Parts
Size
Shape
Position
Character
Time Associated Findings
Infection
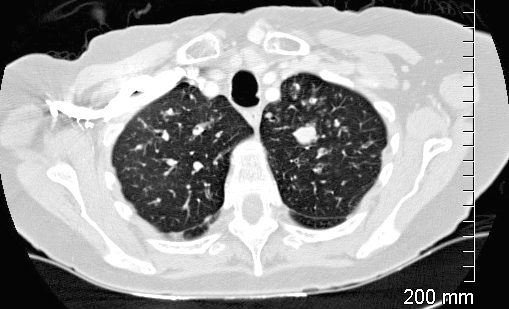
CT of the upper lobes show ground glass micronodules reminiscent of small airway disease
Impacted bronchus is noted in the left apex
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 135123
Inflammation
Follicular Bronchiolitis
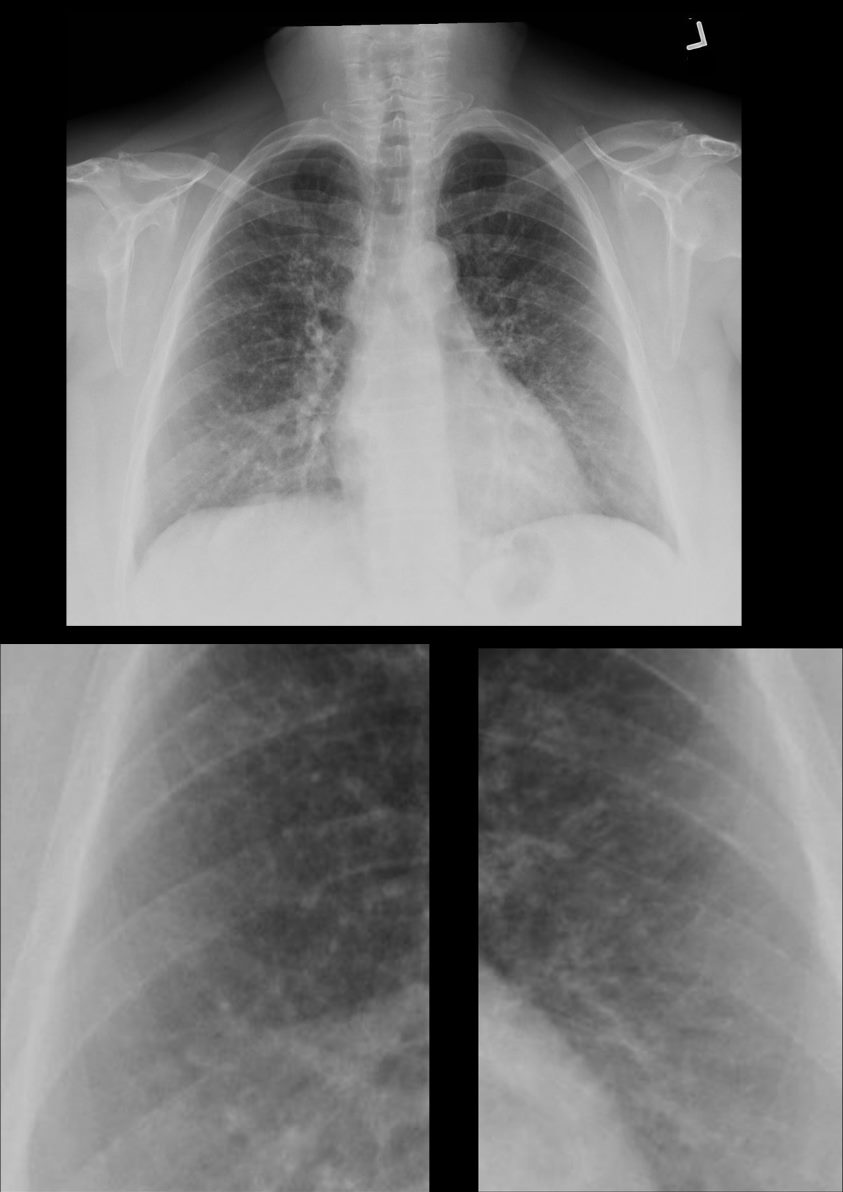
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea. Frontal view of the chest reveals a coarsened nodular interstitial pattern with magnified views showing the micronodularity in the lower panels.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136650c01
