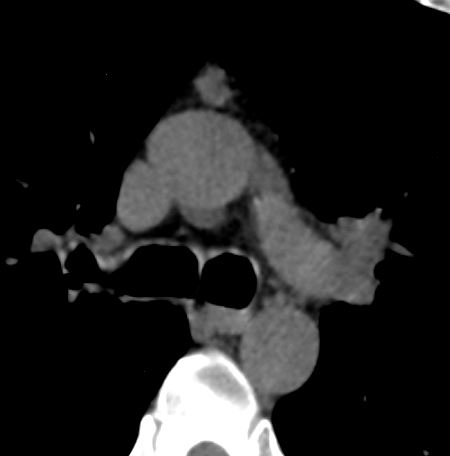
- Thymus :
- Primary lymphoid organ
- located in the
- superior and anterior mediastinum
- important for the maturation of T lymphocytes (T cells).
- Composed of two lobes and is
- most active during infancy and childhood.
- Evolution of Thymus Atrophy with Age:
- Infancy to Puberty:
-
- active and crucial for immune system development.
- production and maturation of T cells.
-
- Adolescence to Young Adulthood:
- gradually decreases in size and activity.
- reduction in T cell production.
- Adulthood to Elderly:
- undergoes involution,
- decreased output of new T cells.
- Thymic Rebound
- stress
- bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
