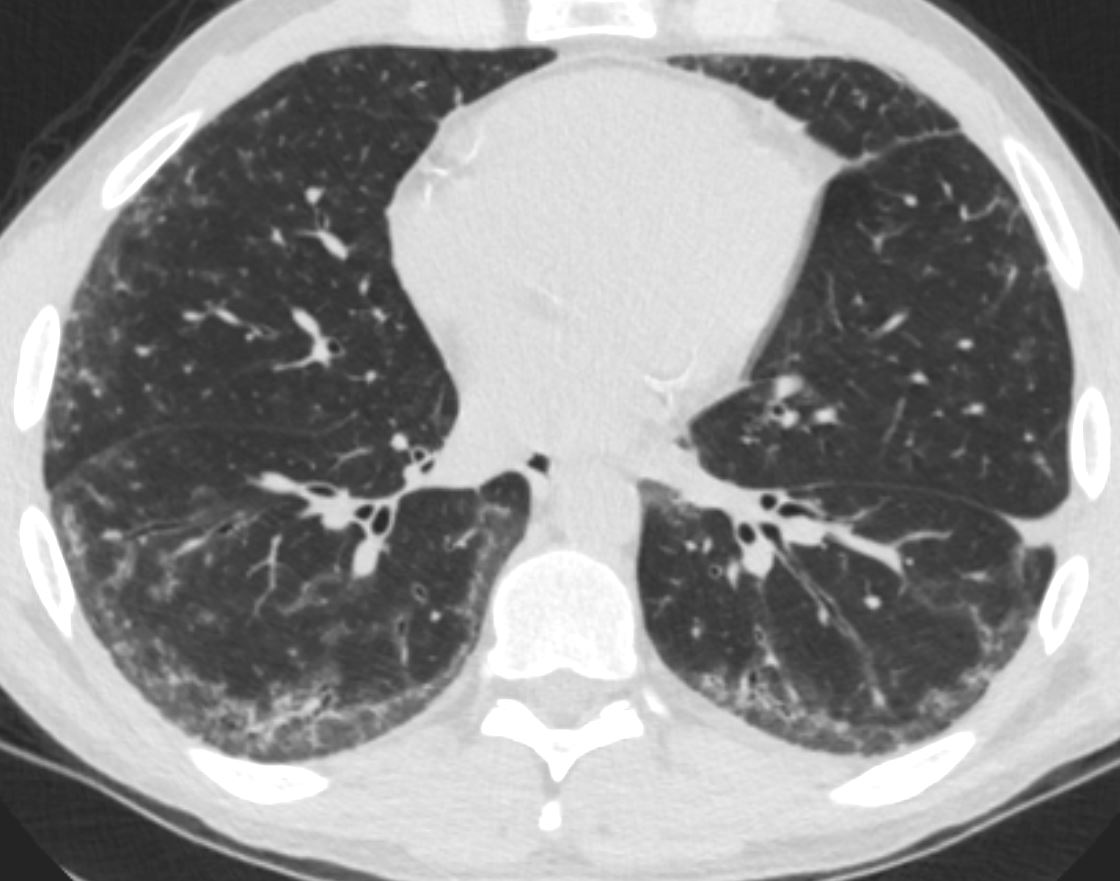
Chronic eosinophilia is characterised by alveolar filling with eosinophils and inflammatory exudates(a) and interalveolar interstitial thickening, (overlaid in red in b). The infiltrates are classically peripherally positioned, usually upper lobes, more commonly bilateral but can be unilateral, and manifest as consolidation and or ground glass opacities. The CT shows bilateral peripheral consolidations in the upper lobes
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0775e
Infection
