The Cardiac Evaluation on the CXR – PA
First step – Is the heart enlarged?
- Cardiothoracic ratio as a global method
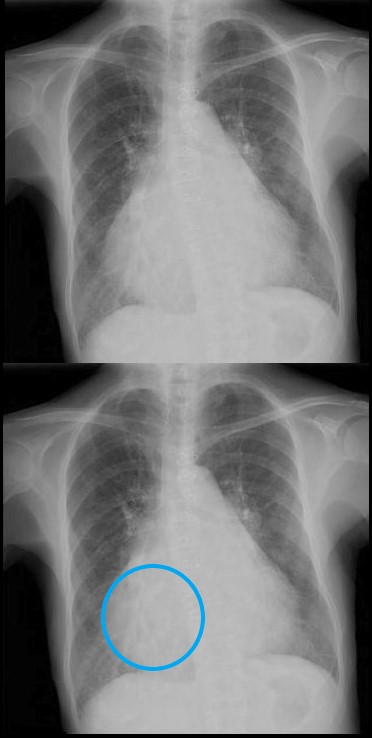
Cardiothoracic Ratio
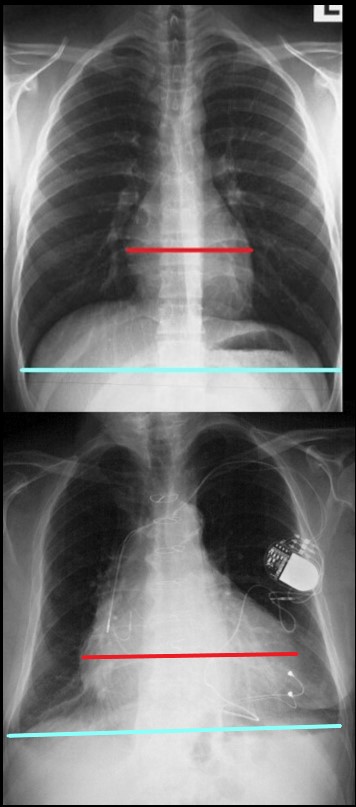
The maximum transverse length of the heart is expressed as a percentage of the maximum length of the internal diameter of the chest. When this ratio – the cardiothoracic ratio (c t r) is greater than 50% cardiomegaly is present. The top image is normal and the bottom reflects cardiomegaly
Ashley Davidoff MD
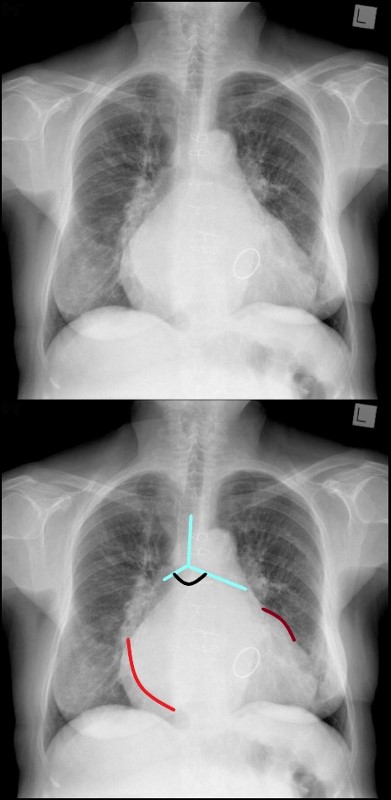
Border Forming Parts of the Heart
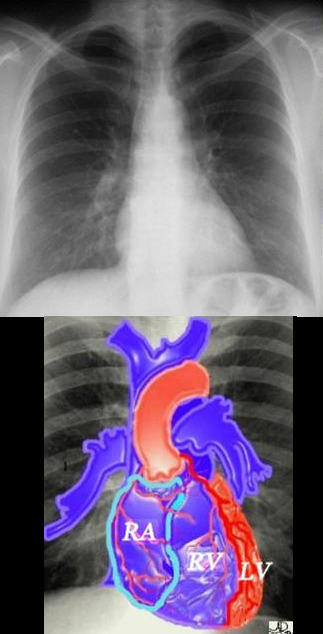 FRONTAL CXR AND PARTS OF THE HEART
