Based on Cause
- CAPT Kangaroo has Mounier-Kuhn
C: cystic fibrosis or congenital cystic bronchiectasis (Williams-Campbell syndrome)
A: allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
P: post-infectious (most common)
T: tuberculosis (granulomatous disease)
K: Kartagener syndrome
M: Mounier-Kuhn syndrome
Based on Shape
Varicoid Bronchiectasis ABPA
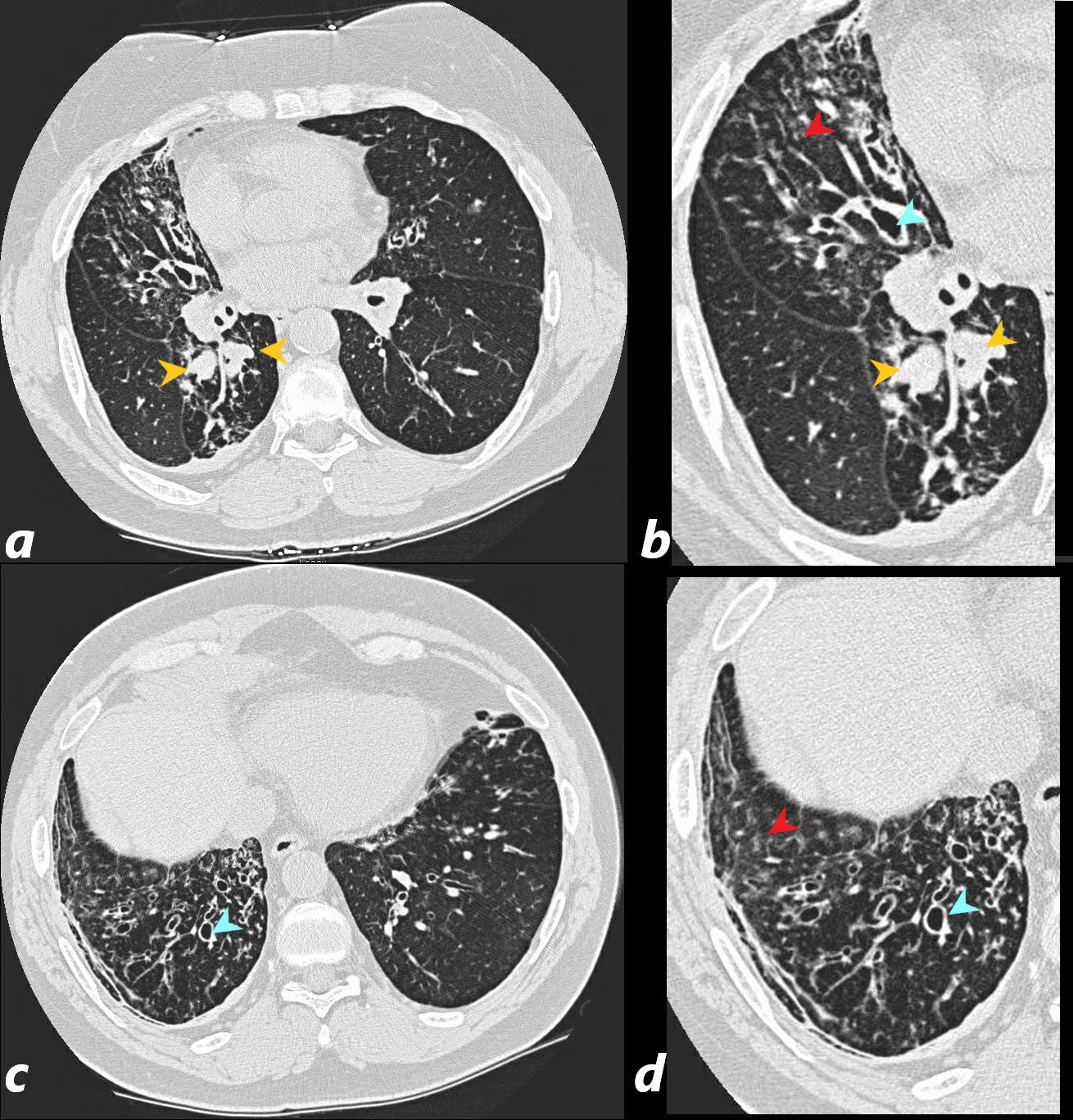
The axial images of the RUL are focused on the air filled varicoid bronchiectasis within the RUL atelectasis (lime green arrow in d) The shape of the posterior subsegmental airways has varicoid shape, and hence the terminology. The axial cuts on the left at 2 different levels, are magnified on the right images. The consolidation (yellow asterisk is noted in all 4 images – solid anteriorly, with the bronchiectatic posterior subsegmental airways posteriorly. There is a small focus of mucoid accumulation in the proximal segmental airway (yellow arrowhead d) The hyperinflated RLL is marked with a teal asterisk in all 4 images .
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Varicoid Bronchiectasis Caused by Traction in Scleroderma
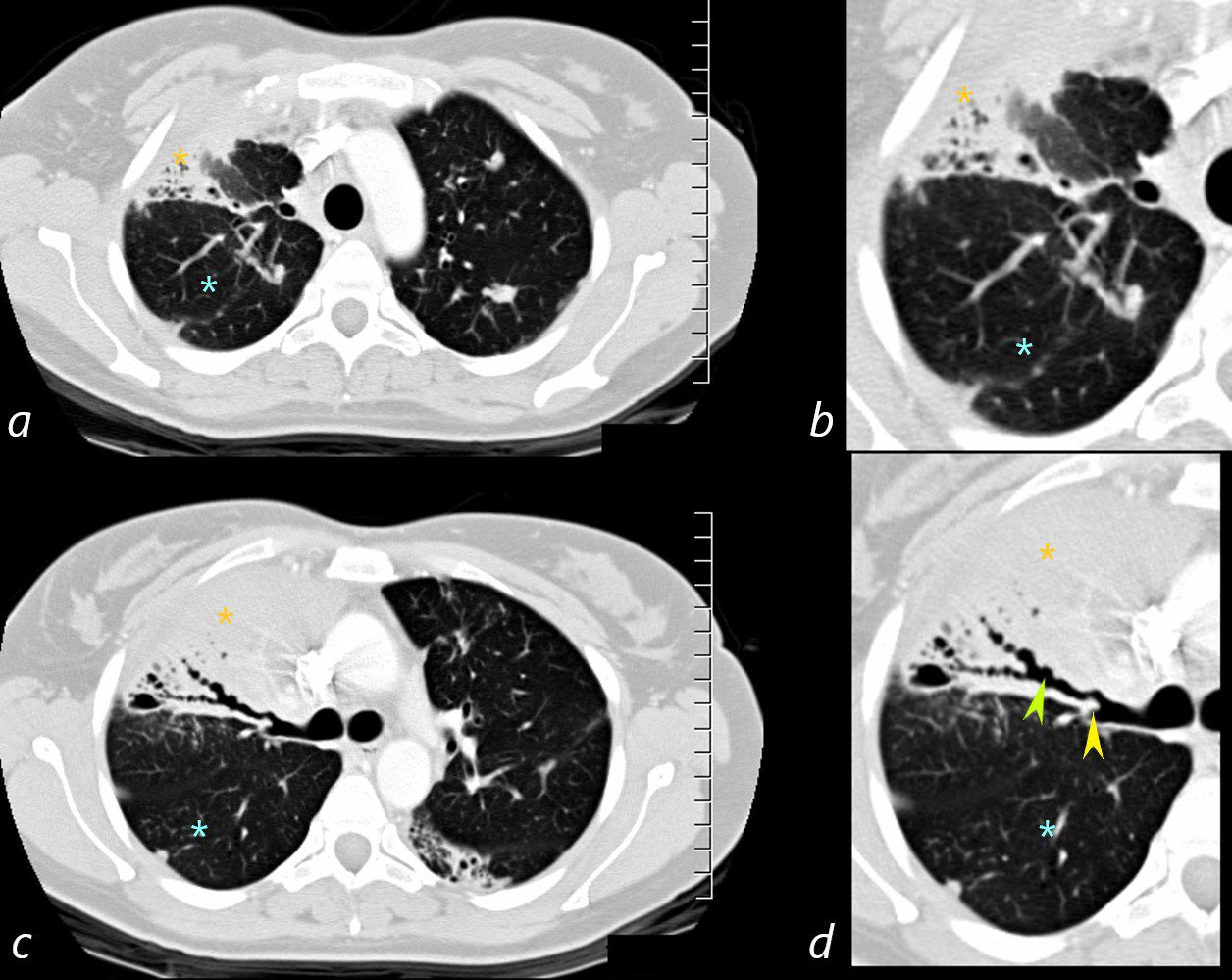
71-year-old female presents with a history of scleroderma, ILD, hypothyroidism and dcSSc
CT of the middle lobe in the axial plane, shows extensive traction bronchiectasis in a background of ground glass changes and reticulations caused by thickening of the interlobular septa.
The fissures show irregular thickening.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 196Lu 136611
Cystic aka Saccular Bronchiectasis
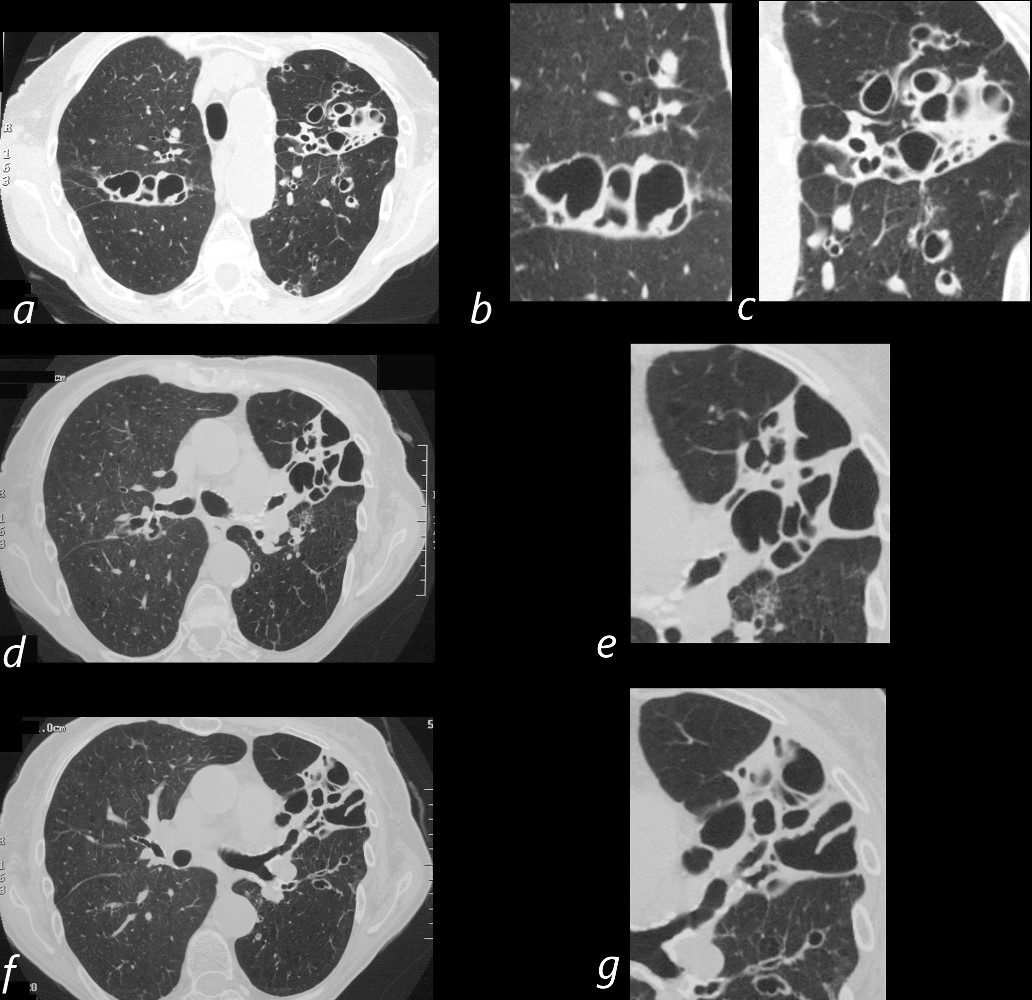
88 year old female with cystic bronchiectasis of the lungs involving the left upper lobe (a magnified in c, d magnified in e and f magnified in g)
A lesser severe area of cystic bronchiectasis in the RUL ( a magnified in b)
aka Saccular Bronchiectasis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
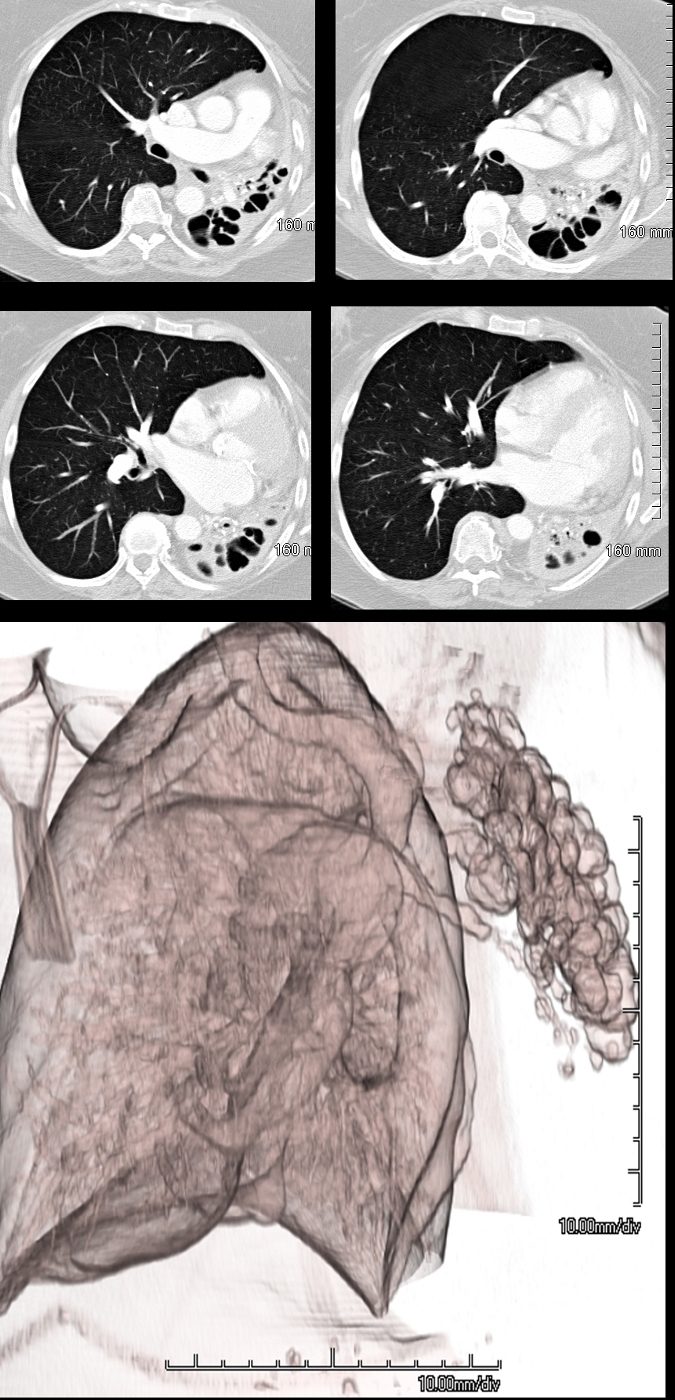
69 year female atrophied right lung secondary to chronic infection and resulting in cystic bronchiectasis (aka saccular bronchiectasis)
The axial images show a totally collapsed right lung with leftward mediastinal shift and hyperinflation of the right lung. The airways of the left lung are large and patent allowing for a 3Dreconstruction of the airways and confirming the diagnosis of saccular bronchiectasis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net
Infection Inflammation
– Hyperinflation,
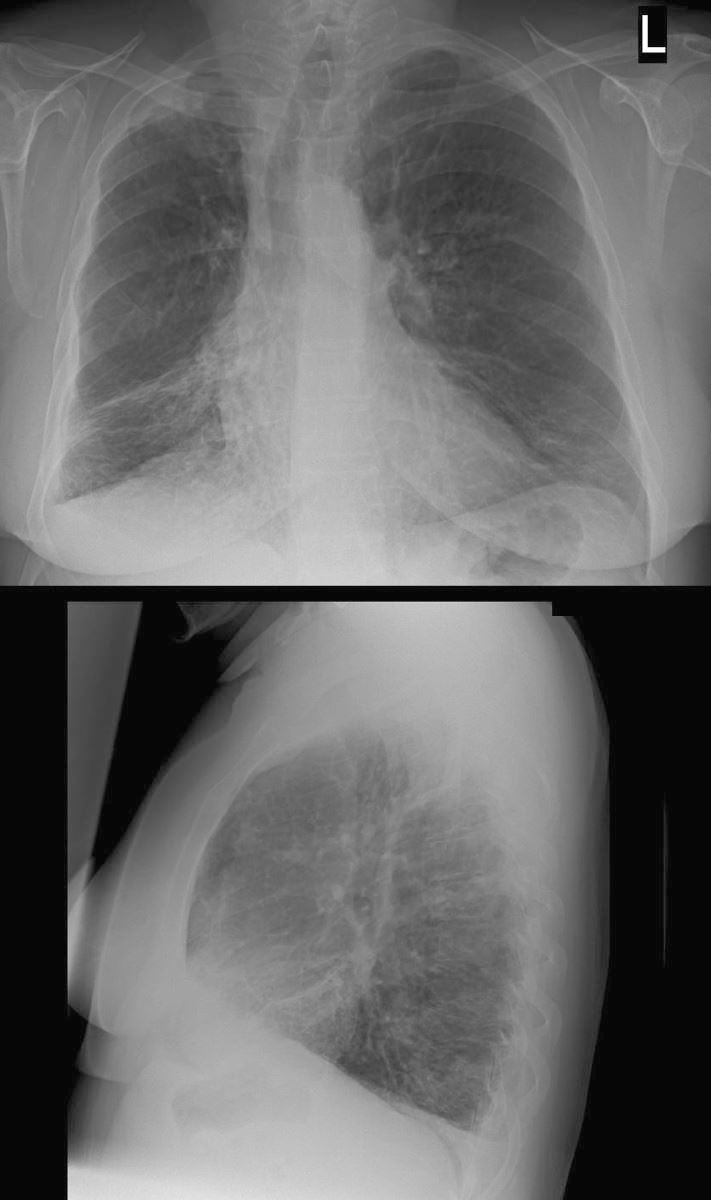
54 year old female with history of asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, ABPA
CXR shows hyperinflation, with flattening of the hemidiaphragm bronchiectasis and volume loss of the right lung with rightward deviation of the trachea and downward displacement of the major fissure )
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 220Lu 31258b
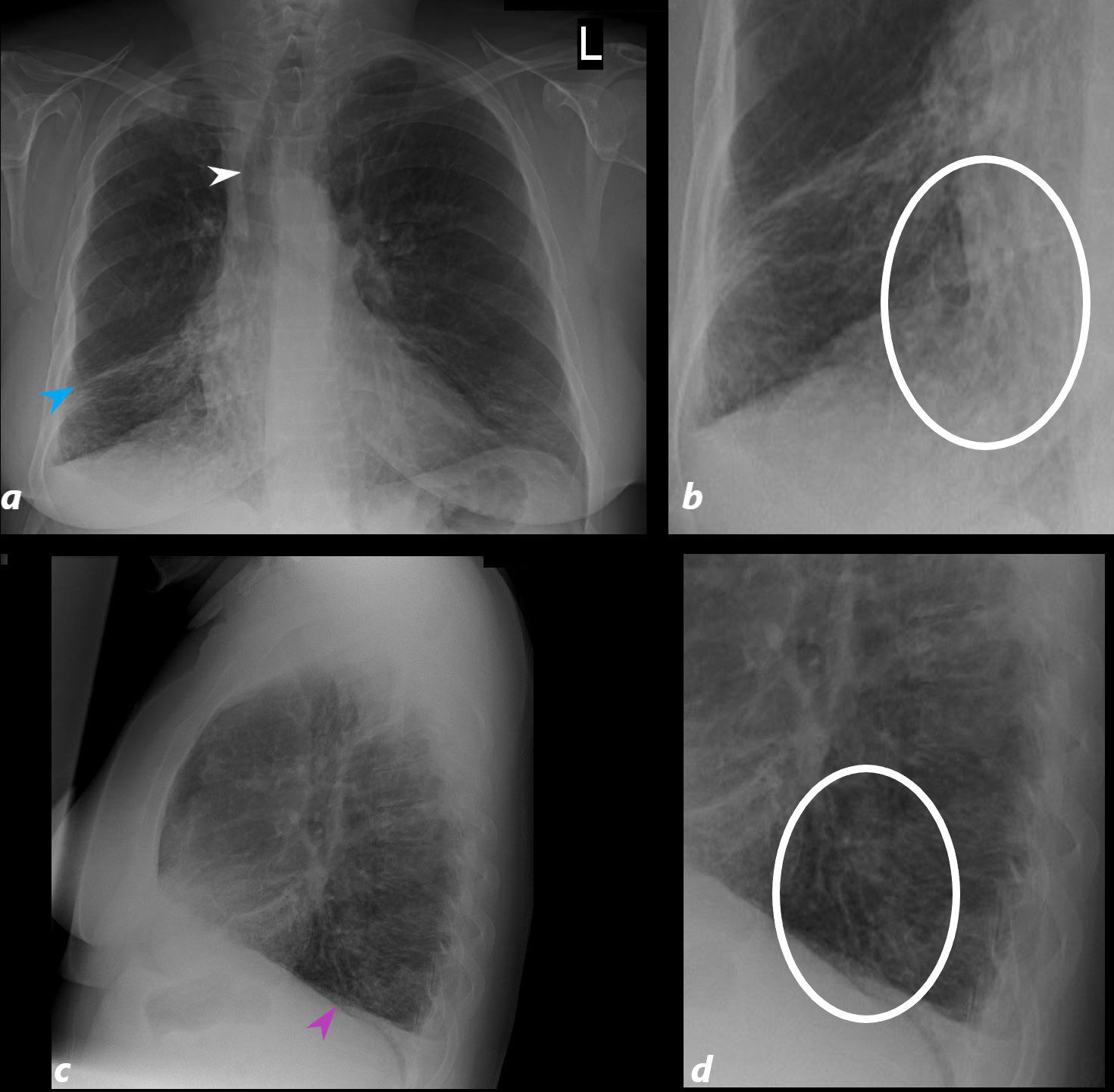
54 year old female with history of asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, ABPA
CXR shows hyperinflation, with flattening of the hemidiaphragm (pink arrowhead c) bronchiectasis (oval white ring b.and d) and volume loss of the right lung with rightward deviation of the trachea (white arrowhead (a) and downward displacement of the major fissure (blue arrowhead, a)
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 220Lu 31258aL
ABPA Bronchiectasis Bronchitis Bronchiolectasis
Right Lower Lobe and Middle Lobe
Current CT – ABPA Bronchiectasis Bronchitis Bronchiolectasis and Small Airway Disease Right Lower Lobe and Middle Lobe
54 year old female with history of asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, ABPA
Current CT scan shows proximal impaction of bronchectatic lower lobe bronchi (orange arrowheads a, and magnified in b) with bronchiectasis in the middle lobe (teal arrowhead in b) and in the right lower lobes (teal arrowheads in c and d ) with suggestion of small airway disease characterized by ground glass micronodules indicating small airway disease (red arrowheads b and d).
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 220Lu 31258b03c
Latent TB
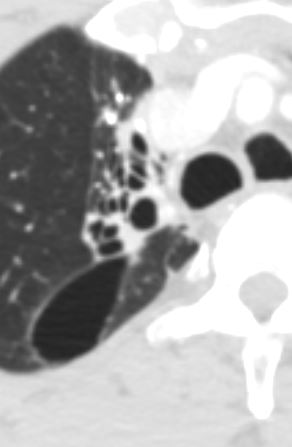
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
MAC and Lady Windermere
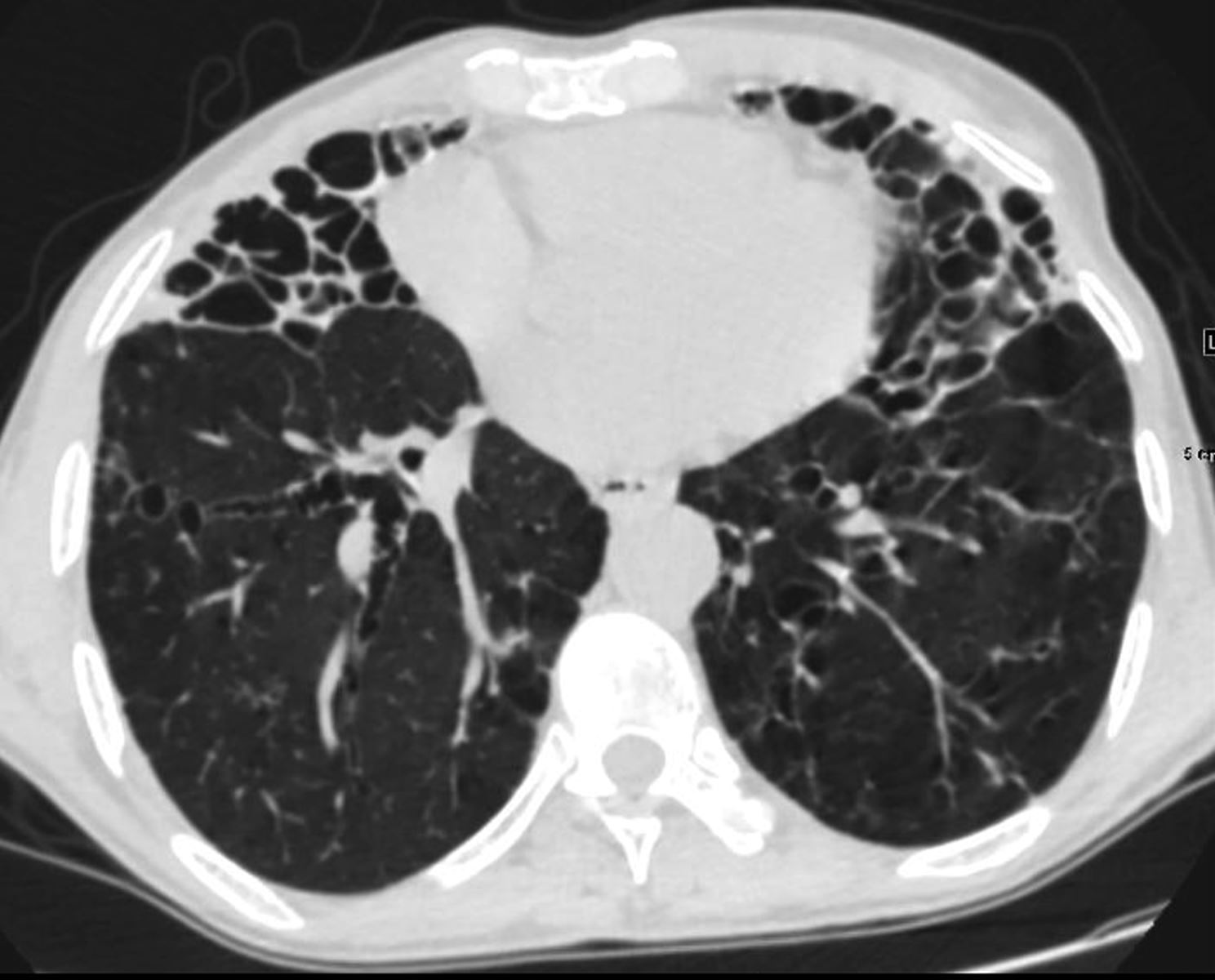
61-year-old male with a history of treated mycobacterial infections including MAC and chronic cough.
Axial CT at the level of the mid to lower chest shows mildly ectatic segmental airways to the lower, and middle lobe bronchi but significant bronchiectasis to the middle lobe and lingula involving the subsegmental airways. There is a relative paucity of mucus in the ectatic airways. The history of MAC and the distribution of the bronchiectasis in the middle lobe and lingula are reminiscent of the diagnosis of Lady Windermere syndrome
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 250Lu 135877
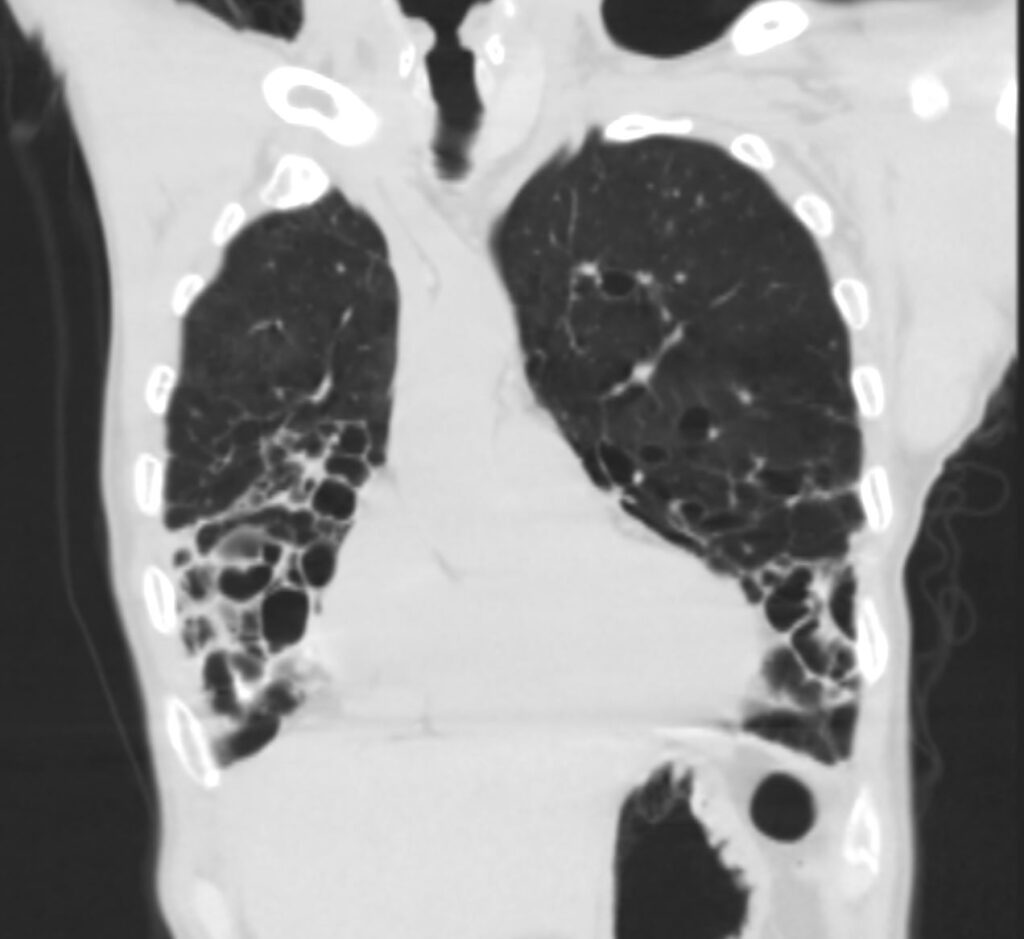

