Authors Neelou Etesami MS4 and Ashley Davidoff MD
- An air bronchogram is a
- radiological sign where
- air-filled bronchi
- become visible
- due to
- surrounding lung tissue being opacified by
- fluid,
- exudate, or
- other material, often seen in conditions like
- pneumonia,
- pulmonary edema,
- ARDS, or
- lung cancer.
- surrounding lung tissue being opacified by
- It occurs when the
- alveoli are filled with substances
- denser than air, such as
- fluid,
- infection,
- blood, or
- cancerous cells,
- while the
- bronchi remain air-filled.
- Functionally
- This impairs gas exchange,
- Leading to symptoms like
- shortness of breath and
- hypoxemia.
- Diagnosis involves
- clinical evaluation,
- chest X-rays or
- CT scans
- showing
- air density bronchi against
the soft tissue of filled alveoli
- air density bronchi against
- showing
- Laboratory tests results
- depend on the underlying cause.
- radiological sign where
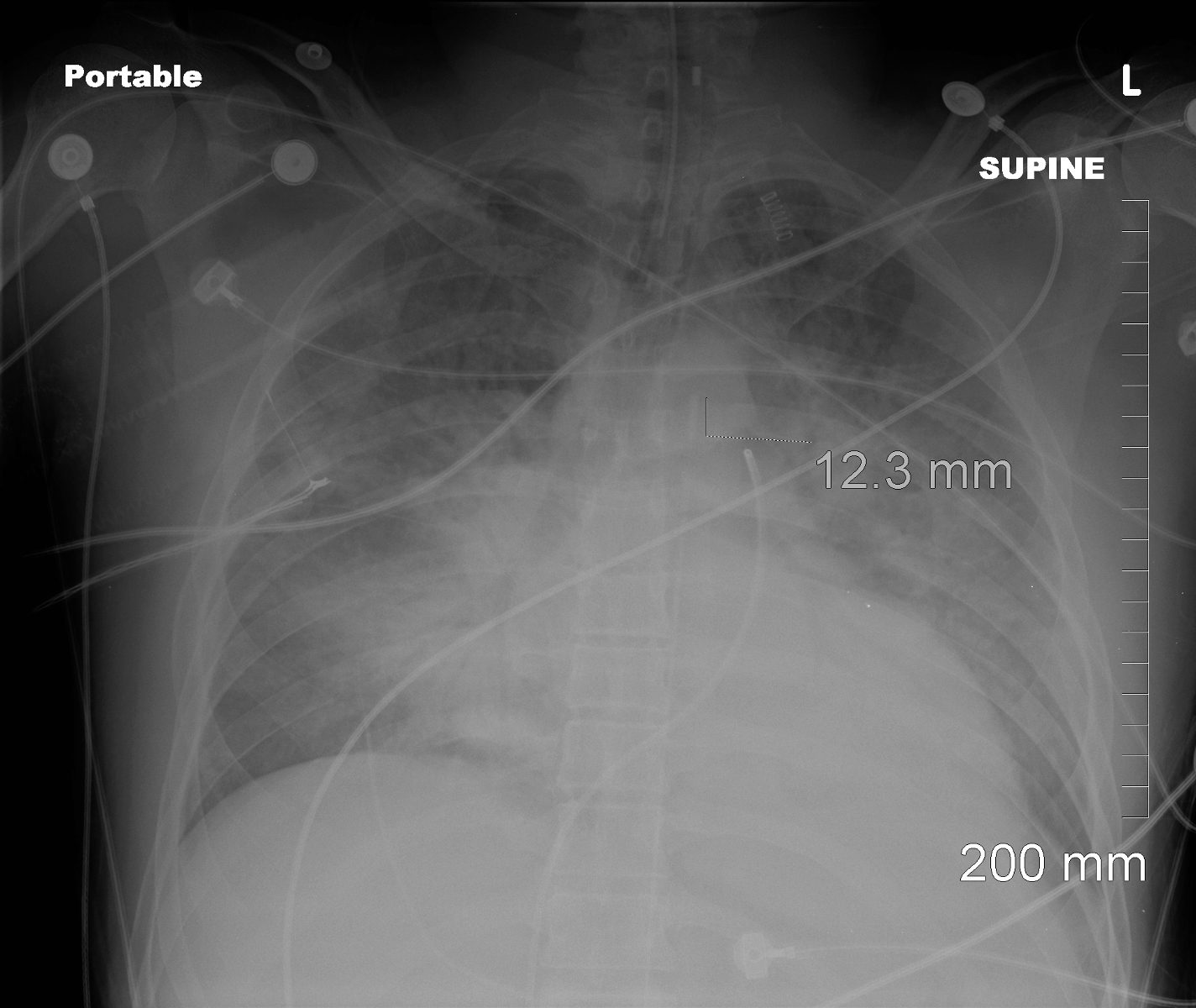
Portable frontal CXR shows a multifocal pneumonic consolidations with air bronchograms in the right upper, left upper right lower and left lower lobes. There is silhouetting of the right heart border reflecting middle lobe involvement. The patient is intubated with an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) and Swan Ganz line.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 136501
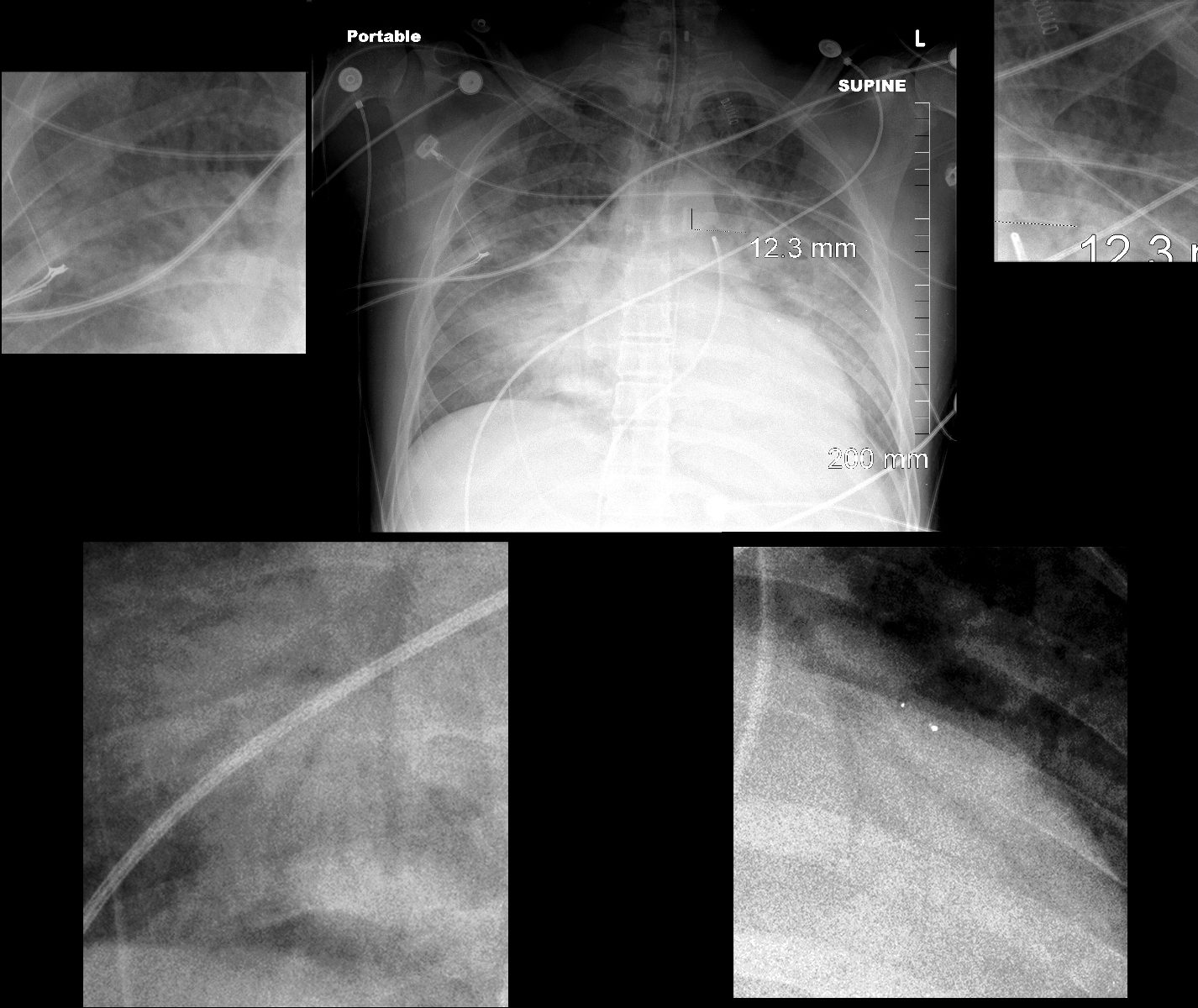
45-year-old immunocompromised male presents with a cough fever and shock.