FRONTAL CXR AND PARTS OF THE HEART
Two Basic Shapes of Cardiomegaly
-
- Oval down and outer of LV
- Triangular RV disease
- Each of the Chambers
- LA, LV, RA, V
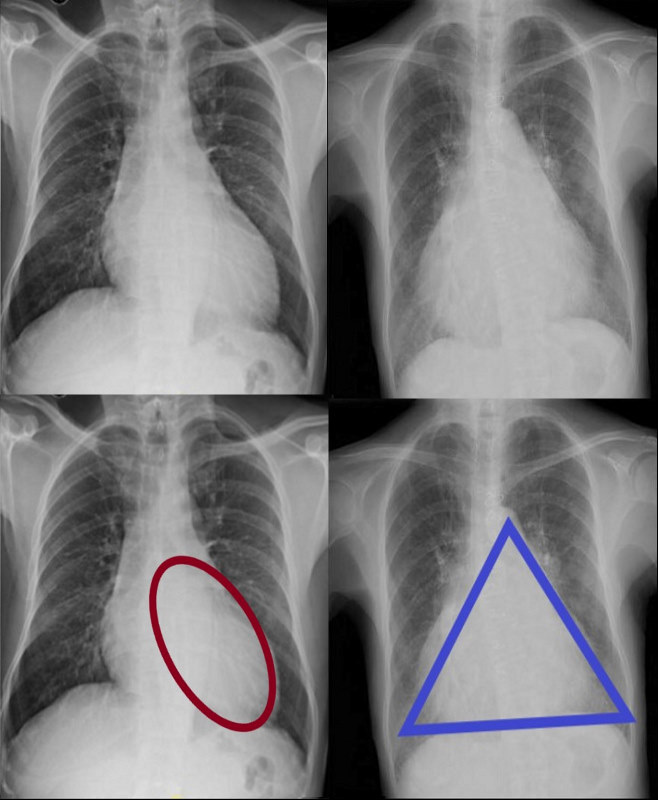
CARDIOMEGALY – TWO BASIC TYPES -OVOID and TRIANGULAR
The ovoid form which suggests left ventricular dominance and triangular form which suggests right ventricular dominance.
Ashley Davidoff MD
LVE
Subtle Ovoid Form Suggestive on the PA and Confirmed on the Lateral – Using Both Views
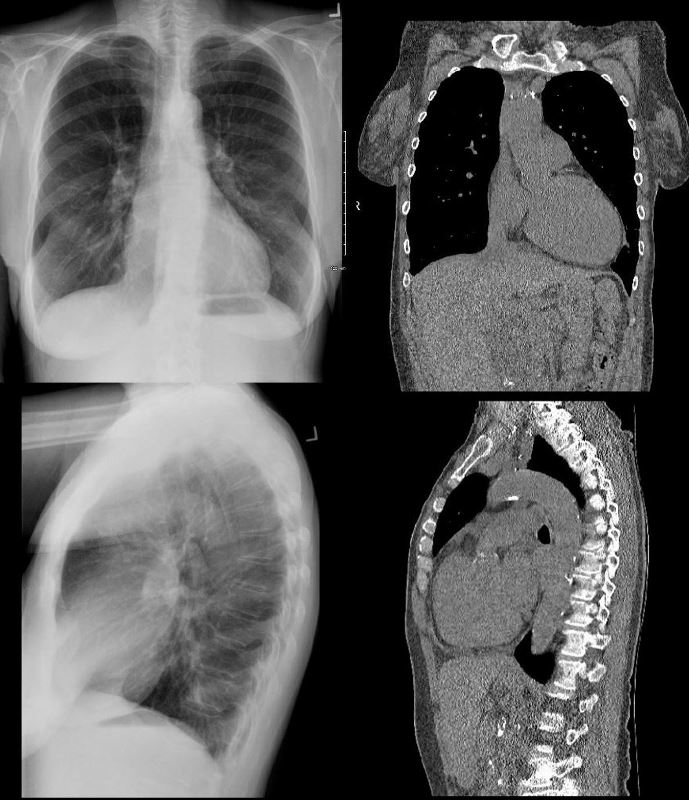
62 year old female with acute chest pain atrial fibrillation, hypotension admitted to ICU. Clinical evaluation was considered to be non-ischemic cardiomyopathy with EF by echo of about 