Infection
Right Upper Lobe Atelectasis
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergilloses (ABPA) and Atelectasis and Luftsichel Sign
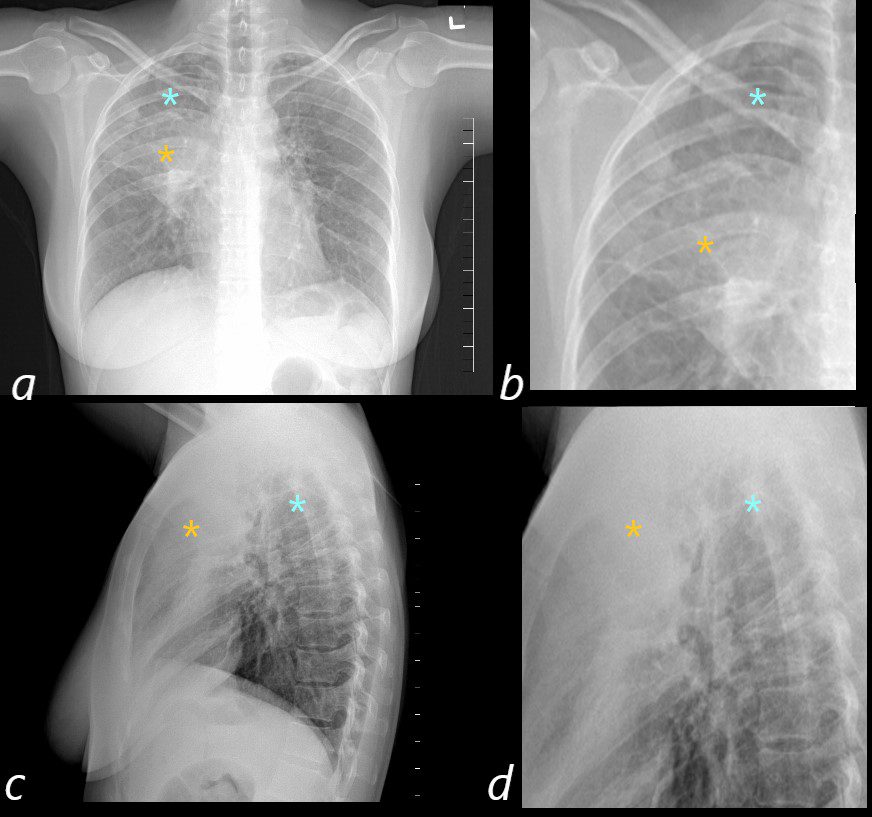
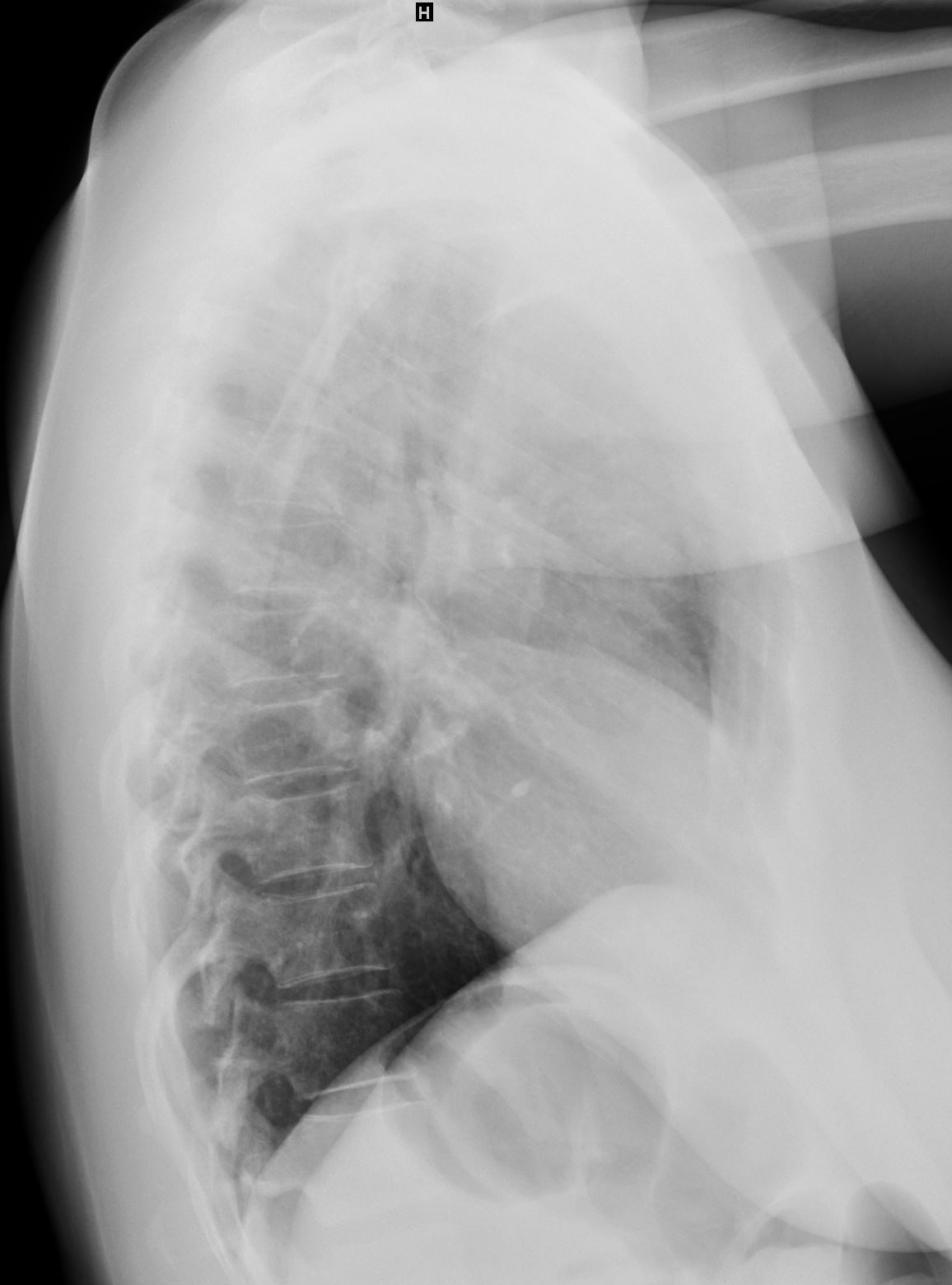
50 year old female with a history of asthma represents with productive cough. CXR in the PA projection (a magnified in b) shows an ill defined density in the right upper lobe of the lung (orange asterisk) and a relatively lucent right apex (blue asterisk Luftsichel sign)) with only minimal elevation of the right hemidiaphragm and minimal rightward mediastinal deviation . The lateral CXR shows a poorly defined density of the atelectatic RUL (orange asterisks c and D) filling in the retrosternal air space, with the hyperinflated right lower lobe reaching the right apex (orange asterisks c and d) . The significantly hyperinflated right lower lobe likely reduces the overall volume loss and hence the subtle compensatory changes of the elevated right hemidiaphragm and the mediastinal shift.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
ABPA
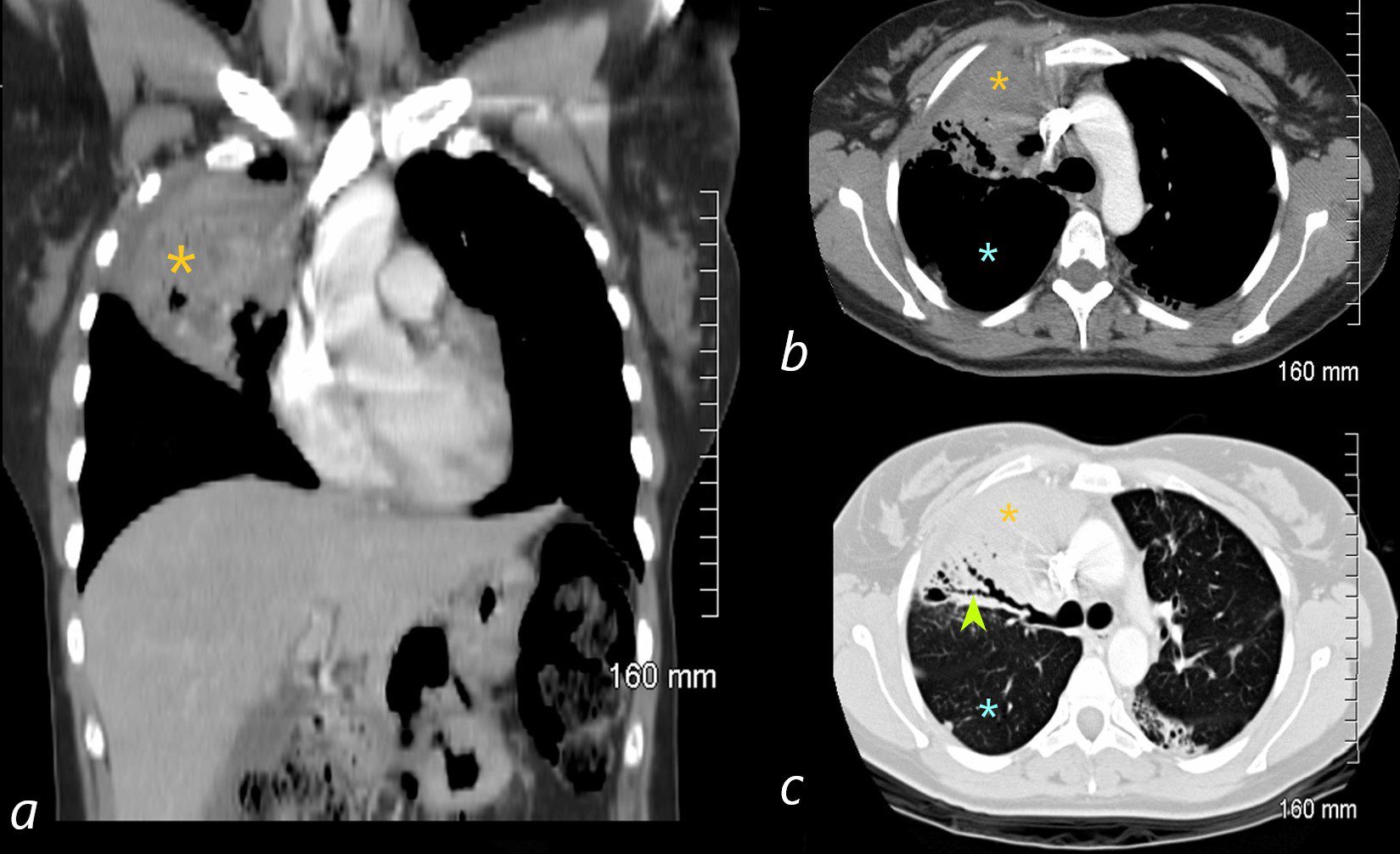
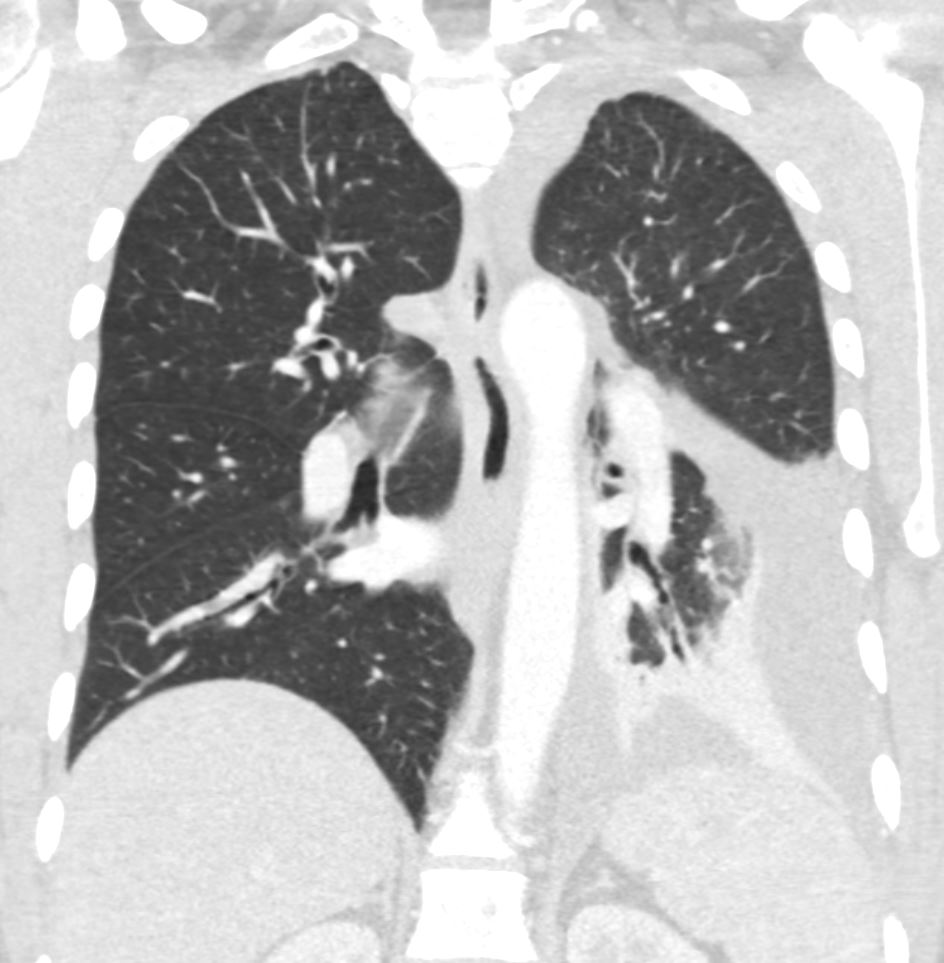
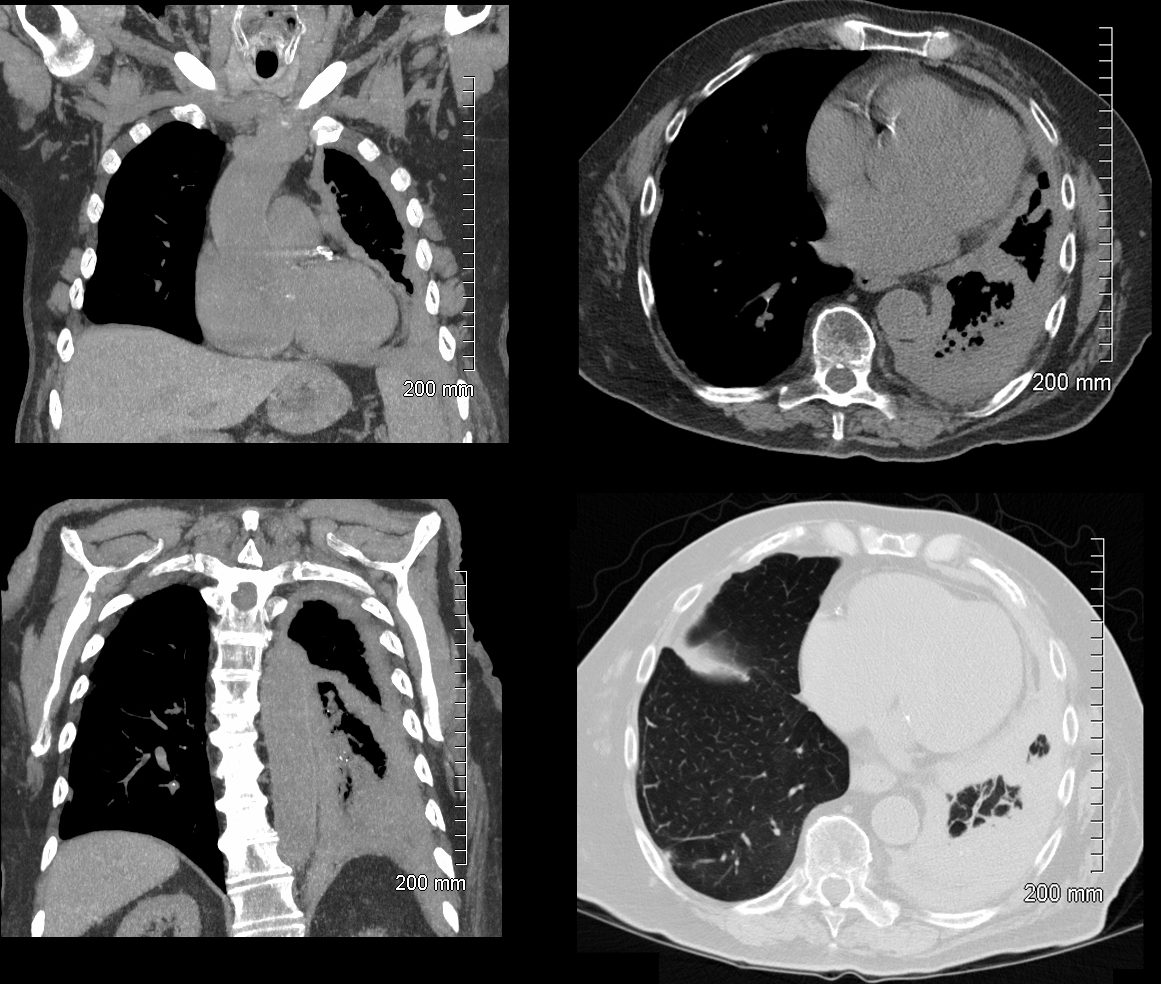
The coronal image is relatively anterior and hence presents as a dense consolidation of atelectasis (orange asterisk, a) In the axial images the hyperinflated RLL is seen posteriorly (teal asterisks in b and c) The region of varicose bronchiectasis is noted posteriorly (lime green arrow, c) When the net density of these 3 findings (consolidation, hyperinflated RLL and bronchiectasis in the LUL) are superimposed on CXR they present with a difficult interpretation since it is the overall net density that gets reflected. The CT scan helps us understand the findings
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
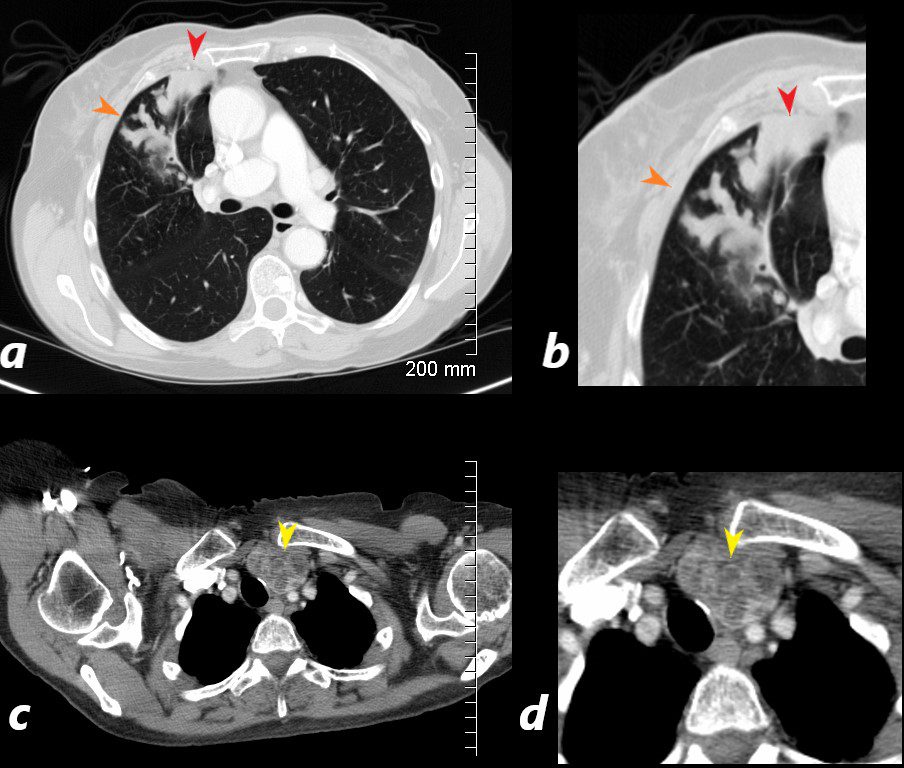
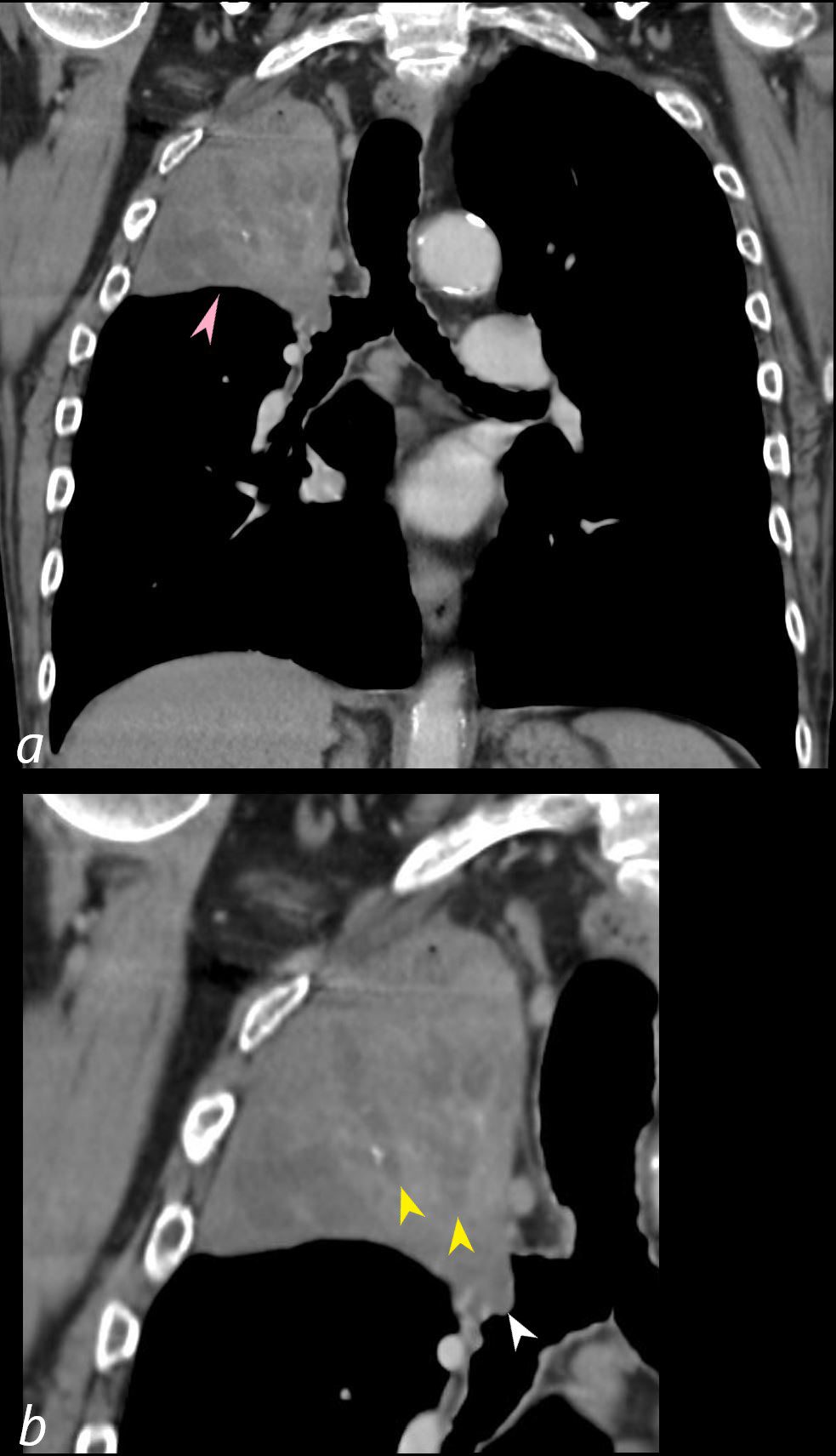
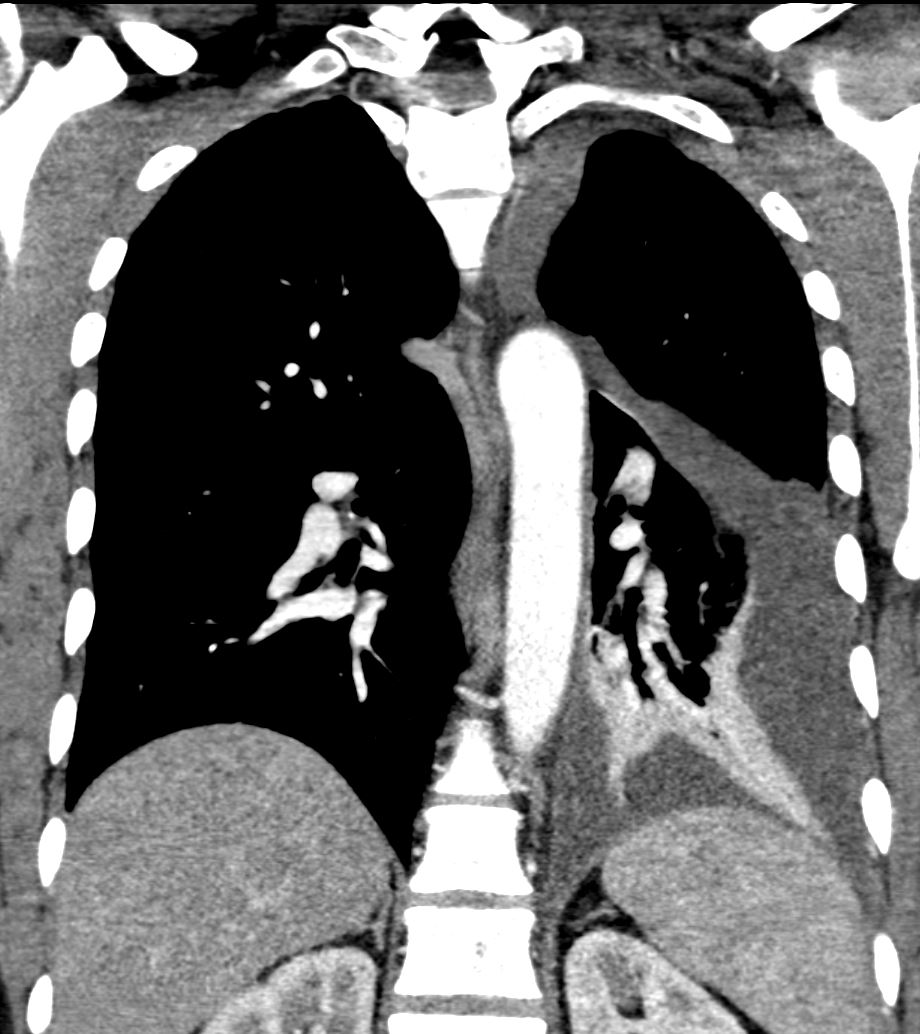
CT scan with contrast shows finger in glove appearance of the anterior segmental airways of the right upper lobe (orange arrowheads a, b) with a focal region of subsegmental atelectasis (red arrow head a,b).
The lower panel shows a cluster of low density lymph nodes in the anterior mediastinum in the retro-clavicular region (yellow arrowheads c,d) .
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net
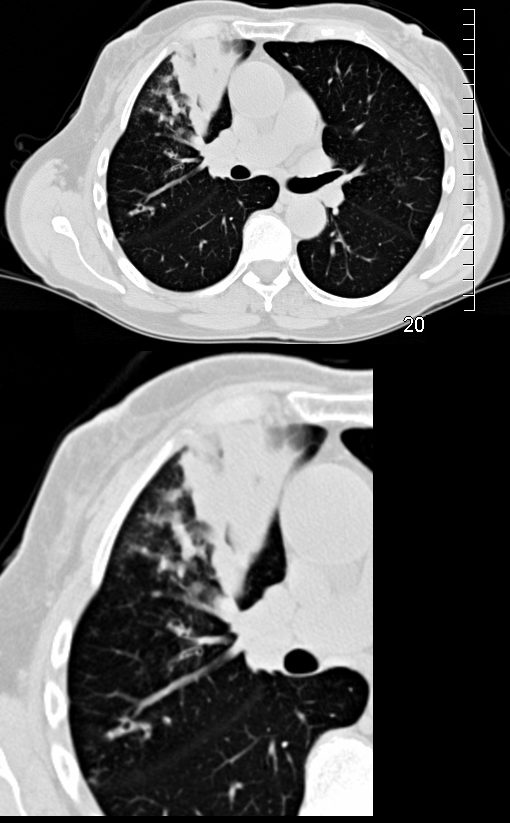
CT Scan RUL
72 year old female with asthma presented 2 years prior with acute dyspnea.
CT in the axial plane shows subsegmental atelectasis of an anterior subsegment of the RUL with impaction and bronchiectasis of visualized anterior segmental airways and a posterior subsegmental airway
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 294Lu 135116c.0017
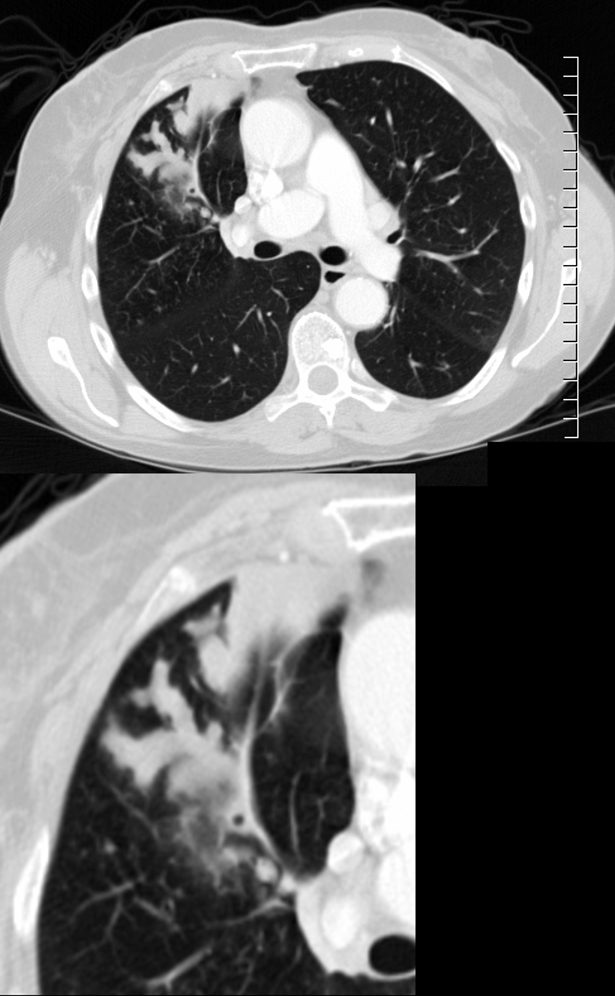
CT scan with contrast shows finger in glove appearance of the anterior segmental airways of the right upper lobe ) with a focal region of subsegmental atelectasis medially. The finger in glove sign results thick, mucus plugs within the bronchi due to the exaggerated inflammatory and immune response caused by Aspergillus fumigatus leading to airway inflammation, mucus production, bronchial wall thickening, and bronchiectasis.
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net 294Lu 117966c
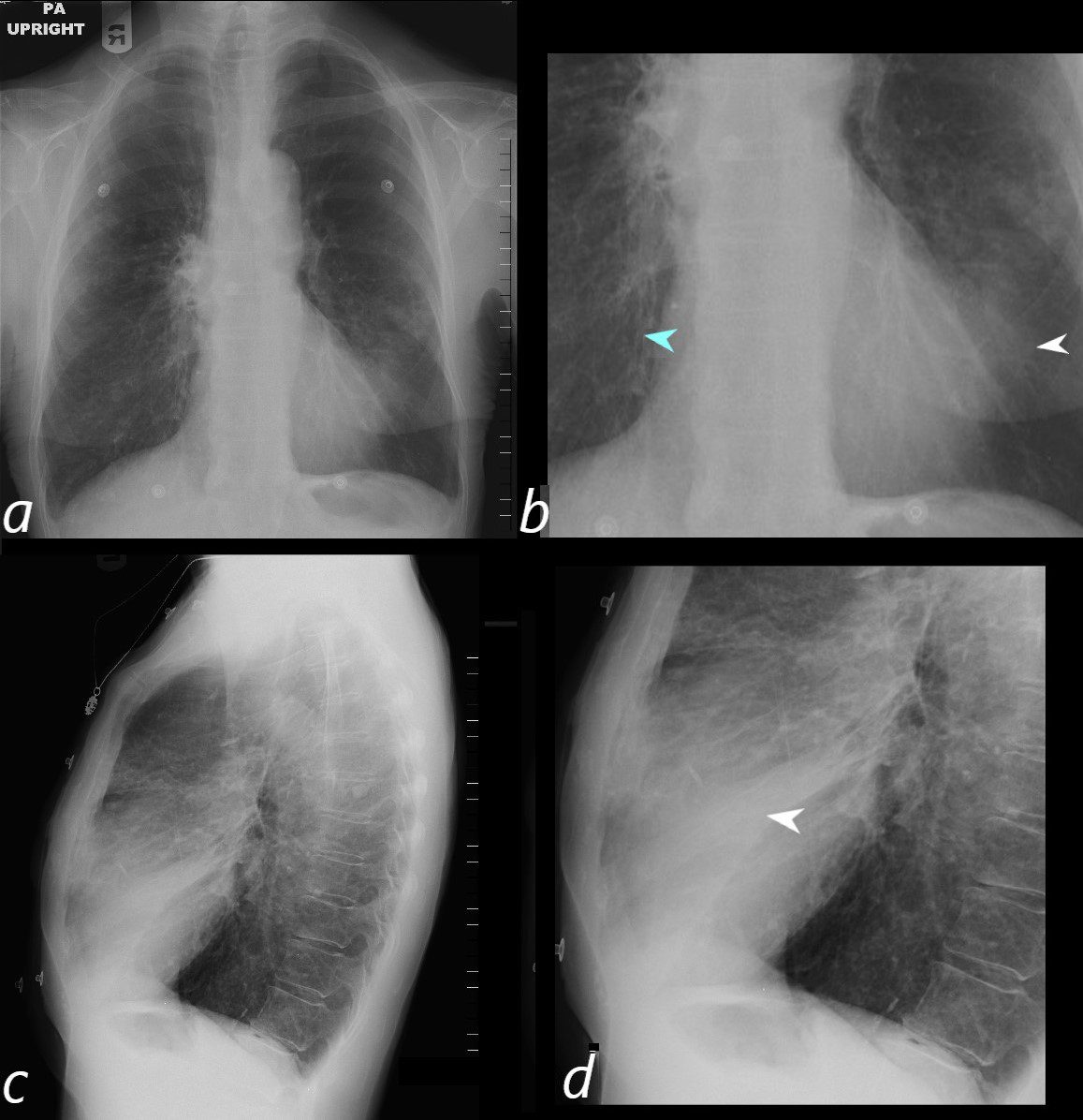
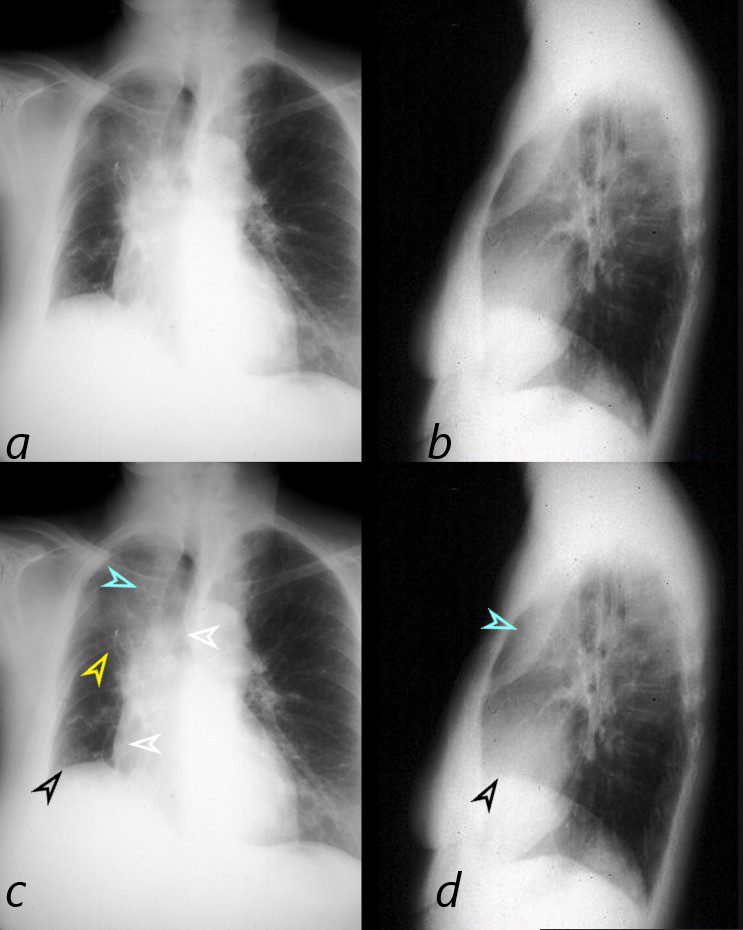
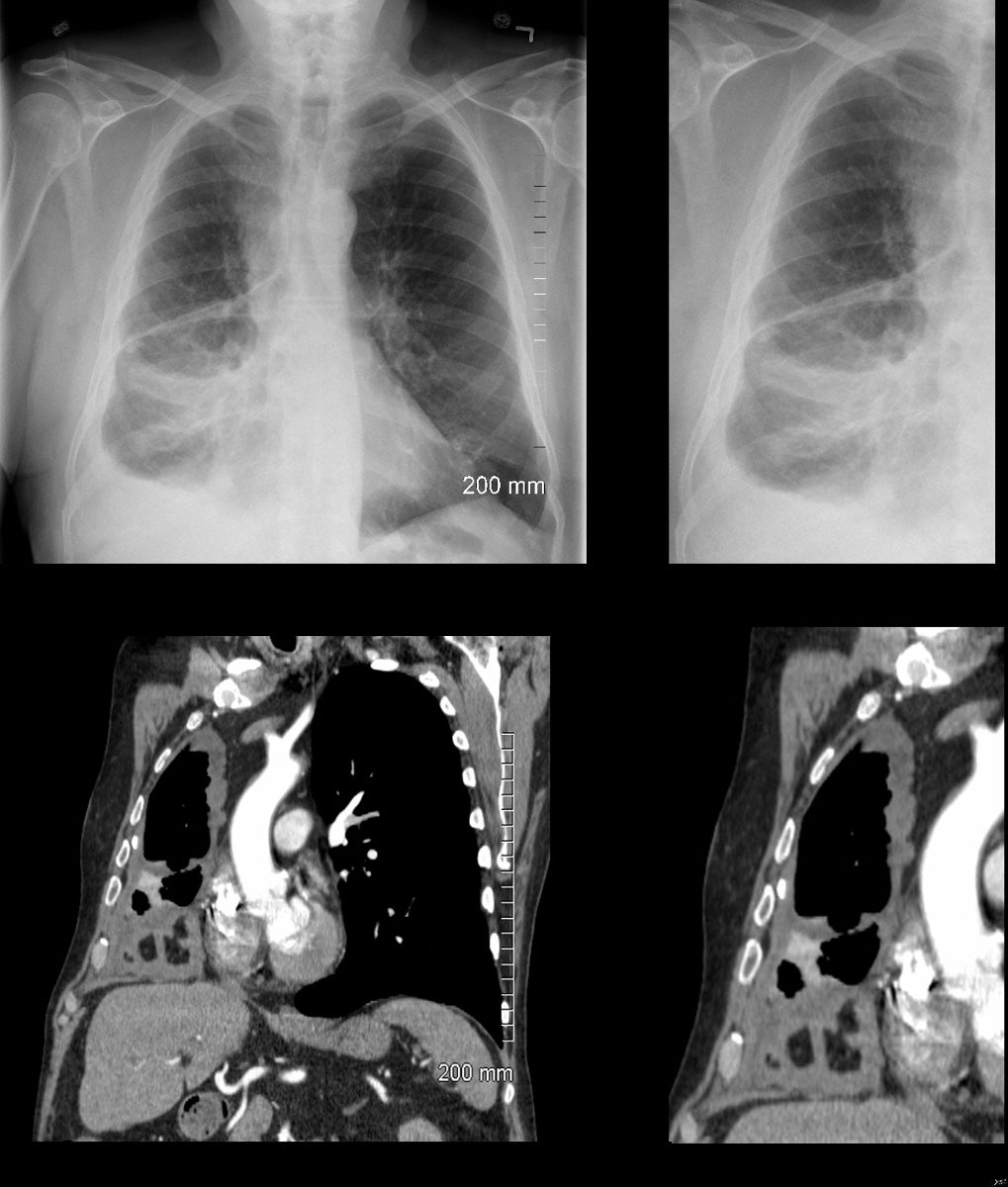
72 year old female with asthma presents with a cough and dyspnea
CXR in frontal and lateral projection show hyperinflated lung fields characterized by flattening of the hemidiaphragms, pectus carinatum and a barrel chest. There is partial silhouetting of the left heart border resulting from segmental consolidation of the medial segment of the ligula (b, white arrowhead) and confirmed on the lateral exam (d, white arrowhead). There is thickening of the airways subtending the right lower lobe (b, teal arrowhead).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 294Lu 117965cL
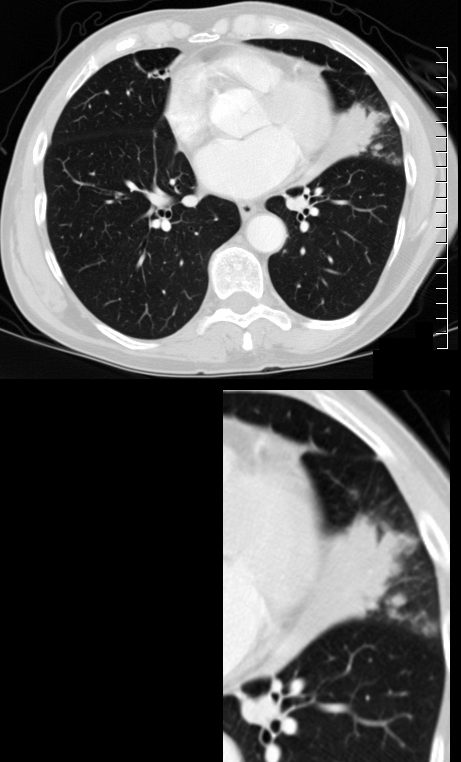
ABPA Current CT Scan
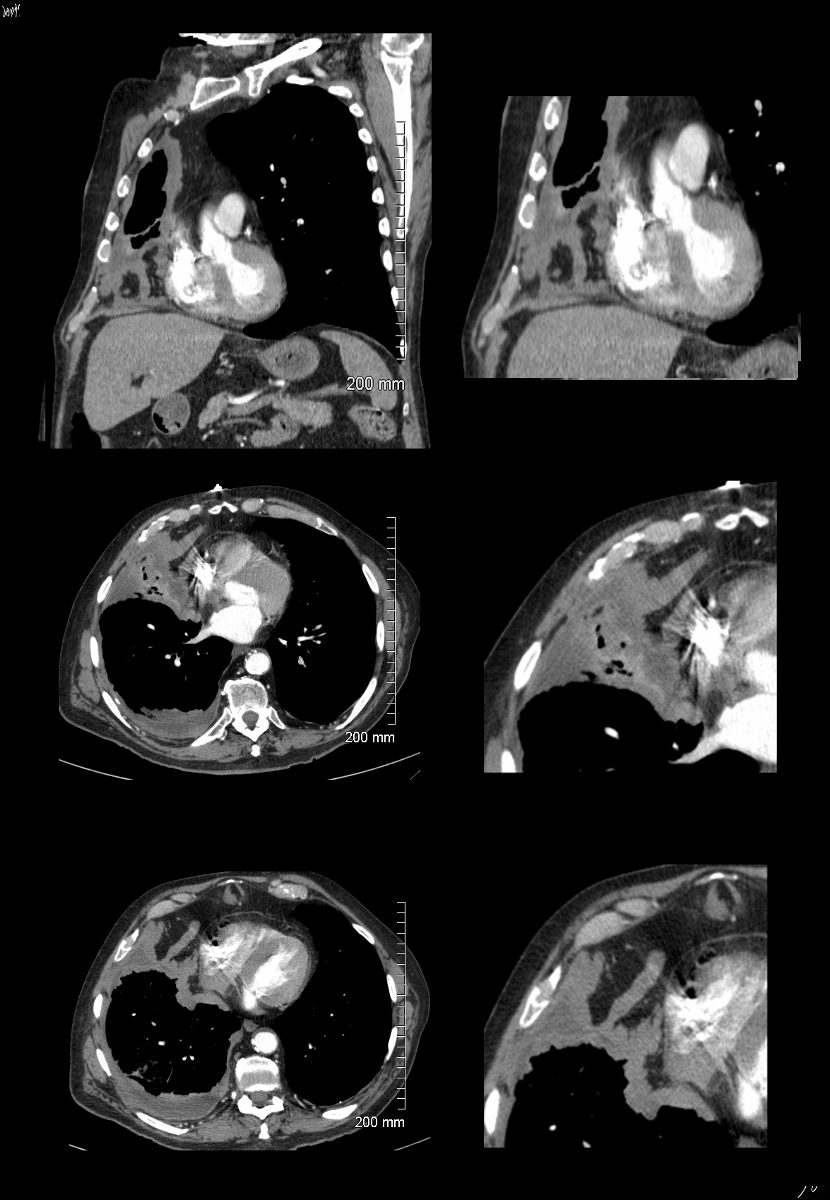
72 year old female with asthma with cough and chronic dyspnea.
CT in the axial plane shows subsegmental atelectasis of the lingula likely caused by mucoid impaction
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 294Lu 117969c
Right Middle Lobe
Segmental Atelectasis
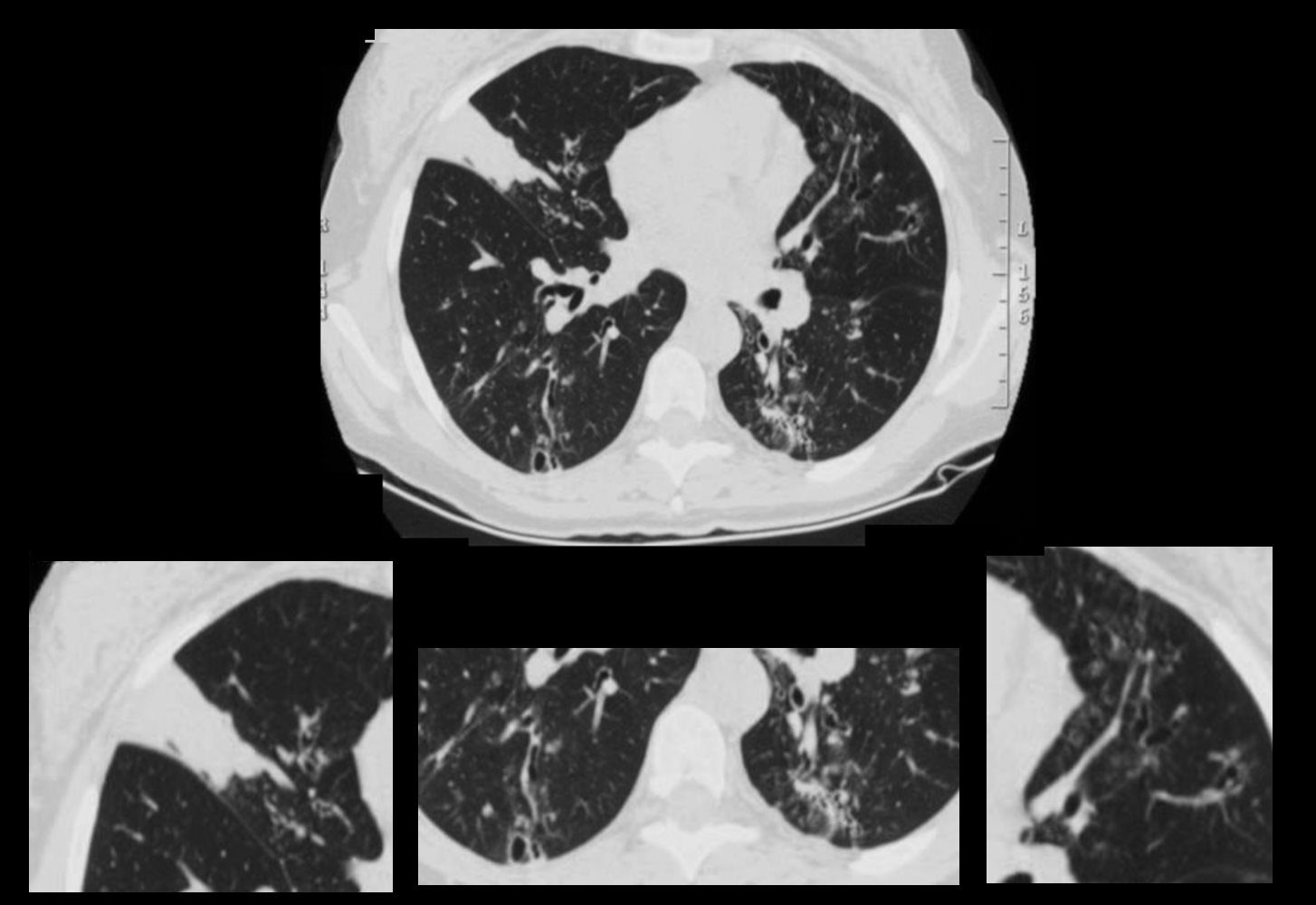
CT Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
48 year old female with a history of asthma presents with productive cough. CT scan 18 months prior confirms atelectasis in the middle lobe (upper panel and right lower panel) . There is diffuse mild multicentric foci of bronchial wall thickening in the segmental and subsegmental airways of the middle lobe, lingula and the lower lobes bilaterally (upper panel magnified in lower 3 panels).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Inflammation
Malignancy
Right Upper Lobe Collapse
Squamous Cell Causing
Obstruction but Airways Filled with
Tumor or Infection or Mucus
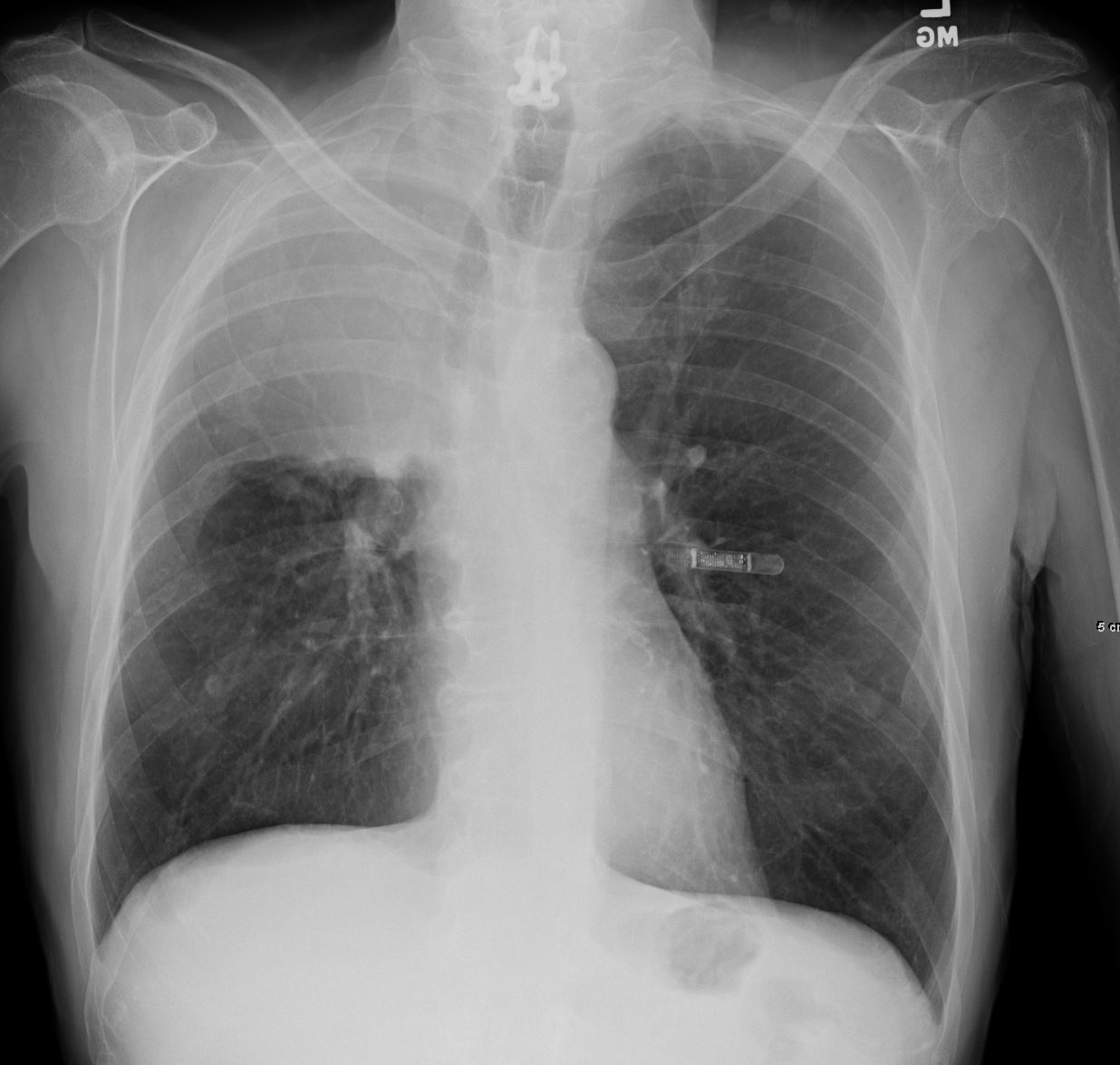
55-year-old male presenting with dyspnea
Frontal CXR shows right upper lobe (RUL) atelectasis characterized by rightward deviation of the trachea elevation of the right hemidiaphragm and opacification of the right upper lobe. Final diagnosis was a central RUL proximal squamous cell carcinoma with extensive filling of the distal bronchi-ectatic segmental and subsegmental airways
