Trachea
Main Stem Bronchi
Segmental and Subsegmental Bronchi
Small Airways
Secondary Lobule
Alveoli
Lymph Nodes
Arteries
Trachea
- Format
- Tracheobronchuail
- Nodular
- subpleural
- lower lobes and within the peripheral and subpleural regions.
- extracellular amyloid deposits may form in the
- airways
- wall of blood vessels (including the pulmonary arteries),
- alveolar septa,
- pleura
- lymph nodes,
- Alveolar Septal
- Most common forms of amyloidosis include
- systemic AL (formerly primary),
- systemic AA (formerly secondary),
- systemic wild-type ATTR (formerly age-related or senile systemic), and
- systemic hereditary ATTR amyloidosis (formerly familial amyloid polyneuropathy).
- Three forms of amyloidosis can be seen in the lungs:
- tracheobronchial amyloidosis.
- nodular pulmonary amyloidosis, and
- diffuse alveolar-septal amyloidosis,
Tracheobronchial Amyloidosis.
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center
TheCommonVein.net
Main Stem Bronchi
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center
TheCommonVein.net
Segmental and Subsegmental Bronchi
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center
TheCommonVein.net
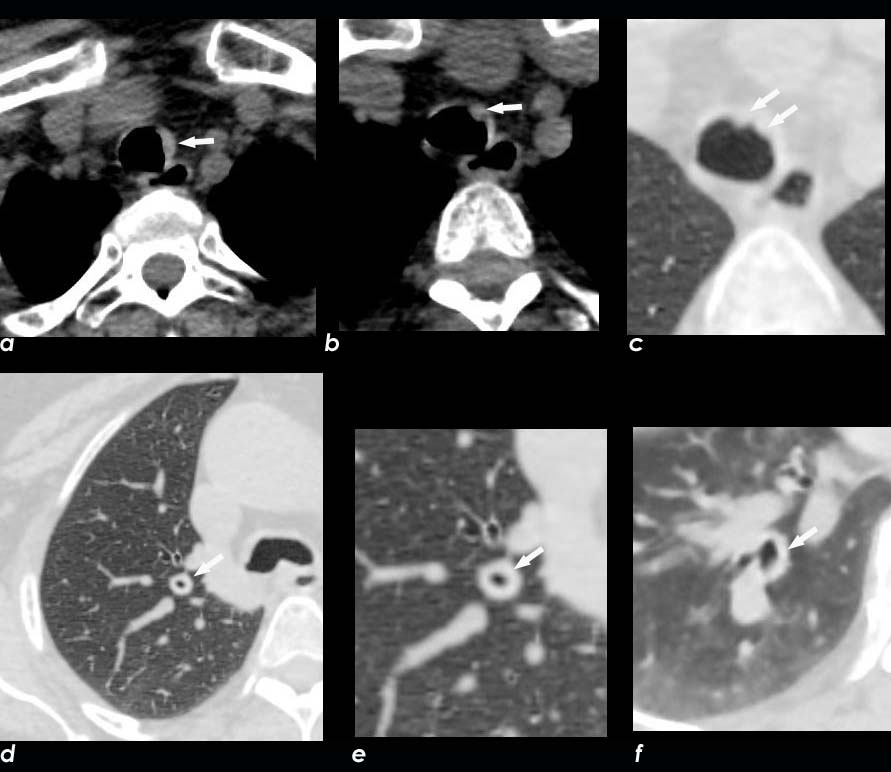
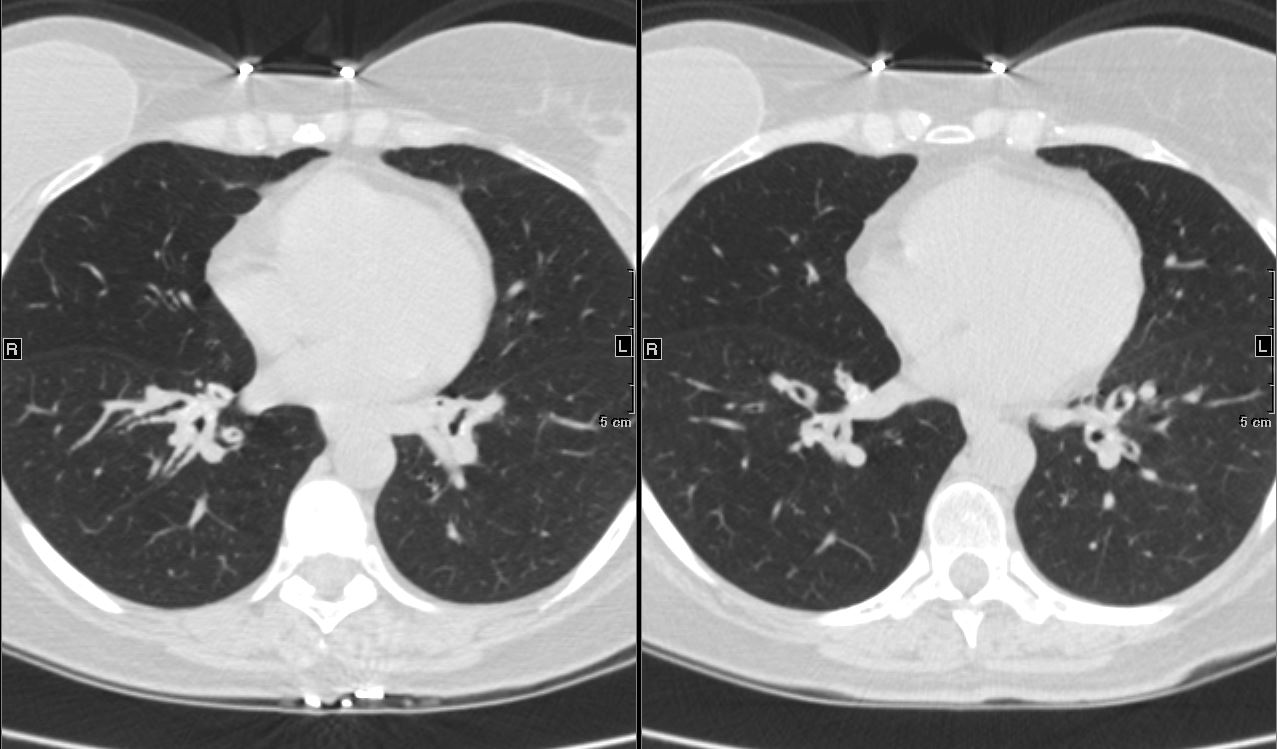
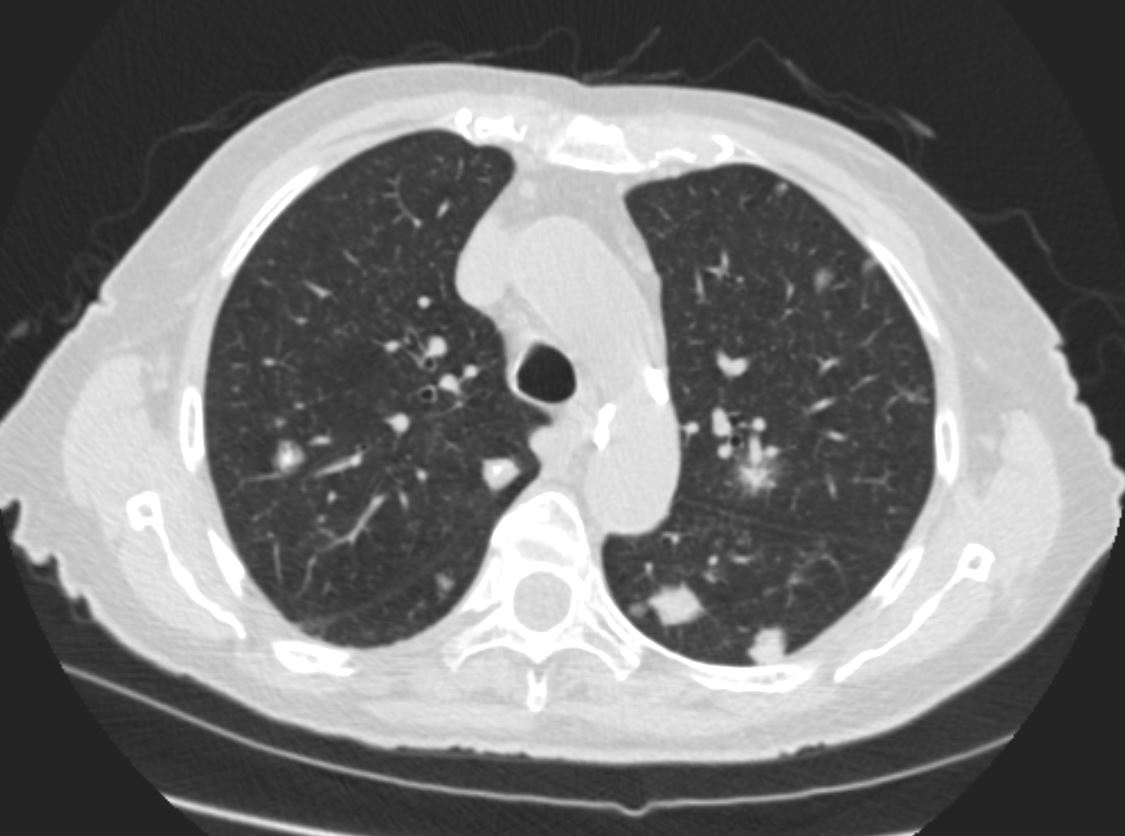
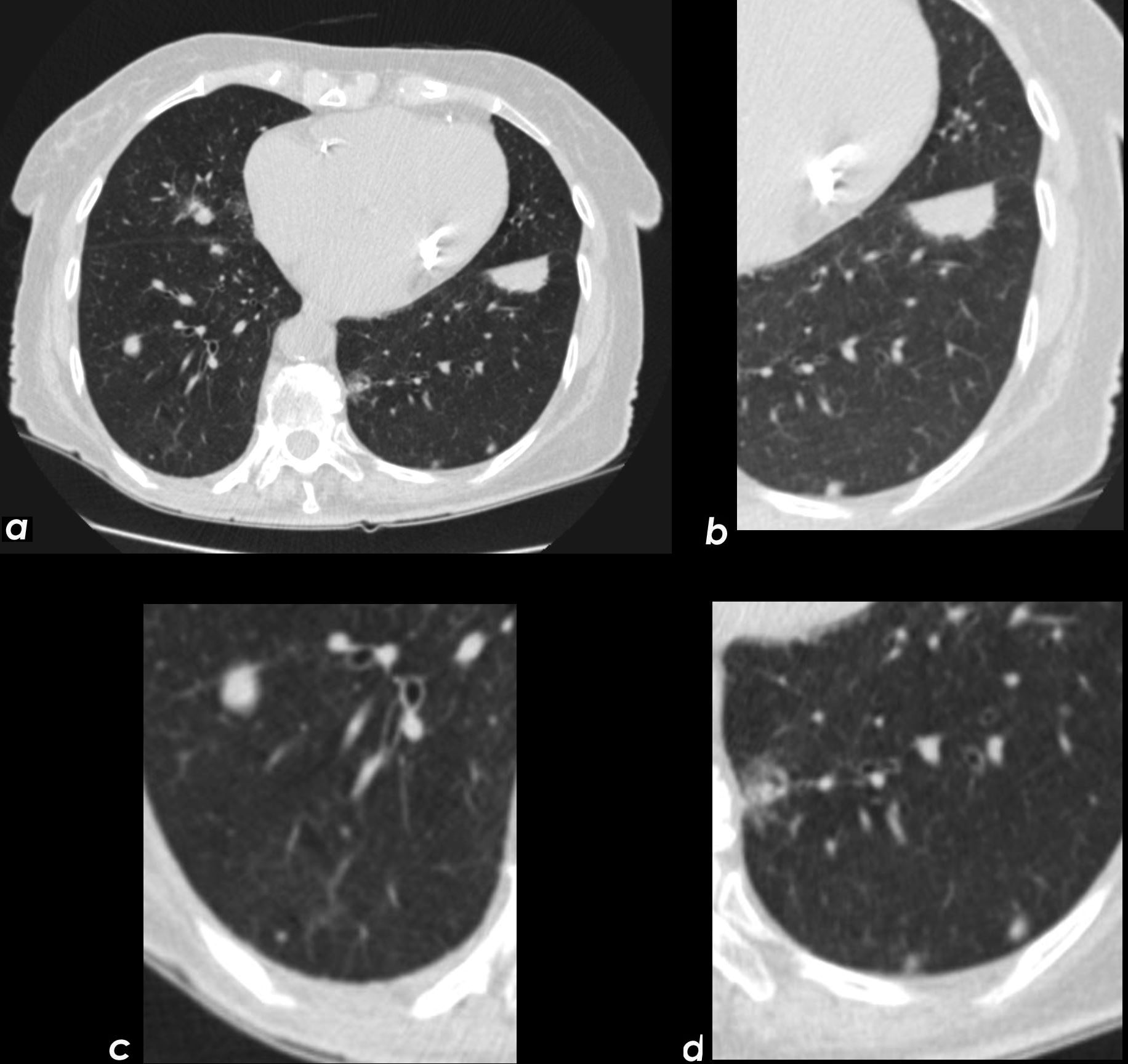
Axial CT image shows involvement of known amyloid in the trachea (a,b,c,d) as well as the segmental and subsegmental airways (d,e,f)
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center
TheCommonVein.net amyloid-airways-001b
A Second Case



