Definition
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant condition of the epithelial lining of the airways, most commonly the peripheral airways, and is now the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for 30-40% of all cases.
The causative factors are not as clear as in squamous cell cancer, and the association with smoking although present, is not as strong as with squamous cell carcinoma. It occurs in secretory cells. A subtype of adenocarcinoma is called bronchioalveolar cell carcinoma (BAC). Thus adenocarcinoma can originate from the bronchial mucosa, or from the acinus in which case it results in the bronchioloalveolar type. A pattern from adenomatous hyperplasia, through pure bronchioloalveolar carcinoma to a combination of BAC and adenocarcinoma to adenocarcinoma is noted, similar to the hyperplasia, adenoma, dysplasia, malignancy pattern noted in colon carcinoma.
Structures Involved
1. Bronchial Glands of Bronchi and Bronchioles
2. Peripheral Lung Tissue
Structurally, it is characterized by its location in the periphery, and the occasional association with a known scar. It rarely cavitates but it may calcify. At a histopathological level rosettes of glandular epithelium often with mucus are noted.
Adenocarcinomas tend to grow more slowly than squamous cell carcinomas.
It is complicated by early metastasis to local nodes and to distal parts of the body, commonly the pleura, brain, adrenals and bone.
Clinically adenocarcinoma tends to as peripherally placed tumors and hence they are often asymptomatic, but their relationship to the pleura, may incite pleuritic pain or pleural effusion. Their initial silent nature often precludes early diagnosis and so presentation is relatively late and it is not uncommon for the patient to present with metastatic disease.
Imaging Findings
-
- Peripheral Location
- Pulmonary Nodules or Masses
- Ground-Glass Opacities (GGOs) Lepidic Growth
- Pneumonia
- Pseudocavitation
- Scarring desmoplastic changes with bronchiolectasis
- Cystic FormThe diagnosis is made after endoscopic or CT guided biopsy, and after staging with PET scan or with additional biopsy of remote sites, treatment is initiated based on the staging.
Stage I, II, and IIIA are treated surgically with a hope of cure, and the more advanced stages are treated with combinations of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
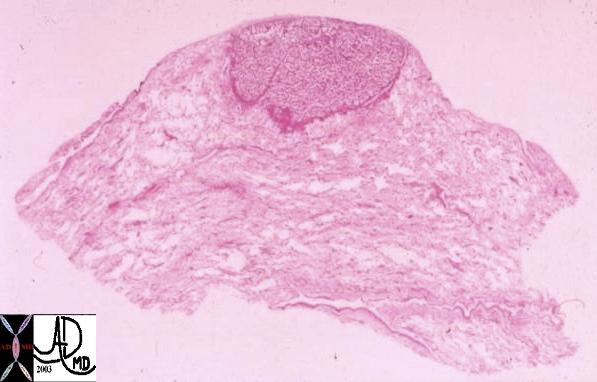
This whole mount of a part of the periphery of the lung reveals a peripherally located nodule without evidence puckering of overlying pleura. Microscopically this proved to be a papillary carcinoma.
Courtesy Armando Fraire MD. TheCommonVein.net 32812
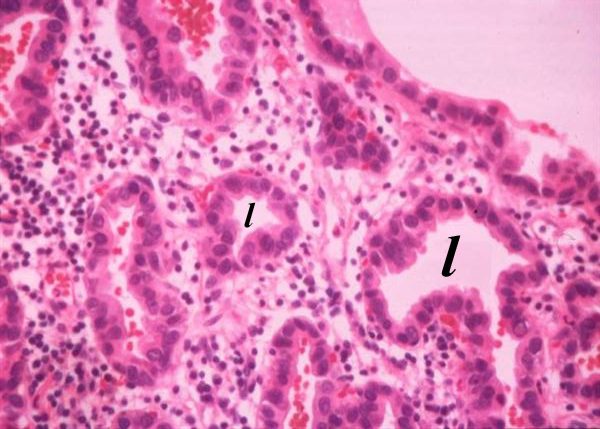
The histological section shows rosettes of malignant glandular epithelium surrounding their respective lumens (l). The malignant cells have dark nuclei, with the cells showing a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio consistent with carcinoma, and the rosette shape and the glandular appearance, characterize the section as an adenocarcinoma code lung cancer adenocarcinoma rosettes malignant lumen
Courtesy Armando Fraire MD.
TheCommonVein.net
32510b01
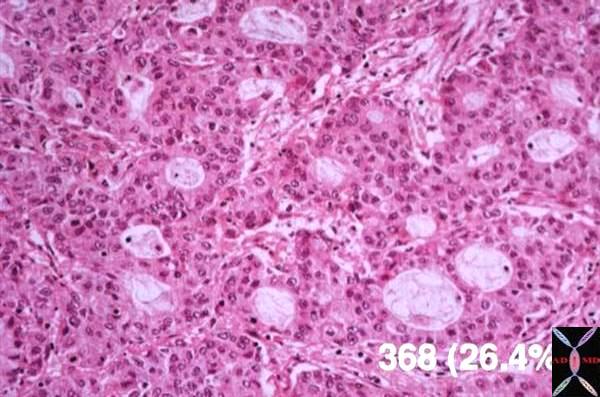
Histological section of an adenocarcinoma of the lung showing accumulation of mucus globules in the lumina of the glands .