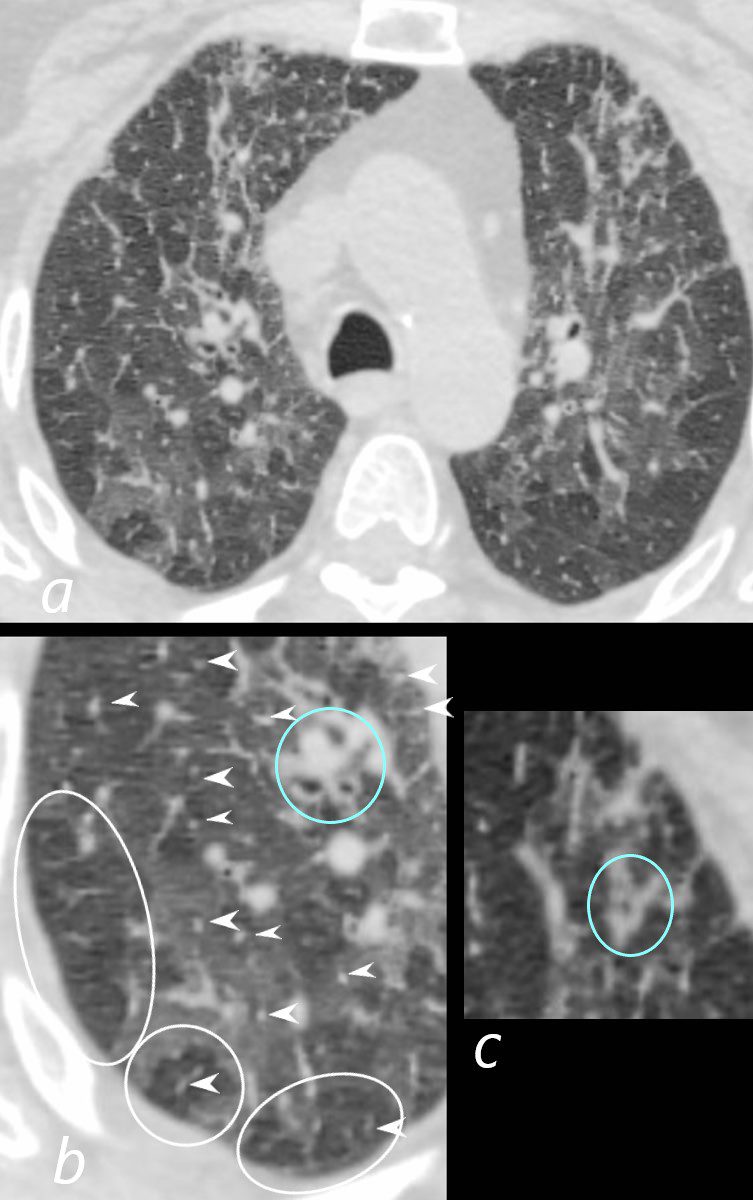
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the aortic arch reveals centrilobular nodules (b, white arrowheads) , ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (b, white rings) likely due to air trapping in this context, and bronchial wall thickening (b, c teal rings). There is some irregular thickening of the interlobular septa. In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136652cL
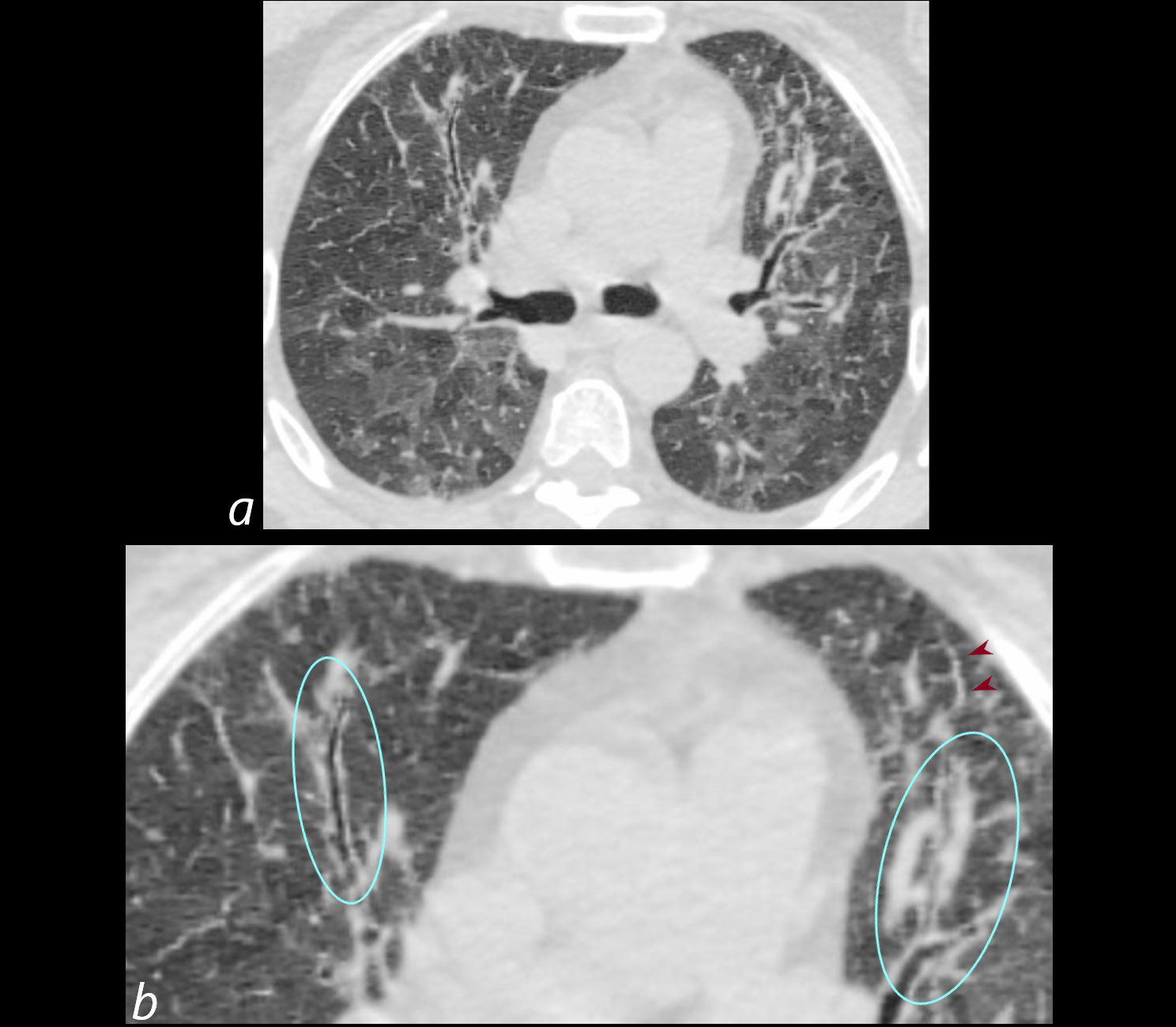