- Can also occur in certain pathological conditions or during heightened immune activity.
- bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
- stress
- First image is 9 months prior showing no thymic tissue and second during chemotherapy – 9 months later showing thymic hyperplasia
Thymic Rebound Following Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer
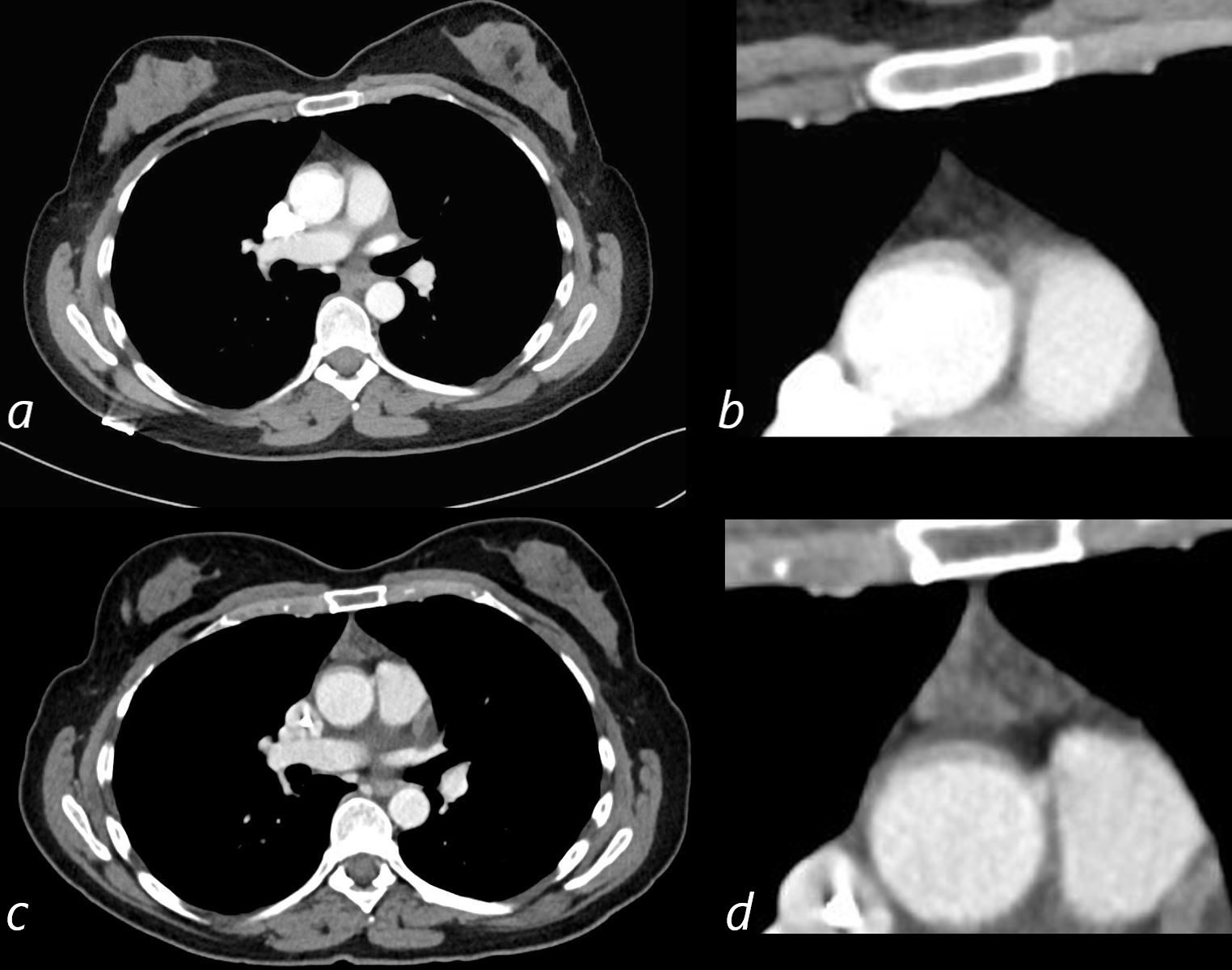
47-year-old female with a history of pancreatic cancer shows a normal appearing thymus prior to chemotherapy 9a,b)
9months later following chemotherapy, is evidence of thymic hyperplasia characterized by a nodular appearance of the thymus (c, d)
