Infection
Inflammation Inhalation
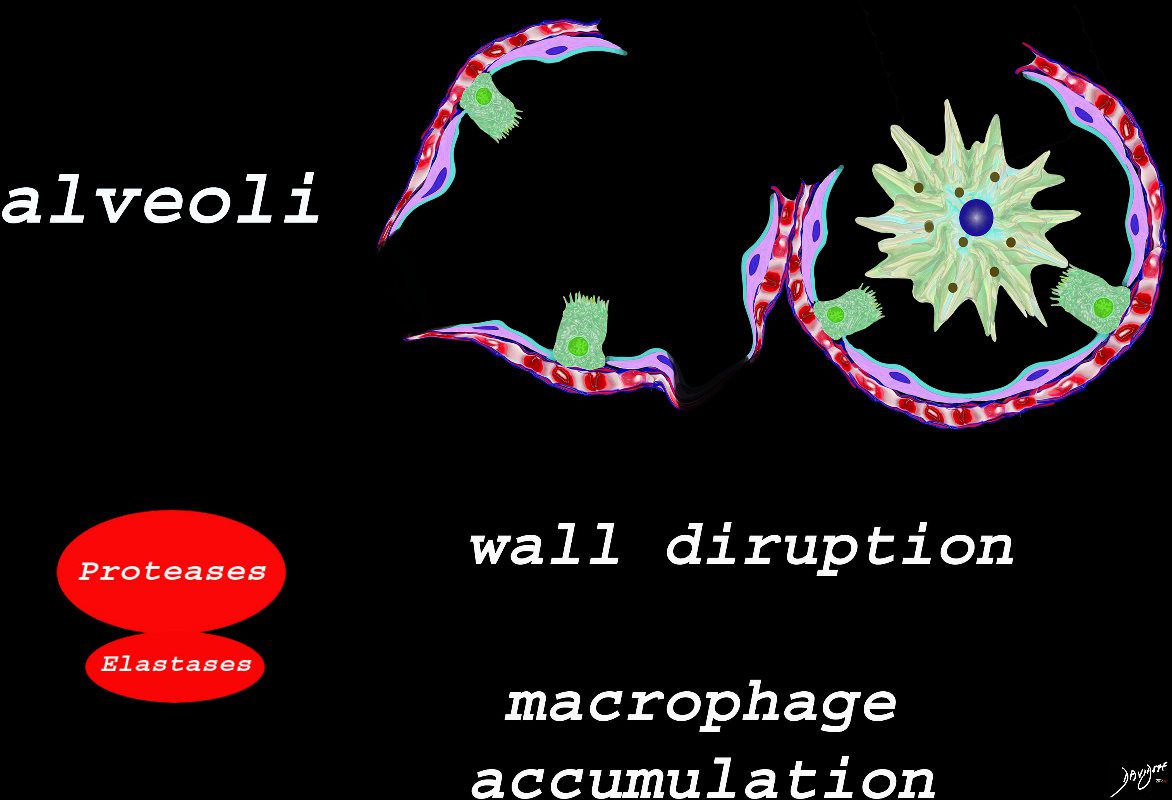
The effect of the proteases and and elastases cause destruction of the alveoli and loss of elasticity, and therefore overall function. The destruction leads to bullous disease
The accumulation of smokers macrophage, and in the case of Langerhans cell histiocytosis leads to space occupation of the alveoli also reducing function
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
lungs-00687
Immune
Langerhans

Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
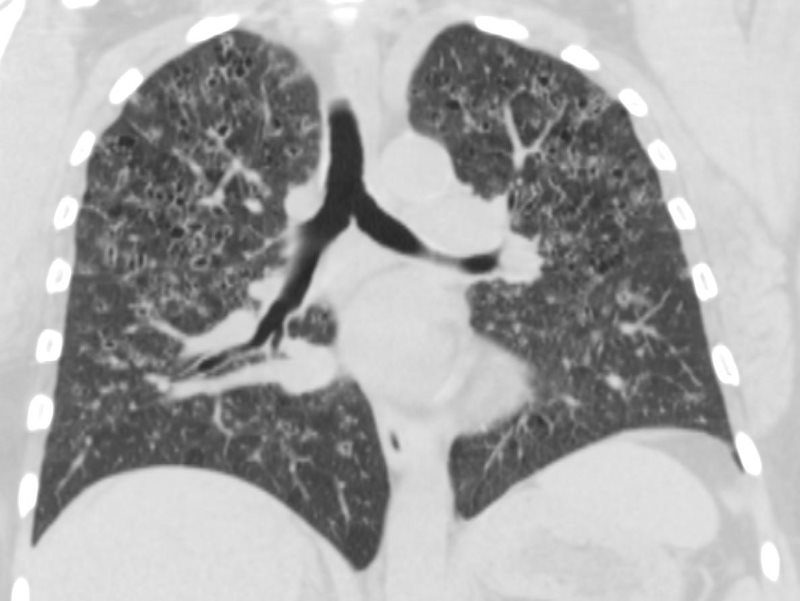
53-year-old female with nicotine dependence presents with dyspnea and cough
CXR (PA and Lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular nodular changes slightly more prominent in the upper lung zones
CT scan from 16 months prior showed multiple relatively thick-walled cysts predominantly in the upper lobes. The cysts are round and air filled large and are between 5mm-8mm
CT scan 9 months later shows improvement in the thickened walls of the cysts but maintenance of diffuse cystic changes predominantly in the upper lobes
A CT scan done 2 years later shows no significant change in the diffuse bilateral cystic changes, dominant in the upper lobes and consistent with Langerhans histiocytosis
Ashley Davidoff MD
DIP Macrophages
Eosinophils