Courtesy Armando Fraire
TheCommonVein.net
MD. 32512
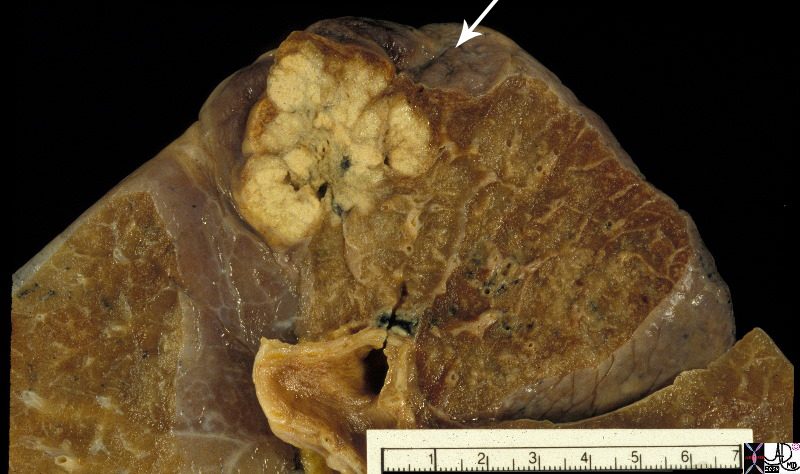
The 3.5cms carcinoma is peripherally situated and is sub-pleural in location. It reveals fibroblastic (aka desmoplastic) effect as witnessed by the puckering of the pleura (arrow). It is remote from central bronchovascular structures and therefore remains relatively asymptomatic for an extended duration unless it causes pleuritic pain. The location and desmoplastic puckering of the pleura are characteristic of an adenocarcinoma.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
32201b.81s
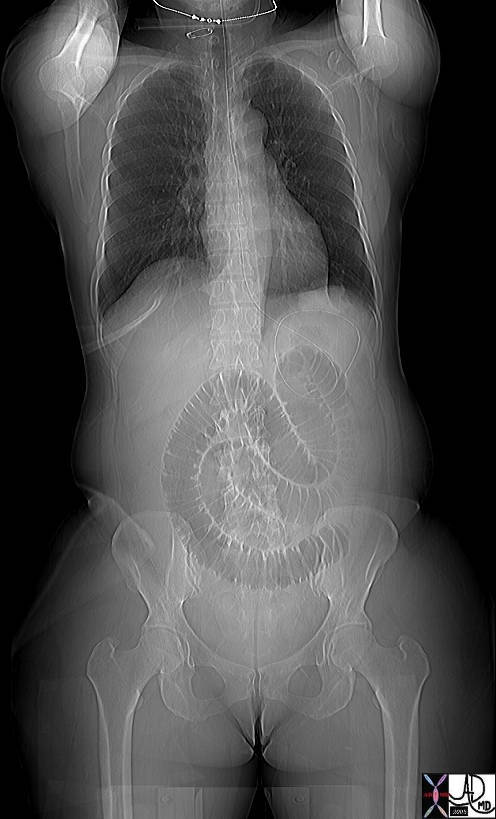