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the carina reveals centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context) and bronchial wall thickening . Bronchial wall thickening (b, maroon arrowheads) and irregular septal thickening (b maroon arrowheads) are noted.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136654cL
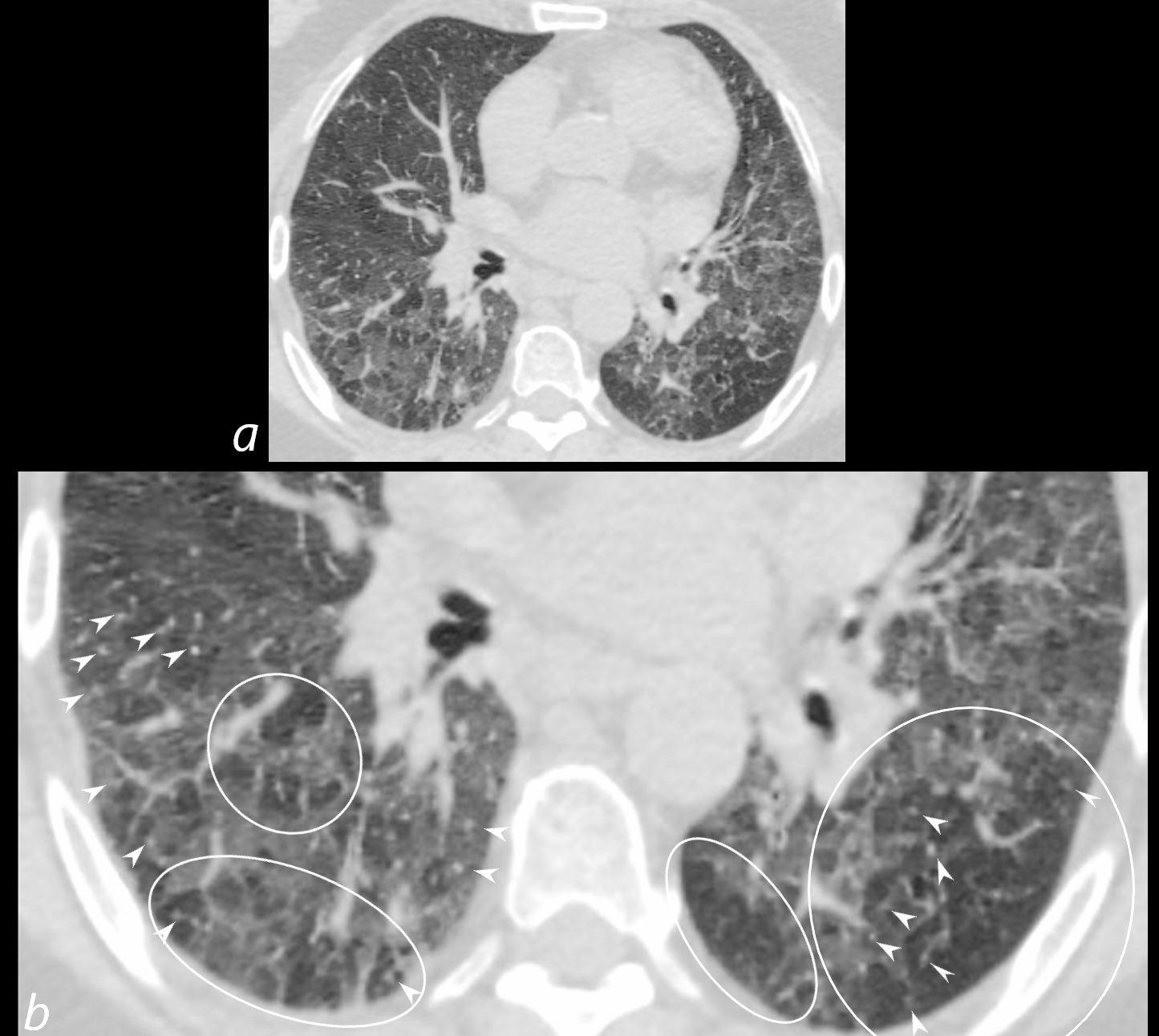
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
Axial CT of the chest at the level of the lower lung fields reveals centrilobular nodules (b white arrowheads), ground-glass