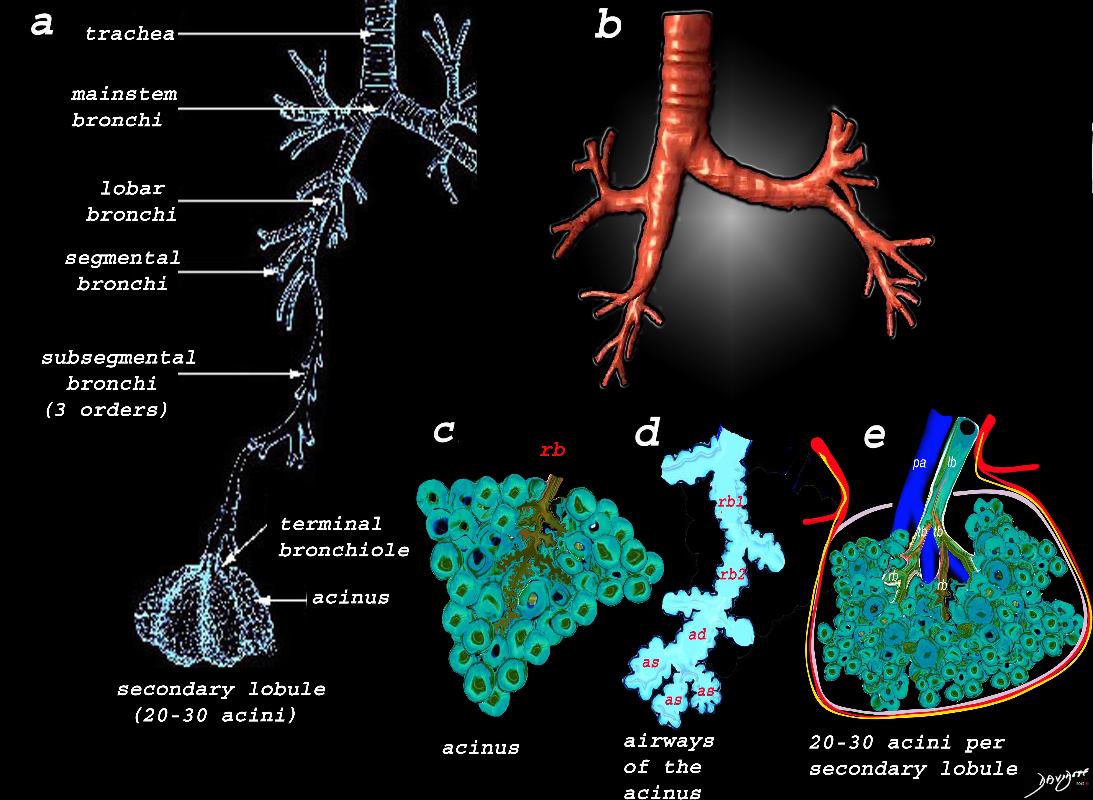
Image a shows the airways starting in the trachea and continuing to the mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi, segmental bronchi, and subsegmental bronchi,. The subsegmental bronchi have 3 subsequent generations until the bronchiole is reached. The terminal bronchiole is the last of the transporting airways and is considered the most proximal small airway with a diameter of 2mm or less, and it gives rise to the respiratory bronchiole which is the feeding airway for the acinus . The acinus is the functional unit of the lung.
Image b is a 3D reconstruction of a CT scan showing the proximal airways from the trachea to the segmental airways.