This plain film of the chest and abdomen shows is from a 51year old female who presented with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distension. A loop of dilated small bowel is associated with absence of air in the decompressed colon and rectum. In addition a mass is seen in the left lower lobe (green overlay). A barium study showed thumb printing consistent with distal ischemia of the small bowel. The diagnosis in the lung was shown to be adenocarcinoma.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
43459c01.8s
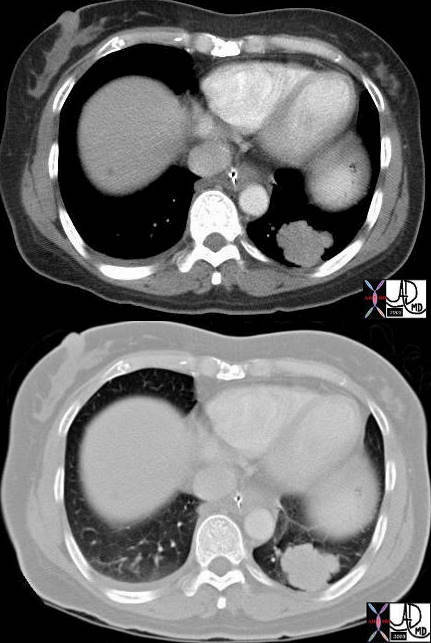
Axial images of the case shown above through the lung mass in a 51 year old female who presents with nausea vomiting and abdominal distension and who was shown to have a small bowel obstruction. The mass