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 212Lu 136430
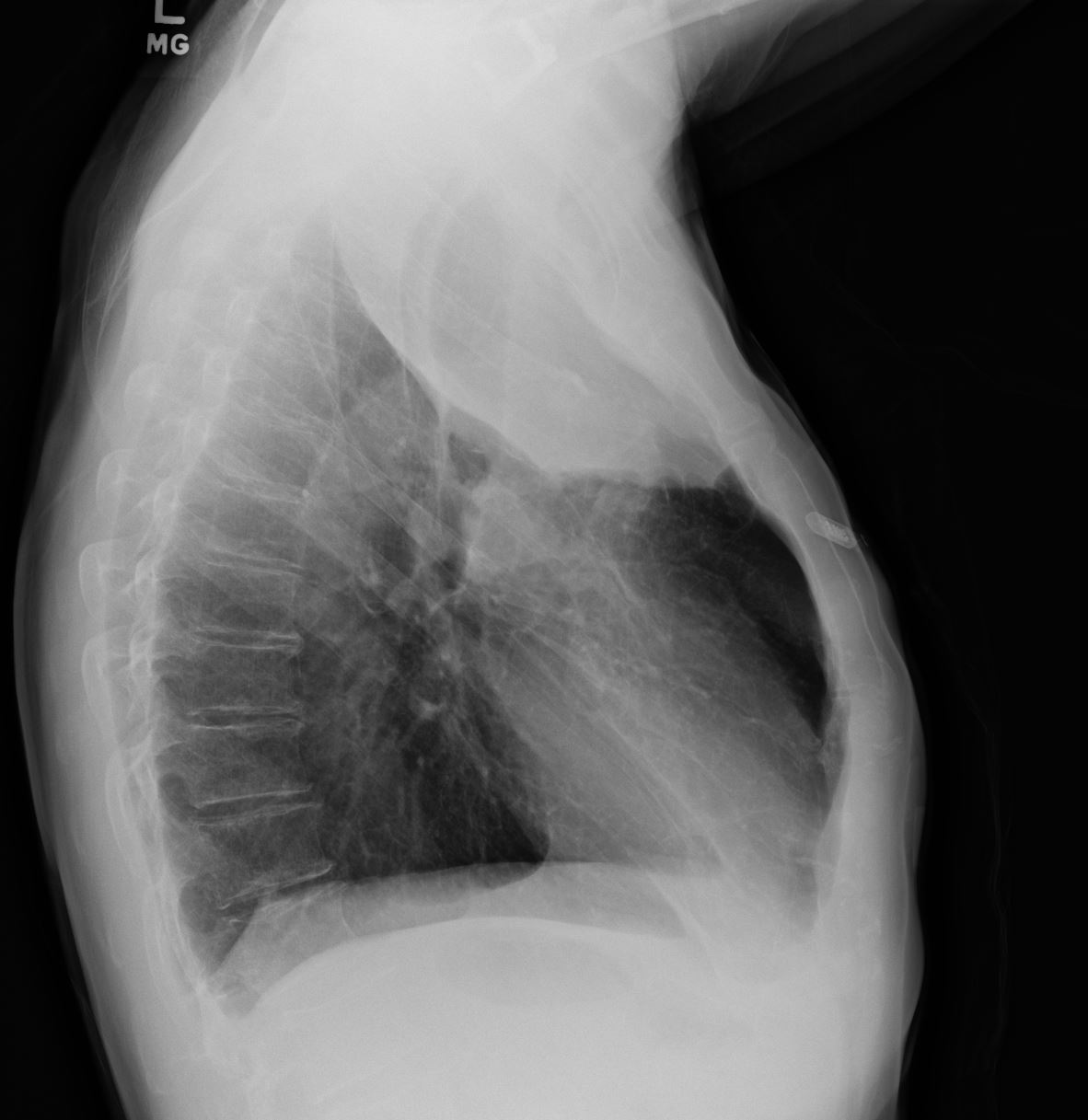
55-year-old male presenting with dyspnea
Lateral CXR confirms atelectasis of the RUL characterized by pie shaped consolidation of the anteriorly position right upper lobe, hyperinflation of the right lower lobe mild elevation of the right hemidiaphragm. Final diagnosis was a central RUL proximal squamous cell carcinoma with extensive filling of the distal bronchi-ectatic segmental and subsegmental airways
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 212Lu 136430
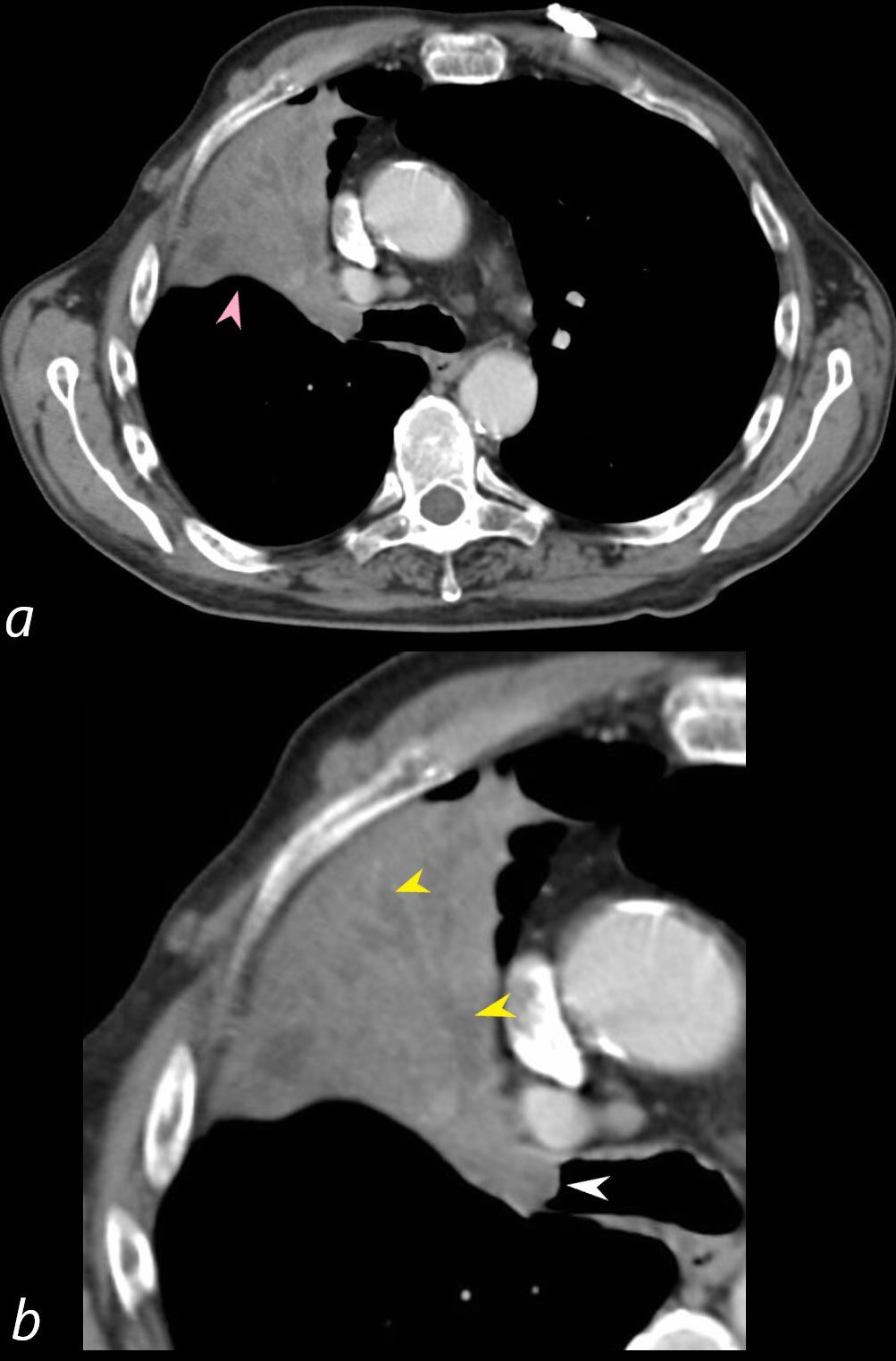
55-year-old male presenting with dyspnea
Axial CT at the level of the carina shows atelectasis of the RUL caused by a central obstructing lesion in the right upper lobe bronchus (b, white arrowhead) resulting in atelectasis of the RUL characterized by a wedge-shaped consolidation of the anteriorly positioned right upper lobe. The major fissure is displaced anteriorly (a, pink arrowhead). There is extensive filling of the distal bronchiectatic segmental and subsegmental airways of the RUL (b, yellow arrowheads). Final diagnosis was a central RUL proximal squamous cell carcinoma.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 212Lu 136432cL
55-year-old male presenting with dyspnea
Coronal CT at the level of the trachea and mainstem bronchi, shows atelectasis of the RUL caused by a central obstructing lesion in the right upper lobe bronchus (b, white arrowhead) resulting in atelectasis of the RUL characterized by a wedge-shaped consolidation of the right upper lobe with superiorly displaced major fissure (a, pink arrowhead). There is extensive filling of the distal bronchiectatic segmental and subsegmental airways of the RUL (b, yellow arrowheads). Final diagnosis was a central RUL proximal squamous cell carcinoma.
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 212Lu 136433cL
Lobar Collapse
Right Upper Lobe Collapse
Occluded Right Main Stem Bronchus by Carcinoma with Pathology Correlation
This combination of images shows the manifestations of a malignant mass in the hilum causing compression of the right mainstem bronchus. The PA CXR shows signs of volume loss (atelectasis characterized by elevation of the right hemidiaphragm (black arrowhead), rightward tracheal and mediastinal shift (white arrowheads) and elevation of the minor fissure contributing to the reverse S sign of Golden. There is a vague infiltrate in the right upper lobe correlating with an anterior pie shaped density of the lateral (blue arrowheads), consistent with collapse of the anterior segment of the RUL
32292cL01
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
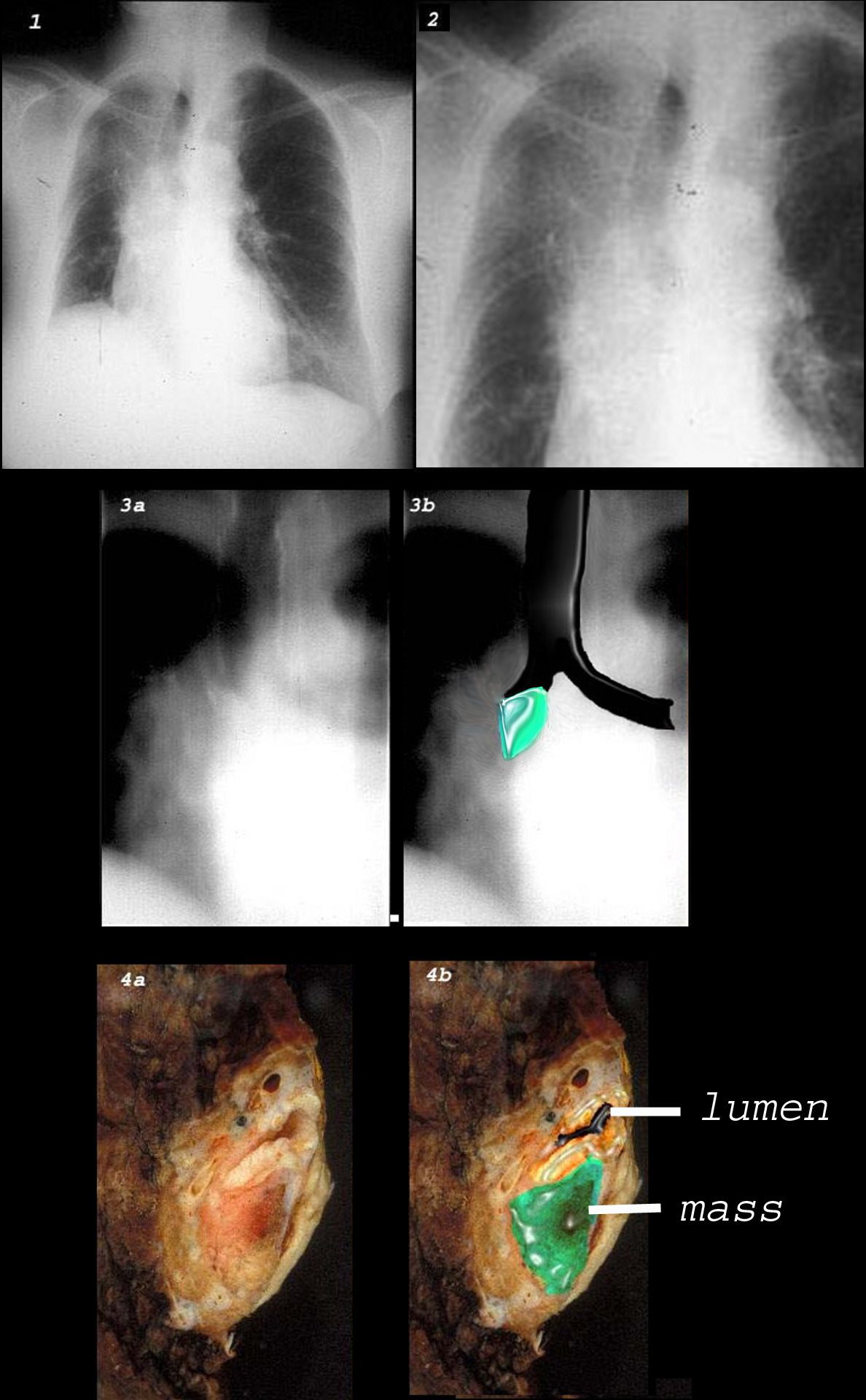
This combination of images shows the manifestations of a malignant mass in the hilum causing compression of the right mainstem bronchus. There is elevation of the right hilum on the CXR, associated with collapse of the anterior segment of the RUL seen as a vague density in the P-A . The tomogram (3a) shows an abrupt cut off of the right mainstem bronchus while the overlay in 3b shows the occlusion of the right mainstem bronchus, the implied tumor overlaid in green. Images 4a and 4b are the correlative gross pathology images showing the tumor in green pushing and occluding the right mainstem
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
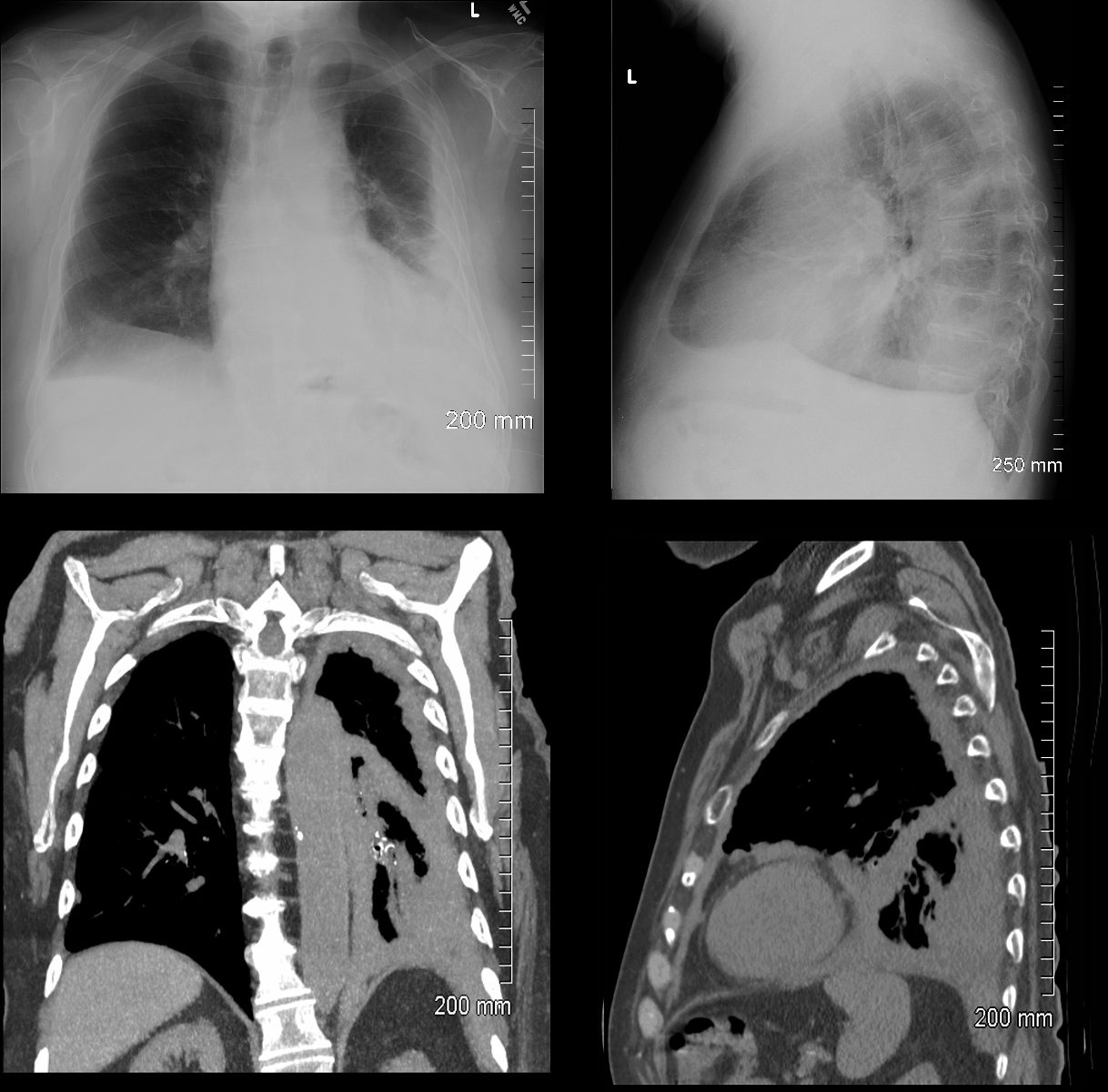
Right Upper Lobe Atelectasis
Reversed S Sign of Golden
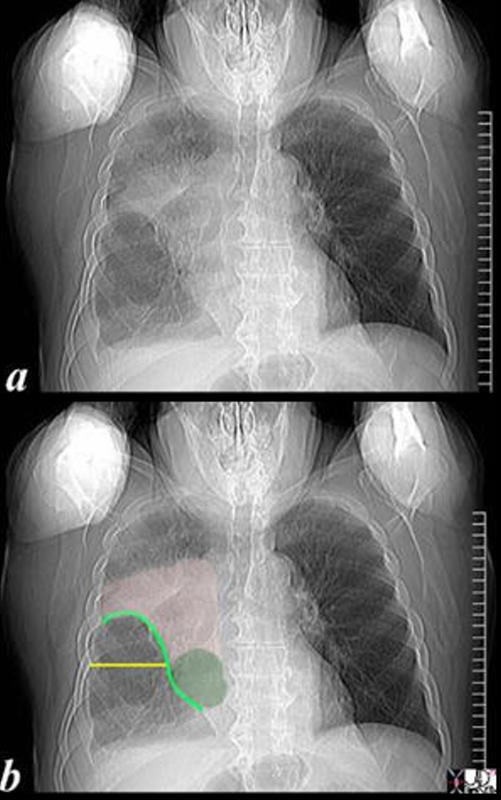
The scout film performed prior to a CT scan from a 76-year-old man with chest pain and shortness of breath. The appearance suggests atelectasis of the right upper lobe with the normal position of the minor fissure (yellow) altered so that the upper portion (light green above the yellow line) is shifted upward caused by volume loss of an atelectatic right upper lobe (pink). The lower portion of the fissure (light green below the yellow line) is bulging rightward and outward caused by an implied mass (dark green). The “reversed S sign of Golden” is demonstrated in this case and infers a central mass causing obstruction and resulting in the shape described by the light green line of the minor fissure.
Courtesy: Ashley Davidoff, M.D.
Segmental Subsegmental
Subsegmental Obstruction of the
Apical Segment of the Right Upper Lobe
Carcinoid Tumor Causing Obstruction
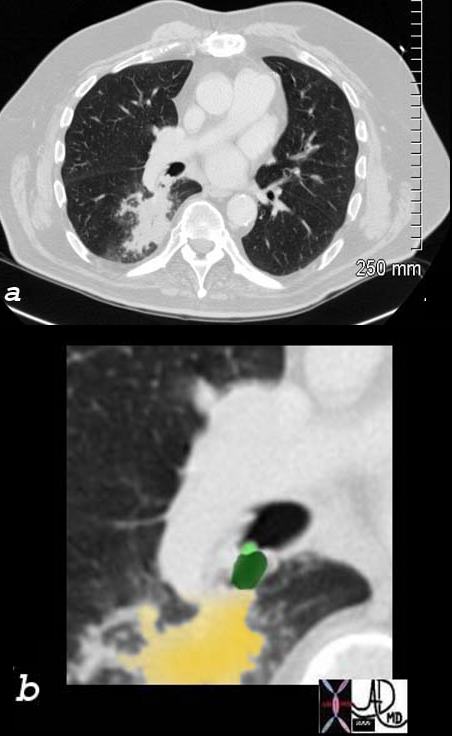
65 year old female presents with a cough. CT shows a mass (green) in proximal portion of the right lower lobe bronchus with post obstructive atelectasis in the superior segment of the right lower lobe (yellow) pathology revealed carcinoid tumor
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
75679c02
Mechanical – Compressive
Compressive Atelectasis From Pleural Effusions
Compressive Atelectasis Manifesting as Ground Glass Changes
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Mild Bilateral Crescentic Pneumonic Consolidation
58year old male presents with dyspnea. CT scan shows bilateral pleural effusions with crescentic region of compressive atelectasis in the left lower lobe
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net

