- is a pulmonary infection
- caused by
- an atypical yeast-like fungus
- most common opportunistic infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
- typically occurs at CD4 counts <200 cells/mm
- (btw Pneumocystis carinii has been reclassified as Pneumocystis jiroveci)
- virtually never seen in immunocompetent individuals
- an atypical yeast-like fungus
- resulting in
- pulmonary infection
- insidious, dyspnea, non productive cough
- but can be more dramatic
- life threatening
- dx
- BAL (85-90 sensitivity)
- The Organism
-
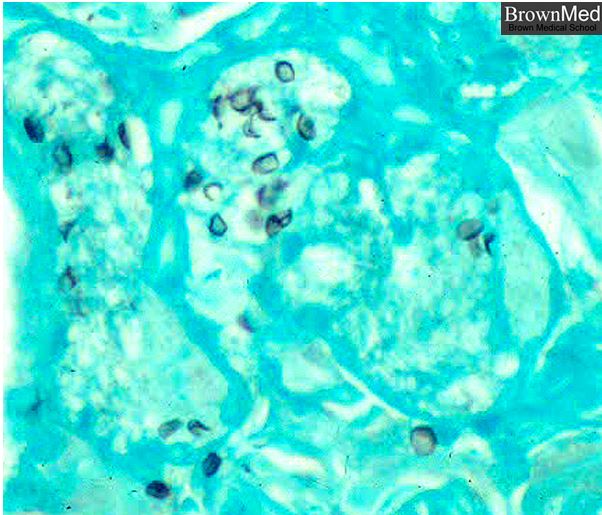
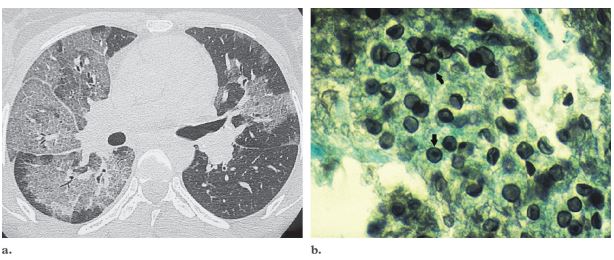
In this GMS stained section the organisms stain black.
From the slide collection of the late Dr. Charles Kuhn
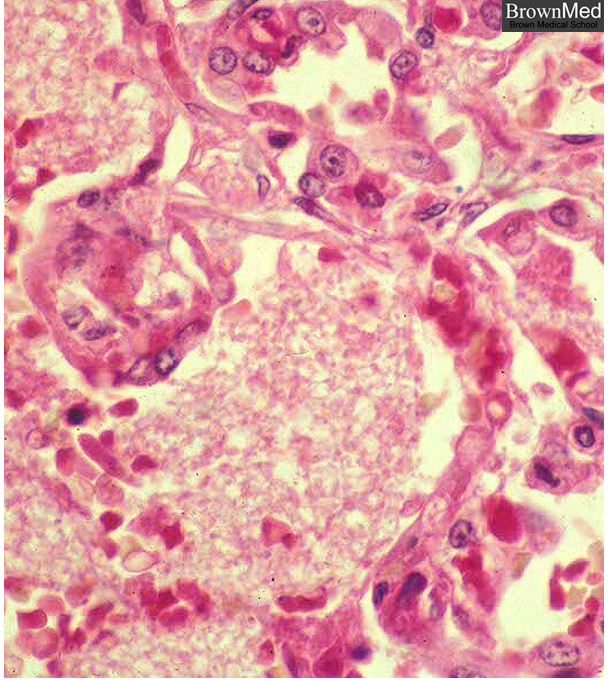
Brown.edu Department of PathologyResponse by the Lungs – Fluid Filled Exudate

The alveoli are filled with an exudate. The apparently empty spaces in the alveoli in this H&E stain represent P. carinii. This organism usually offers no hazard to the immunocompetent.