is situated in the left lower lobe and was an incidental asymptomatic finding. It measures in the 3cms range is lobulated and peripherally located. Pathology showed an adenocarcinoma.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
43460c
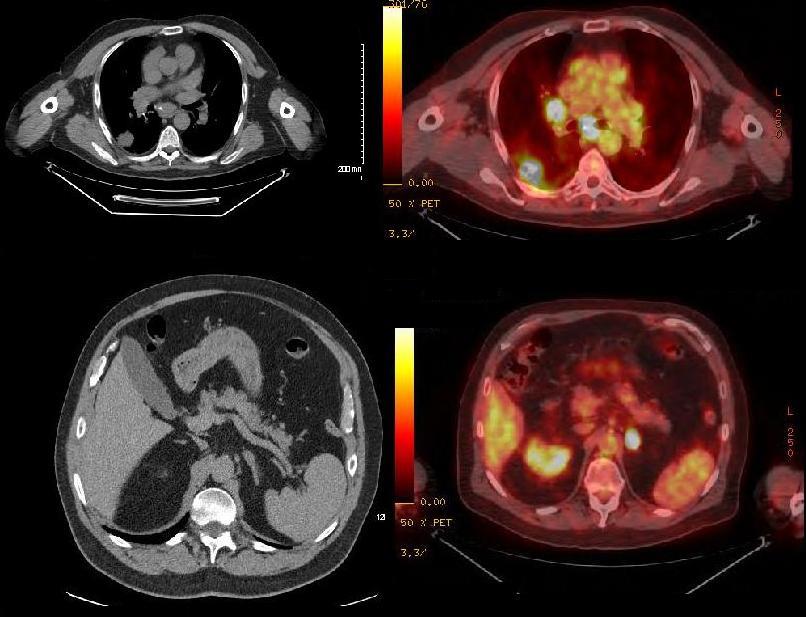
Adenocarcinoma PET negative
Ashley Davidoff THECOMMONVEIN.net
Ashley Davidoff
THECOMMONVEIN.net
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
118601
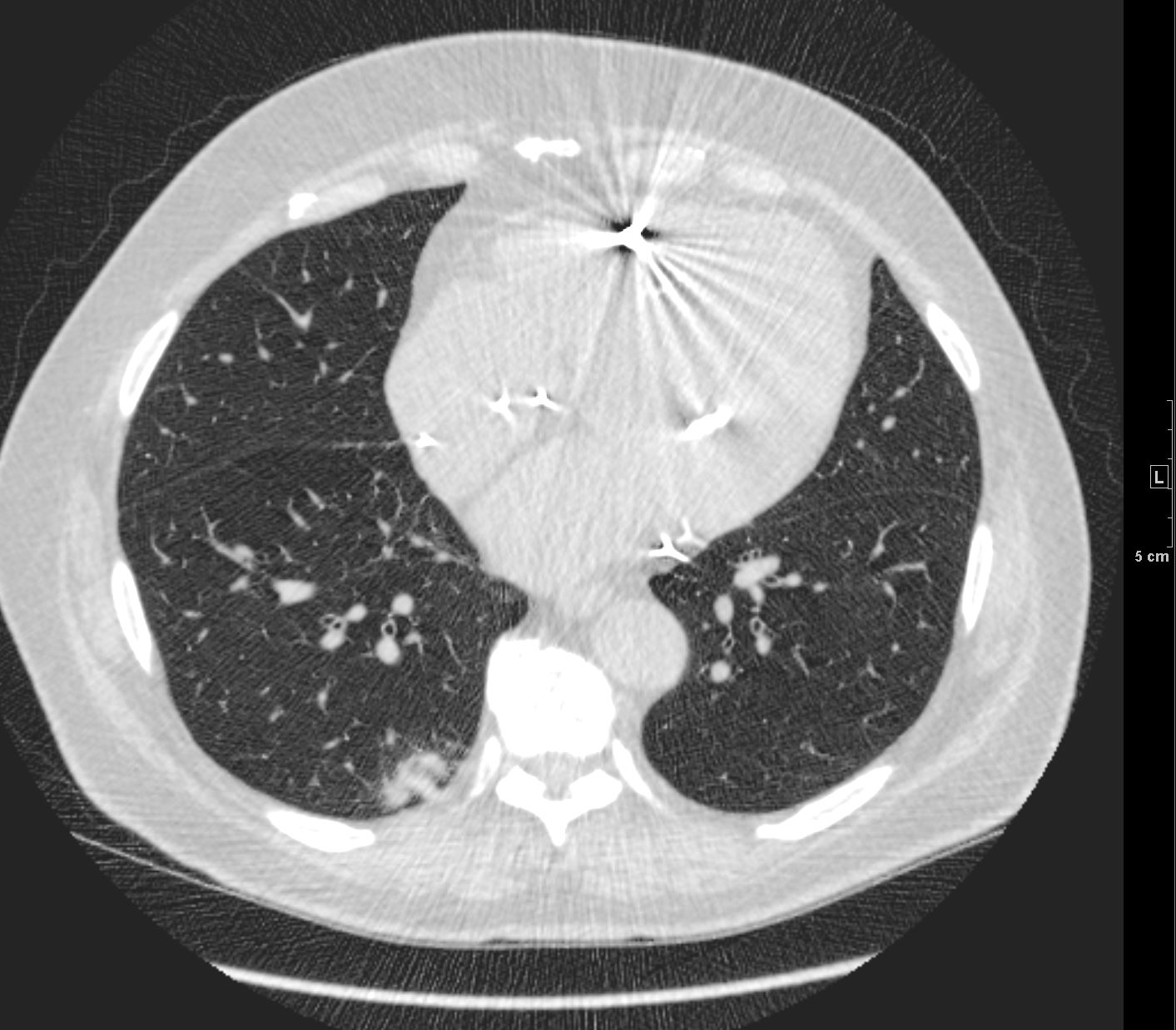
Adenocarcinoma with Air Bronchograms

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
70m – adenocarcinoma-02

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
70m – adenocarcinoma-02
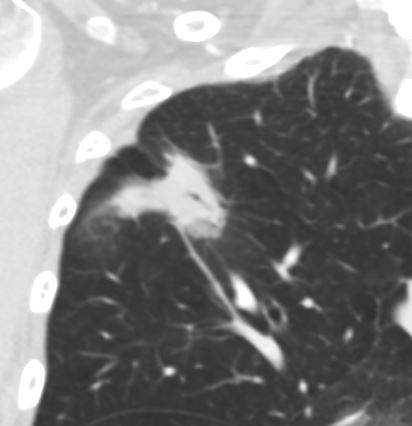
