Air crescent sign
- The air crescent sign is a radiological finding
- characterized by a
-
- crescent-shaped radiolucency that
- forms between
- a mass or nodule and the surrounding lung tissue.
- It is often associated with
- infectious or inflammatory conditions like
- invasive aspergillosis,
- especially in immunocompromised patients, where damaged lung and necrotic tissue
- begins to retract,
- leaving a space filled with
- air (cavitation).
- invasive aspergillosis,
- infectious or inflammatory conditions like
- Structurally, the air crescent sign indicates
- cavitary lesions or areas of necrosis,
- Clinically
- presents with symptoms like
- cough and hemoptysis.
- presents with symptoms like
- Diagnosis is made through
- clinical symptoms,
- imaging (primarily CT), and
- laboratory tests, including
- cultures or
- serology for infectious agents like
Aspergillus.
-
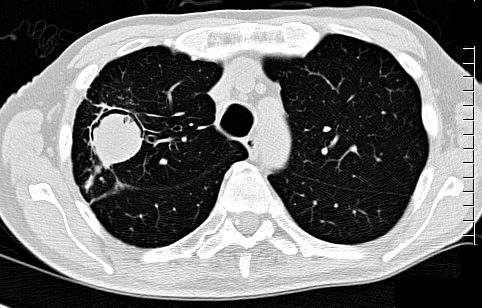
66 year malnourished immunodeficient male with right upper lobe aspergilloma in the lung
CT scan in the axial plain shows an air-crescent sign with right Upper lobe mass consistent with aspergilloma
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 113530b01
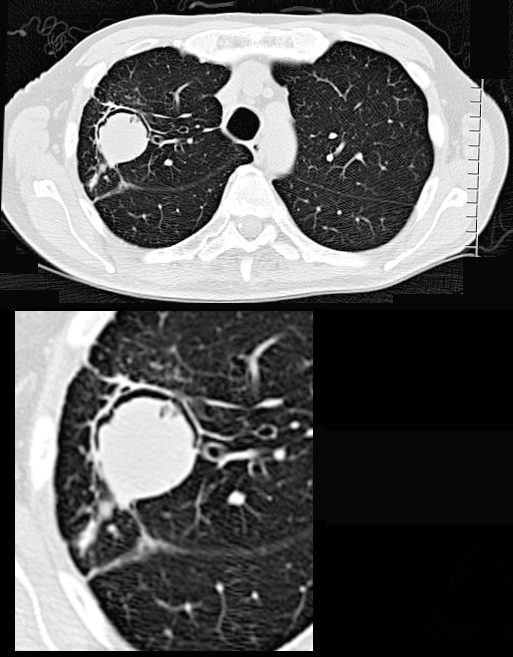
66- year-old malnourished, immunodeficient male presents with a chronic cough.
CT in the axial plane shows a 3.2cms right upper lobe mass with a rim of a crescentic accumulation of air in the dependant portionof the mass (magnified in the lower image) while the aspergilloma “sinks” to the most dependent portion of the cavity . This finding reflects an air -crescent sign and is consistent with a diagnosis of an aspergilloma
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 293Lu 113528c
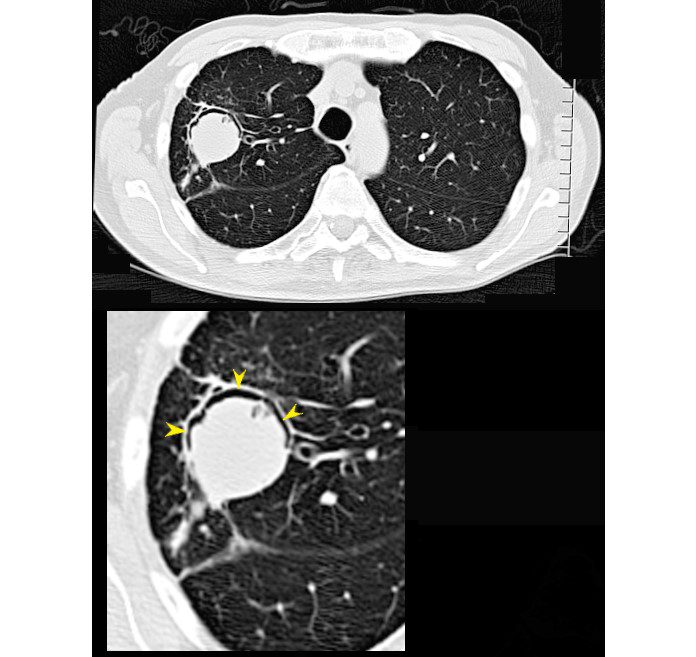
66- year-old malnourished, immunodeficient male presents with a chronic cough.
CT in the axial plane shows a 3.2cms right upper lobe mass with a rim of a crescentic accumulation of air in the dependant portionof the mass (magnified in the lower image- yellow arrowheads) while the aspergilloma “sinks” to the most dependent portion of the cavity . This finding reflects an air -crescent sign and is consistent with a diagnosis of an aspergilloma
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 293Lu 113528cL

Source
Signs in Thoracic Imaging
Journal of Thoracic Imaging21(1):76-90, March 2006
The air crescent sign appears as a variably sized, peripheral crescentic collection of air surrounding a necrotic central focus of infection on thoracic radiographs (Fig. 1A) and CT (Fig. 1B).2–4 It is often seen in neutropenic patients who have undergone bone marrow or organ transplantation and is most characteristic of infection with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The fungus invades the pulmonary vasculature, causing hemorrhage, thrombosis, and infarction. With time, the peripheral necrotic tissue is reabsorbed by leukocytes and air fills the space left peripherally between the devitalized central necrotic tissue and normal lung parenchyma.5 Thus, the presence of the air-crescent sign heralds recovery of granulocytic function.4 Other causes of the air crescent include cavitating neoplasms, bacterial lung abscesses, and infections such as tuberculosis or nocardiosis.6

Ashley Davidoff MD

Ashley Davidoff MD
Links and References
Fleischner Society
air crescent
Radiographs and CT scans.—An air crescent is a collection of air in a crescentic shape that separates the wall of a cavity from an inner mass (,Fig 3). The air crescent sign is often considered characteristic of either Aspergillus colonization of preexisting cavities or retraction of infarcted lung in angioinvasive aspergillosis (,9,,10). However, the air crescent sign has also been reported in other conditions, including tuberculosis, Wegener granulomatosis, intracavitary hemorrhage, and lung cancer. (See also mycetoma.)