Image c shows the structures that make up the acinus and the other parts of the small airways, starting with the respiratory bronchiole (rb) . The diagram in d, shows the detail of the small airways that participate in gas exchange, including the respiratory bronchiole, (rb) alveolar duct, (ad) and alveolar sac (as)
Image e shows the secondary lobule made from about 20-30 acini, arising from a single lobular bronchiole accompanied by a single pulmonary arteriole (pa).. Structure that surround and enclose the secondary lobule include the pulmonary venule, (red) lymphatics,(yellow) and a fibrous septum (pink).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
lungs-0739
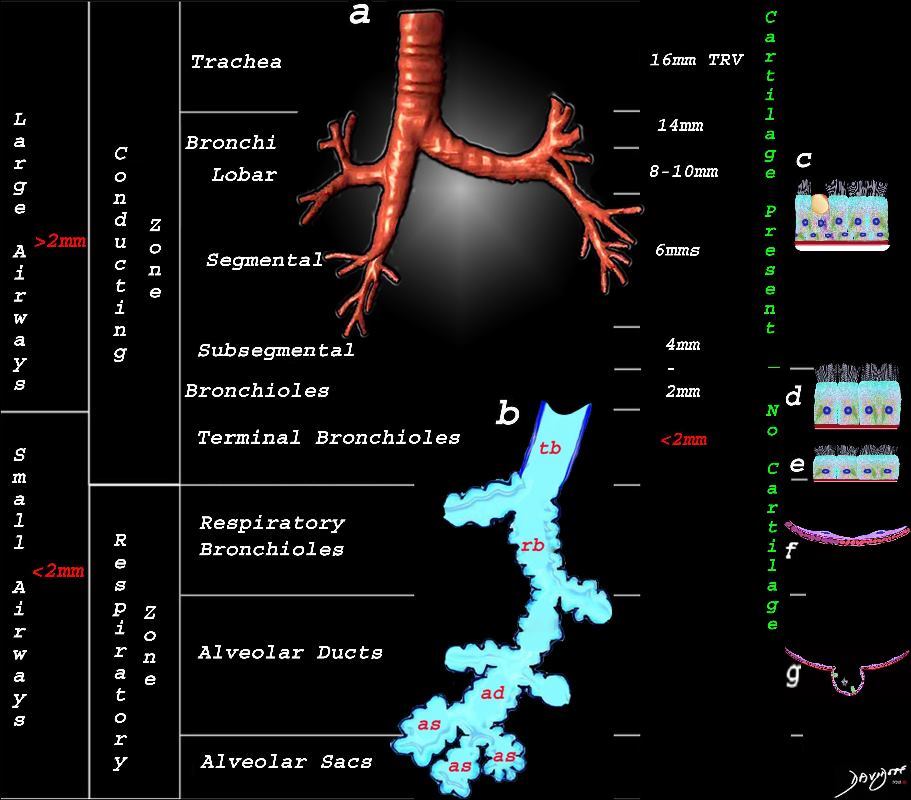
This image shows the division of the airways in the lungs classified as large airways and small airways.
A large airway is considered any airway larger than 2mm, and therefore includes all the airways involved with transport of air except for the terminal bronchiole. Included as seen in image a, are the trachea, mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi segmental and subsegmental airways and the 3 subsequent divisions of subsegmental bronchi and bronchioles till the last transporting airway – the respiratory bronchiole which is usually about 2mm and is considered a small airway Image (a) shows the airways starting in the trachea and continuing to the mainstem bronchi, lobar bronchi, segmental bronchi, and subsegmental bronchi.
Image b shows the structures that make up the small airways starting with the terminal bronchiole (tb) followed by the respiratory bronchiole (rb) alveolar duct, (ad) and alveolar sacs (as)
Image (c) shows the histologic makeup of the large airways that include a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with mucus secreting goblet cells a muscular layer (red) and a prominent cartilage layer (white) In the larger bronchioles (d) the epithelium remains as a pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium with prominent muscular layer (red). The columnar epithelium transitions to a stratified ciliated cuboidal epithelium by the terminal bronchiole s (f) both still with a muscular layer. The respiratory epithelium transitions from a cuboidal epithelium to a squamous epithelium (f) with alveoli and type I and II pneumocytes starting to branch (g)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0740nL
-
- largest – trachea and
- smallest, -respiratory a diameter of 0.5 millimeters
- airways (trachea to the respiratory bronchiole)
- average of 23 airways generations (
- bronchi are distinguished from bronchioles
- presence of cartilage
- conducting branches
- bronchi and bronchioles, to terminal bronchiole,
- respiratory bronchioles have
- alveoli
- transport,
- function in respiration (
- alveoli
- airways – two zones that reflect the differences in
airway resistance and flow. T- large airways, with diameters greater than 2 mm
- 75% of the airway resistance
- small airways, with diameters of less than 2 mm,
- large number of small airways,
- overall cross-sectional area is > large airways.