68year old male presents with dyspnea. Ultrasound of the right chest shows a moderate sized pleural effusion (+) with crescentic region of compressive atelectasis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net

86 year-old female presents with a dyspnea. US shows a left effusion with compressive atelectasis. CT scan shows bilateral pleural effusions with atelectasis of the left lung.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
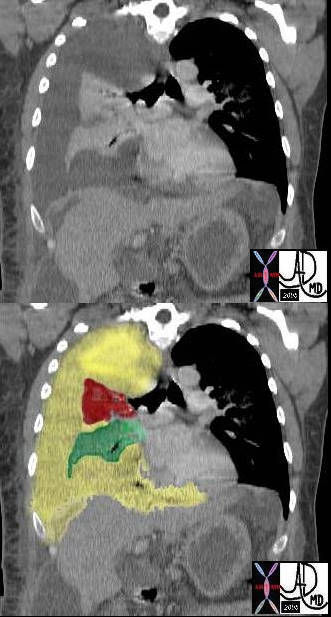
In this case there a large right sided pleural effusion (yellow) with secondary atelectasis of the right lung. (red and green) This coronal CT of the chest at the level of the left ventricle shows a large right pleural effusion which lies between the visceral and parietal pleura. Once the effusion is large enough to weaken the capillary forces that hold the parietal and visceral pleura together, it fail, and the lung collapses which is what is noted on this image – ie total lung collapse because of loss of cohesive adhesive forces.
Courtesy of: Ashley Davidoff, M.D. TheCommonvein.net 42558c
Effusion without Findings of Atelectasis on CXR
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Compressive Atelectasis due to Bilateral Pleural Effusion
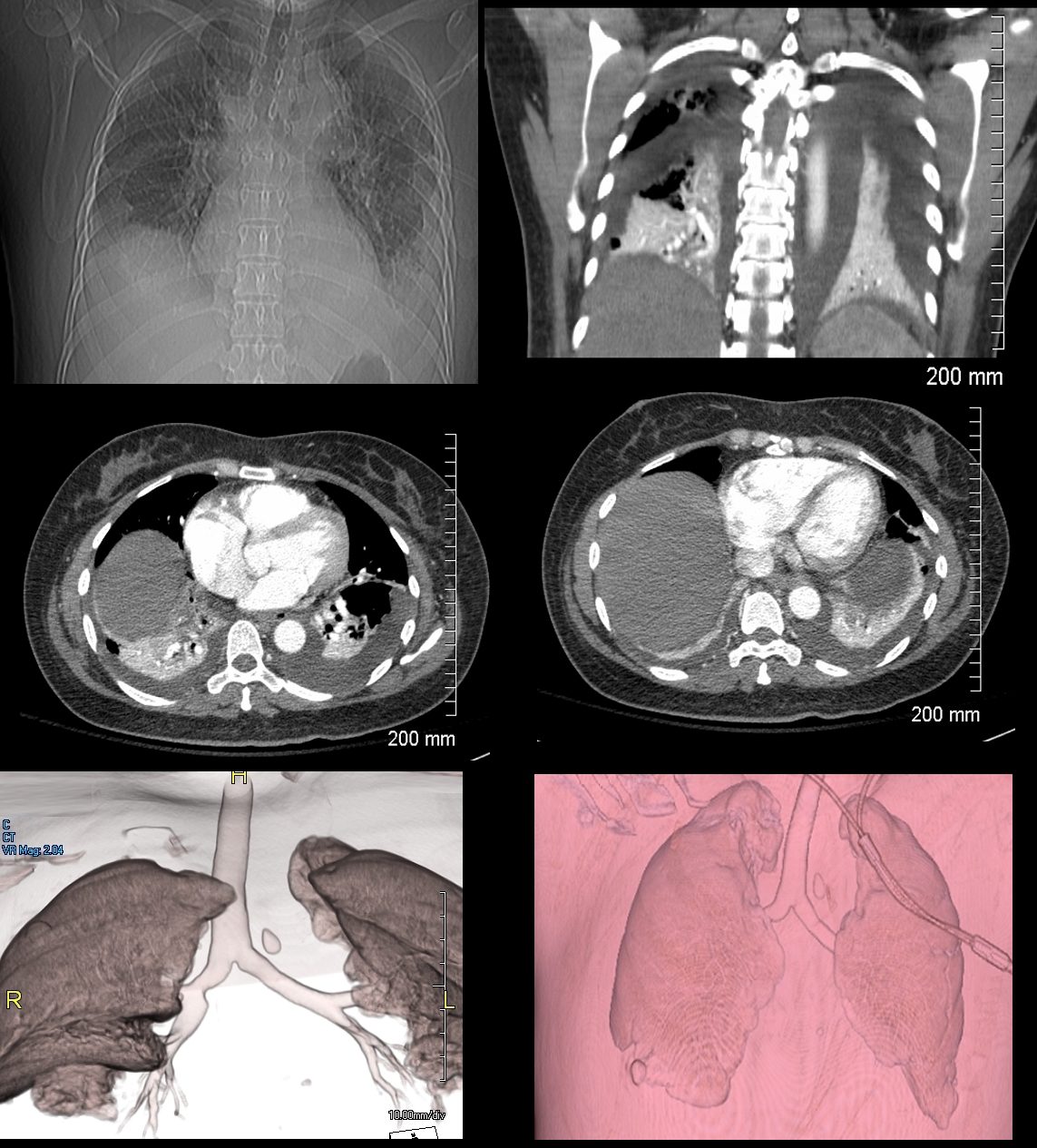