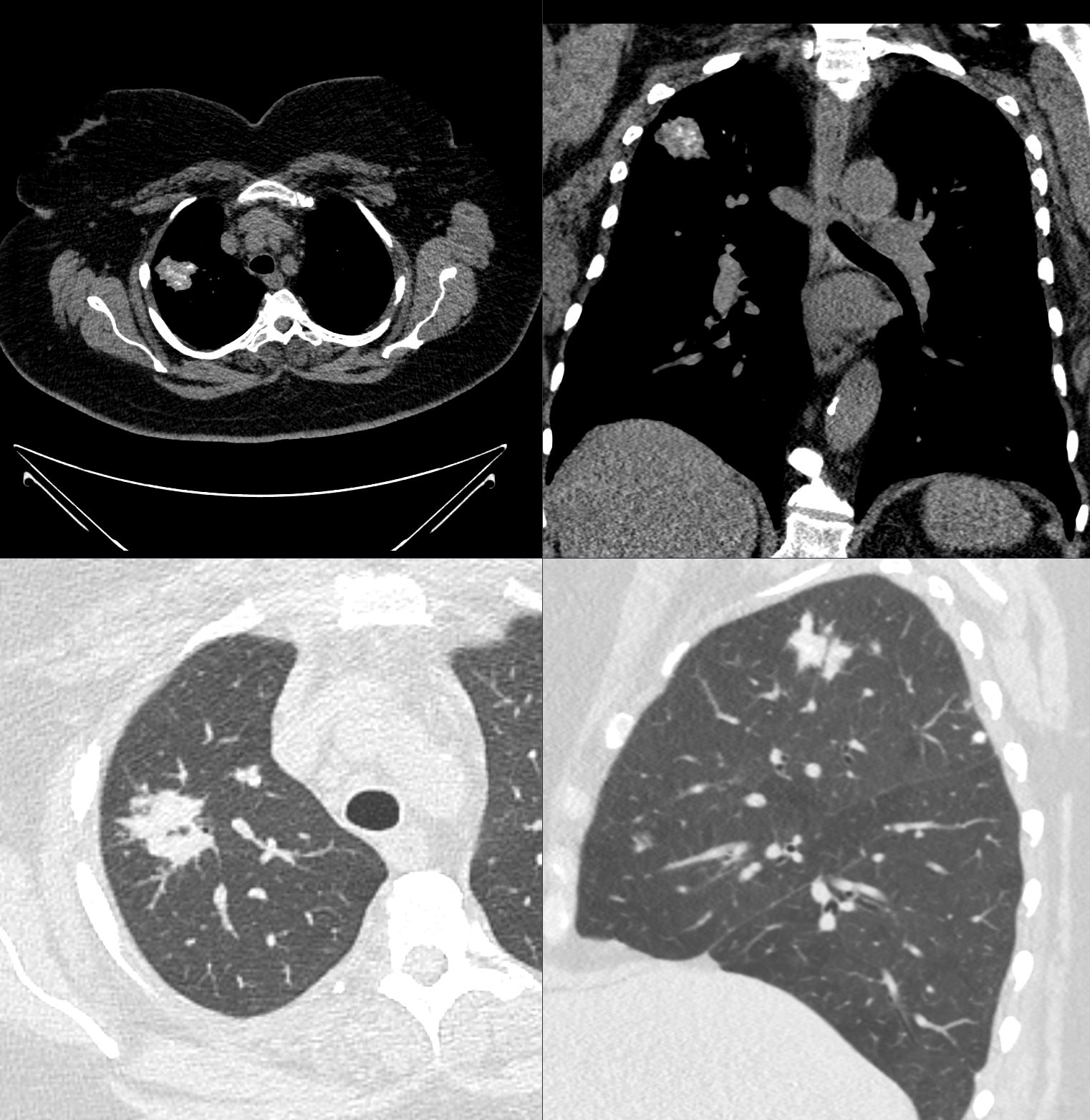
Axial CT image shows involvement of known amyloid in the trachea (a,b,c,d) as well as the segmental and subsegmental airways (d,e,f)
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center
TheCommonVein.net amyloid-airways-001b
PET Positive Hypermetabolic Bronchocentric Calcified Focus of Amyloidosis

(bronchocentric amyloid)
CT scan shows a calcified right apical focus of amyloidosis shown to be PET positive
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
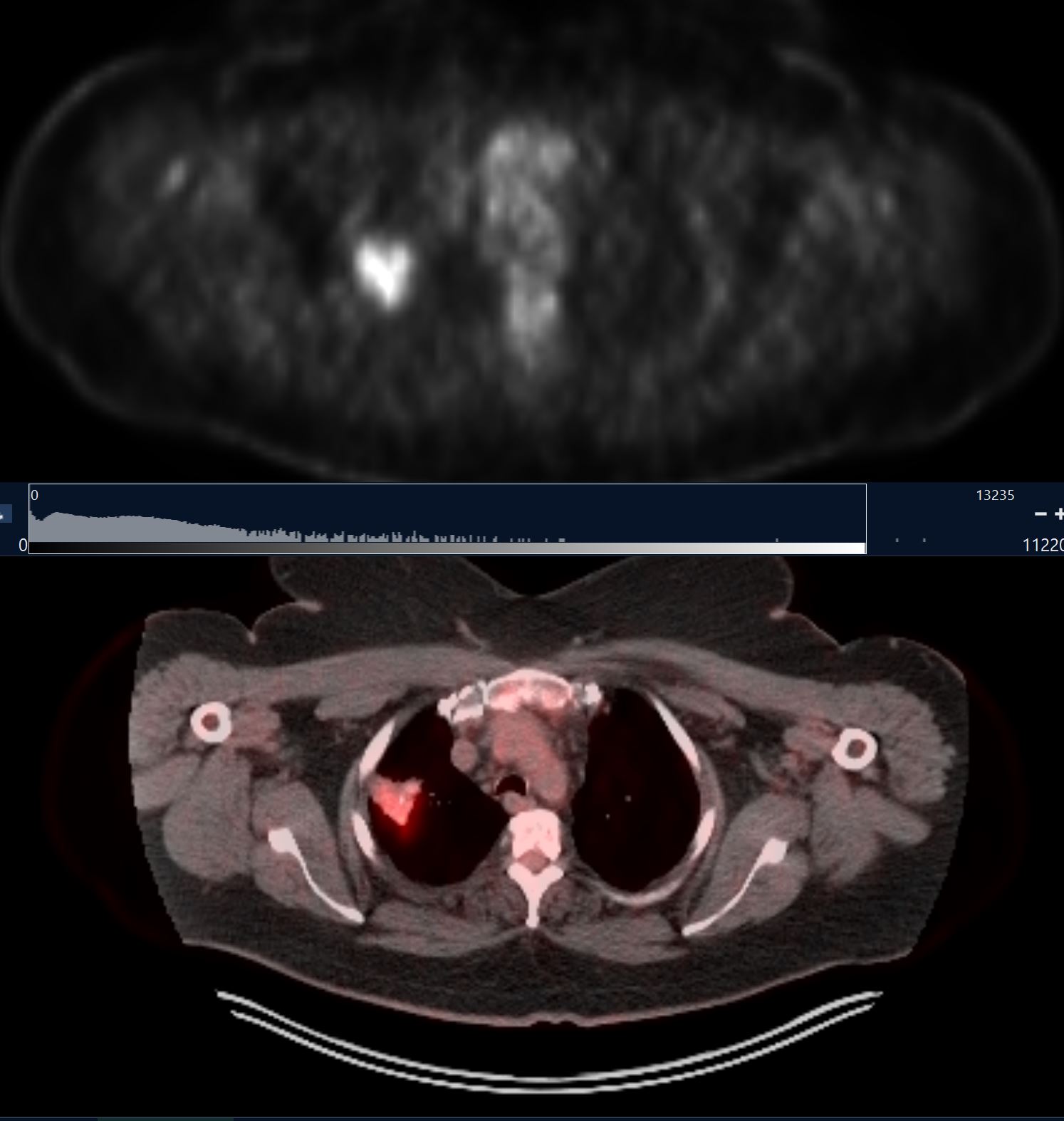

(bronchocentric amyloid)
PET CT shows a hypermetabolic right apical focus of amyloidosis
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Nodular Form
Most Commonly Around Small Airways and Small Vessels