opacities, and mosaic attenuation (b, white rings) likely due to air trapping in this context.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136657cL
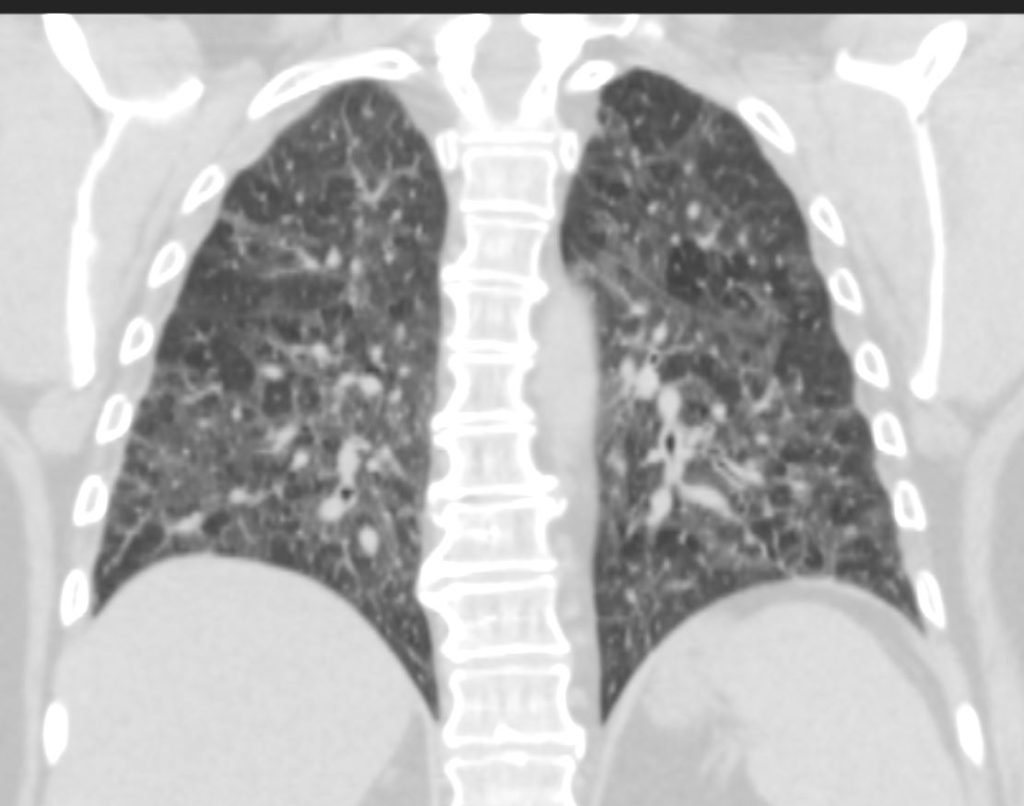
70-year-old female former smoker with long standing history of RA presents with chronic dyspnea.
CT in the coronal plane of the chest at the level of the spine reveals bilateral diffuse changes in the lungs characterized by centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities, mosaic attenuation (likely due to air trapping in this context) and irregular thickening of the interlobular septa.