61-year-old male with a history of treated mycobacterial infections including MAC and chronic cough.
Coronal CT at the level of the heart shows significant bronchiectasis to the middle lobe and lingula and as a result abut the right and left heart border accounting for the CXR findings of a “shaggy heart border”. There is a relative paucity of mucus in the ectatic airways. The history of MAC and the distribution of the bronchiectasis in the middle lobe and lingula are reminiscent of the diagnosis of Lady Windermere syndrome
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 250Lu 135879
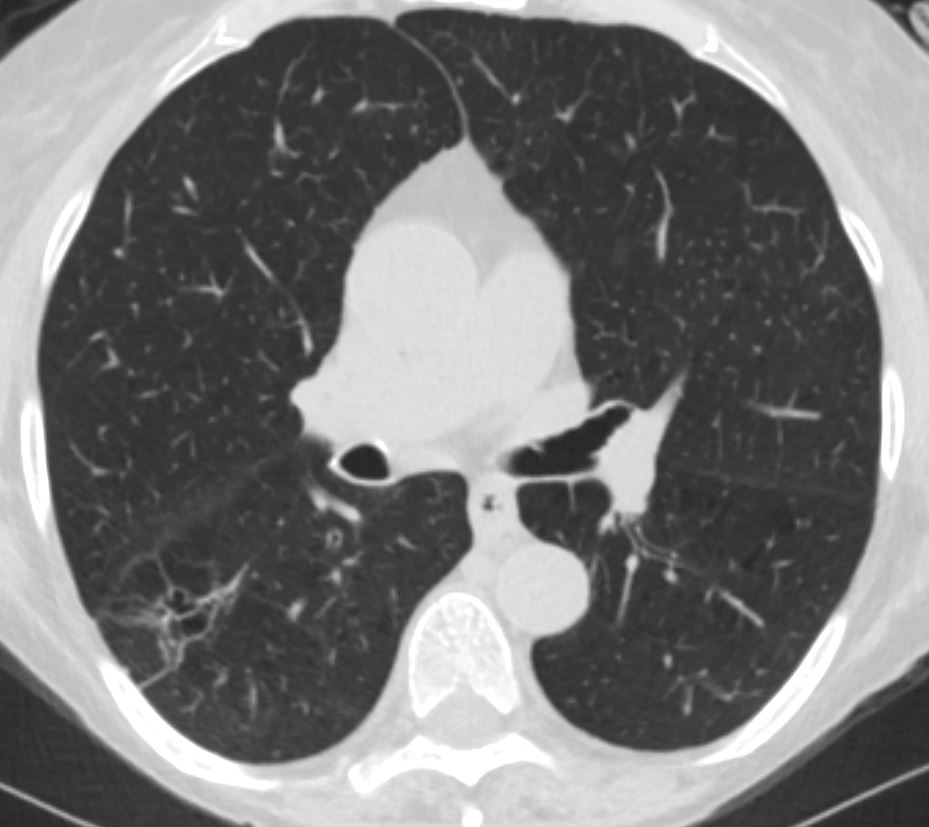