46-year-old female presents with a dyspnea and a cough. Imaging of the chest shows cardiomegaly with bilateral moderate sized pleural effusion with crescentic region of compressive atelectasis noted on the axial images at the bases and crowding of the bronchovascular bundles best evaluated on the coronal image. The 3D reconstructions show functionally “bare” lower lobe segmental airways.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
White Out – Large Pleural Effusion and
Total Collapse of the left Lung
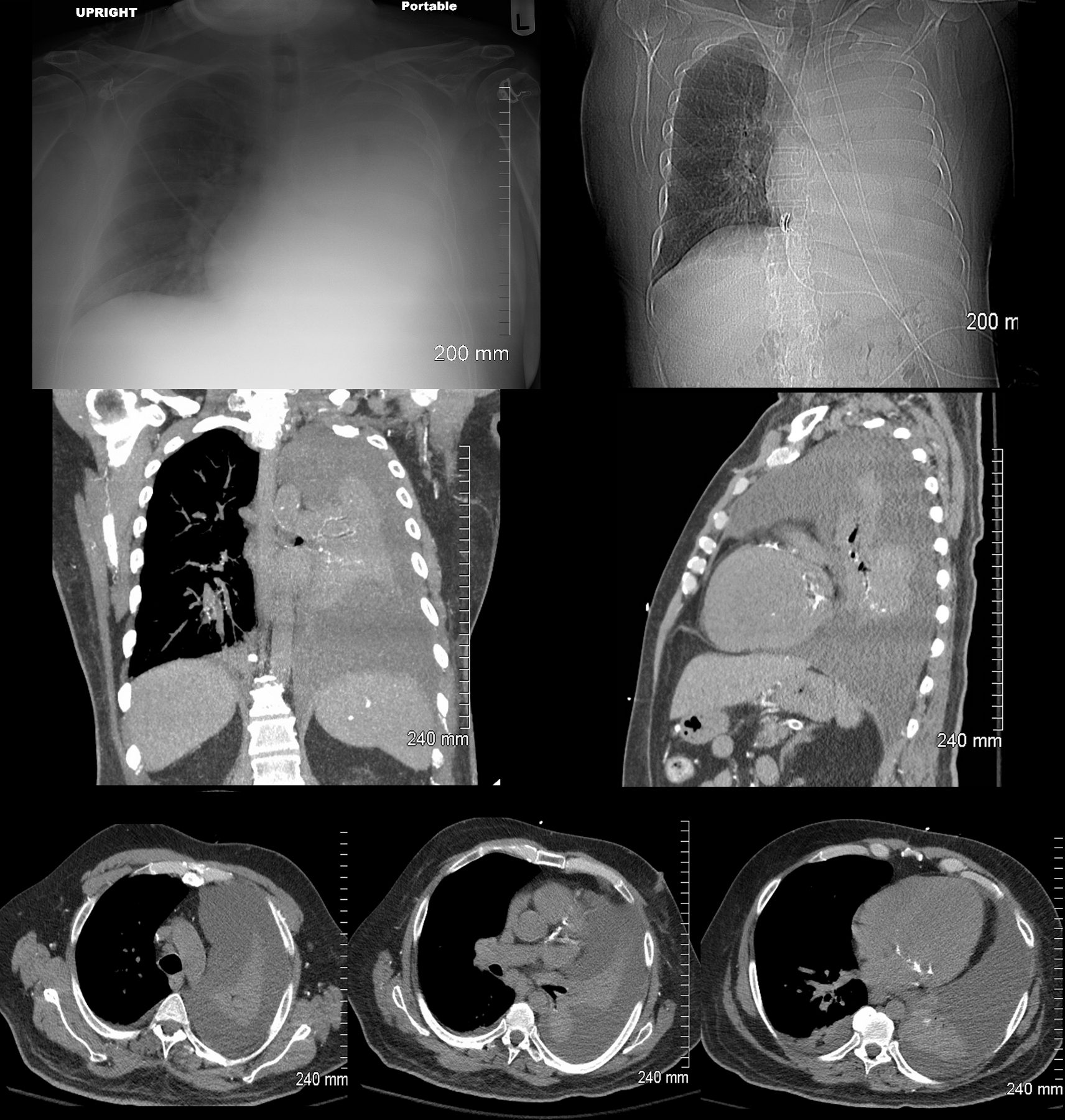