In the context of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis a diagnosis of follicular bronchiolitis is likely. However radiologically fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is included in the differential diagnosis
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136663
Scleroderma Obliterative Bronchiolitis vs Cellular NSIP
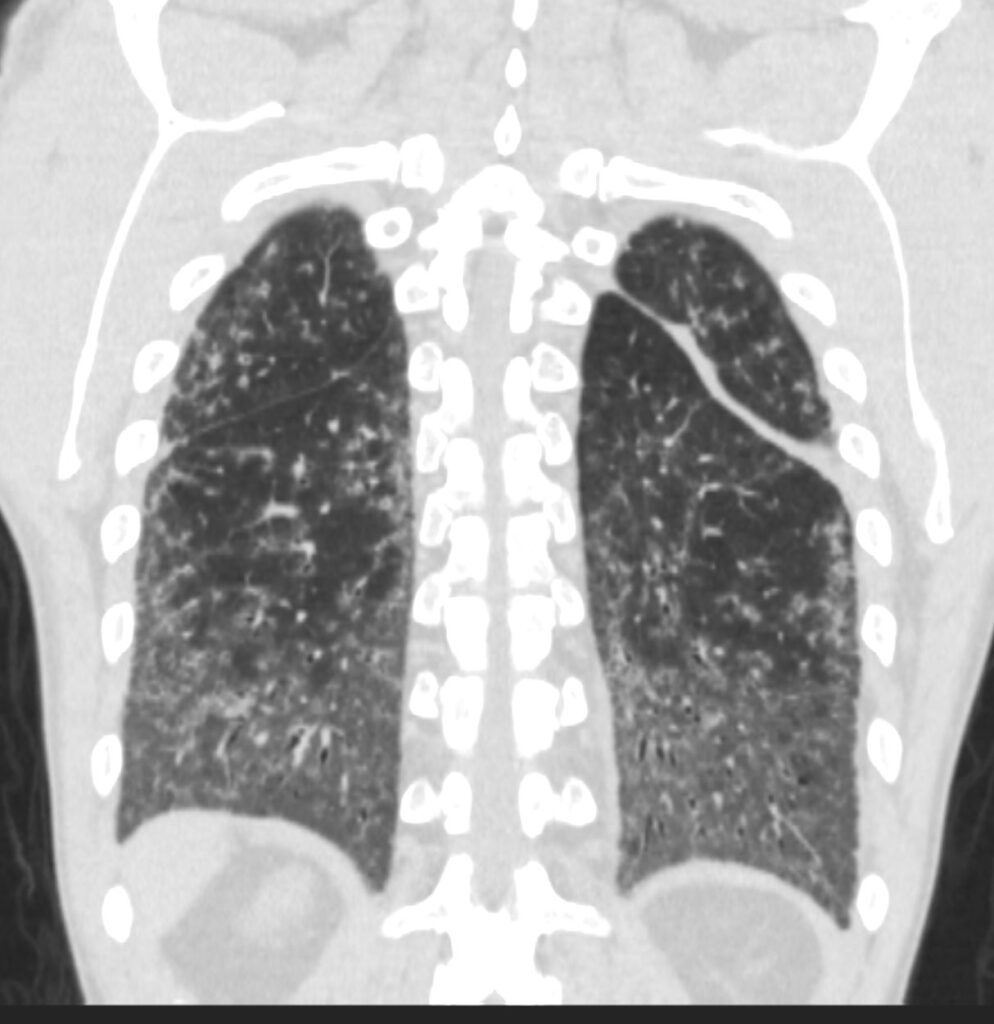
39-year-old-male with a history of scleroderma associated with ILD and digital vasculopathy with ulcers.