69 year old female presents with a cough. CT in the axial plane shows a focal region of bronchiectasis in the right lower lobe. Note the associated linear scarring that contributes to the reticular CXR findings
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net TCV 215Lu
Infection from Genetic Disorder
19 year old female with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis
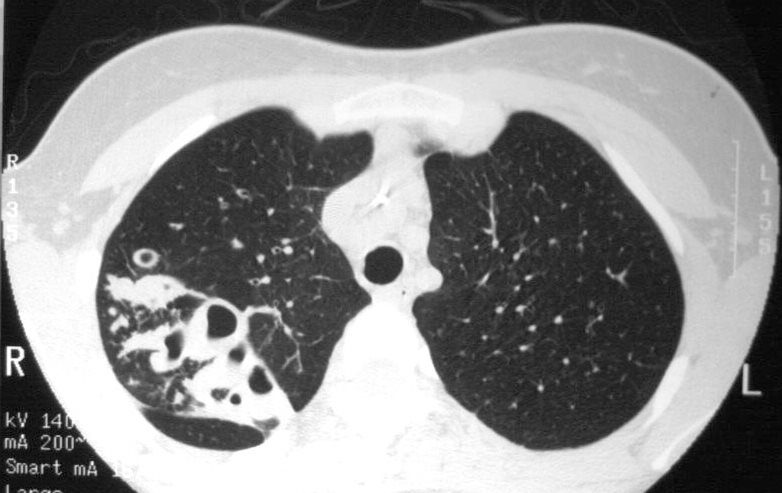

