- Buzz Words
- Alveolar destruction
- Loss of elasticity
- starting in the respiratory bronchiole and progressing toward the proximal and central portion of the secondary lobule
Normal (above) And Centrilobular Emphysema Starting at the Respiratory Bronchiole

Image on the left shows normal size and appearance of terminal bronchioles and alveoli. On the right the image shows the effects on the respiratory bronchioles and when severe, on the alveoli as well
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Definition
- Emphysema is an inflammatory disease of the lung
- characterized
- alveolar and small vessels destruction with
- Loss of elasticity
- starting in the respiratory bronchiole and progressing toward the proximal and central portion of the secondary lobule
- clinically characterised by
- shortness of breath, and other respiratory problems.
- characterized
- Caused by
- smoking
- Results
- Structurally
- alveolar wall destruction
- progressive expansion of the acinus without fibrosis,
- decreased lung elasticity,
- architectural distortion of the capillary bed.\ loss of functioning surface are
- alveolar wall destruction
- Clinically
- presents in middle age and older,
- as a barrel chested
- “pink-puffer,
- breathing often with pursed lips, with
- insidious and unrelenting dyspnea.
- Diagnosis
- CXR shows
- hyperinflated lungs, with
- propensity for the upper lobes,
- flattened diaphragms and a
- s carinatum)”barrel chest”
- CT
- Swiss Cheese appearance
- areas of low attenuation correspond to the regions where the alveoli and bronchioles are enlarged due to destruction
- resemble the appearance of holes or gaps, similar to the holes in Swiss cheese.
- Swiss Cheese appearance
- Lug Function tests
- reduction in the maximal expiratory flow during forced exhalation. (decreased FEV1)
- Treatment
- bronchodilators,
- diuretics,
- corticosteroids,
- antibiotics
- low-flow oxygen,
- pulmonary rehabilitation.
- CXR shows
- Structurally
Centrilobular Emphysema Dilated Air Spaces Localized around a Bronchovascular Bundle.
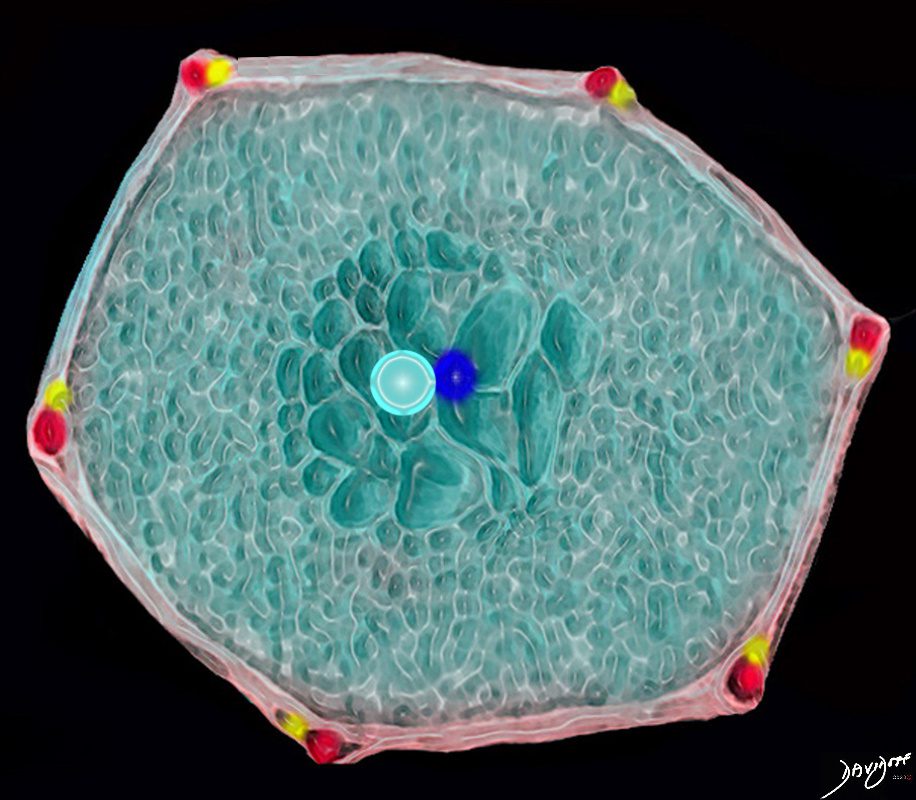
This drawing shows a secondary lobule with centrally located dilated airspaces starting with the respiratory bronchiole and extending to the proximal structures including the alveolar ducts, sacs and alveoli
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Alveolar Wall Destruction Localized around a Bronchovascular Bundle.
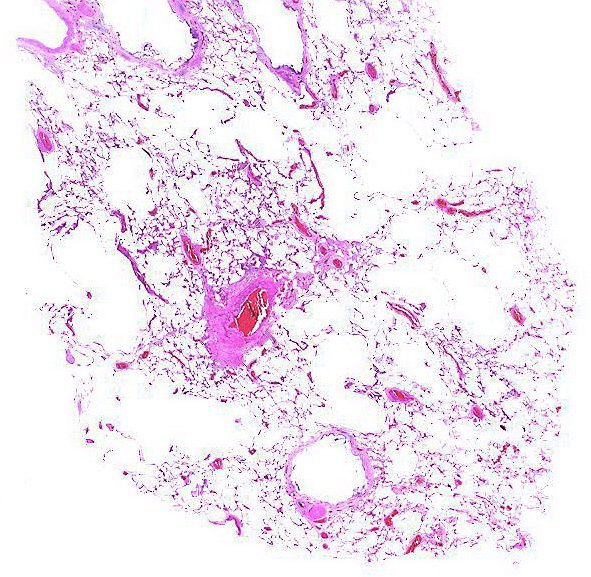
Alveolar wall destruction is localized around a bronchovascular bundle.