NIH National Toxicology Program
- The nodules
-
- vary in size from 0.5–15 cm
- well-defined with
- lobulated contours
- lower lobe and
- subpleural predominance
- Involvement of
- vascular walls
- peribronchial area
- perilymphatic (fissures pleura)
-
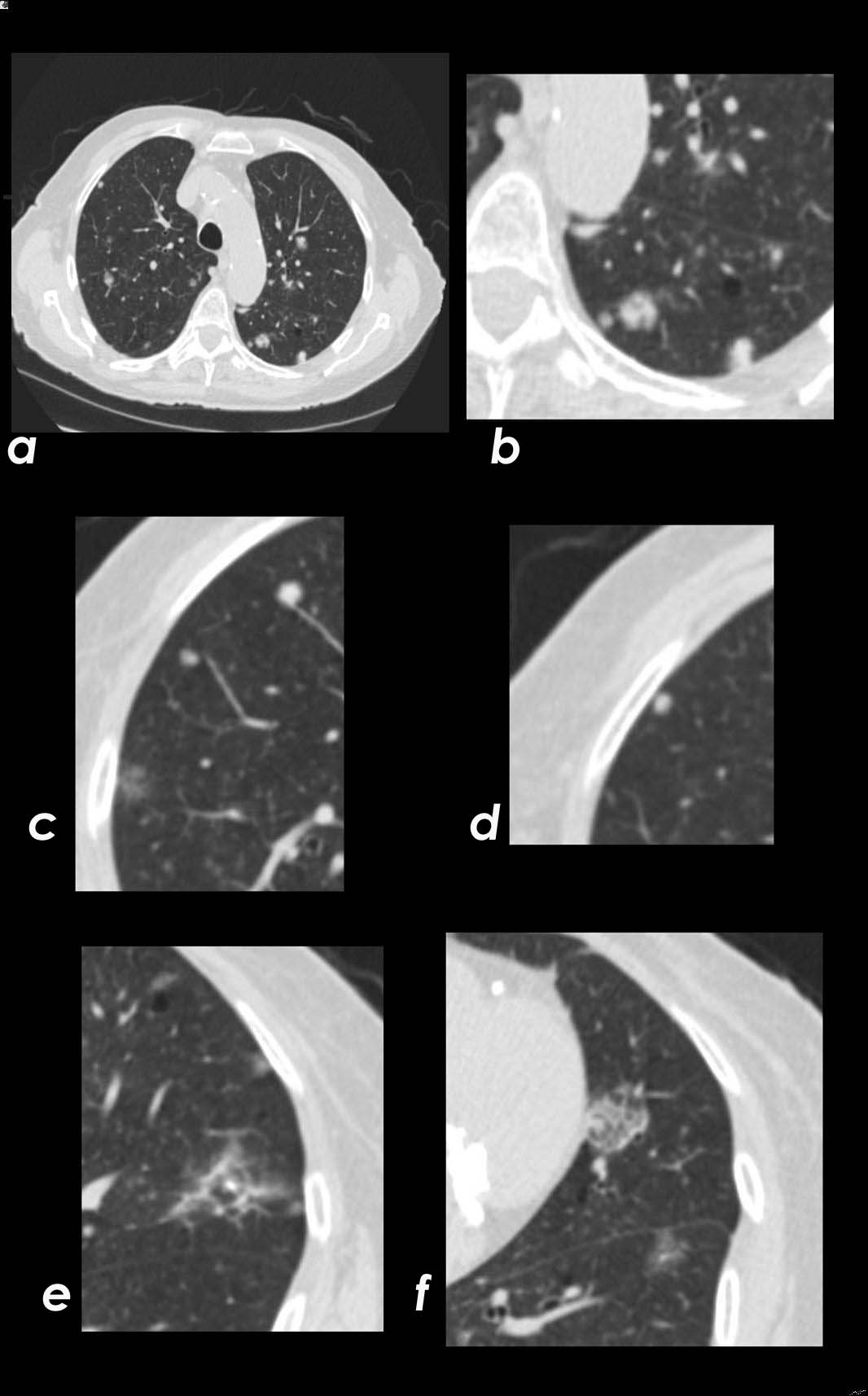

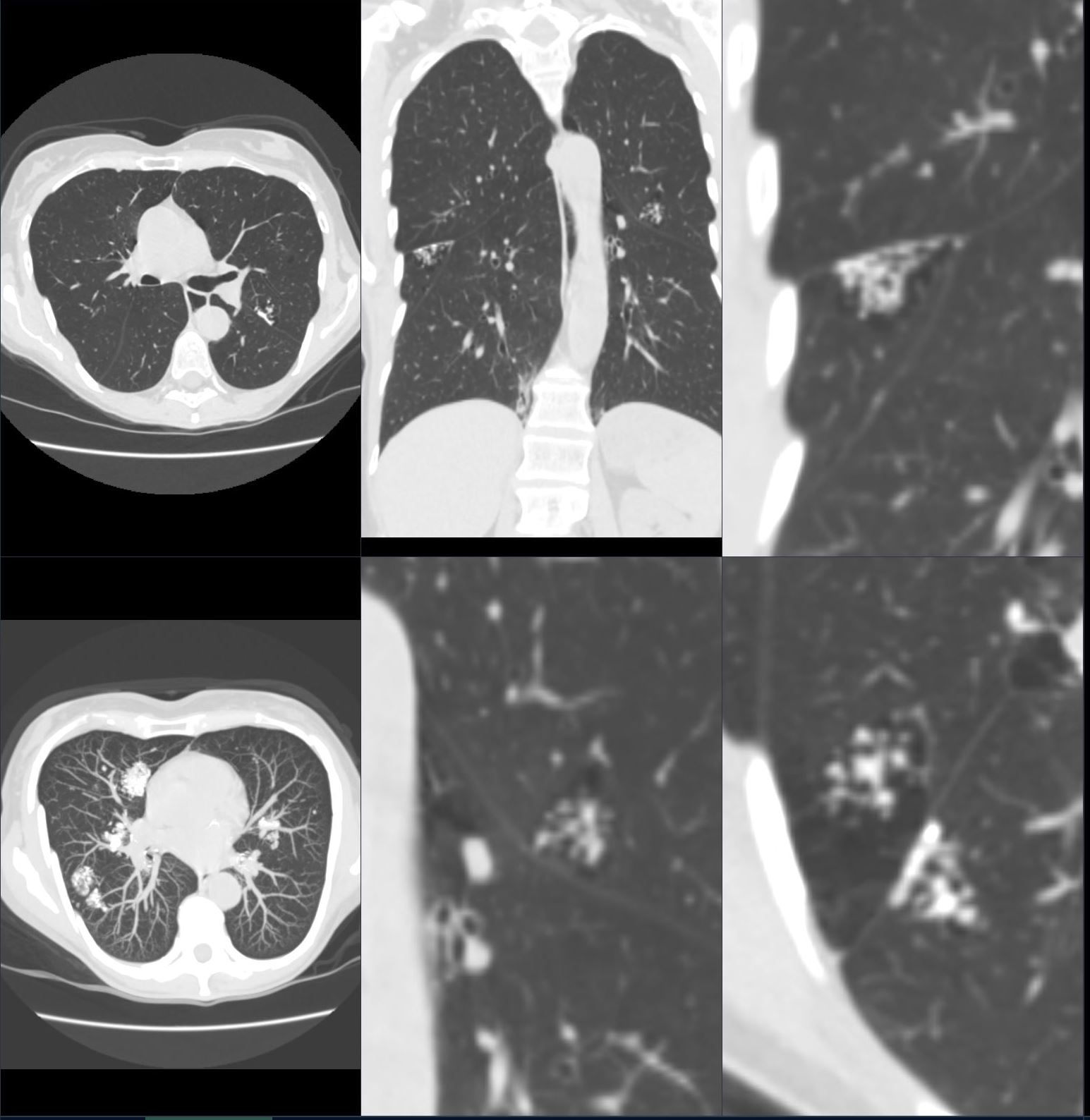
Axial CT images through the chest exemplifies the nodular form of amyloidosis, with bronchovascular, centrilobular and peripheral distribution. Image a shows multiple solid and mixed nodules that are peripherally distributed. Image b,c,and d, show solid, ground glass and mixed density nodules that have a peripheral location and association with the bronchovascular bundle and centrilobular distribution. Images e and f show centrilobular nodules, with interlobular septal thickening (e)and an intralobular reticular pattern (f) both a manifestation of the diffuse alveolar-septal amyloidosis
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net LV-005 cL

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net amyloid nodule cardiac 54M 001
-
-
- calcify,(about 50%)
- lobular
- often heterogeneous
- central
- they rarely cavitate.
- calcify,(about 50%)
-
Fissural Based

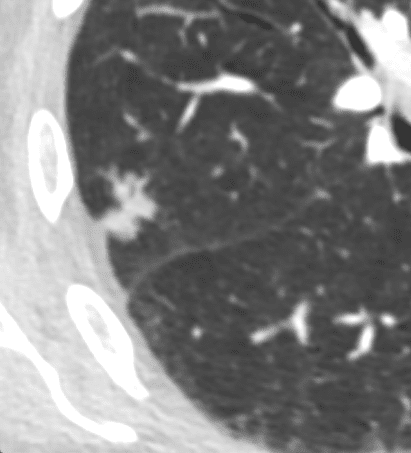
The nodule on the right close to the spine is fissural based
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-006

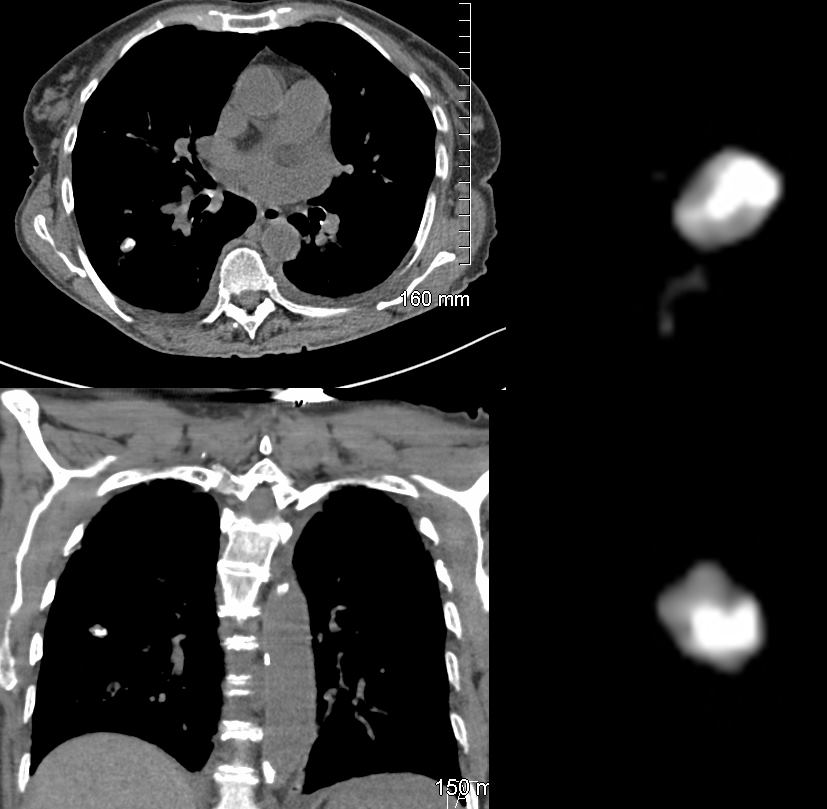
Axial CT images through the right upper lobe shows a solid amyloid nodule with central calcification abutting the major fissure. These features, although not pathognomonic are characteristic. Sarcoidosis would be a radiological consideration as well
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-006


CT scan in a patient with history of amyloidosis shows a focus of amyloid accumulation with a flat side abutting the fissure indicating that it is a relatively soft lesion
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net b11710


Axial CT images through the chest shows a Fissural based amyloid nodule along the left major fissure (a,b) Images c and d show posterior peripheral centrilobular nodules. In image c the nodules are associated with mosaic attenuation. The ground glass nodule in d could reflect alveolar septal disease with ground glass changes surrounding a centrilobular nodule
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-014c

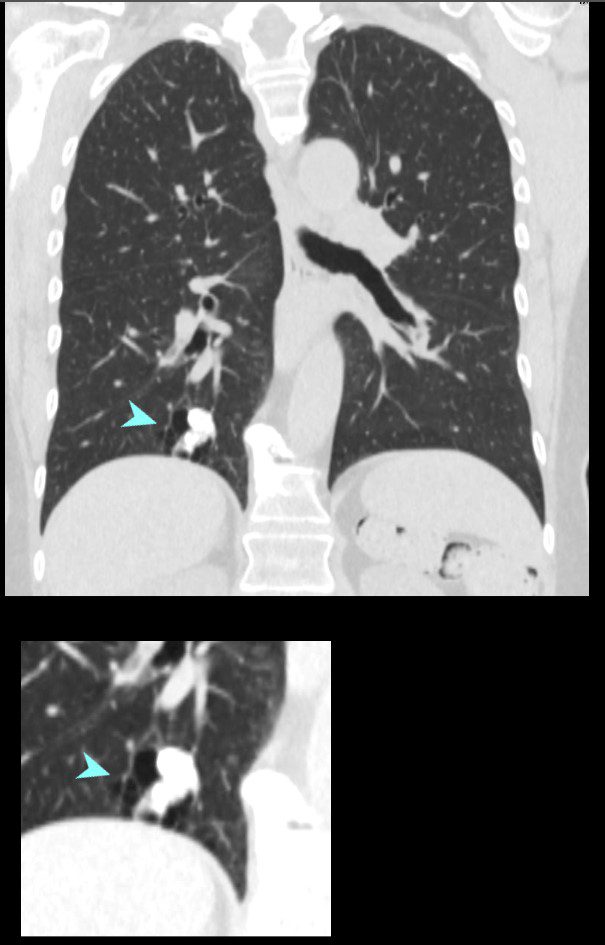
Scattered foci of nodular and calcified changes of secondary lobules involving the centrilobular region and interlobular septa. The affected secondary lobule in the right lower lobe abuts the and involves the fissure
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net b11802
Irregular Calcifications Possible Amyloidosis