19 year old female with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis
CT scan through the upper lung fields shows multiple thickened and mucin filled subsegmental bronchi of the posterior segment of the right upper lobe
Courtesy Priscilla Slanetz MD MPH TheCommonVein.net
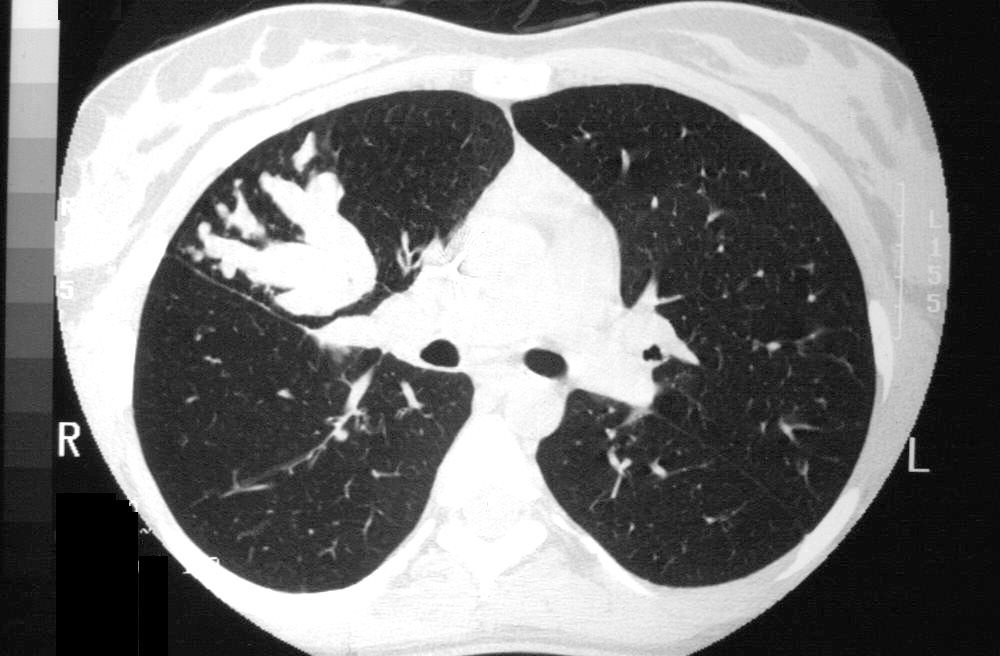

