-
- Staging
-
Stage 0 is a normal chest radiograph
-
Stage I is lymphadenopathy only
-
Stage II is lymphadenopathy and lung parenchymal disease
-
Stage III is parenchymal lung disease only
-
Stage IV is pulmonary fibrosis
-
- Staging
Although in general the staging is a mark of progression of disease the staging does not does not correlate with clinical severity. CXR appearance in addition does not correlate with clinical severity
-
-
Staging
-
Stage 0 – Normal Chest Radiograph
5-10%
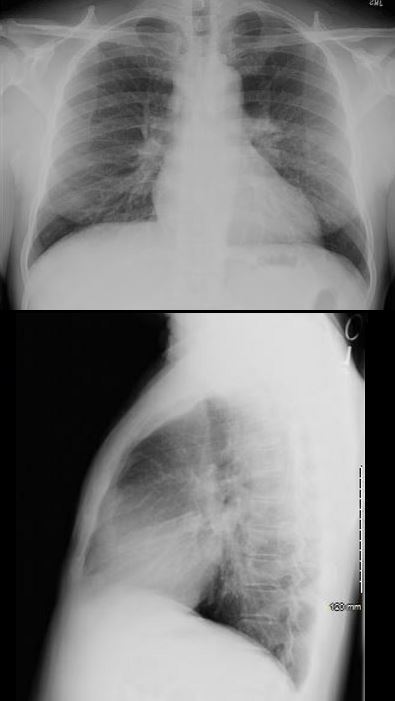
SARCOID CARDIOMYOPATHY with LIVER and LYMPH NODE INVOLVEMENT
57-year-old male with pathology findings consistent with granulomatous hepatitis and non-necrotizing granulomas in inguinal lymphadenitis both consistent with sarcoidosis but without pulmonary findings. Lymphadenopathy was present in the axillae and groins without involvement of the mediastinum
Associated cardiovascular findings include findings consistent with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with:
o Diabetes and Hypertension
o Focal nodular LGE in the anterior apical region in mid myocardial/subendocardial region and in the inferior mid myocardial wall medially
