- Characteristics
- shown to exhibit plasticity and can change their phenotype depending on the local environment
Courtesy Wiki
web lungs 437
Types
- M1 pro-inflammatory
- involved direct destruction of intracellular pathogens, and produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as a T helper 1 (Th1)-cell environment
- M2 ant-inflammatory
- more heterogeneous group involved in
- down-regulating inflammation or pro-resolution and tissue repair, producing a Th2 environment.
- Further Subcategorization
- M2a (parasite destruction)
- M2b (immune regulation) and
- M2c (tissue remodelling and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition).18
- more heterogeneous group involved in
- Resident alveolar macrophage (AMs)
- reside within the airway and alveoli
- maintain their population
- by proliferation in situ rather than having a reliance on the macrophage precursors in the blood.7 8
- Interstitial Macrophages
- located between alveolar epithelial cells
- Non resident Macrophages
- Evolve from monocytes .9
-

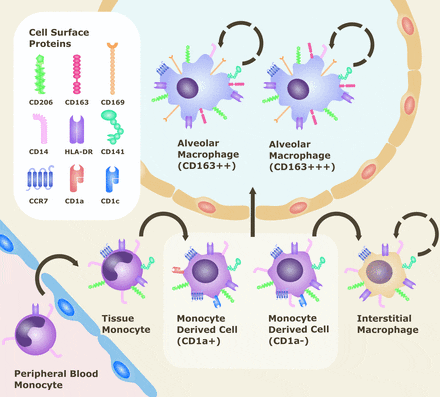
Cell surface markers of monocyte/macrophage populations within the lung.
Lugg, SL et al Cigarette smoke exposure and alveolar macrophages: mechanisms for lung disease BMJ Thorax

Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
Many of the functions of the alveolar macrophage have been shown to be dysregulated following exposure to cigarette smoke.
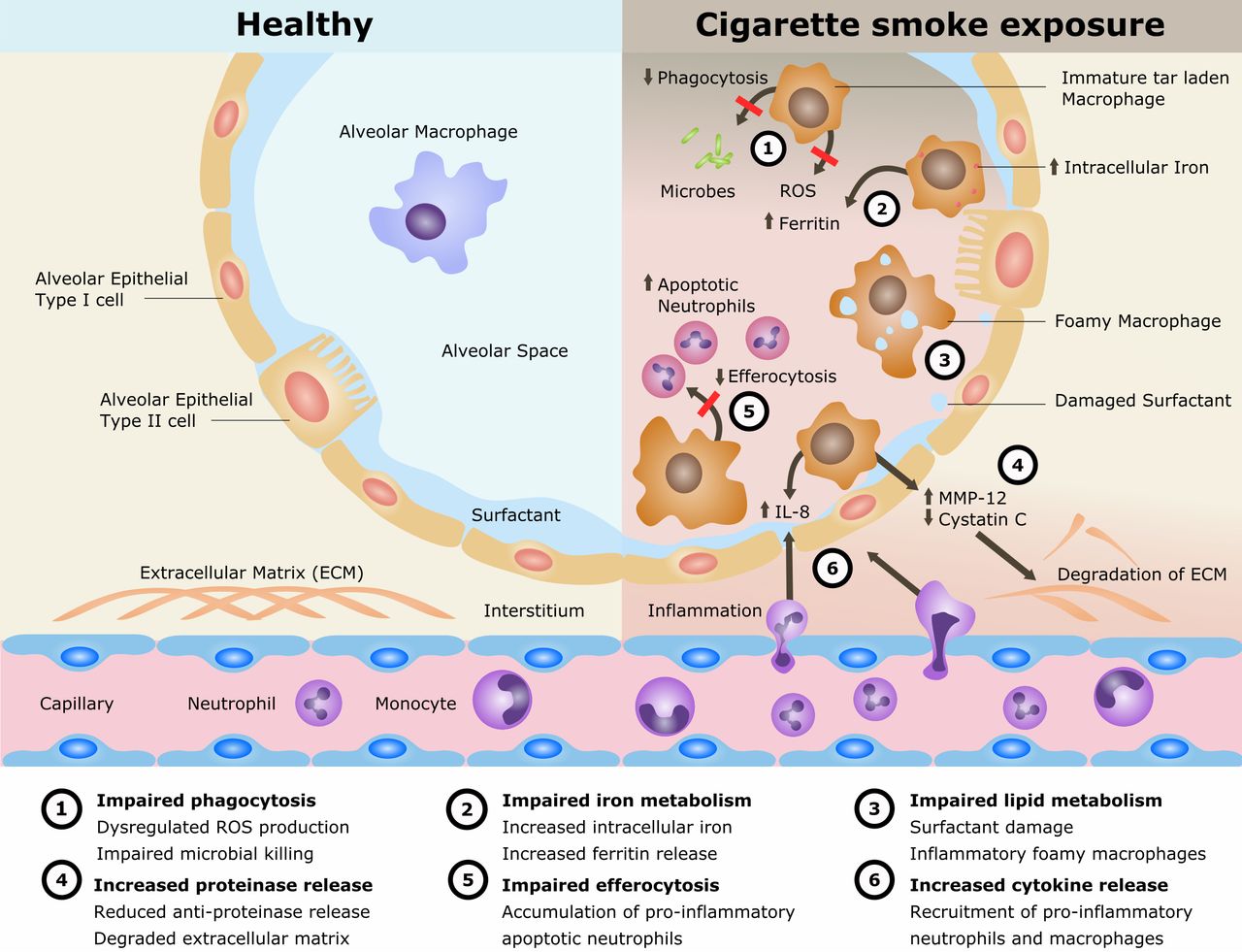
Lugg, SL et al Cigarette smoke exposure and alveolar macrophages: mechanisms for lung disease BMJ Thorax
Links and References
- Lugg, SL et al Cigarette smoke exposure and alveolar macrophages: mechanisms for lung disease BMJ Thorax