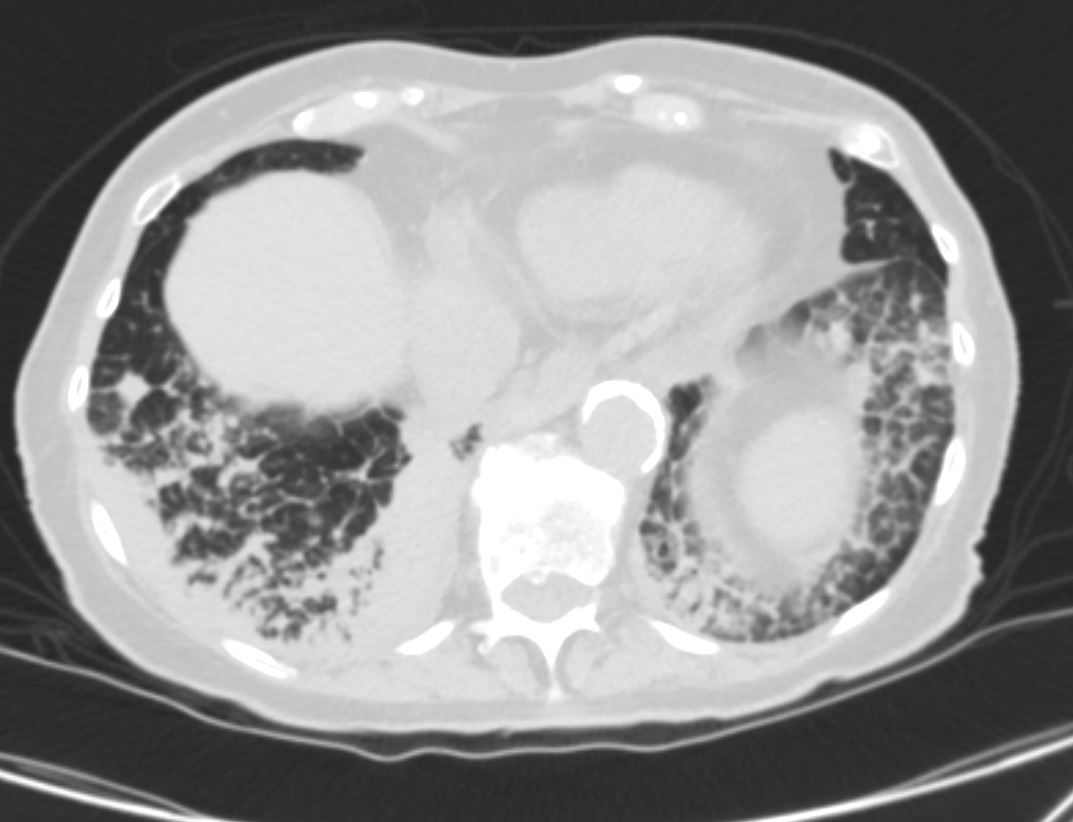
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
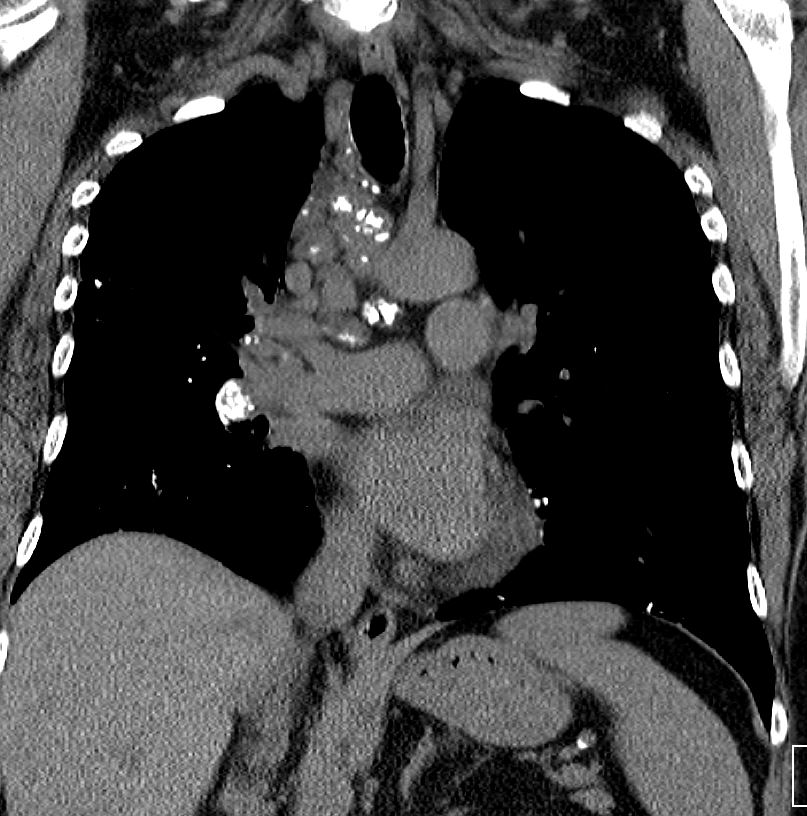
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

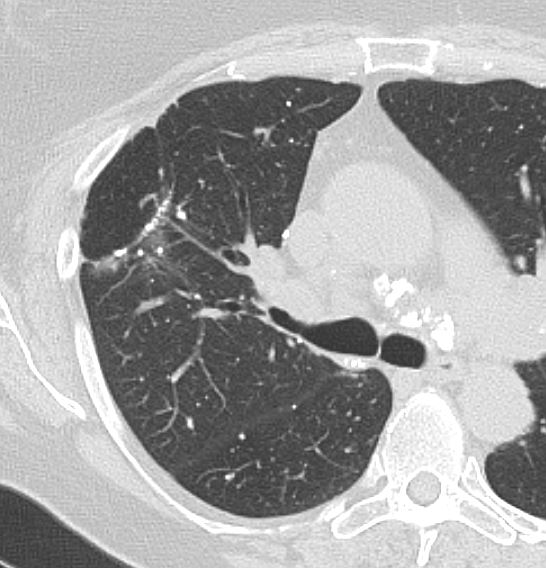
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
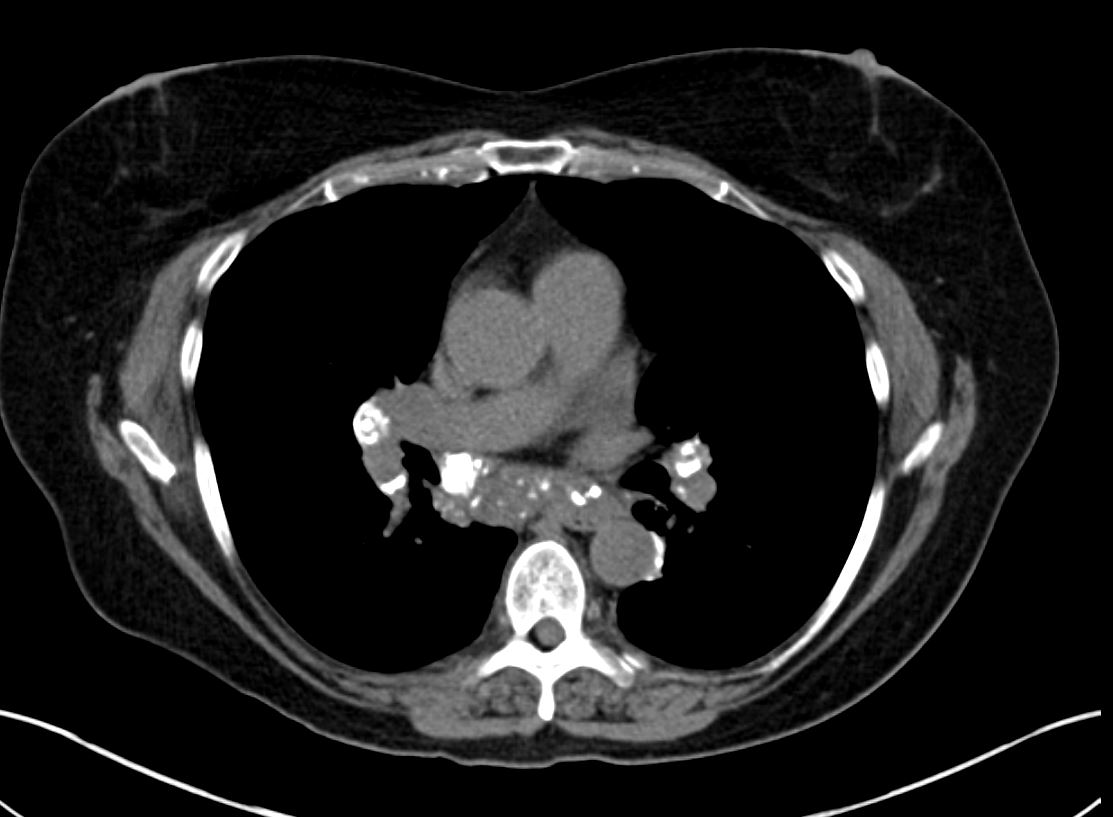
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.netSoft Tissue Infiltration

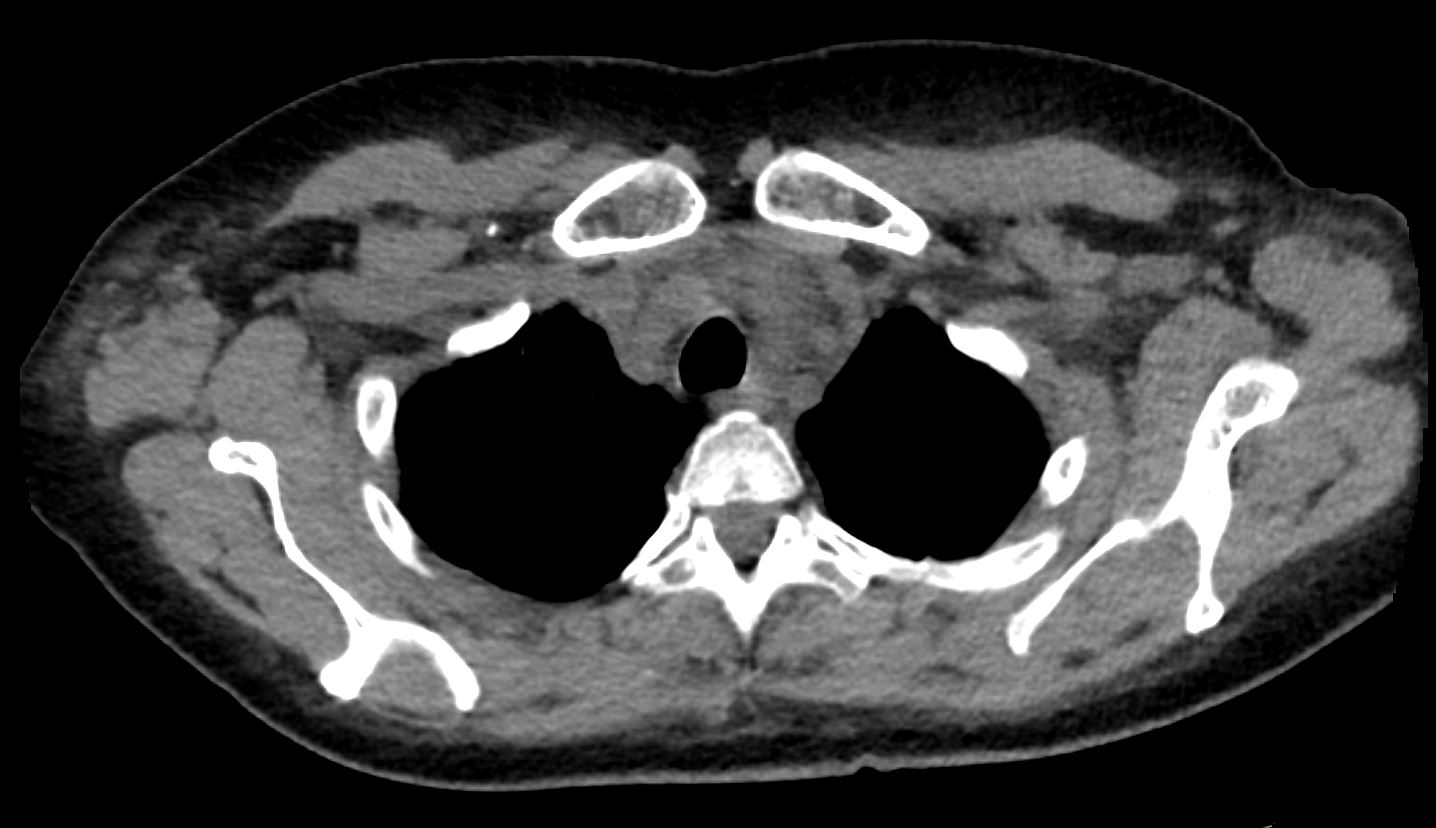