TB Apices
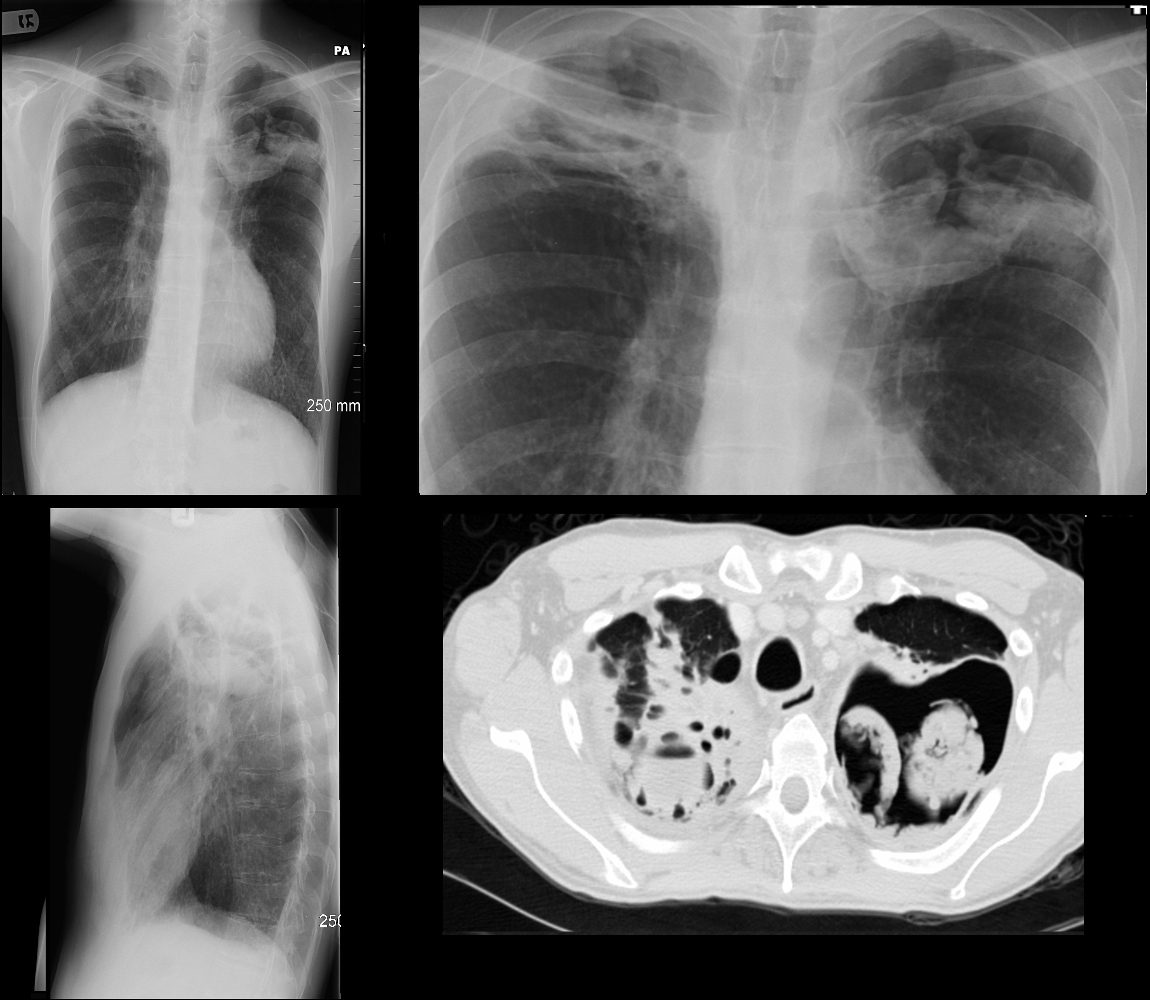
CXR and CT of a 54 year old male shows hyperinflation of the lungs, with large left apical cavity with aspergilloma and pneumonic consolidation and abscess formation in the apex of the right lung. These findings are consistent with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net
Inflammation
COP
UIP IPF
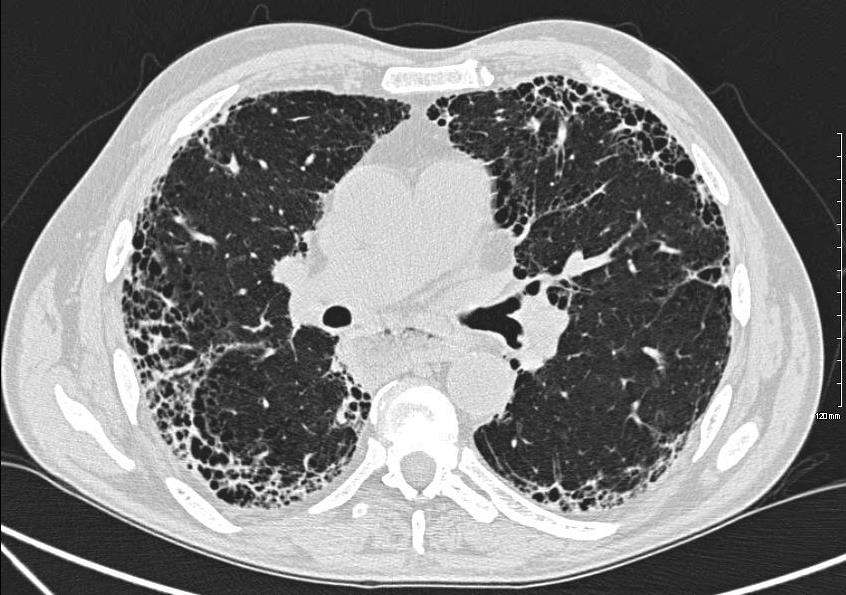
Ashley Davidoff MD thecommonvein.net 134900-lungs UIP
NSIP
Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
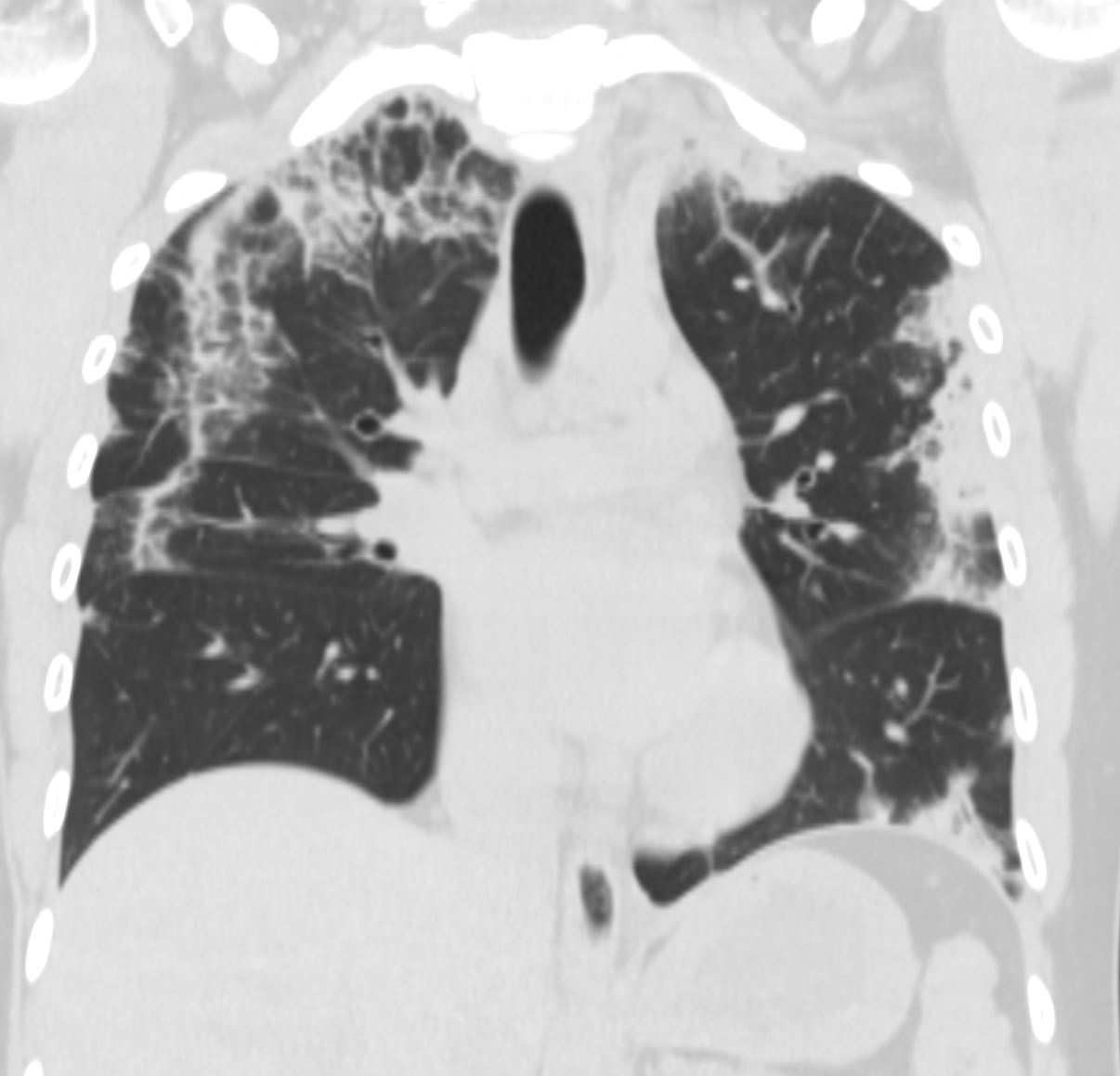
