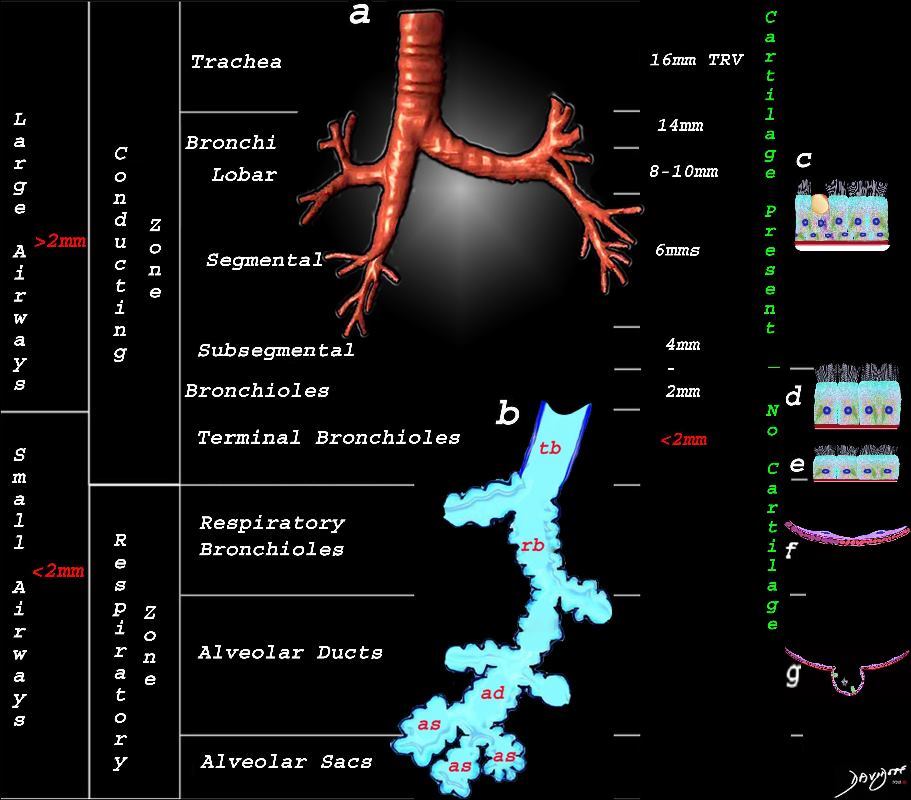
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0740nL
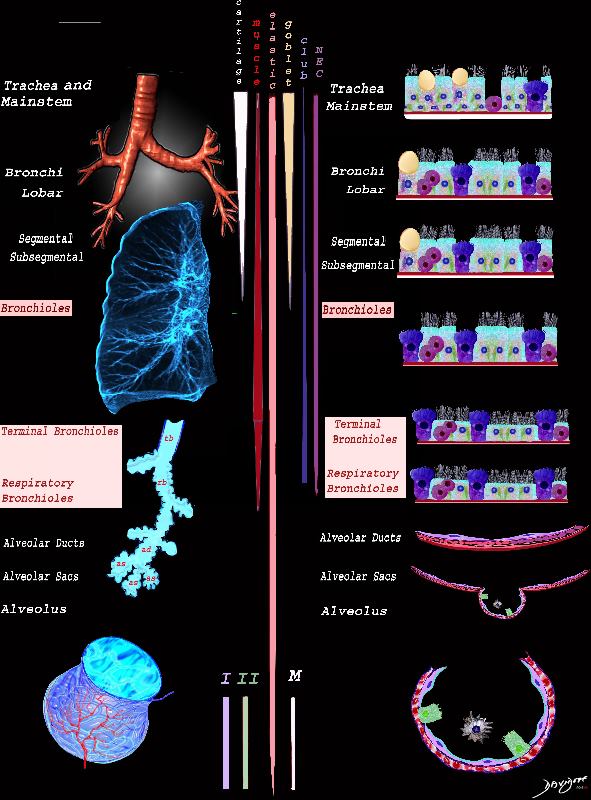
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0742n
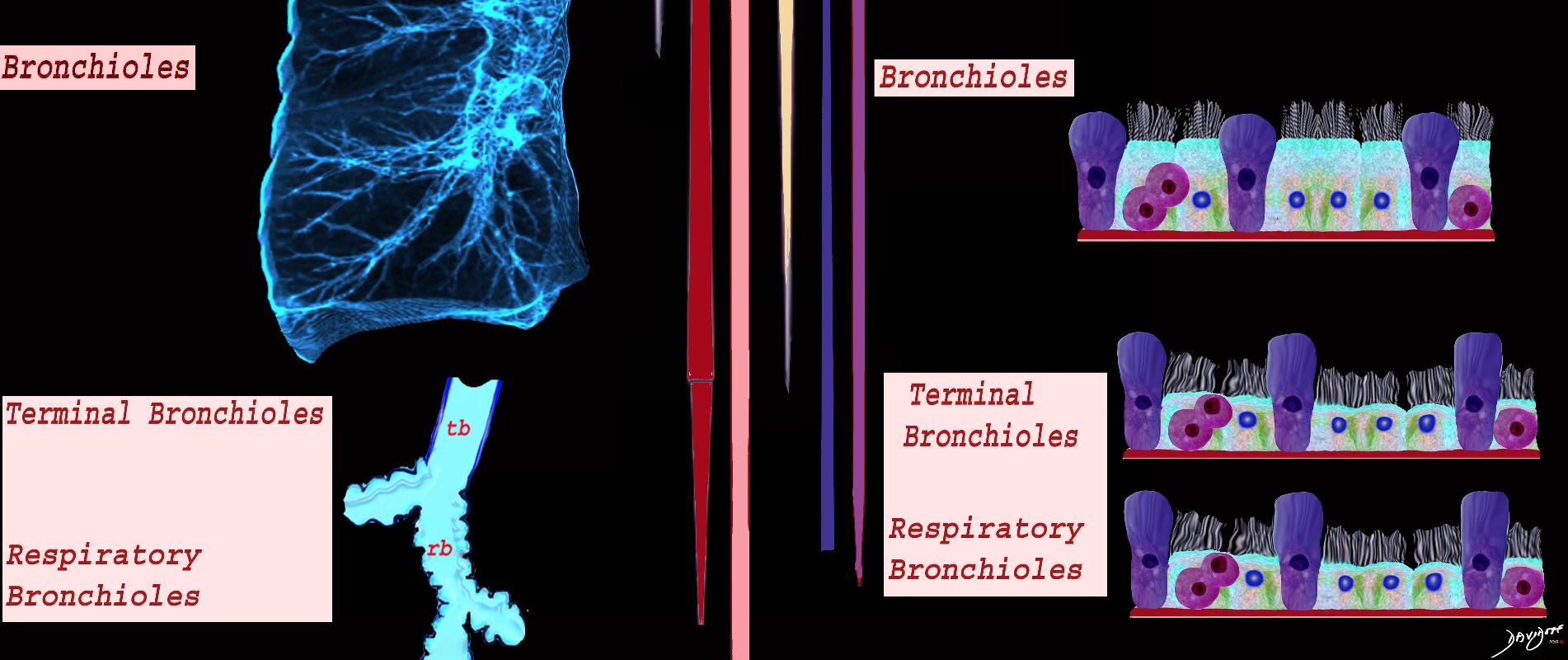
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0742 -lo resb
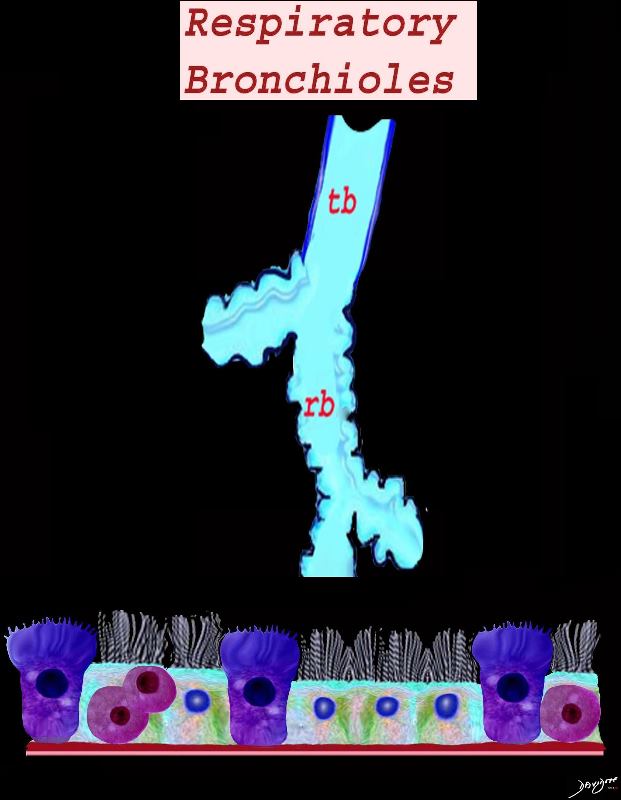
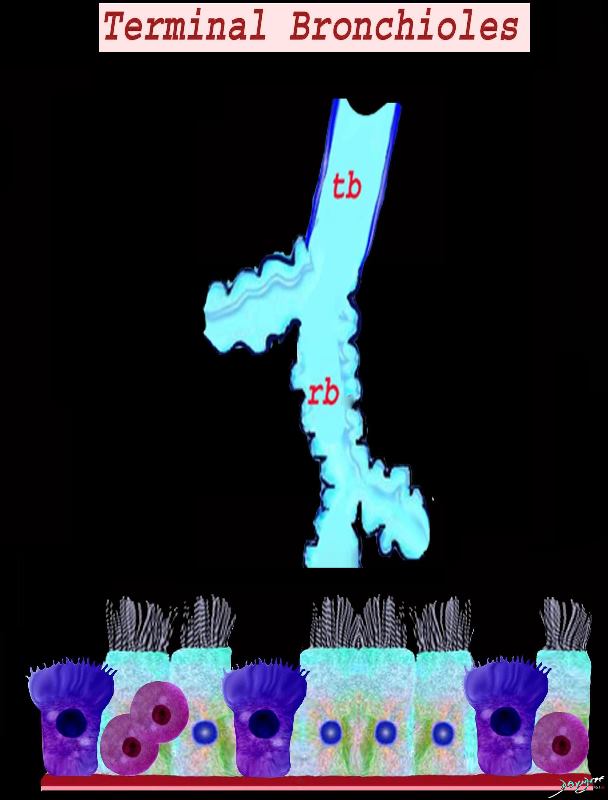
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0747
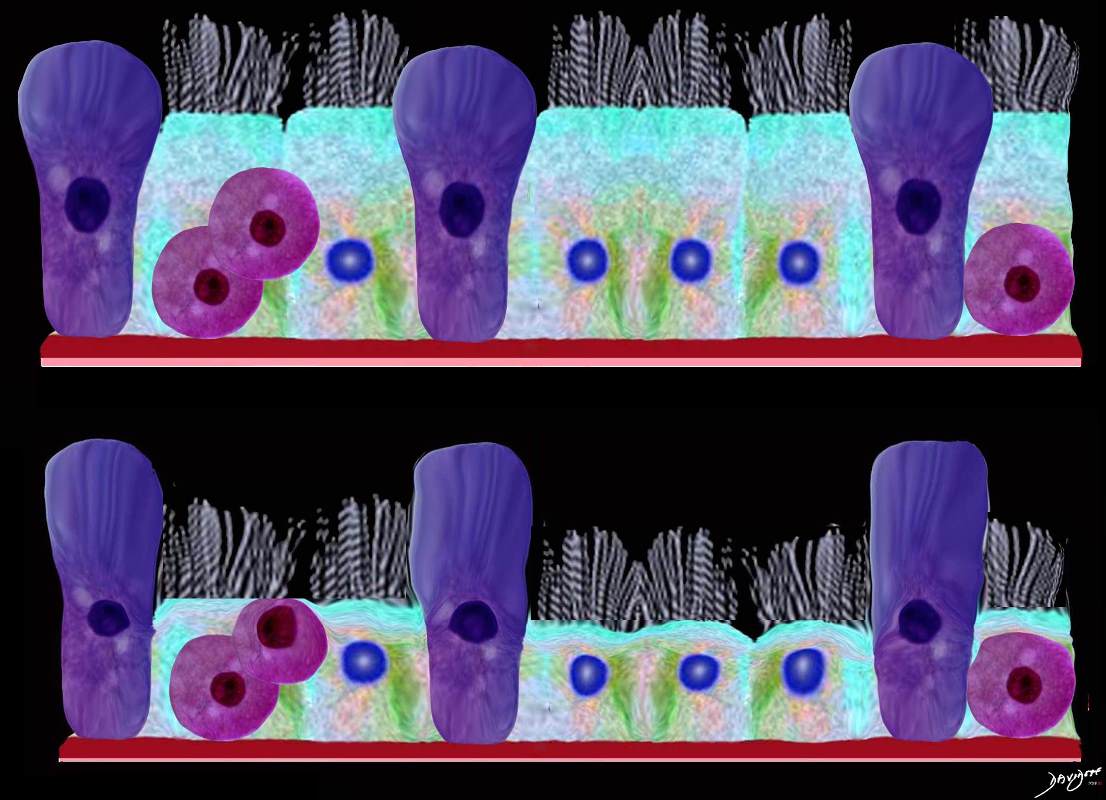
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0746
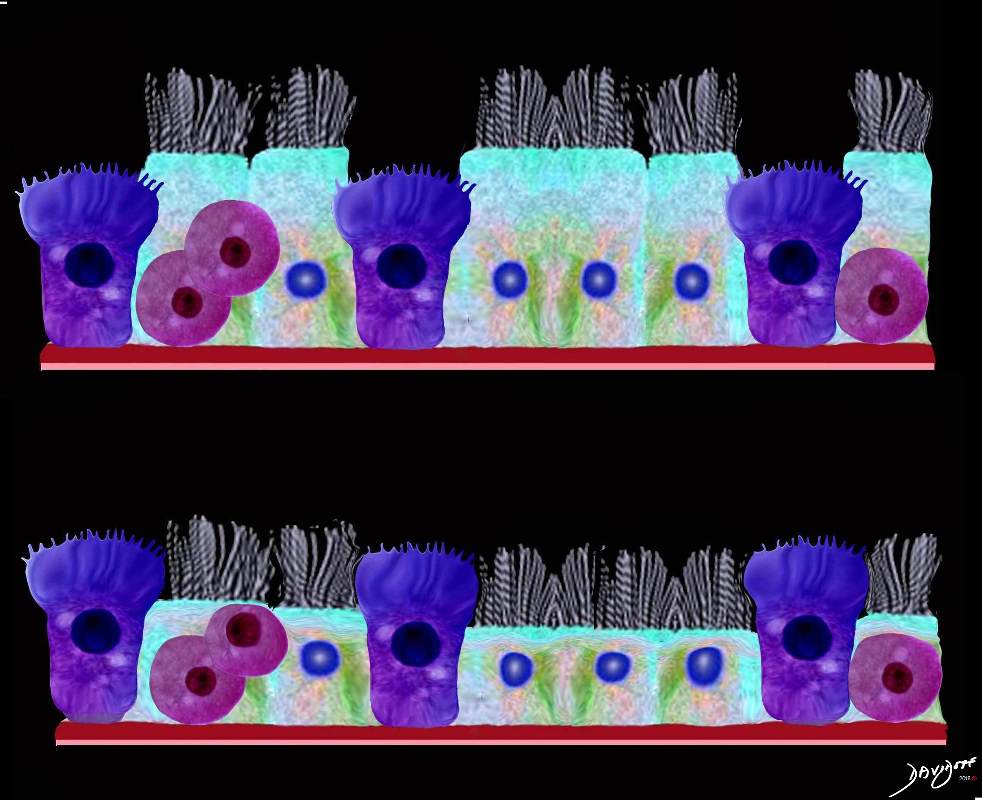
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0741