48 year-old male presents with a dyspnea. CXR shows a total white out of the left chest with pulmonary congestion. CT scan shows a large left pleural effusion with total atelectasis of the left lung. Incidental note is made of premature calcific coronary artery disease.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
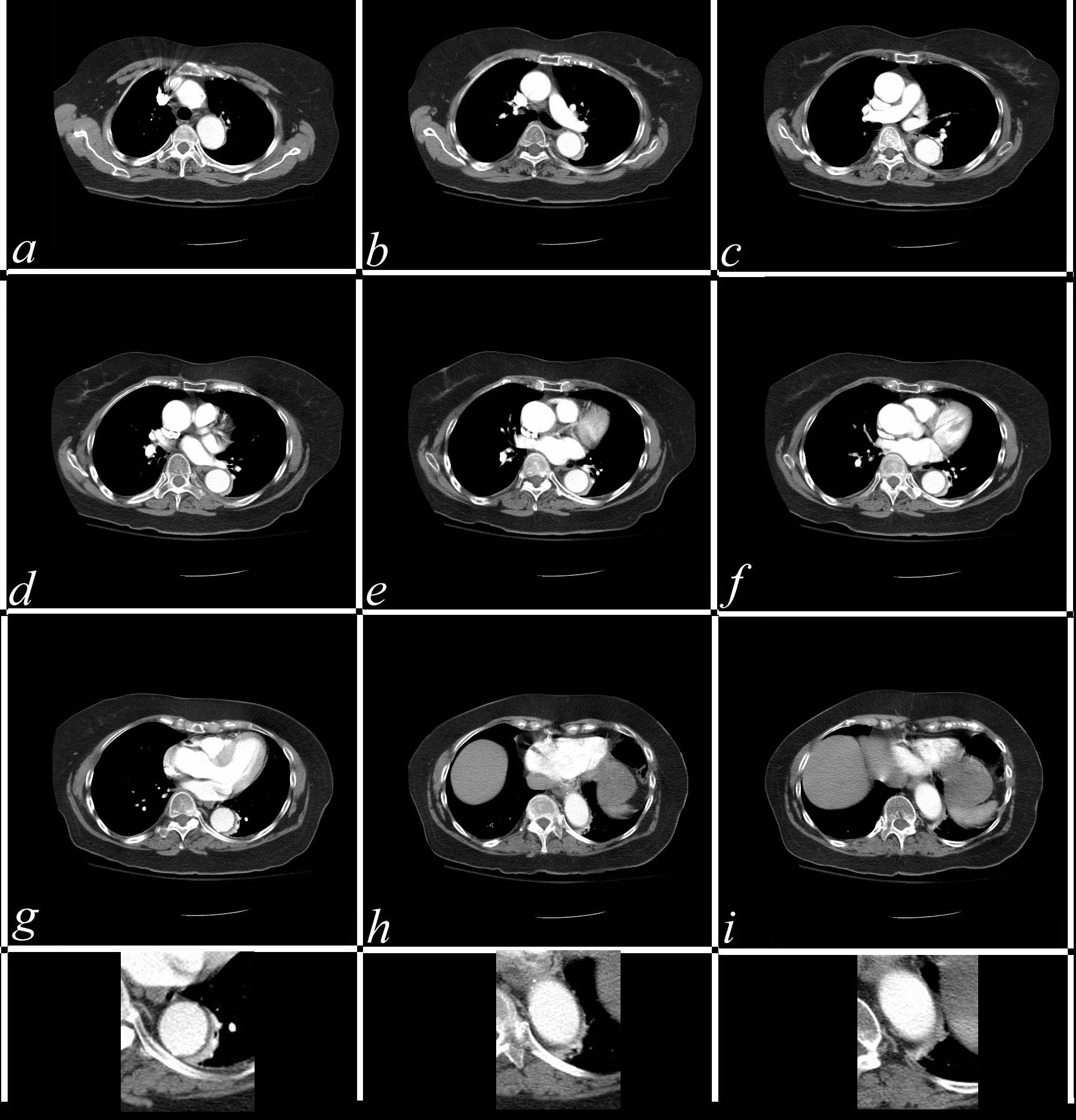
Normal vs Lobar Atelectasis
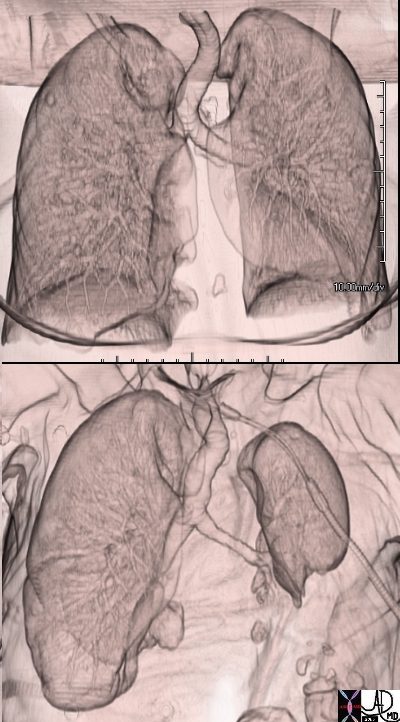