o Subsequently developed episodes of paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia with EP ablation and placement of a defibrillator (ICD)
o LH and RH catheterization performed 6 years after initial studies showed elevation of PC WP of 25 mmHg, mean RA pressure of 16 mmHg, mean PAP of 34 mmHg no CAD
o Subsequent CT showed mildly enlarged LA and RA with mild TR
o 6 years after initial presentation he had symptoms of biventricular failure with increasing dyspnea and pedal edema culminating in an acute episode of monomorphic VT episode, ectopic atrial flutter/fibrillation, and left bundle branch aberrancy requiring amiodarone and cardioversion. Underwent upgrade to biventricular upgrade ICD Arrhythmias likely due to cardiac involvement with sarcoidosis
Ashley Davidoff MD
Stage I -Lymphadenopathy only
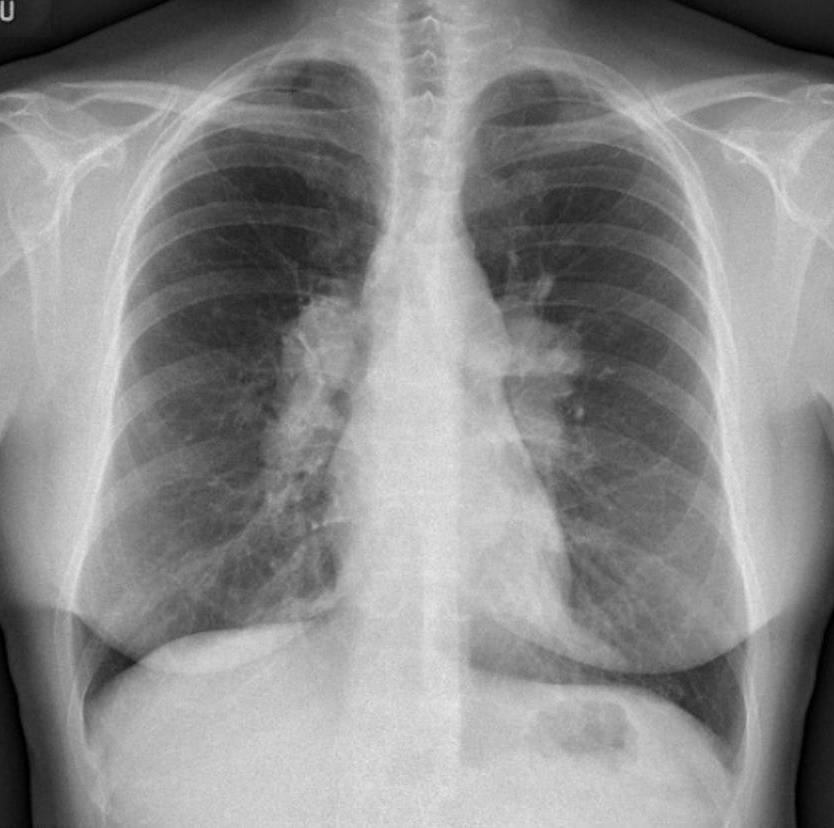
Case courtesy of Dr Eric F Greif, Radiopaedia.org,
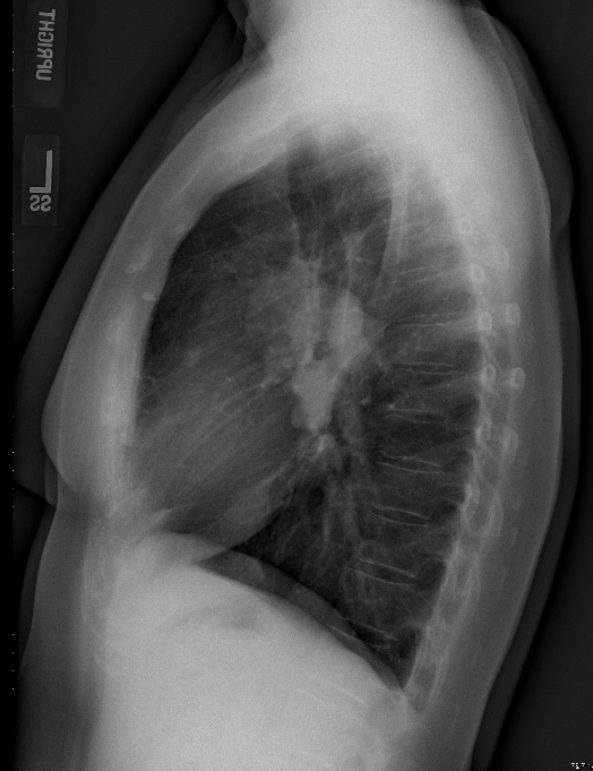
31- year-old male with stable mediastinal and hilar adenopathy, no parenchymal disease, with splenomegaly and an enlarged main pulmonary artery . The cardiac echo was normal without pulmonary hypertension
