- TCV Anatomy: Subsegmental Bronchi
- Etymology
- Derived from the Latin words “sub-” meaning below or under, and “segmental,” referring to the bronchial branches that serve specific segments of the lungs.
- AKA and Abbreviation
- Also known as tertiary bronchi.
- What is it?
- Subsegmental bronchi are the airways that branch off the segmental bronchi.
- They represent the next division in the bronchial tree, leading to smaller airways within each segment of the lung.
- Principles
- Parts
- Cartilaginous support diminishing as the bronchi become smaller.
- Mucosal lining and smooth muscle layer.
- Size
- Diameter: approximately 1-4 mm, depending on the generation of branching.
- Shape
- Tubular structures with progressively tapering ends.
- Position
- Located within lung segments, branching further into smaller bronchioles.
- Character
- Contain respiratory epithelium with cilia to aid mucociliary clearance.
- Time
- Dynamic structures, showing variability in tone due to smooth muscle contraction.
- Blood supply
- Supplied by bronchial arteries originating from the thoracic aorta.
- Venous Drainage
- Drained by bronchial veins into the azygos and hemiazygos systems.
- Lymphatic drainage
- Drains to peribronchial and hilar lymph nodes.
- Nerve Supply
- Innervated by the autonomic nervous system (vagus nerve and sympathetic fibers).
- Embryology
- Develops from the secondary bronchial buds during the fifth to sixth week of gestation.
- Histology
- Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium transitioning to simpler columnar epithelium as the bronchi branch.
- Physiology and Pathophysiology
- Conduct air to the bronchioles.
- Commonly affected by airway diseases such as asthma and bronchitis.
- Parts
- Applied Anatomy to Radiology
- CXR
- Subsegmental bronchi are not directly visible as distinct structures but can be inferred by the presence of secondary findings such as atelectasis, hyperinflation, or peribronchial cuffing in the corresponding segments of the lung.
- Indirect indicators of subsegmental bronchial pathology may include localized air trapping or linear opacities suggestive of infection or inflammation.
- CT
- Subsegmental bronchi are typically seen as small, branching, air-filled structures extending into the lung periphery.
- Pathologies such as bronchial wall thickening, luminal narrowing, or obstruction (e.g., mucus plugging or foreign bodies) can be identified.
- Specific conditions, like bronchiectasis, may show dilated subsegmental bronchi with lack of normal tapering.
- Air trapping or mosaic attenuation patterns on inspiratory and expiratory imaging can indicate small airway disease involving the subsegmental bronchi.
- MRI
- While not a primary imaging modality for the subsegmental bronchi, MRI can provide supplementary information in cases of complex thoracic pathologies.
- Contrast-enhanced MRI can identify vascular or inflammatory changes surrounding the bronchi, and advanced techniques such as 3D respiratory gating can enhance visualization of small airways in research settings.
- Nuclear Medicine
- Although not directly visualized, functional studies like ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans can detect perfusion defects secondary to obstruction in subsegmental bronchi.
- PET-CT can reveal increased metabolic activity around subsegmental bronchi in infectious, inflammatory, or neoplastic conditions.
- Ultrasound
- Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) can assess abnormalities in larger airways but is generally not used for subsegmental bronchi.
- Key Considerations
- Radiological assessment of subsegmental bronchi requires careful correlation with clinical and functional data, especially in conditions like asthma, bronchiectasis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Dynamic studies, such as forced expiratory CT or cine MRI, can provide additional insights into airway collapsibility and obstruction at the subsegmental level.
- CXR
- Not typically visible as distinct structures on chest X-ray but inferred by associated pathologies (e.g., atelectasis or hyperinflation).
- CT
- Seen as small branching structures extending into lung segments.
- Can demonstrate thickening or obstruction in conditions like bronchiectasis or infection.
- MRI
- Rarely visualized directly but can be assessed using contrast-enhanced imaging in certain pathologies.
- CXR
- Pathological Implications
- Diseases affecting the subsegmental bronchi include:
- Infections: bronchiolitis or bronchopneumonia.
- Obstructive diseases: asthma or COPD.
- Structural abnormalities: bronchiectasis or congenital defects.
- Diseases affecting the subsegmental bronchi include:
- Key Points and Pearls
- Subsegmental bronchi are essential for air distribution to the smallest functional units of the lungs.
- Early changes in subsegmental bronchi can be indicative of systemic diseases (e.g., cystic fibrosis or primary ciliary dyskinesia).
