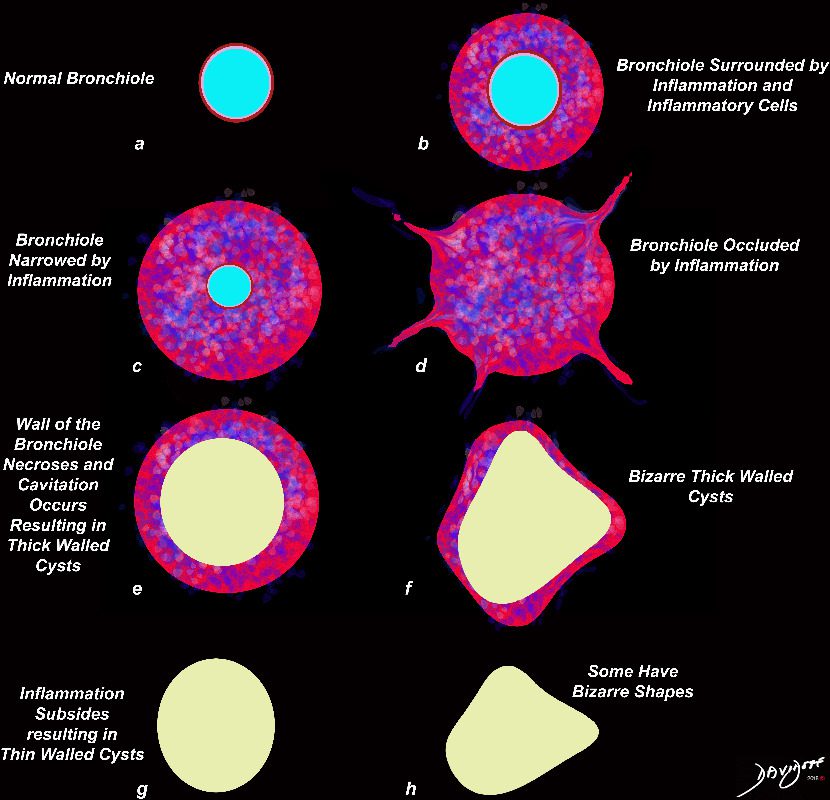
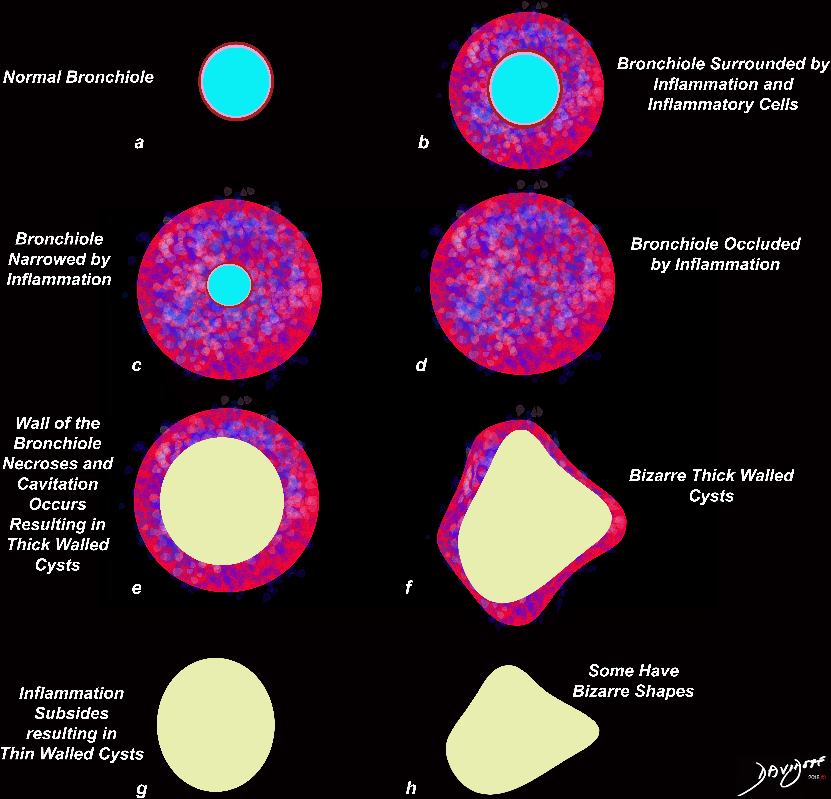
Normal
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
lungs-0739
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0740nL01bronchioloes
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0740nL
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0744
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0749
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0746
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0747
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0034
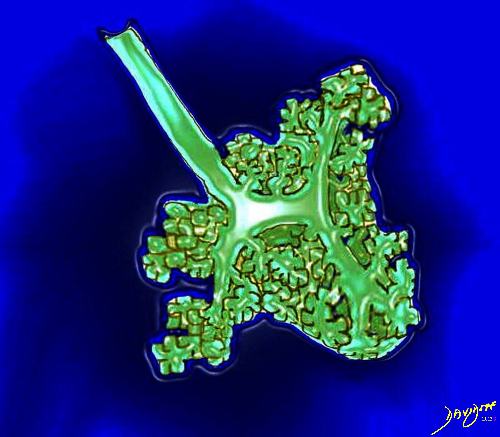
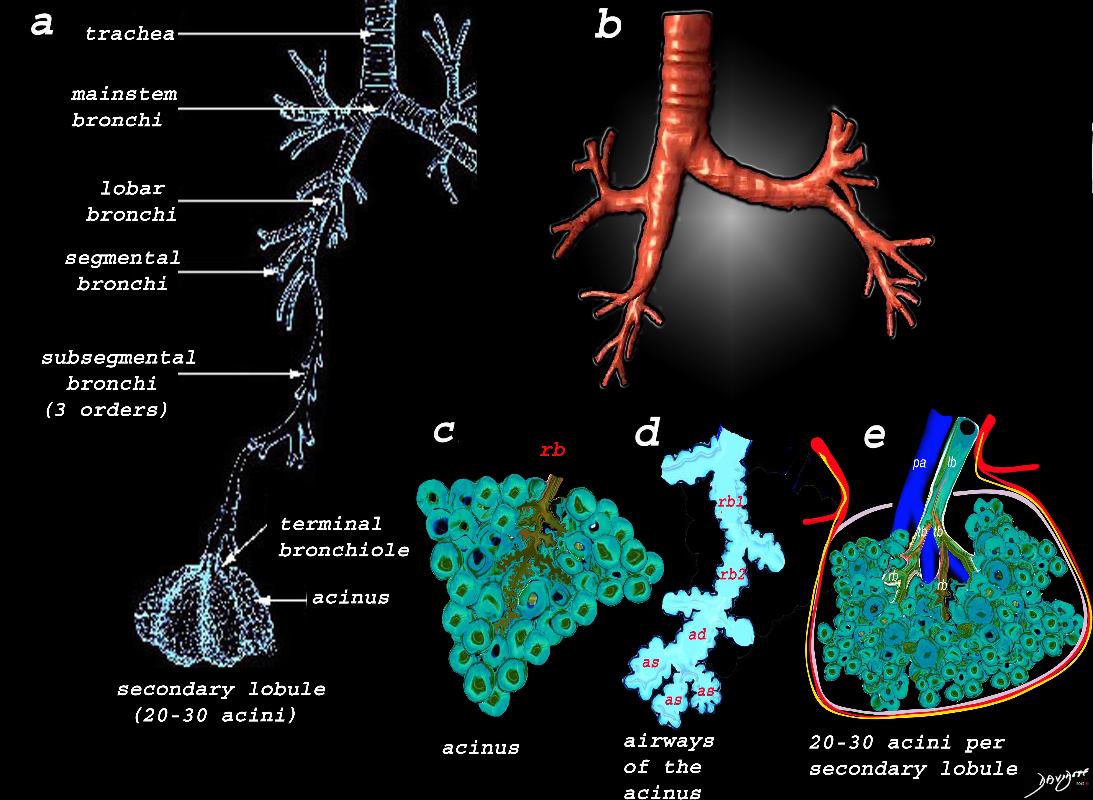
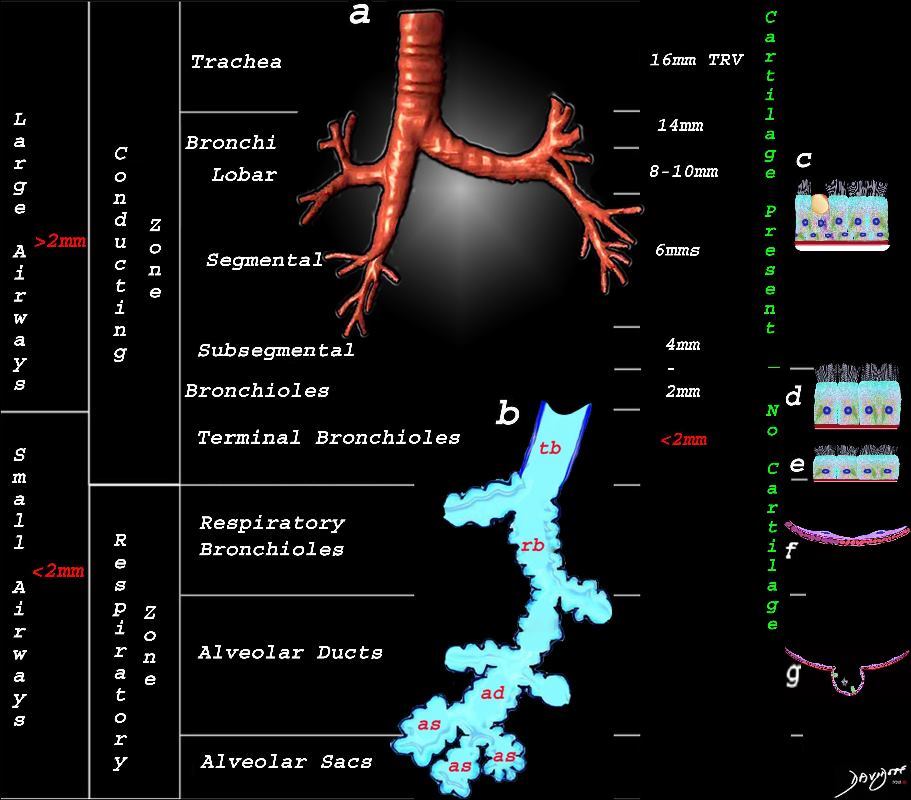
The lobular (most distal of the subsegmental airways give rise to the terminal bronchiole which give rise to the membranous airways. These include in order, the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-0007