Courtesy Yale Rosen MD
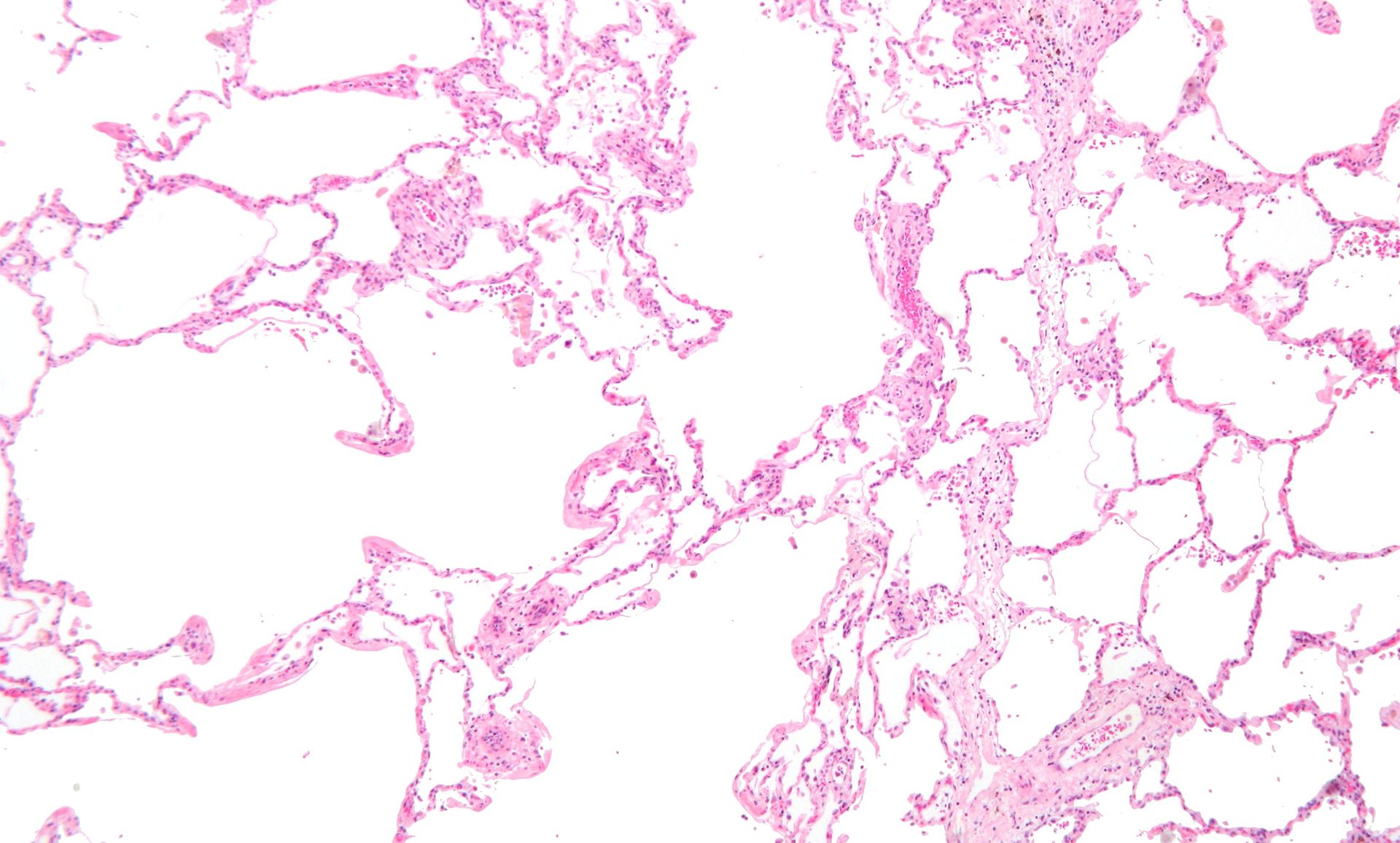
Low magnification micrograph of emphysema. H&E stain. The left of image shows severe emphysema (large empty spaces). The lung tissue on the right of the image has relative preservation of the alveoli. The top of the image is very near the pleural surface.
Courtesy Nephron
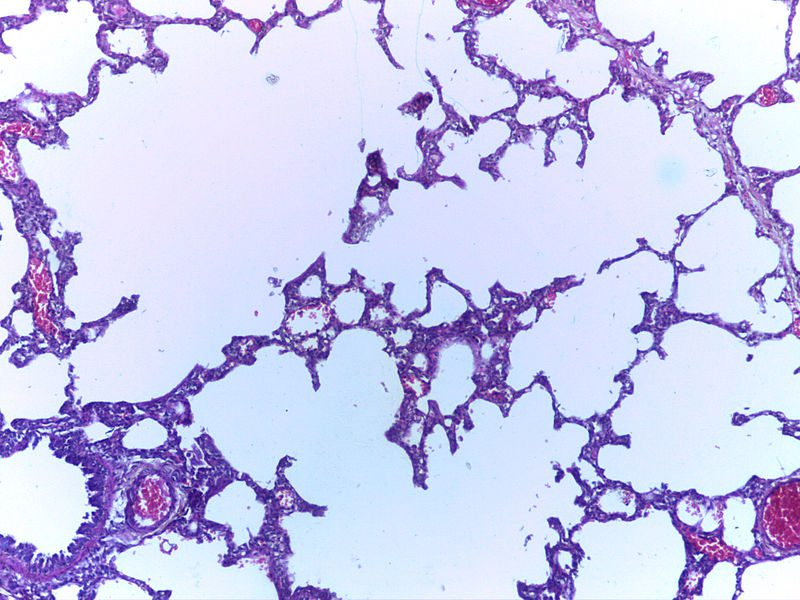
Micrograph of empysema lung showing dialated, large alveoli separated by thin septa. Some septae are ruptured and appear to be floating in the alveloar spaces. Grossly emphysematous lung appears pale and voluminous.