From the slide collection of the late Dr. Charles Kuhn
Brown.edu Department of Pathology
- pulmonary infection
54420
Radiology
- 90% of chest radiographs in patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia are abnormal
- Commonly Non Specific
- Characteristic Features
- shape – reticular changes
- position – perihilar
- character – small cysts – pneumatoceles
- character – – subpleural blebs
- associated fx –
- uncommon pleural effusion
- CD4 counts <200/mm3
Perihilar Reticular Changes

Courtesy Priscilla Slanetz MD TheCommonVein.net 30662 see lateral image 30664 key words RS lungs interstitium infiltrate pneumonia hilum hilar PCP infection pulmonary imaging plain film CXR
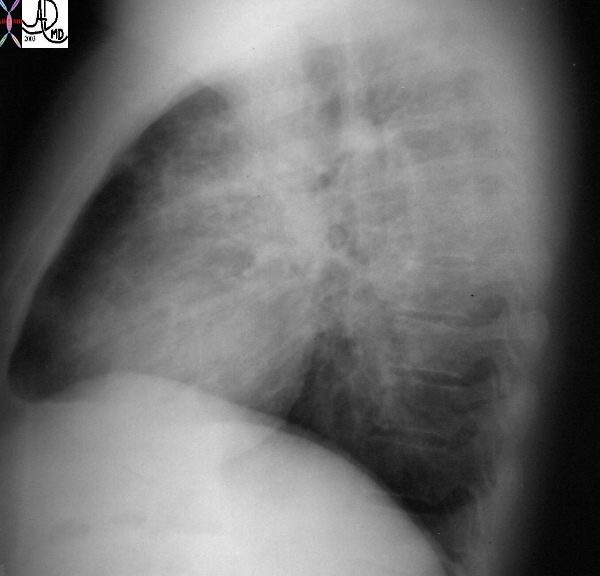
Reticular Pattern

46 year old female with HIV presents with dyspnea. CXR scan shows a diffuse reticular pattern with suggestion of upper lobe predominance
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 30755c
Pneumonic Infiltrate
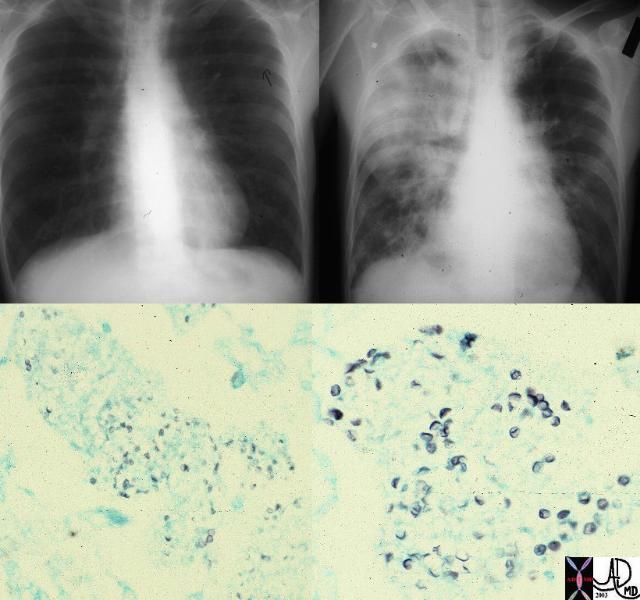
This combination is from a patient with immune deficiency shows a progression of disease from near normal CXR to a consolidated right lung dominating in the right upper lobe. Pneumocystis (lower images) was identified (GMS stain) as the incriminating organism. The most frequently described appearance on chest radiograph is a diffuse, bilateral interstitial infiltrate, consisting of fine-to-medium reticular interstitial change. .