Portable frontal CXR shows a multifocal pneumonic consolidations with air bronchograms in the right upper, left upper right lower and left lower lobes, magnified in the surrounding images. There is silhouetting of the right heart border reflecting middle lobe involvement. The patient is intubated with an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) and Swan Ganz line.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 136501c
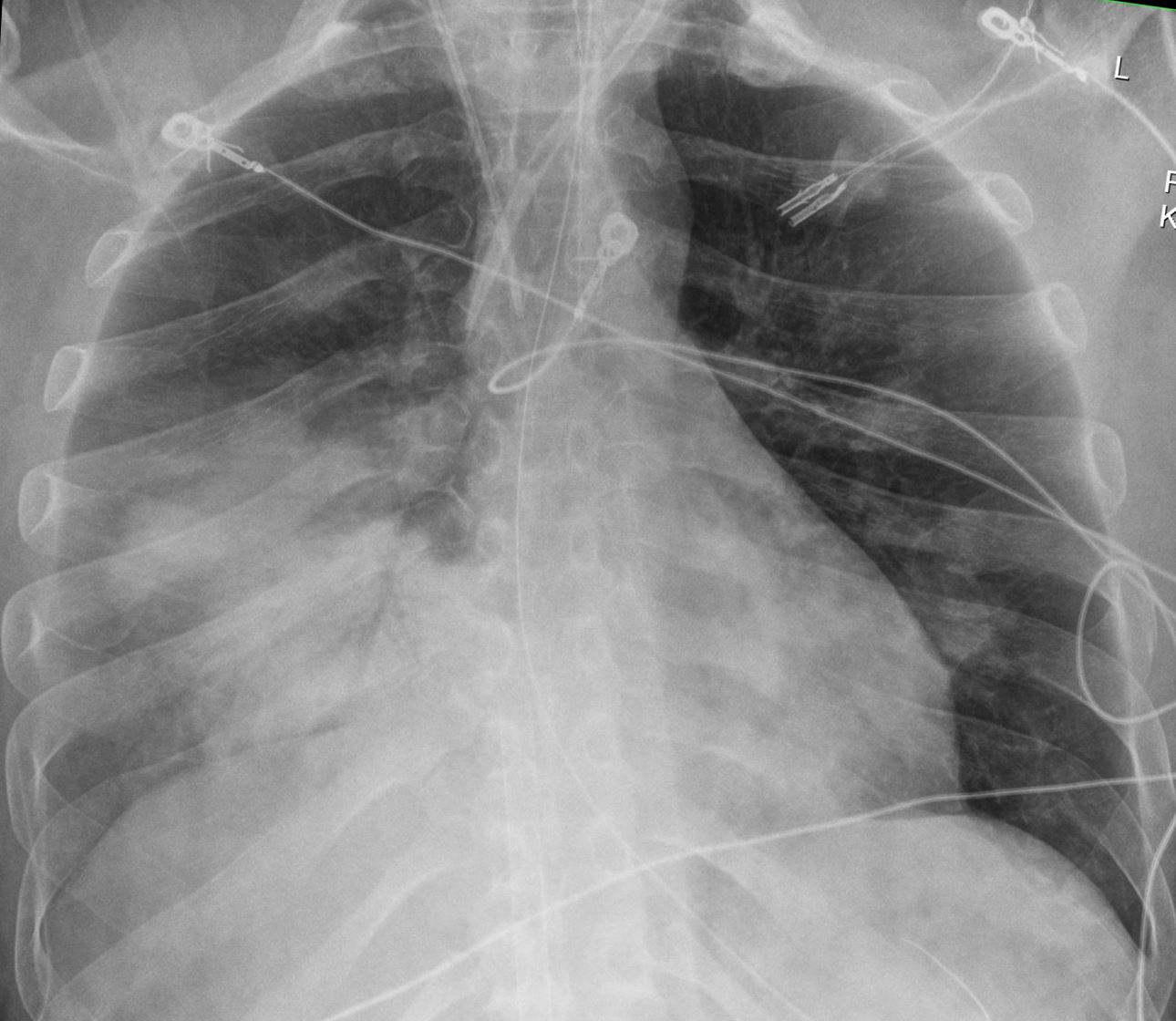
CXR shows a consolidation silhouetting the right heart border with an air bronchogram indicating a right middle lobe pneumonia
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 137791
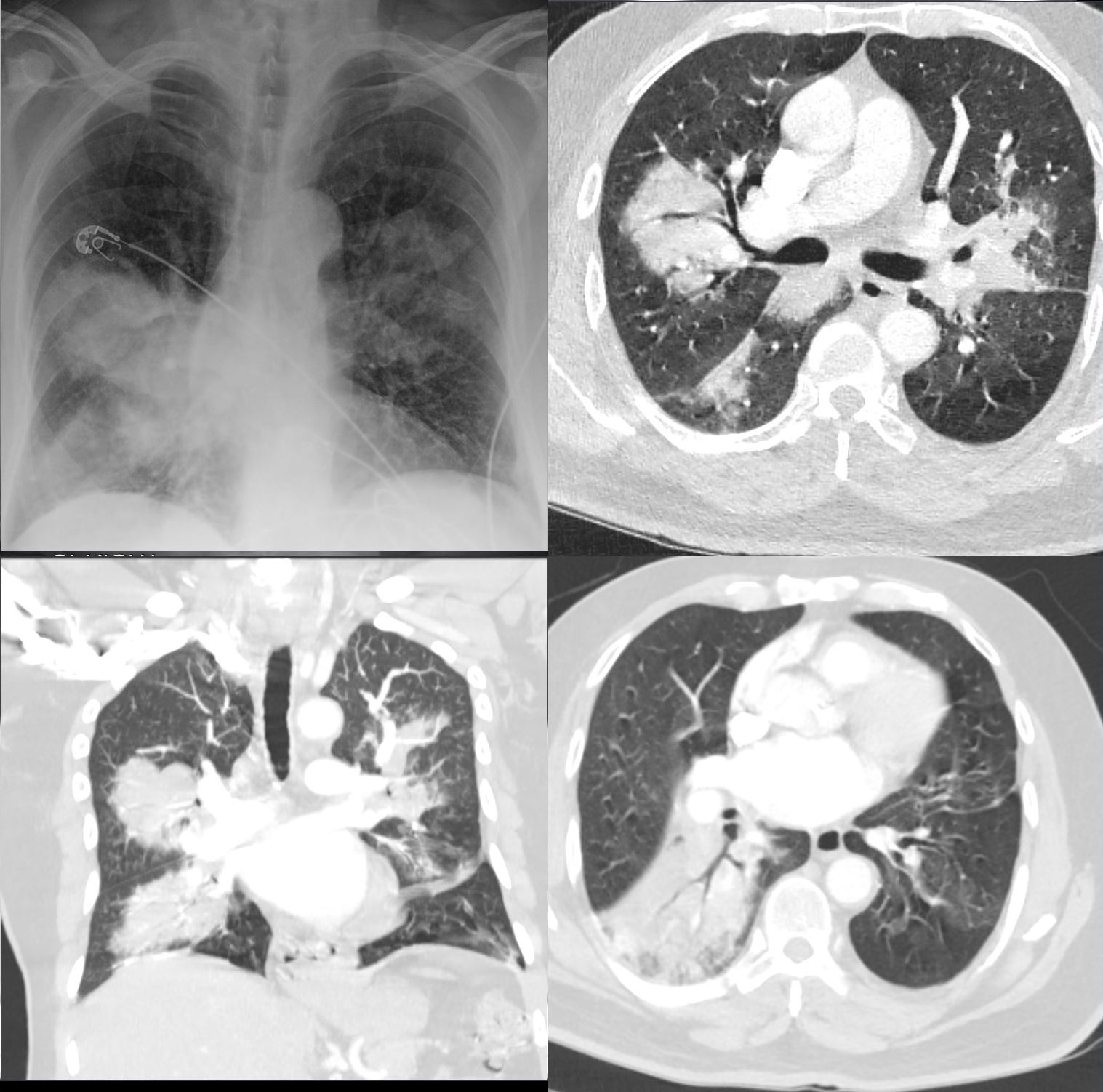
CXR and CT scan shows multifocal pneumonia involving right upper lobe, right lower lobe and to lesser extent the left upper lobe characterised by segmental and subsegmental consolidations and air bronchograms