CT Alveolar Septal Amyloidosis with Dystrophic Calcifications and Soft Tissue Changes
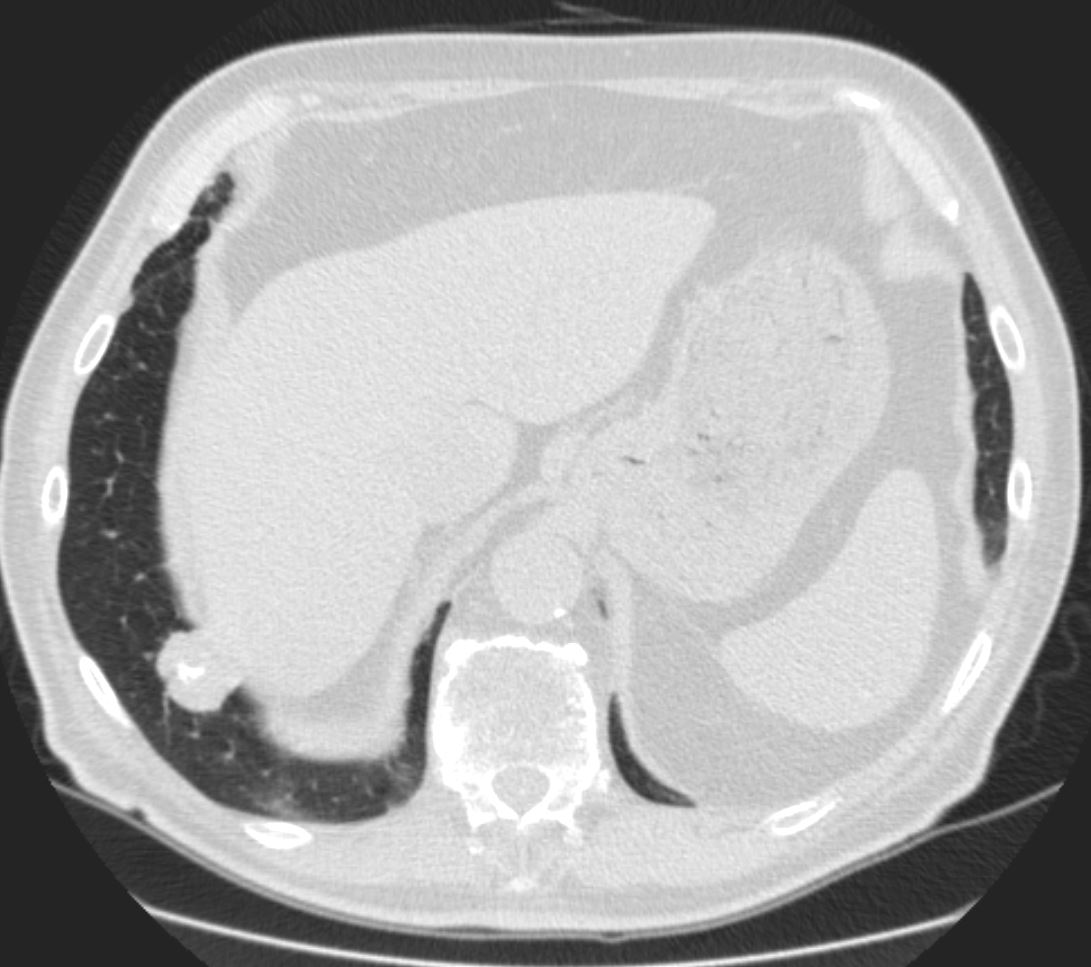
56 -year-old female with a history of amyloidosis (AL) presents for follow up. Axial CT of the chest shows diffuse soft tissue changes with thickening of the subcutaneous tissues in the right axilla and to lesser extent the left axilla surrounding the left lobe of the thyroid gland and in the subpectoral regions. There is a punctate dystrophic calcification in the right subpectoral region