The widened carina is likely as a result of the subcarinal adenopathy
Ashley Davidoff MD
Bilateral hilar adenopathy is most common and usually symmetric (50 percent of cases) or the right may be slightly more prominent . Unilateral adenopathy is uncommon (<5 percent of cases).
Most patients with Rx show regression of the lymphadenopathy
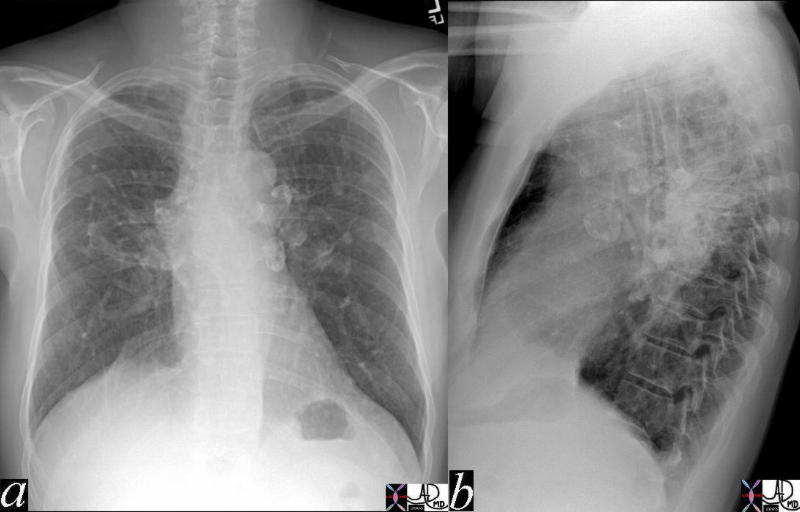
The A-P and lateral view of the chest is from a patient with sarcoidosis showing classical egg shell calcification of the mediastinal nodes and hilar nodes.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 42195c01
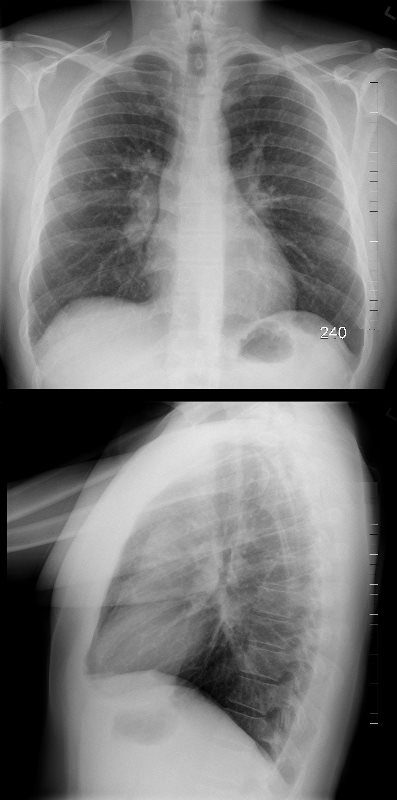
Stage II Lymphadenopathy and Lung Parenchymal disease
Reticular opacities with shrinking hilar nodes
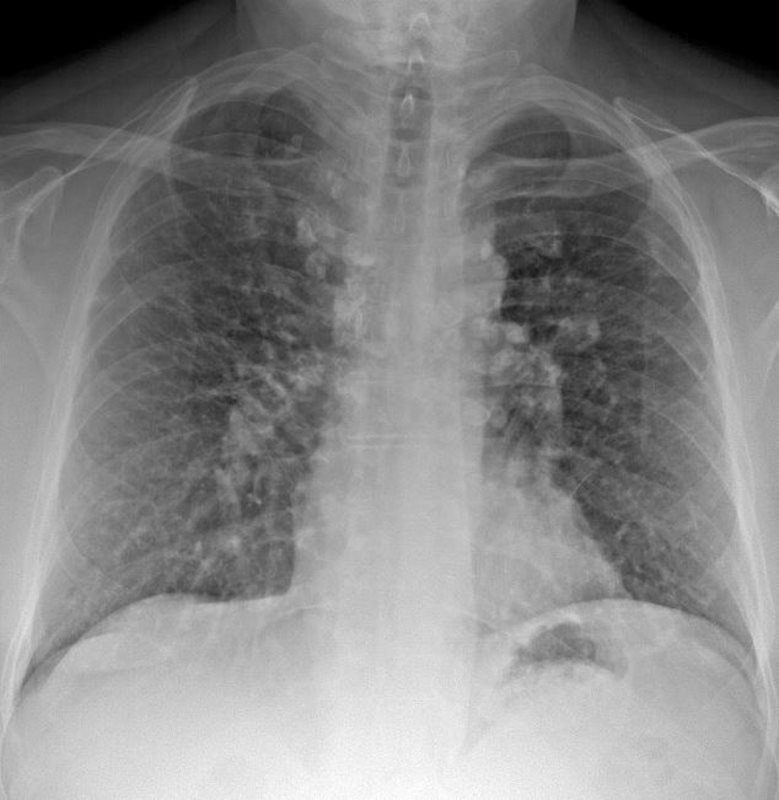
51-year-old male with Stage II sarcoidosis and egg shell calcification of lymph nodes
51-year-old male with Stage II Sarcoidosis and egg shell calcification of lymph nodes
Ashley Davidoff MD
Stage III
Stage III is parenchymal lung disease only