Source DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, CALICUT MEDICAL COLLEGE
Gross Anatomy of Upper Lobe and Apical Centrilobular Emphysematous Changes and Normal Lung Below
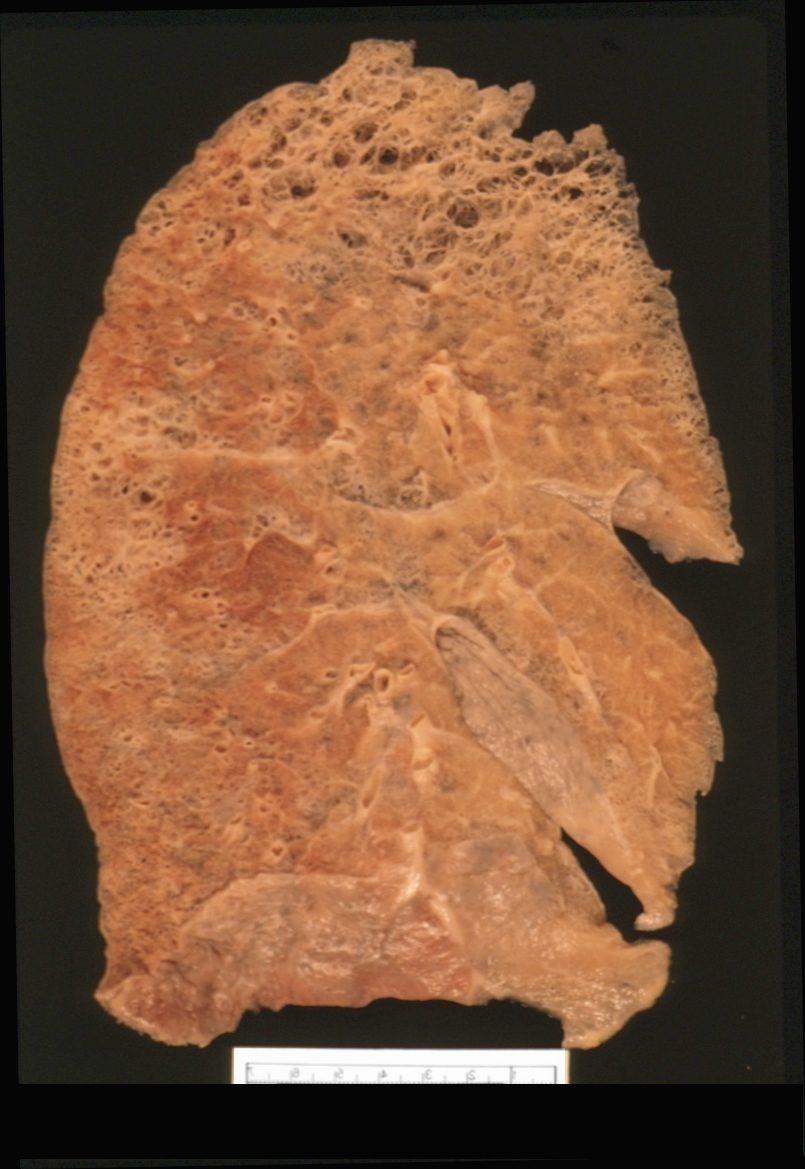
Ashley Davidoff MD
Normal Secondary Lobule
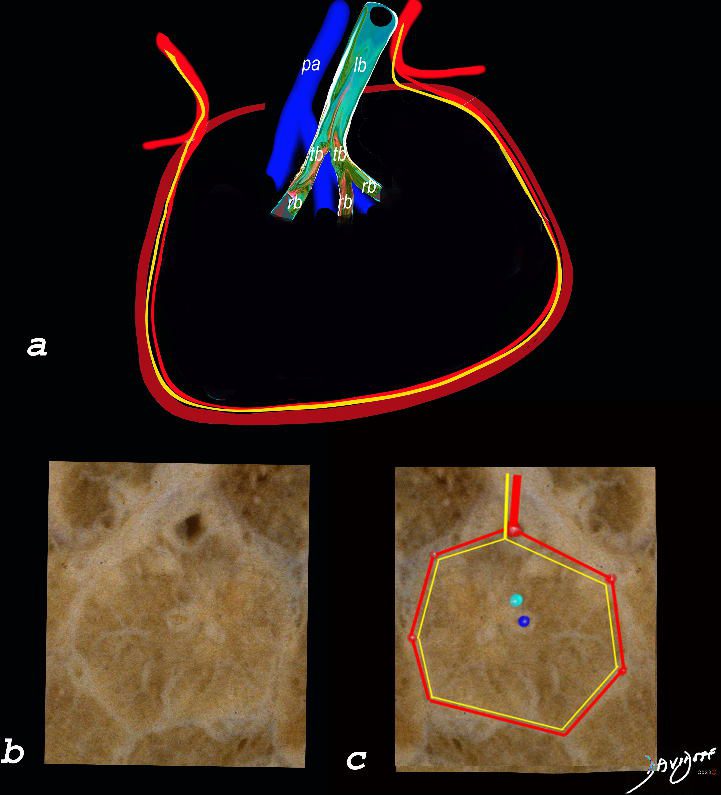
The top image (a) shows an anatomic drawing of a secondary lobule of the lung subtended by a lobular bronchiole (lb) and arteriole (pa). The interlobular septum contains the venule (red) lymphatic (yellow) and septum (maroon)
The anatomical specimen of the lung (b) shows normal intralobular parenchyma while image c shows the centrilobular arteriole (navy blue) and centrilobular bronchiole (teal) and interlobular venule (red) and lymphatics (yellow) The interlobular septum is slightly thickened
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Normal CT
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Centrilobular Emphysema Gross Pathology
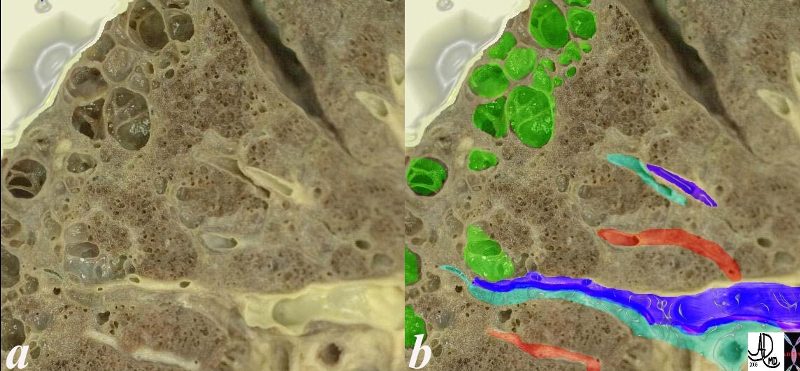
This is an image of an emphysematous lung. Note the larger air spaces where the septae between the alveoli, alveolar sac alveolar ducts and respiratory bronchioles have been broken down (green).