Coronal CT at the level of the spine shows extensive ground glass in the lower lung fields, with subpleural sparing better visualized on the left. Ill defined ground glass centrilobular nodules and mosaic attenuation suggest small airway disease.
In this clinical setting obliterative bronchiolitis (aka bronchiolitis obliterans aka constrictive bronchiolitis) and cellular NSIP are radiological considerations.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136667
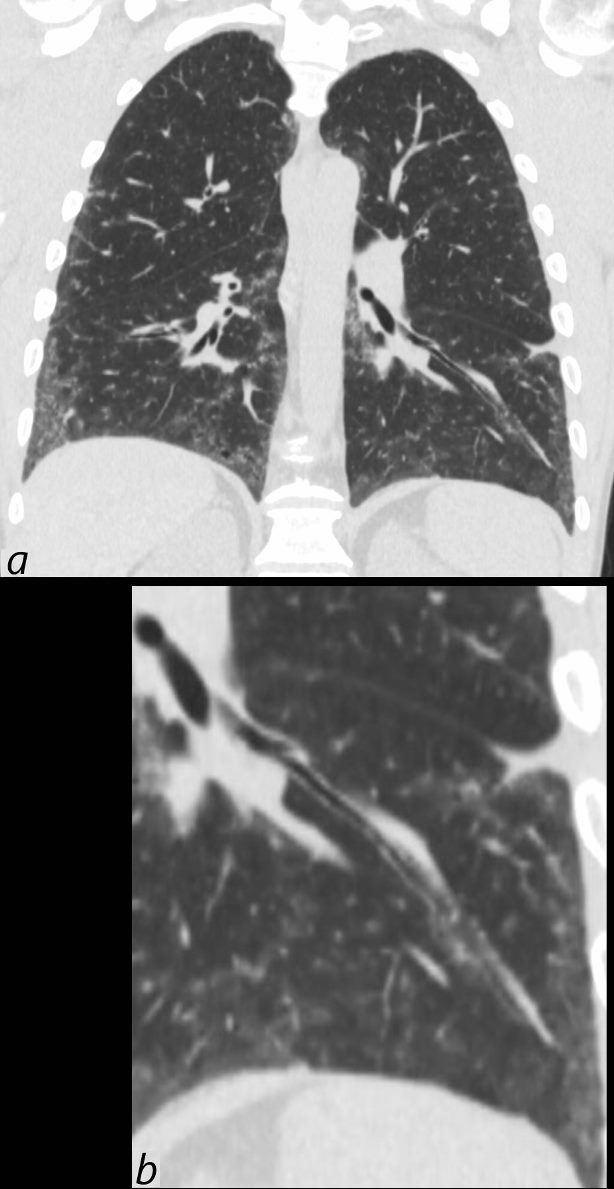
39-year-old-male with a history of scleroderma associated with ILD and digital vasculopathy with ulcers.