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
70m – adenocarcinoma-02
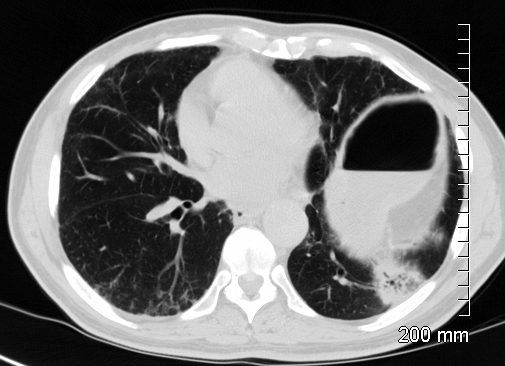
Adenocarcinoma with Bronchiectasis
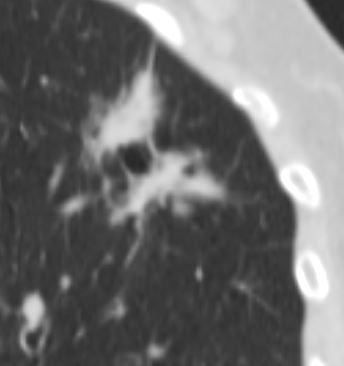
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net adenocarcinoma 01 CT
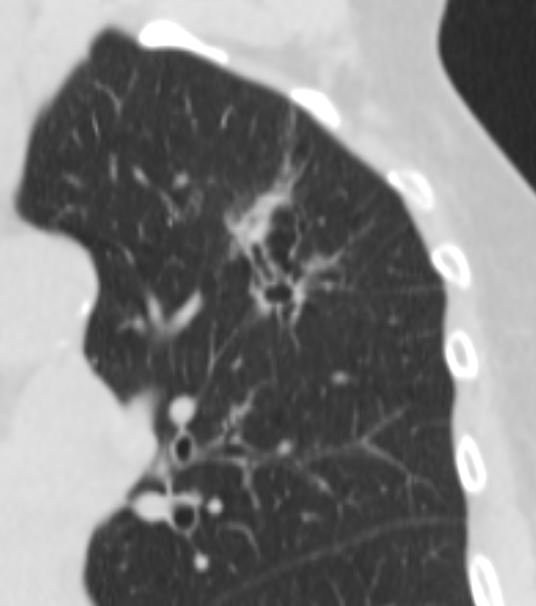
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net adenocarcinoma 02 CT
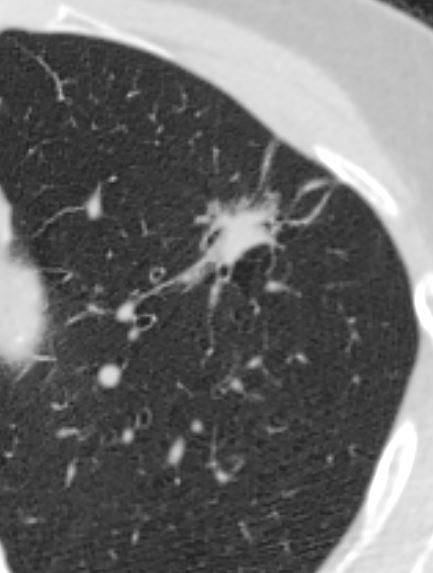
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net adenocarcinoma 03 CT
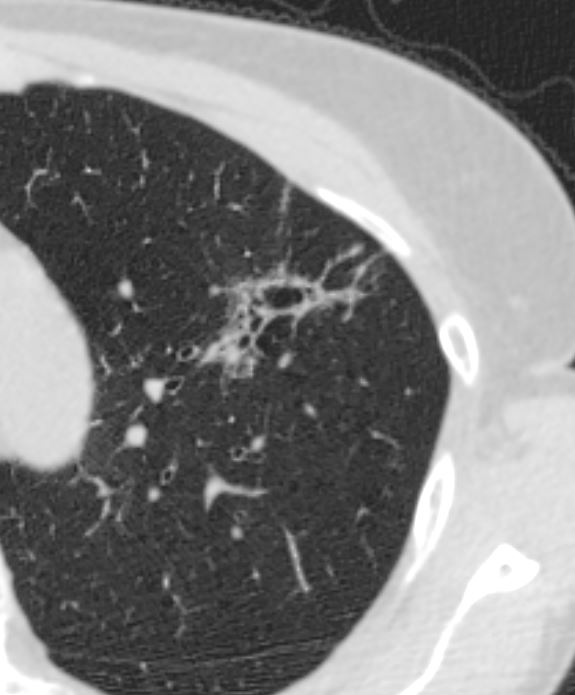
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net adenocarcinoma 04 CT
Invading the Chest Wall and Adrenal Metastases