20%. She was hypotensive and, in the ICU, and CXR showed acute CHF with cardiomegaly. The TEE was more in keeping with segmental dyssynergy, Cardiac cath showed occluded RCA bot good collateralization from the LAD. MRI showed subendocardial LGE in the inferior and inferolateral portions of the LV consistent with a prior infarction and EF of 20%
Ashley Davidoff MD
Triangular Heart with RVE
With Mitral Stenosis
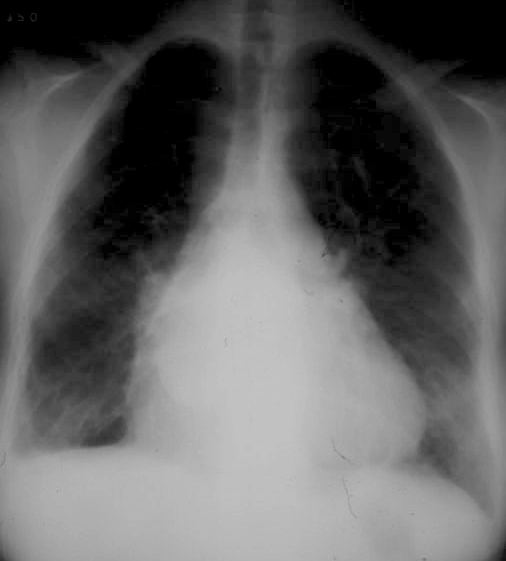
Triangular shaped heart with RVE LAE
Ashley Davidoff MD
With Pulmonary Hypertension
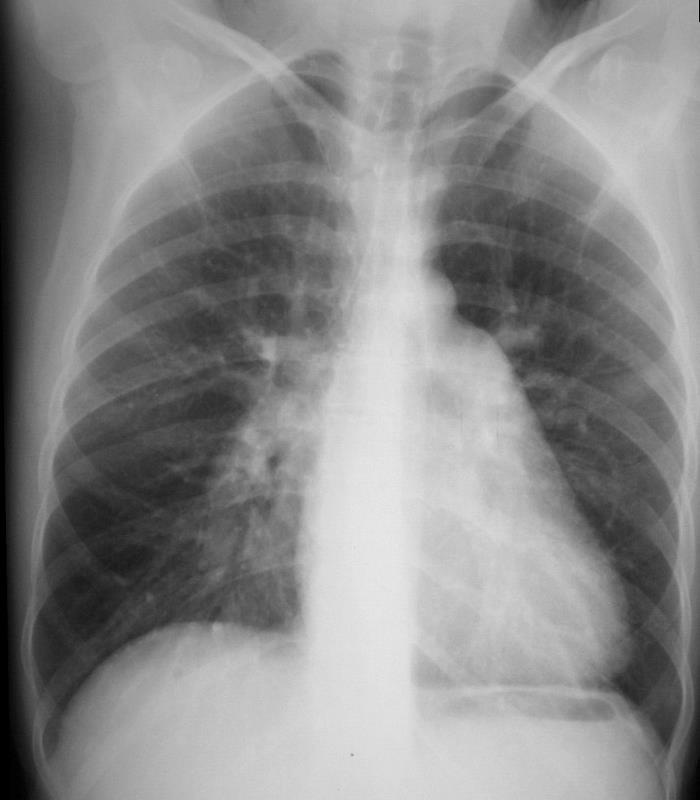
Frontal x-ray with triangular shaped heart due to pulmonary hypertension with enlarged MPA and enlarged descending RPA .