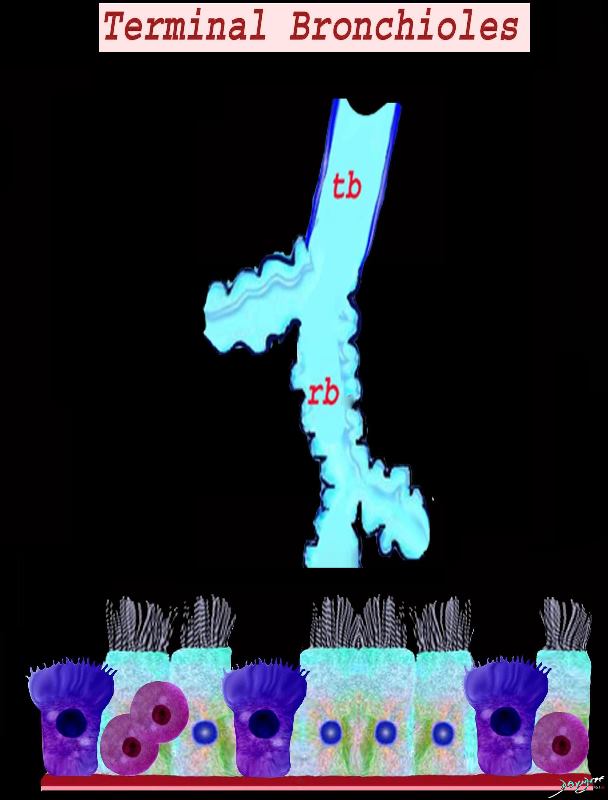
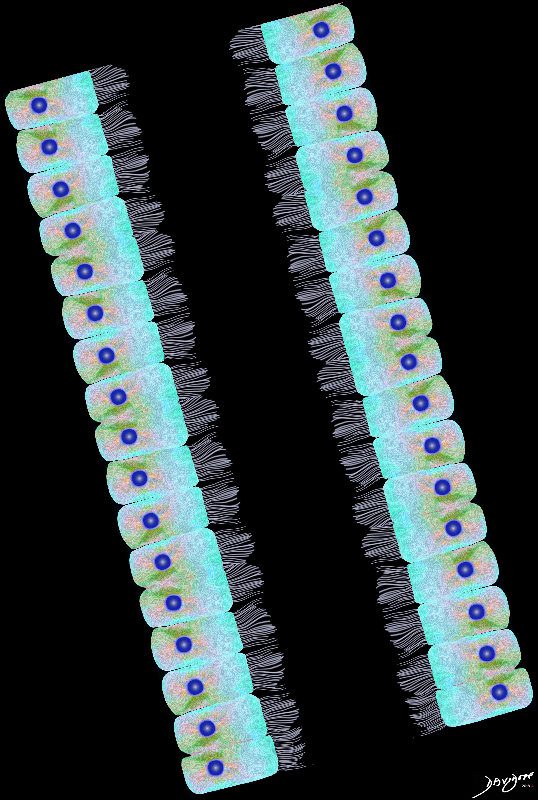
Airways are lined by a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium interspersed with mucus secreting goblet cells
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00674b01-lo res
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
lungs-00675-lo-res
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00676
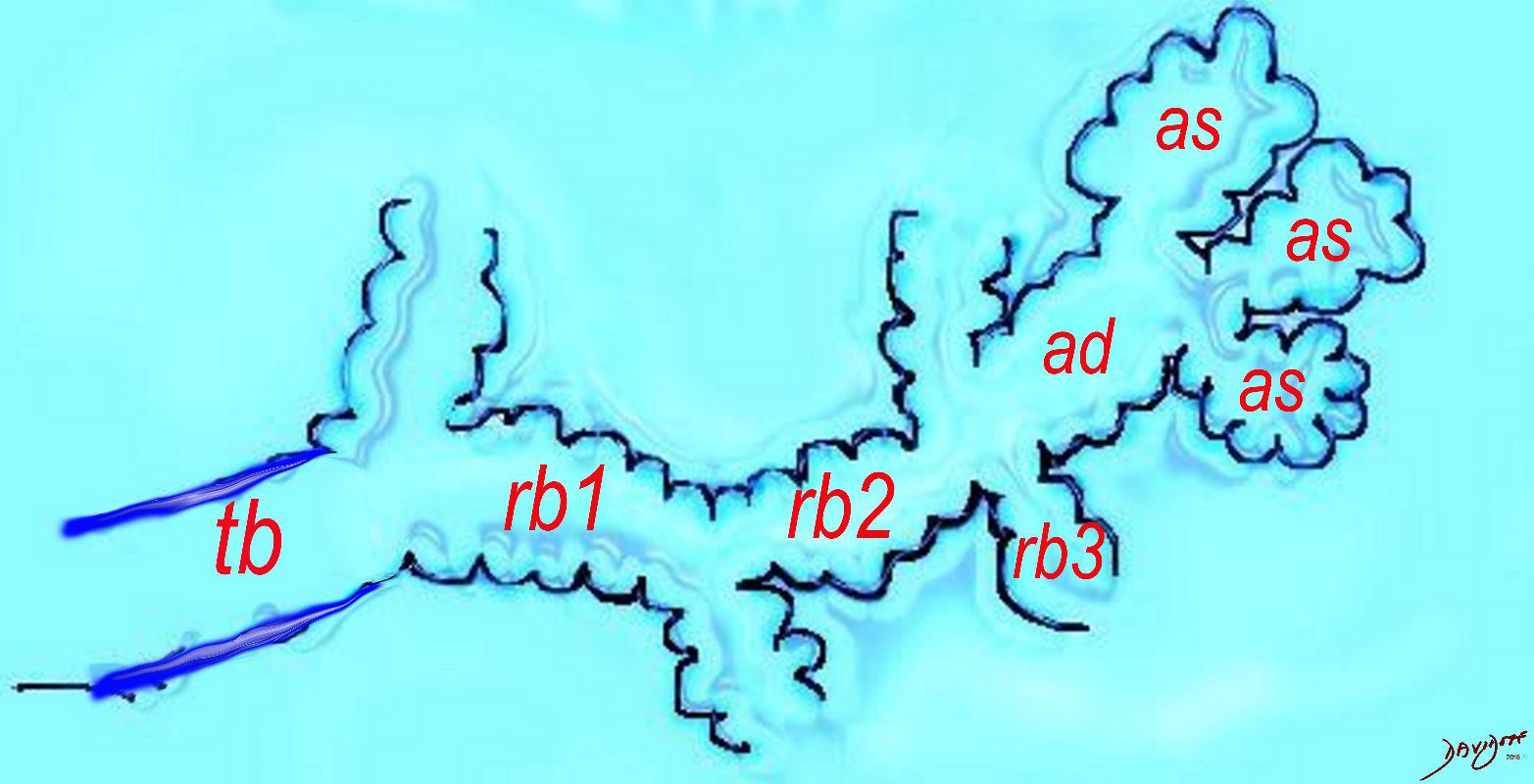
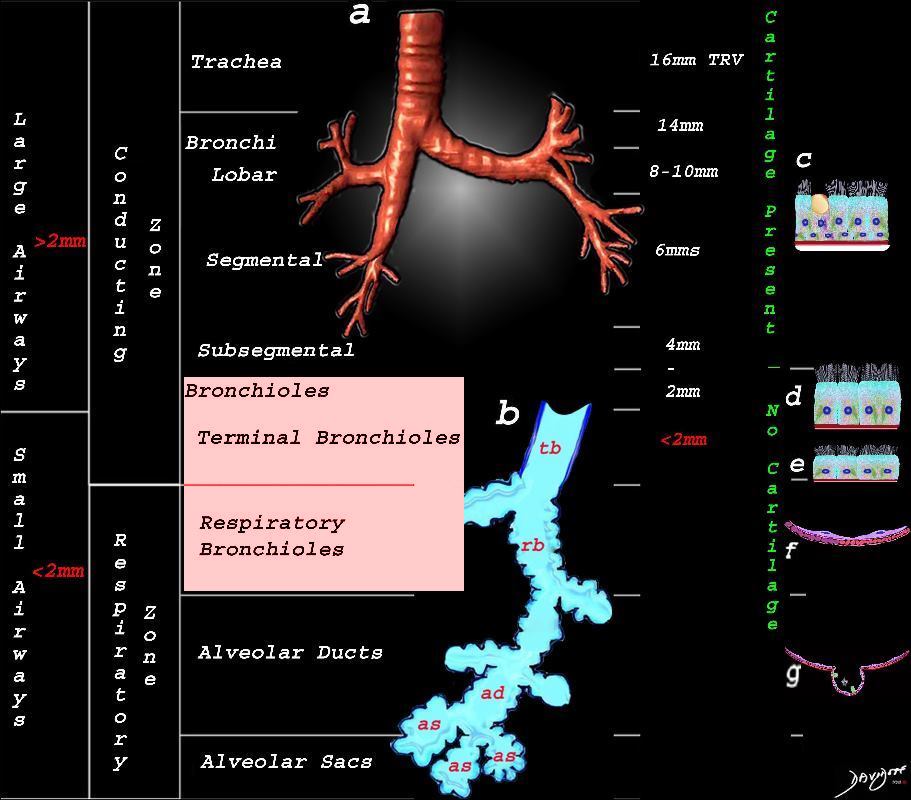
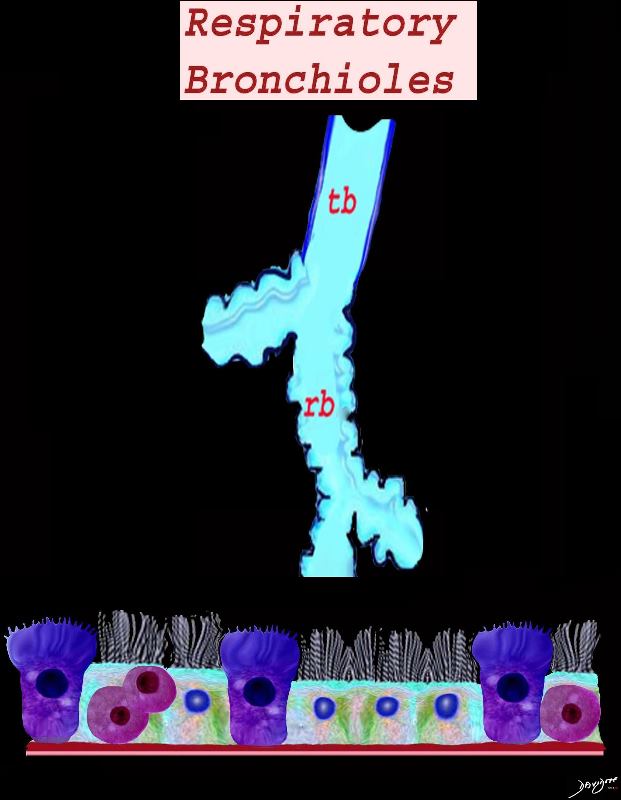
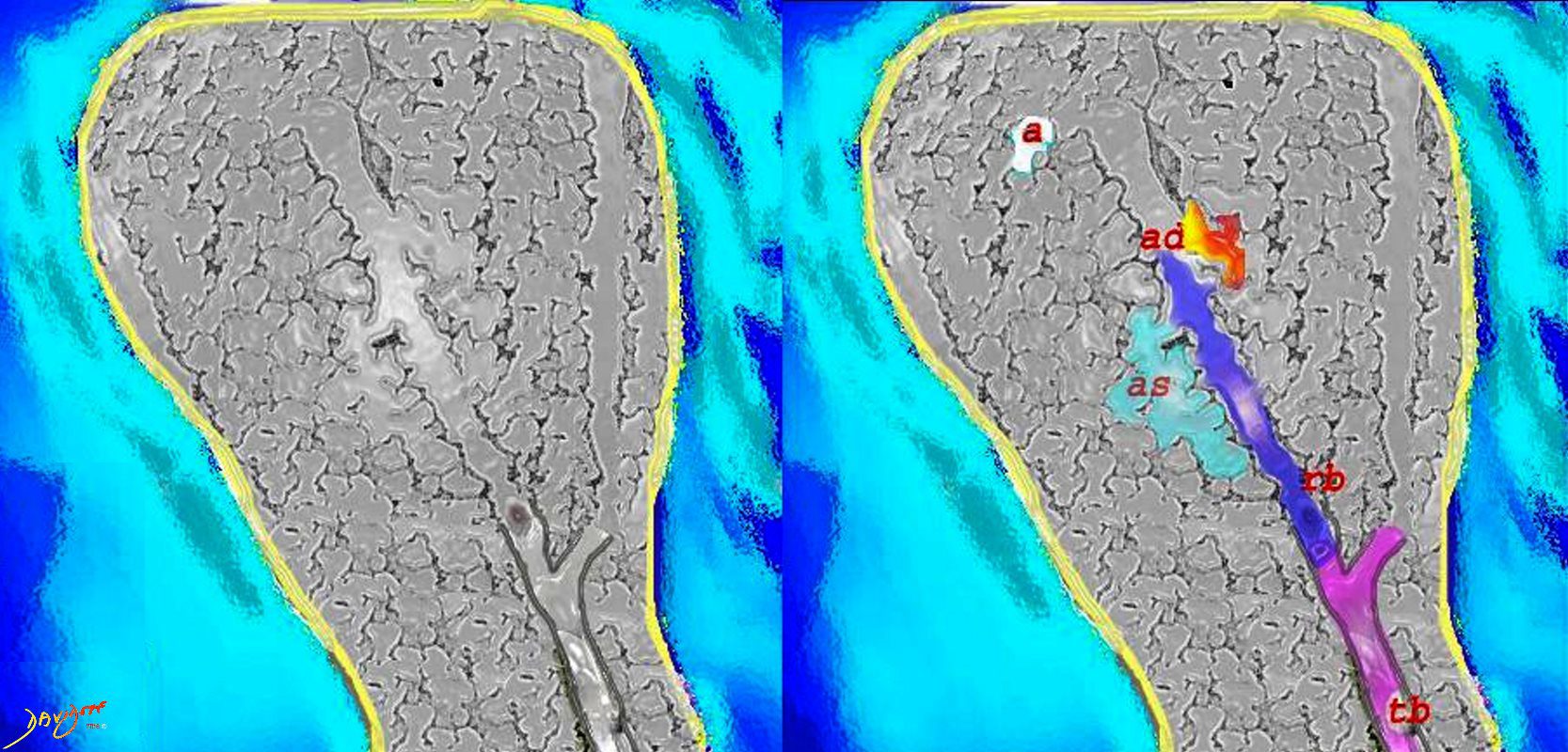
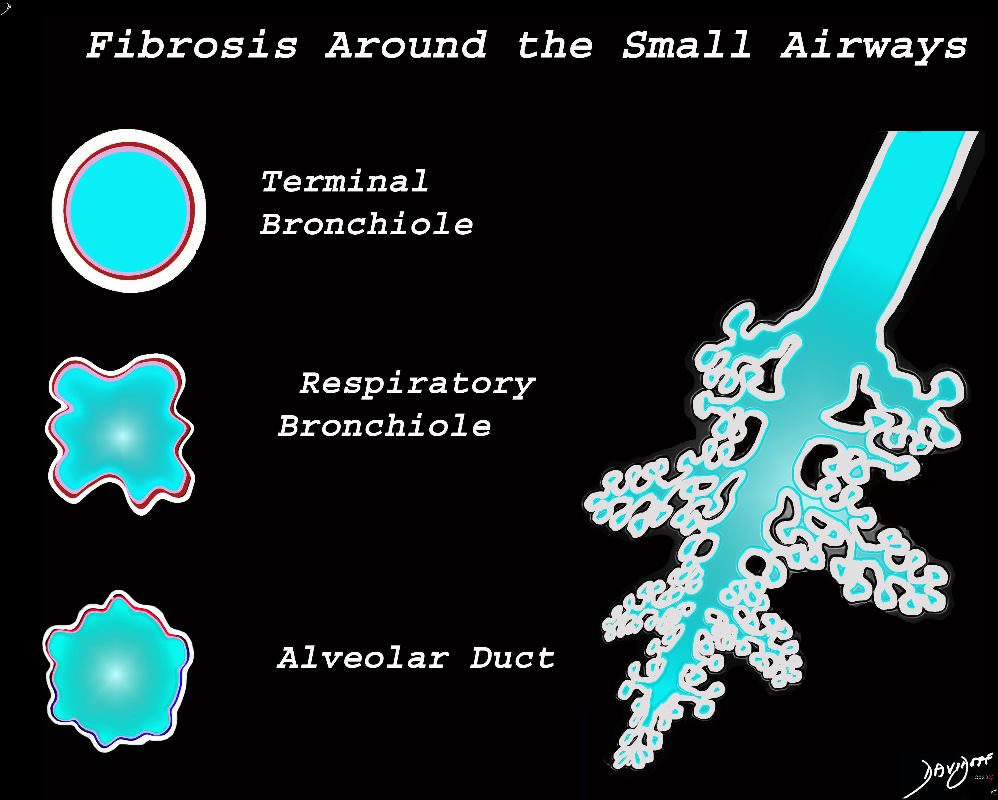
The diagram shows the small airways of the lung ie airways less than 2mm in size including the terminal bronchiole (tb), respiratory bronchiole (rb), alveolar ducts (ad) and alveolar sacs (as) The terminal bronchiole is relatively thick walled and it is last duct of the conducting system of the airways. The respiratory bronchiole (rb) enters the secondary lobule and is the first duct to have gas exchange capability. There can be 3 orders of rb’s, and they branch into alveolar ducts, which branch in turn to alveolar sacs until they reach the alveoli, which is the final destination.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0032-low res