- Parallels with Human Endeavors
- Analogous to local roads branching off a main highway, ensuring distribution and connectivity.
- Dysfunction or obstruction in these pathways can disrupt the “traffic” of oxygen and carbon dioxide, akin to bottlenecks in infrastructure systems.
- Etymology
Subsegmental bronchi are smaller airways that branch off from the
segmental bronchi within the lungs. They lead to the bronchioles
and eventually to the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs. Each
segmental bronchus supplies a specific bronchopulmonary
segment, and the subsegmental bronchi further subdivide to
provide airflow to smaller regions within these segments. The
structure and function of subsegmental bronchi are essential for
proper ventilation and distribution of air throughout the lungs.
Understanding the anatomy of subsegmental bronchi is important in
bronchoscopy, surgical procedures, and diagnosing conditions like
bronchiectasis, atelectasis, and localized infections. On imaging,
such as CT scans, abnormalities in the subsegmental bronchi can
present as narrowing, thickening, or dilatation, which can help in
identifying underlying diseases or obstructions.
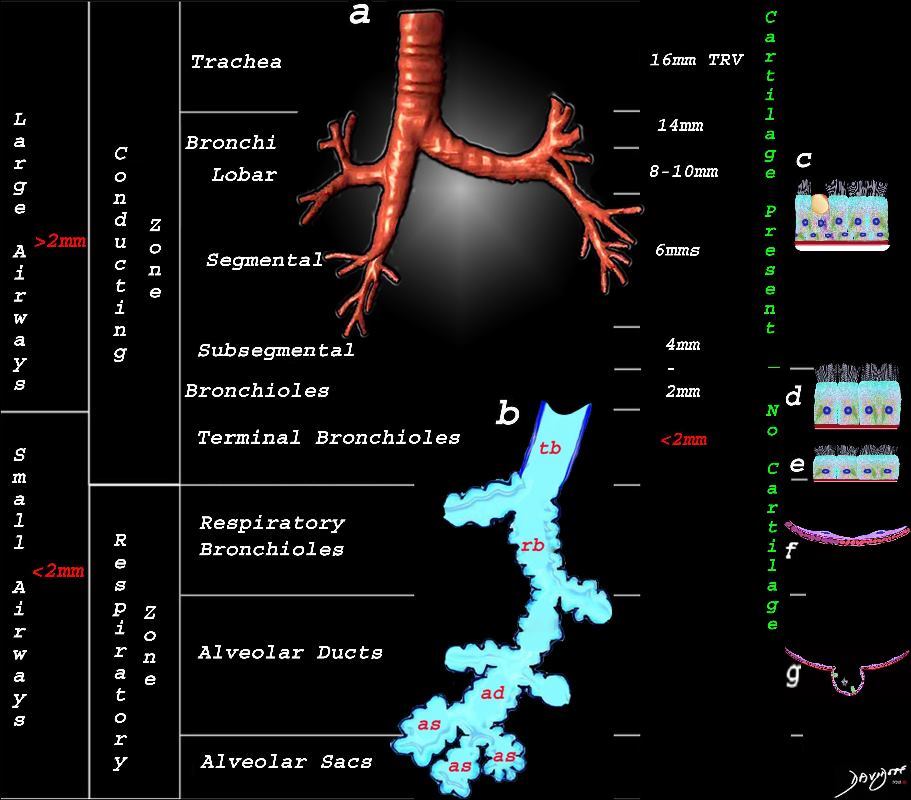
This image shows the division of the airways in the lungs classified as large airways and small airways.
A large airway is considered any airway larger than 2mm, and therefore includes all the airways involved with transport of air except for the terminal bronchiole. Included as seen in image a, are the trachea, mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi segmental and subsegmental airways and the 3 subsequent divisions of subsegmental bronchi and bronchioles till the last transporting airway – the respiratory bronchiole which is usually about 2mm and is considered a small airway Image (a) shows the airways starting in the trachea and continuing to the mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi, segmental bronchi, and subsegmental bronchi.