Ashley Davidoff MD
The Enlarged Left Atrium
Widened Carinal Angle
Double Density
Straightened right Heart Border – prominent LA appendage
Triangular Heart
Right Atrial Enlargement
-
- enlarged, globular heart
- narrow pedicle
- gross enlargement of the right atrial shadow, i.e. increased convexity in the lower half of the right cardiac border
- right atrial convexity is more than 50% of the cardiovascular height
- right atrial margin is more than 5.5 cm from the midline
 RIGHT ATRIAL ENLARGEMENT ON FRONTAL X-RAY
RIGHT ATRIAL ENLARGEMENT ON FRONTAL X-RAY
The right atrium is the most difficult chamber to assess unless it is very large in which case it will present on the frontal CXR with a very large right paravertebral border. This is a 71 year old female person with rheumatic heart disease with pulmonary hypertension and tricuspid regurgitation hence resulting in a large right atrium (RAE)
Ashley Davidoff MD
If there is time you may want to run through the collage of congenital heart disease cases
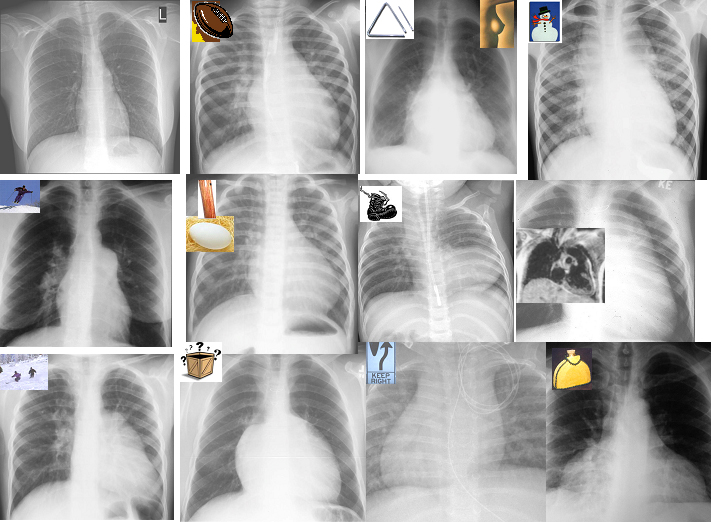
The Shapes of the Heart in Health and Disease
From top left ti right and across the rows they are: The normal heart , the “football” of LV enlargement the “triangle” or “proud breast” of RV enlargement, “snowman” of total anomalous pulmonary venous return, big PA mogul of pulmonary hypertension, “egg on its side” of D transposition of the great vessels, “boot shaped” heart seen in both pulmonary atresia and Tetralogy of Fallot, the long smooth combined Ao and PA mogul that has a differential diagnosis of L transposition, absence of the pericardium, and juxtaposition of the atrial appendages, the box shaped large heart of Ebstein’s anomaly, dextrocardia , and the water bottle” heart of a large pericardial effusion.
07197 Images are a combination of images from a personal collection and borrowed from the internet for educational purposes only. Some of the sources are unknown and are used for educational purposes alone 86774b02
TCV Links for extra info
The Cardiac Evaluation on the CXR -Lateral Exam
Normal and Abnormal
THE CV STRUCTURES VISIBLE ON THE LATERAL EXAM –
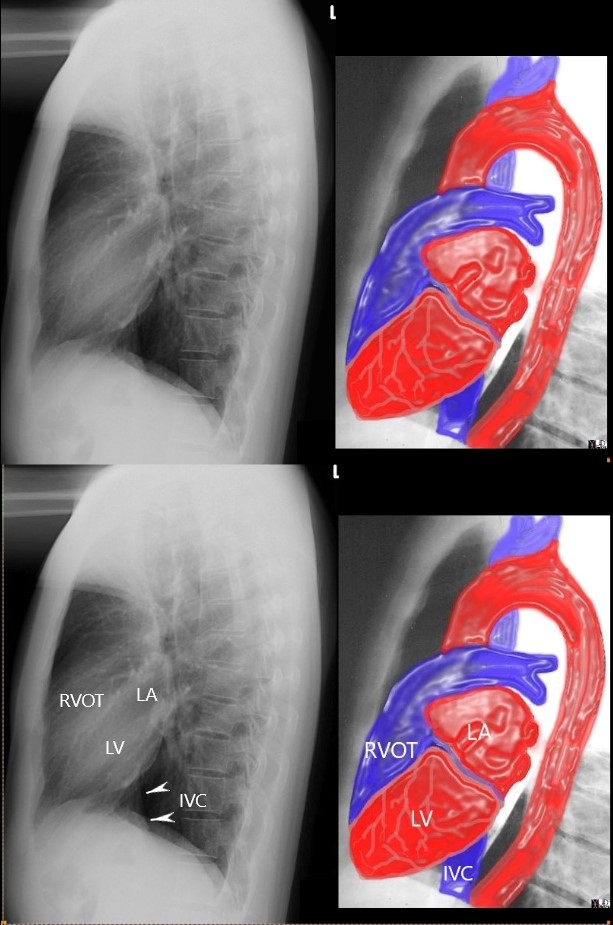
Ashley Davidoff MD
RULE OF 1/3 rds
- Normal Anteriorly
- RV takes up 1/3 of retrosternal space ((Sternomanubrial jn to xiphi)
- Inferiorly
- LV takes up 1/3 of the hemidiaphragm
- Posteriorly
- LA 1/3, LV 2/3

the anterior border of the chest is divided into thirds; 1/3 for the RVOT and 2/3 for the retrosternal air space
the posterior border of the heart is divided into thirds; 1/3 for the LA and 2/3 for the LV.