Keywords lungs pulmonary consolidation infiltrate RUL infection pneumonia imaging plain film CXR histopathology
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 78378
Another Patient with a Pneumonic Infiltrate
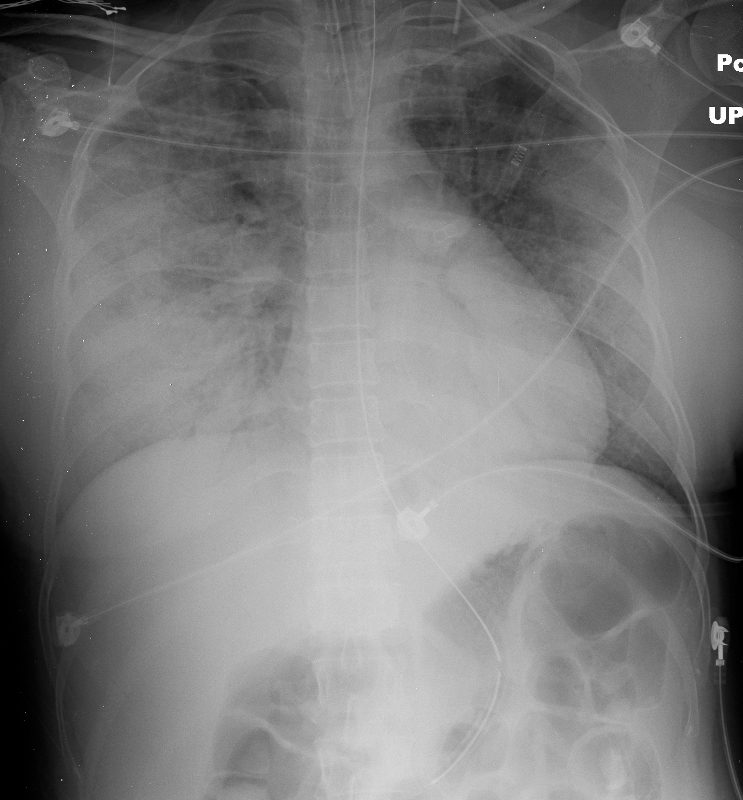
50 year old female with HIV presents with dyspnea. CXR shows extensive multifocal pneumonia with air bronchograms in the right upper and lower lobes