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net
hamartoma 0001c01 86f

and amyloidoma
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net
hamartoma calcifications 004c stable



Axial CT images through the chest shows a Fissural based amyloid nodule along the left major fissure (a,b) Images c and d show posterior peripheral centrilobular nodules. In image c the nodules are associated with mosaic attenuation. The ground glass nodule in d could reflect alveolar septal disease withground glass changes surrounding a centrilobular nodule
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-014c
Spiculated Nodule
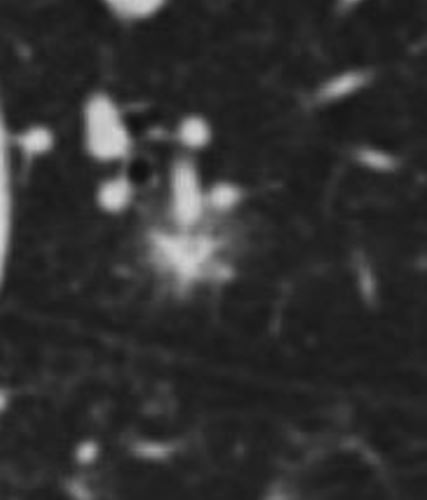

87 year old female with known nodular form of amyloidosis. The axial CT scan shows a spiculated nodule with surrounding ground glass changes
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-006 mag spiculatedb
Micronodules and Microcalcifications
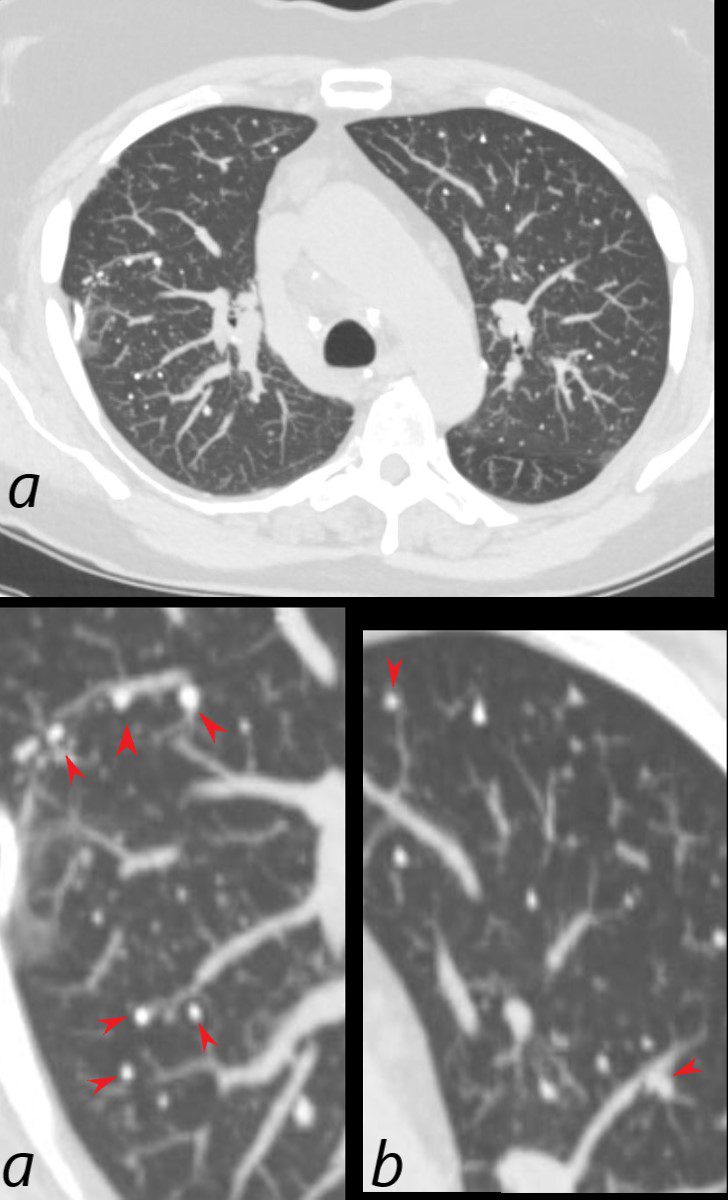

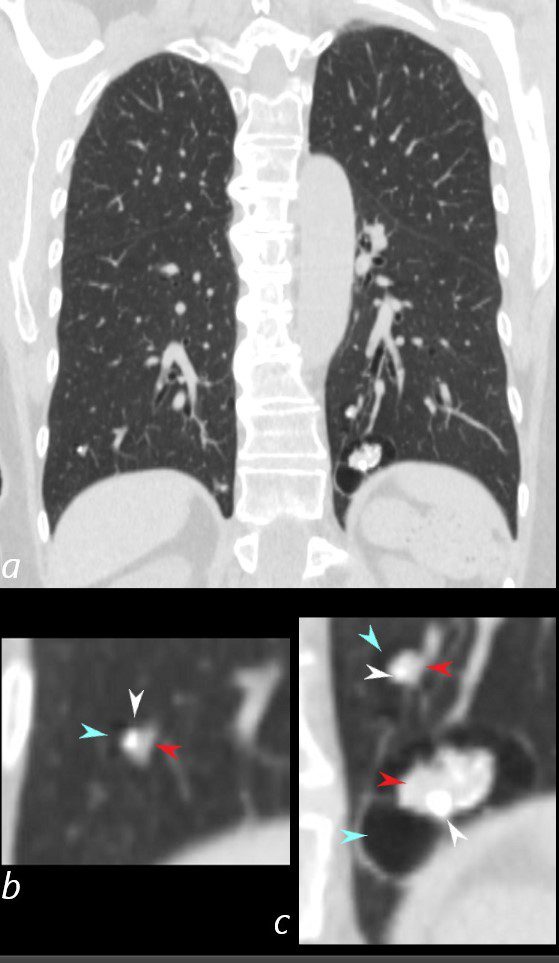
CT scan in the axial plane of a 60-year-old female with known diagnosis of AL amyloidosis shows multiple microcalcifications in the periphery of the mid and lower lung zones in close association with the blood vessels (b, and c red arrowheads) and also subpleural (c, yellow arrowheads).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 266Lu 136183cL
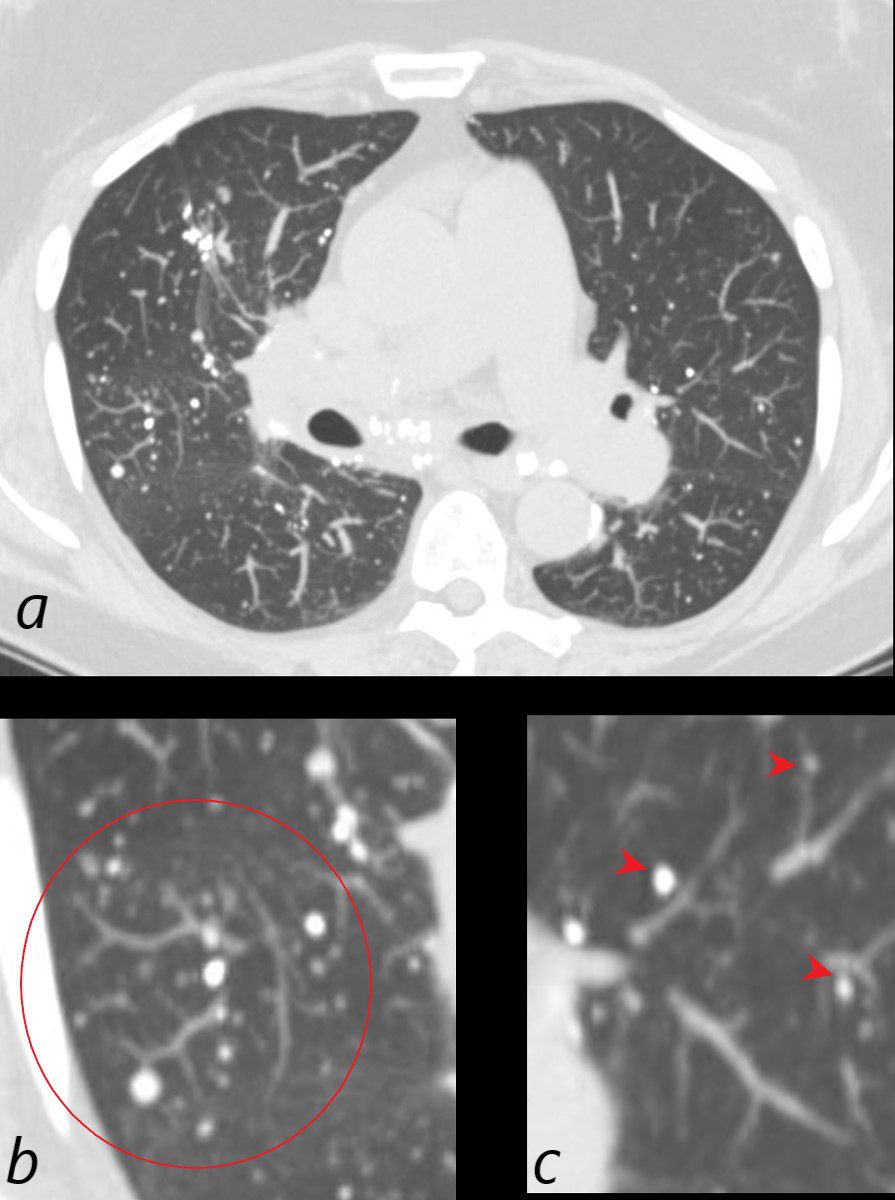

CT scan in the axial plane of a 60-year-old female with known diagnosis of AL amyloidosis shows multiple microcalcifications in the periphery of the mid and lower lung zones in close association with the blood vessels (b, (red ring and c red arrowheads)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 266Lu 136184cL
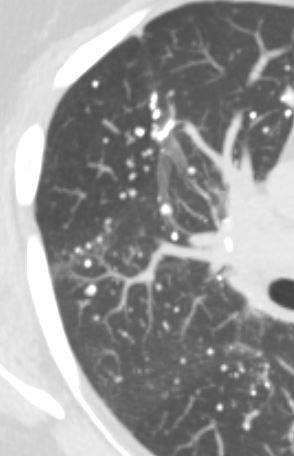

CT scan in the axial plane of a 60-year-old female with known diagnosis of AL amyloidosis shows multiple microcalcifications in the periphery of the mid and lower lung zones in close association with the blood vessels
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 266Lu 136185
Secondary Lobule
Alveoli
Alveolar Septal Amyloidosis
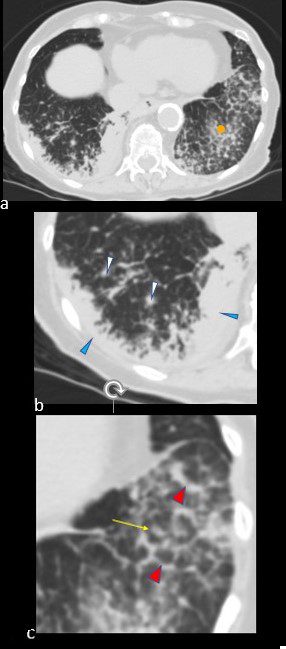


