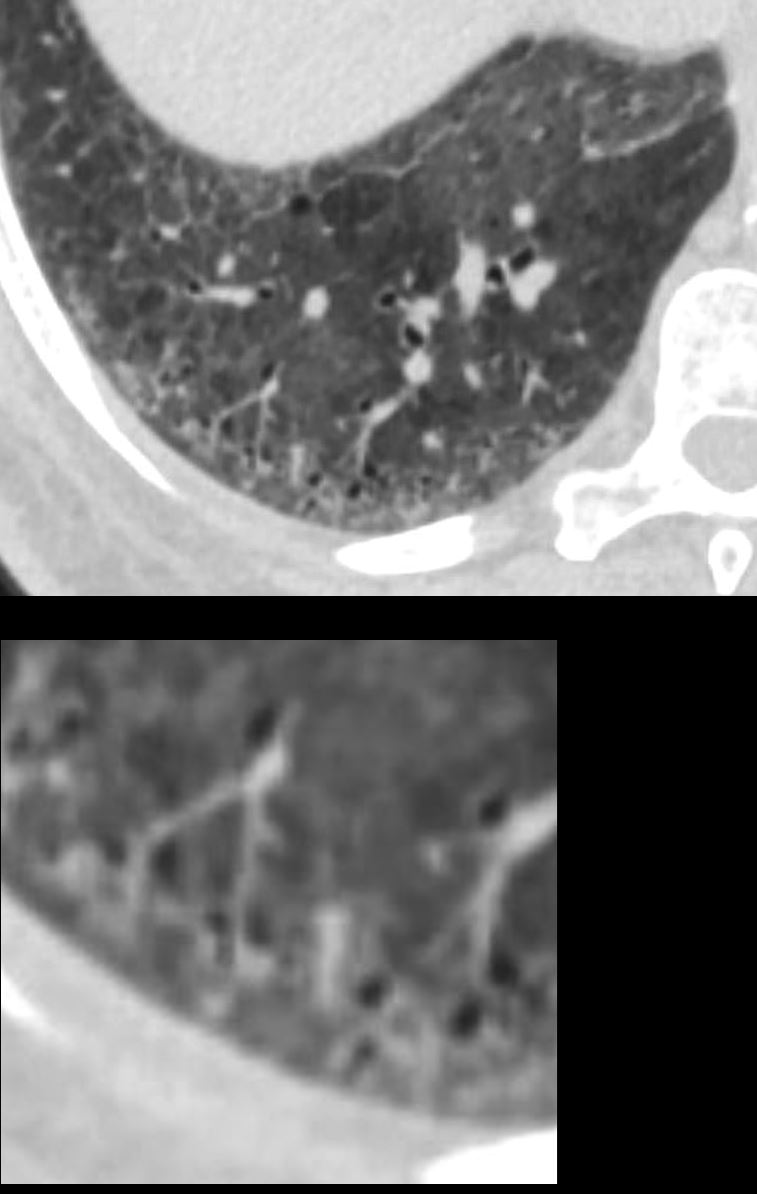
51-year-old female smoker with a history of COPD asthma and pulmonary hypertension presents with progressive dyspnea. Axial CT through the right posterior recess shows patchy ground glass changes with some regions of mosaicism. The bronchovascular bundle subtending 2 secondary lobules is highlighted in the lower panel. The centrilobular arteriole and ectatic bronchiole are magnified
Pathology confirmed a diagnosis of DIP
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 252Lu 135981c
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Links and References
Fleischner Society
bronchiolectasis
Pathology.—Bronchiolectasis is defined as dilatation of bronchioles. It is caused by inflammatory airways disease (potentially reversible) or, more frequently, fibrosis.
CT scans.—When dilated bronchioles are filled with exudate and are thick walled, they are visible as a tree-in-bud pattern or as centrilobular nodules (,31,,32). In traction bronchiolectasis, the dilated bronchioles are seen as small, cystic, tubular airspaces, associated with CT findings of fibrosis (,Fig 12). (See also traction bronchiectasis and traction bronchiolectasis, tree-in-bud pattern.)