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net 136748c

Thymoma
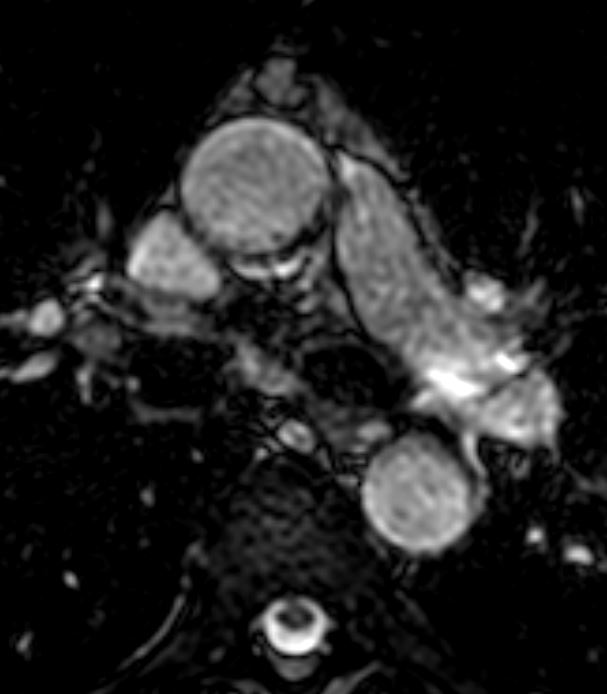
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
T2 bright
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
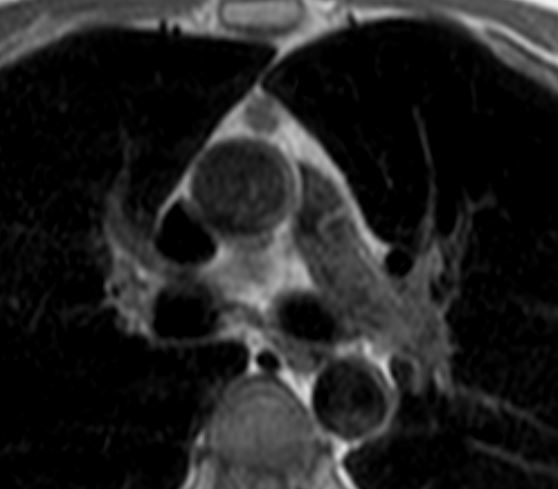
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.netT1
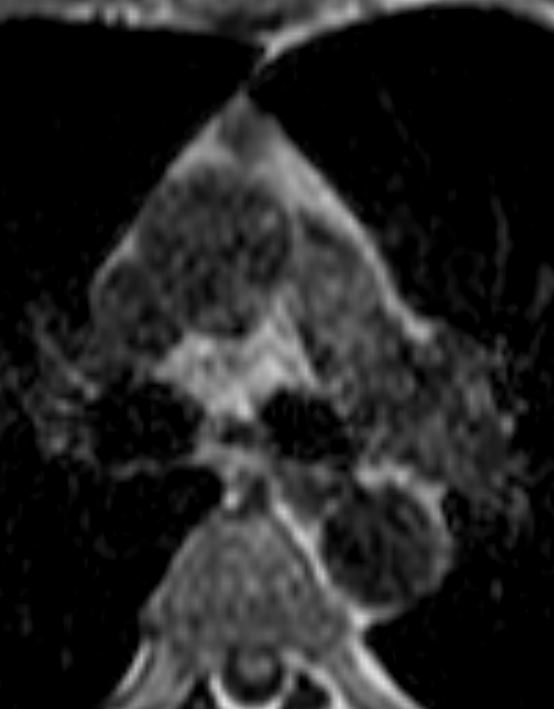
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
In Phase
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
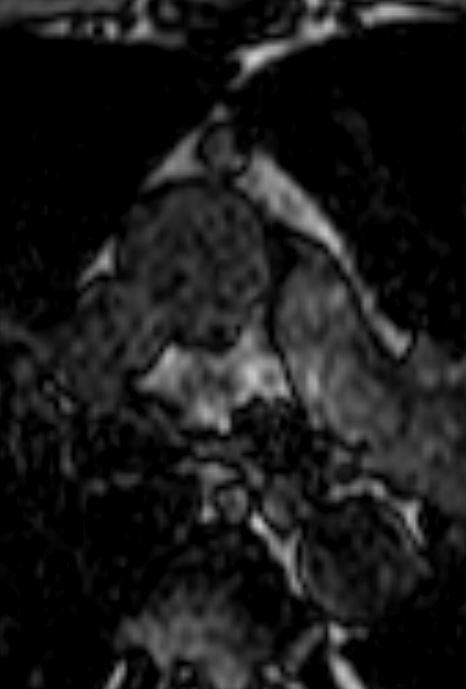
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
Out of Phase
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
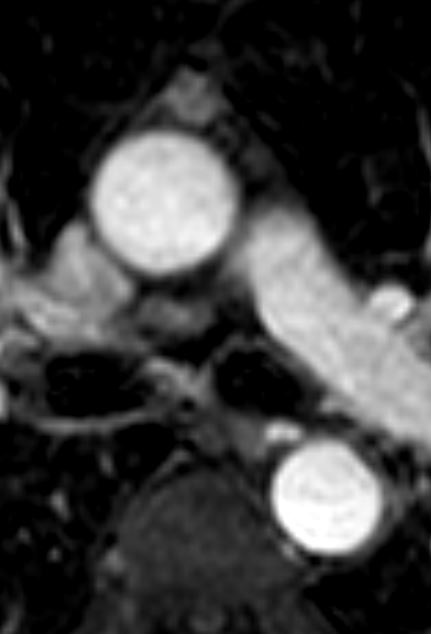