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 244 Lu 135741d05
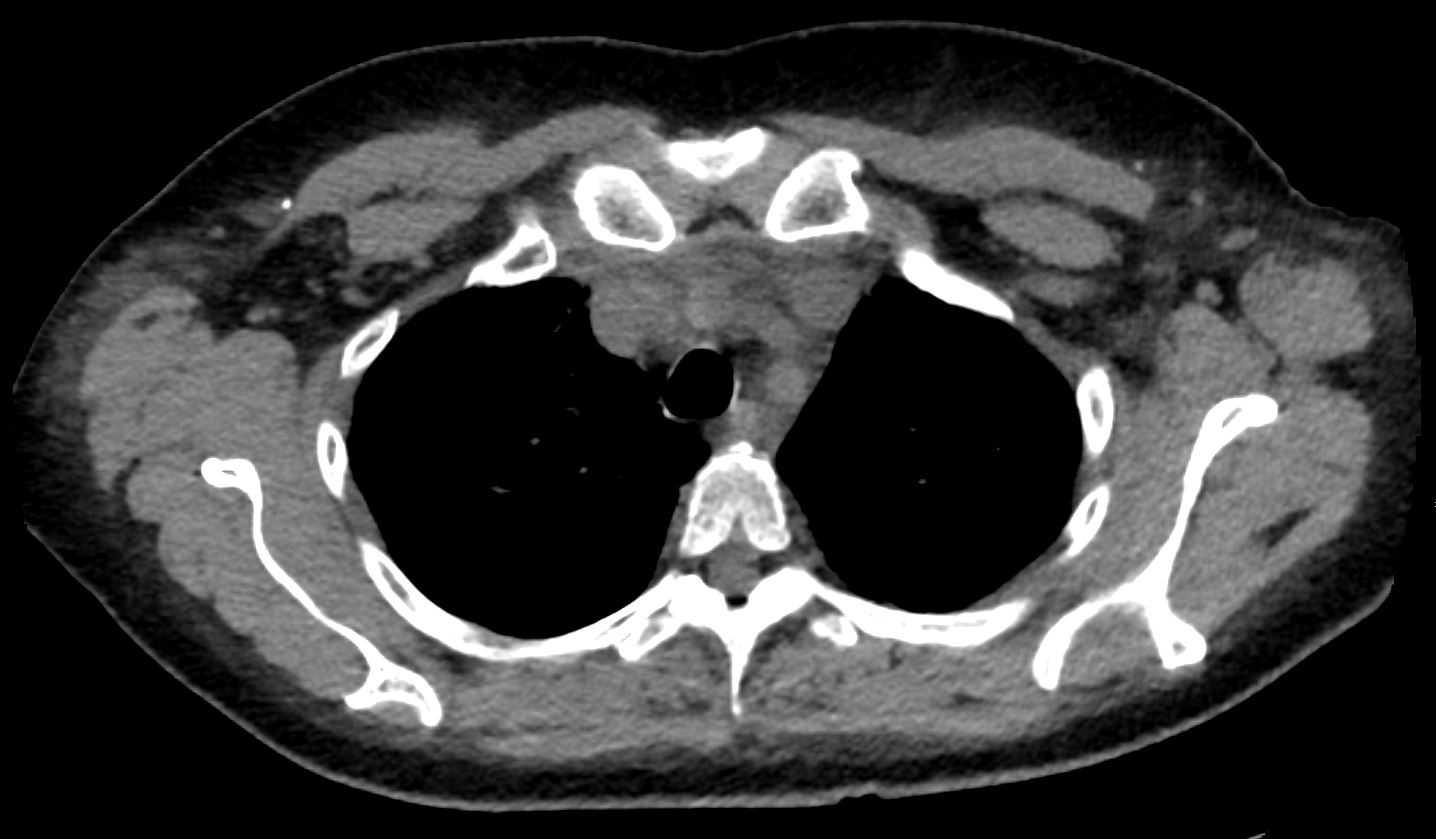
CT Alveolar Septal Amyloidosis with Dystrophic Calcifications and Soft Tissue Changes
56 -year-old female with a history of amyloidosis (AL) presents for follow up. Axial CT of the chest shows diffuse soft tissue changes with thickening of the subcutaneous tissues in the right axilla and to lesser extent the left axilla, and in the anterior superior mediastinum