- 25% of the airway resistance,
- large airways, with diameters greater than 2 mm
- High-resolution CT (1 .0- 1 .5-mm collimation)
- allows identification of
- airways 1-2 mm in diameter and
- vessels 0. 1 -0.2 mm in diameter
- The secondary pulmonary lobule
- supplied by three to five terminal
bronchioles (aka Reid lobule) - terminal bronchiole and artery supplying the lobule are
- center
- intralobularbronchioles cannot be identified because the
thickness of their walls is less than 0. 1 5 mm.
- supplied by three to five terminal
- allows identification of
Mainstem Large and Medium Sized Bronchi
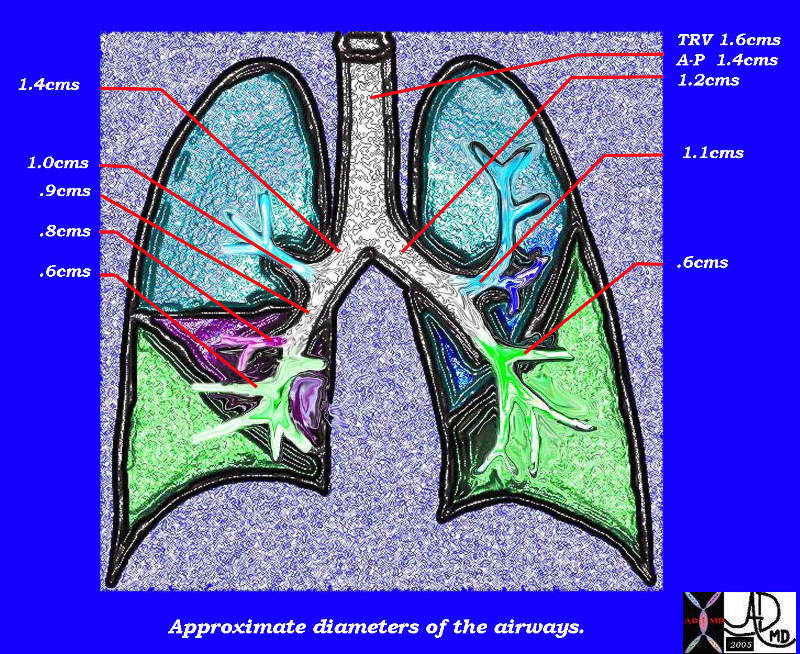
This diagram of the airways reveals the approximate diameters of the airways. Note that the left main stem bronchus is thinner than right whose length is truncated by the take off of the right upper lobe bronchus.
Ashley Davidoff MDTheCommonVein.net
32686b05L05b
Acinus
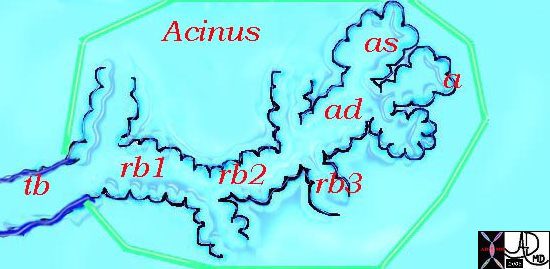