The bronchovascular bundle consisting of the arteriole (navy blue) and bronchiole (teal) subtends the secondary lobule. The pulmonary venule (red) originates from interlobular septa where it is intimately related to the lymphatics. 19932e
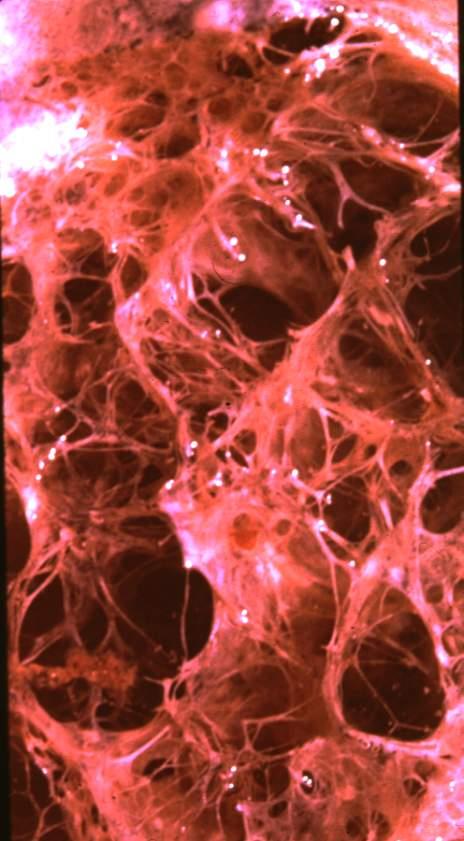
Ashley Davidoff MD 19.jpg
Electron Microscopy
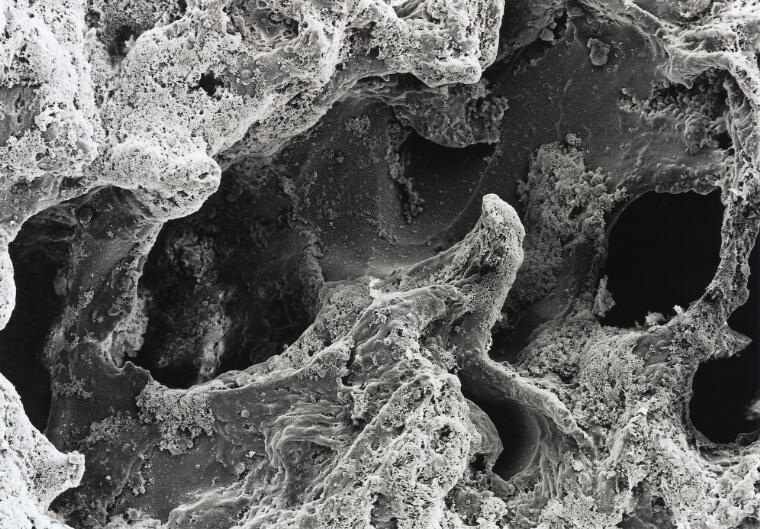

David Gregory & Debbie Marshall
Licence: Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
CXR Emphysema
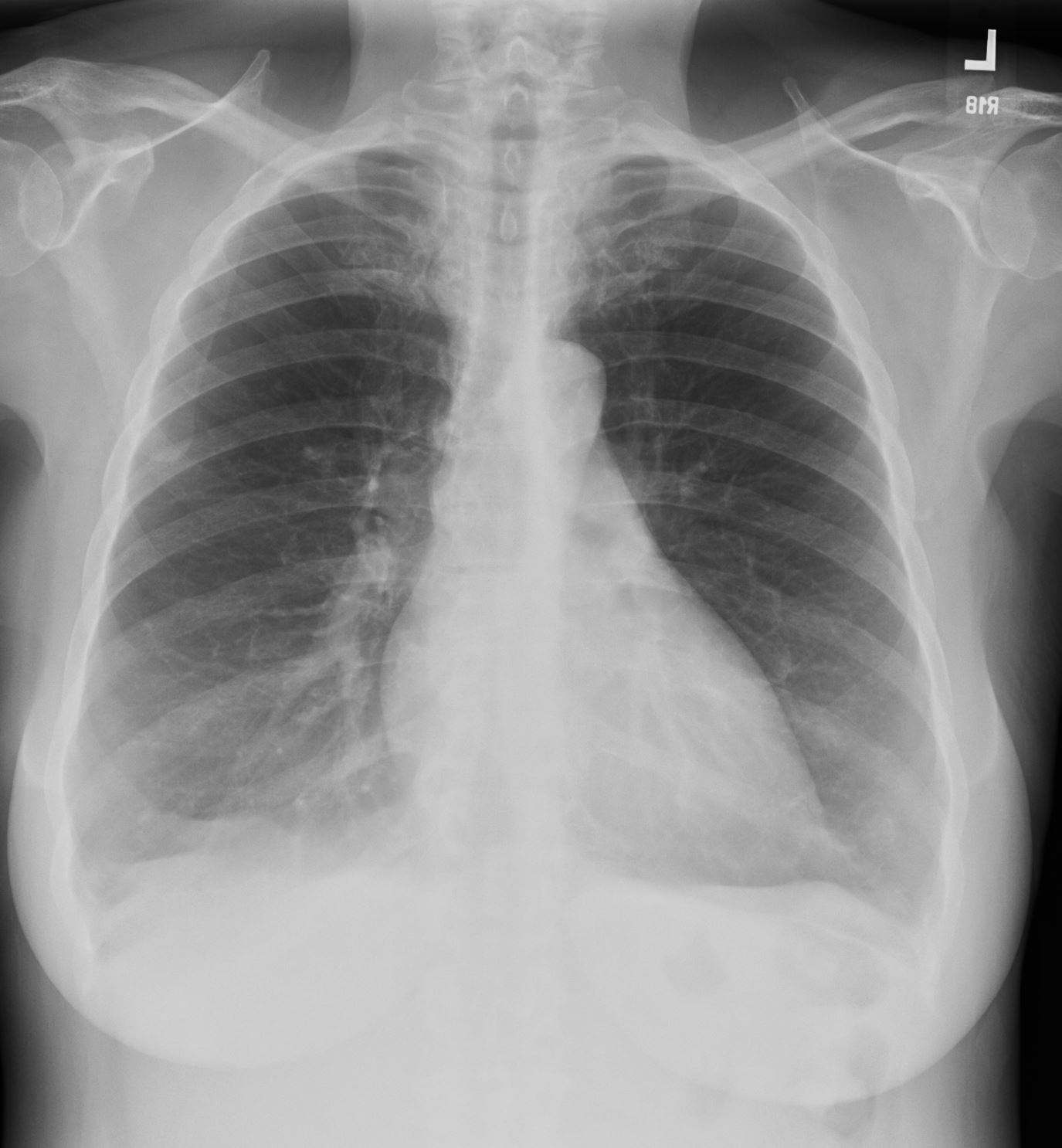