3D reconstruction of a normal patient (above) and of a patient with compressive atelectasis (below) The image below is from an 88 year old male with bilateral complex effusions with compressive atelectasis of the lower lobe and portion of the lingula
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Left Lower Lobe Compressive Atelectasis and
Bilateral Complex Effusions
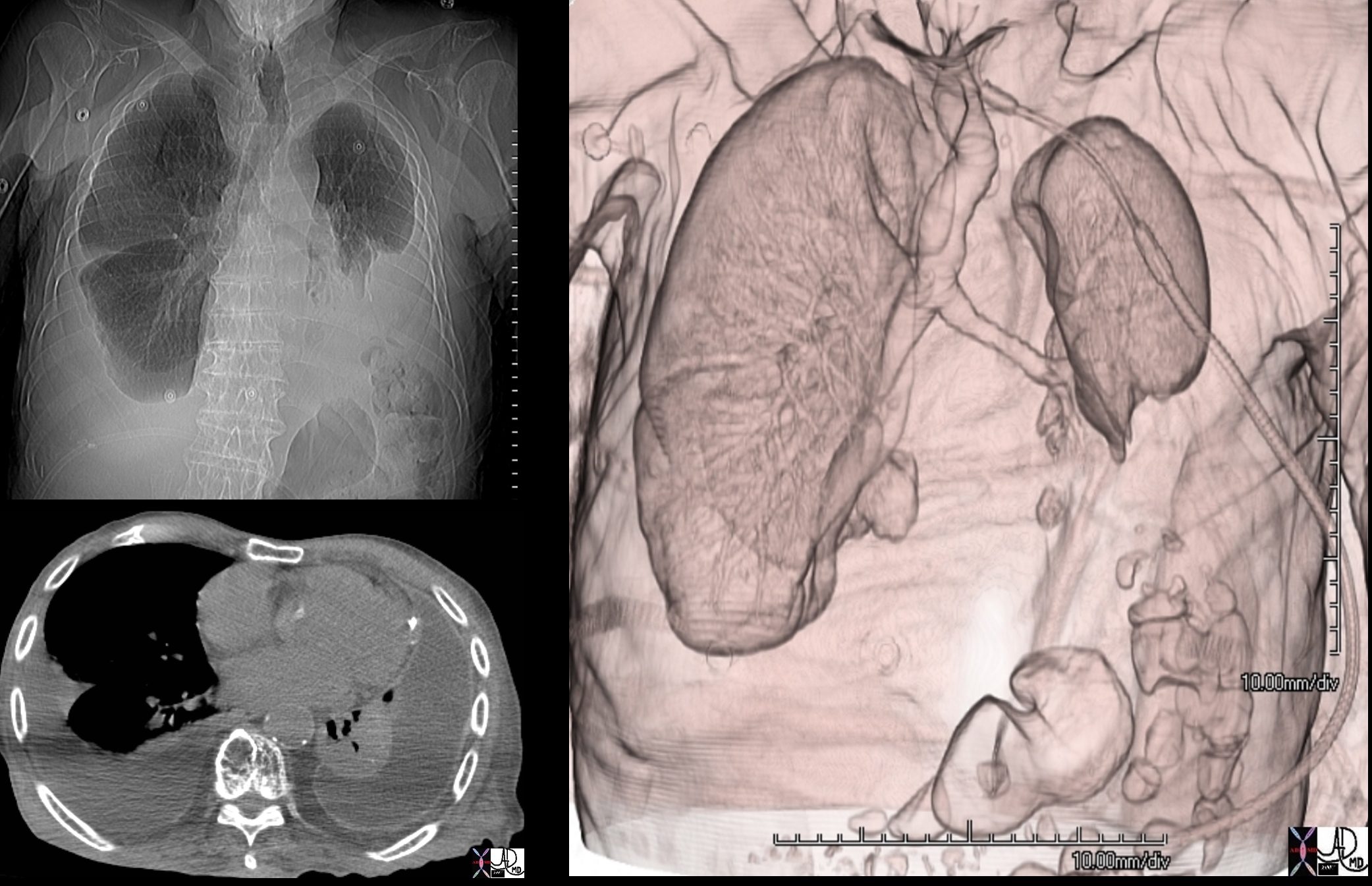



88 year old male with bilateral effusions shown on the CXR. Axial CT shows thickened pleura on the left with compressive atelectasis of the lower lobe and a smaller region of crescentic compressive atelectasis on the right. 3D reconstruction shows atelectasis of the left lower lobe and portion of the lingula. The left effusion is complex.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
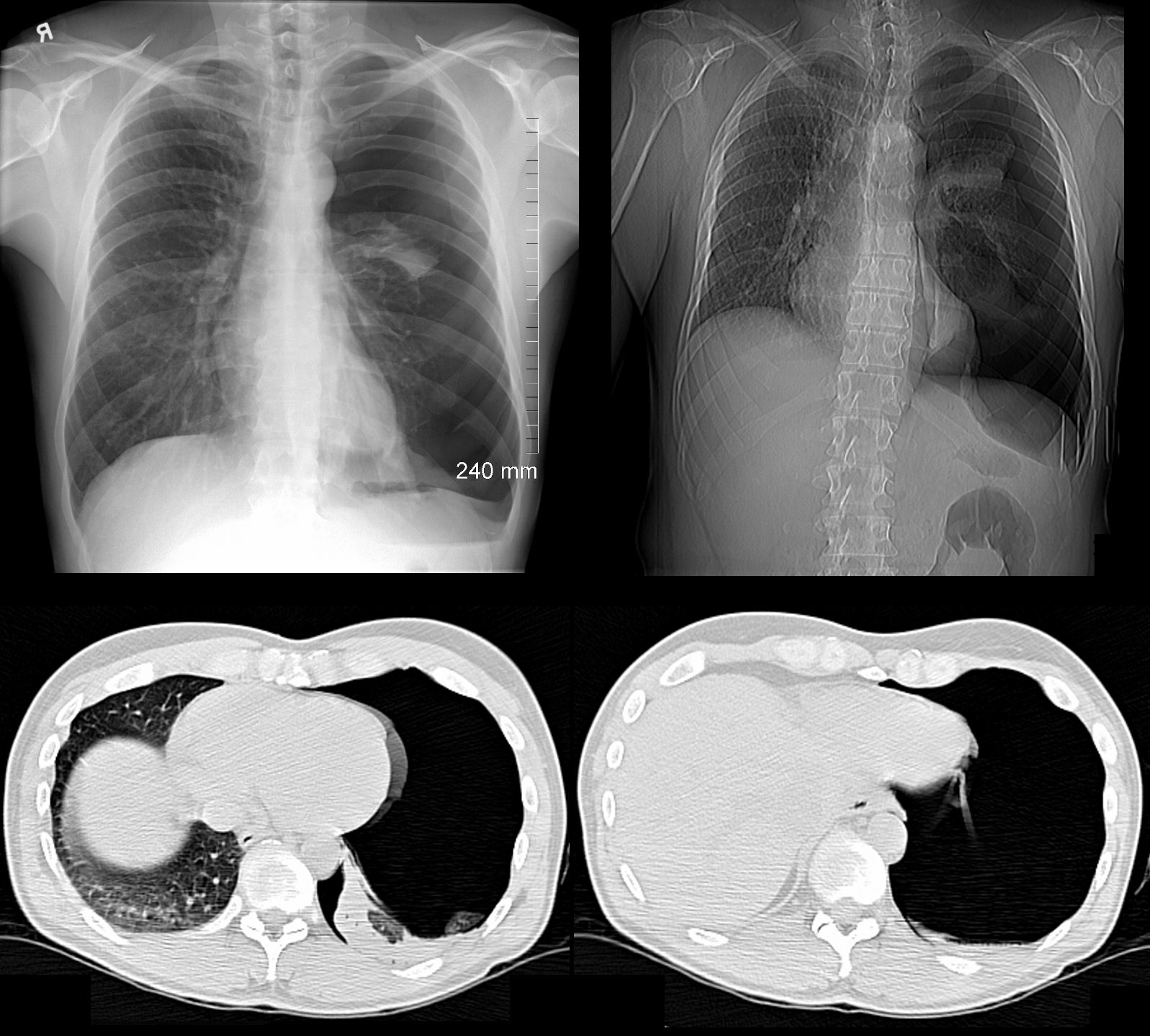
Tension Hydrothorax
Right Lung Collapse


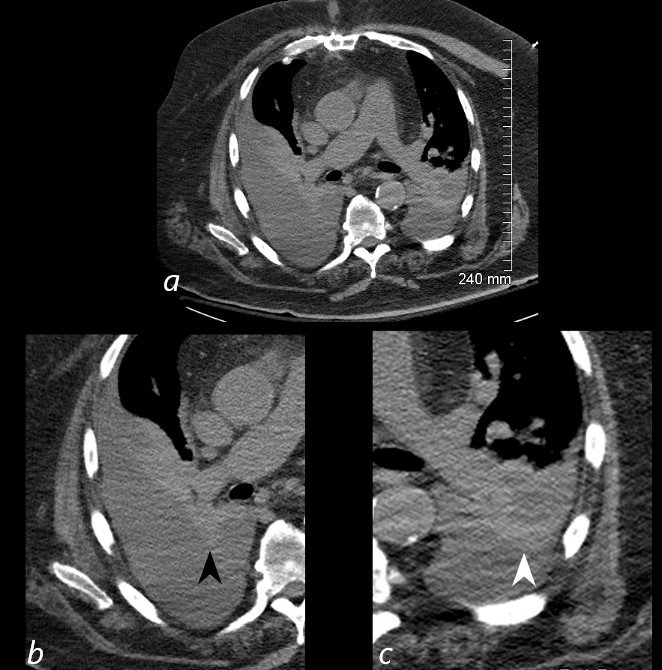
85-year-old female with a history of lung cancer, presents with a dyspnea and hypotension. CT scan shows a large right pleural effusion under pressure, with mediastinal shift to the right. In addition, there is compression of the heart with back up of venous return due the pressure effect on the heart and vascular structures. Among the structures showing venous distension are the SVC (blue arrowhead, a) right sided upper limb veins (blue arrowhead b) and the left upper pulmonary veins (red arrowhead, b. The effusion in the right pleural cavity with atelectatic lung herniates into the left hemithorax, (white arrowhead, c). There is a dense sediment in the pleural fluid (red arrowhead, d) suggesting blood in the pleural cavity. The left atrium is compressed (maroon arrowhead, d)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Pneumothorax and Total Lung Atelectasis
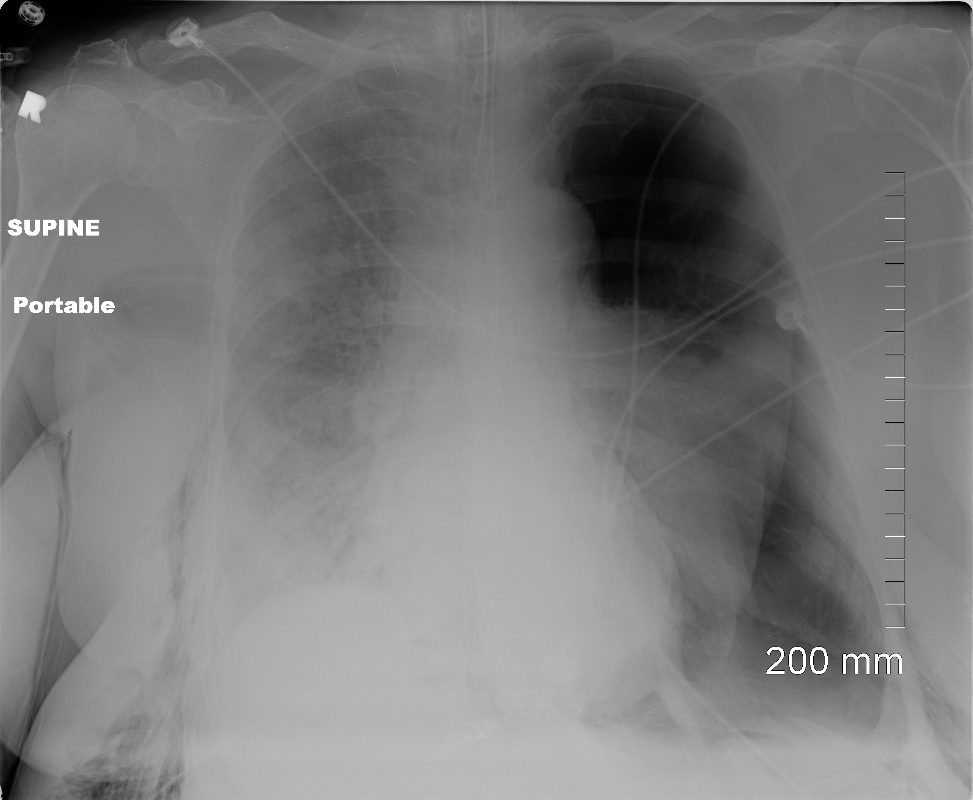