the diaphragmatic border is divided into thirds; 1/3 for the LV and 2/3 for the rest of the diaphragm
Ashley Davidoff MD
15416C02Wlateral.8 rule of thirds
- Abnormal
-
- Anteriorly
- RVE
- RV > 1/3 of retrosternal space
- RVE
- Posteriorly
- LAE
- LA >1/3 of posterior heart border
- Also elevates left main stem bronchus
- LAE
- Anteriorly
-
Normal vs Abnormal – Left Ventricular Enlargement
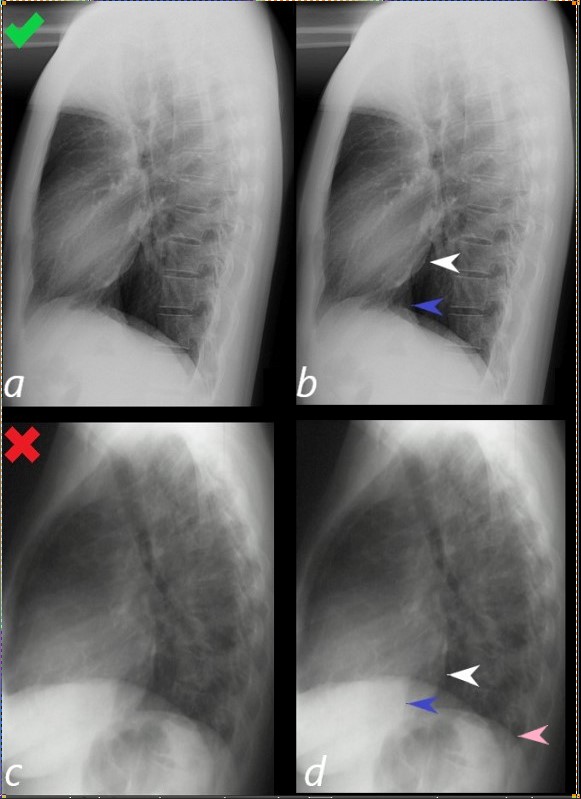 Assessment of the Size of the left Ventricle (LV) on the Lateral CXR
Assessment of the Size of the left Ventricle (LV) on the Lateral CXR
Lateral examination of a chest x-ray (CXR) shows the normal in the upper row (a,b) and the abnormal and enlarged in the bottom row (c,d).
The objective evaluation is based on the relative positioning and size of the LV (white arrowhead) in relation to the IVC, (blue arrowhead), and the left hemidiaphragm (pink arrowhead)
Ashley Davidoff MD
15416C02Wlateral LV01L.8
RVE
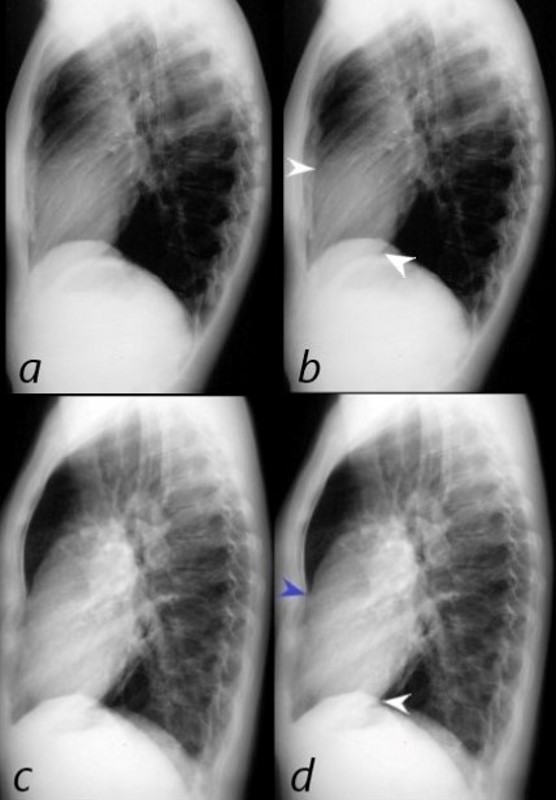 NORMAL and RVE
NORMAL and RVE
The normal lateral CXR (a,b), shows anterior and superior border of the heart (anterior white arrowhead) occupying 1/3 of the border between the sternomanubrial junction and the diaphragm.
The posterior and inferior white arrowhead shows the posterior border of the heart occupied by the RV taking up 1/3 of the distance of the diaphragm.