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 244 Lu 135741d06
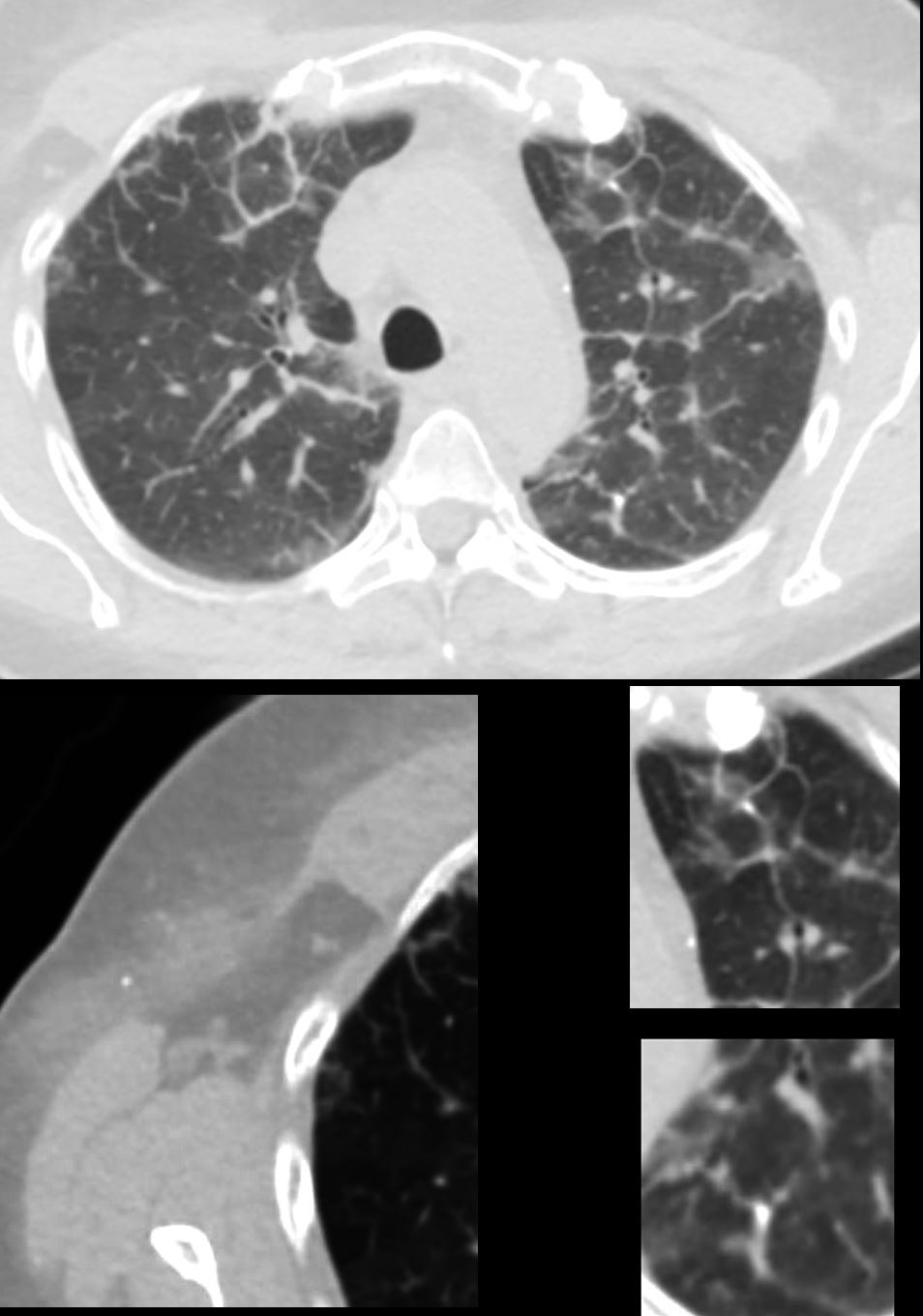
CT Alveolar Septal Amyloidosis with Calcifications
56 -year-old female with a history of amyloidosis (AL) presents for follow up. Axial CT of the chest shows diffuse reticular process best appreciated anteriorly with thickening of the interlobular septa. Punctate, dystrophic calcifications are seen in the interlobular septa (white arrowheads a, c and d), as well as in the pleura