as well as the left lower lobe. The patient required intubation
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 134685
- Position – Depends on use of prophylactic aerosolized meds
- On Meds –
- more prominent
- upper lobes
- more prominent
- Not On Meds More prominent
- lower lobes
- peripheral sparing – perihilar
- On Meds –
- Character
- ground glass
- reticular opacities or
- septal thickening
- crazy paving
- pneumatoceles 30%
- varying
- size
- shape
- wall thickness
- varying
- consolidation
- often patients without HIV
- caused by inflammatory response
- nodules
- sometimes cavitate
- lymphadenopathy
- pleural effusion uncommon
Examples
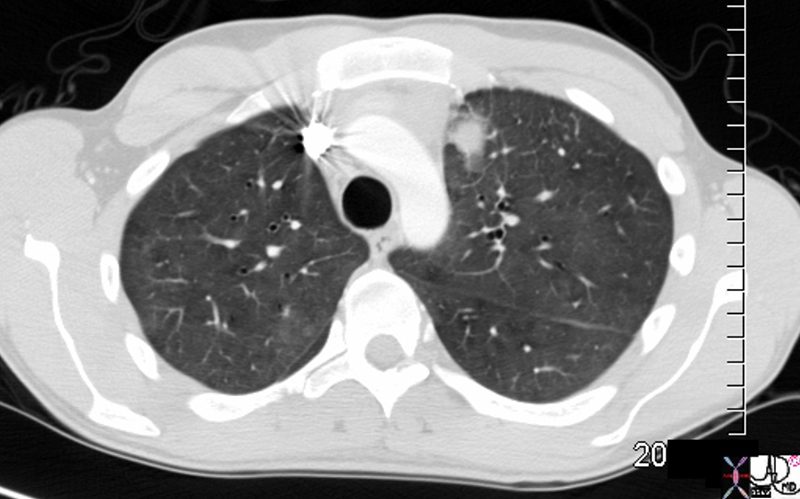
Reticular Pattern with Ground Glass Dominantly in the Lower Lobes