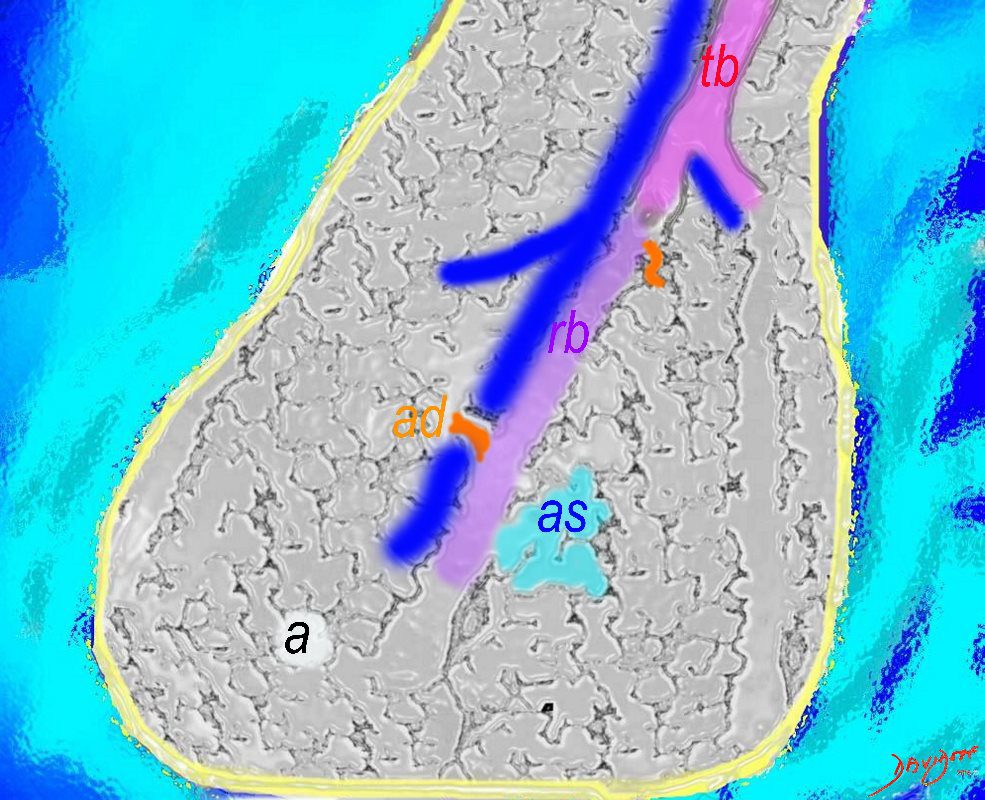
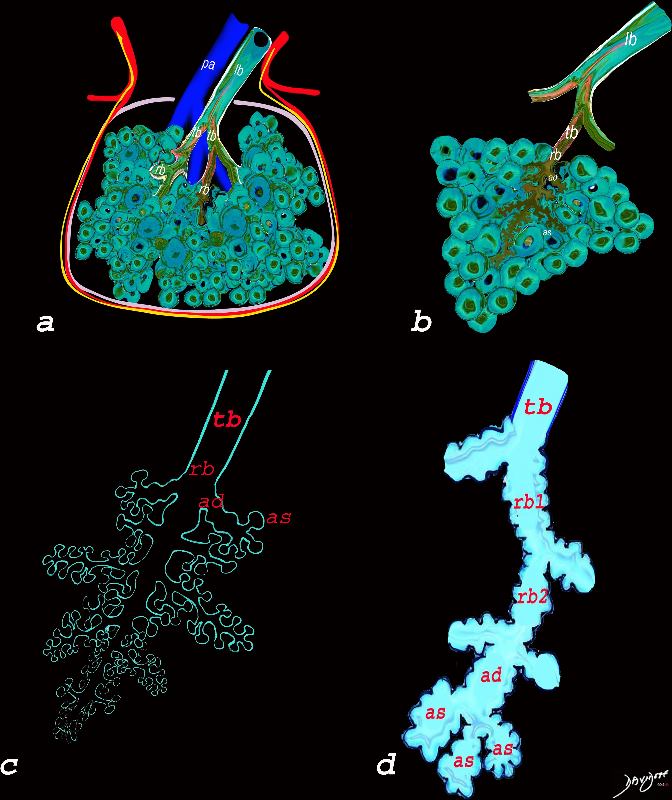
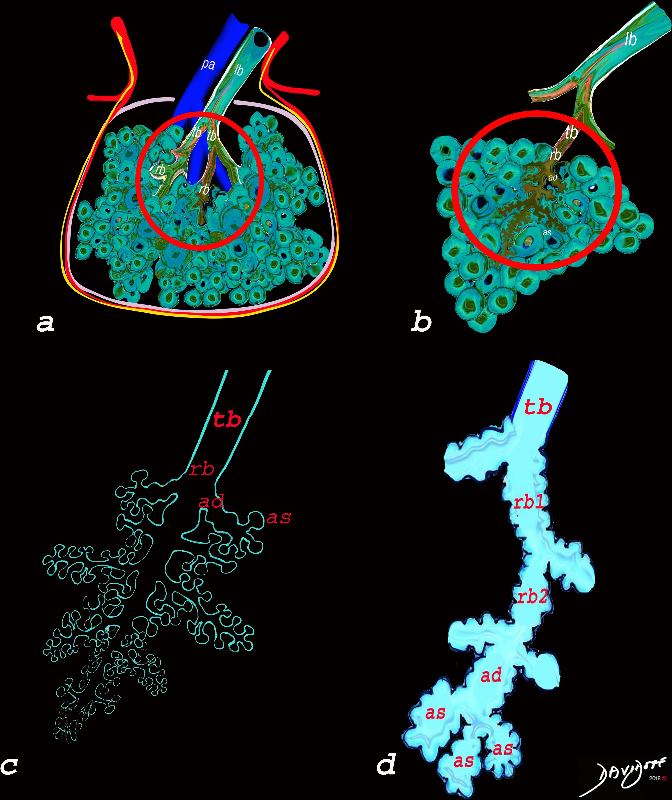
The Duct, and the Artery
The pulmonary arteriole accompanies the airway as it carries oxygen from the trachea to the alveoli. They part ways at the alveoli where the pulmonary venule then takes the oxygenated blood from capillary network around the alveoli back to the left atrium.
The intimate relationship of the airways and the pulmonary artery and their close approximation in size, is helpful in radiology, firstly to identify theese structures and secondly to define disease such as heart failure and bronchiectasis.
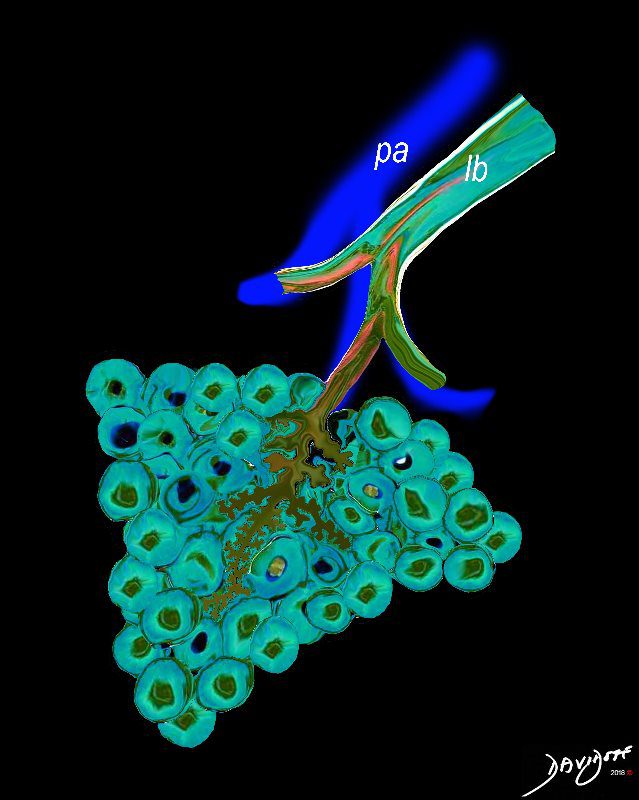
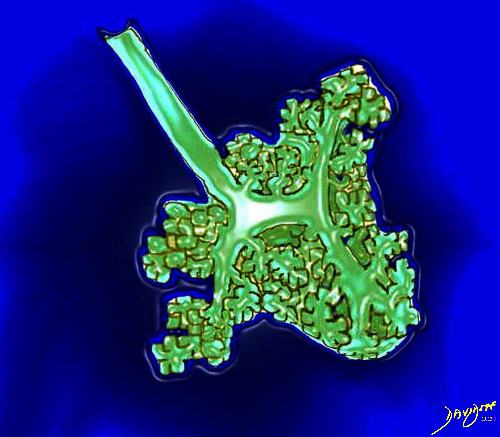
The acinus as shown in this image is defined as a unit of lung consisting of a single first order respiratory bronchiole that subtending a cluster of alveoli reminiscent of a bunch of grapes or berries (acinus in Latin means berry) . The lobular bronchiole (lb) branches into the terminal bronchiole (tb), which then branches into the first order respiratory bronchiole (rb). Subsequent branching after the respiratory bronchiole, includes in order, the alveolar duct (ad), alveolar sac (as), and then finally the berry like alveoli.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff 2019