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
77949

49 year old male with a cough presents for a Chest Xray which showed a tension pneumothorax. Chest tube was placed emergently in the radiology department.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
117300c
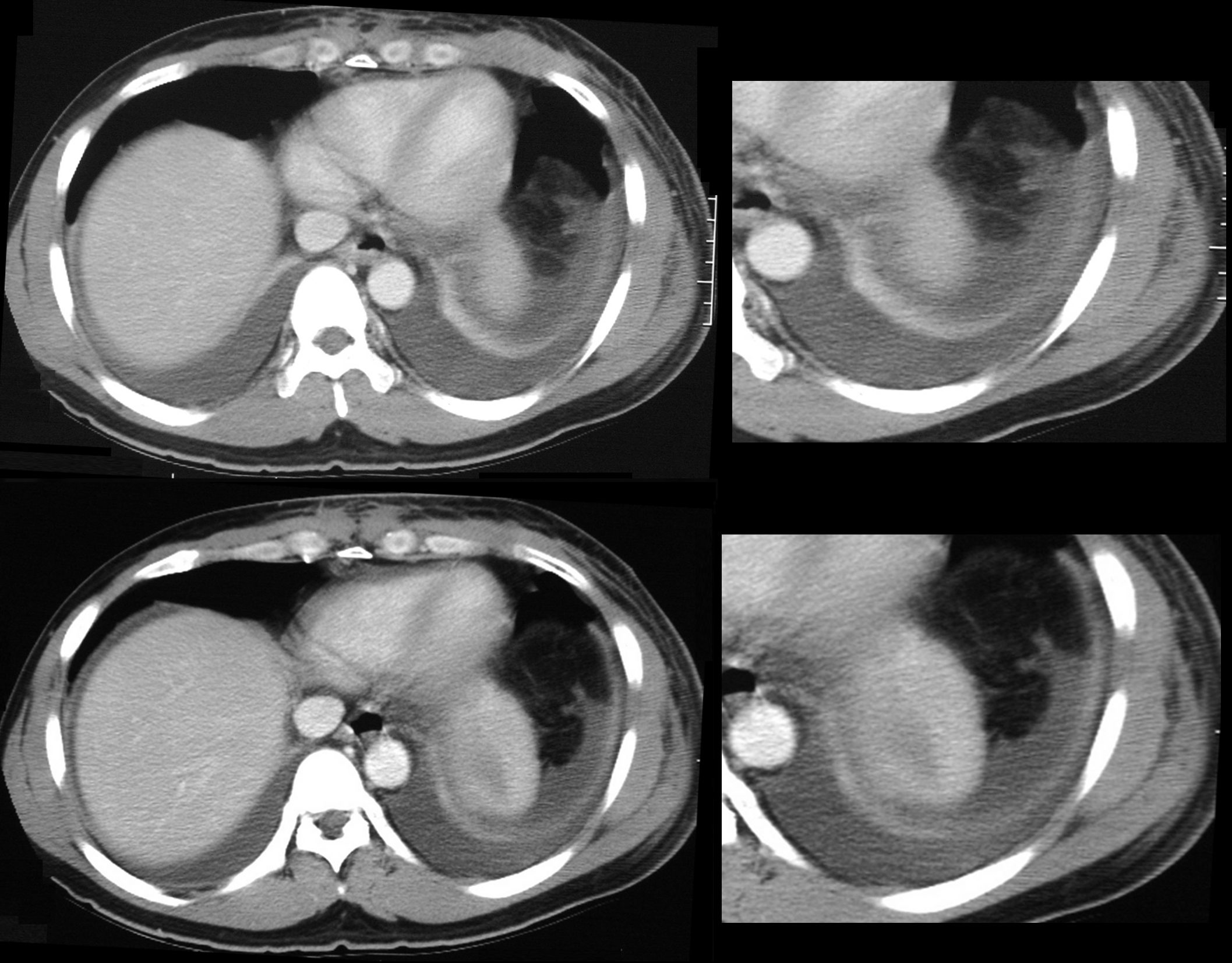
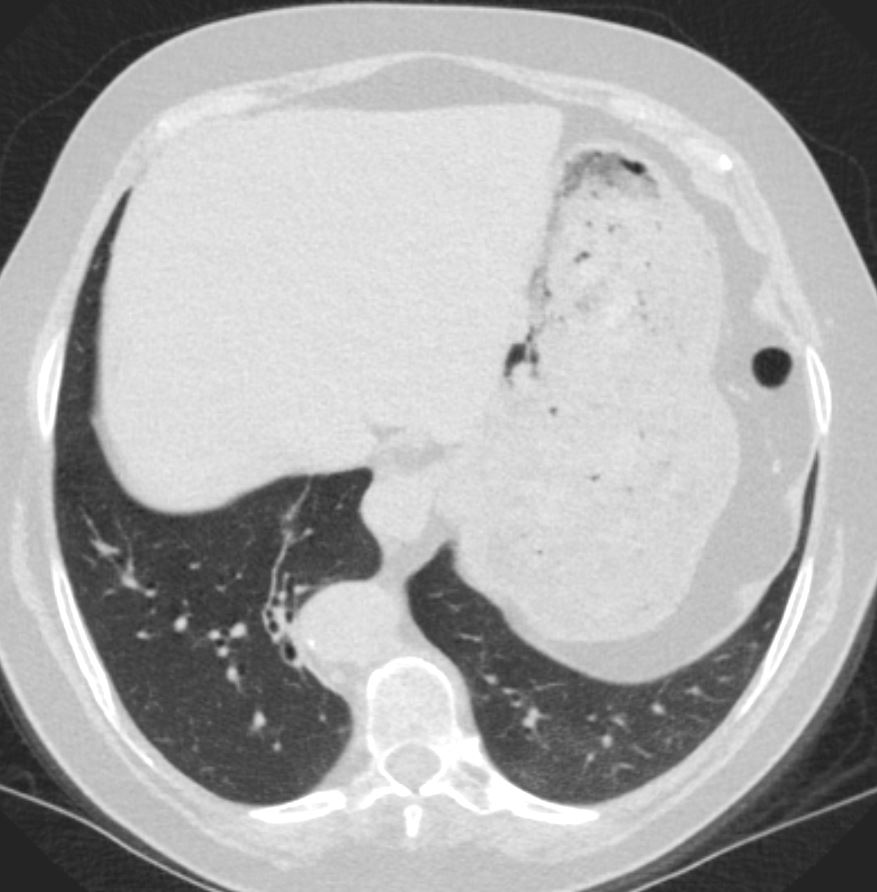
Compressive Atelectasis Alongside the Aorta

68 year old male with a cough.
CT shows Compressive Atelectasis alongside the pulsating aorta
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
37493
Compressive Atelectasis by Tortuous Aorta

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
01 CT 58F
Mesothelioma and Atelectasis

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
pleura mesothelioma 0060c

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
pleura mesothelioma 0100c

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
pleura mesothelioma 0028c

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
pleura mesothelioma 0028c01
Trauma
Metabolic
Circulatory- Hemorrhage
Immune
Infiltrative
Idiopathic Iatrogenic Idiopathic
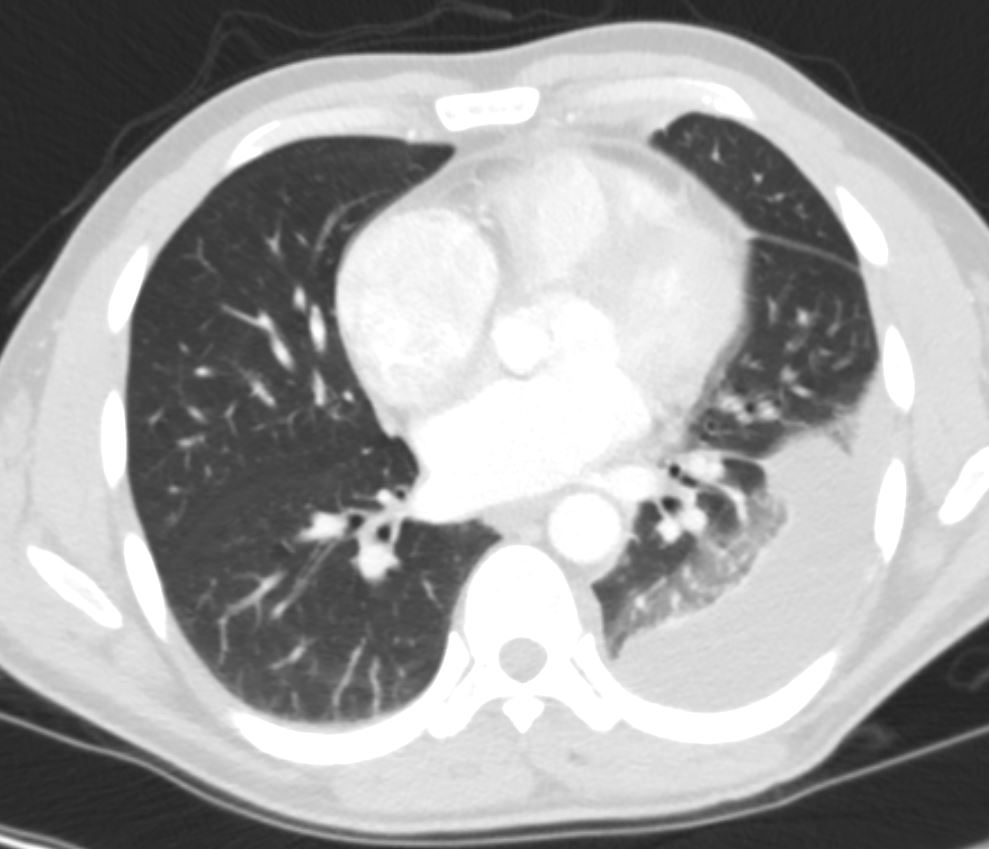
Middle Lobe Lateral Segmental Atelectasis
Right Lower Lobe Atelectasis and ABPA
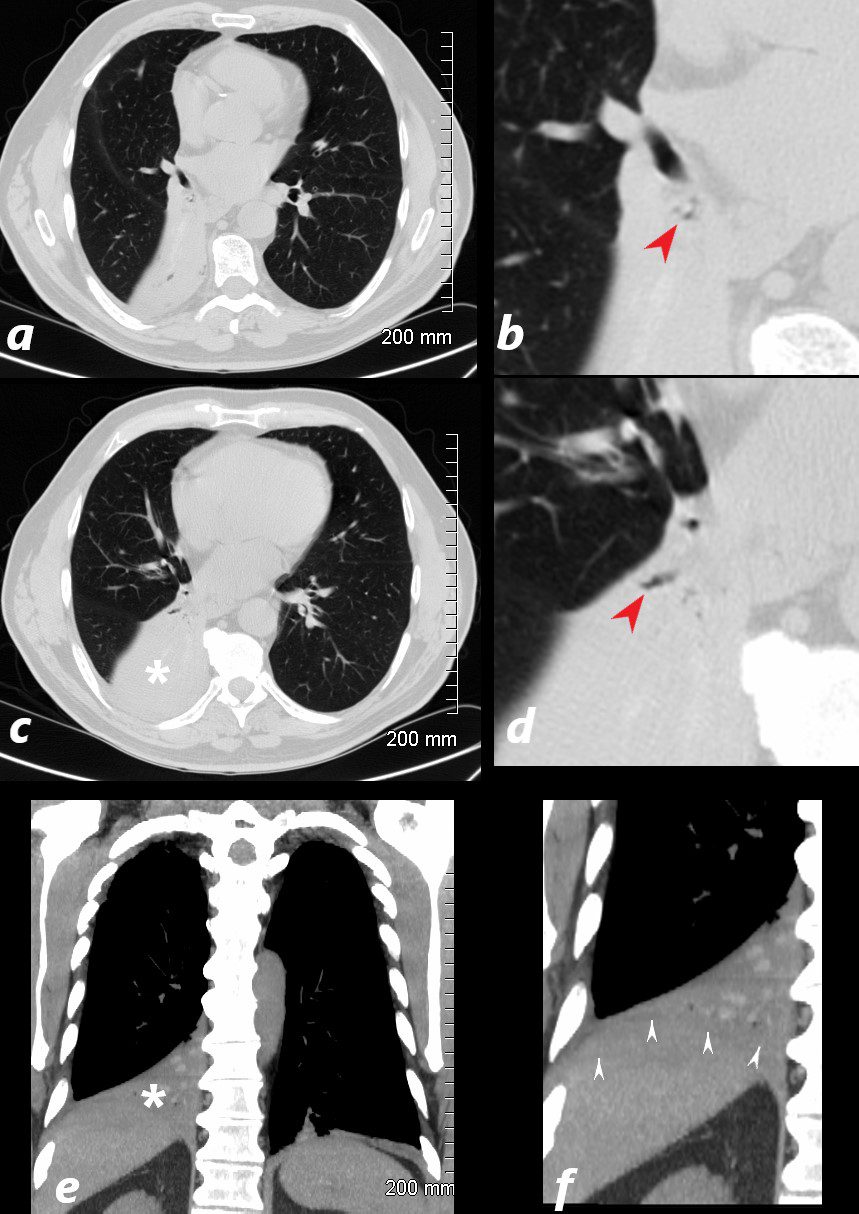