63F SARCOIDOSIS CALC RETICULO- NODULAR PATTERN
Ashley Davidoff MD
Stage IV
Reticular opacities with evidence of volume loss, predominantly distributed in the upper lung zones Conglomerate masses with architectural distortion traction bronchiectasis. Calcification cavitation and cyst formation may also be seen
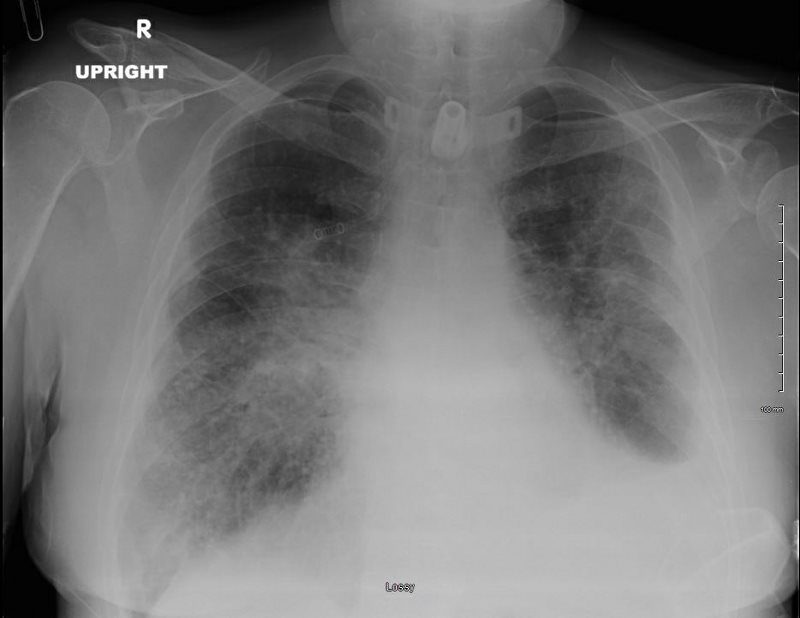
SARCOIDOSIS, STAGE IV, PTX, ENCASEMENT
Ashley Davidoff MD
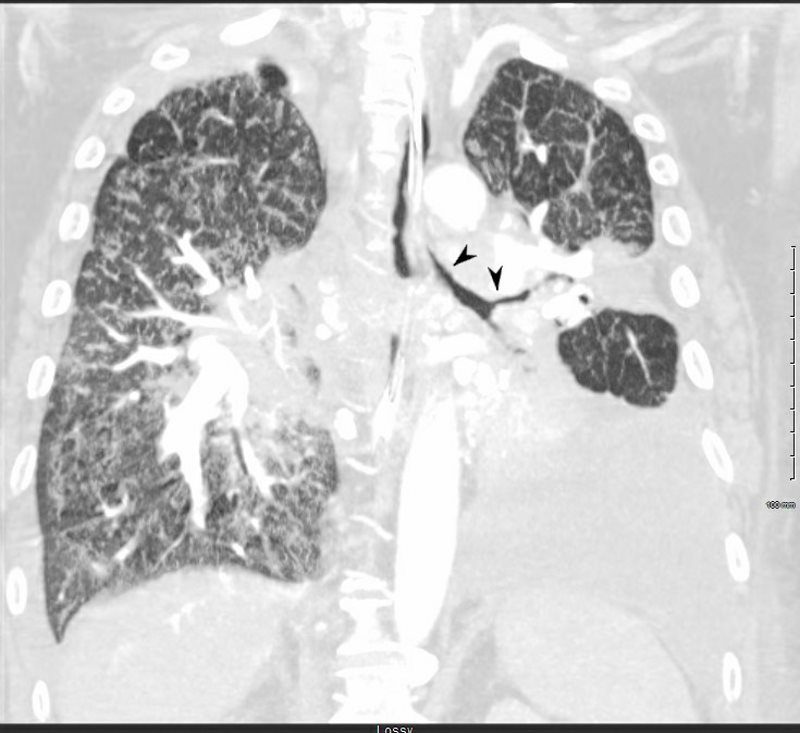
SARCOIDOSIS, STAGE IV, PTX, ENCASEMENT
Lymph Nodes
Calcified
Calcification of hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes becomes more common with longer disease duration
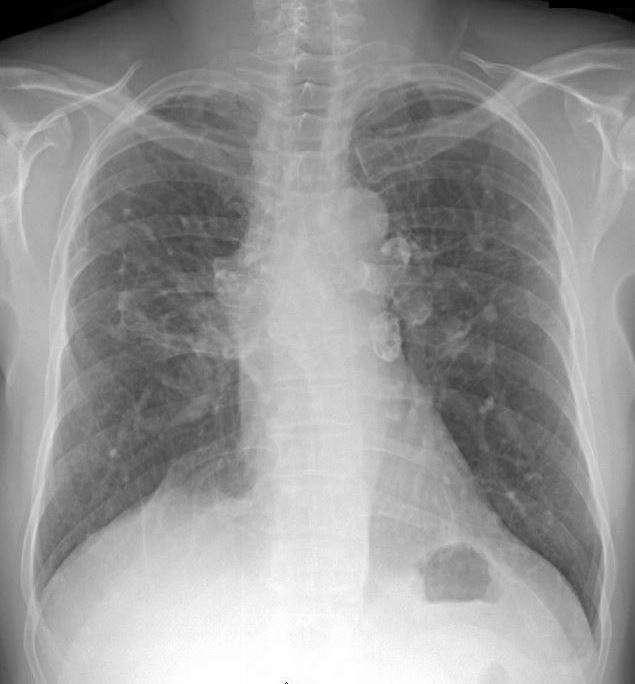 STAGE II with EGG SHELL CALCIFICATIONS AND ILD
STAGE II with EGG SHELL CALCIFICATIONS AND ILD
70 year old male with history of sarcoidosis presents with a cough. There upper lobe retractile reticular process associated bilateral hilar /mediastinal egg shell calcifications of the lymph nodes
Ashley Davidoff MD
Nodules
Solid Focal
Clustered
MicronoDular
Miliary
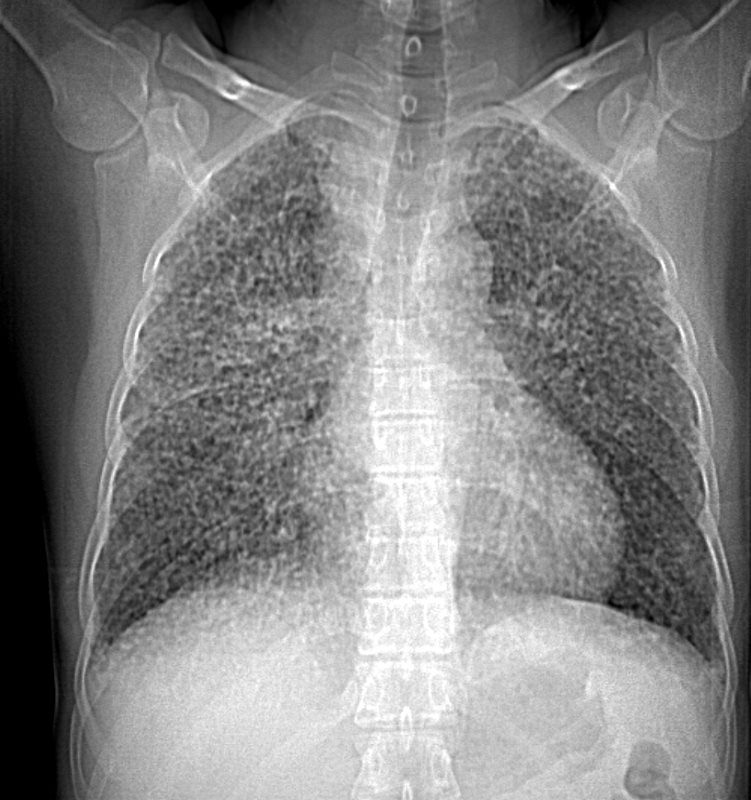
42-year-old cement worker presents with dyspnea .