48 year old male with HIV presents with dyspnea. CT scan shows a reticular pattern within ground glass background, dominantly in the lower lobes, and affecting the right lower lobe more than the left
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 30755c
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 78378
Crazy Paving
Rossi, S.E et al “Crazy-Paving” Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: RadiologicPathologic Overview Radiographics Volume 23 – Number 6, 2003
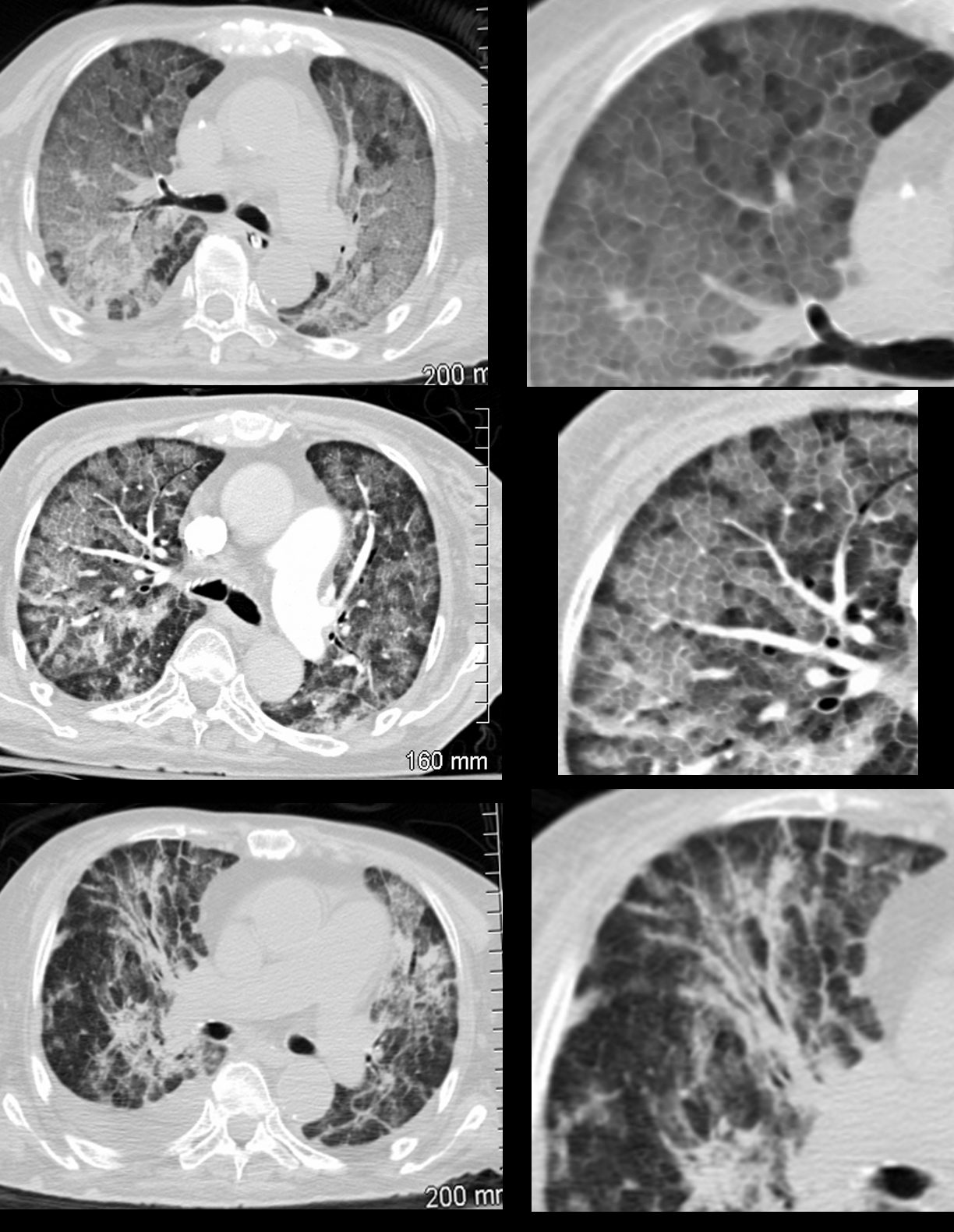
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 30755c
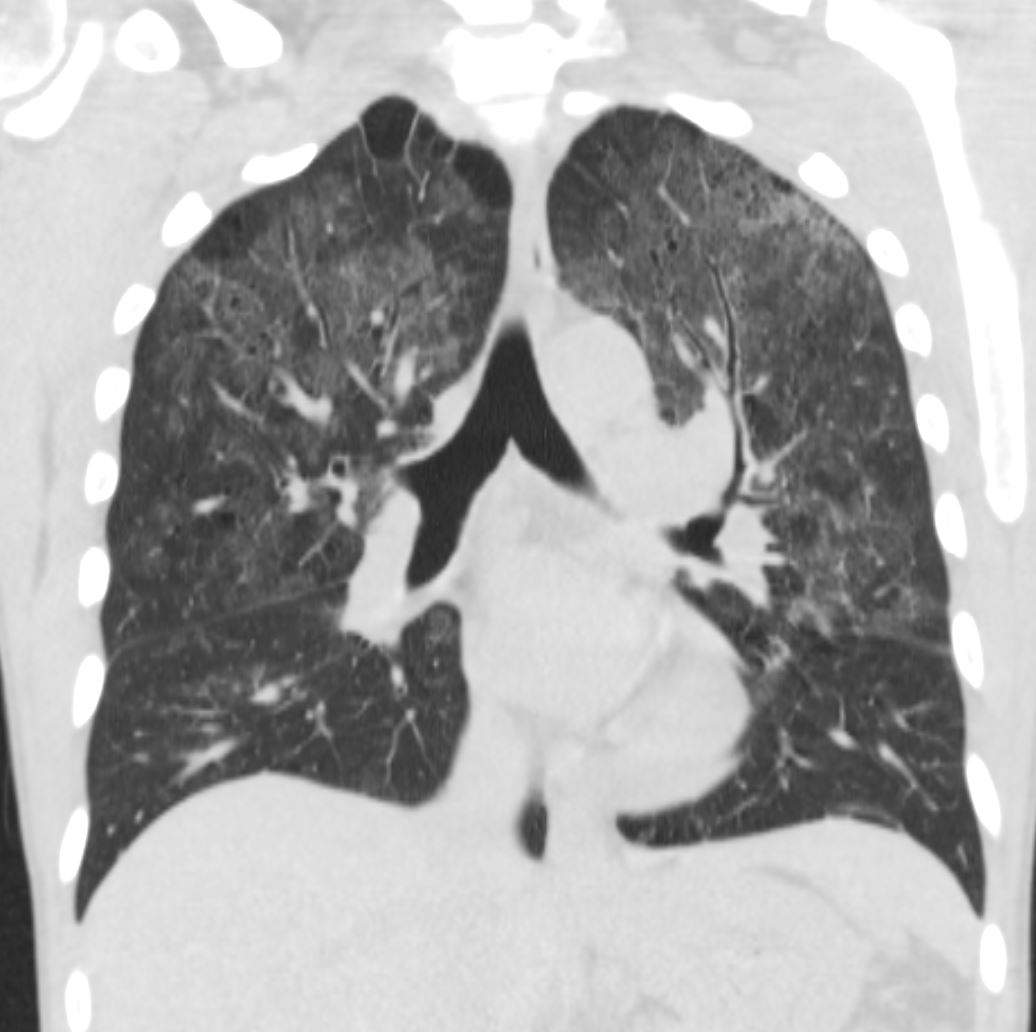
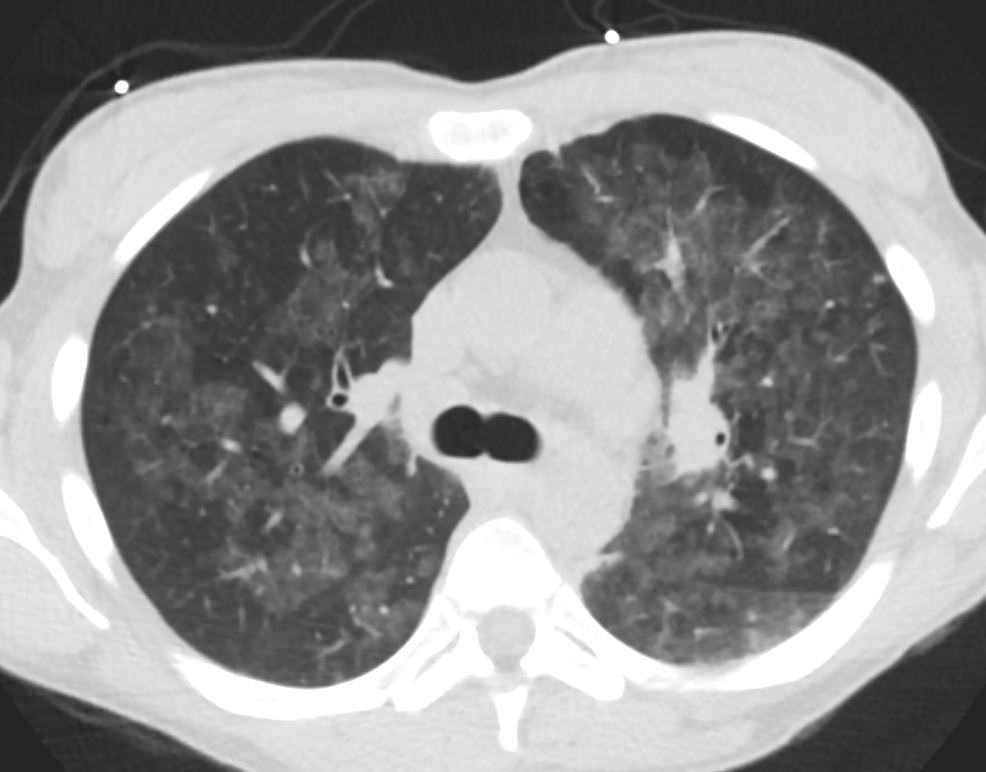
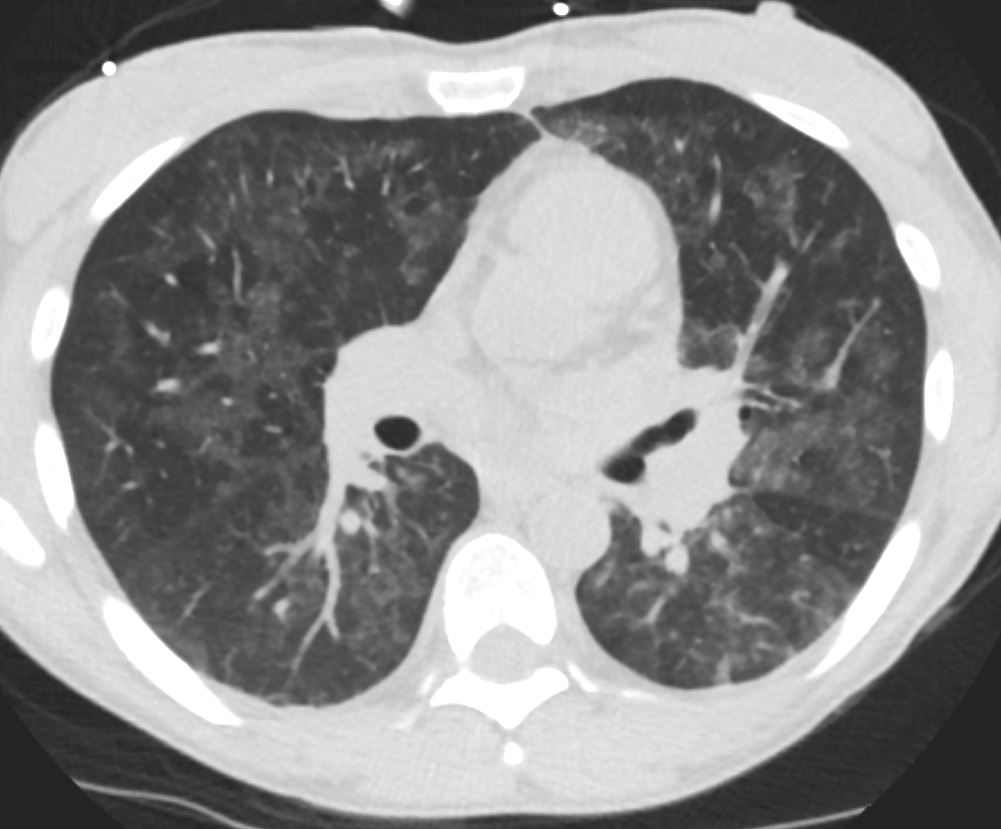
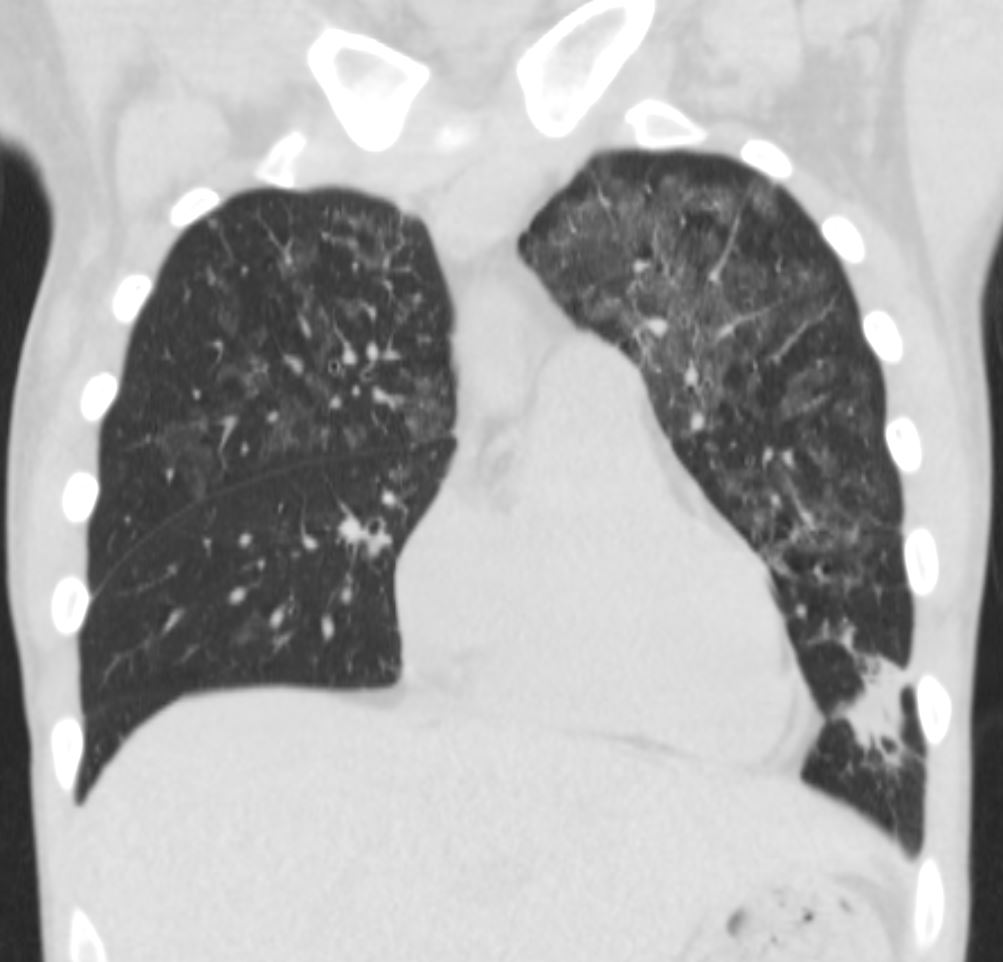
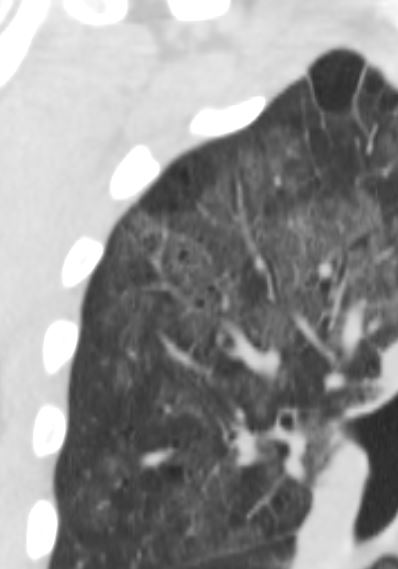
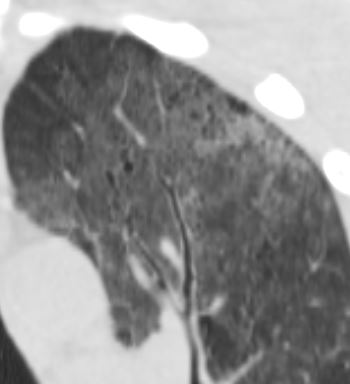
- Cysts
- 33%.