abutting the mediastinum (white arrowhead a). Image b shows similar calcifications, likely deposits of amyloid in the axilla with surrounding soft tissue changes
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 244 Lu 135741d02cL
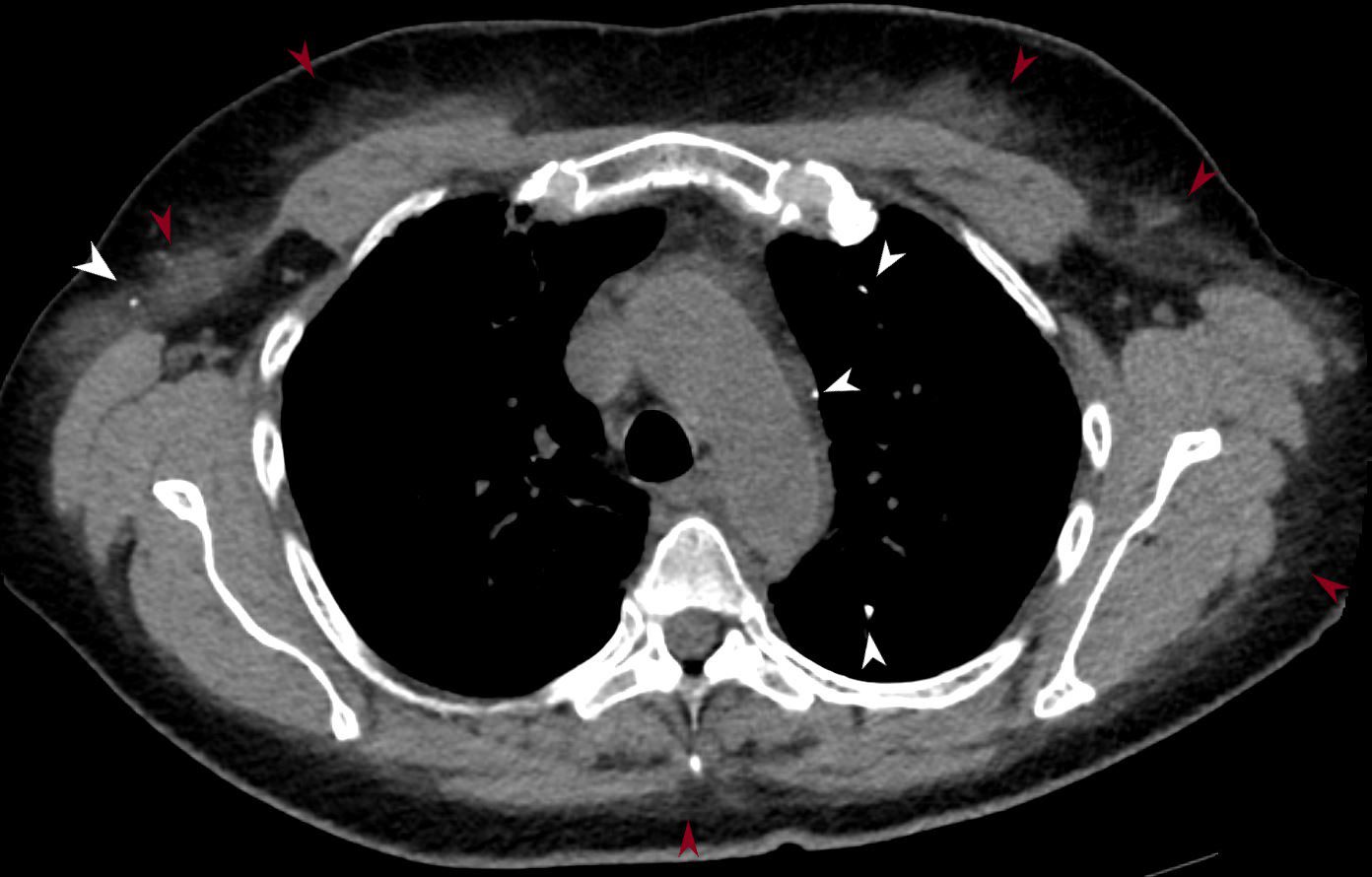
CT Alveolar Septal Amyloidosis Soft Tissue Calcifications
56 -year-old female with a history of amyloidosis (AL) presents for follow up. Axial CT of the chest shows punctate, dystrophic calcifications in the left upper lobe, pleura abutting the mediastinum and in the right axilla (white arrowheads). There is induration in the soft tissues suggesting amyloidosis (maroon arrowheads).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 244 Lu 135741d02m05L
-
-
- Associated with Cysts
- Uncommon
- lower lobes
- peribronchovacsular disease
- often in patients with
- systemic amyloidosis due to
- Sjögren syndrome (21).
- may be associated with
- calcified nodules or
- noncalcified nodules.