Images c and d represent left ventricular enlargement showing that the LV occupies about half the length of the diaphragm, (red arrowhead) while the retrosternal distance is unchanged and normal (white arrowhead).
Ashley Davidoff MD
Normal vs Abnormal – RVE and LAE
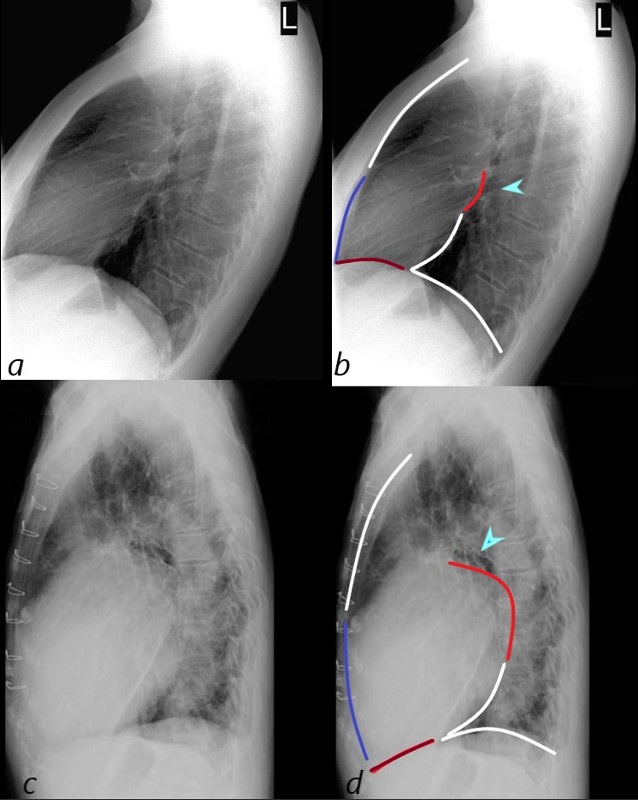 LATERAL EXAMINATION RVE AND LAE – MITRAL STENOSIS PULMONARY HYPERTENSION AND COR BOVINUM
LATERAL EXAMINATION RVE AND LAE – MITRAL STENOSIS PULMONARY HYPERTENSION AND COR BOVINUM
71 year old Asian female with rheumatic heart disease dominated by calcific mitral stenosis mild MR, moderate tricuspid regurgitation
Right Atrial Disease on the Lateral _ Only when it is very enlarged
Where is the Right Atrium?
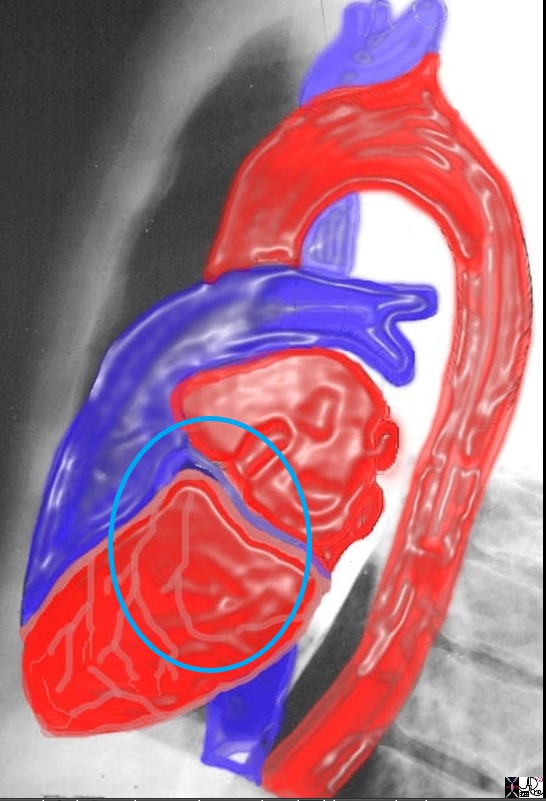