This diagram illustrates the acinus which consists of the respiratory bronchioles (rb 1, 2, 3) the alveolar duct (ad) the alveolar sac (as) and the alveoli. (a)
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 42446b12
TheCommonVein.net
Secondary Lobule
Contains up to 30 acini
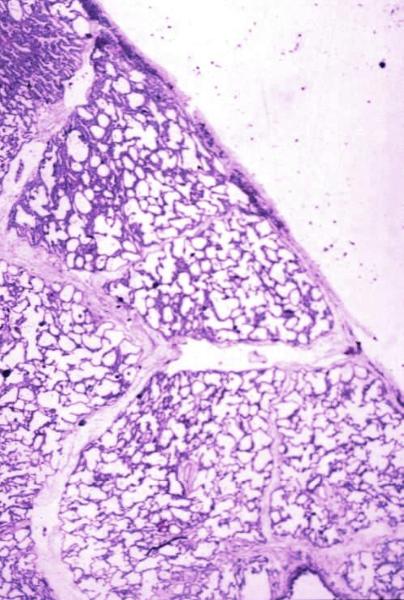
Normal lung histology
This image is a panoramic view of the lung showing secondary lobules and interlobular septa. Within the interalveolar septae, one sees small venules and lymphatics.Courtesy Armando Fraire MD. 32649b
code lung pulmonary alveoli alveolus secondary lobule interlobular septa vein lymphatic histology
interstitium interstitial
32649b
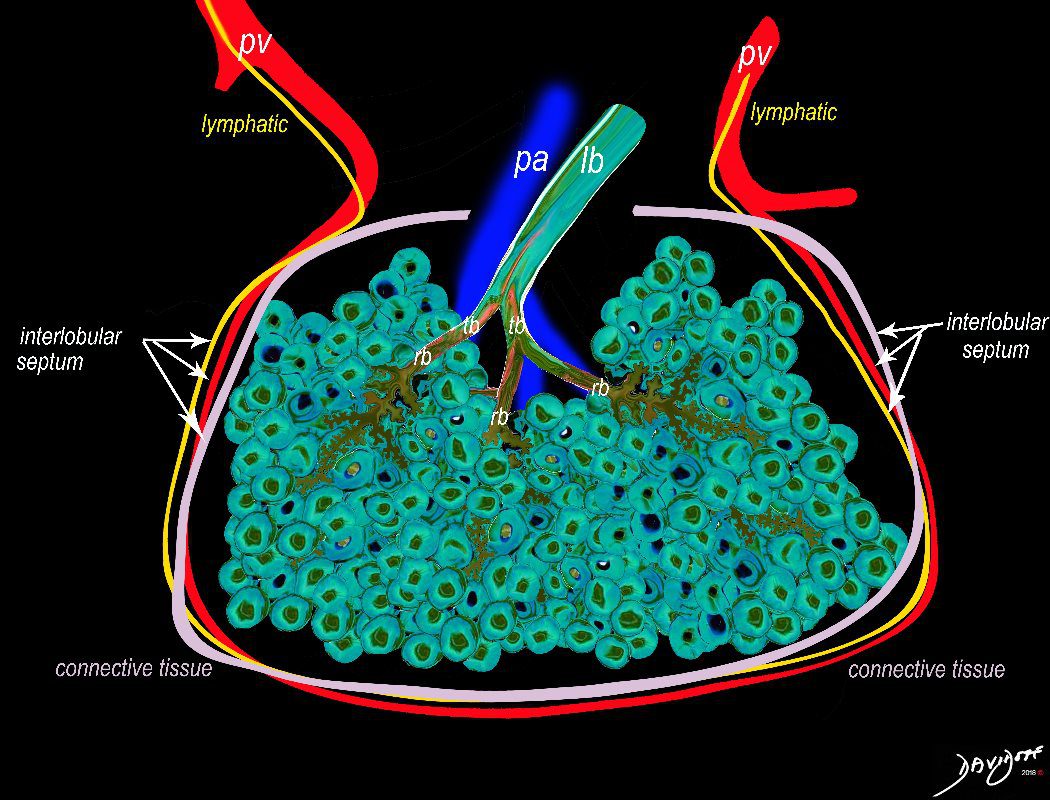
The secondary lobule is housed in a connective tissue framework in which run the lymphatic and venular tributaries . Together these 3 structures form the interlobular septum.
The lobar arteriole enters the framework, accompanied by the lobar bronchiole, and they all run together and form the interlobular septa. This structure measures between .5cms and 2cms and is visible on CT scan.