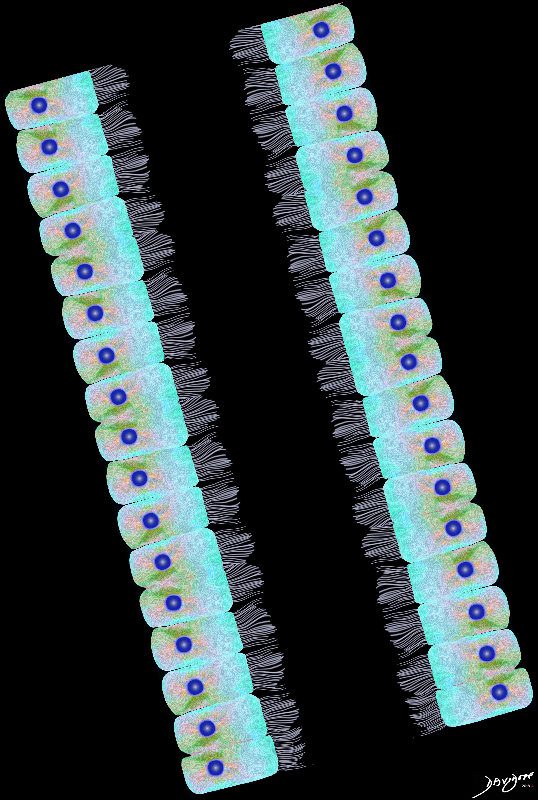
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0741n

Airways are lined by a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium interspersed with mucus secreting goblet cells
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00674b01-lo res
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
lungs-00675-lo-res
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00676
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net lungs-00677
Cells
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0743
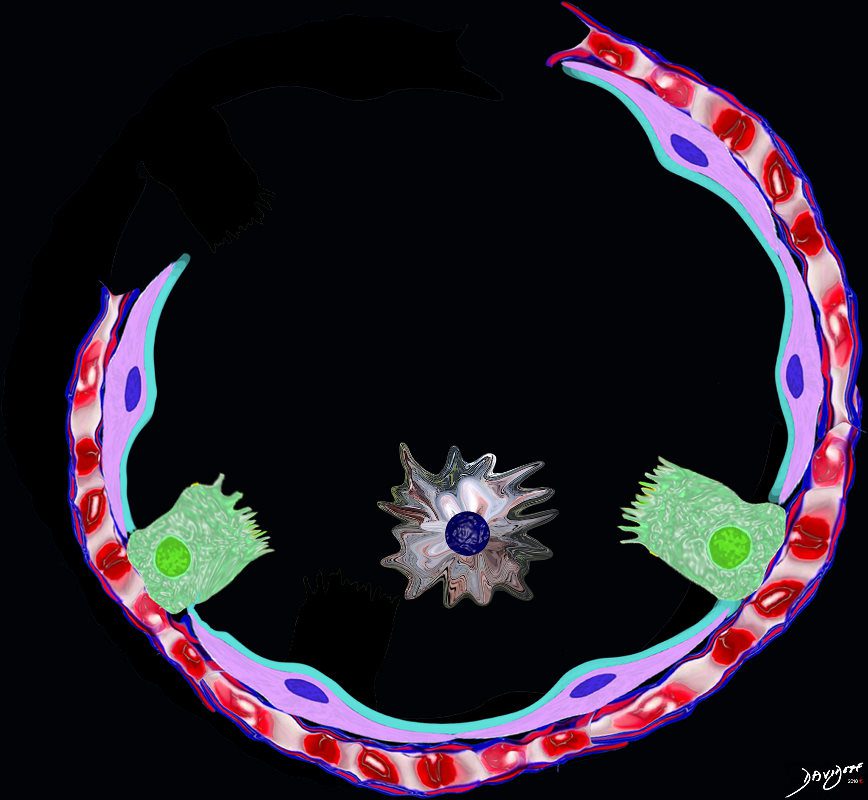

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00679