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net b11521
Air Bronchogram Secondary to a Lingula Pneumonia
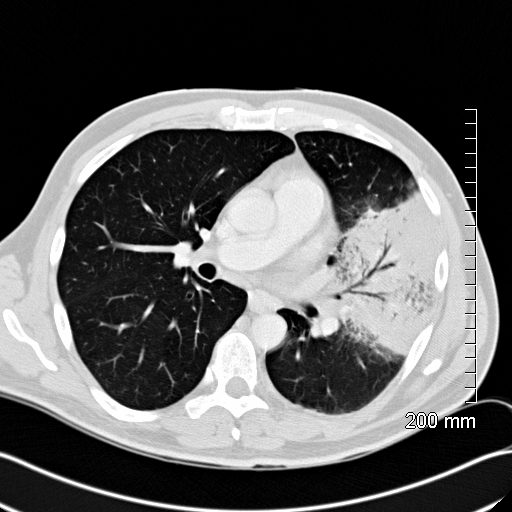
52 year old male presents with a cough and fever
CT scan in the axial plane shows a lingular consolidation with air bronchograms and a positive silhouette sign. Both the superior and inferior lingular segments are involved
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
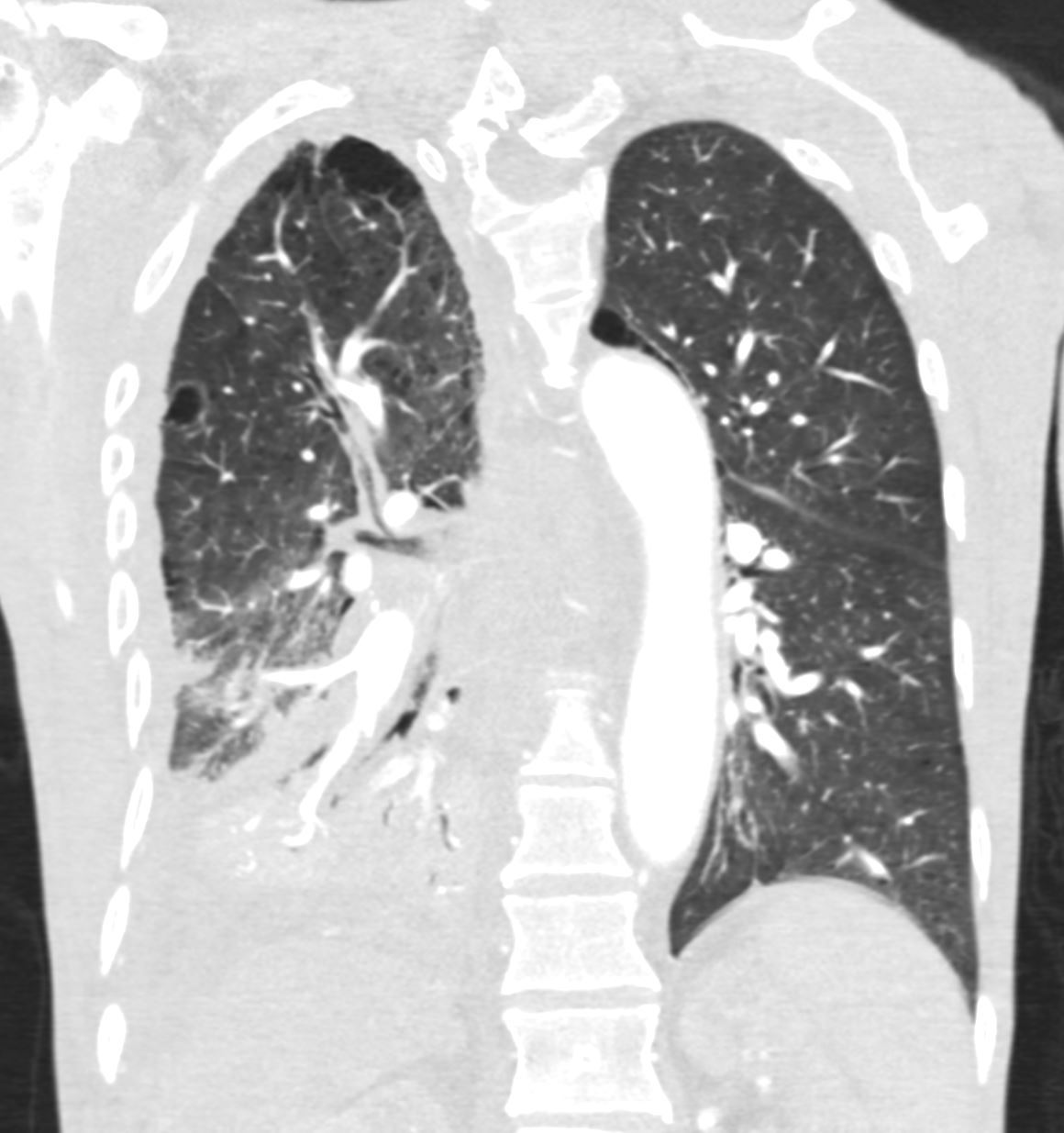
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net RML RLL 004
Chronic Eosinophillic Pneumonia
Upper Lobe Peripheral Consolidations with
Air Bronchograms
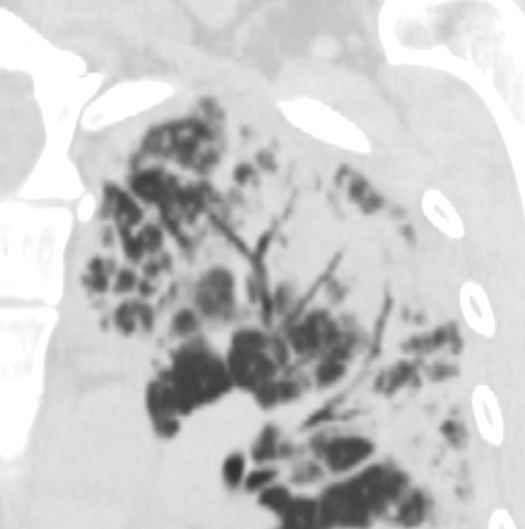