It is important in clinical radiology since many of the structures can be identified in health, and more particularly in disease, enabling the identification and characterization of many pathological processes.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
lungs-0036-low res

Airways are lined by a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium interspersed with mucus secreting goblet cells
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
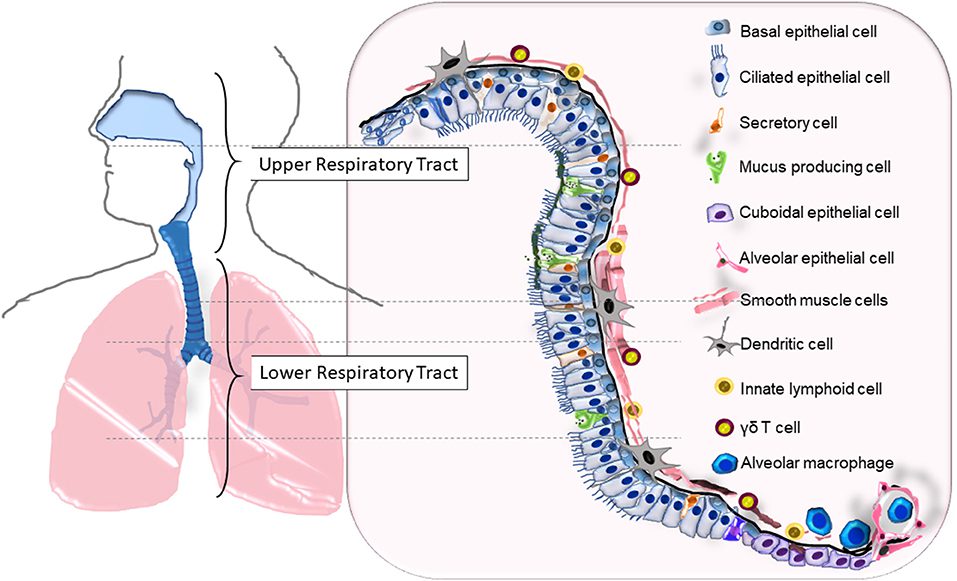
LeMessurier K.S et al Respiratory Barrier as a Safeguard and Regulator of Defense Against Influenza A Virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae Front. Immunol., 04 February 2020
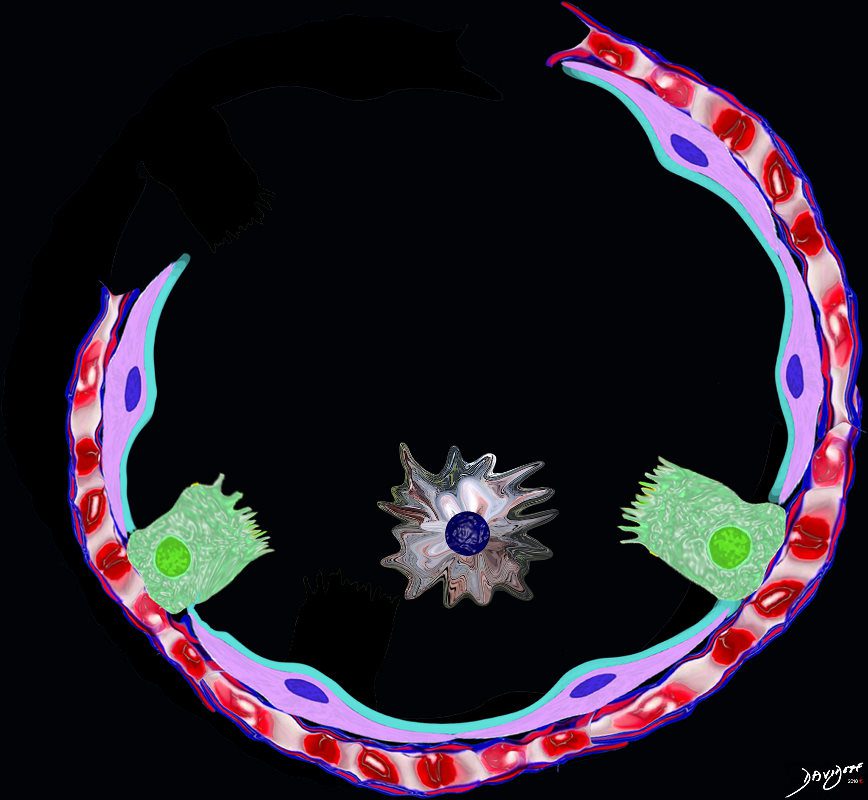

The Buck Ends Here
The alveolus is lined by a simple epithelium – one cell layer thick. There are two types of lining cells; Type 1 pneumocytes are squamous cells that cover 90% of the surface of the inner lining of the lung , and type II cuboidal pneumocytes that are in fact much more numerous than Type I. They are involved in the production of surfactant . In the lumen there are resident macrophages which play a crucial role in the immune system. The mucosa is grounded by a basement membrane and a lamina propria, and connected to the lamina propria and basement membrane of the surrounding capillary. The alveolus is lined by a thin layer of surfactant. (teal blue)
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
References and Links
- TCV