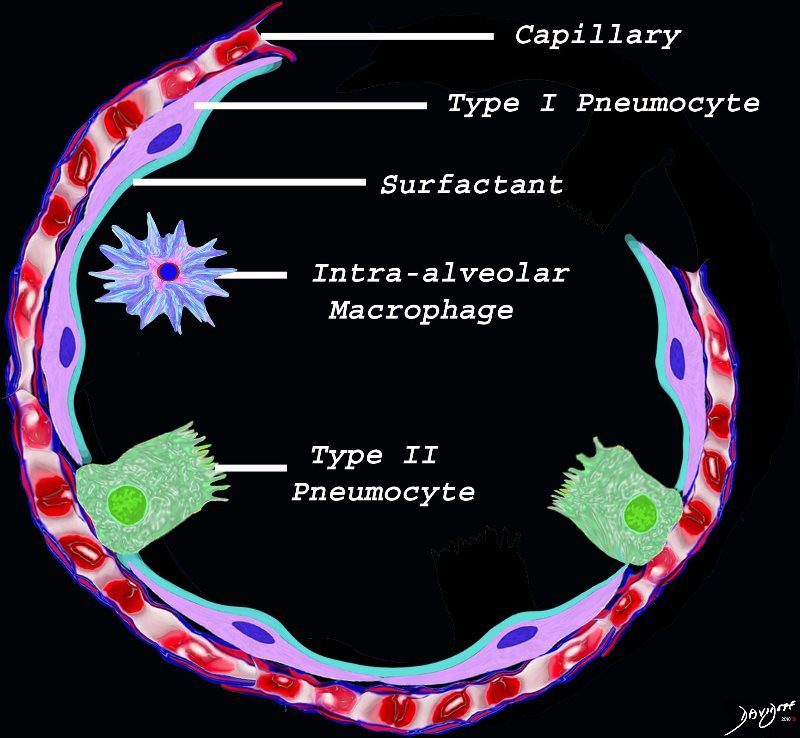
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0689
Ashley Davidoff MD The4CommonVein.net cells-0072

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00686

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0063

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0062

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0061
Diseases
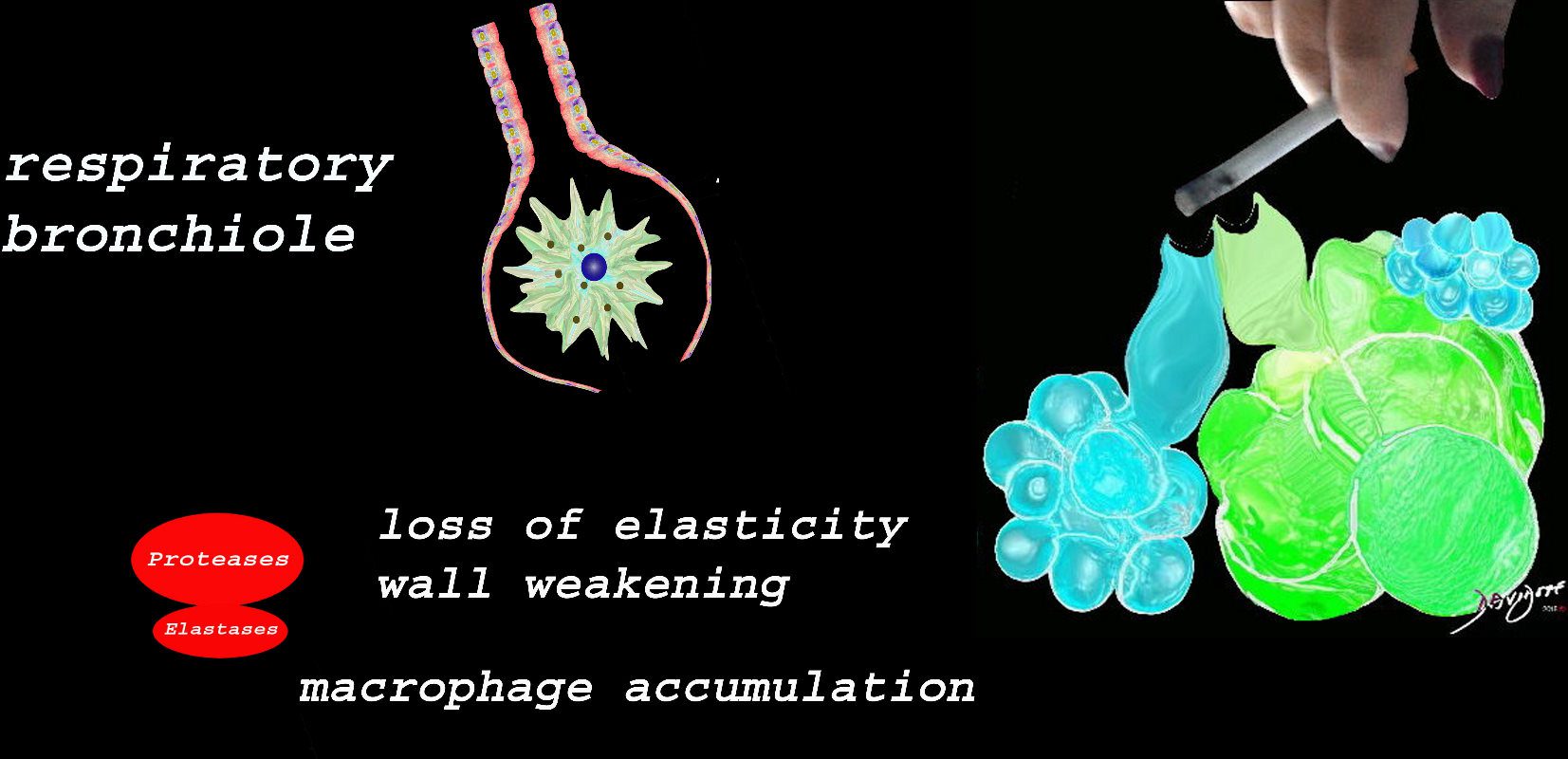
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00685

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00684
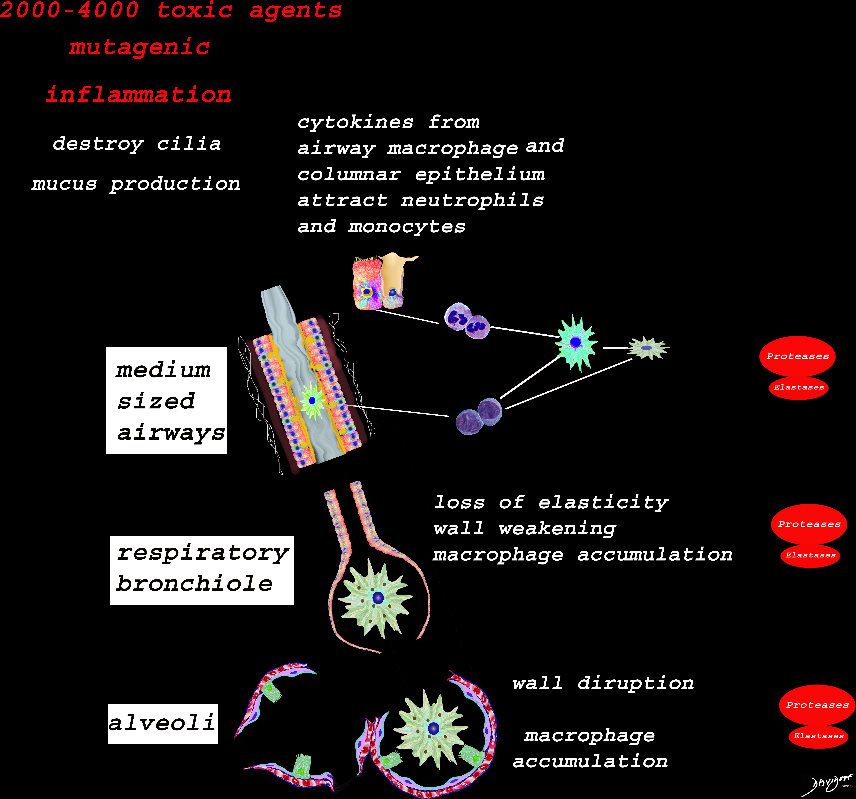
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00683