lungs-0033-low res
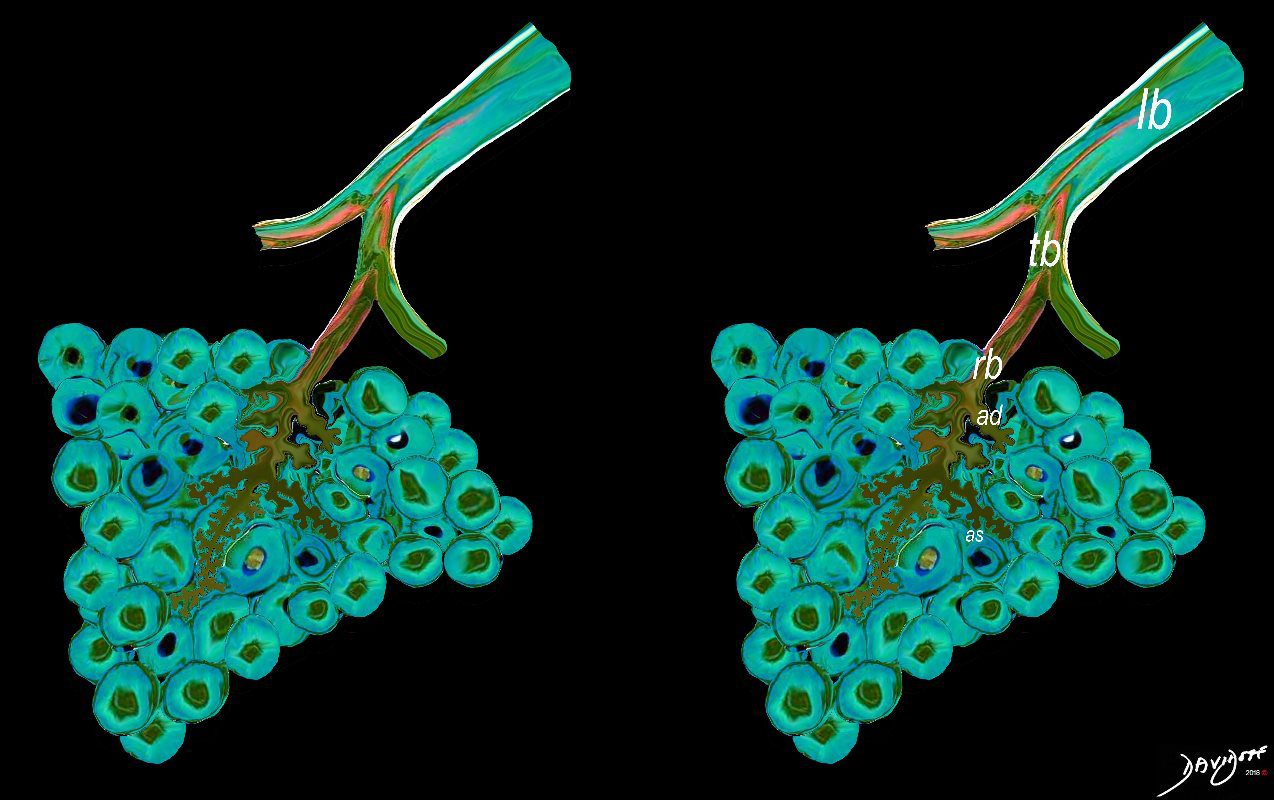
The acinus is defined as a unit of lung consisting of a single first order respiratory bronchiole that subtending a cluster of alveoli reminiscent of a bunch of grapes or berries (acinus in Latin means berry) . The lobular bronchiole (lb) branches into the terminal bronchiole (tb), which then branches into the first order respiratory bronchiole (rb). Subsequent branching after the respiratory bronchiole, includes in order, the alveolar duct (ad), alveolar sac (as), and then finally the berry like alveoli.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff 2019
lungs-0030-low res
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
lungs-0028-low res
The lobular (most distal of the subsegmental airways give rise to the terminal bronchiole which give rise to the membranous airways. These include in order, the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-0007
The lobular (most distal of the subsegmental airways give rise to the terminal bronchiole which give rise to the membranous airways. These include in order, the respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net lungs-0004