19 year old female with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis
CT scan through the upper lung fields shows mucin filled subsegmental bronchi of the right upper lobe with morphology reminiscent of the “finger in glove” sign
Courtesy Priscilla Slanetz MD MPH TheCommonVein.net
Kartagener’s Syndrome
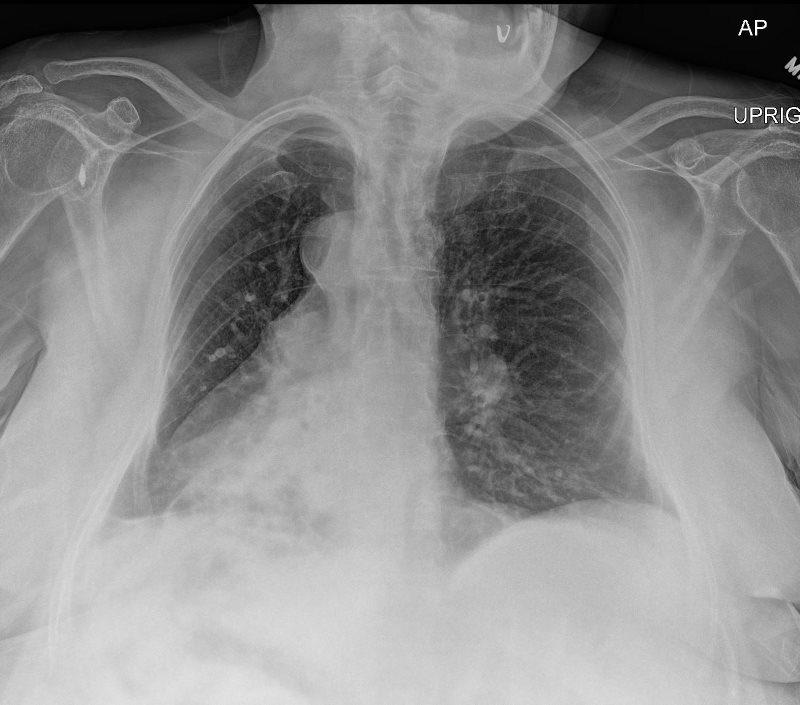

62 year old female with situs inversus totalis, dextrocardia, {SLL} heart, inversus of the lungs, left sided liver, right sided stomach and spleen, bronchiectasis, and chronic sinusitis.
aka Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive genetic disorder
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
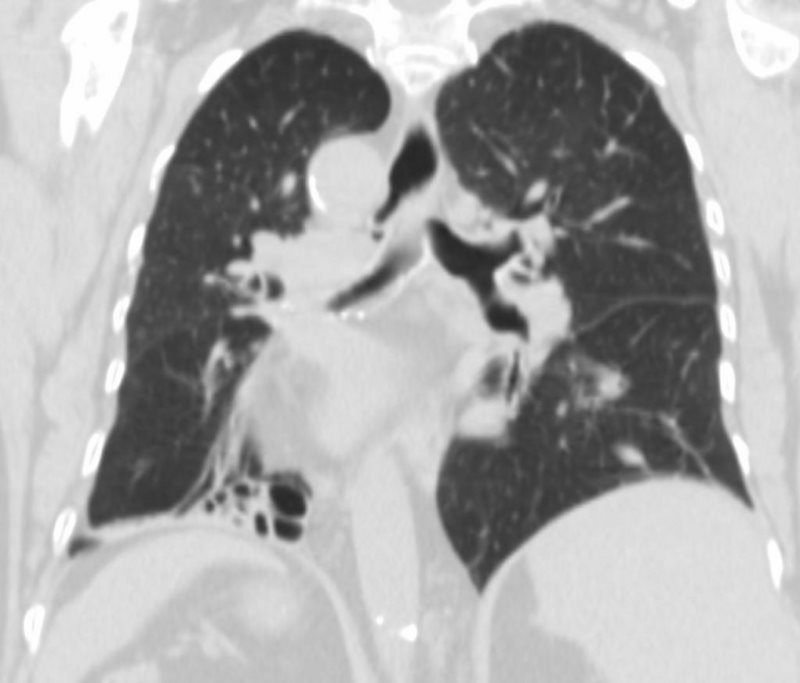

SITUS INVERSUS OF BRONCHI,- HYPARTERIAL BRONCHUS ON RIGHT, EPARTERIAL BRONCHUS ON LEFT
62 year old female with situs inversus totalis, dextrocardia, {SLL} heart, inversus of the lungs, left sided liver, right sided stomach and spleen, bronchiectasis, and chronic sinusitis.
aka Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive genetic disorder
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
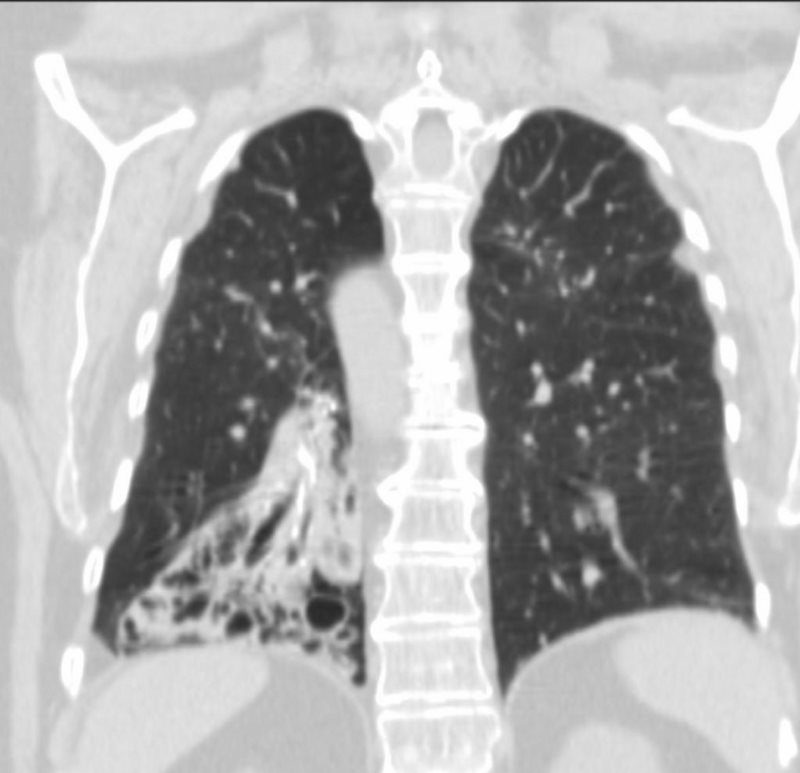