CT scan in the axial projection at the base of the lungs show many features of amyloidosis including lung nodules (white arrowheads) and infiltrates (b), and diffuse deposition within the alveolar septa (red arrowheads, c) and centrilobular nodules(yellow arrow c)
Ashley Davidoff MD Boston Medical Center
TheCommonVein.net septal-amyloidosis-001b
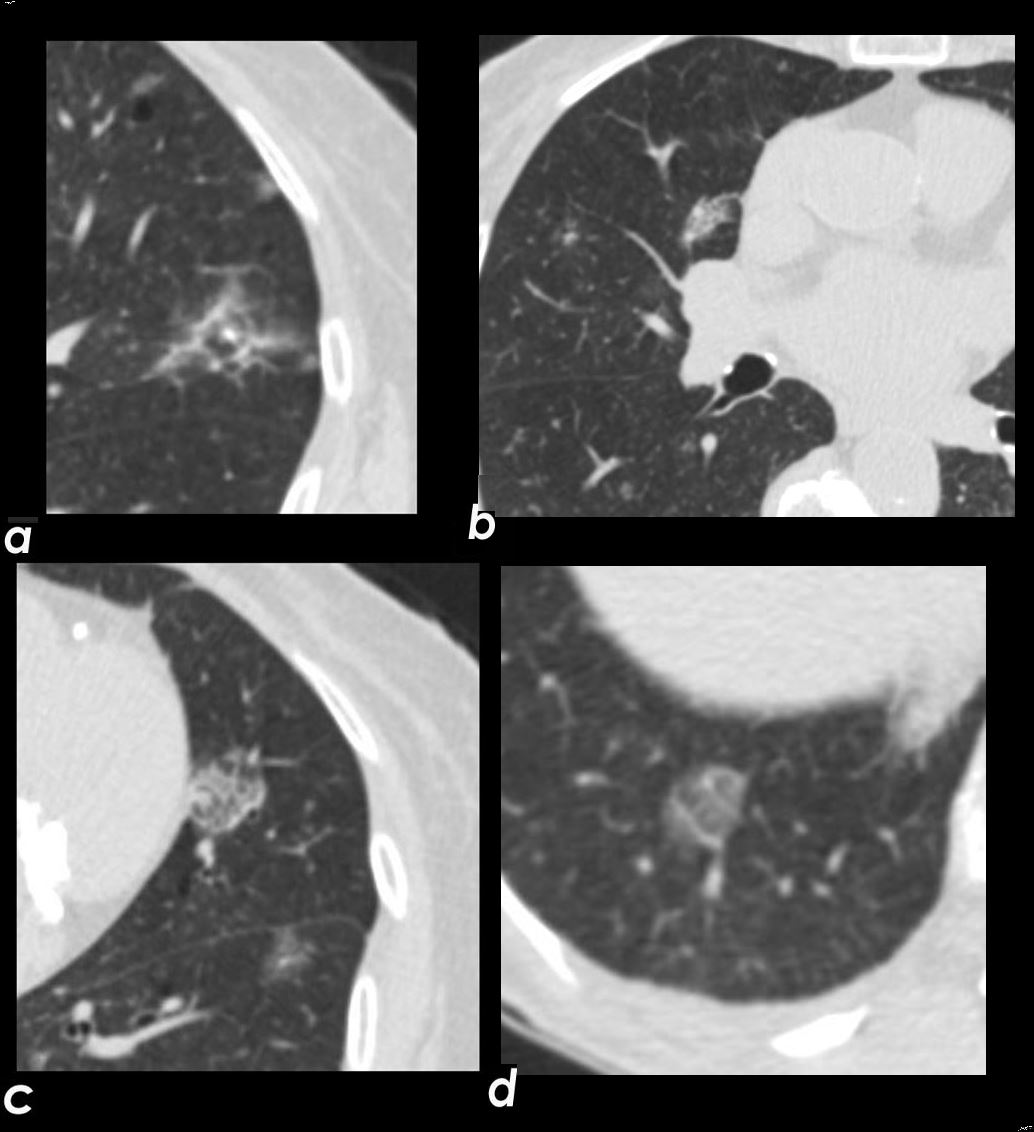

Axial CT images through the chest exemplifies the diffuse alveolar-septal amyloidosis at its mildest and earliest form
Image a, shows a secondary lobule with thickened interlobular septa with a centrilobular nodule either reflecting peribronchial or periarteriole involvement. Image b shows a mixed nodule likely reflecting intralobular alveolar involvement. Images c and d show thickened interlobular septa and a reticular intralobular ground glass abnormality pattern each with a centrilobular nodule
Ashley Davidoff Boston Medical Center TheCommonvein.net LV-005 c01
Lymph Nodes
Arteries
-
-
-
- Parenchyma
- Mass Like that may
- calcify,
- cavitate, and
- slowly enlarge.
- Mass Like that may
-
-


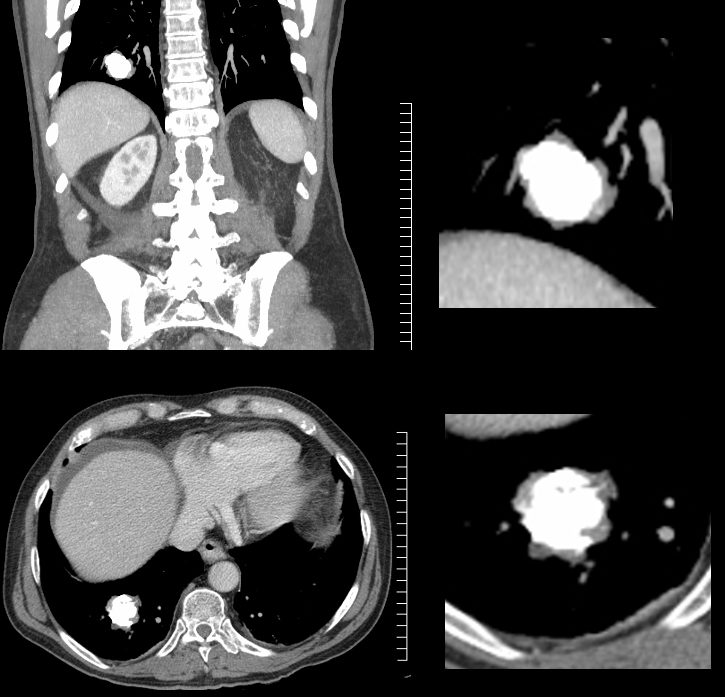
83 y.o. male with biopsy proven nodular lung AL amyloidosis diagnosed by lung biopsy 5 years ago . His underlying amylogenic protein was typed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry as kappa.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
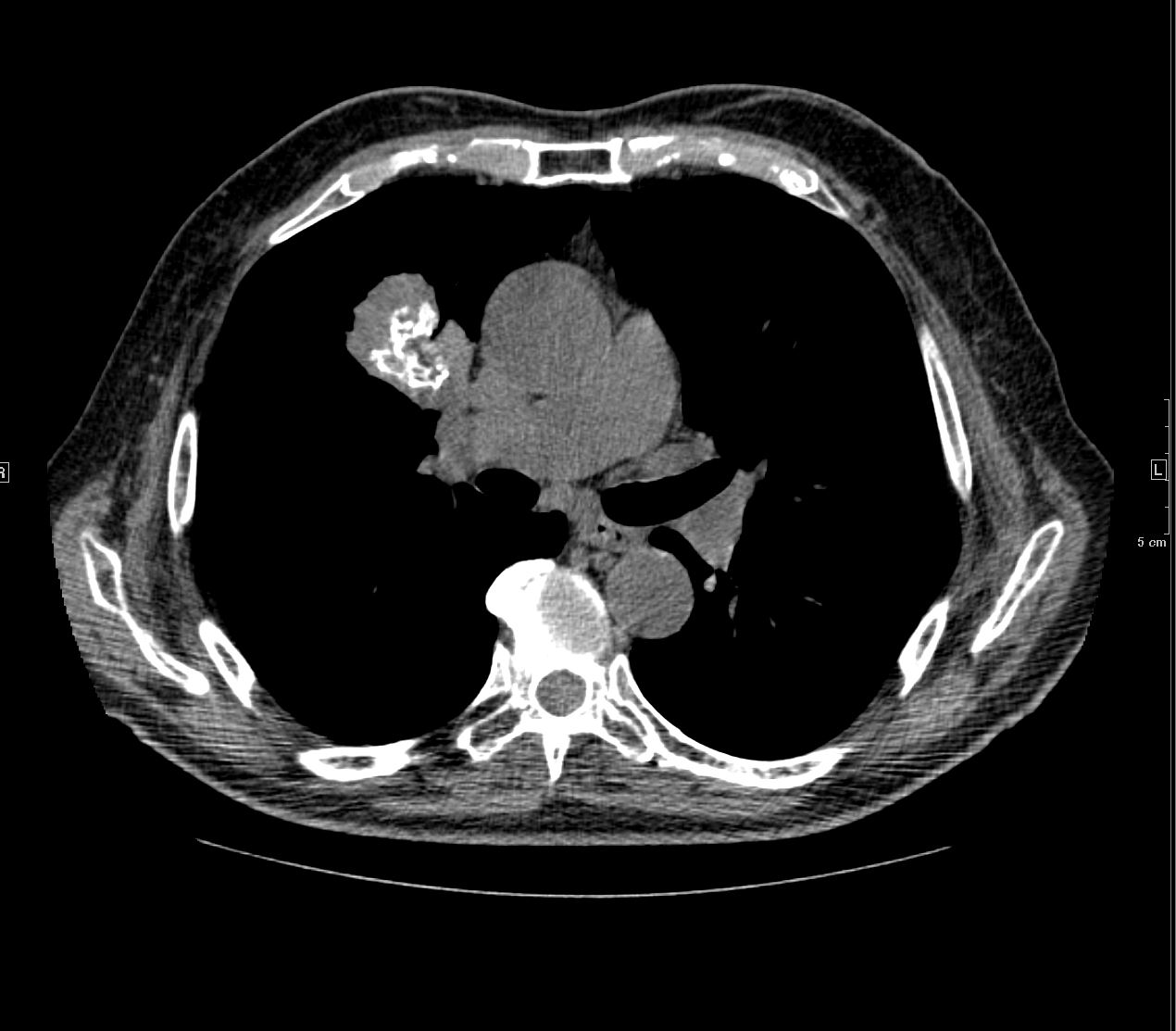

83 y.o. male with biopsy proven nodular lung AL amyloidosis diagnosed by lung biopsy 5 years ago . His underlying amylogenic protein was typed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry as kappa.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
- Nodular Form that may
-
- calcify,
- cavitate, and
- slowly enlarge.
-