- in the acute or
- postinfective
- range in
- number – commonly multiple
- size,
- shape, and
- position- predilection for the upper lobes.
- Cause
- unclear,
- ? release of elastase from alveolar macrophages,
- ? vascular invasion with infarction;
- ? cavitation obstruction of small airways,
- a ball-valve effect.
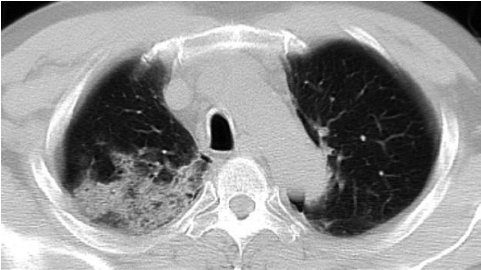
Lu, Pu-Xuan, et al Correlation between imaging features of Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonitis (PCP), CD4+ T lymphocyte count, and plasma HIV viral load: A study in 50 consecutive AIDS patients Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery 2(2):124-9, June 2012
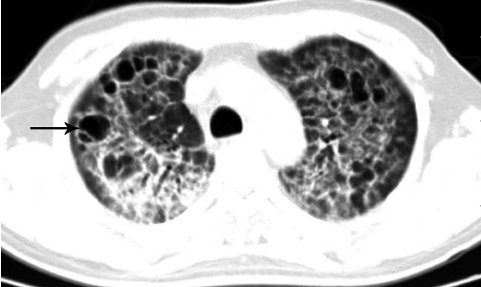
Lu, Pu-Xuan, et al Correlation between imaging features of Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonitis (PCP), CD4+ T lymphocyte count, and plasma HIV viral load: A study in 50 consecutive AIDS patients Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery 2(2):124-9, June 2012
35M with small PCP cysts

Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net

Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net

Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net

Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
Ashley Davidoff
thecommonvein.net
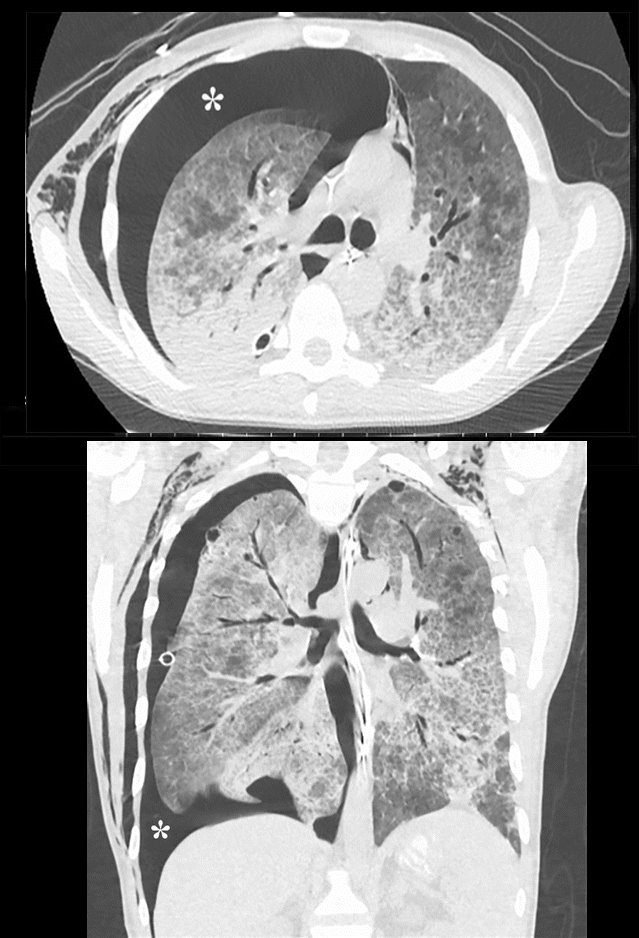
Spontaneous pneumothorax
- feature of PCP infection,
- incidence 35% in patients with cysts
- frequently bilateral
- often refractory to chest tube Rx,
- frequently need surgery eg pleurodesis
- associated higher mortality rate,
- especially in patients on ventilation.
Parekh, M et al Review of the Chest CT Differential Diagnosis of Ground-Glass Opacities in the COVID Era Radiology Vol. 297, No. 3 July 2020