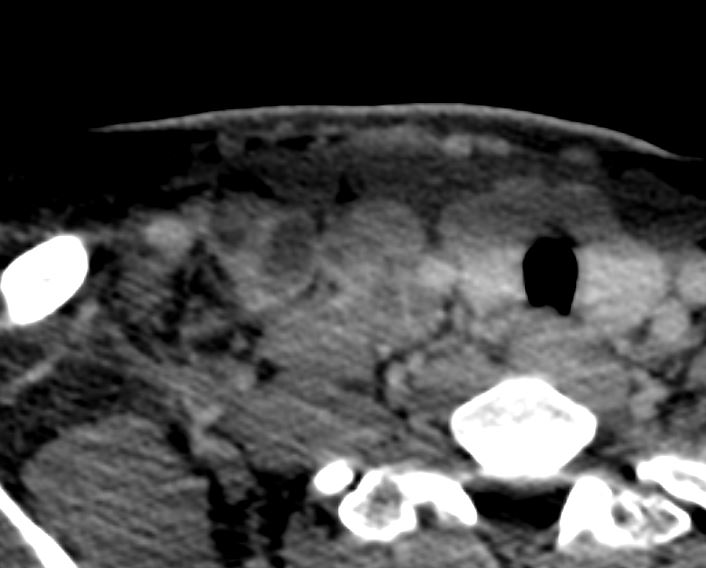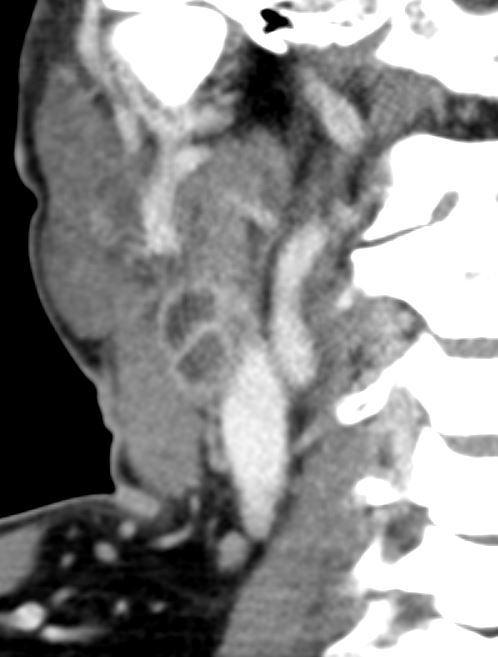
Rim sign
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lymph nodes spleen TB 024
Patient with Lymphoma
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 118884
-

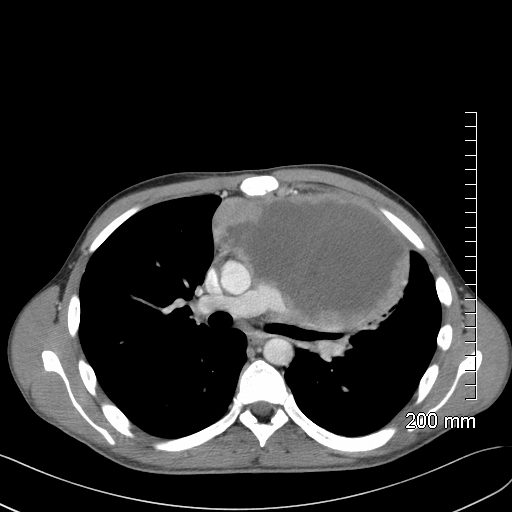
21 year old male with history of lymphoma CT scan through the chest shows a giant rim enhancing mediastinal node
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 118872 - Low density lymph nodes
- low-density center surrounded by a
- peripheral rim enhancement.
- Causes
- TB
- atypical mycobacteria,
- histoplasmosis,
- metastases (from head/neck/testicular malignancy), and
- lymphoma
- Rim sign lymph nodes are a characteristic radiological finding seen in tuberculosis (TB) infections. In TB, the lymph nodes become enlarged and show a characteristic thickening of the outer rim or cortex of the node on imaging studies such as CT or MRI. This thickening appears as a rim of increased density or enhancement around the node.The rim sign is thought to be caused by the accumulation of inflammatory cells in the outer layer of the lymph node, which leads to the formation of a granuloma. The granuloma produces cytokines that stimulate angiogenesis and neovascularization, which leads to the development of the dense rim.The presence of the rim sign is a useful diagnostic tool in TB, particularly in extrapulmonary TB where other imaging findings may be less specific. However, it should be noted that the rim sign is not specific to TB and can also be seen in other infectious and non-infectious conditions such as sarcoidosis and lymphoma. Therefore, other clinical and laboratory data should be taken into consideration to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.