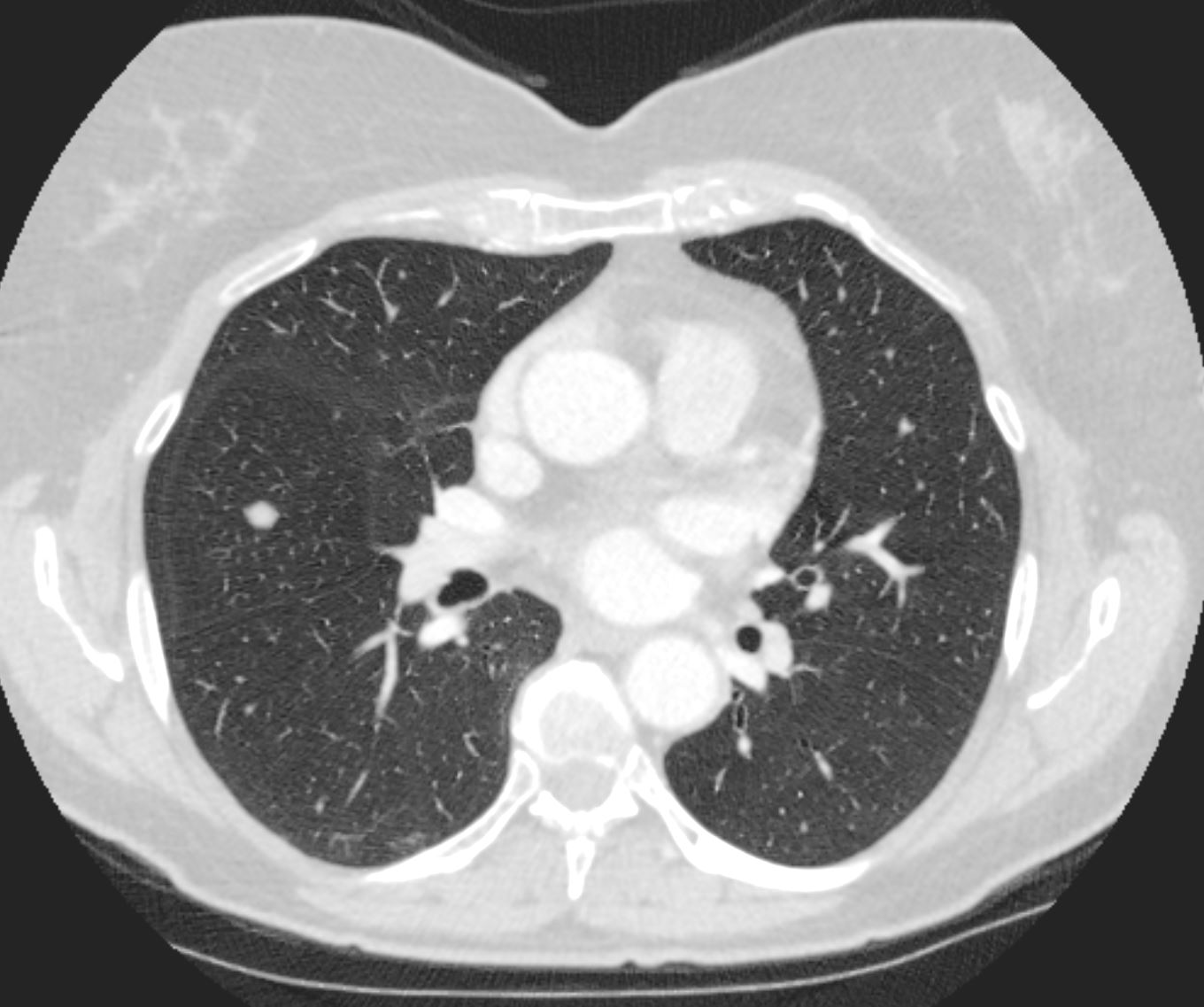
Small non descript nodule in a 65 year old female with path proven lung amyloid
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
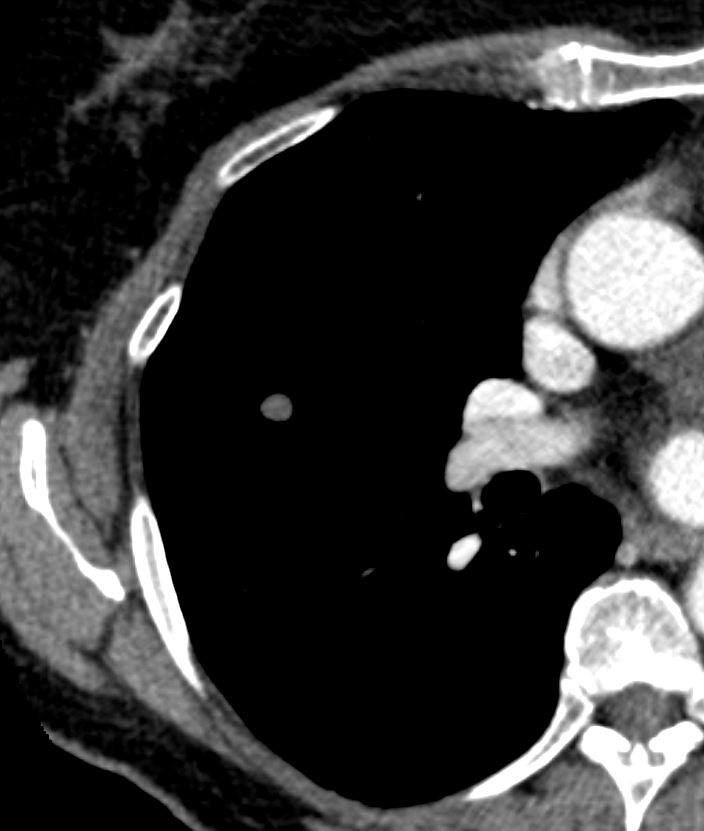
Small non descript nodule in a 65 year old female with path proven lung amyloid
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
- Multiple parenchymal nodules that may
- Alveolar septal pulmonary amyloidosis
- Diffuse reticulonodular interstitial thickening,
- Alveolar septal pulmonary amyloidosis is
- less common
- clinically more important than the nodular parenchymal form.
- more commonly symptomatic
- more likely to progress to pulmonary hypertension and respiratory failure
- systemic involvement,
- an independent predictor of poor survival,
- more common in this subtype.
-



CT scan in the axial projection at the base of the lungs show many features of amyloidosis including lung nodules (white arrowheads) and infiltrates (b), and diffuse deposition within the alveolar septa (red arrowheads, c) and centrilobular nodules(yellow arrow c)
TheCommonVein.net
-
-
-

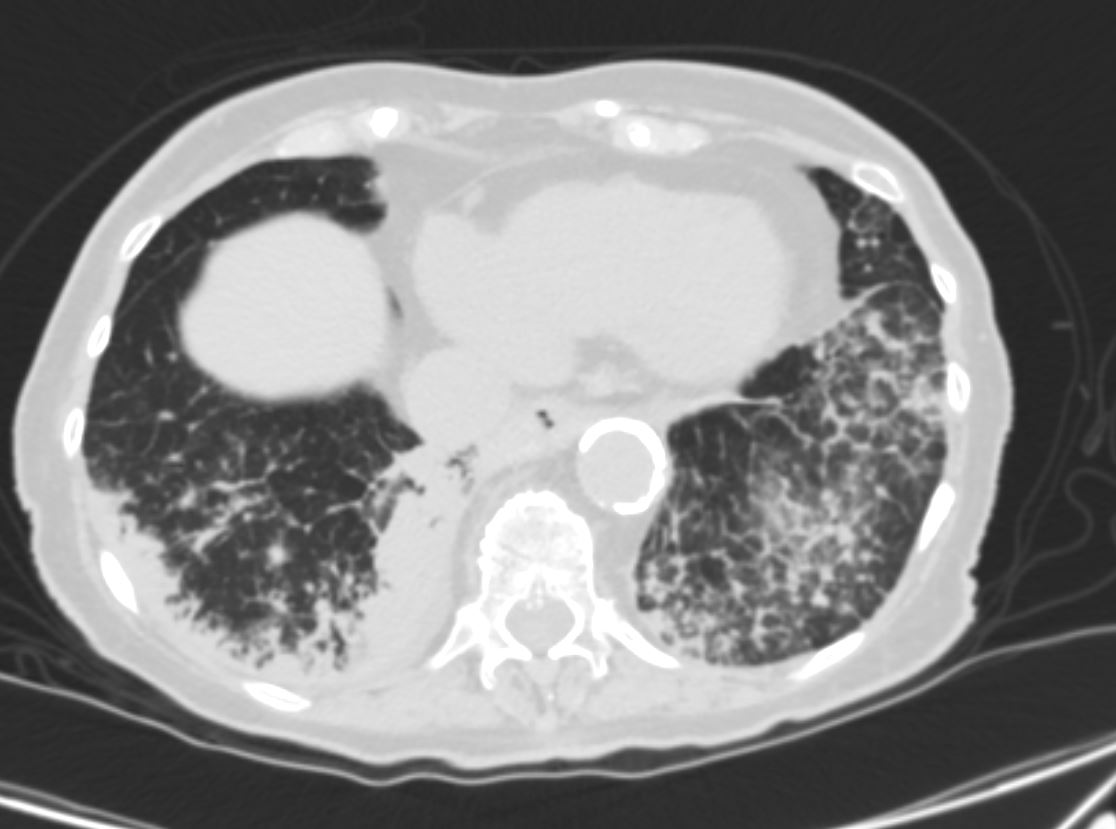

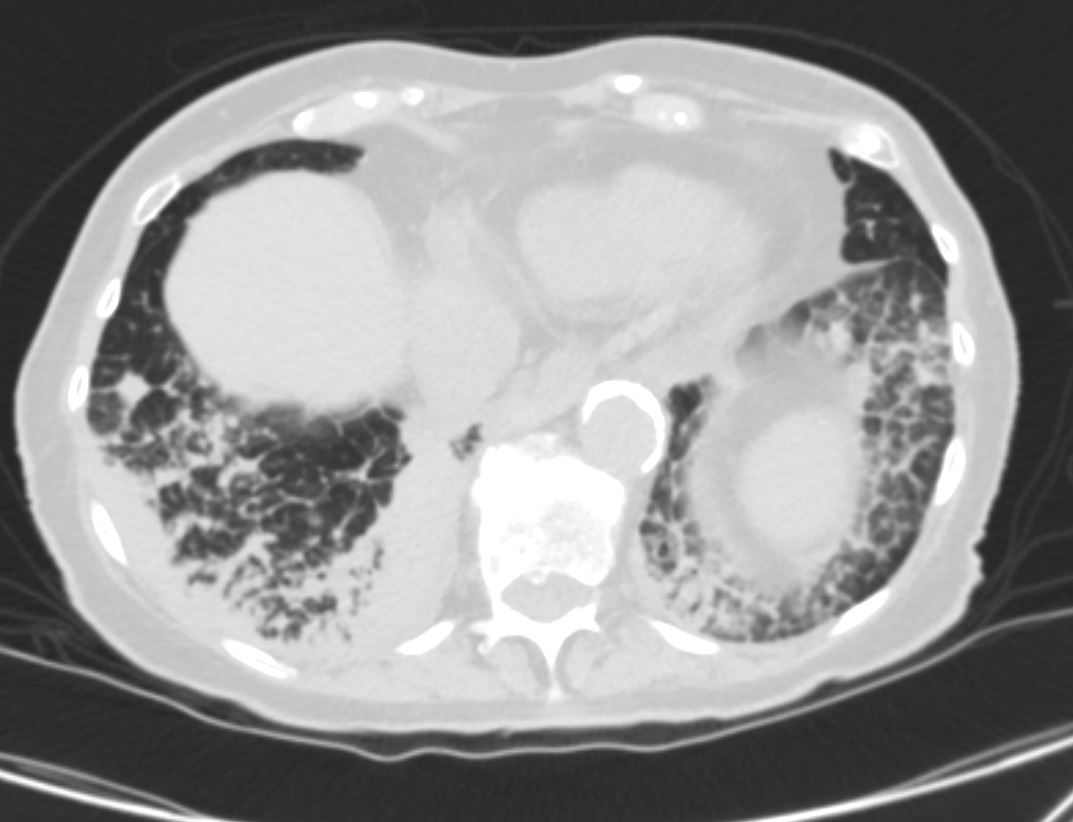
- consolidations, or
- Nodular form
- solitary or
- solitary or
- Pleural involvement most commonly manifests as
- pleural effusions.
- nodules