Ashley Davidoff MD
Confluent
Alveoalar
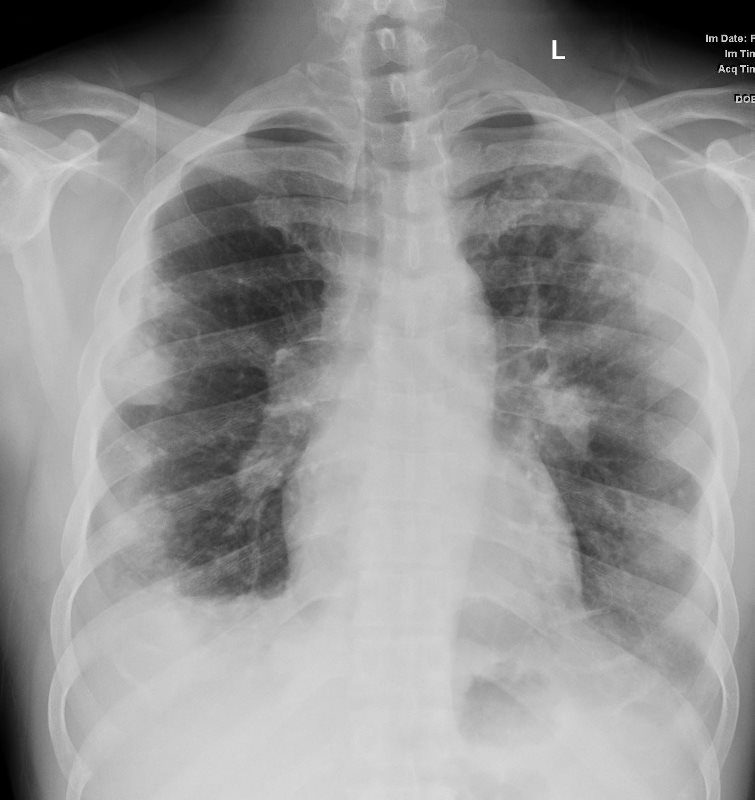
Ashley Davidoff MD
SARCOIDOSIS, ACTIVE – ALVEOLAR FORM
Ashley Davidoff MD
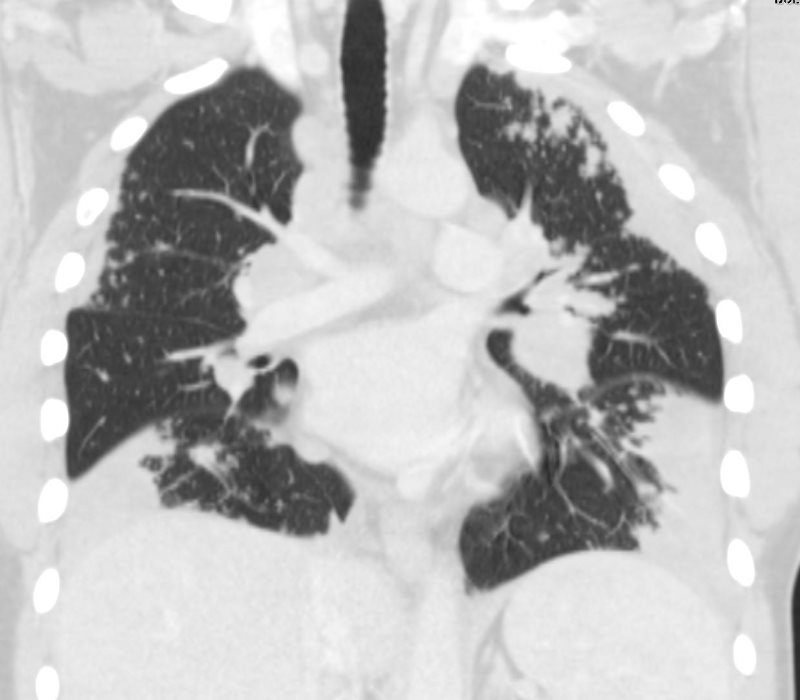
Ground Glass
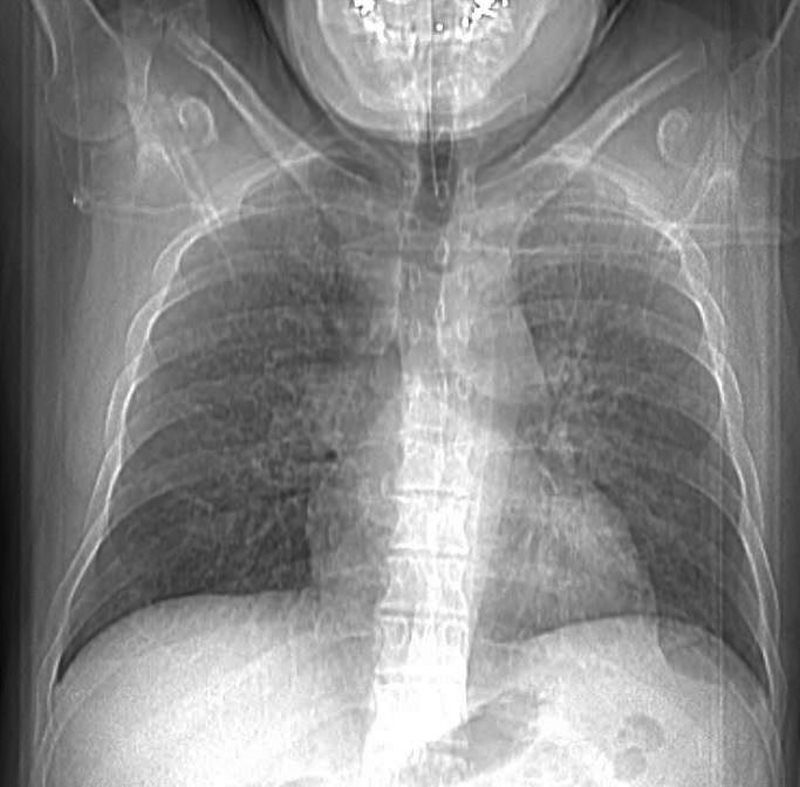
44-year-old male presents with history of sarcoidosis manifesting as diffuse ground glass involving the upper lobes and lower lobes sparing the middle lobe and lingula to some extent.