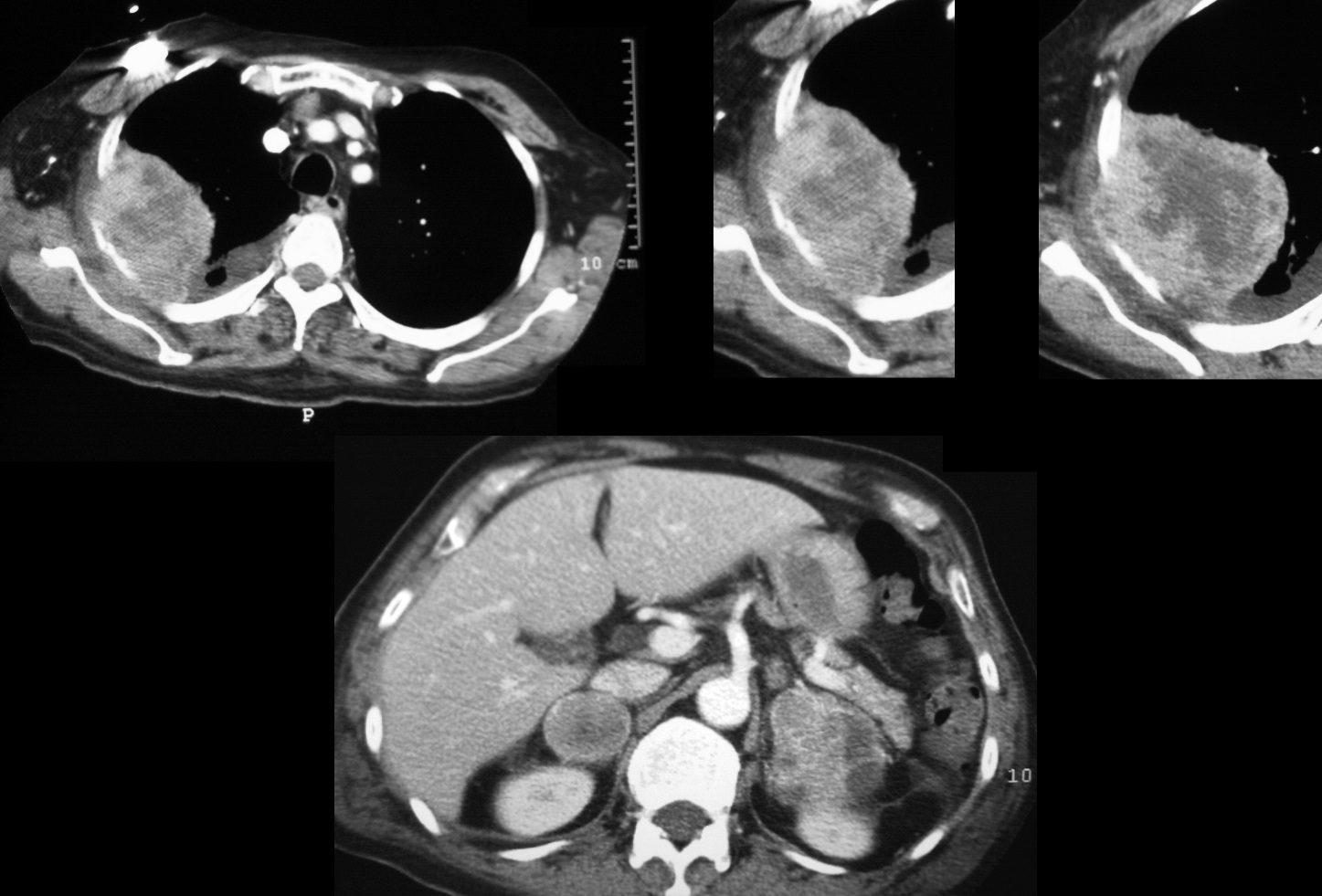
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
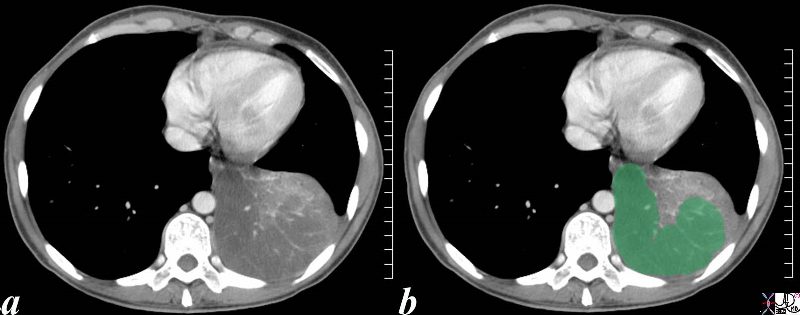
This is an unusual appearance of an adenocarcinoma showing a large lobar consolidation without significant distortion of the vessels. The vessels in the infiltrated section (green overlay) are spread apart. Infiltrative adenocarcinoma was identified on biopsy.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
46589c02.8s
56 year old male with mucinous adenocarcinoma
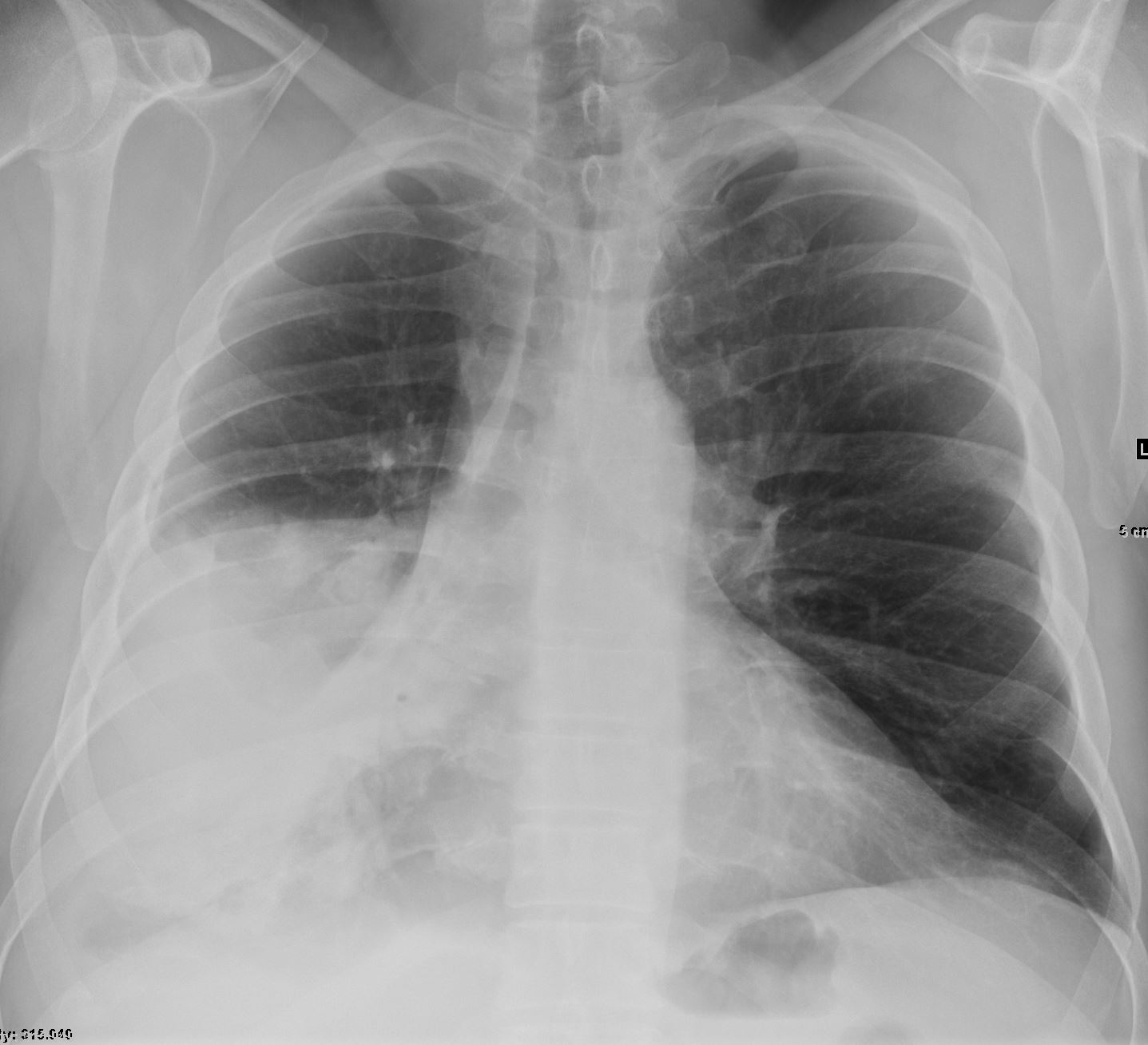
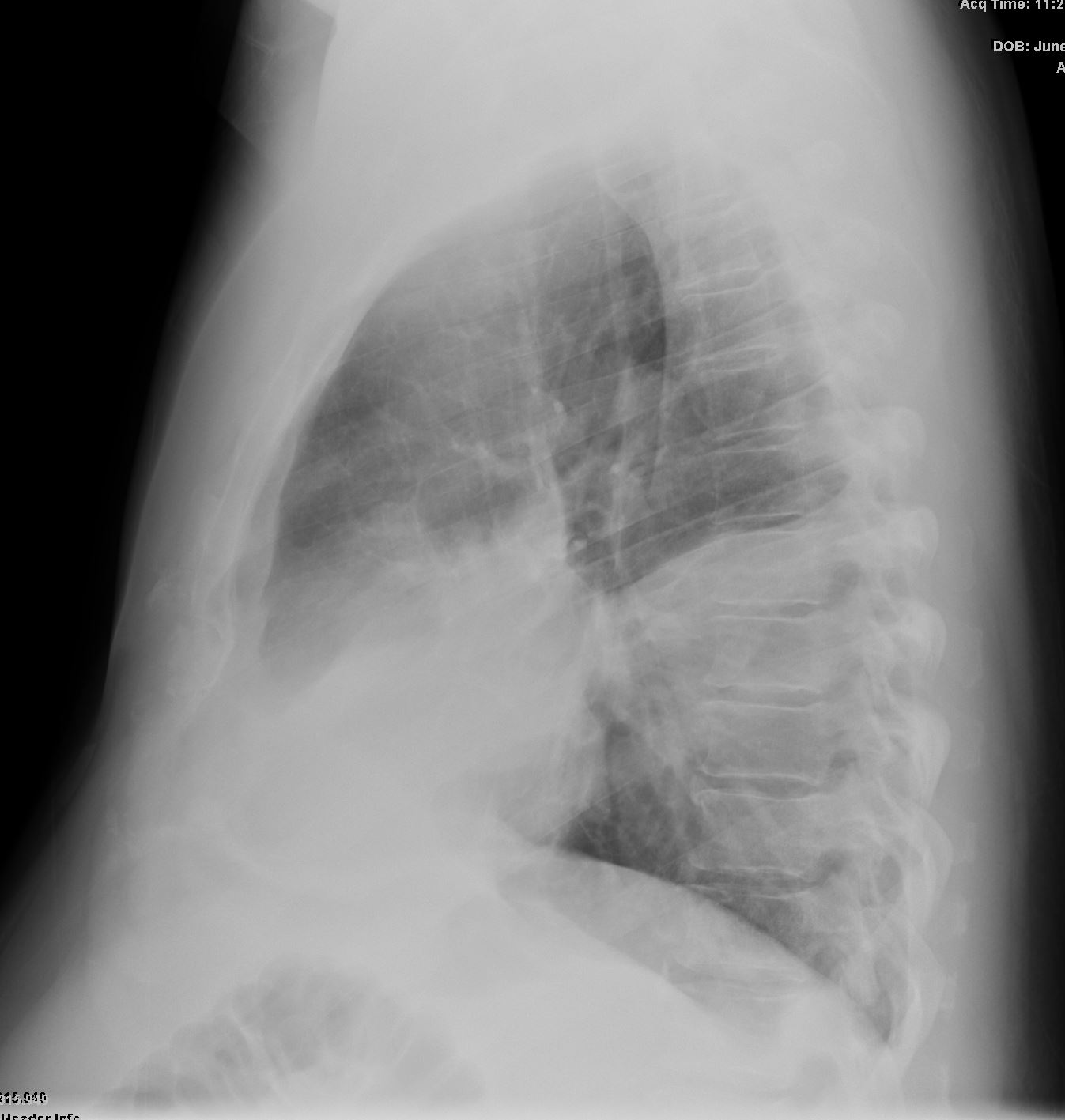
CXR showing right lower and middle lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
56 pneumonic mucinous adenoca 001