In the normal patient the RA is not border forming and is not visible. It lies to the right and slightly inferior and anterior to the left atrium, posterior and superior to the right ventricle, and to the right and superior to the left ventricle
Ashley Davidoff MD
- Axial Imaging Explaining why the RA cannot be see on the Lateral –
- since it is neither anterior nor posterior border forming
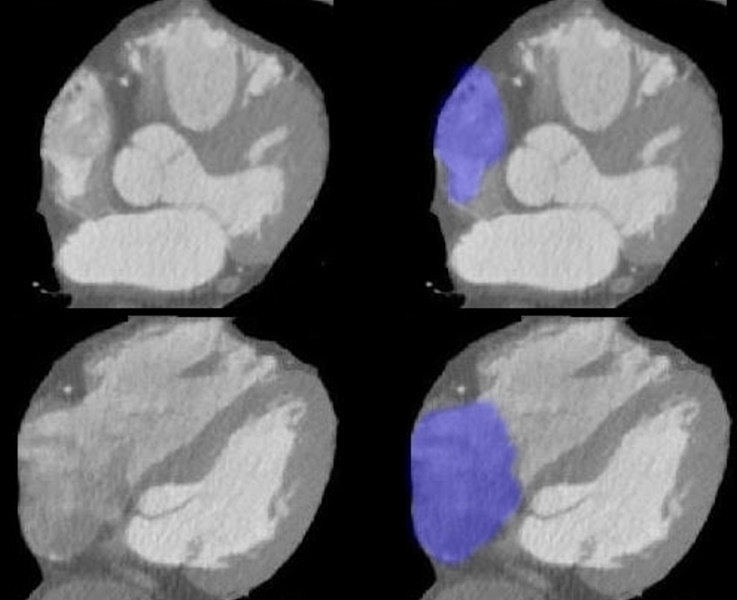
Axial images through the RA show the right atrial appendage in the top row and the body of the RA in the bottom row, neither of which would be visible on the lateral exam.
Ashley Davidoff MD
- When the RA enlarges-
- it moves laterally and anteriorly see CT below so that it can now be an anterior border forming structure
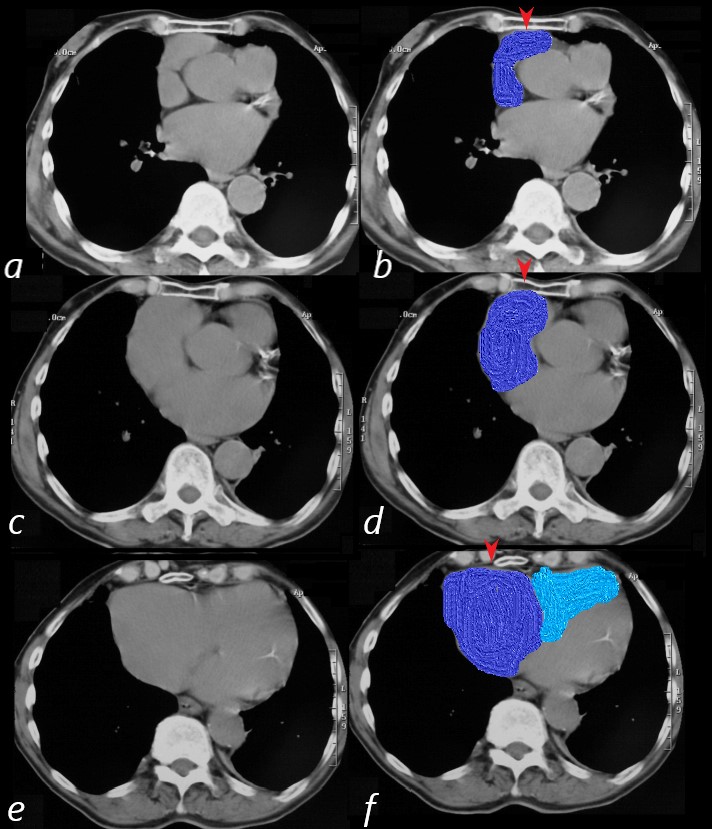
83-year-old male with significantly enlarged right atrium, as well as a mildly enlarged left atrium with evidence of CAD, atrial fibrillation and hypertension.