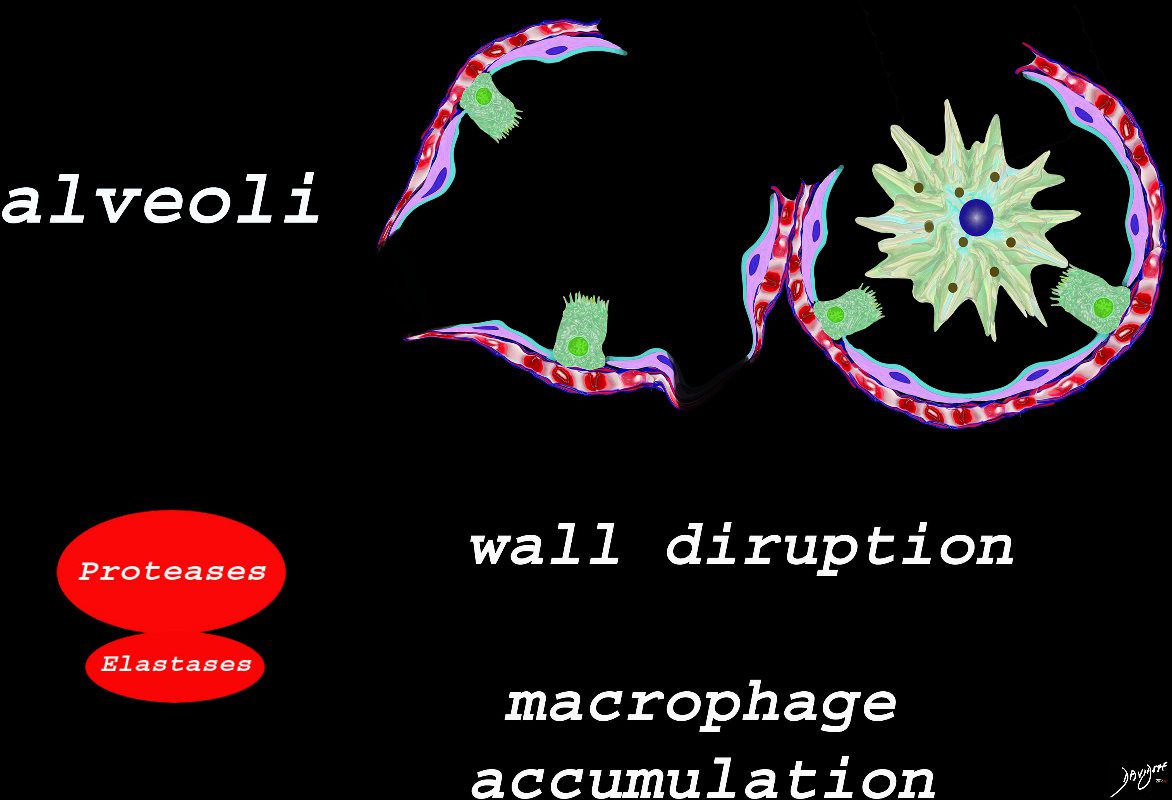
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-00687
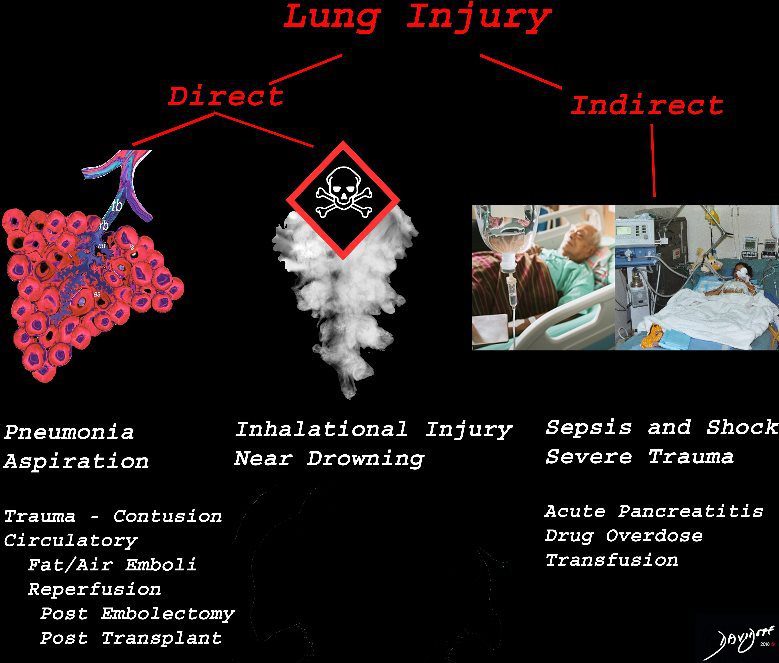
The lung is injured either by direst causes most commonly pneumonia, aspiration or from inhalation of toxic substances. Severe systemic illnesses, most commonly sepsis with shock, and severe trauma are considered indirect causes.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0690
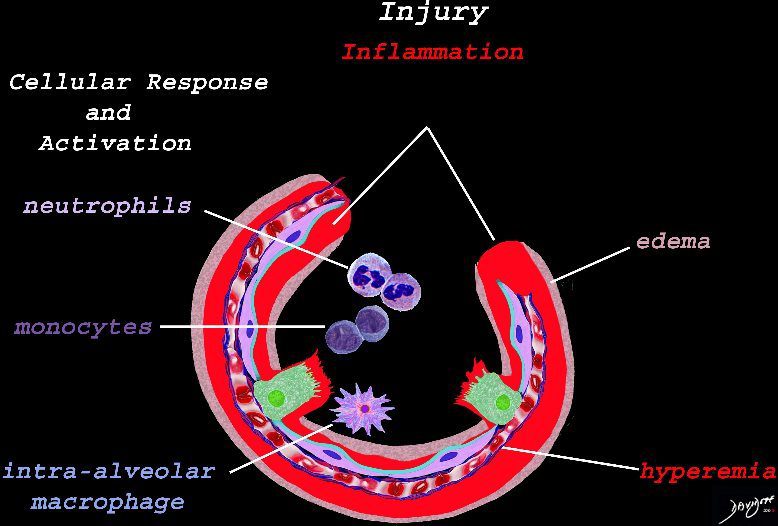
The initial injury results in an acute severe inflammatory response consisting hyperemia , edema with migration initially of neutrophils in the first 6-24 hours followed by monocytes (24-48hours). The intra -alveolar macrophages are activated.