CT findings of restrictive lung disease may vary depending on the specific etiology or underlying condition causing the restriction. Restrictive lung diseases are characterized by reduced lung compliance, leading to decreased lung volumes. Here are some common CT findings associated with restrictive lung disease presented in table form:
| CT Finding | Description | Common Etiologies |
|---|---|---|
| Ground-Glass Opacities (GGOs): | Hazy areas in the lung parenchyma without obscuration of vessels. | Interstitial lung diseases (e.g., idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis). |
| Parenchymal Bands: | Linear opacities that represent fibrotic changes in the lung parenchyma. | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), connective tissue diseases. |
| Honeycombing: | Clustered cystic airspaces resembling honeycombs, indicative of advanced fibrosis. | Advanced stages of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. |
| Reticular Opacities: | Fine reticular patterns reflecting interstitial thickening. | Interstitial lung diseases (e.g., pneumoconiosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis). |
| Fibrotic Bands: | Thickened fibrotic bands extending through the lung parenchyma. | Progressive systemic sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. |
| Subpleural Fibrosis: | Fibrotic changes near the pleural surface. | Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis, asbestosis. |
| Reduced Lung Volumes: | Smaller lung volumes and decreased expansion. | Chest wall deformities, neuromuscular diseases. |
| Shrunken Lung Appearance: | Reduced overall lung size with increased opacity. | End-stage fibrotic lung disease. |
| Pleural Effusion: | Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. | Often secondary to underlying conditions (e.g., heart failure). |
| Thickened Pleura: | Thickening of the pleural lining. | Pleural fibrosis in interstitial lung diseases. |
- Restrictive Lung Diseases
Pneumoconiosis
Silicosis
Berylliosis
Asbestosis
Medication
Busulphan
Bleomycin
Amiododrone
reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5wn916moUy8
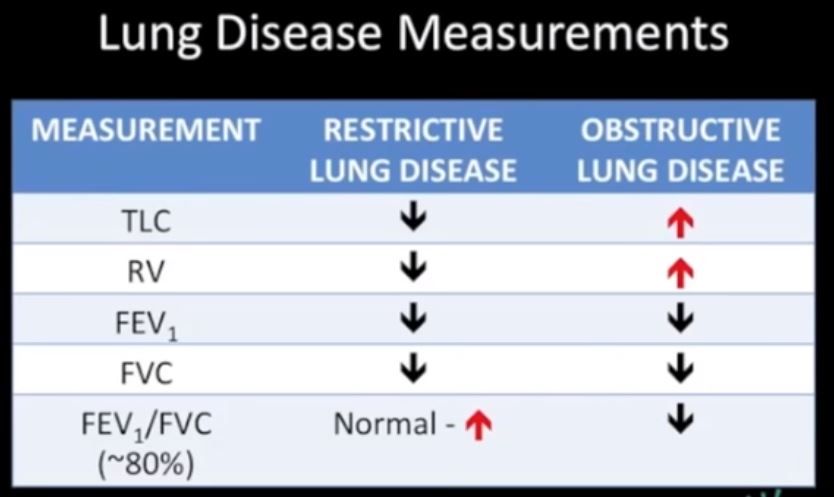
TLC Total Lung Capacity = Amt of air when lungs are maximallly filled
RV residual volume = amount of air left in the lungs after maximal expiration
FEV1 – Forced expiration after 1 second of expiration is the amount of air that comes out in 1st second of expiration
FVC Forced Vital Capacity – Is the total volume of air of air that can exhaled after after a maximal inspiration