62 year old female with situs inversus totalis, dextrocardia, {SLL} heart, inversus of the lungs, left sided liver, right sided stomach and spleen, bronchiectasis, and chronic sinusitis.
aka Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive genetic disorder
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Inflammation
Mechanical Causes
Mounier Kuhn Loss of Elasticity
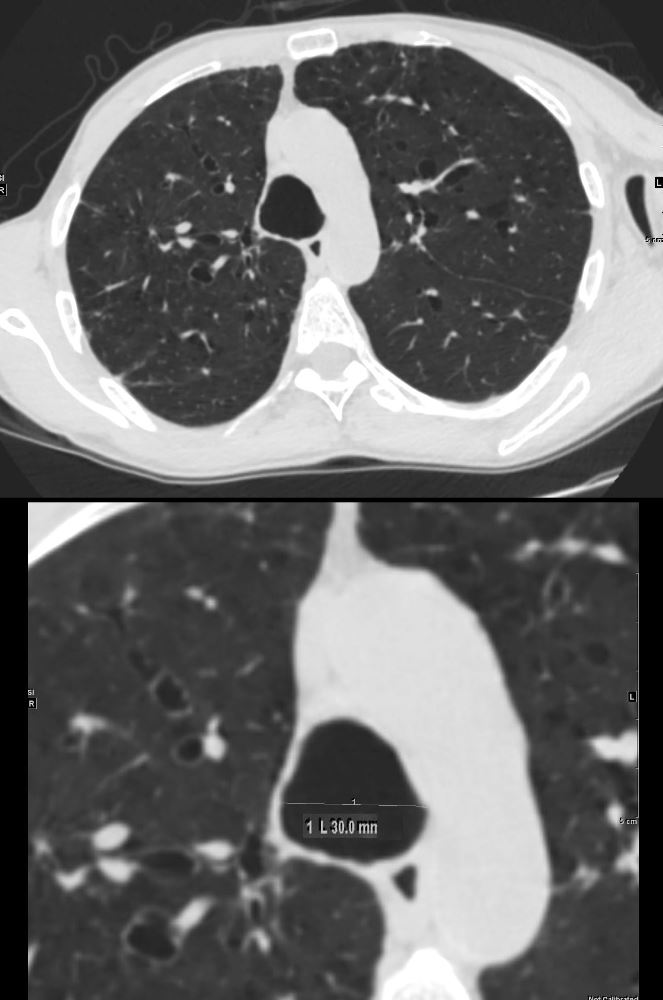

61 year old male with a history of treated mycobacterial infections and chronic cough
Axial CT at the level of the brachiocephalic vessels shows an enlarged trachea that measures 3cms which is abnormally enlarged. There are thin-walled cystic changes of the airways along the subsegmental arteries in the upper lobes likely reflecting bronchiectasis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 250Lu 135874ac
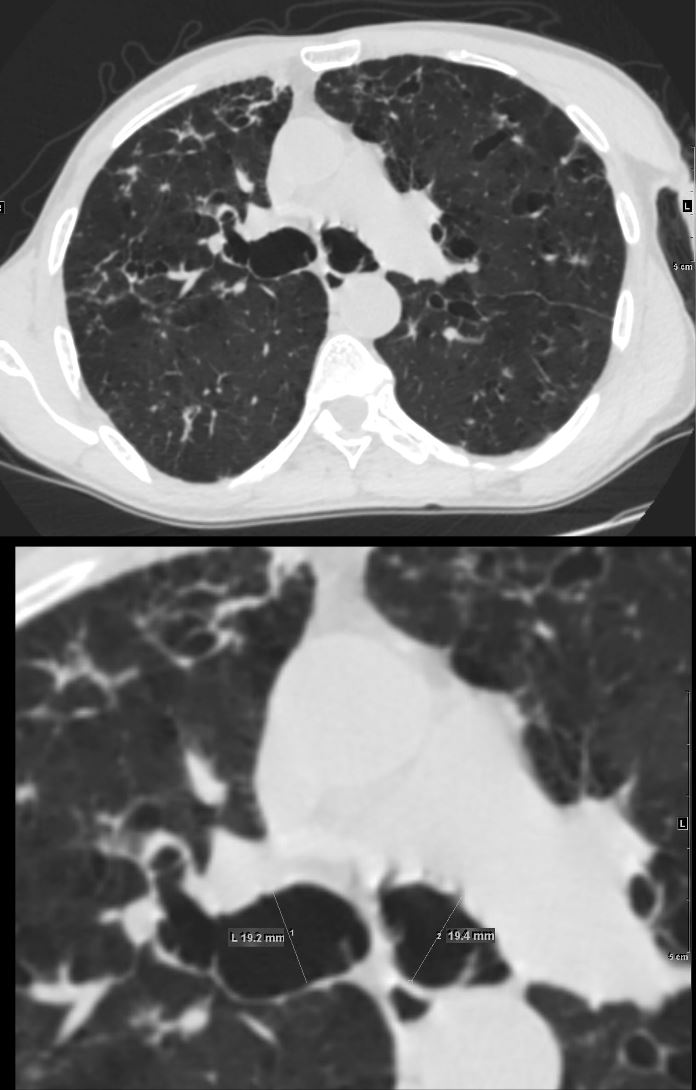

61 year old male with a history of treated mycobacterial infections and chronic cough
Axial CT at the level of the carina shows bilaterally enlarged mainstem bronchi that measure 1.9cms. each which are abnormally enlarged. There are both thin-walled cystic changes of the airways along the subsegmental arteries in the upper lobes likely reflecting bronchiectasis . Some of these cystic changes in the right upper lobe (upper panel) have thicker walls
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 250Lu 135875a



61-year-old male with a history of treated mycobacterial infections including MAC and chronic cough.
Axial CT at the level of the mid to lower chest shows mildly ectatic segmental airways to the lower, and middle lobe bronchi but significant bronchiectasis to the middle lobe and lingula involving the subsegmental airways. There is a relative paucity of mucus in the ectatic airways. The history of MAC and the distribution of the bronchiectasis in the middle lobe and lingula are reminiscent of the diagnosis of Lady Windermere syndrome
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 250Lu 135877
Traction Bronchiectasis
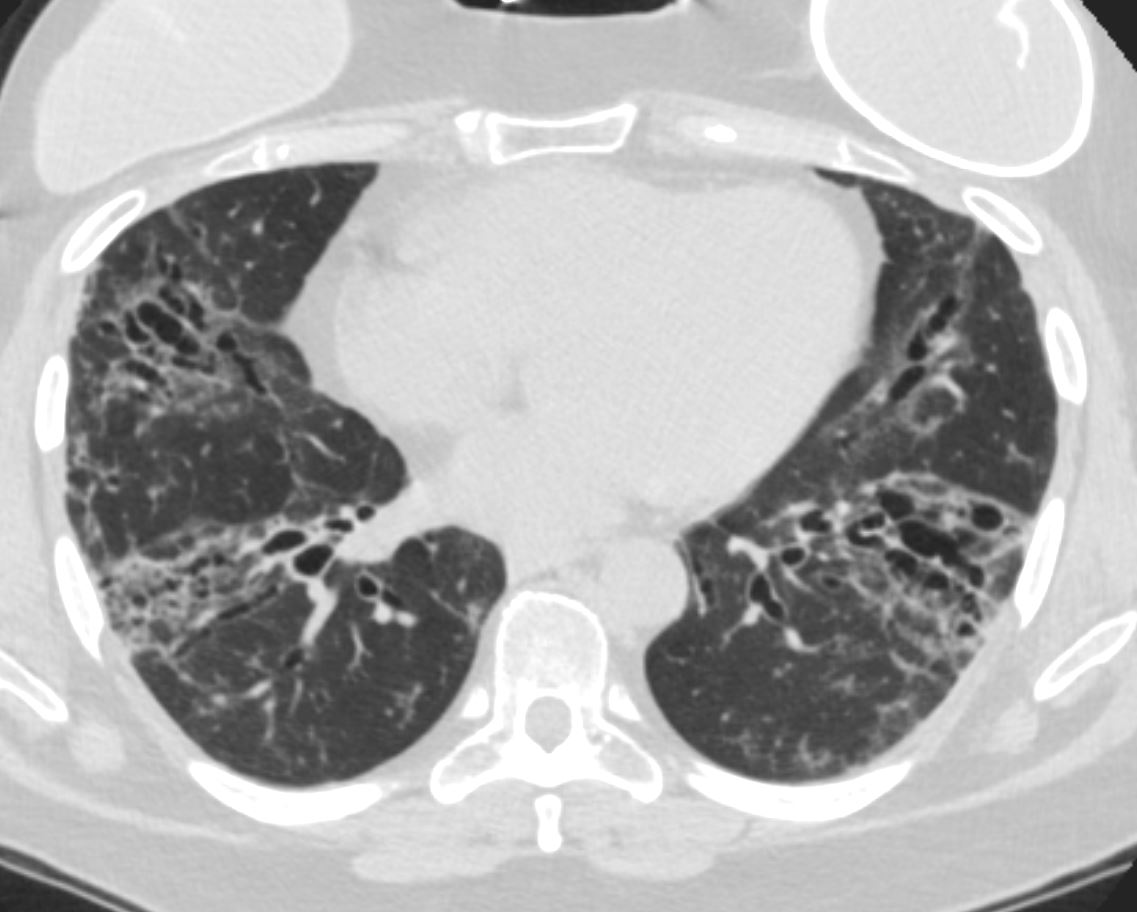

Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
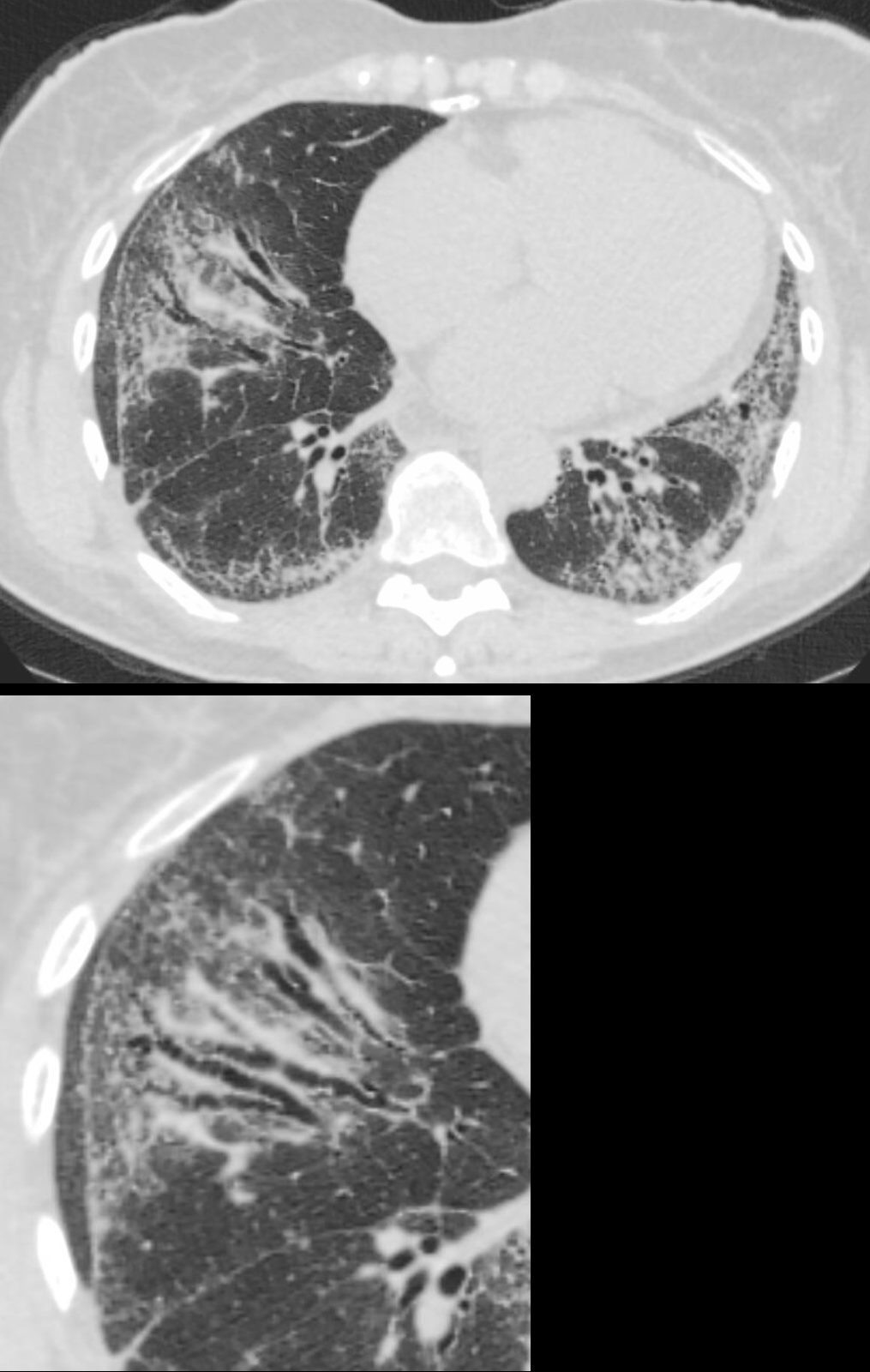

71-year-old female presents with a history of scleroderma, ILD, hypothyroidism and dcSSc
CT in the axial plane,shows extensive ground glass changes in the inferior lingula middle lobe and traction bronchiectasis in the middle lobe. The left lower lobe shows bronchovascular changes, and bronchiolectasis and there is bilateral subpleural sparing
The fissures show irregular thickening.
The lower image exemplifies the traction bronchiectasis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 196Lu 136610c
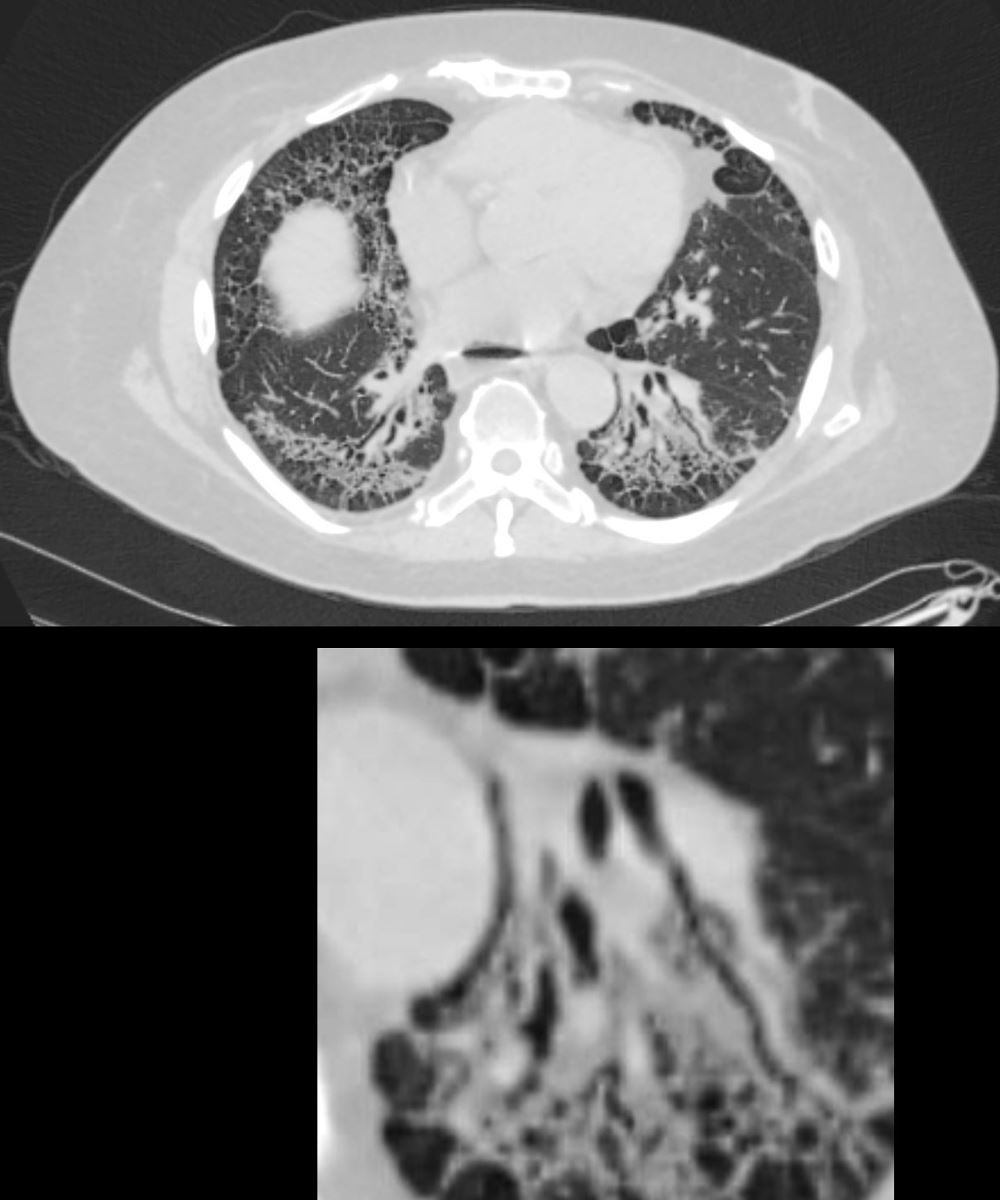

59-year-old male presents with history of scleroderma, Raynaud’s disease, and ILD
Upper Image
Axial CT shows bibasilar peripheral reticular changes, ground glass, bronchiectasis, and bronchiolectasis with volume and with crowding of the bronchovascular bundles posteriorly. There is subpleural sparing posteriorly. Note air-fluid level in the distended esophagus.
Lower Image
The lower image focuses on the traction bronchiectasis caused by the fibrotic process
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 110Lu 136598c