Associate pathological lymphadenopathy was relatively stable as well
The only available CXR shows a diffuse interstitial pattern with little suggestion of the moderate sized adenopathy apparent on the CT
A cardiac echo was normal, and there was no suggestion of cardiac disease on his CT or CXR.
Ashley Davidoff MD
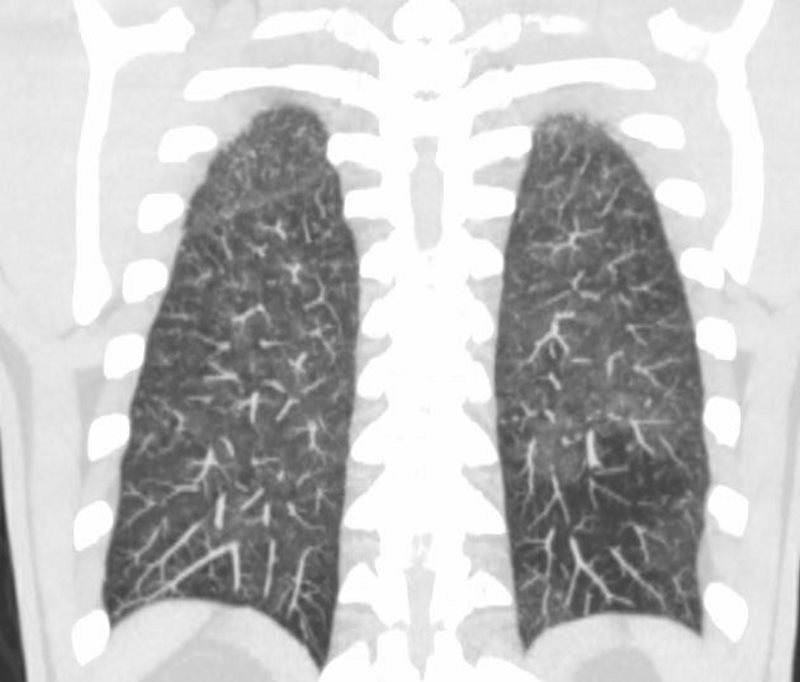
Ashley Davidoff MD
ILD
Pleural Involvement
Pleural involvement is unusual (<5 percent of patients), but can result in lymphocytic exudative effusion, chylothorax, hemothorax, and pneumothorax
Pneumothorax
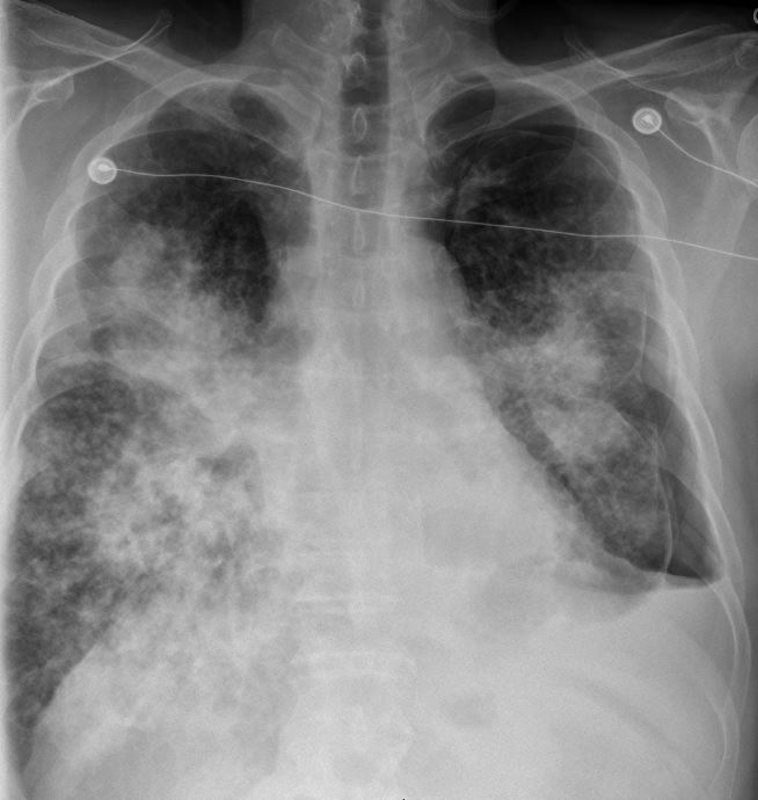
Ashley Davidoff MD
Cardiovascular Involvement
Cardiomegaly
Myocardial Infiltration
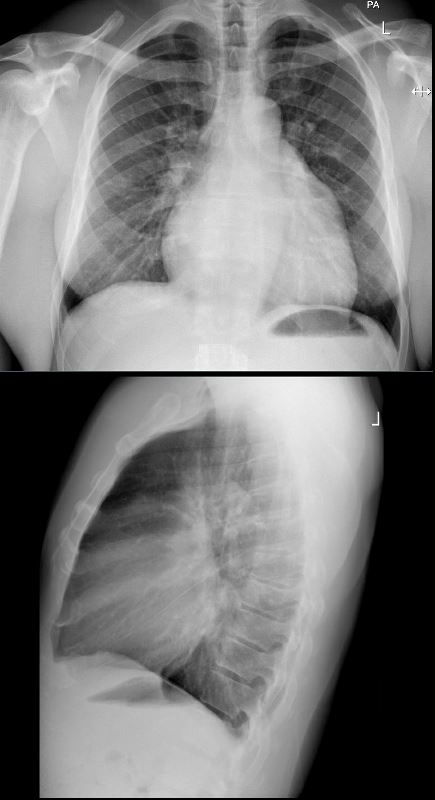
CXR shows LAE and LVE with cephalisationAshley Davidoff MD

The MRI (systole above and diastole below) shows moderate mitral regurgitation, (arrows in top image showing turbulence )and bottom image showing significant left atrial enlargement (A-P dimension 77.4mms) LVH (septum 21 mms and free wall 15.4 mms) Calculated LV mass was LVH 95 gms/sq m) (normal = 50-86 g for males) On cine studies there was diffuse hypokinesis with EF of 39%,Ashley Davidoff MD
Pericardial Effusion
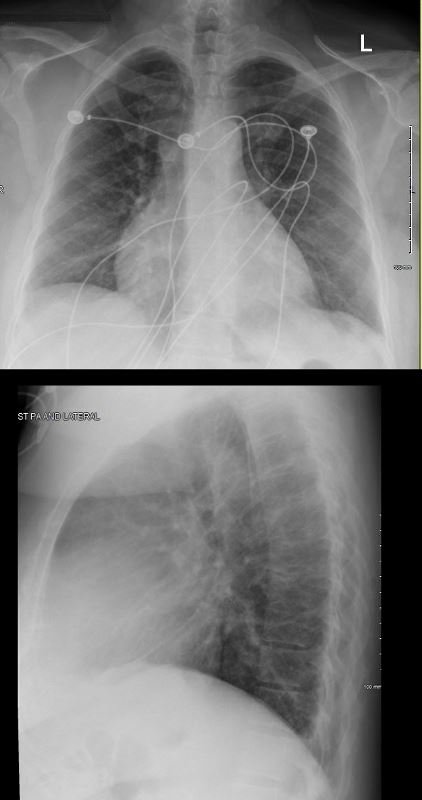
54-year-old female with peripheral adenopathy who had an inguinal node biopsied 6 years prior showing sarcoidosis. Who chest examinations at the time showed little evidence of sarcoid except for a few small nodules. She has a history of hypertension COPD; sleep apnea, on CPAP; diabetes mellitus, on metformin; lumpectomy x2; GERD; and vertigo
4 years ago she presented with SOB and was noted to have a pericardial effusion by echo without tamponade
The pericardial effusion was drained with negative cytology and negative for TB . CT at the time following the drainage showed a thickened pericardium with pericardial drain in place
She represented 1 year later with symptoms of worsening intermittent chest pain, and shortness of breath exacerbated with exertion. An echocardiogram, showed recurrent increasing pericardial effusion confirmed by CT. She was placed on steroids but did not tolerate the steroids.
Later in that year she underwent surgery for pericardial window and VATS biopsy of her left lower lobe. Her pericardium was noted to be thickened
Pathology revealed Non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation involving pulmonary interstitium and occasional airways; AFB, GMS, and PAS stains were negative for micro-organisms.
The left pericardial biopsy showed diffuse and extensive non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation and AFB, GMS, and PAS stains were negative for micro-organisms.
CT scan at the end of that year (131555) showed thickened pericardium.
An MRI at the time showed diffuse thickening of the pericardium with enhancement as well as nodular mid myocardial changes at the hinge points and the inferolateral aspects. Subendocardial changes were also noted.