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
30 secs
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
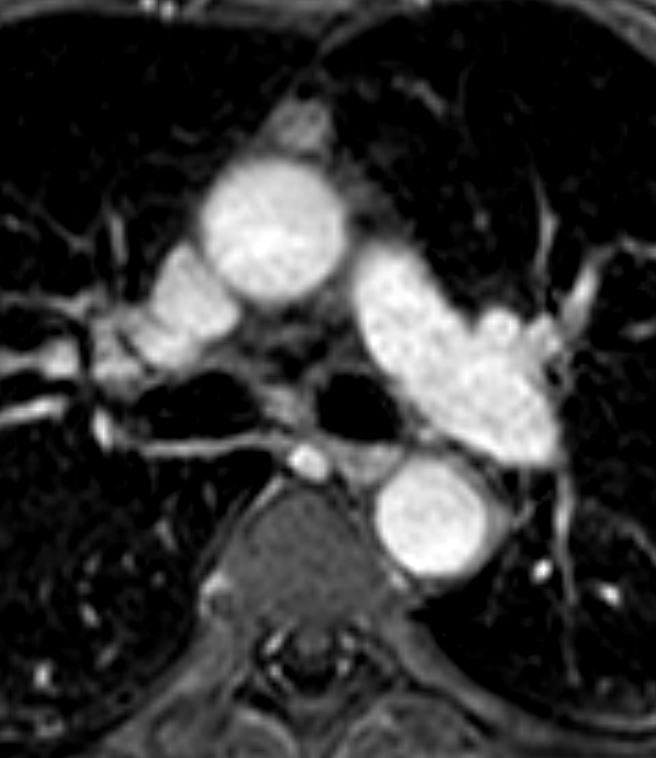
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
60 secs
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
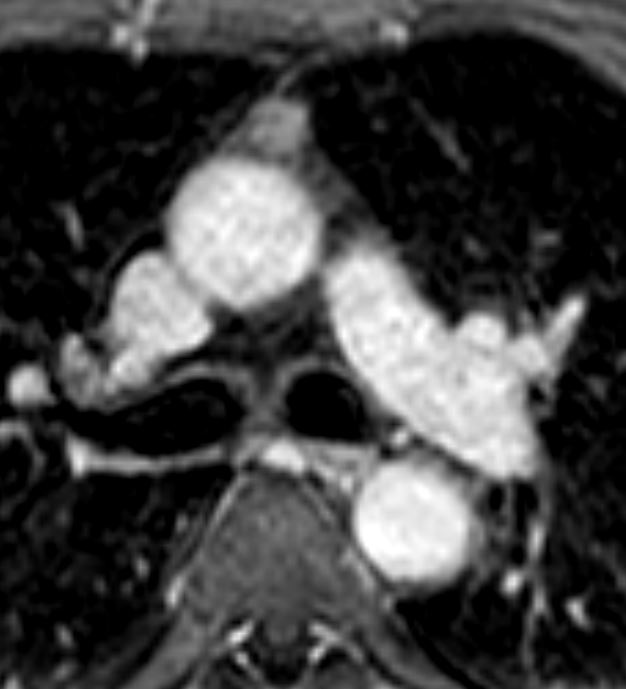
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
180 secs
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
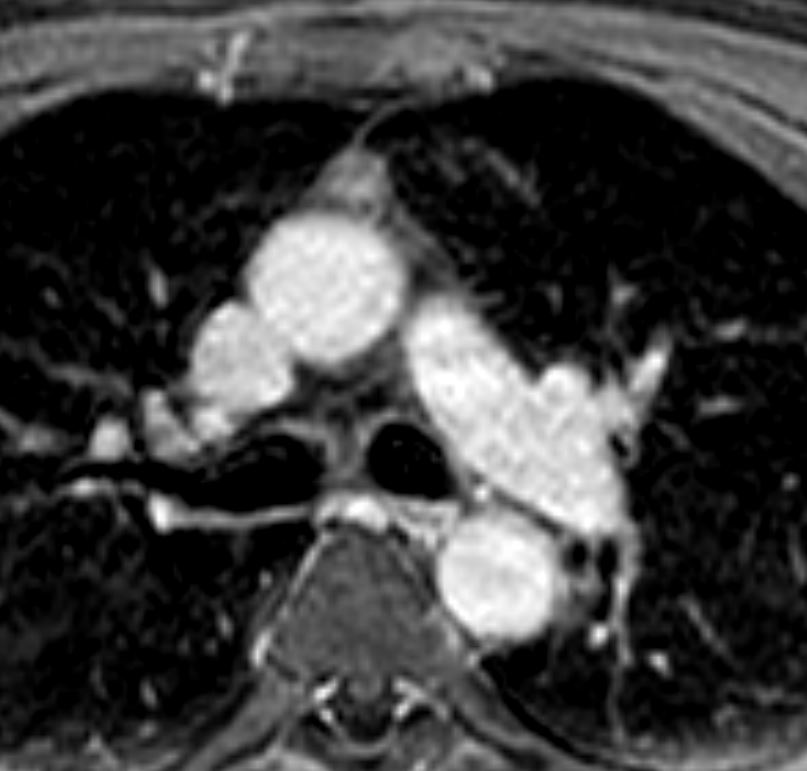
Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
5mins
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net

Thymoma type AB pT1 pNx
Modified Masoka stage IIa
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net