CT scan in the coronal performed 6 months ago at the time of clinical presentation shows upper lobe predominant peripheral infiltrates with small left lower lobe peripheral infiltrate Subsequent diagnosis by BAL of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP)
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Malignancy
Adenocarcinoma
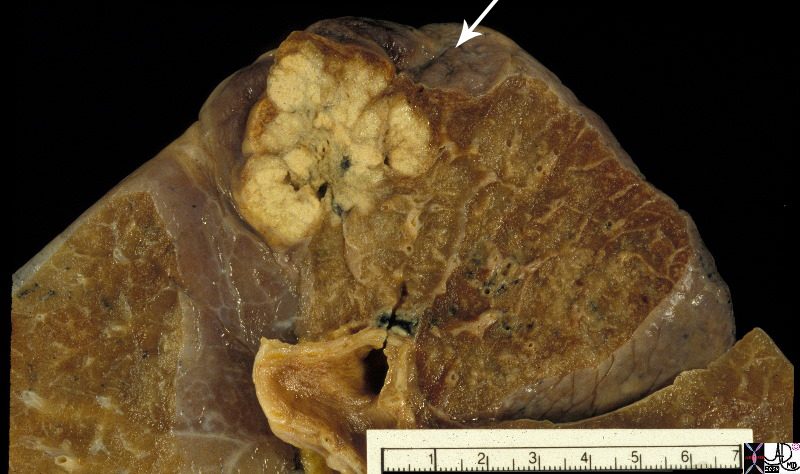
The 3.5cms carcinoma is peripherally situated and is sub-pleural in location. It reveals fibroblastic (aka desmoplastic) effect as