- Smoking Related ILD
-
- Smoking related
- small airways
- upper lung fields
- interstitial changes fibrosis
- ILD
- restrictive lung disease
- impaired gas exchange
- 3 Major Groups
- Group 1
- Group 2
- Acute ILD
- smoking seems to have an important pathogenetic role, although to a lesser extent than in the first group
- acute eosinophilic pneumonia and
- pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome,
- Group 3
- , diseases in which smoking creates an increased risk for developing
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) UIP. The combination of lower lung fibrosis and upper lung emphysema is being increasingly recognized as a distinct clinical entity in smokers. High-resolution computed t
- Rheumatoid arthritis-related ILD (RA-ILD)
- Group 4
- diseases that are actually less likely to develop in smokers . The protective effect of smoking in these diseases may result from suppression of T-helper cell (Th)1 immunity
- Sarcoidosis
- Nonetheless,
- when smokers develop the disease
- outcome is worse than in nonsmokers
- Nonetheless,
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Sarcoidosis
- diseases that are actually less likely to develop in smokers . The protective effect of smoking in these diseases may result from suppression of T-helper cell (Th)1 immunity
- Others
- Smoking related
-
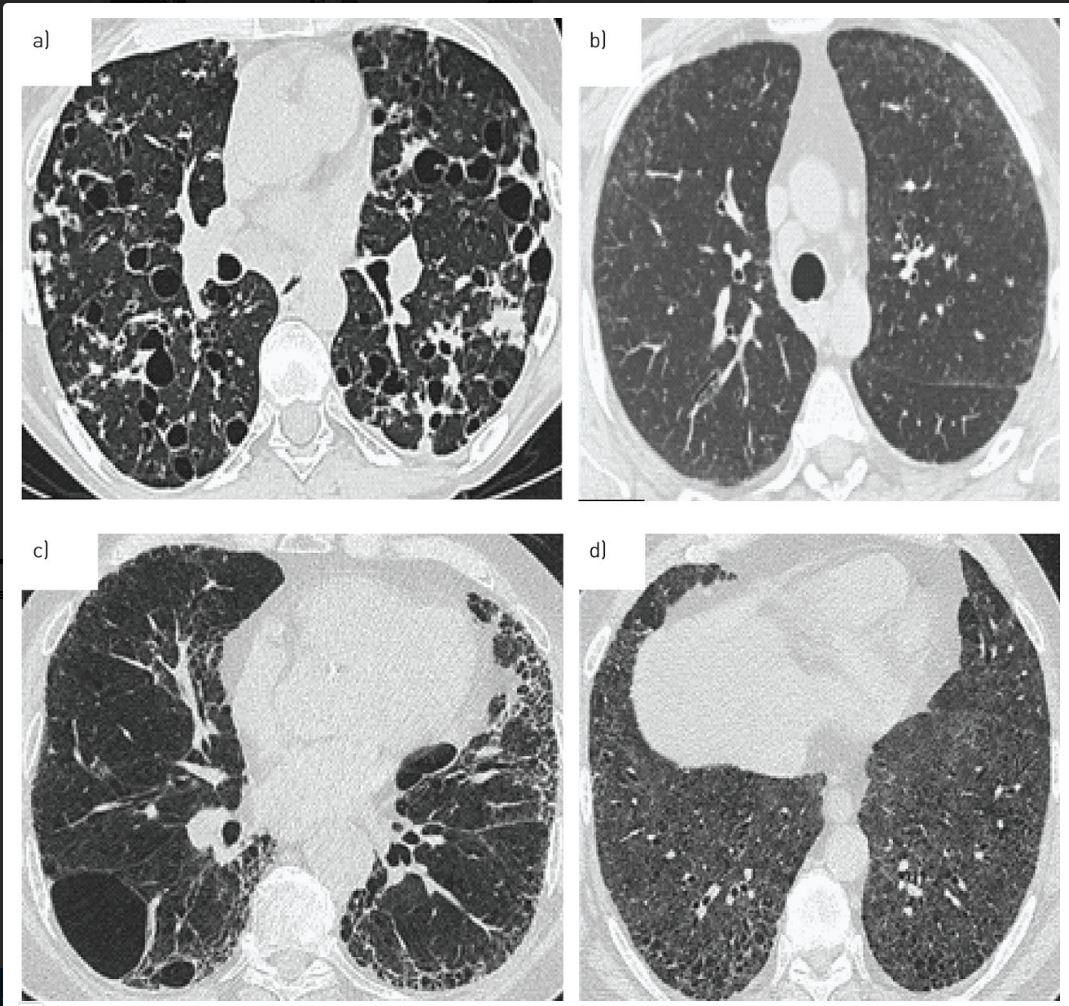
a Pulmonary Lahngerhans cell histiocytosis b) BronchiolitisAssociated ILD c Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema d) desquamative interstitial pneumonia
Margaritopoulos, G A. et al Smoking and interstitial lung diseases European Respiratory Review 2015 24: 428-435; 2015

Margaritopoulos, G A. et al Smoking and interstitial lung diseases European Respiratory Review 2015 24: 428-435; 2015
Links and References
Ryu J.H. et al Smoking-related interstitial lung diseases: a concise review
Smoking and interstitial lung diseases