Flattened and Partially Inverted
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
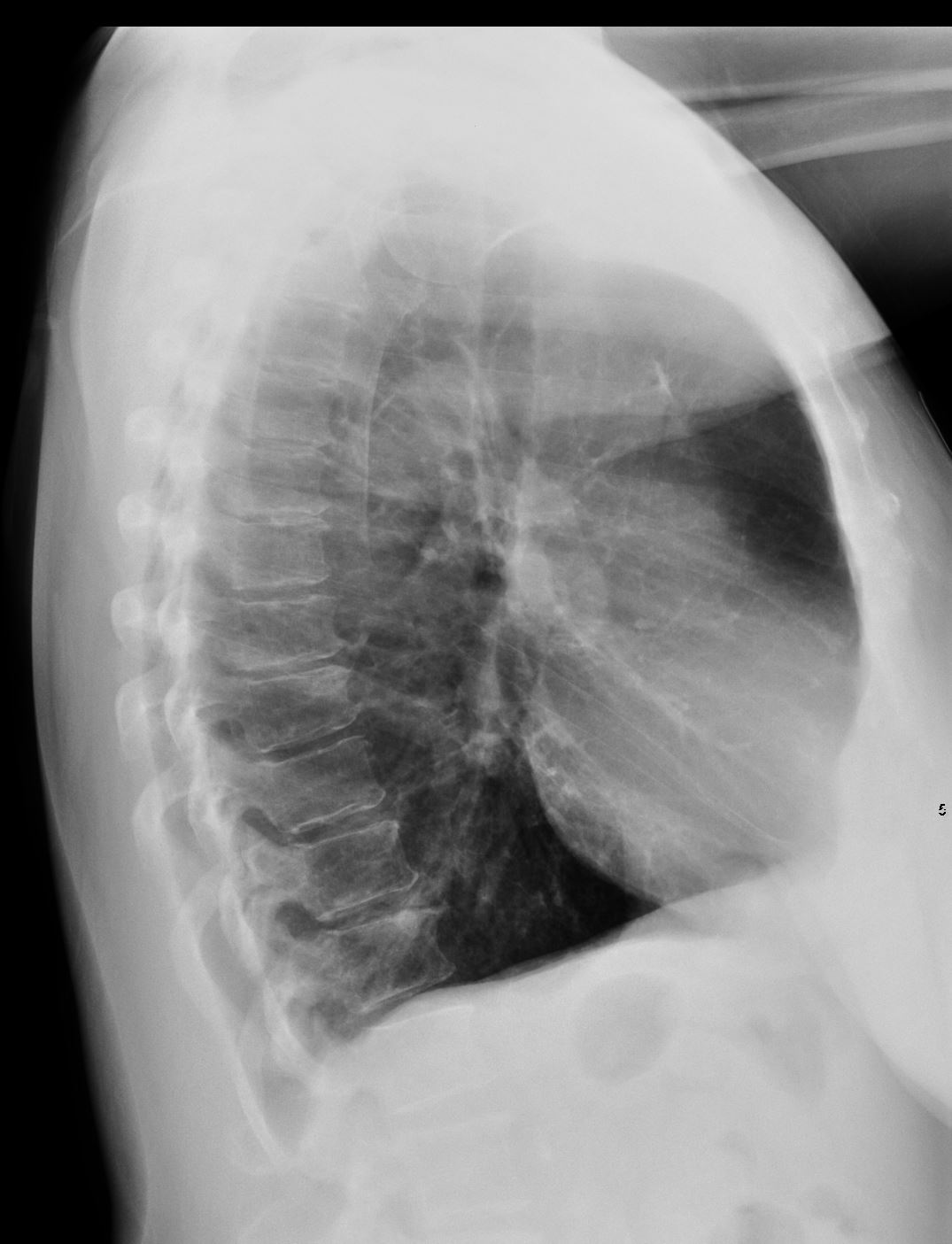
Flattened and Partially Inverted
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net

#signs in medicine
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
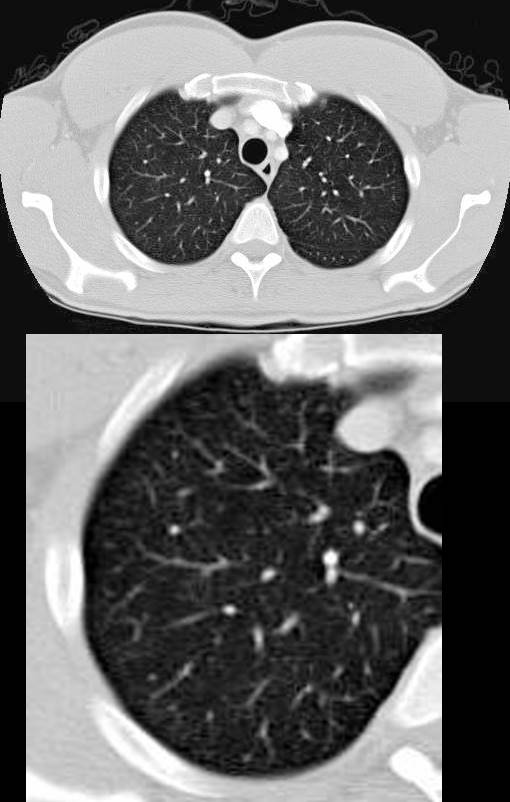
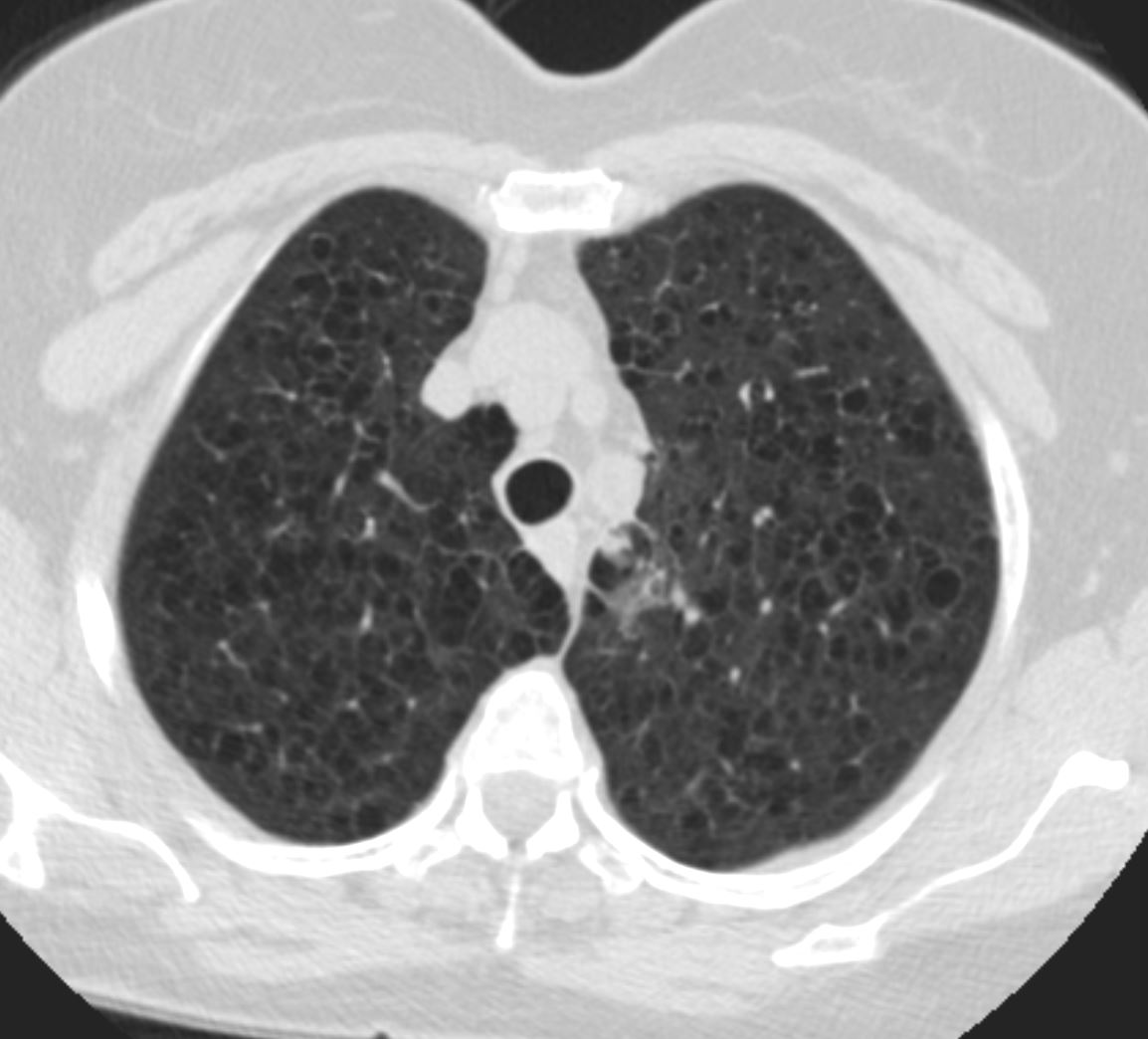
CT Scan of Centrilobular Emphysema Swiss Cheese
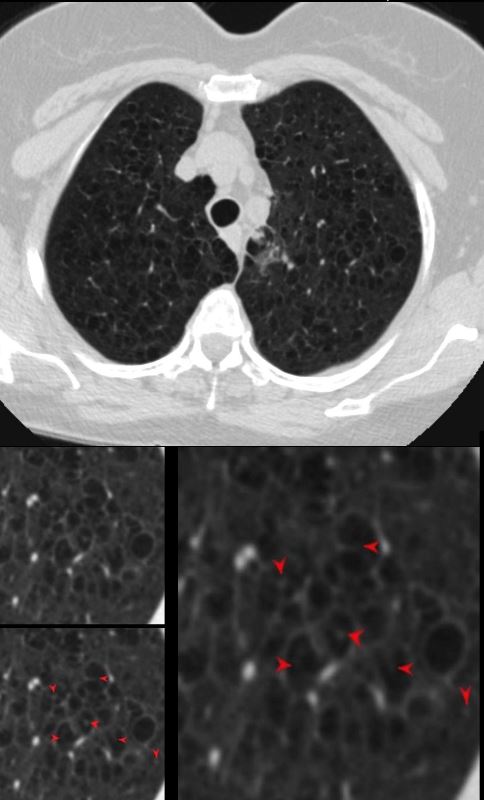
The axial CT of a 66 year old female with moderately severe centrilobular emphysema