Broncho vascular distribution associated with increased reticular changes, more prominent traction bronchiectasis, decreased lung volumes , and decreased lung volumes, dominantly in the lower lobes but to some extent in the middle lobe and upper lobes. Pulmonary hypertension becomes more common.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net lungs-0771d
Infection
Inflammation
Malignancy
Small Cell Lung Cancer
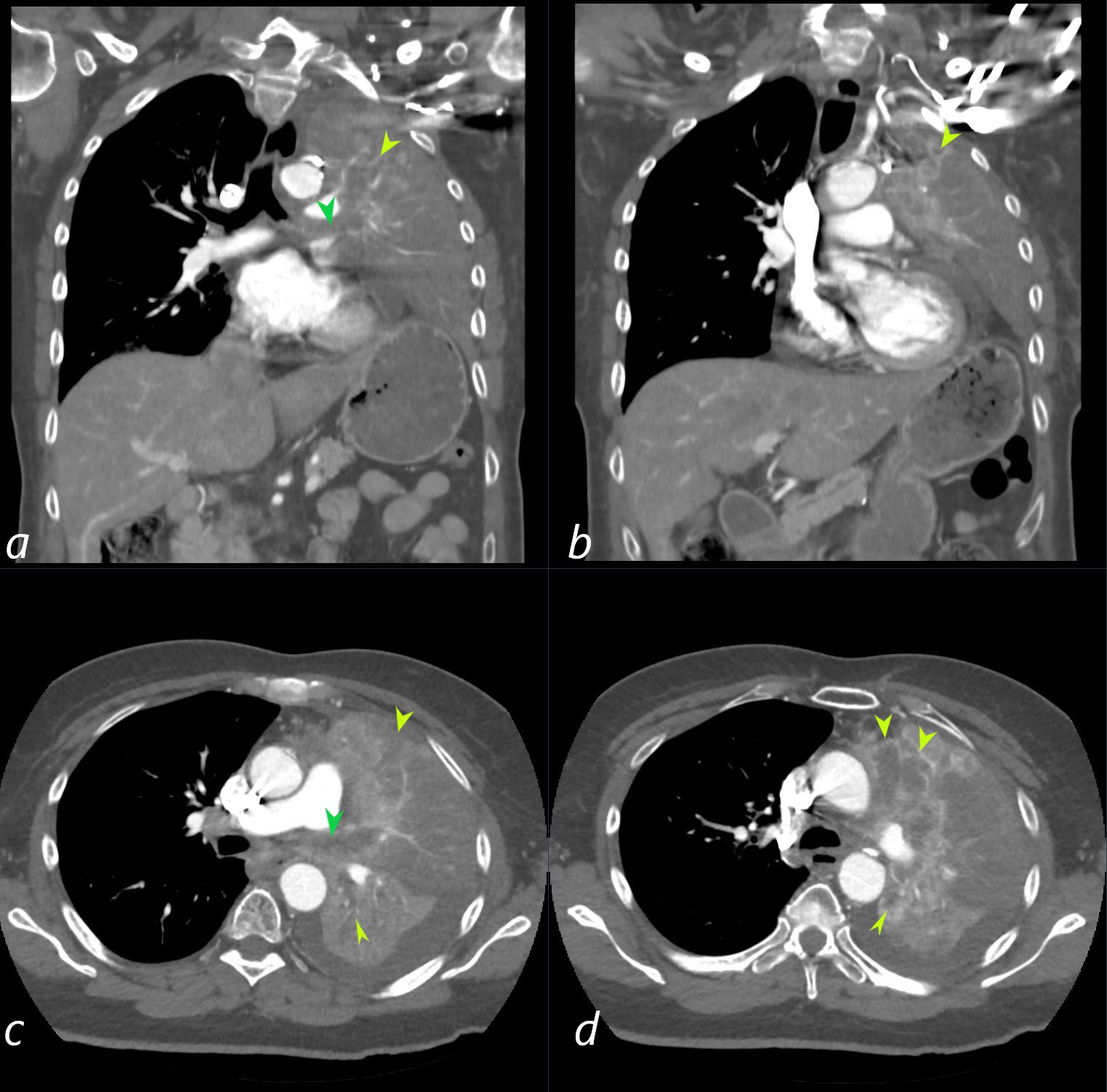

62-year-old female presents with acute dyspnea and chest pain
Coronal CT confirms the presence of an obstructing lesion in the left mainstem bronchus, (dark green arrowhead, a), with extension of the soft tissue into bronchiectatic upper lobe bronchi (light green arrowheads b, c, d) There is total collapse of the left lung.
Subsequent pathological diagnosis of small cell lung carcinoma was established
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 298Lu 136704
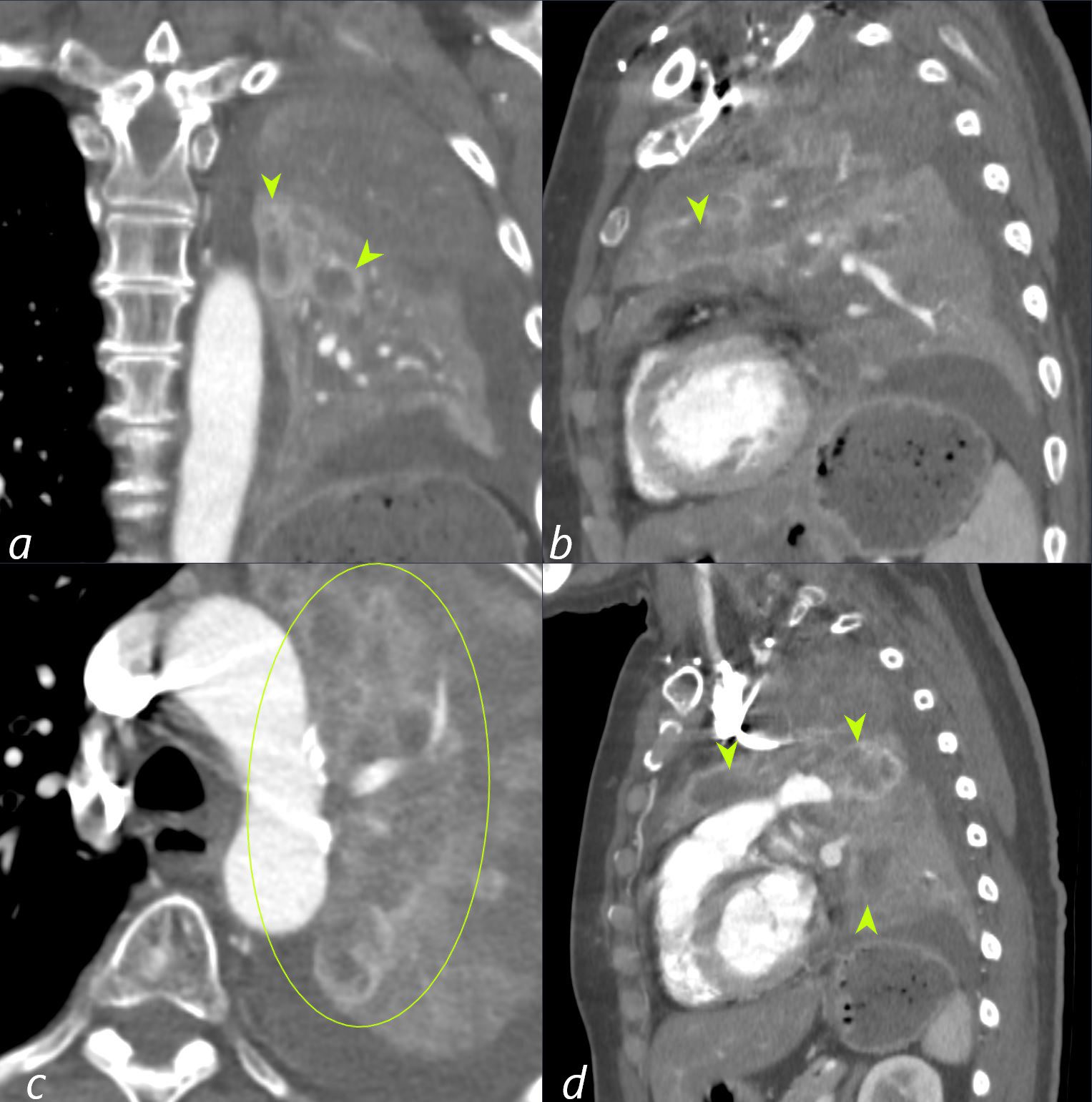

62-year-old female presents with acute dyspnea and chest pain
Coronal CT shows inspissation and bronchiectasis of the left upper lobe segmental an subsegmental airways (green arrowheads and ringed in green) likely due to extension of the the central small cell cancer. There is total collapse of the left lung.
Subsequent pathological diagnosis of small cell lung carcinoma was established
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 298Lu 136706