witnessed by the puckering of the pleura (arrow). It is remote from central bronchovascular structures and therefore remains relatively asymptomatic for an extended duration unless it causes pleuritic pain. The location and desmoplastic puckering of the pleura are characteristic of an adenocarcinoma.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
32201b.81s

Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Large Cell
Mechanical/Atelectasis
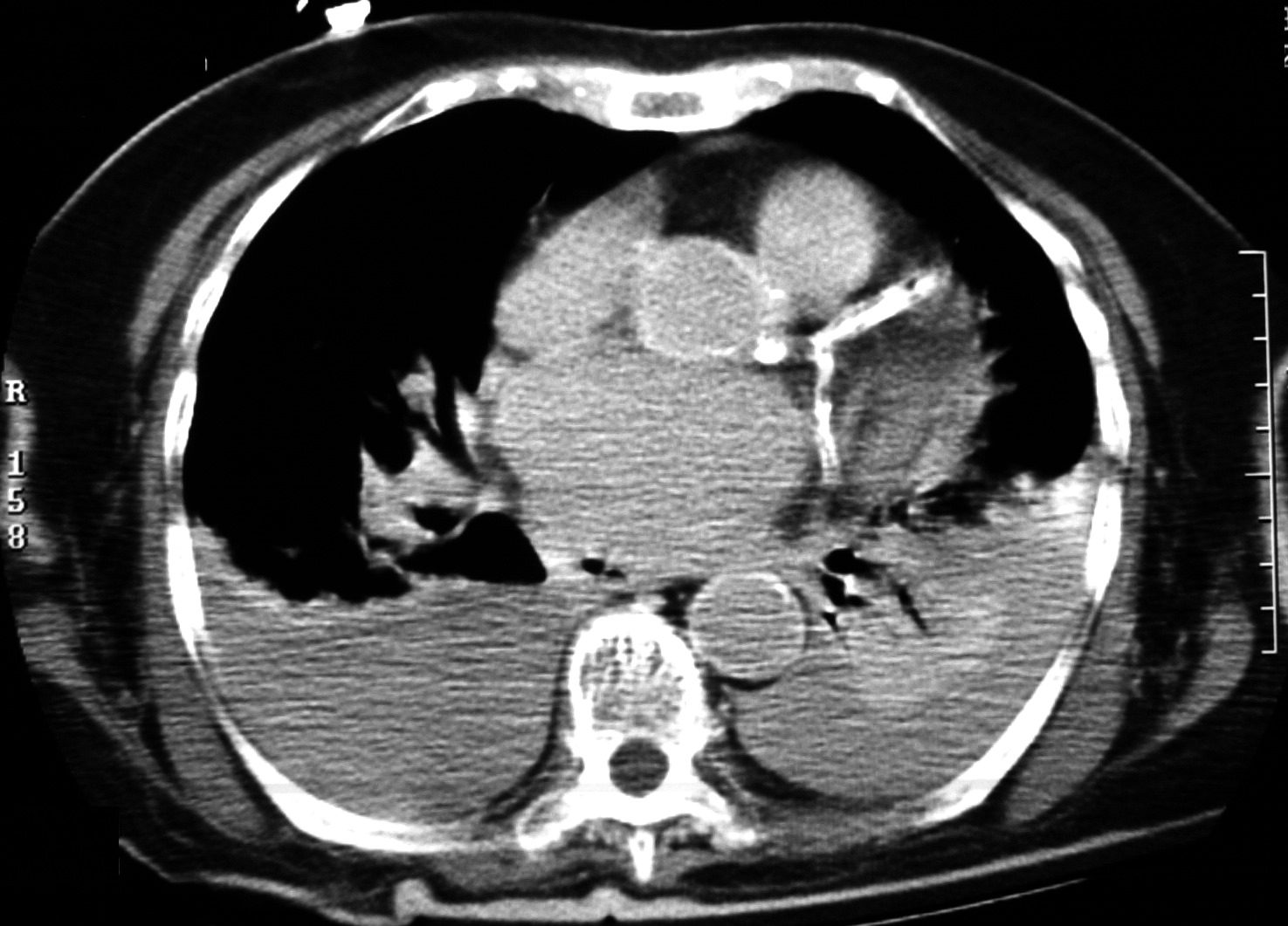