On CT scan the right atrium and appendage (blue overlay (b,d,f) are positioned against the anterior chest wall and sternum (red arrowheads). On the superior most images (b,d) the RV is not present and only takes up a retro-sternal position alongside the right atrium on the most inferior image (f)
Ashley Davidoff MD
RAE on the Lateral
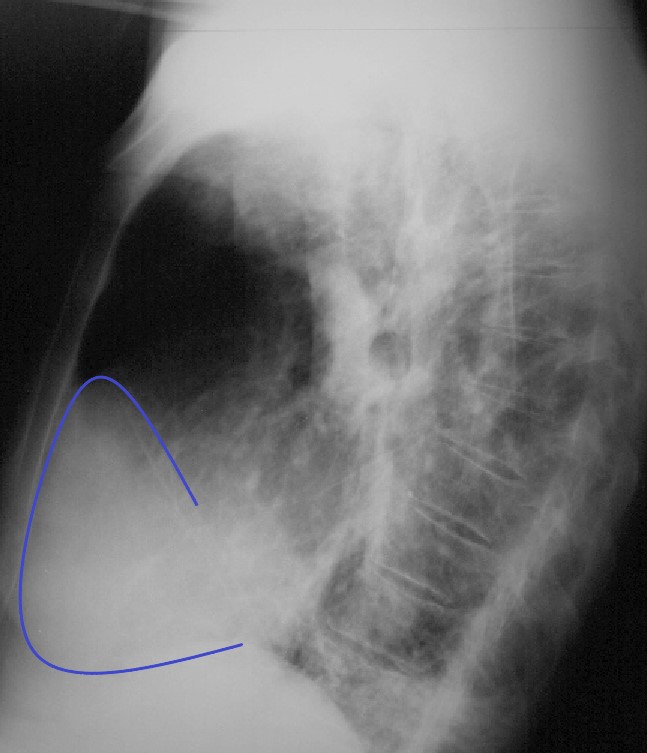
83-year-old male with significantly enlarged right atrium, as well as a mildly enlarged left atrium with evidence of CAD, atrial fibrillation and hypertension.
On the lateral CXR, the right atrium the blue line overlay indicates the position of the RV against the anterior chest wall. In addition, the right atrial appendage is so large (see CT below) that it lies against the sternum. The RA therefore occupies the entire retrosternal air space and results in decrease of the retrosternal airspace. This is the rare instance when the RA shares with, but dominates the anterior retrosternal position with the RV.
Ashley Davidoff MD
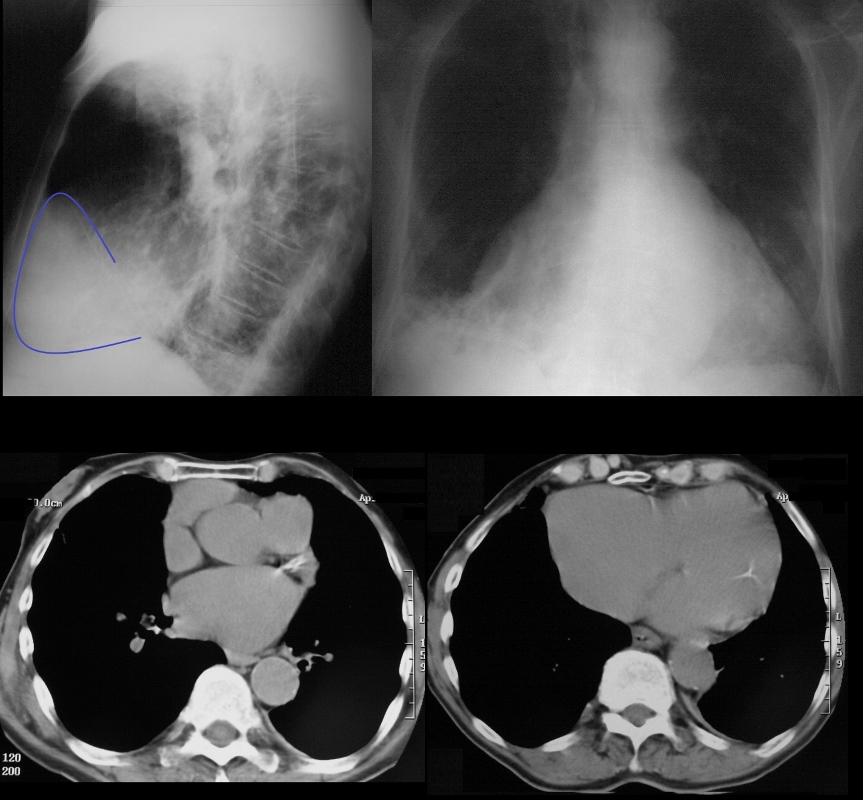
83 year old male with significantly enlarged right atrium, as well as a mildly enlarged left atrium with evidence of CAD, atrial fibrillation and hypertension.
On CT scan the right atrium is positioned against the anterior chest wall. In addition, the right atrial appendage is so large that it lies against the sternum as well resulting in a decrease in the retrosternal air space. On the lateral, the cardiac shadow takes up more than 1/2 of the diaphragm. In this uncommon instance this finding is caused by the enlarged right atrium rather than LVE
Ashley Davidoff MD