of the upper lobes. The magnified views show the focal central punctate density of the pulmonary artery indicating the presence of the central bronchovascular bundle (red arrow)
Ashley Davidoff MD The Common Vein.net
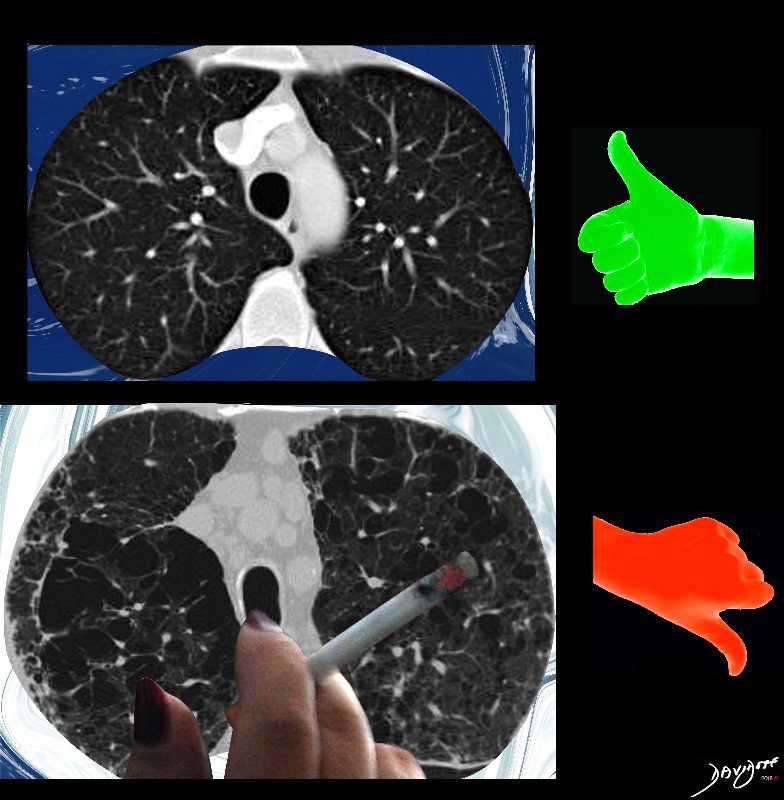
Side by Side Normal and Centrilobular Emphysema
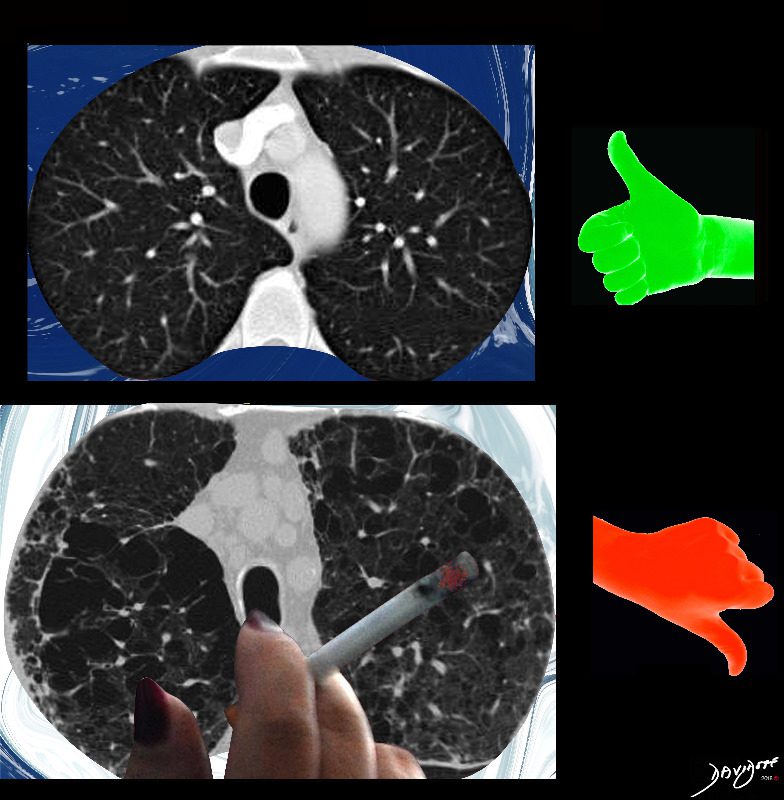
The imaging difference between healthy lungs (thumbs up) and emphysematous lungs (thumbs down)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVeein.net lungs-0071