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0691
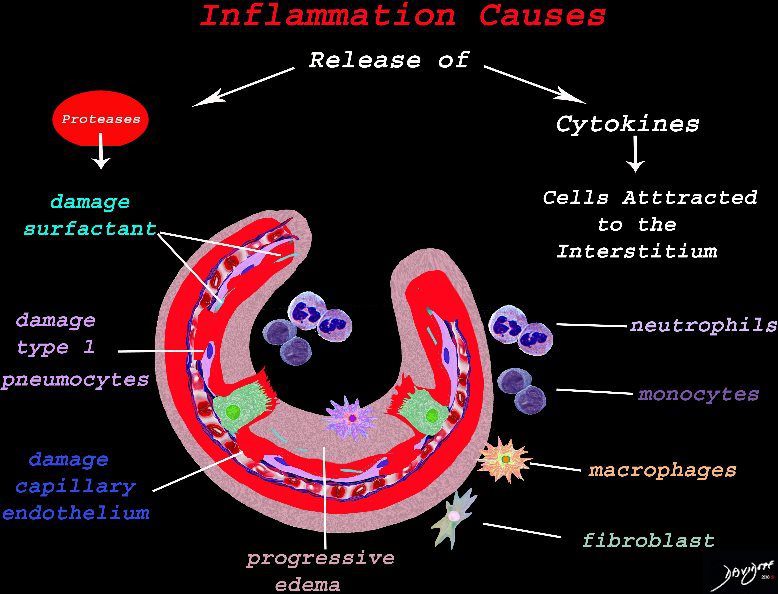
The cells of the immune system release cytokines, chemotactic agents and proteases. Immune cells , macrophages and fibroblasts are attracted to the interstitium. Some of proinflammatory agents are toxic to the cell lining causing damage to the surfactant, type 1 pneumocytes and the capillary endothelium. There is progressive edema.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0692

A hyaline membrane evolves covering the damaged surface of the alveolus. This impedes gas exchange
