- Anthracosis, also known as black lung disease,
- benign occupational disorder
- characterized by the
- deposition of coal dust particles in the lungs.
- affects individuals exposed to
- coal dust or
- other carbon-containing particles
- over an extended period, such as
- coal miners or workers in certain industrial occupations.
Structures Involved
- Bronchi and Bronchioles:
- Alveoli:
- Interstitial Tissue:
- Lymph Nodes:
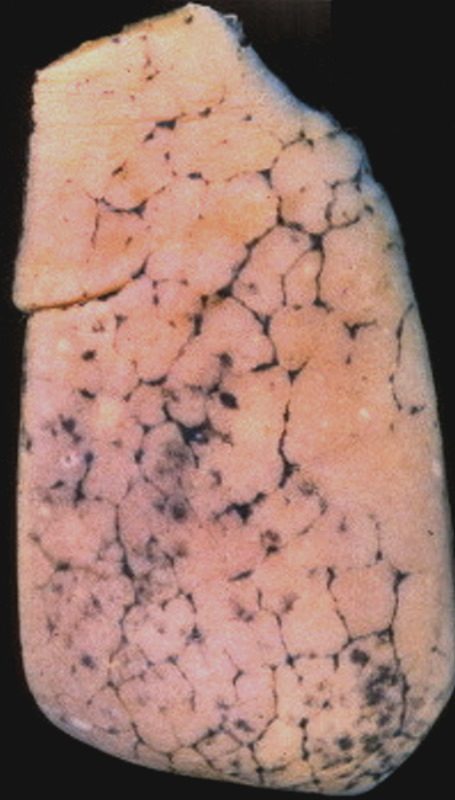
Anthracosis – Note the accumulation of carbon particles within the lymphatics along the interlobular septa, outlining the secondary lobules. The carbon particles are inhaled from an anthracotic urban environment. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 32291 code lung interlobular septum septa secondary lobule pulmonary lobule intertstitium interstitial grosspathology carbon
Imaging Manifestations
Affects both upper and lower lobes
- Prominent Bronchovascular Markings
- May show prominent bronchovascular markings, reflecting the distribution of coal dust along the larger airways and blood vessels.
- Peribronchial and Perivascular Opacities:
- Opacities around the bronchi and blood vessels, indicating the deposition of coal dust in these regions, may be visible on imaging studies
- Linear and Nodular Opacities:
- Linear and nodular opacities may be visible on chest X-rays or CT scans. These opacities represent the accumulation of coal dust along the bronchovascular bundles and may appear as streaks or small nodules.
- Fibrotic Changes:
- Interstitial Fibrosis
- honeycombing.
- Hilar and Mediastinal Lymph Node Enlargement:
- Reactive enlargement