77 year old male presents chest discomfort
CT scan without contrast shows atelectasis of the right lower lobe )asterisk c and r) and also seen axial projection (a) magnified in (b) and in (c) magnified in {d) Red arrowheads in b and d show airways filled with material. Aspergillus was isolated at bronchoscopy. Coronal imaging (e magnified in f) show silhouetting of the right hemidiaphragm by the atelectatic lung (white arrowheads
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 117786cL
Multi-Lobar Atelectasis
Right Middle and Lower Lobe Atelectasis
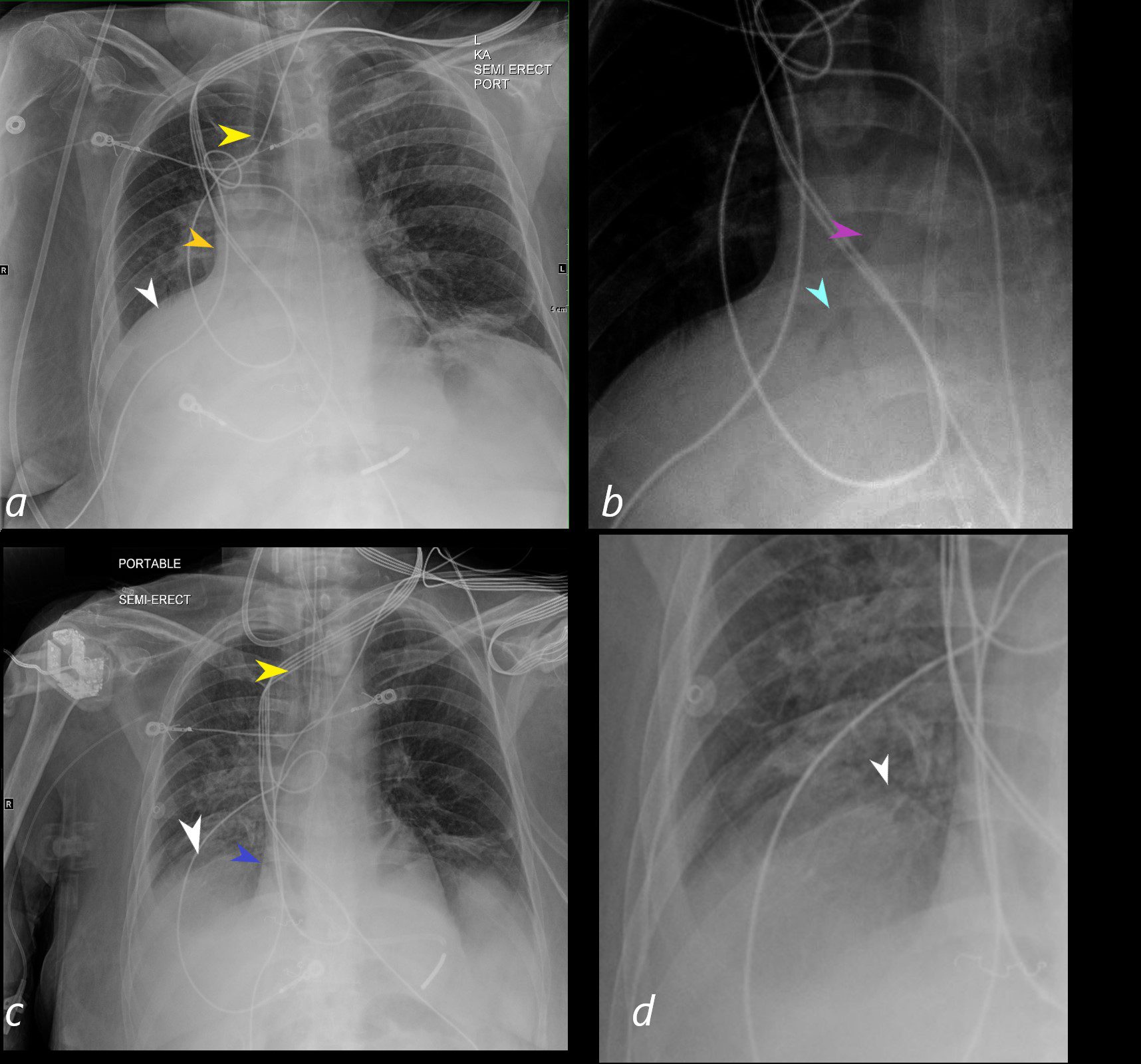

A PA CXR shows signs of atelectasis including mediastinal shift to the right (yellow arrowhead), elevation of the right hemidiaphragm (white arrowhead in a), curtain like density along the right heart border with loss of the right heart border (orange arrowhead). The right lower lung field magnified in b, shows an air bronchogram of the bronchus intermedius (purple arrowhead) with middle lobe and right lobe bronchi (light blue arrowhead) confirming atelectasis of the middle lobe and right lower lobe of the lung. The CXR in c shows resolution of the atelectasis with return of the mediastinum (almost) to its central location (yellow arrowhead in c , visualisation of the right heart border (blue arrowhead in c) and full visualisation of the right hemidiaphragm (white arrowhead in c and magnified in d).
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Mechanical Causes
CT Compressive Atelectasis and Enhancement
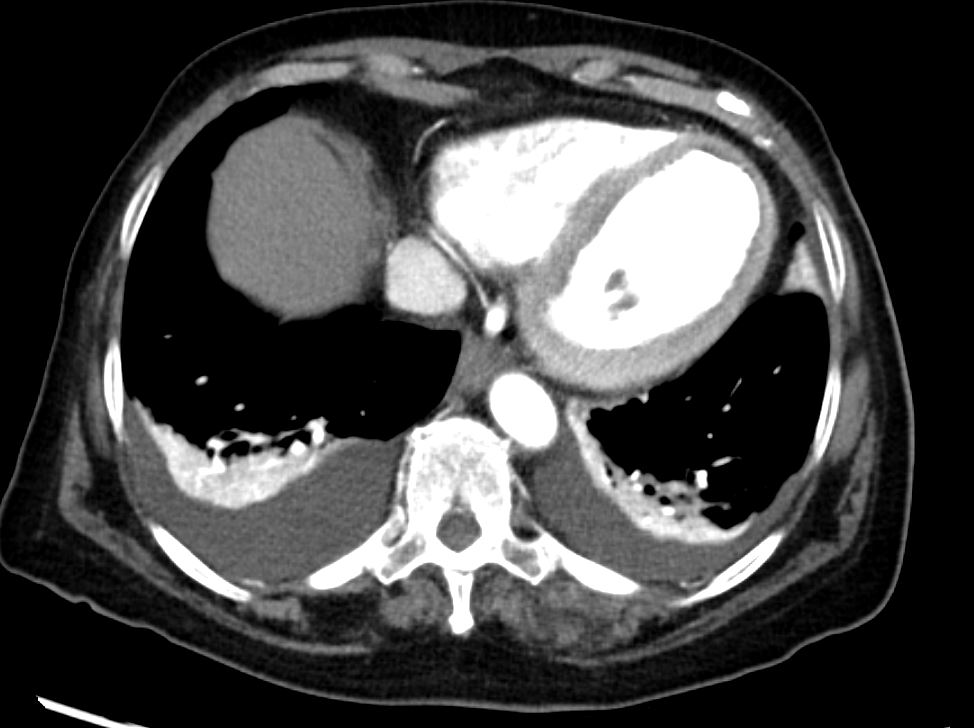

CT scan of the lung bases shows moderate sized bilateral effusions with compressive atelectasis. The atelectatic lung shows hyper-enhancement
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135685
Left Lower Lobar Compressive Atelectasis
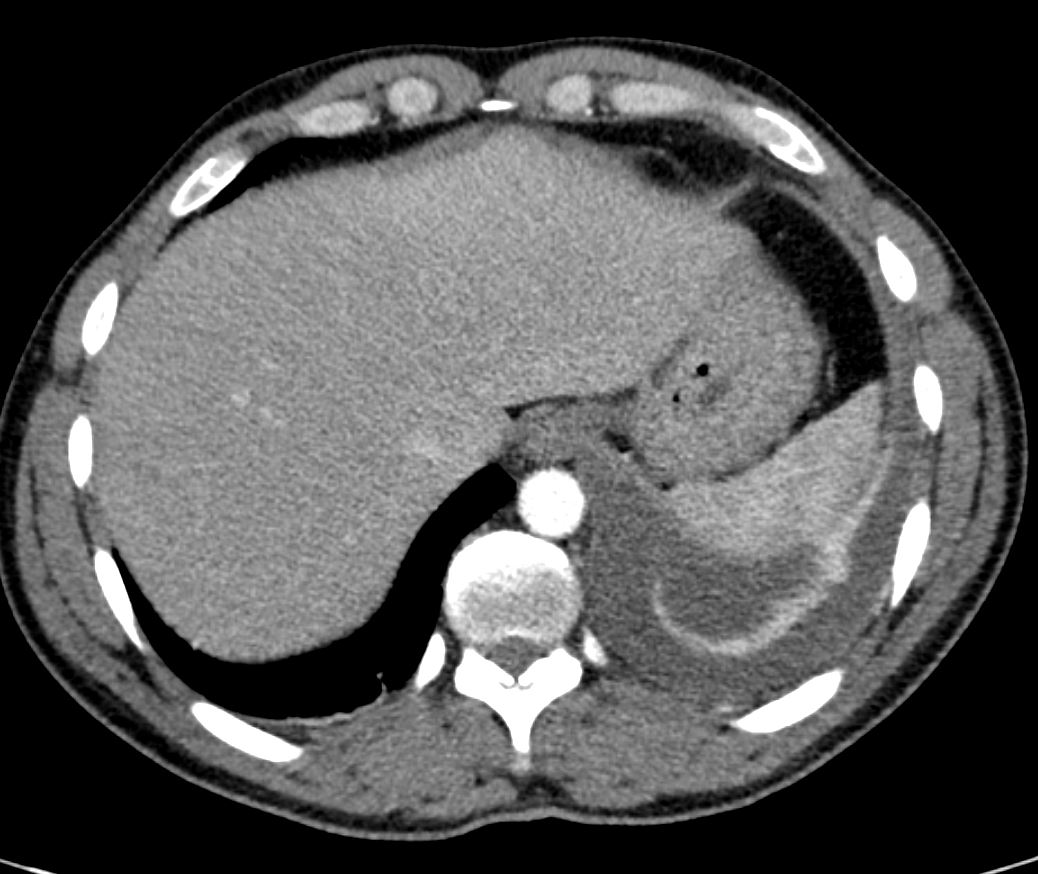

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
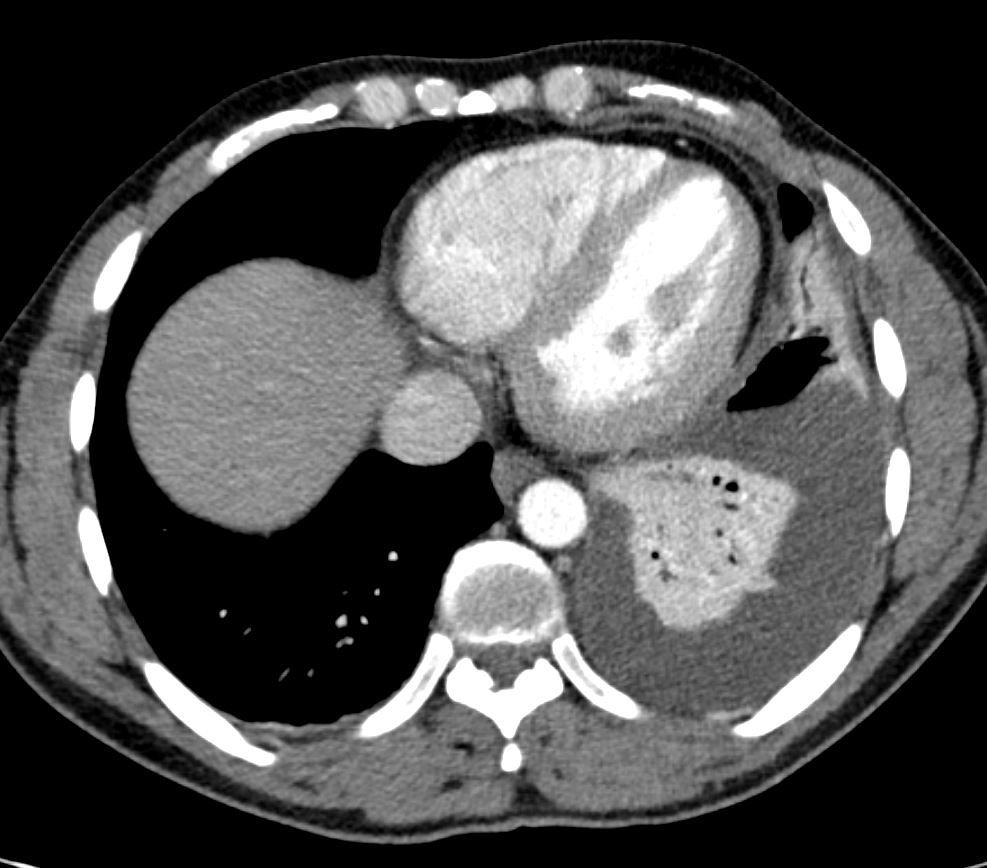

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net



Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Left Lower Lobar Compressive Atelectasis




88 year old male with bilateral effusions shown on the CXR. Axial CT shows thickened pleura on the left with compressive atelectasis of the lower lobe and a smaller region of crescentic compressive atelectasis on the right. 3D reconstruction shows atelectasis of the left lower lobe and portion of the lingula
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
74242c
Types of Atelectasis
Compressive Atelectasis




88 year old male with bilateral effusions shown on the CXR. Axial CT shows thickened pleura on the left with compressive atelectasis of the lower lobe and a smaller region of crescentic compressive atelectasis on the right. 3D reconstruction shows atelectasis of the left lower lobe and portion of the lingula
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
74242c
Rounded Atelectasis
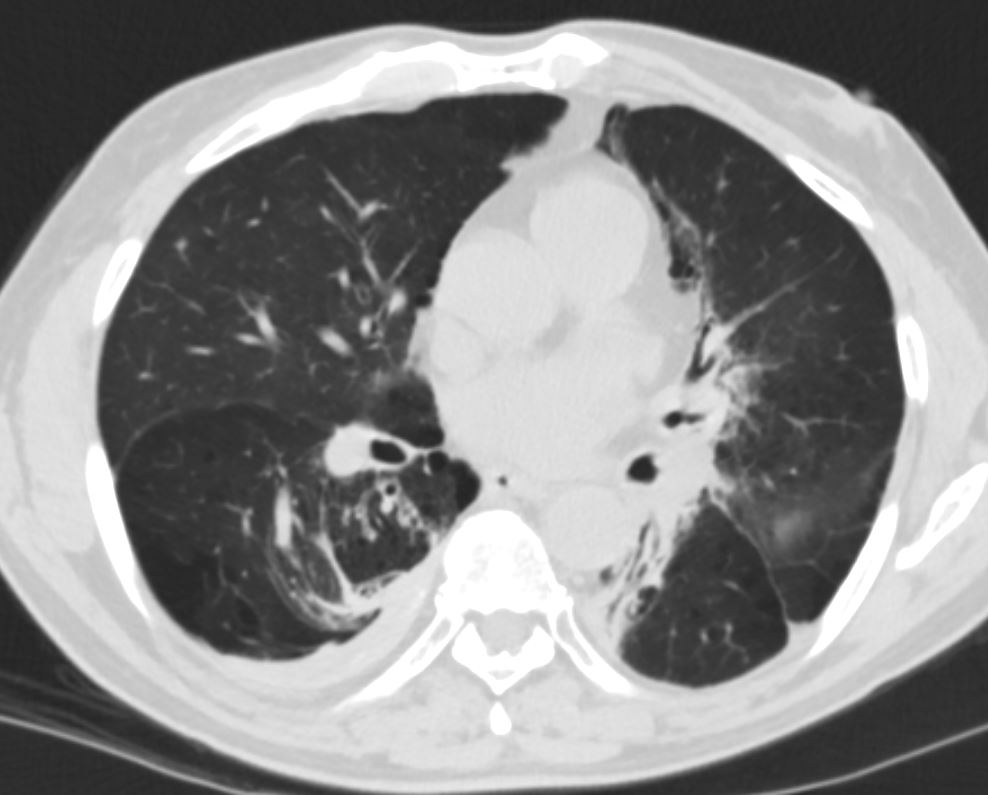

CT shows focal region of pleural thickening with calcification
Also note hyperlucent right lower lobe
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
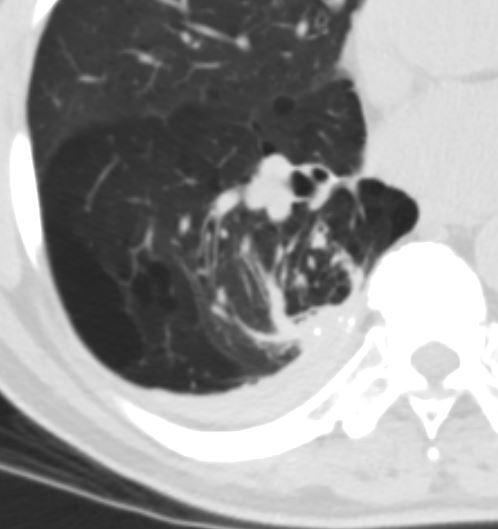

CT shows focal region of pleural thickening with calcification
Also note hyperlucent right lower lobe
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
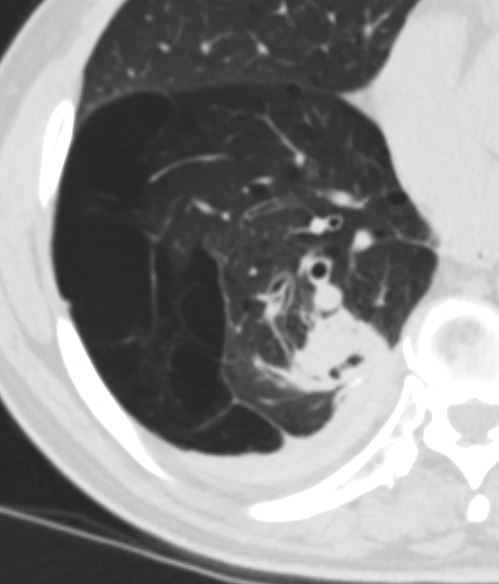

CT shows focal region of pleural thickening with calcification
Also note hyperlucent right lower lobe
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Cancer and Atelectasis
Right Upper Lobe Proximal Squamous Cell Carcinoma


CXR shows right upper lobe (RUL) atelectasis. Final diagnosis was a central RUL proximal squamous cell carcinoma with extensive filling of the distal bronchi-ectatic segmental and subsegmental airways
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net


CXR shows right upper lobe (RUL) atelectasis. Final diagnosis was a central RUL proximal squamous cell carcinoma with extensive filling of the distal bronchi-ectatic segmental and subsegmental airways
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net


Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net


Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net


Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net