key words emphysema, CTscan cigarettes smoking
Pathophysiology of Cigarette Smoking on Medium Sized Airways, Small Airways and Alveoli
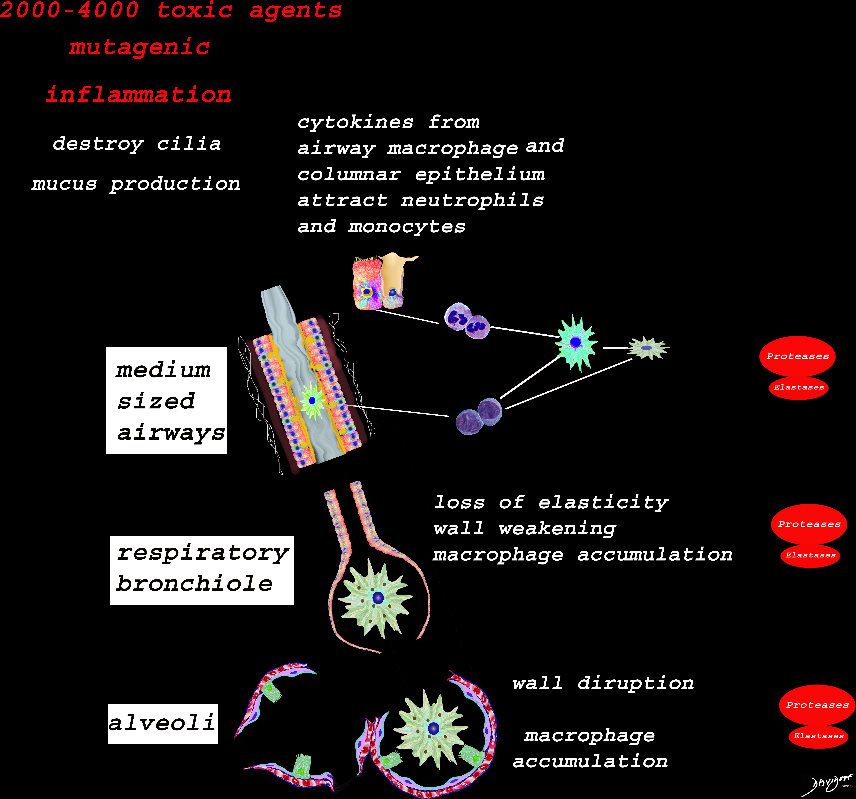
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00683
Structural Effects of Smoking on the Respiratory Bronchiole , Alveolar Ducts and Alveolar Sacs
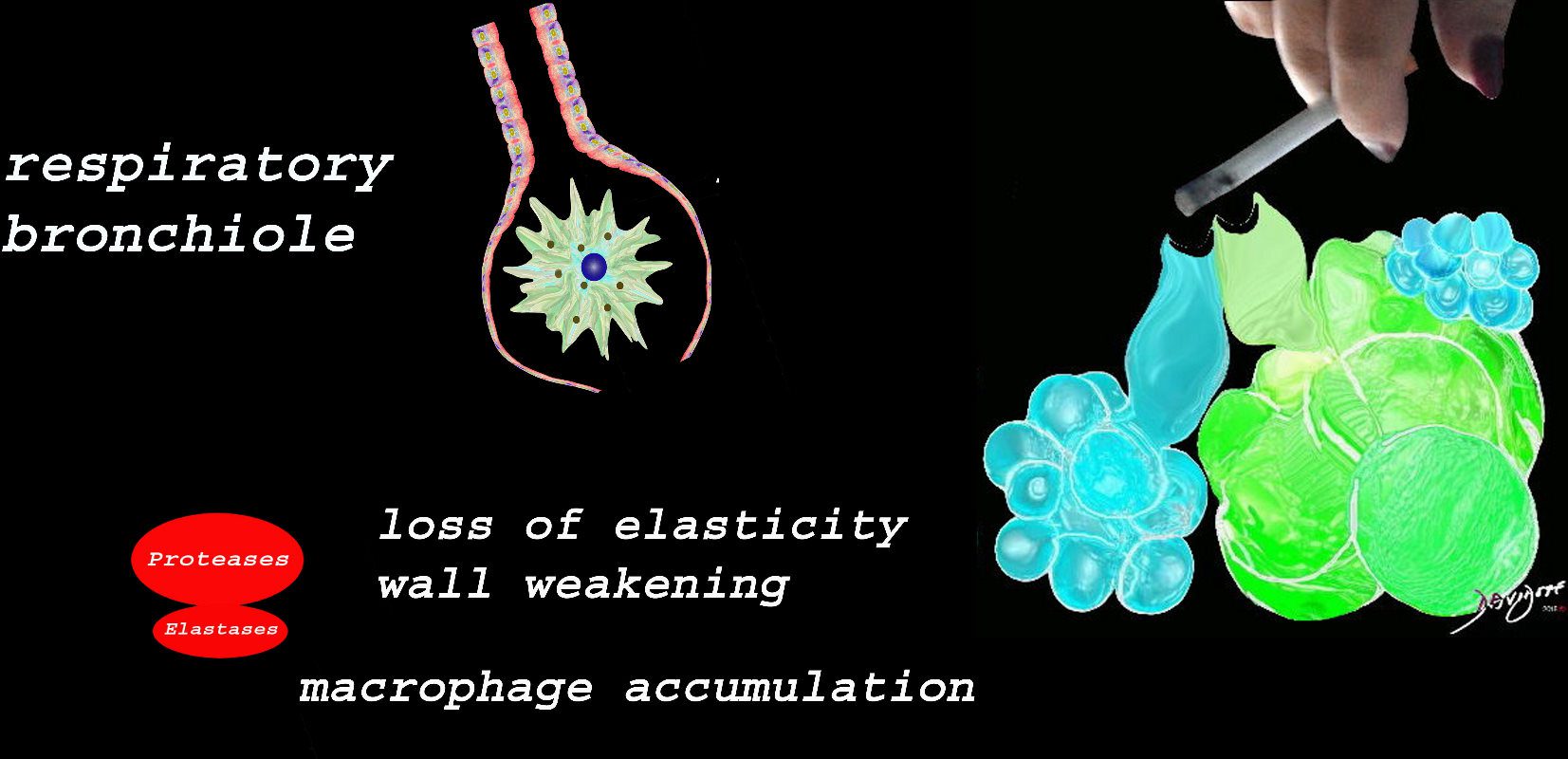
At the level of the membranous airways the effect is predominantly related to the loss of elasticity, vessel destruction and aberrant accumulation of smoking related macrophages.