CXR showing right lower and middle lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
56 pneumonic mucinous adenoca 002
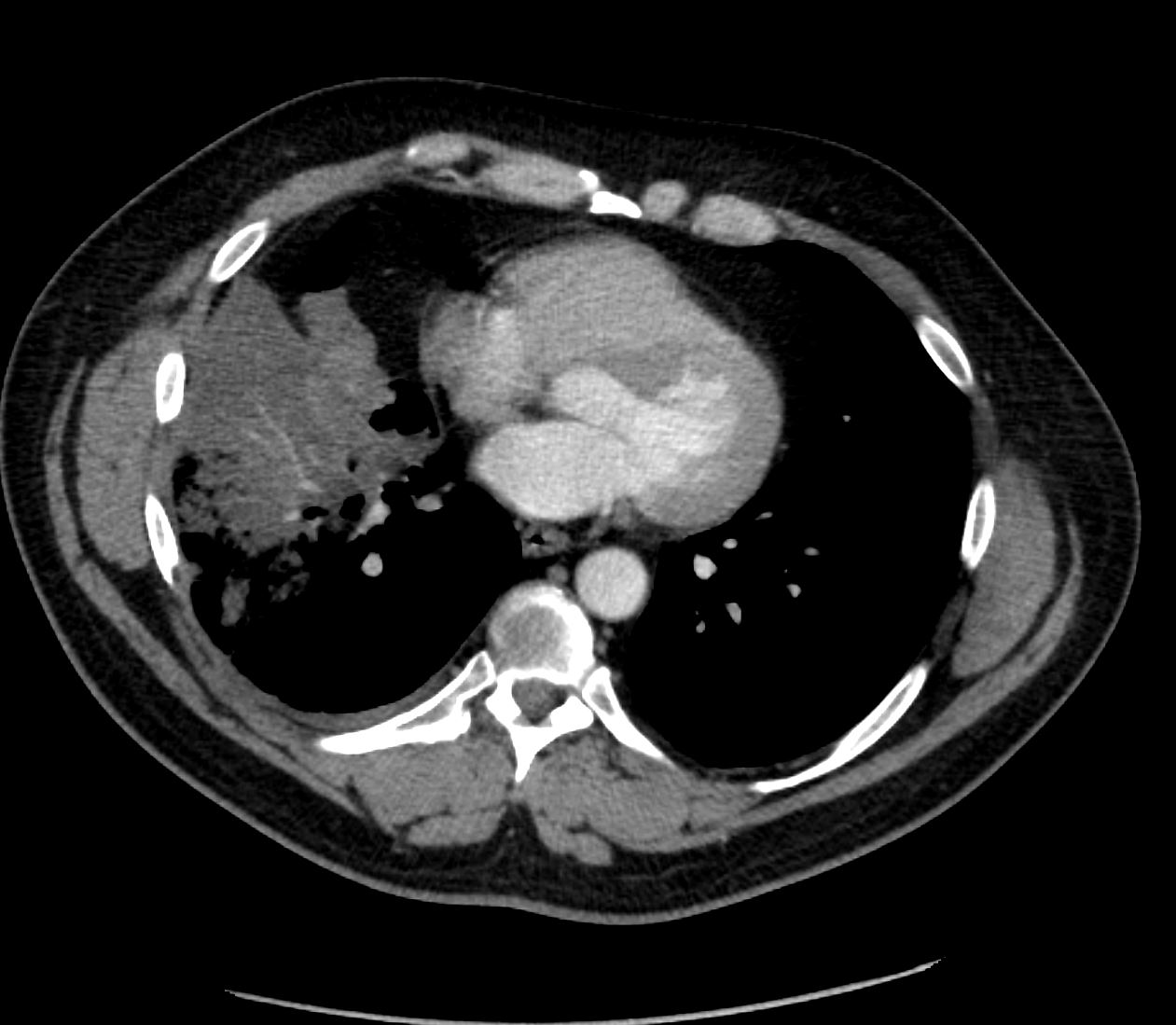
CT showing right lower and middle lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
56 pneumonic mucinous adenoca 005
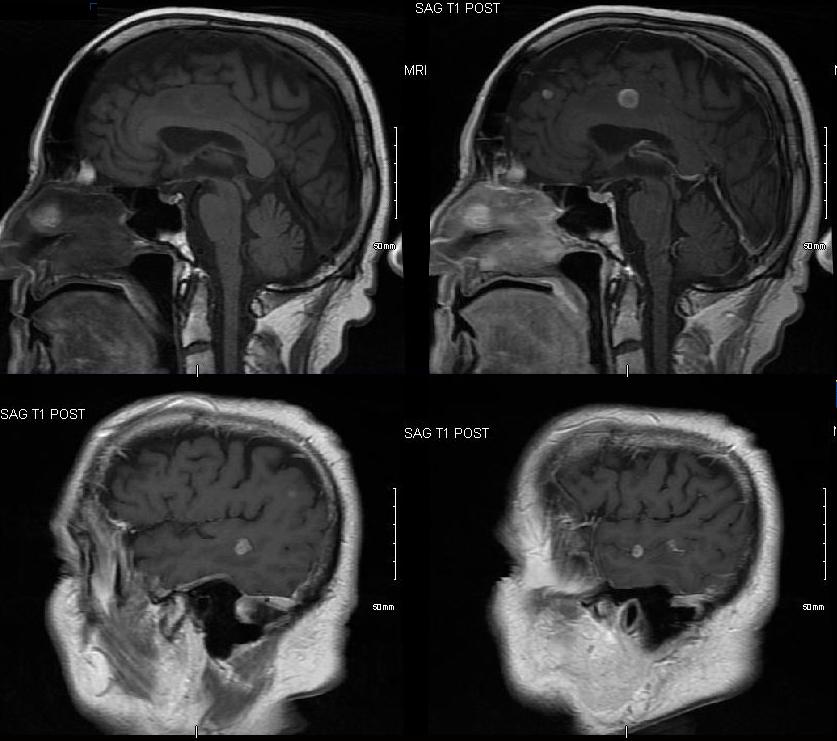
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
121893
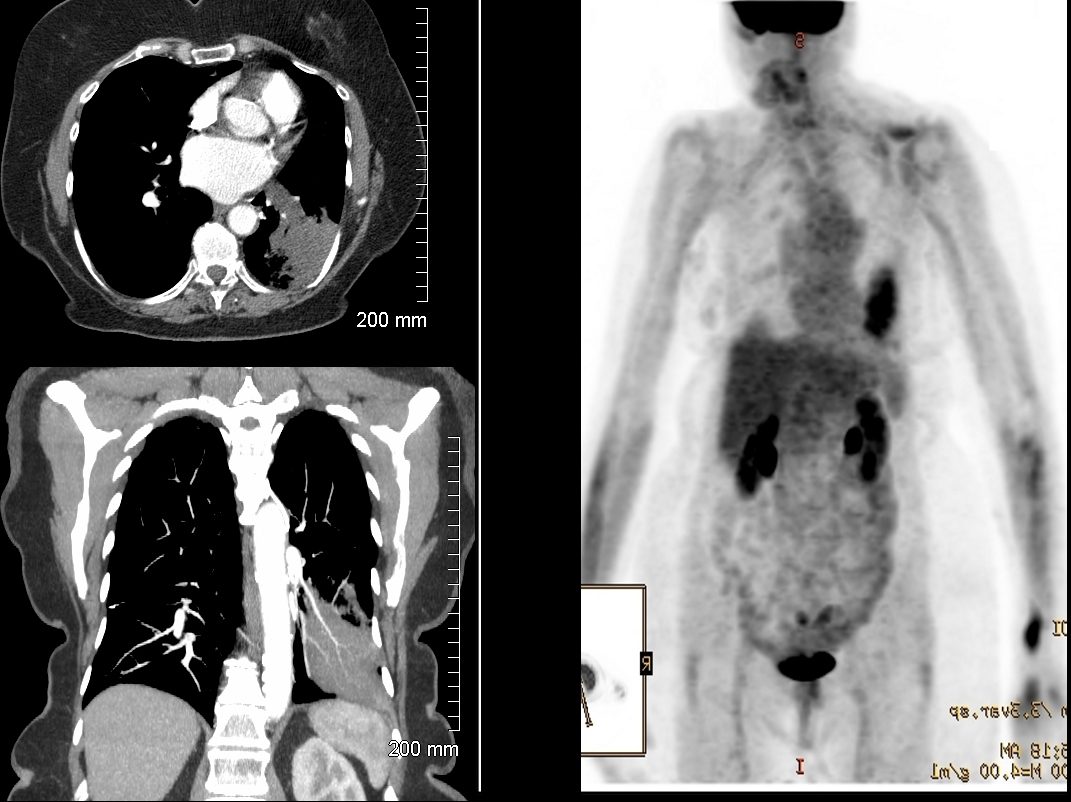
75 year old female presents with a left lower lobe infiltrate on CT scan and PET CT positivity
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
-

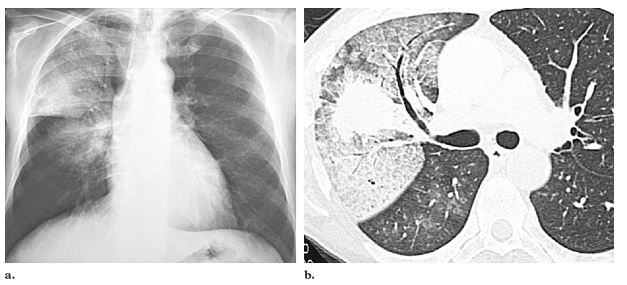
Primary lung adenocarcinoma in a 54-year-old man with hemoptysis. (a) Posteroanterior chest radiograph shows a centrally located mass adjacent to an area of diffuse ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe. Note
the air trapping in the lung base. (b) CT scan shows typical crazy-paving ground-glass attenuation associated with
septal thickening surrounding the mass, which is perihilar. Adenocarcinoma with surrounding pulmonary hemorrhage was confirmed at surgery
Rossi, S.E et al “Crazy-Paving” Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: RadiologicPathologic Overview Radiographics Volume 23 – Number 6, 2003
Previous resection of a Stage 1 Adenocarcinoma – now with lower Lobe Recurrence Along the Suture Margin
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net