Pleural and Fissural based Nodules some with Calcification
83 y.o. male with biopsy proven nodular lung AL amyloidosis diagnosed by lung biopsy 5 years ago . His underlying amylogenic protein was typed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry as kappa.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
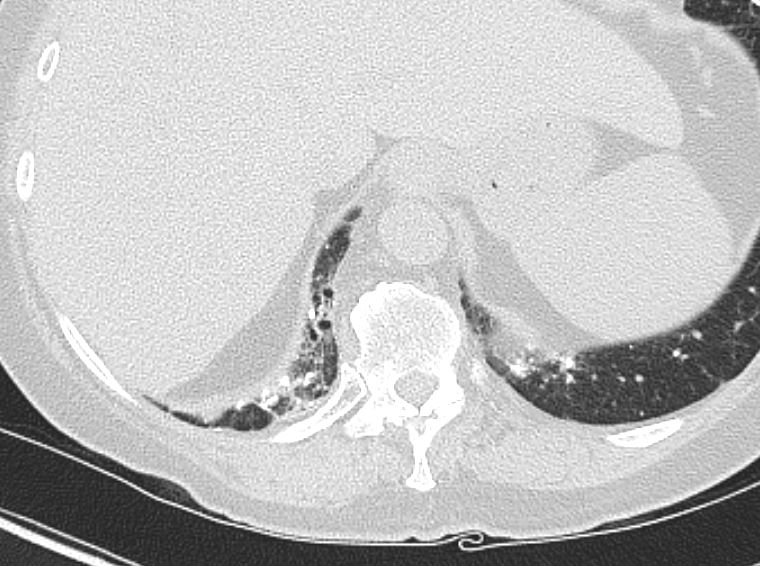
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules on the pleural surfaces
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net

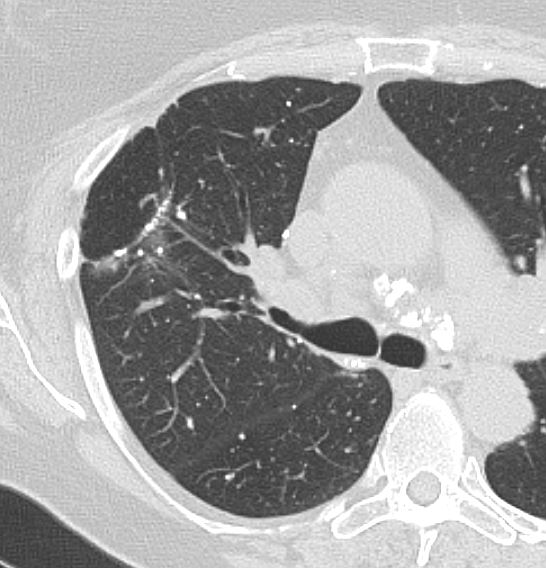
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
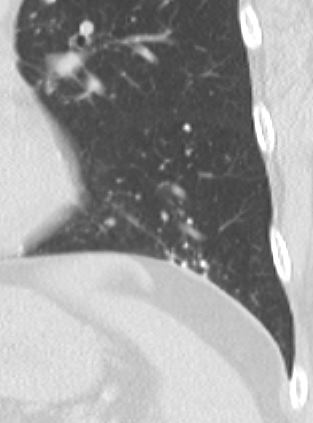
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
-
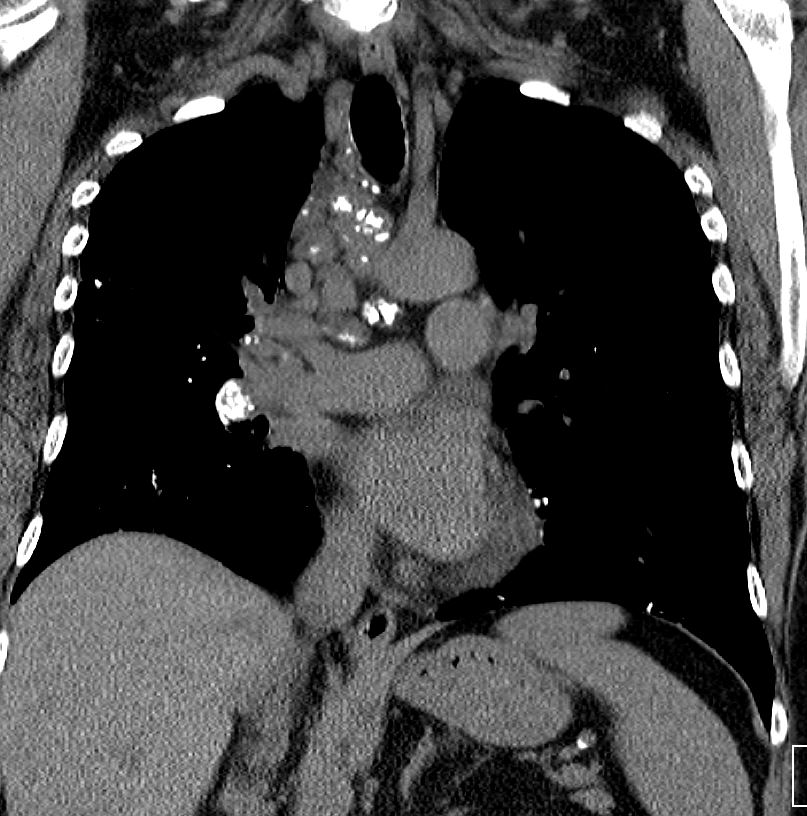
- Mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes may
-
-
- enlarge and
- frequently calcify.
-

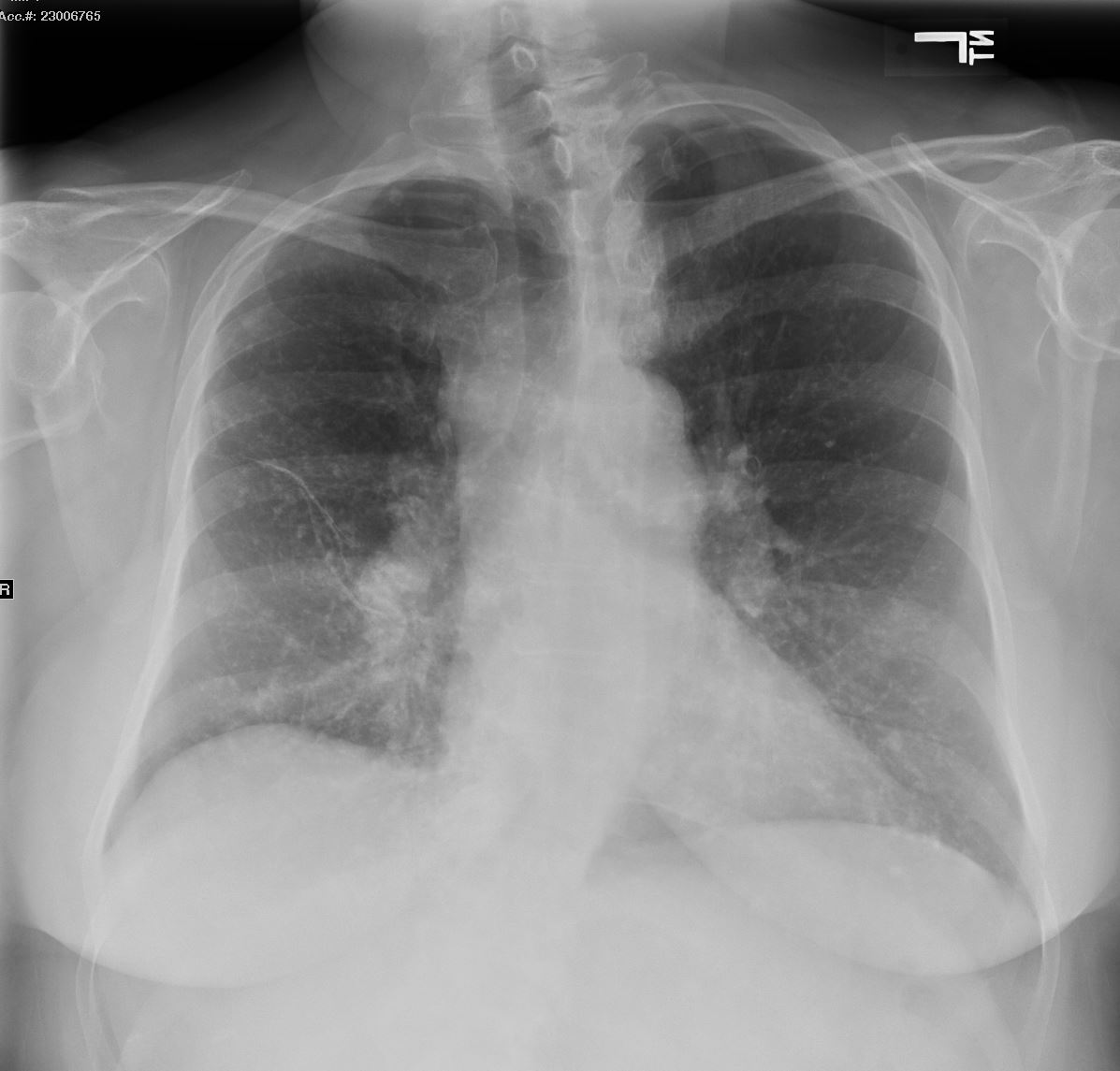
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
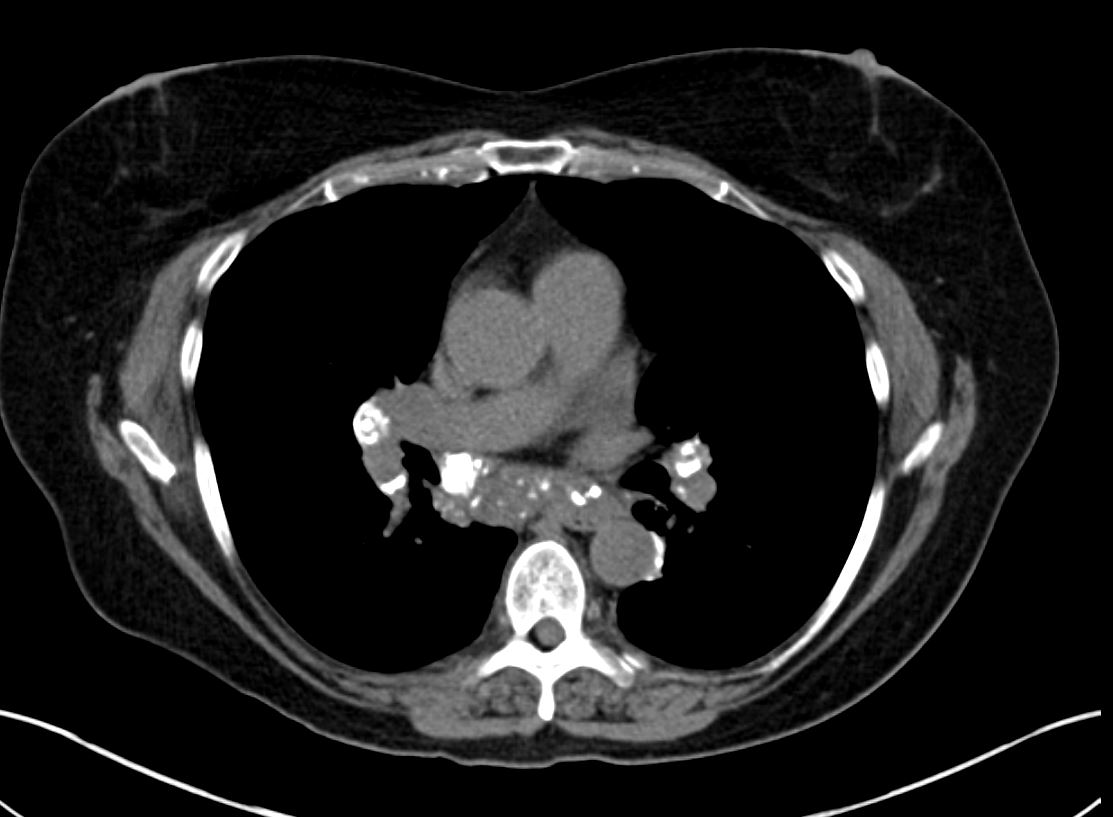
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net