- cysts may be a
- manifestation of lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia in Sjögren syndrome
- or a manifestation of amyloidosis (possibly due to small airway obstruction by amyloid deposits)
- Uncommon
-
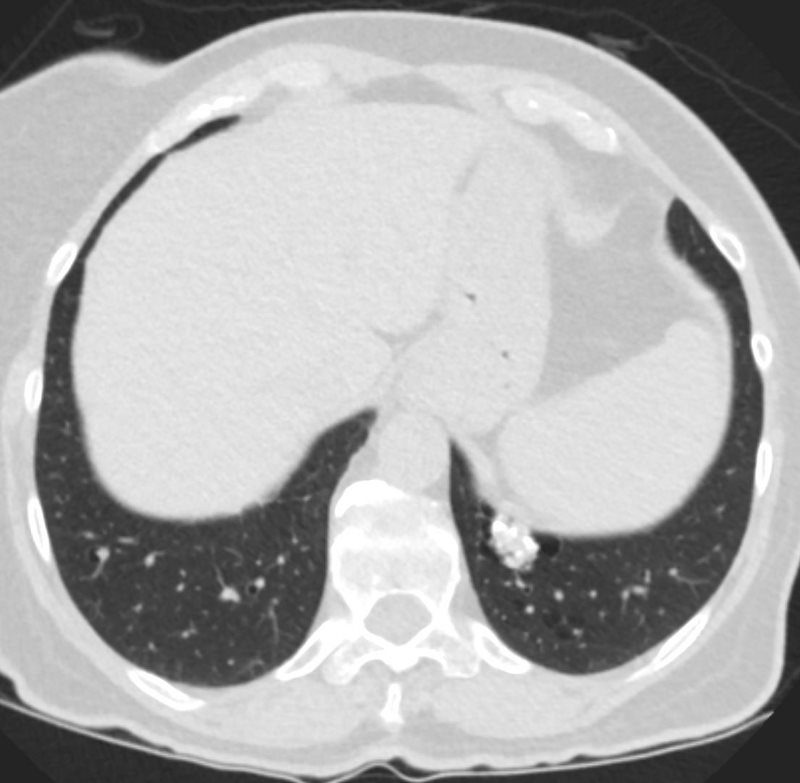

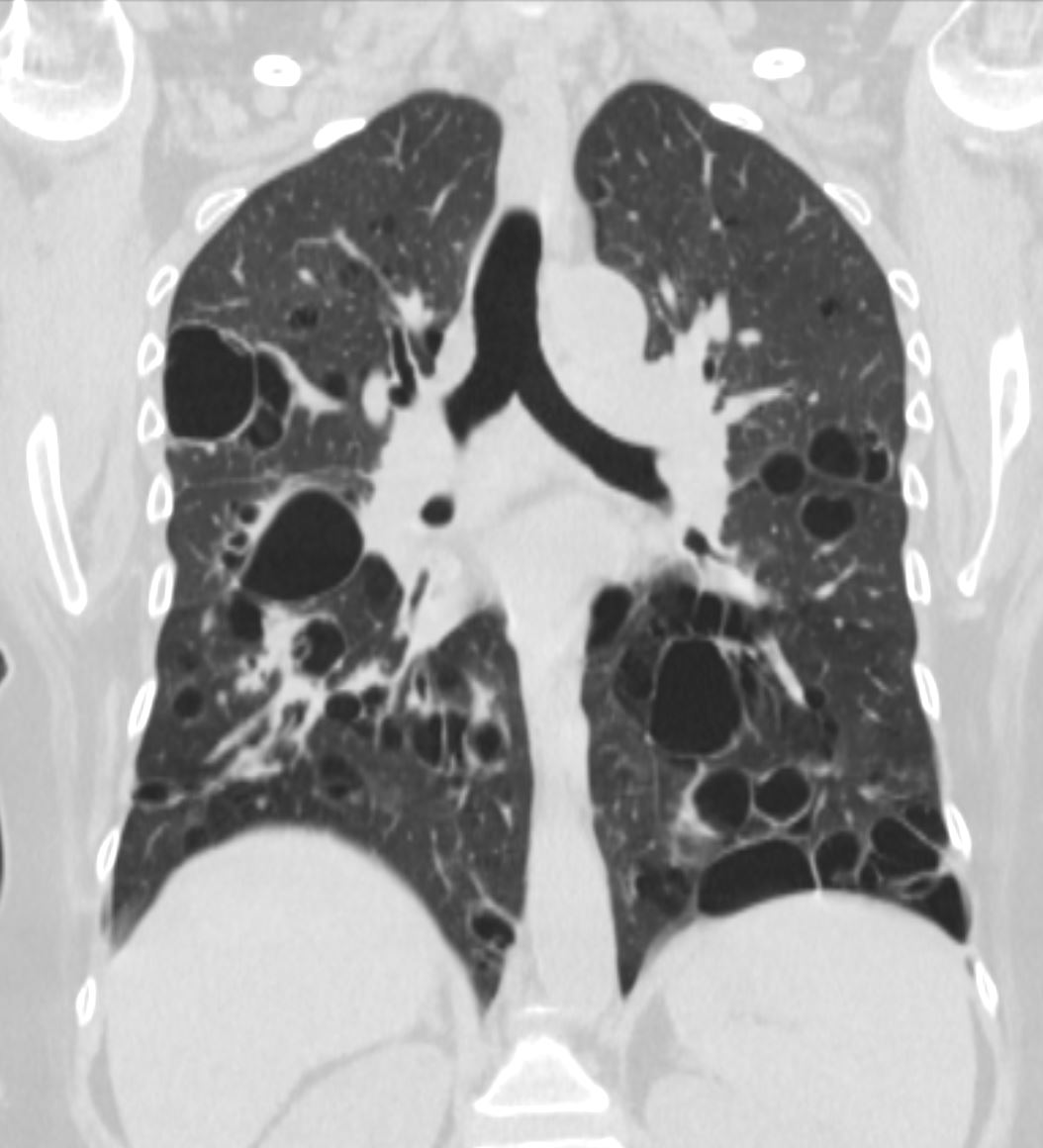
67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
NODULAR FORM OF PULMONARY AMYLOIDOSIS
67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
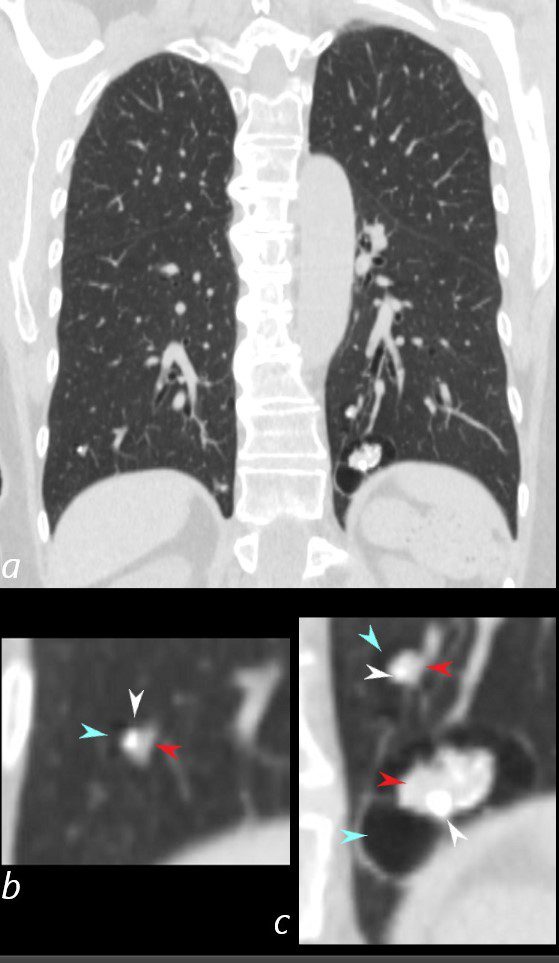

67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
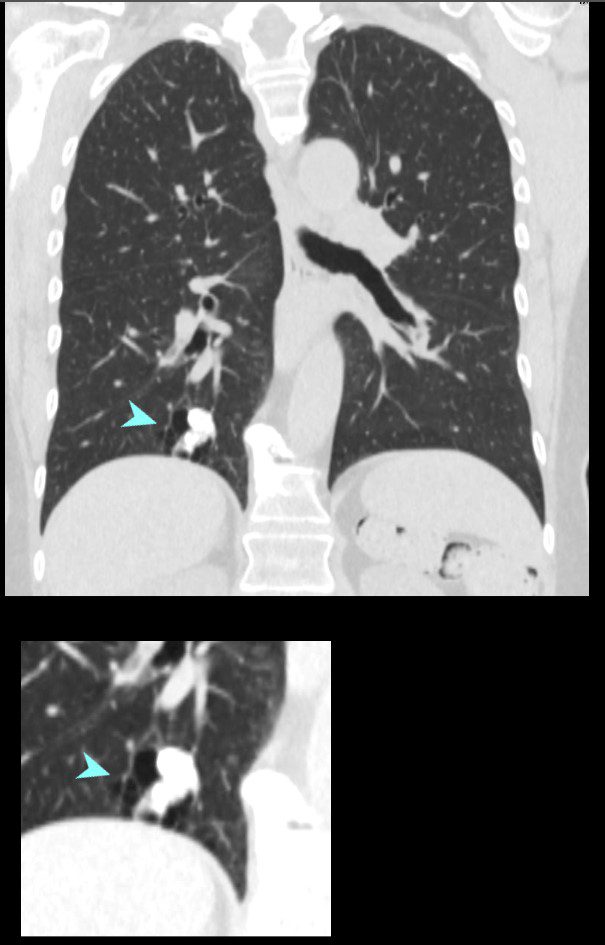

67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
Likely Sjogren’s Cystic Lung Disease and Amyloid

47 F SLE Sjogrens LIP vs Birt-Hogg-Dube basilar thin walled cysts lymphadenopathy
Subsegmental right lower lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net


47 F SLE Sjogrens LIP vs Birt-Hogg-Dube basilar thin walled cysts lymphadenopathy