CT scan in the coronal performed 6 months ago at the time of clinical presentation shows upper lobe predominant peripheral infiltrates more prominent in the left upper lobe. Subsequent diagnosis by BAL of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) was made
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Lobar
Segmental
Subsegmental
“Air bronchogram refers to the phenomenon of air-filled bronchi (dark) being made visible by the opacification of surrounding alveoli (grey/white). It is almost always caused by a pathologic airspace/alveolar process, in which something other than air fills the alveoli. Air bronchograms will not be visible if the bronchi themselves are opacified (e.g. by fluid) and thus indicate patent proximal airways.
Air bronchograms can be seen with several processes:
- pulmonary consolidation
- pulmonary edema: especially with alveolar edema 3
- non-obstructive atelectasis
- severe interstitial lung disease
- neoplasms: bronchioloalveolar carcinoma; pulmonary lymphoma
- pulmonary infarct
- pulmonary hemorrhage
- normal expiration
Air bronchograms that persist for weeks despite appropriate antimicrobial therapy should raise the suspicion of a neoplastic process. CT may be planned in such cases.”
Links and References
Fleischner Society
air bronchogram
Radiographs and CT scans.—An air bronchogram is a pattern of air-filled (low-attenuation) bronchi on a background of opaque (high-attenuation) airless lung (,Fig 2). The sign implies (a) patency of proximal airways and (b) evacuation of alveolar air by means of absorption (atelectasis) or replacement (eg, pneumonia) or a combination of these processes. In rare cases, the displacement of air is the result of marked interstitial expansion (eg, lymphoma) (,8).