Ashley Davidoff The CommonVein.net lungs-0002

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0721
Diseases
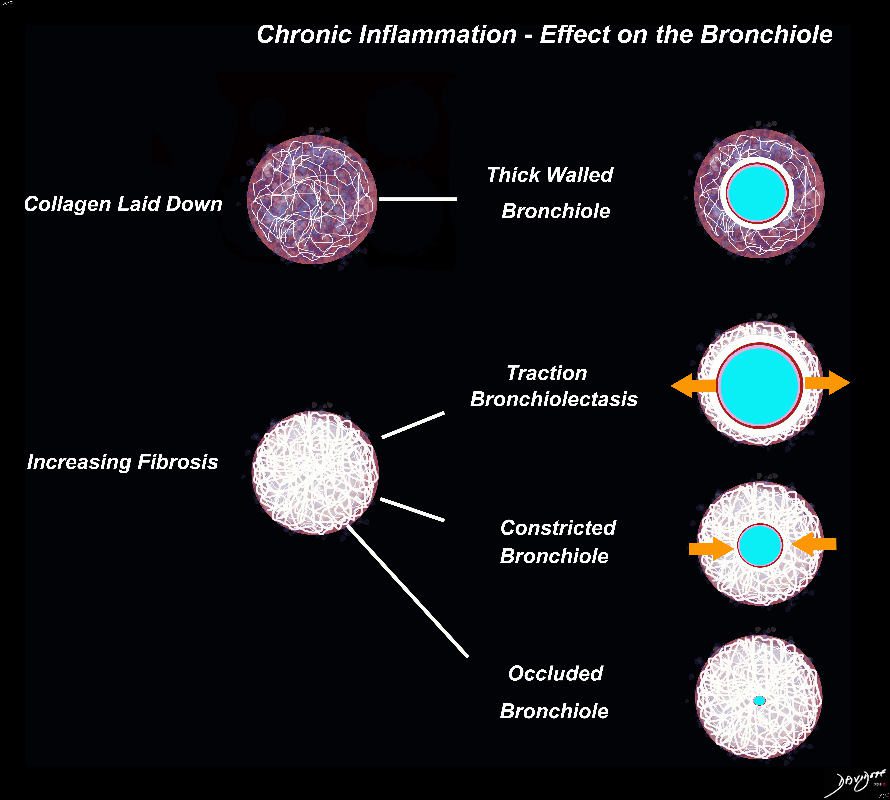
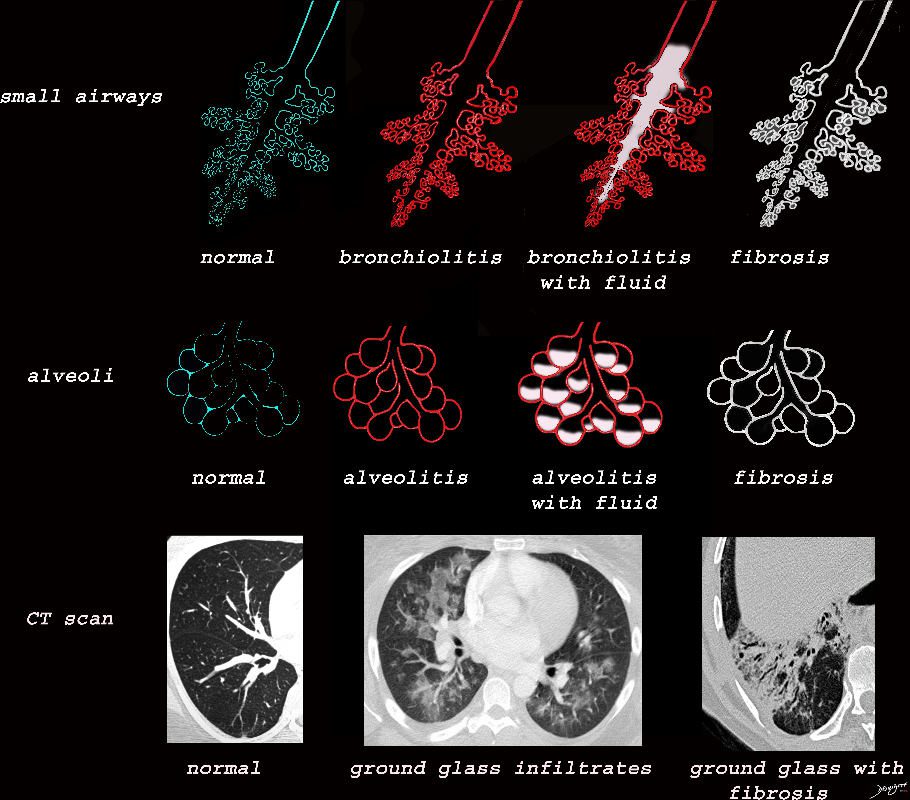
I the early phases collagen starts to get laid down resulting in a thick walled bronchiole surrounded by a subacute inflammatory response of cells and resolving fluid. As the fibrotic process advances it gets denser resulting in traction bronchiectasis and bronchiolectasis. The ongoing may eventually constrict the airway and subsequently occlude occlude the airway
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0700d
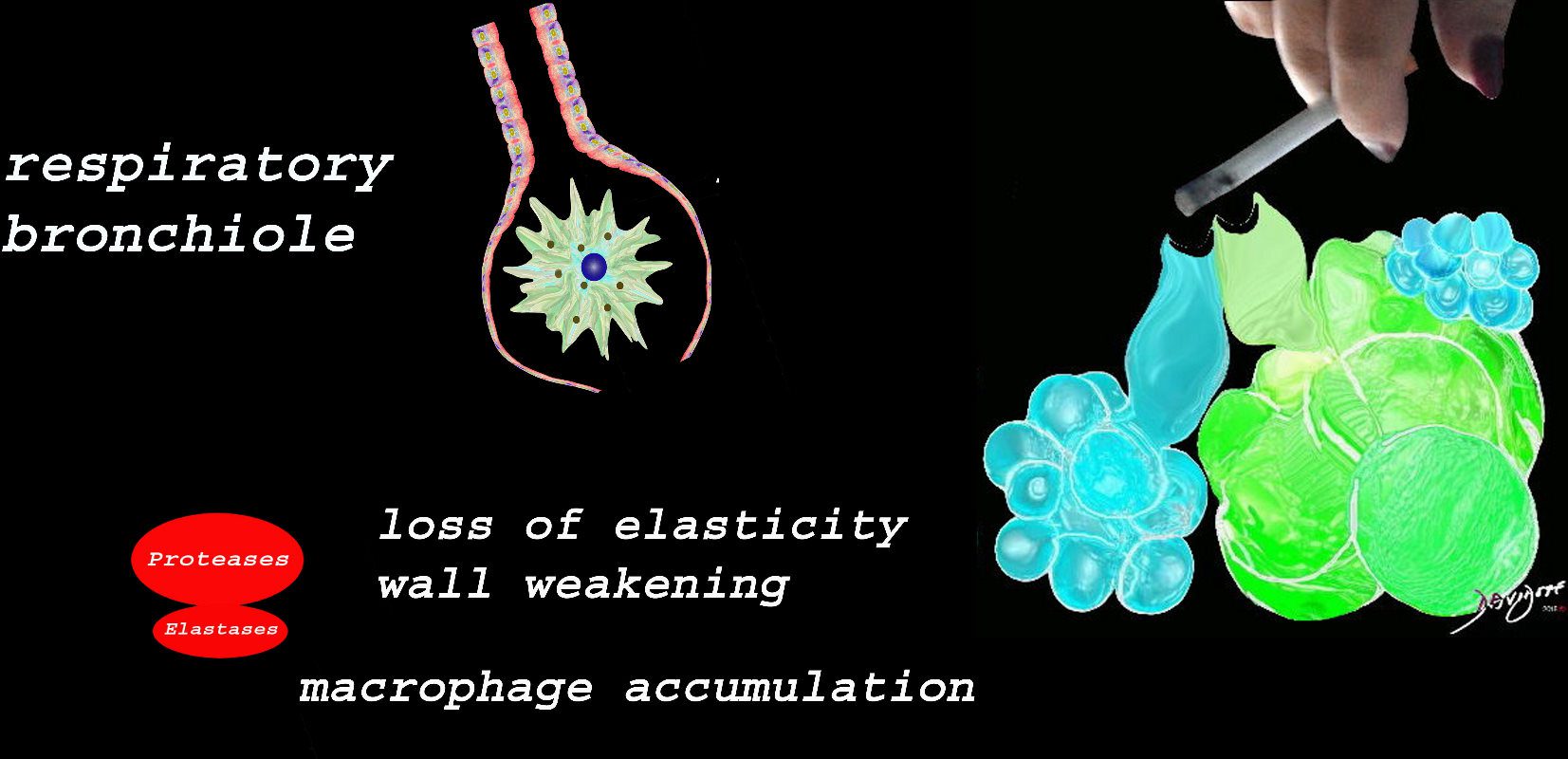