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net lungs-0694
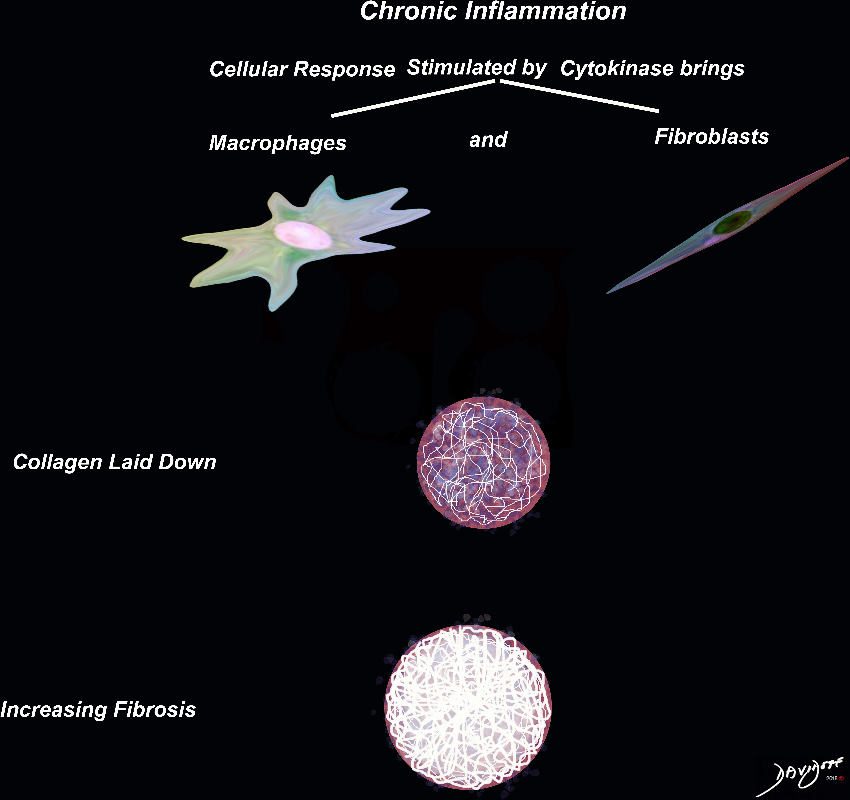
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net Chronic Inflammation – The Basics
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net lungs-0699d
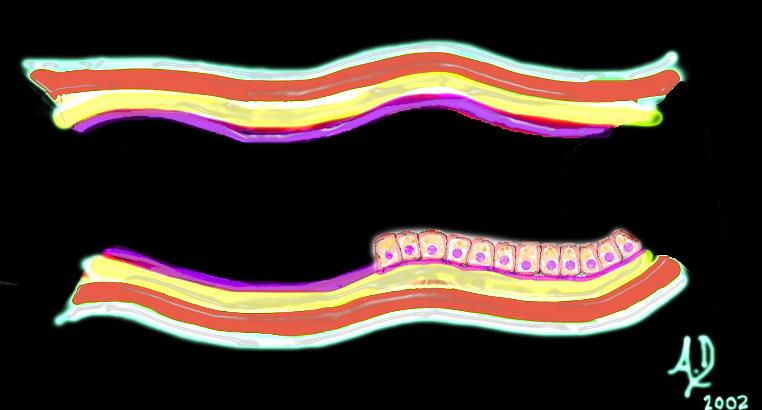
key words art mucosa submucosa muscularis adventitia serosa histology tube colon small bowel lung bronchus bronchi esophagus stomach large bowel bile duct ureter tube principles Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32347
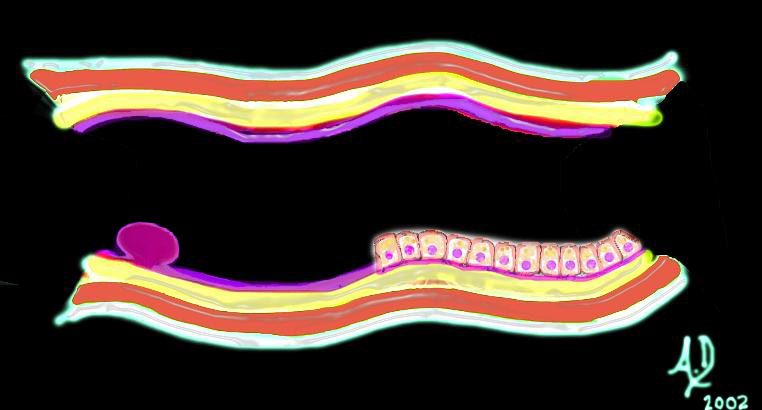