Repeat MRI the next year showed similar findings
Ashley Davidoff MD
Pericardial Best Evaluated on the Lateral Exam

RECURRENT PERICARDIAL EFFUSION CXR,CT CORRELATION
The lateral examination soft pericardial effusion layering dependently and posteriorly.
CHF
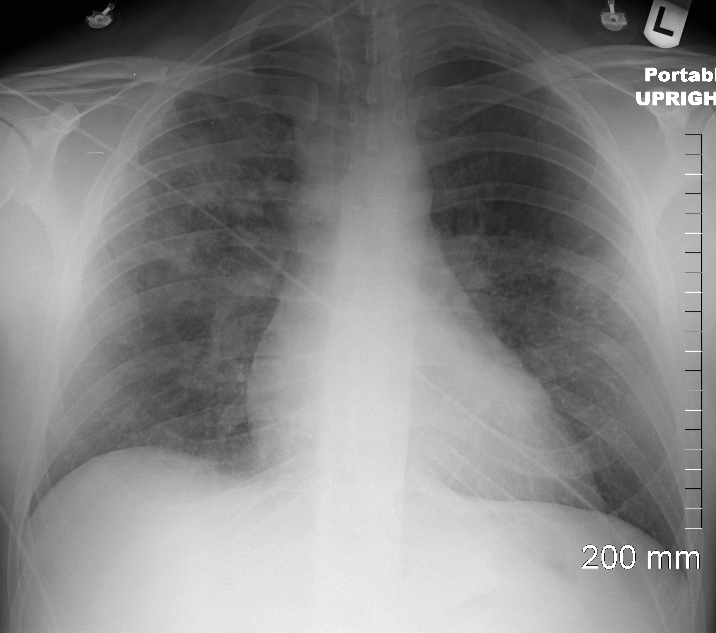
CXR shows upper lobe predominance interstitial changes, slightly more prominent on the right side. There is evidence of CHF with enlargement of the LA (widening of the carinal angle) and cephalization of the vessels
Ashley Davidoff MD
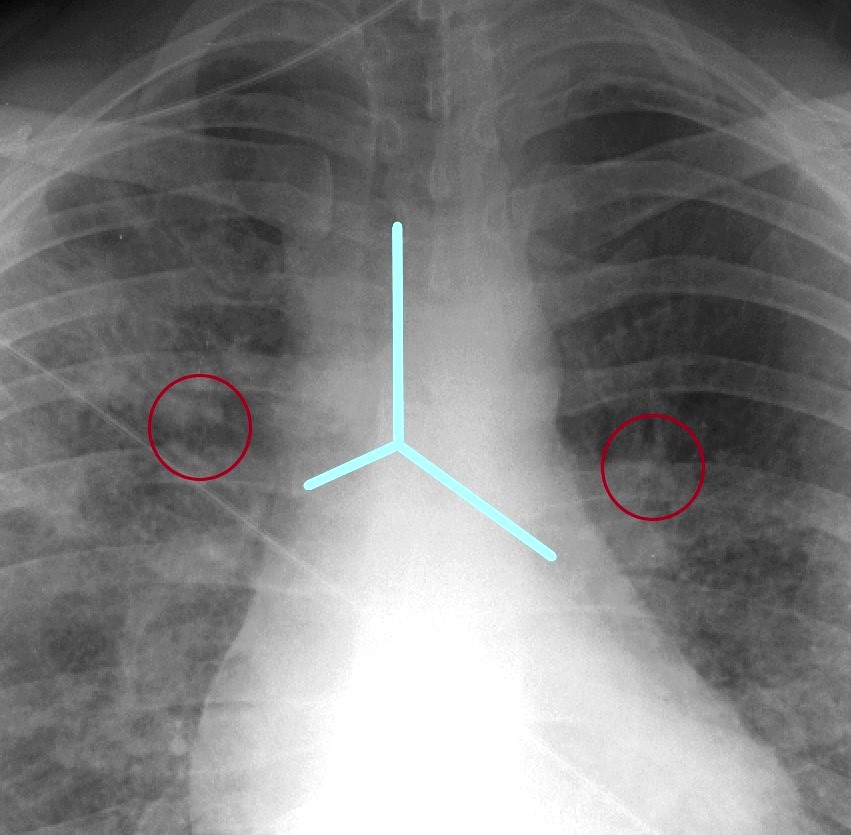
CXR shows upper lobe predominance interstitial changes, slightly more prominent on the right side. There is evidence of CHF with enlargement of the LA (widening of the carinal angle) and cephalization of the vessels
Ashley Davidoff MD
Pulmonary Hypertension
As of 1999, the official American Thoracic Society guidelines recommended CXR for initial evaluation
It is recommended to reserve CT scan for patients with atypical clinical or CXR ray findings or for concern of complications of lung disease, eg bronchiectasis or fungal superinfection
References and Links
Levy, A et al Is it time to scrap Scadding and adopt computed tomography for initial evaluation of sarcoidosis? F1000Res. 2018; 7: F1000 Faculty Rev-600.