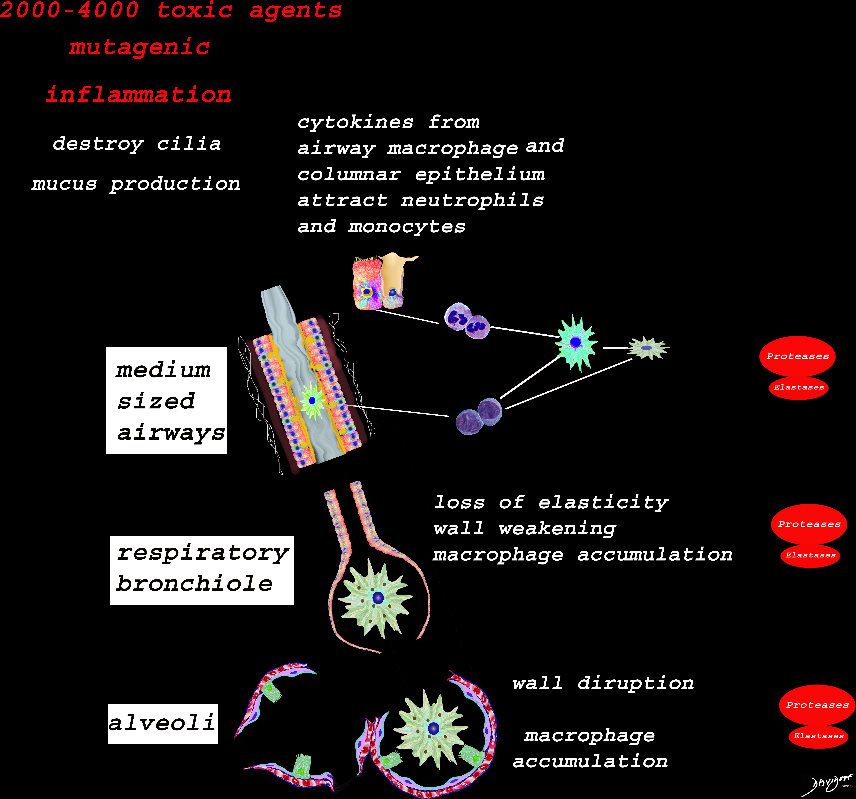
At the level of the membranous airways the effect is predominantly related to the loss of elasticity, and aberrant accumulation of smoking related macrophages.
The weakening and destruction results in emphysema and the abnormal accumulation of smoking related macrophages relates to DIP
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00685


Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00684

Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00683
Amyloid

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net



Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0700d


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0725
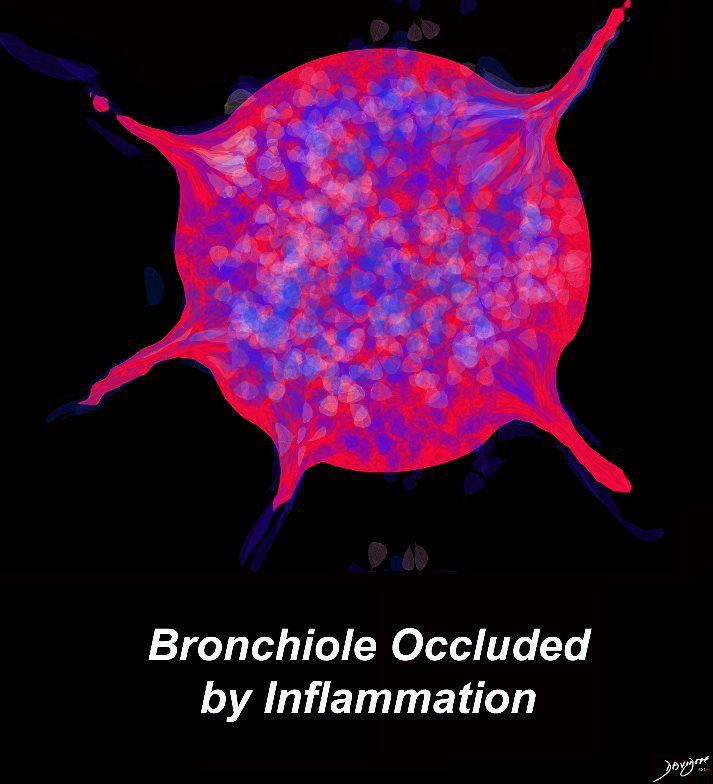

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0724
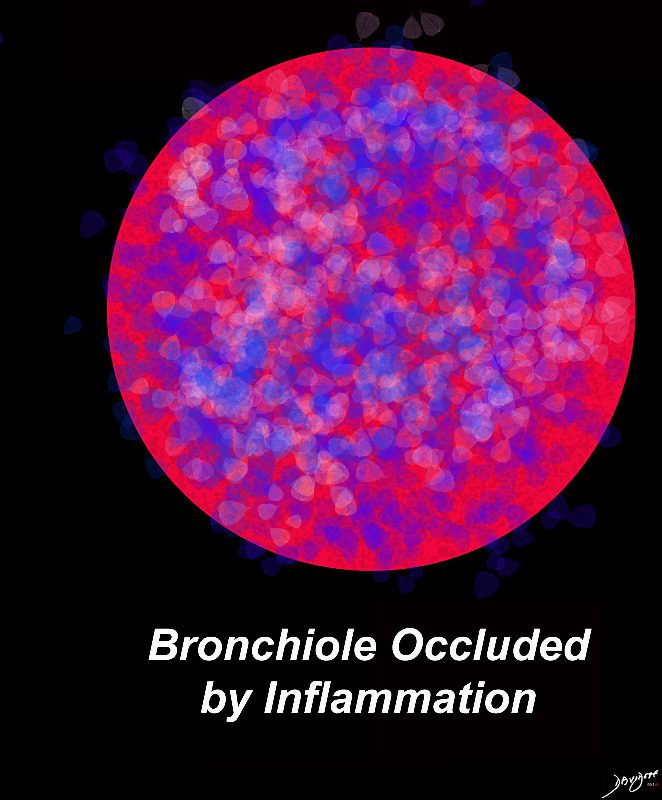