Subsegmental right lower lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
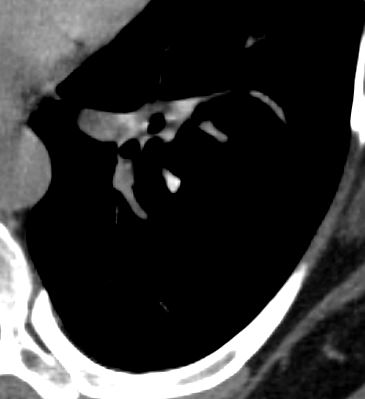

47 F SLE Sjogrens LIP vs Birt-Hogg-Dube basilar thin walled cysts lymphadenopathy
Subsegmental right lower lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
References and Links
Czeyda-Pommersheim F etal Amyloidosis: Modern Cross-sectional Imaging Radiographics Vol. 35, No. 5
- TCV
- Faces of Amyloidosis
- Case Studies
- 014Lu Nodular Parenchymal Amyloid and Cystic Changes
- 014Lu Nodular Parenchymal Amyloid and Cystic Changes
- 037Lu Amyloidosis of the Trachea and Bronchi
- 038Lu Amyloidosis Hilar Lymph Nodes Pericardium CAD
66Lu Amyloid nodules alveolar septal and bronchiole and MAC - 89Lu Amyloid Calcified Mass and Pleural Involvement
- 68Lu Trachea Amyloid
- 70Lu Amyloid Consolidative Nodular Septal
- 89Lu Amyloid Calcified Mass and Pleural Involvement
90Lu Amyloid Interstitial and Calcified Micronodules
92 LU Amyloid Lung and Heart