Image b shows the structures that make up the small airways starting with the terminal bronchiole (tb) followed by the respiratory bronchiole (rb) alveolar duct, (ad) and alveolar sacs (as)
Image (c) shows the histologic makeup of the large airways that include a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with mucus secreting goblet cells a muscular layer (red) and a prominent cartilage layer (white) In the larger bronchioles (d) the epithelium remains as a pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium with prominent muscular layer (red). The columnar epithelium transitions to a stratified ciliated cuboidal epithelium by the terminal bronchiole s (f) both still with a muscular layer. The respiratory epithelium transitions from a cuboidal epithelium to a squamous epithelium (f) with alveoli and type I and II pneumocytes starting to branch (g)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0740nL
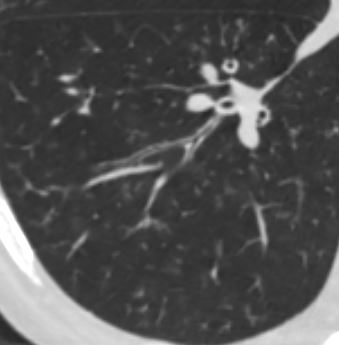
lungs airways segmental subsegmental small airway disease micronodules
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
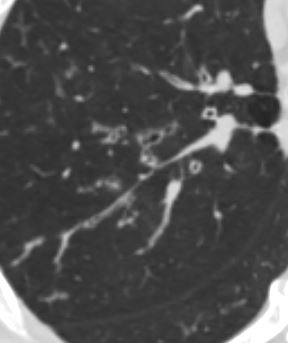
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
CHF

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-004-CT

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-005-CT

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-009-CT

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 50-010-CT
Chemotherapy
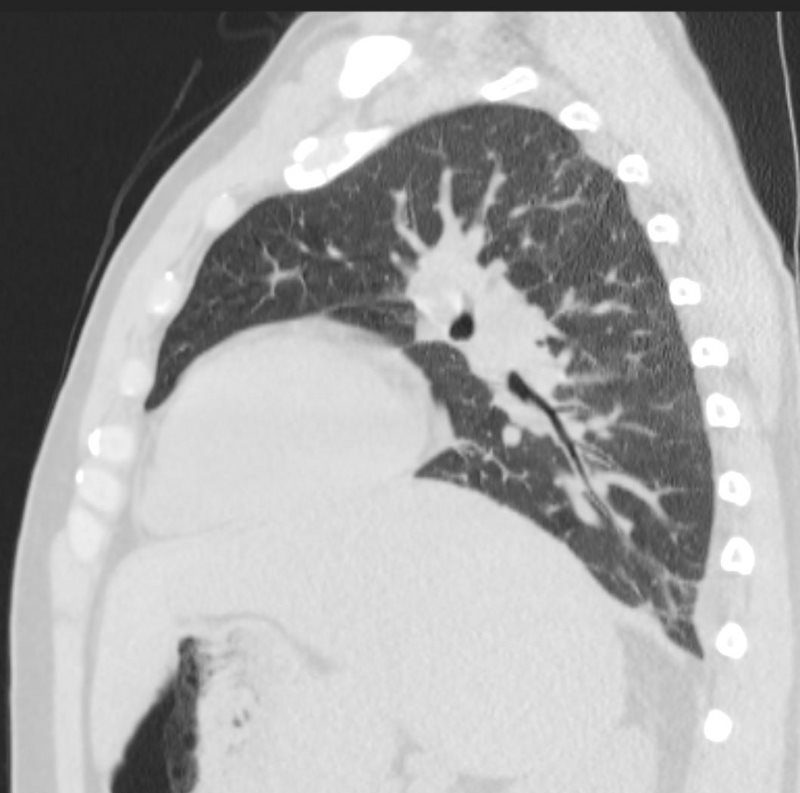
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff MD
Amyloidosis
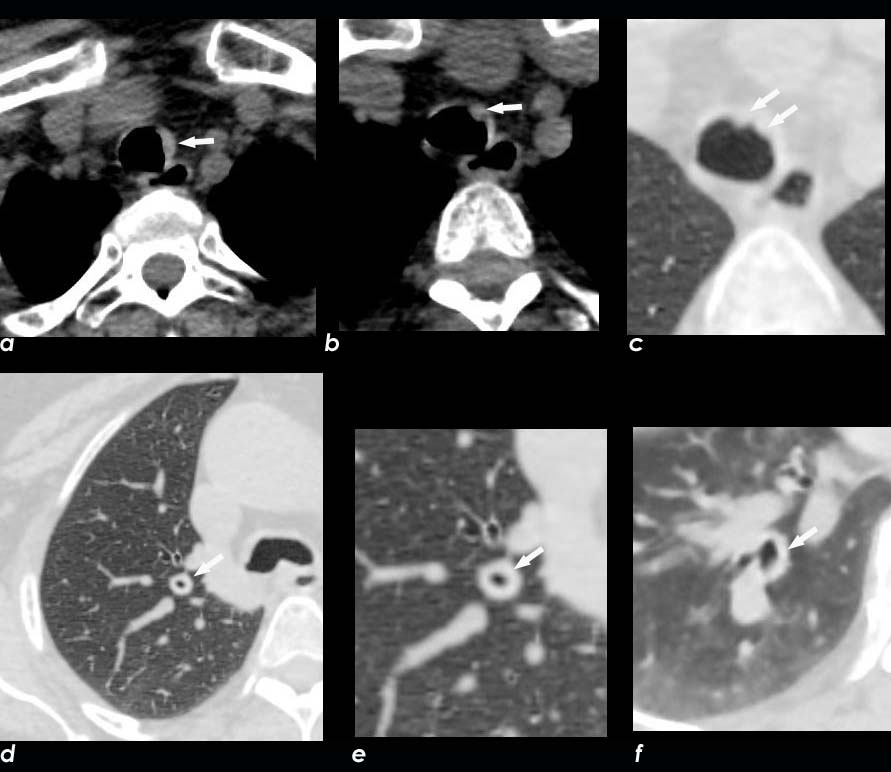
Axial CT image shows involvement of known amyloid in the trachea (a,b,c,d) as well as the segmental and subsegmental airways (d,e,f)
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net amyloid-airways-001b

Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net 44f Amyloid airways 004
Miliary TB