83 year old with bilateral pleural effusions, right larger than left with bibasilar compressive atelectasis. There is significant coronary calcification including left main disease and possible LAD stent. The left atrium is enlarged likely secondary to elevated left ventricular end diastolic pressure. This finding and the pleural effusions suggest CHF. Visualization of the wall of the aorta without the usual coarsened calcification raises the possibility of anemia
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net RnD image
Compressive Atelectasis
Trauma
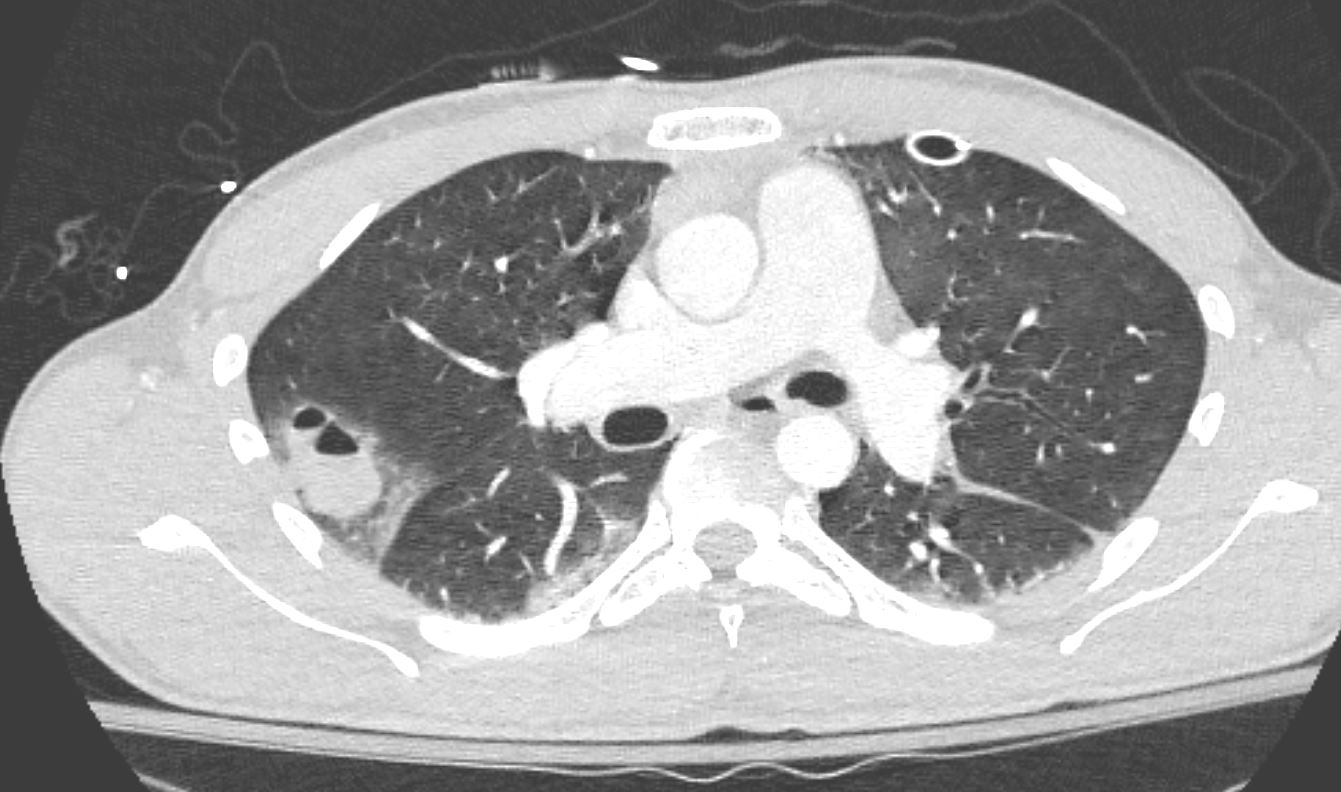
CT in the axial plane shows a peripheral air and fluid containing surrounded by a region of ground glass changes.
These findings are consistent with a hemorrhagic pneumatocele surrounded by contusion Ashley Davidoff TheCommonvein.net pneumatocele 31 M
Metabolic Circulatory- Hemorrhage Immune Infiltrative Idiopathic Iatrogenic Idiopathic
- IPF
- COP
- Subpleural and Extension Along the Fissures
- IPF and UIP
- NSIP
- Subpleural and Extension Along the Fissures
- Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