key words mucosa submucosa muscularis adventitia serosa mucosal mass polyp neoplasm carcinoma acute angles with the lumen histopathology imaging diagnosis Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32347d01
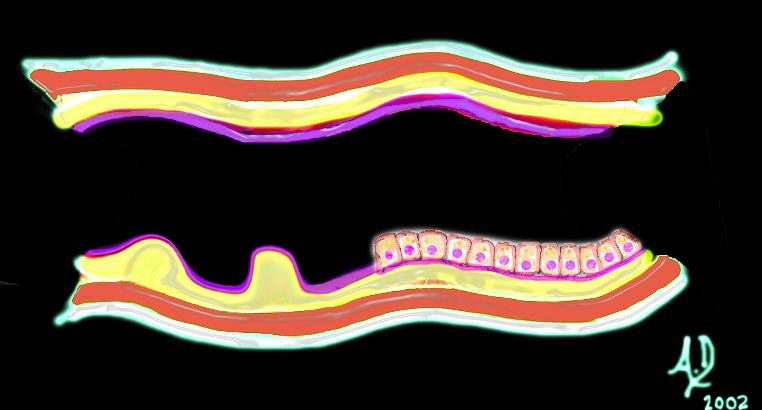
key words mucosa submucosa muscularis adventitia serosa submucosal mass edema hemorrhage obtuse angles or right angle 90 degree ninety degree angle with the lumen histopathology imaging diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32347d02
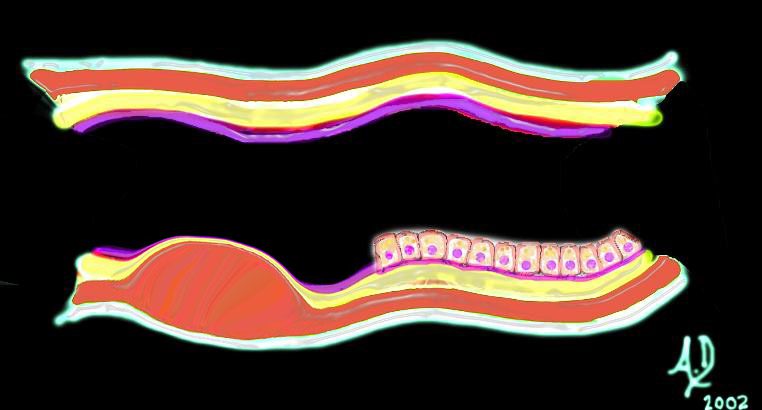
key words mucosa submucosa muscularis adventitia serosa submucosal mass edema hemorrhage obtuse angles or right with the lumen histopathology imaging diagnosis Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32347d03