68 year old female presented with malaise night sweats weight loss QuantiFeron gold positive, with a past history of treated TB in her native country as a child. Axial CT images through the upper lobe shows a miliary pattern of disease affecting interlobular septa along the venules , centrilobular and tree in bud nodular patterns. Bronchoscopy isolated Mycobacterium complex. She was treated with good result
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net mycobacterium-complex-TB-68-004

68 year old female presented with malaise night sweats weight loss QuantiFeron gold positive, with a past history of treated TB in her native country as a child. Axial CT images through the upper lobe shows a miliary pattern of disease affecting interlobular septa along the venules , centrilobular and tree in bud nodular patterns. Bronchoscopy isolated Mycobacterium complex. She was treated with good result
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net mycobacterium-complex-TB-68-005
Aspergillosis
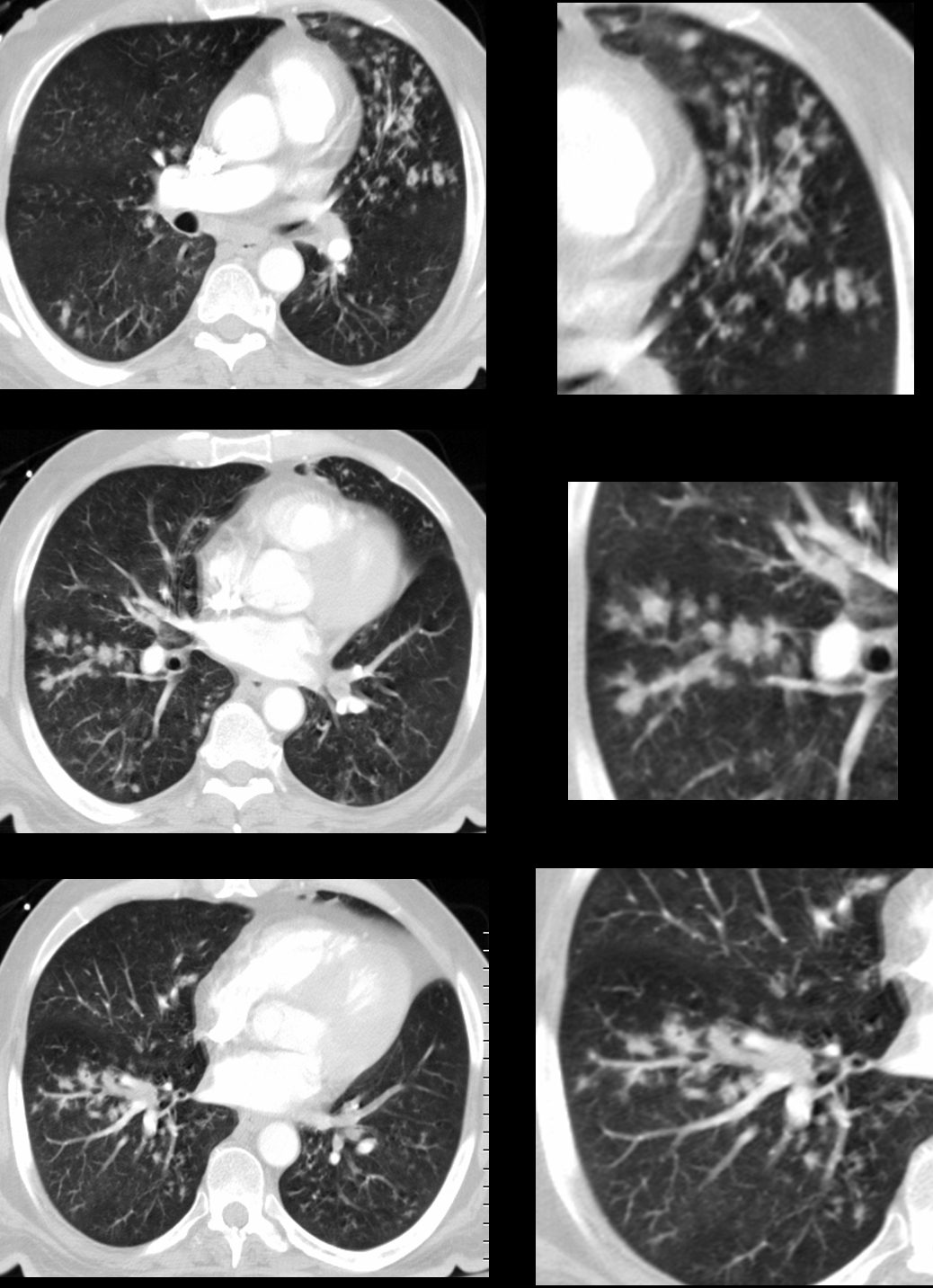
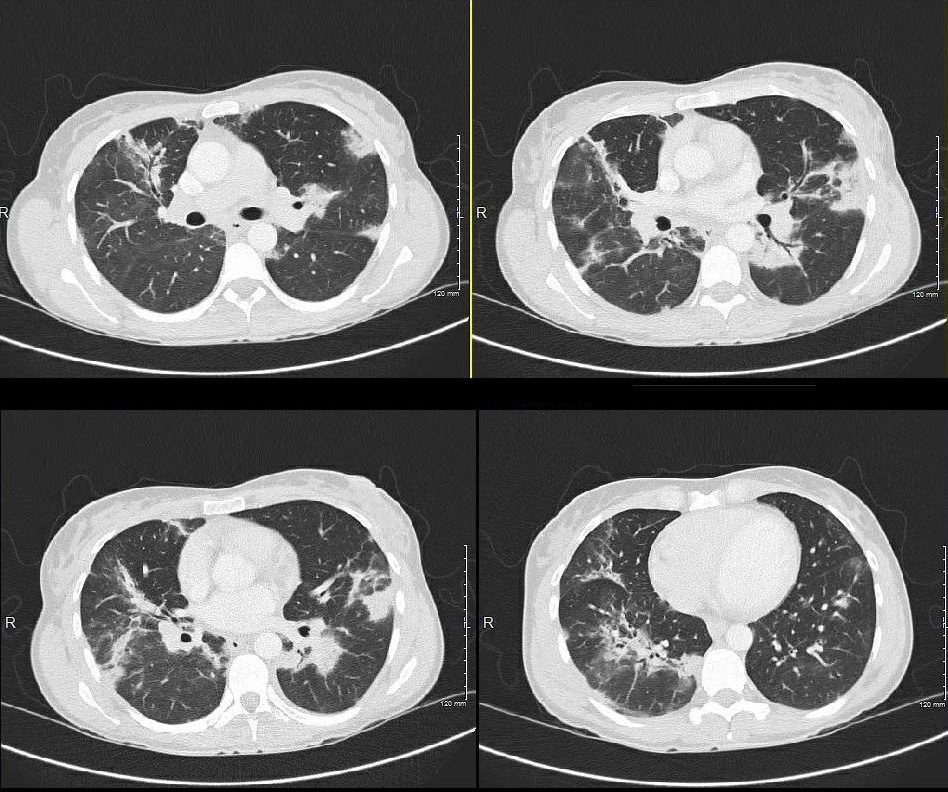