The weakening and destruction results in emphysema and the abnormal accumulation of smoking related macrophages relates to DIP
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00685
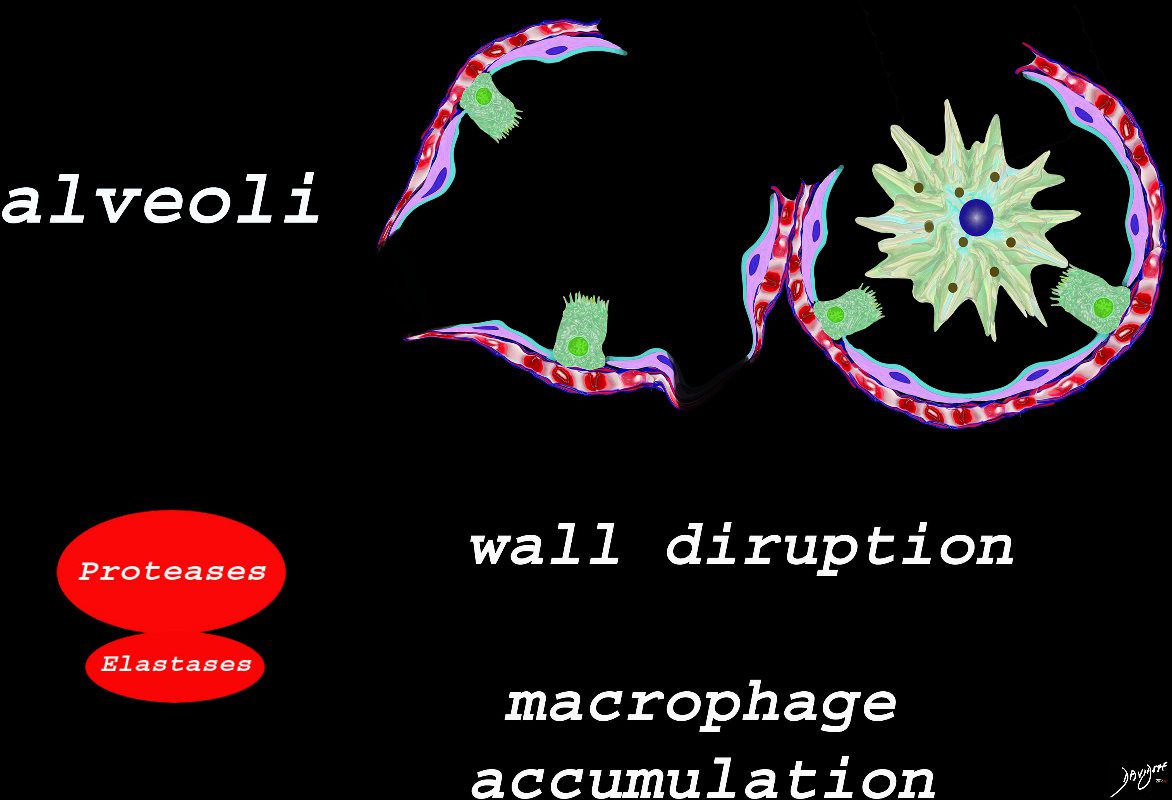
The effect of the proteases and and elastases cause destruction of the alveoli and loss of elasticity, and therefore overall function. The destruction leads to bullous disease
The accumulation of smokers macrophage, and in the case of Langerhans cell histiocytosis leads to space occupation of the alveoli also reducing function
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00687
It Starts at the Respiratory Bronchiole

Image on the left shows normal size and appearance of terminal bronchioles and alveoli. On the right the image shows the effects on the respiratory bronchioles and when severe, on the alveoli as well
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff Art TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
Emphysema
- Centrilobular emphysema is an
- obstructive lung disease
- caused by
- obstructive bronchiolitis affecting the
- region of the proximal respiratory bronchiole
- allowing air into the secondary lobule but inhibiting
- exhalation with resultant
- air trapping and destruction of lung tissue
- obstructive bronchiolitis affecting the
- Destruction of small airways can lead to the formation of large bullae
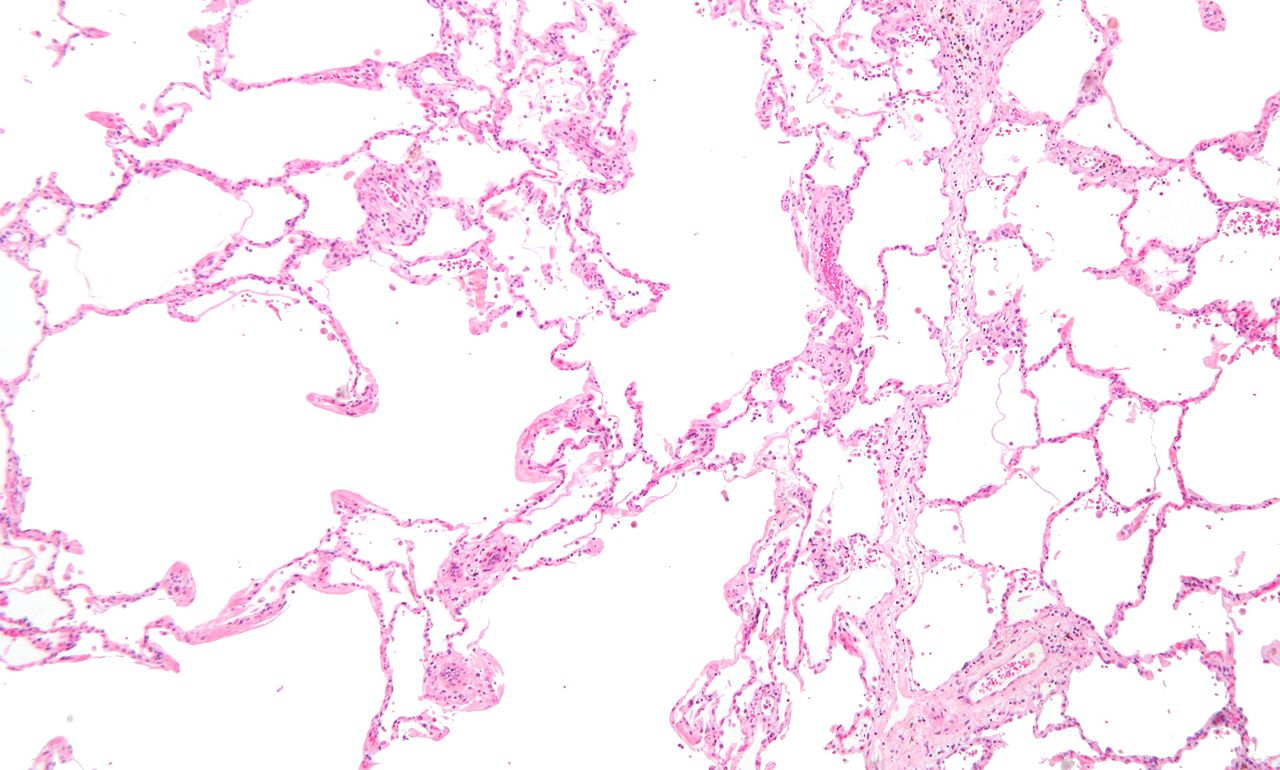
Micrograph showing emphysema (left – large empty spaces) and lung tissue with relative preservation of the alveoli (right)
Courtesy Nephron

Giovanni Battista Morgagni, who made one of the earliest recorded descriptions of emphysema in 1769
Public Domain
References and Links