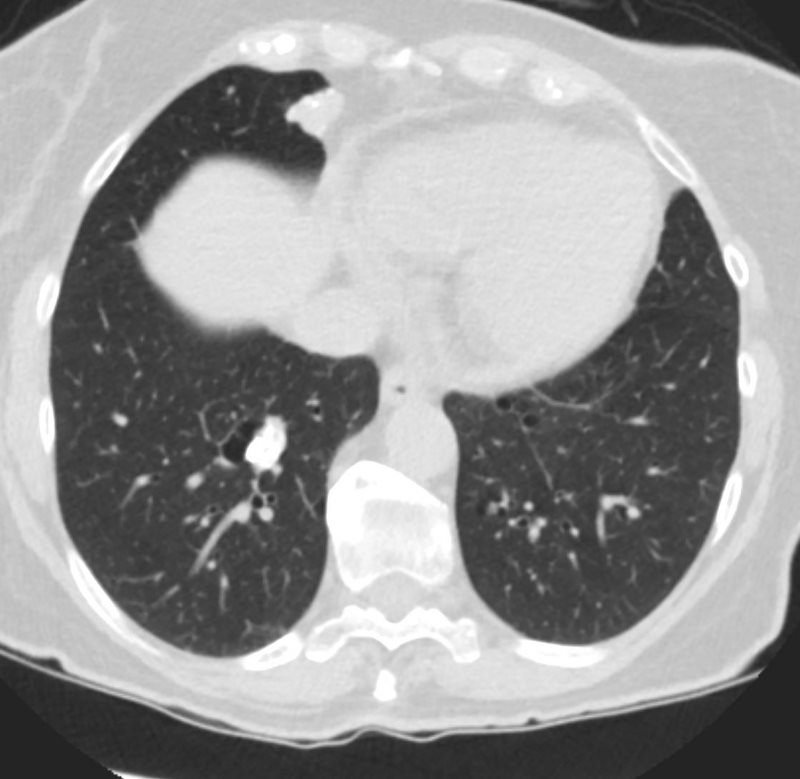
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
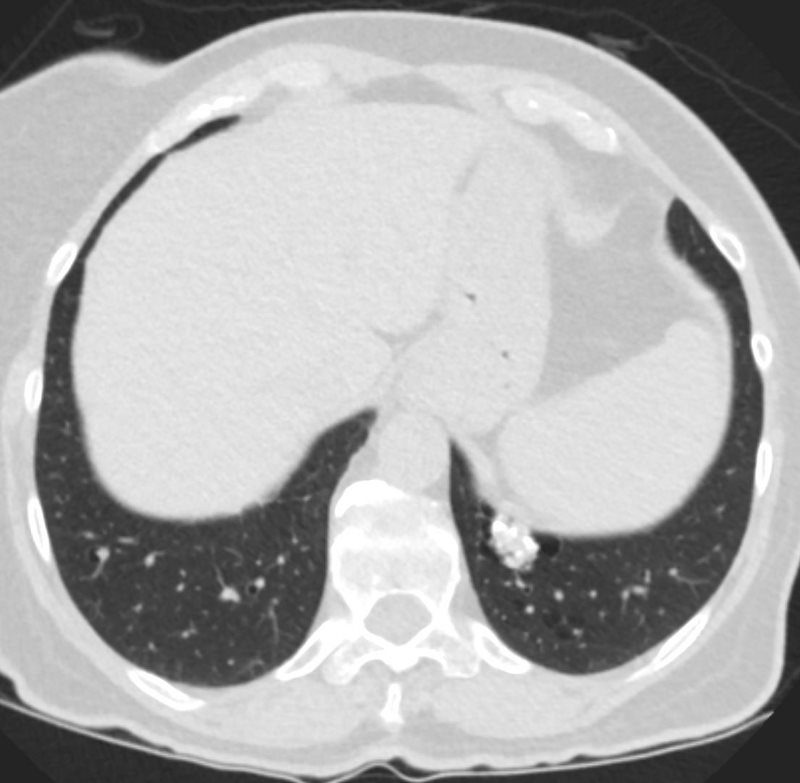
AL Amyloid with calcified micronodules
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
-
-
- Associated with Cysts
- Uncommon
- lower lobes
- peribronchovacsular disease
- often in patients with
- systemic amyloidosis due to
- Sjögren syndrome (21).
- may be associated with
- calcified nodules or
- noncalcified nodules.
- cysts may be a
- manifestation of lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia in Sjögren syndrome
- or a manifestation of amyloidosis (possibly due to small airway obstruction by amyloid deposits)
- Uncommon
-

NODULAR FORM OF PULMONARY AMYLOIDOSIS
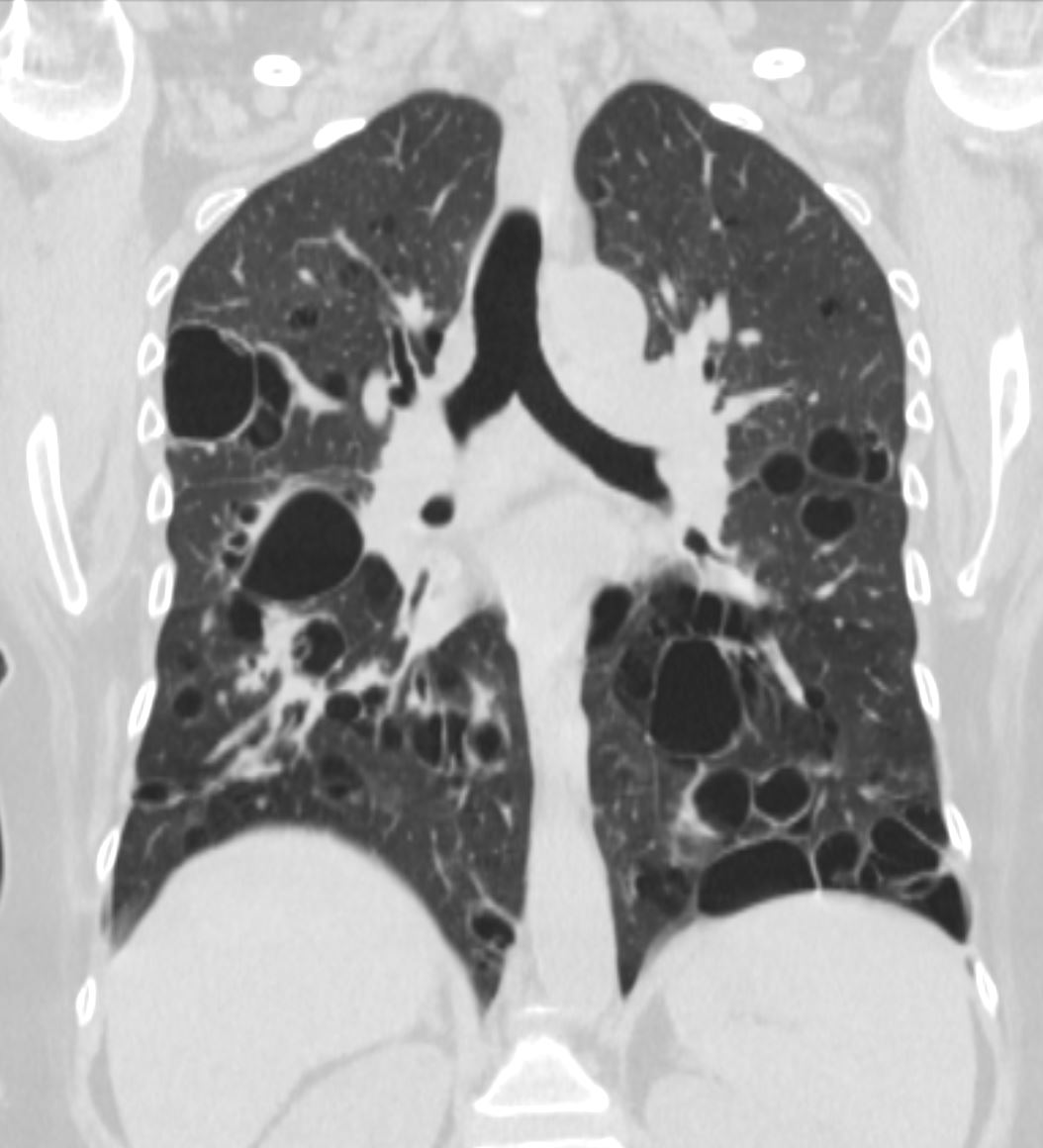
67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
NODULAR FORM OF PULMONARY AMYLOIDOSIS
67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
NODULAR FORM OF PULMONARY AMYLOIDOSIS
67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MD
NODULAR FORM OF PULMONARY AMYLOIDOSIS
67 year old female with a nodular form of pulmonary amyloidosis characterised parenchymal calcified nodules, many of which have cystic changes around the nodules.
Courtesy Geraldine Tran MDLikely Sjogren’s Cystic Lung Disease and Amyloid

Stable Cystic Changes
47 F SLE Sjogrens LIP vs Birt-Hogg-Dube basilar thin walled cysts lymphadenopathy
Subsegmental right lower lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net

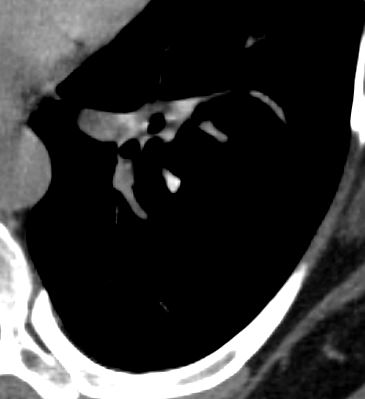
Stable Calcification in a Cyst ? Amyloid
47 F SLE Sjogrens LIP vs Birt-Hogg-Dube basilar thin walled cysts lymphadenopathy
Subsegmental right lower lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Stable Calcification in a Cyst ? Amyloid
47 F SLE Sjogrens LIP vs Birt-Hogg-Dube basilar thin walled cysts lymphadenopathy
Subsegmental right lower lobe infiltrate
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
-
References and Links
Czeyda-Pommersheim F etal Amyloidosis: Modern Cross-sectional Imaging Radiographics Vol. 35, No. 5
- TCV
- Faces of Amyloidosis
- Case Studies
- 014Lu Nodular Parenchymal Amyloid and Cystic Changes
- 014Lu Nodular Parenchymal Amyloid and Cystic Changes
- 037Lu Amyloidosis of the Trachea and Bronchi
- 038Lu Amyloidosis Hilar Lymph Nodes Pericardium CAD
66Lu Amyloid nodules alveolar septal and bronchiole and MAC - 89Lu Amyloid Calcified Mass and Pleural Involvement
- 68Lu Trachea Amyloid
- 70Lu Amyloid Consolidative Nodular Septal
- 89Lu Amyloid Calcified Mass and Pleural Involvement
90Lu Amyloid Interstitial and Calcified Micronodules
92 LU Amyloid Lung and Heart