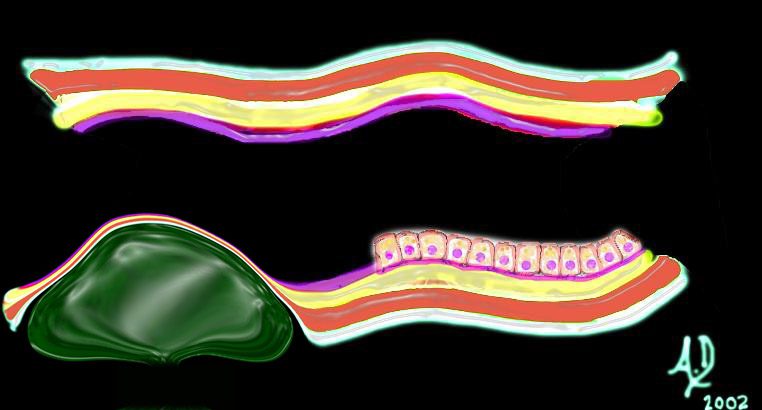
key words mucosa submucosa muscularis adventitia serosa submucosal mass edema hemorrhage neoplasm malignancy benign obtuse angles with the lumen histopathology imaging diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32347d04
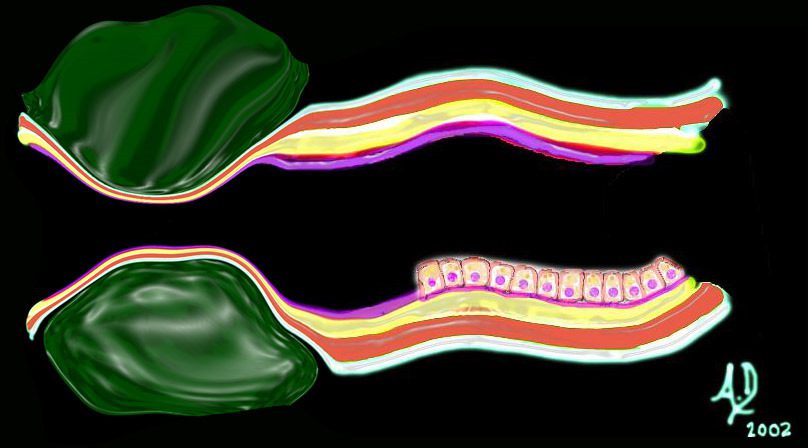
key words mucosa submucosa muscularis adventitia serosa submucosal mass edema hemorrhage neoplasm malignancy benign obtuse angles with the lumen circumferential narrowing constriction obstruction histopathology imaging diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 32347d06