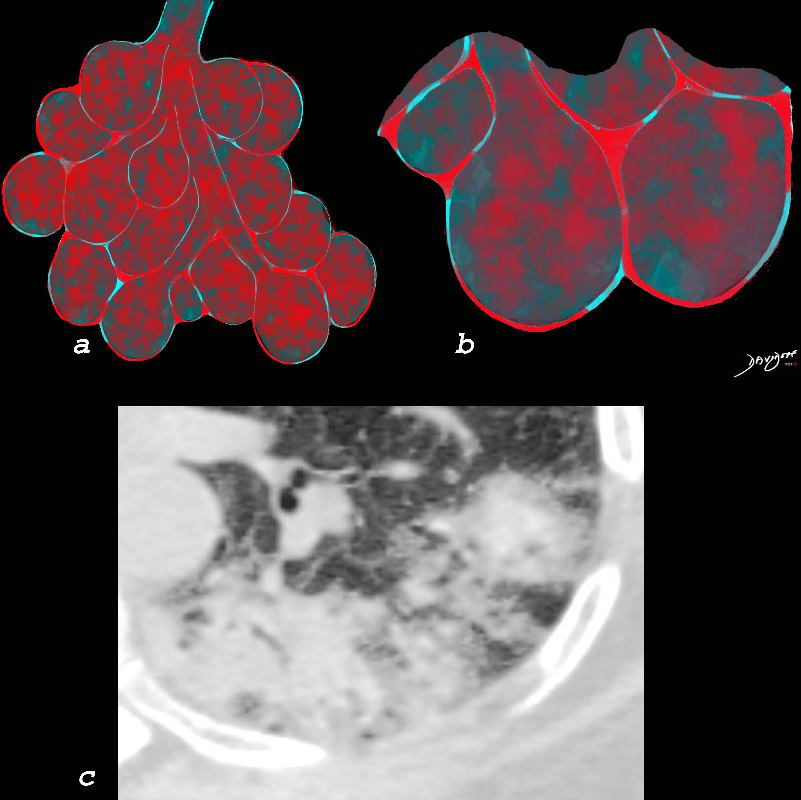
Chronic eosinophilia is characterised by alveolar filling with eosinophils and inflammatory exudates(a) and interalveolar interstitial thickening, (overlaid in red in b). The infiltrates are classically peripherally positioned, usually upper lobes, more commonly bilateral but can be unilateral, and manifest as consolidation and or ground glass opacities. The CT shows a peripheral consolidation in the left upper lobe
Ashley Davidoff MD The CommonVein.net lungs-0764
Malignancy
Lepidic Growth
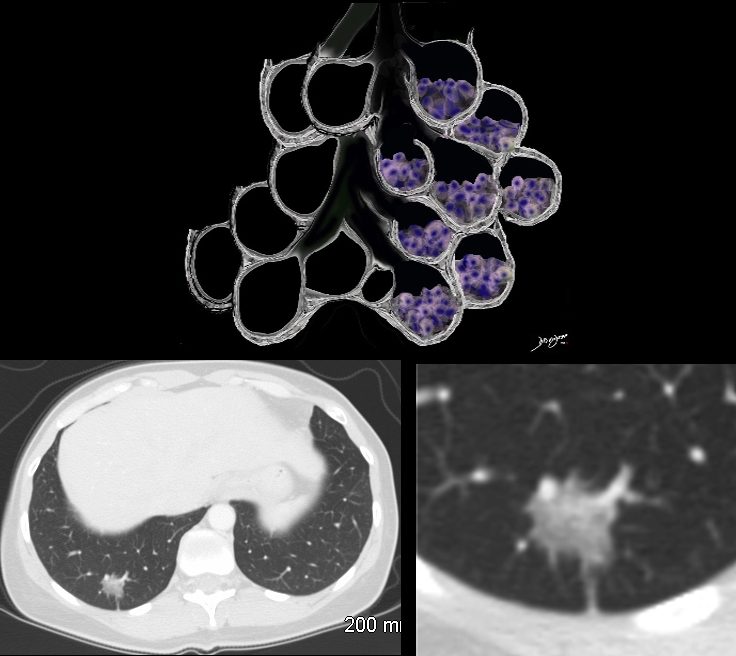
The Ground Glass Opacity (GGO) in this case is caused by partial filling of the alveolus with malignant cells Ground glass opacification may be caused by partial filling of the alveolus with cellular material resulting in partial replacement of air with solid material. The net density is gray rather than white in the situation where the alveolus is fully replaced with cells or fluid. There is blending of the black of the subtending airways and the white of the vessels with the gray density of the cellular infiltrate and hence the normal vessels are not visualized in ground glass opacities.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 134375b01
Mechanical/Atelectasis Trauma Metabolic Circulatory- Hemorrhage Immune Infiltrative Idiopathic Iatrogenic Idiopathic