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0724b
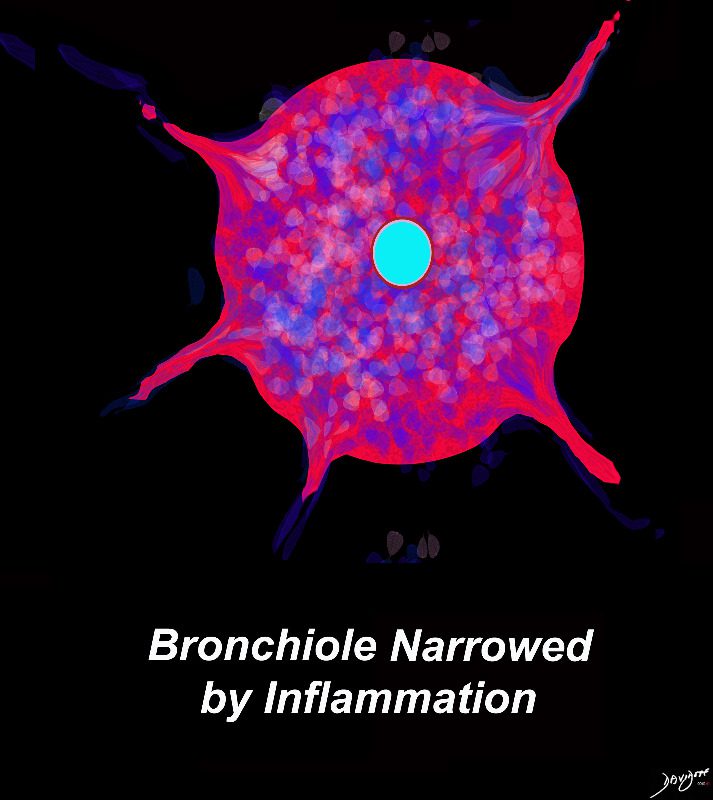

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0723b
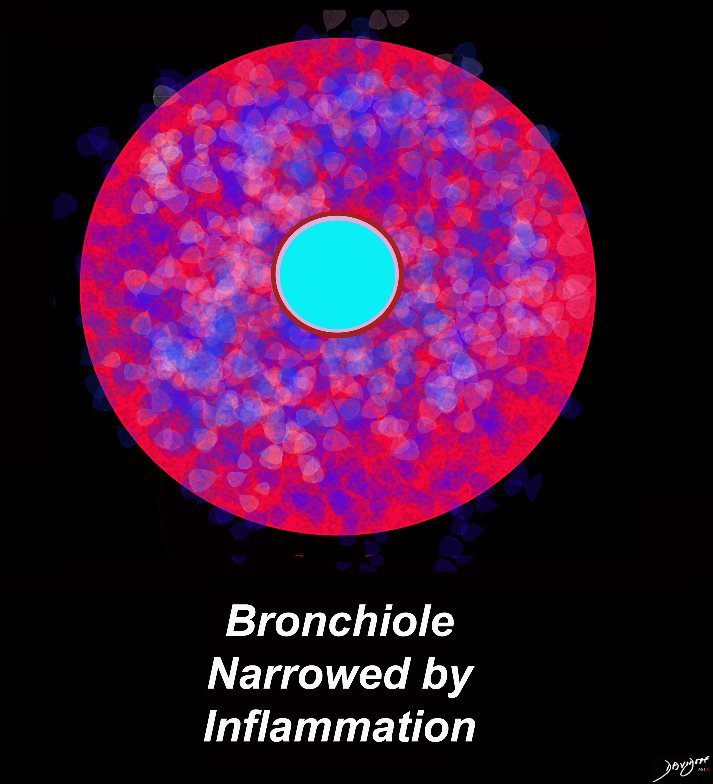

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0723


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0722
Granulomatous Disease

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0731

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0729


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0728b


Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0728b -hi res
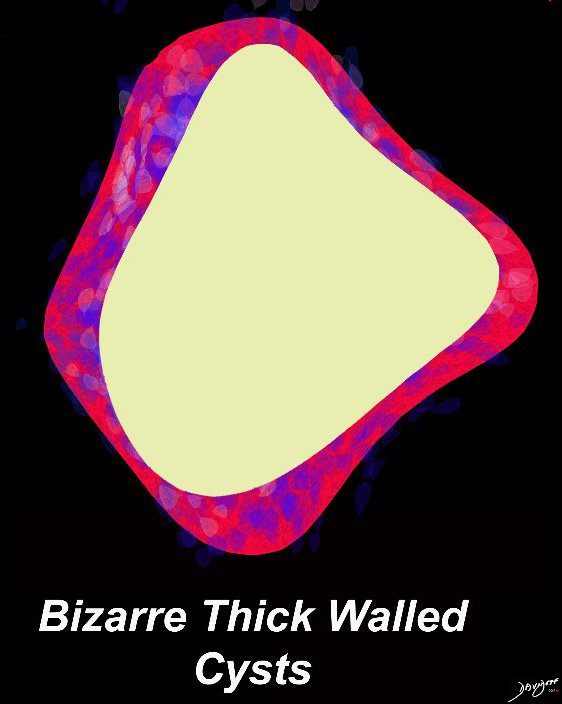

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0726
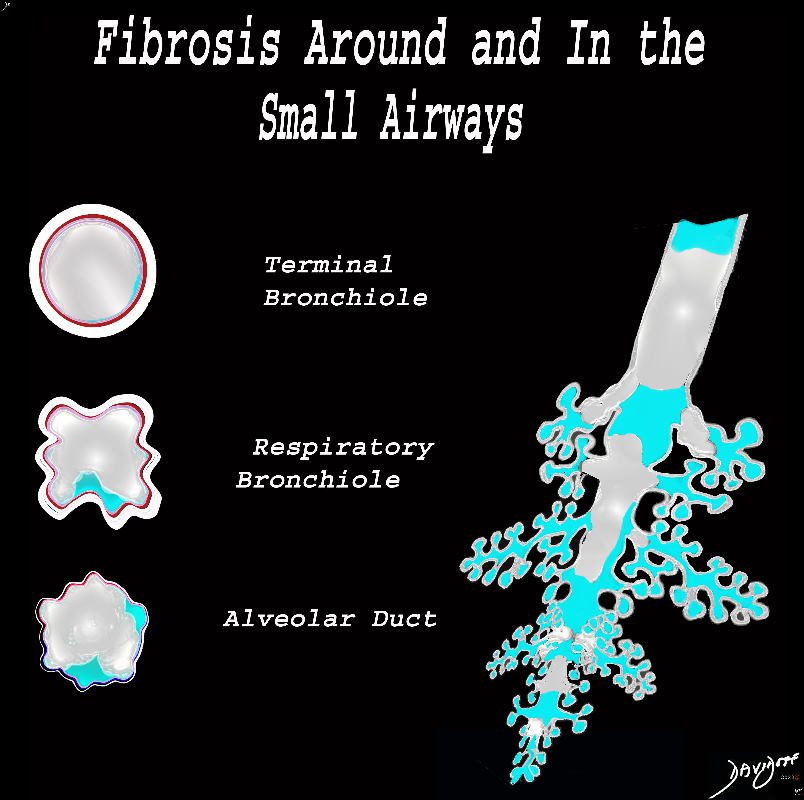

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0778

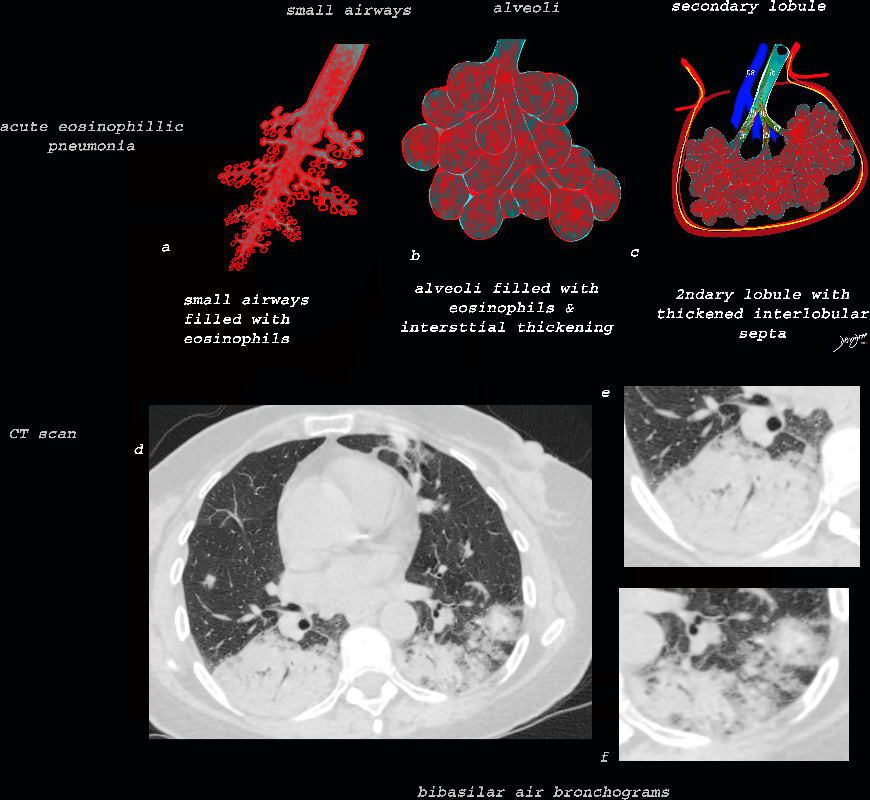
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0777
Eosinophilic Pneumonia

Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0763
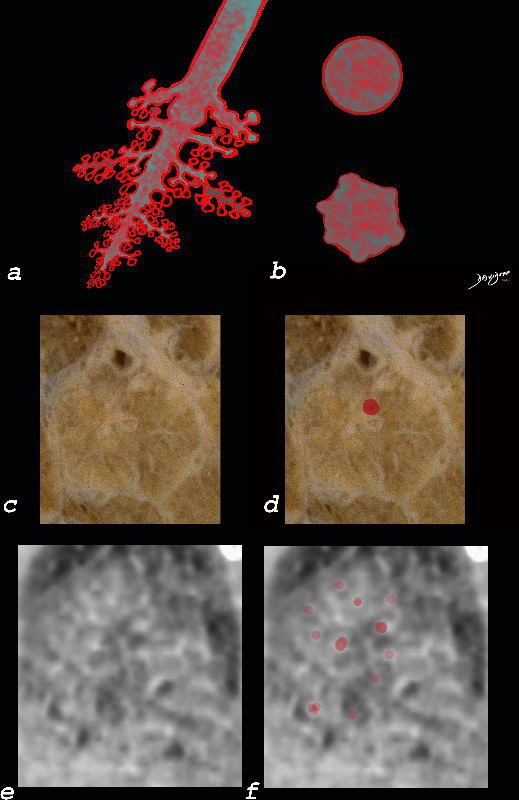

Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0760b
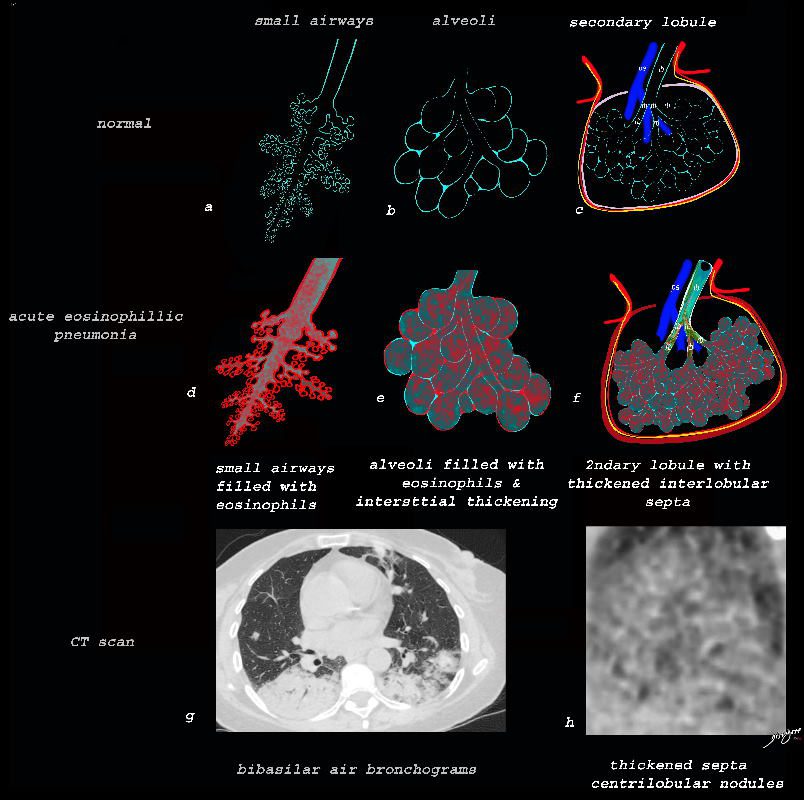

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0757b
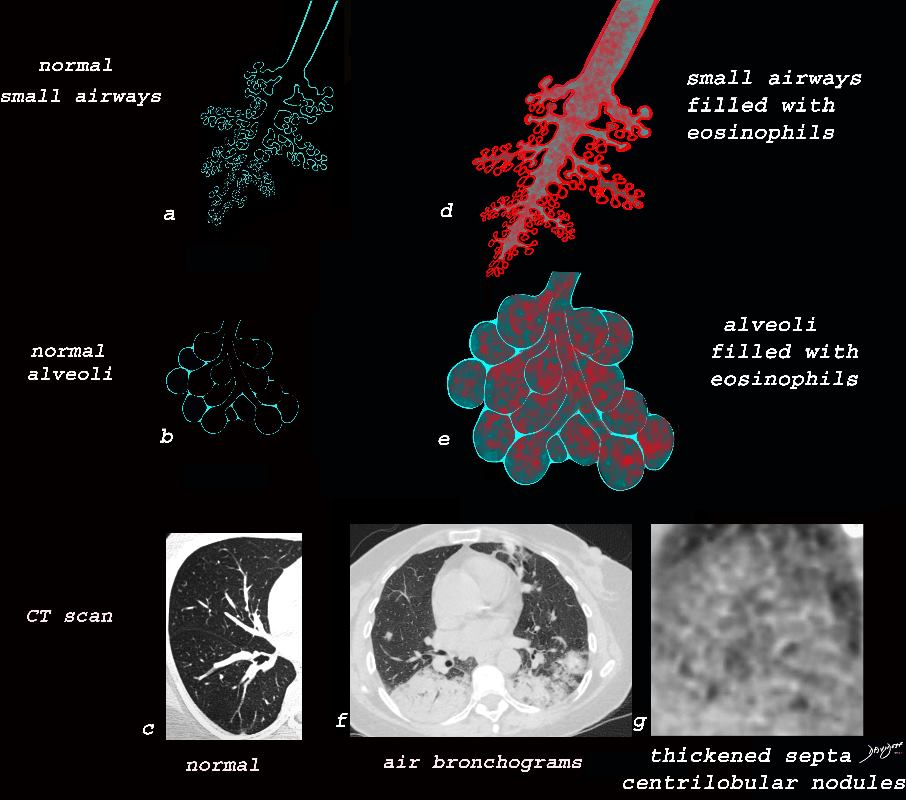

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0757
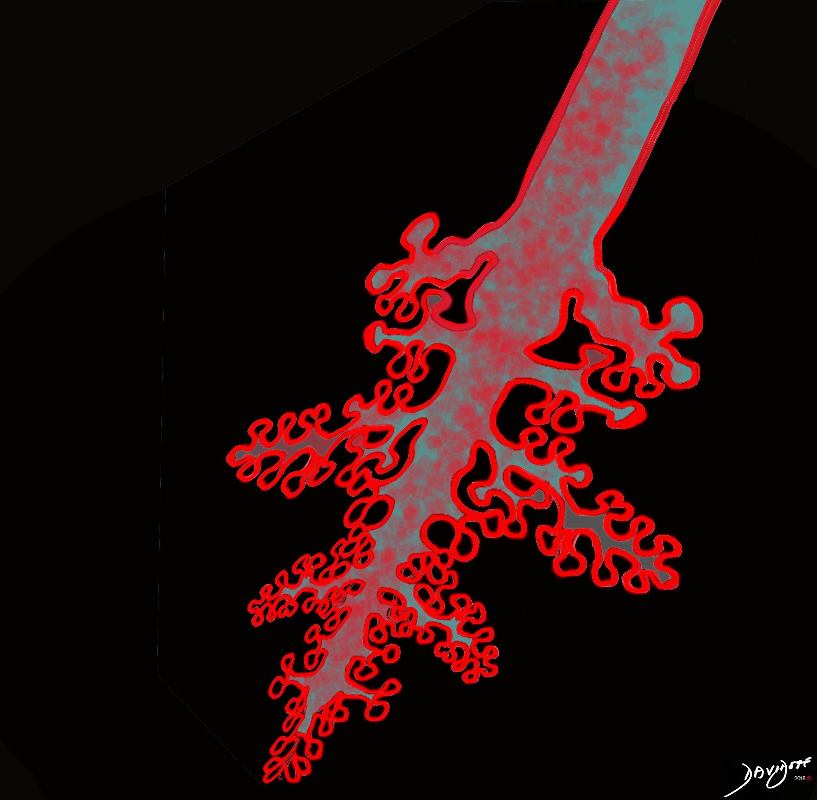

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0755
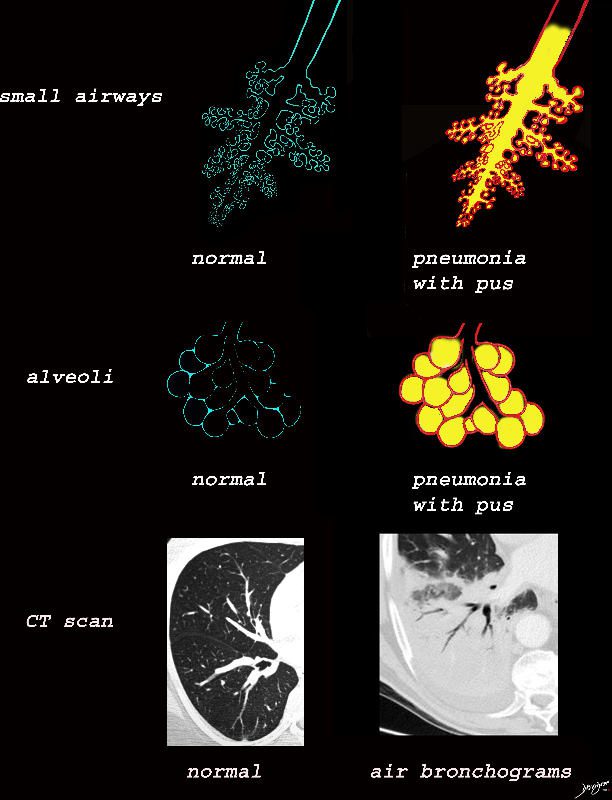

The collage provides a perspective of purulent accumulation in the small airways and the alveoli that results in consolidation. A process that increases the density of the lungs to a net “white” regional density will result in a consolidation and in this case when the fluid is infected it is labelled “pneumonia” The net result on CT is air bronchograms within the non aerated dense lung tissue.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0734

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0733