Coronal CT shows thickening of the segmental and subsegmental airway supplying the lateral basal segment of the left lower lobe. In addition there is a background of peripheral ground glass changes poorly defined ground glass centrilobular nodules and mild reticulation.
In this clinical setting obliterative bronchiolitis (aka bronchiolitis obliterans aka constrictive bronchiolitis) is suggested. Cellular NSIP is also a radiological consideration.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136669c
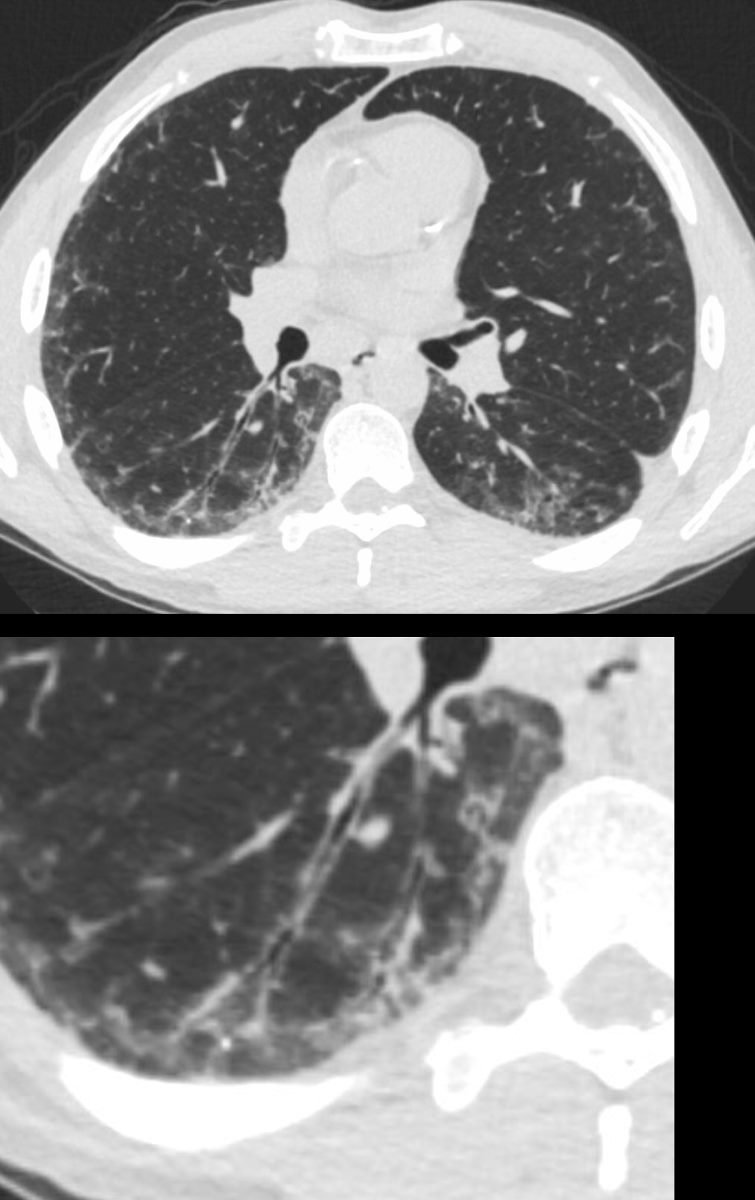
39-year-old-male with a history of scleroderma associated with ILD and digital vasculopathy with ulcers.
Axial CT shows thickening of the segmental, subsegmental and small airways supplying the posterior basal segment of the right lower lobe. In addition there is a background poorly defined ground glass changes and mild reticulation.
In this clinical setting obliterative bronchiolitis (aka bronchiolitis obliterans aka constrictive bronchiolitis) is suggested. Cellular NSIP is also a radiological consideration.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 132Lu 136669c