43 year old man with known aspergillus infection. Note the thickening of the walls of the segmental subsegmental and small airways with extensive tree in bud changes and bronchial wall thickening. There are centrilobular nodules indicating the small airway disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
117816c
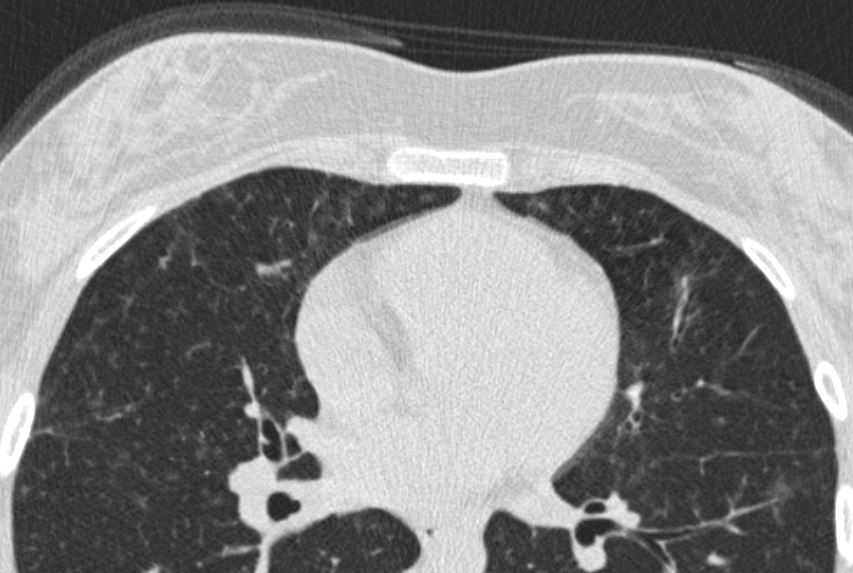
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net CVID small airway disease 006
Metastatic Breast Carcinoma
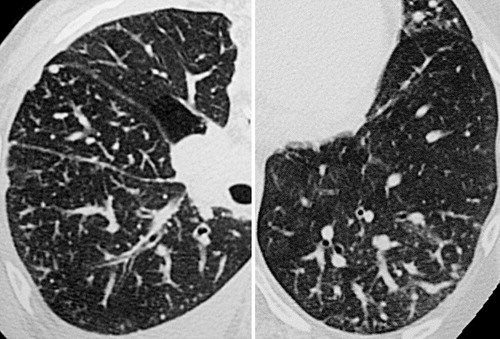
Rossi, SE et al Tree-in-Bud Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: Radiologic-Pathologic Overview RadioGraphicsVol. 25, No. 3 2005
Eosinophillic Pneumonia
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
Asbestosis
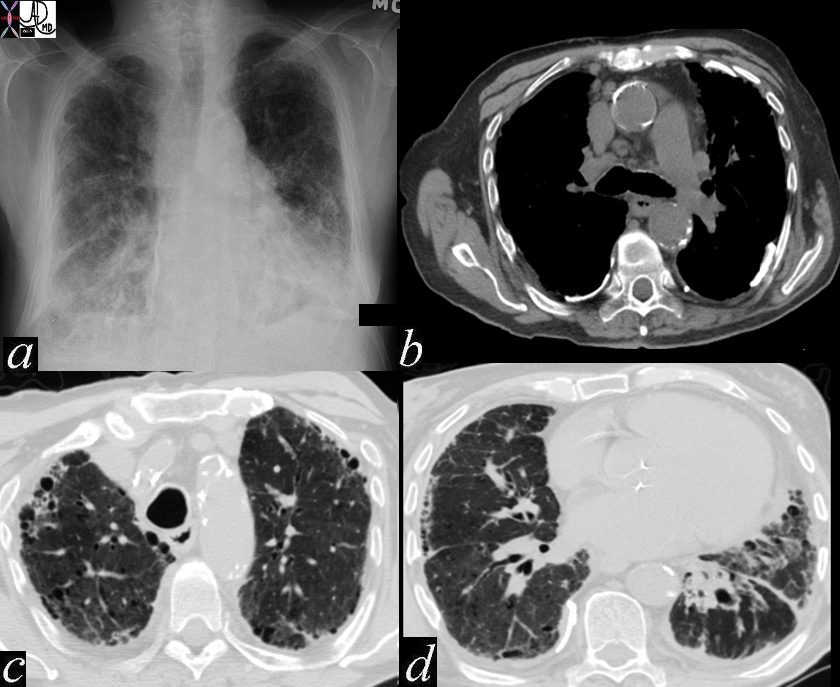
Ashley Davidoff MD thecommonvein.net 47060c01
keywords chest lung fx shaggy heart border reticular changes interstitial lung disease interstitium honeycombing pleural calcification fibrosis dx asbestosis
